Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of geological disasters in the open-pit mining area of western Fushun,Liaoning Province
-
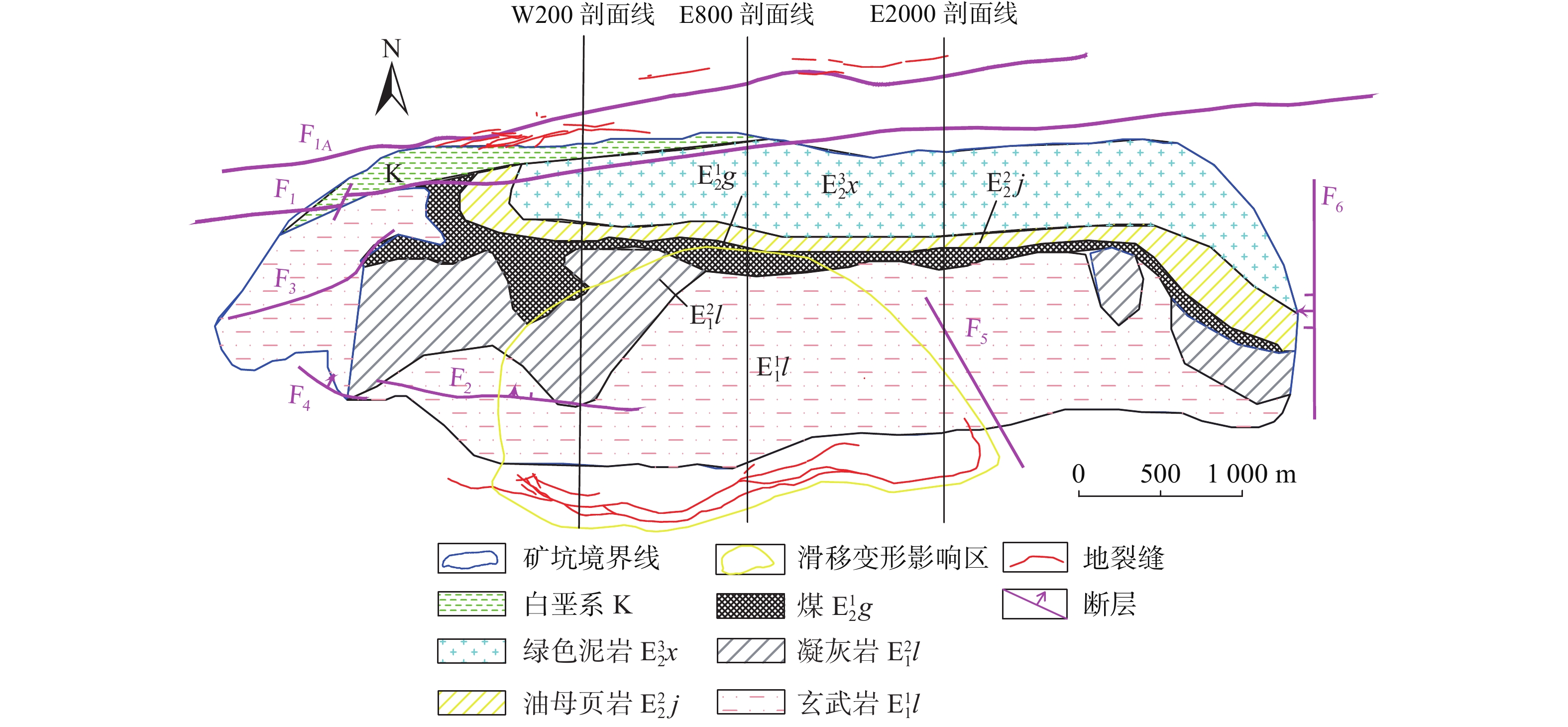
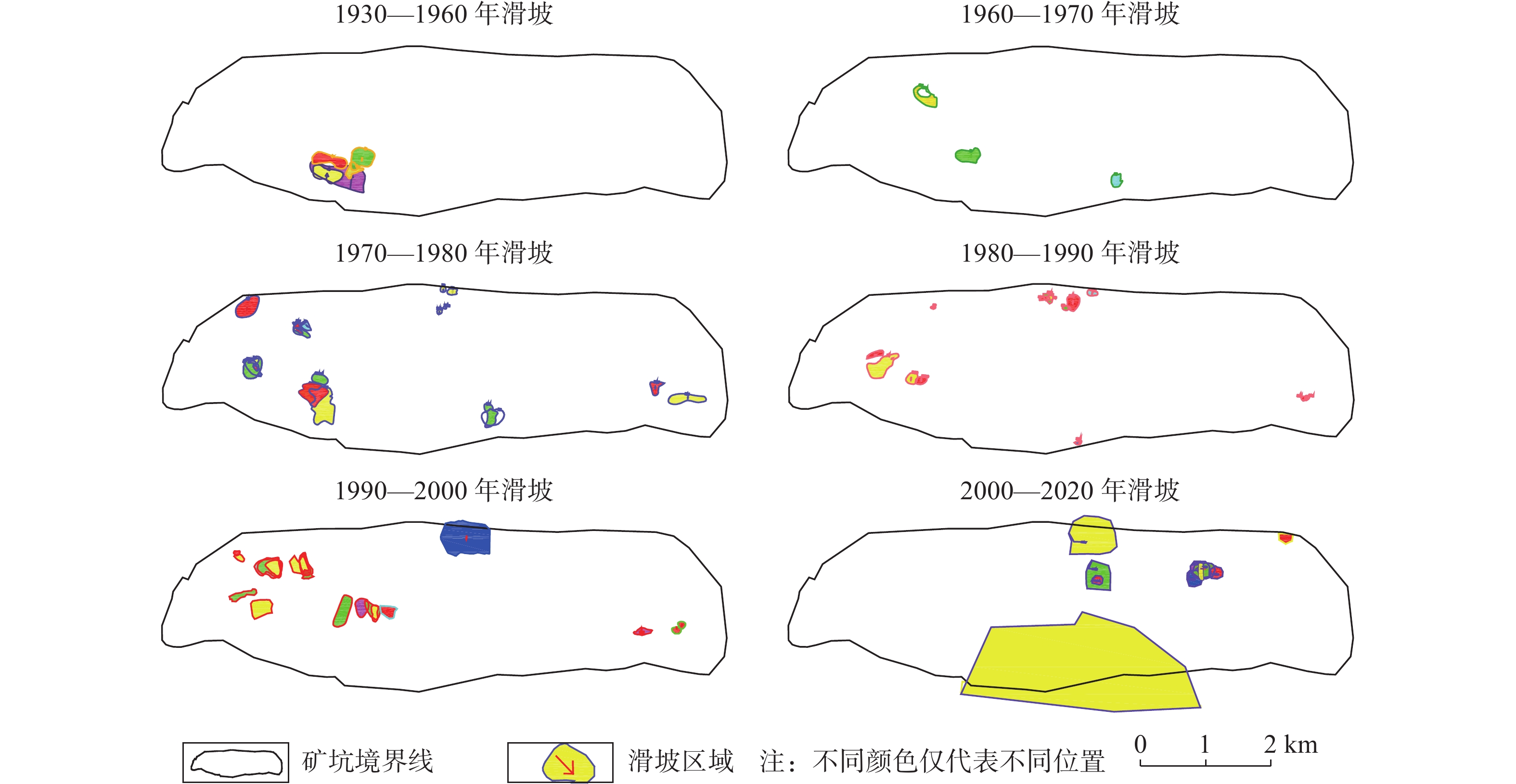
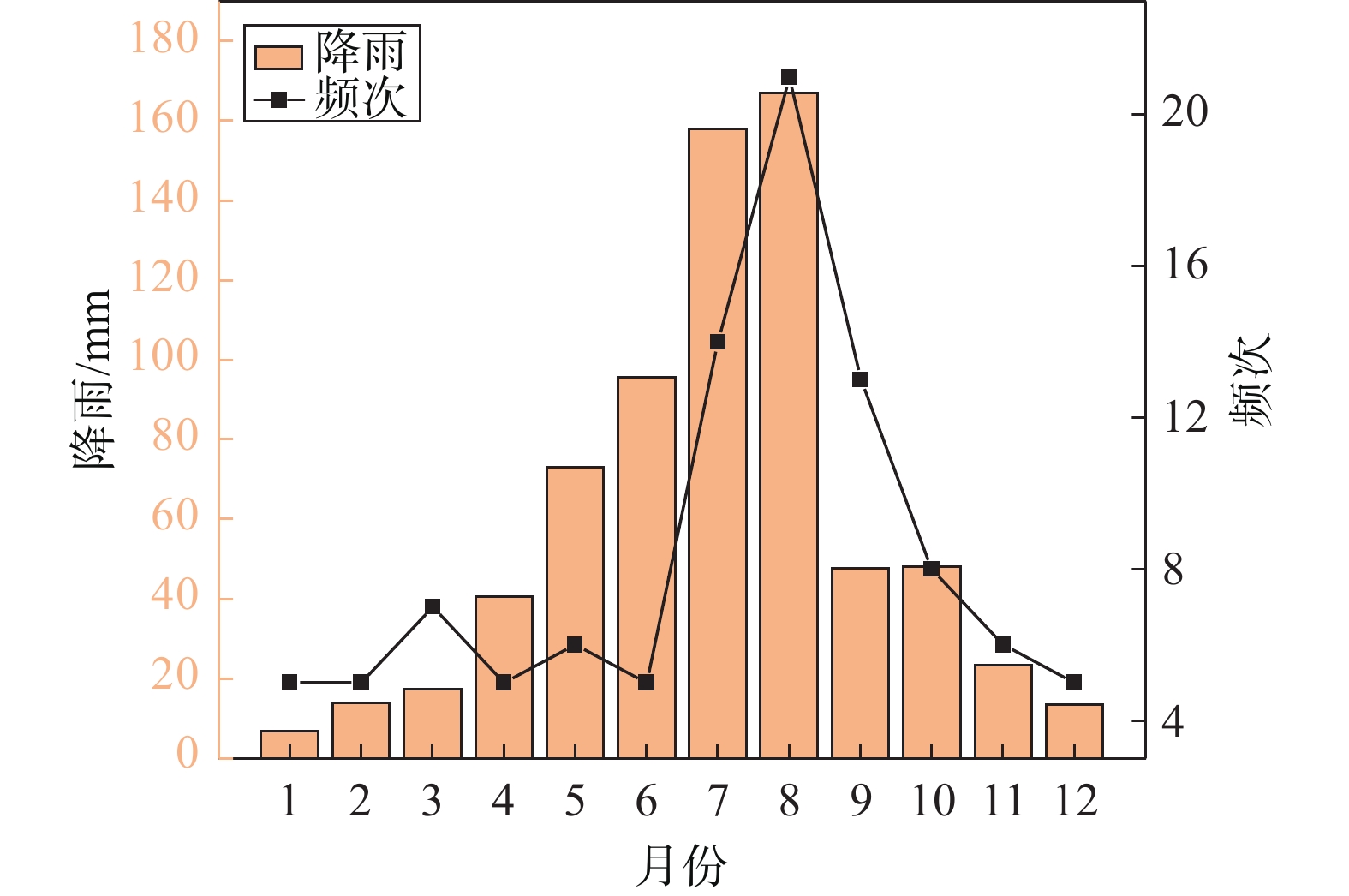
摘要: 已有百年开采历史的抚顺西露天矿进入闭坑期,由于资源的开采,导致西露天矿长期受地质灾害的威胁。为了总结西露天矿地质灾害发生规律、保障矿区及近矿城区的生产生活安全,同时为其他同类露天矿的灾害分析、安全防护提供可参考案例,从时间和空间尺度对抚顺西露天矿滑坡、地裂缝的分布规律和影响因素进行研究分析,基于DPSR模型,从驱动力响应、压力响应、状态响应三个方面提出对应的断链减灾和安全防护措施。地质灾害的时空分布特征为:滑坡灾害最早出现于1927年南帮西部,滑坡主要位置由南帮西部区域向西端帮、北帮西部、北帮中部、北帮东部方向发展,近年南帮出现大规模岩质边坡滑移变形,1970—2000年期间,滑坡灾害最为频发,2000年以后滑坡灾害频次减少,且滑坡灾害多发生在5—9月份;北帮附近地裂缝出现于1960年后,上世纪70、80年代加速发育,走向与F1、F1A断层走向基本一致,南帮地裂缝分布在南帮巨大滑移变形体后缘,呈弧扇型分布,于2009年出现,2012年后迅速发展。通过对灾害影响因素分析发现,滑坡与地裂缝存在同源性和互为因果性的链式关系,影响矿区地质灾害发生的主要因素为地质构造和不良工程地质环境控制、采矿活动驱动、降雨及地下水因素的诱发。Abstract: Fushun west open-pit mine, which has a history of 100 years of mining, entered the pit-closing period. Due to the exploitation of resources, the west open-pit mine was threatened by geological disasters for a long time. In order to summarize the occurrence regularity of geological disasters in the west open-pit mine, ensure the safety of production and life in the mining area and near-mining city, and provide reference cases for disaster analysis and safety protection of other similar open-pit mines, the distribution law and influencing factors of landslides and ground fissures in west open-pit mine are studied and analyzed from time and space scale, based on the DPSR model, the corresponding measures of chain break disaster reduction and safety protection are put forward from three aspects: driving force response, pressure response and state response. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics of landslide: in space, it first appeared in the western part of the southern slope in 1927. In recent hundred years, due to the driving influence of open-pit mining and underground mining, the main location of landslide developed from the western part of the southern slope to the western part of the northern slope, the western part of the northern slope, the central part of the northern slope and the eastern part of the northern slope. In recent years, large-scale rock slope sliding deformation occurred in the southern slope. Actually, from 1970 to 2000, landslide disasters occurred most frequently. After 2000, the frequency of landslide disasters decreased, and most of them occurred from May to September. Spatial-temporal distribution of ground fissures: the ground fissures near the north slope appeared after 1960, and accelerated in 1970s and 1980s, with the strike basically consistent with that of F1 and F1A faults; the ground fissures in the southern slope are distributed in the rear edge of the huge slip deformation body in the southern slope, which are arc-fan shaped and appeared in 2009 and developed rapidly after 2012. Through the analysis of disaster influencing factors, it is found that there is a chain relationship of homology and mutual causality between landslides and ground fissures, and the main factors affecting the occurrence of geological disasters in mining areas are geological structure and control of unfavorable engineering geological environment, driving of mining activities and inducing of rainfall.
-
0. 引言
我国地质灾害种类多、分布广、危害大。为进一步减轻地质灾害风险,最大限度保障人民群众生命财产安全,从2003年起,我国大陆开始开展汛期区域地质灾害气象预警工作,并形成预警产品面向公众的发布,在地质灾害防治中发挥了 “消息树”和“发令枪”的作用,取得了明显的社会经济效益[1],极大地提升了公众社会对防范地质灾害的认知。随着该项工作的不断推进,预警产品的内涵从粗到细逐步走向规范化,包括了预警范围、等级、时段和文字说明等内容[2],且临灾发布工作要求快速、高效和精准。然而这些信息若靠人工获取并不是件易事,比如要经技术人员通过读取预警区划图并研判后,才能粗略得出空间分布范围等定性信息,这一过程耗时耗力,且难以达到定量描述的准确效果。因此自动计算预警结果并快速生成预警产品是预警系统的一个重要功能[2],围绕聚焦解决好地质灾害可能发生的地点、成灾范围等预警预报问题[3-4],考虑如何利用信息技术自动获取预警产品描述信息的实现势在必行。然而经检索发现国内直接进行相关研究还较少,可供参考的文献不多。为了快速形成权威、科学、符合实际的这一产品,本文提出一种可高效自动分析形成初步的预警产品描述信息的技术算法,为有关信息平台的功能模块的研发、支撑专家做出更详尽的预警产品研判提供理论支撑。
1. 算法原理
1.1 技术路线
以研究区行政区划图和预警区划图[2]为数据来源,应用GIS技术将空间位置信息和属性信息无缝结合,结合数学统计和地理知识等,精确获取预警等级在行政区划所处方位、区域占比和防治措施等精细描述的预警信息,将图面内容转换为直观的文本描述,为最终预警产品的快速生成奠定基础(图1)。
1.2 关键数据
为了实现目标,在开始研究前,要准备必要的空间图层作为计算的基础,即将具有不同预警等级属性的矢量栅格地质灾害预警区划图层和反映行政区名称及空间范围的研究区行政区划图层作为数据源,二者要求具有相同的地图投影参数。其中,前者一般通过网格剖分后通过多因子要素叠加进行综合评价得到,这一过程在当前地质灾害空间评价预警研究中是普遍采用的方法[5-6],但因不是本文的重点,故不再赘述。
1.3 预警描述信息各因子获取
1.3.1 预警等级集合概念模型
很显然,前述空间图层叠加结果中,不同预警级别对应的地区预警信息处于离散状态,且一般情况下,这些信息数量较为可观,为了后续分析数据高效便捷,有规律可循,需要提前分析预警等级、地区、方位等数据间的关联性,通过聚类分析建立分类簇集合信息,这一预警等级集合概念模型设计见图2。
图2中可以看出,预警等级集合以三级预警等级为唯一的主键,包括了这一等级下的地区列表预警信息子集合,而该子集合以地区名称为主键,包括了一对多的分布方位和面积占比列表,该列表以分布方位为唯一索引,在实际计算时,相同分布方位需要进行去重处理,所占的面积要进行求和运算。最终通过综合计算,形成该预警等级下的总体分布区域、分布方位等综合预警描述信息。
1.3.2 空间信息叠加与判别
空间关系描述是GIS系统的基本功能之一,GIS的技术支持的地质灾害风险区划的最终目的是划分不同灾害等级的区域,可为地质灾害预警提供依据[7-8]。通过将预警区划图层和行政区划分区图层进行空间叠加,遍历判断每个预警等级矢量栅格单元和行政区划单元的空间拓扑关系,确定该行政单元是否包括某预警级别(图3)。如果二者拓扑关系为不相离,说明该地区具备该等级,反之如果是包含、相交、穿越等非相离关系,则还需进行两两拓扑求交运算,并重新采用交集中的预警等级区参与面积计算更具科学性和精确性。
1.3.3 预警等级分布面积占比求算
一个由N个拐点(xi, yi)确定的封闭多边形的面积如式(1)计算:
(1) 式中:i——拐点序号;
N——拐点个数;
xi——第i个拐点x坐标;
yi——第i个拐点y坐标;
A——封闭多边形的面积。
相同方位的预警等级所占行政区划单元的面积占比(R)是对预警等级广泛程度的描述,算式如下:
(2) 式中:i——拐点序号;
N——拐点个数;
R——某预警等级的面积占比;
Ai——某预警等级单元的面积;
Si——某行政区划单元面积。
1.3.4 预警等级分布范围描述
对分布范围则用绝大部分、大部分、局部、个别四级进行空间范围的广泛程度描述,判别指标为集合中单元格之和的占比(R),定义见表1。
表 1 预警等级占比描述表Table 1. Description of the proportion of early warning levels某预警等级在行政单元中的占比 程度描述 R≥0.9 基本全域 0.7≤R<0.9 绝大部分 0.5≤R<0.7 大部分 0.2≤R<0.5 局部 R≤0.2 个别 1.3.5 预警等级单元分布方位求算
空间方向的定性描述是用若干主方向粗略地描述空间方向。而定量描述则是用方位角来量测空间目标之间的方向关系,因此方位角是空间方向描述的一个重要手段[9]。要获取一个预警等级单元在行政区划中的分布方向,实际上是通过计算该等级相对于所处区域的方位角得到(图4),结合地理知识,根据实际情况共划分出了8个方位角区间和对应的分布关系(图5)。
1、方位角计算
(1)形心求算
本次方位角计算要获取行政区划单元和预警等级单元的几何形心。一个由N个拐点(xi, yi)确定的封闭多边形的中心如式(3)、式(4)计算:
(3) (4) 式中:i——拐点序号;
N——拐点个数;
A——多边形的面积,由式(1)得出;
xi——第i个拐点x坐标;
yi——第i个拐点y坐标;
Cx——几何形心x坐标;
Cy——几何形心y坐标。
(2)方位角求算
当在平面上2个点的坐标已知时,给出方位角(十进制度数)公式如式(5):
(5) 式中:X2——平面上终点x坐标;
X1——平面上起点x坐标;
Y2——平面上终点y坐标;
Y1——平面上起点y坐标;
α——方位角。
(3)分布方向描述
当方位角得出后,便可以根据方位角与分布方向的映射关系图(图5)获取具体的分布方向。
1.4 预警描述信息提取
经过前述步骤后,将得到一个以预警等级为索引的数据集合,其中包括各个地区的预警信息子集合。将地区预警信息子集合按照预警方位的个数进行升序排列,为了简洁,可以选取前若干个方位作为主要的方位,其余的则以“等地区”代替,而该级别的防治措施则从表2中对照获取[2]。
表 2 预警等级防治措施描述表Table 2. Early warning level control measures description table预警等级 防治措施 1 请严密防范 2 请加强防范 3 请注意防范 4 请监测分析 1.5 形成预警描述综合信息
通过遍历预警等级集合,形成该地区综合的预警产品描述信息。最终某地区预警信息描述格式形成通用模板举例如下:风险大(Ⅱ级)主要分布于××地区的西北部、北部、东北等局部地区,请加强防范;风险较大(Ⅲ级)主要分布于××地区的西南、南部等个别地区,请注意防范。
2. 应用实现
2.1 数据准备
考虑到预警信息的范围划分取决于行政区划图,不同的划分将得到不同的预警产品描述信息,故可将行政区划图看作一个相对的变量,为了验证工作的灵活性和可扩展性,本次通过GIS软件形成了包括11个虚拟乡镇的地区作为预警范围实验数据进行工作(图6),该地区某日的矢量栅格地质灾害预警区划图层业已形成(图7),采用3 km×3 km为预警等级单元,预警单元总数为5194个。上述文件均为Shapefile格式,其投影参数为CGCS2000。
2.2 基于GDAL信息模块的研发
GDAL库(Geospatial Data Abstraction Library)是一个开源的用于栅格和矢量地理空间数据格式的C++转换器库,由开源地理空间基金会在MIT(麻省理工学院)风格的开源许可下发布,目前几乎所有的GIS和RS软件底层都使用GDAL来读写空间数据[10]。由于GDAL库能够很好地支持包括Shp格式在内的很多数据格式,因此本次工作基于GDAL和C++语言,在Visual Studio 2019平台下实现了整个研发验证过程。研发过程中,以本算法为理论基础,结合UML理论建立了空间分析类、因子获取类、信息处理类,并形成了类的方法、属性和事件(图8),最后编译形成了预警信息生成软件工具。
2.3 预警产品信息结果
利用已有的实际数据图层和软件工具,耗时不足1分钟形成了预警产品信息(表3)。从表中可以看出,该日预警级别包括了Ⅱ级、Ⅲ级,主要是以风险较大(Ⅲ级)为主,分布于秦姜董镇、王家湾镇、白堆子镇等地,并且有方位和分布范围程度描述。依据表中信息,通过组合可形成规范格式的综合预警产品描述信息,见图9。
表 3 某地区预警产品描述信息表Table 3. Table of product description for a specific region级别 分布地区 方位 占比/% 防治措施 风险大(Ⅱ级) 王家湾镇 西北等个别地区 8.40 加强防范 五里埔乡 东北、东部等个别地区 4.40 秦姜董镇 南部、东南、东北等个别地区 1.70 风险较大(Ⅲ级) 秦姜董镇 基本全域 96.60 注意防范 孙各庄乡 东北、西北、东南等 31.88 王家湾镇 基本全域 91.00 别山镇 东北、西南、西部等局部地区 33.00 白堆子镇 基本全域 96.60 龚家庄镇 西北、东南、东北等局部地区 24.60 雁儿湾镇 绝大部分 74.60 邱家庄乡 西南、东南、西部等局部地区 34.30 西岗镇 大部分地区 58.20 五里埔乡 东南、东部、东北等局部地区 32.00 上营镇 东北、西南、西北等 30.40 2.4 与传统人工分析对比验证分析
为了进一步验证算法的正确性和优越性,将风险预警范围图(图6)和预警区划图层(图7)进行叠加,通过逐一人工判断每个乡镇区域预警区划情况,可看出所有的乡镇的结果和预警区划图层(图7)的空间展现结果完全吻合,如王家湾镇预警产品信息为风险大(Ⅱ级)、分布于西北,占比不大(图10),这一目估结果与采用本算法生成的预警产品描述信息一致,其次应用计算过程耗时短暂,可见算法能完全满足汛期地质灾害风险预警之快速高效的需要,与传统人工定性分析相比,具有规范、快速、准确的特点,没有遗漏,其优越性显著。
3. 结论
文章提出了基于GIS技术支撑下的地质灾害风险预警产品描述信息的自动化生成技术方法,并以随机的行政区划图和已有的地质灾害预警区划图为数据源,采用GDAL库,通过研发预警信息获取模块进行了实例验证。结果表明,采用本算法形成预警产品描述信息快速高效,结果科学规范、完整全面,进一步提高了预警信息精度,不仅大大降低了预警产品信息获取的繁琐程度,而且节省了时间成本,又兼顾了产品的准确性,可为相关信息系统功能研发及专家研判提供基础理论支撑,将显著提高预警精细化程度和工作效率,适合在实际工作推广使用。
-
表 1 部分区域地下开采时间表
Table 1 Part of underground mining status table
采区 标高/m 开采时间 东区 下一路 −305~ −337 1952年10月—1955年12月 下二路 −342~ −380 1955年10月—1961年10月 下二高落 −342~ −362 1960年5月—1961年6月 下三路 −350~ −417 1962年5月—1964年5月 中区 下一路 −305~ −337 1954年3月—1958年4月 下二路 −342~ −380 1956年7月—1962年5月 下二高落 −342~ −378 1960年5月—1960年6月 西区 下一路 −305~ −337 1957年6月—1961年12月 上一路 −100~ −160 1964年1月—1973年12月 上二路南 −170~ −210 1971年1月—1973年12月 上二路北 −170~ −210 1972年6月—1977年5月 -
[1] 高国骧. 抚顺西露天矿开采技术[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1993 GAO Guoxiang. Mining technology of the Fushun west open pit[M]. Beijing: China Coal Industry Publishing House, 1993. (in Chinese)
[2] 王永胜, 郭静芸, 董高峰, 等. 辽宁抚顺西露天矿北帮边坡稳定性分析及变形分区[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2012,23(4):86 − 93. [WANG Yongsheng, GUO Jingyun, DONG Gaofeng, et al. Slope stability evaluation of Fushun west open-pit mine[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2012,23(4):86 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Yongsheng, GUO Jingyun, DONG Gaofeng, et al. Slope stability evaluation of Fushun west open-pit mine[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2012, 23(4): 86-93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 滕超, 王雷, 刘宝华, 等. 辽宁抚顺西露天矿南帮滑坡应力变化规律及影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(2):35 − 42. [TENG Chao, WANG Lei, LIU Baohua, et al. Stress variation within the southern landslide of Fushun West Open-Pit and its influencing factors[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(2):35 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract) TENG Chao, WANG Lei, LIU Baohua, et al. Stress variation within the southern landslide of Fushun West Open-Pit and its influencing factors[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(2): 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 吴季寰, 张春山, 孟华君, 等. 抚顺西露天矿区滑坡易发性评价与时空特征分析[J]. 地质力学学报,2021,27(3):409 − 417. [WU Jihuan, ZHANG Chunshan, MENG Huajun, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of landslide susceptibility in the West open-pit mining area, Fushun, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2021,27(3):409 − 417. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.03.037 WU Jihuan, ZHANG Chunshan, MENG Huajun, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of landslide susceptibility in the West open-pit mining area, Fushun, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2021, 27(3): 409-417. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.03.037
[5] 李泽闯. 抚顺西露天矿南帮滑坡滑动机制与滑坡破坏时间预测预报研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017 LI Zechuang. Study on deformation mechanism and failure prediction of landslide in west open-pit mine in Fushun[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 王宏飞. 抚顺市区地裂缝分布特征、成因机制及活动性预测模型研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017 WANG Hongfei. Study on distribution characteristics, genetic mechanism and activity prediction model of ground fissures in Fushun City[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李淑艳. 抚顺市矿山环境地质灾害形成机制与防治对策研究[D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2008 LI Shuyan. The research of mining environmental geology disaster's forming mechanism and countermeasures of Fushun City[D]. Beijing: China coal research institute, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘大勇, 王恩德, 宋建潮, 等. 抚顺西露天煤矿滑坡与降雨的关系及预报方法[J]. 灾害学,2008,23(2):50 − 54. [LIU Dayong, WANG Ende, SONG Jianchao, et al. The relation between landslide and rainfall and prediction method of western open-pit coal mine of Fushun[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2008,23(2):50 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2008.02.012 LIU Dayong, WANG Ende, SONG Jianchao, et al. The relation between landslide and rainfall and prediction method of western open-pit coal mine of Fushun[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2008, 23(2): 50-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2008.02.012
[9] 翟文杰, 钟以章, 姜德录, 等. 抚顺西露天煤矿地质灾害预测[J]. 自然灾害学报,2006,15(4):132 − 137. [ZHAI Wenjie, ZHONG Yizhang, JIANG Delu, et al. Prediction of geological disaster in Fushunxilutian Coal Mine[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2006,15(4):132 − 137. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2006.04.024 ZHAI Wenjie, ZHONG Yizhang, JIANG Delu, et al. Prediction of geological disaster in Fushunxilutian Coal Mine[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2006, 15(4): 132-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2006.04.024
[10] 高安琪, 王金安, 李飞, 等. 西露天矿周边建筑物损害区位特征分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(4):1320 − 1330. [GAO Anqi, WANG Jin’an, LI Fei, et al. Locational characteristics of damage on buildings around the West Open-pit Mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(4):1320 − 1330. (in Chinese with English abstract) GAO Anqi, WANG Jin’an, LI Fei, et al. Locational characteristics of damage on buildings around the West Open-pit Mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(4): 1320-1330. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 陈毓. 抚顺西露天矿采空区北部区域地质灾害风险评估与适应性评价研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2021,48(3):106 − 111. [CHEN Yu. Study on risk assessment and adaptability evaluation of regional geological hazards in the northern part of goaf in Fushun west surface mine[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2021,48(3):106 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Yu. Study on risk assessment and adaptability evaluation of regional geological hazards in the northern part of goaf in Fushun west surface mine[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2021, 48(3): 106-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 纪玉石, 申力, 刘晶辉. 采矿引起的倾倒滑移变形机理及其控制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(19):3594 − 3598. [JI Yushi, SHEN Li, LIU Jinghui. Deformation mechanism and control of mining-induced toppling-displacement[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(19):3594 − 3598. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.19.032 JI Yushi, SHEN Li, LIU Jinghui. Deformation mechanism and control of mining-induced toppling-displacement[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(19): 3594-3598. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.19.032
[13] 申力, 纪玉石, 刘大勇, 等. 采矿引起的边坡倾倒滑移变形机理与变形安全性分析研究—以抚顺西露天矿边坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2006,17(3):63 − 68. [SHEN Li, JI Yushi, LIU Dayong, et al. Deformation mechanism and stability analysis of slope toppling-sliding rock mass due to mining:A case study on west open pit slope of Fushun Coal Mine[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2006,17(3):63 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2006.03.015 SHEN Li, JI Yushi, LIU Dayong, et al. Deformation mechanism and stability analysis of slope toppling-sliding rock mass due to mining: A case study on west open pit slope of Fushun Coal Mine[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2006, 17(3): 63-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2006.03.015
[14] 杨天鸿, 芮勇勤, 唐春安, 等. 抚顺西露天矿蠕动边坡变形特征及稳定性动态分析[J]. 岩土力学,2004,25(1):153 − 156. [YANG Tianhong, RUI Yongqin, TANG Chunan, et al. Study on deformation features and dynamic stability of creeping slope of Fushun West Strip Mine[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2004,25(1):153 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2004.01.033 YANG Tianhong, RUI Yongqin, TANG Chunan, et al. Study on deformation features and dynamic stability of creeping slope of Fushun West Strip Mine[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2004, 25(1): 153-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2004.01.033
[15] 中国煤炭学会露天开采专业委员会. 中国露天煤炭事业发展报告: 1914—2007[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2010 China Coal Society Open-pit Mining Professional Committee. Development report of open-pit coal industry in China[M]. Beijing: China Coal Industry Publishing House, 2010. (in Chinese)
[16] 毛佳睿, 武雄. 山西省黄土崩塌影响因素及时空分布特征[J]. 科学技术与工程,2020,20(10):3799 − 3807. [MAO Jiarui, WU Xiong. Influencing factors and temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of loess collapse in Shanxi Province[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2020,20(10):3799 − 3807. (in Chinese with English abstract) MAO Jiarui, WU Xiong. Influencing factors and temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of loess collapse in Shanxi Province[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(10): 3799-3807. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 刘向峰, 郭子钰, 王来贵, 等. 降雨矿震叠加作用下抚顺西露天矿边坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):40 − 46. [LIU Xiangfeng, GUO Ziyu, WANG Laigui, et al. Analysis on the slope stability of Fushun West Open-pit Mine under superimposed action of rainfall, mine and earthquake[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):40 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Xiangfeng, GUO Ziyu, WANG Laigui, et al. Analysis on the slope stability of Fushun West Open-pit Mine under superimposed action of rainfall, mine and earthquake[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(4): 40-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 李绍红, 朱建东, 王少阳, 等. 考虑降雨类型的基岩型浅层边坡稳定性分析方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(2):131 − 135. [LI Shaohong, ZHU Jiandong, WANG Shaoyang, et al. Stability analysis methods for the bedrock shallow slope considering rainfall types[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(2):131 − 135. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Shaohong, ZHU Jiandong, WANG Shaoyang, et al. Stability analysis methods for the bedrock shallow slope considering rainfall types[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(2): 131-135. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 张勇, 温智, 程英建. 四川巴中市滑坡灾害与降雨雨型关系探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):178 − 182. [ZHANG Yong, WEN Zhi, CHENG Yingjian. A discussion of the relationship between landslide disaster and rainfall types in Bazhong of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):178 − 182. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Yong, WEN Zhi, CHENG Yingjian. A discussion of the relationship between landslide disaster and rainfall types in Bazhong of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(2): 178-182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 马水山, 雷俊荣, 张保军, 等. 滑坡体水岩作用机制与变形机理研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,2005,22(5):37 − 39. [MA Shuishan, LEI Junrong, ZHANG Baojun, et al. Study on rock-water interaction and deformation mechanism of landslide[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2005,22(5):37 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2005.05.011 MA Shuishan, LEI Junrong, ZHANG Baojun, et al. Study on rock-water interaction and deformation mechanism of landslide[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2005, 22(5): 37-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2005.05.011
[21] 刘新荣, 熊飞, 李滨, 等. 水力作用下岩质斜坡破坏机制和稳定性分析研究现状[J]. 中国岩溶,2020,39(4):547 − 558. [LIU Xinrong, XIONG Fei, LI Bin, et al. Current situation of research on failure mechanism and stability of rock slopes under hydraulic action[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2020,39(4):547 − 558. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Xinrong, XIONG Fei, LI Bin, et al. Current situation of research on failure mechanism and stability of rock slopes under hydraulic action[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(4): 547-558. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 张秀梅. 基于PSR模型的煤炭资源型城市生态安全评价研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2011 ZHANG Xiumei. Ecological security evaluation of coal-mining supported city based on PSR model[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 张天祥,王艳霞,张雪珂,林钏,周汝良. 基于样本优化和机器学习的地质灾害气象风险预报模型研究——以云南省怒江州为例. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 201-215 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴逢涛,杨志全,赵旭光. 基于Stacking集成机器学习模型的川西重大交通干线地质灾害易发性评价. 科学技术与工程. 2025(13): 5340-5350 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 廖常左,李睿达,吴彦灵. 基于生命共同体理念的农业文化遗产地生态保护修复格局识别. 中国城市林业. 2025(02): 107-114 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 高林,张绍波. 大同市地质灾害危险性评价. 中国新技术新产品. 2024(02): 128-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 袁永建,张莲花. 基于AHP-熵值法模糊评价模型在滑坡灾害风险性评价中的应用. 甘肃水利水电技术. 2024(03): 38-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘帅,王涛,曹佳文,刘甲美,张帅,辛鹏. 基于优化随机森林模型的降雨群发滑坡易发性评价——以西秦岭极端降雨事件为例. 地质通报. 2024(06): 958-970 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵鹏,文刚,何展昌,王官洋,陈磊,申晓畅,王开正,唐鸿磊. 基于机器学习的金沙江流域浅层滑坡易发性评价. 水利水电技术(中英文). 2024(10): 53-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈锡锐,陈思尧,杨剑红,刘虹强,袁兆平,朱国宝,谢晓文,蔡国军. 四川什邡市地质灾害基本特征与易发性评价. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(06): 153-163 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(8)





 下载:
下载:
















 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS