Progress of the special-subjects study on the construction of comprehensive geological disaster prevention and control system in Yunnan Province
-
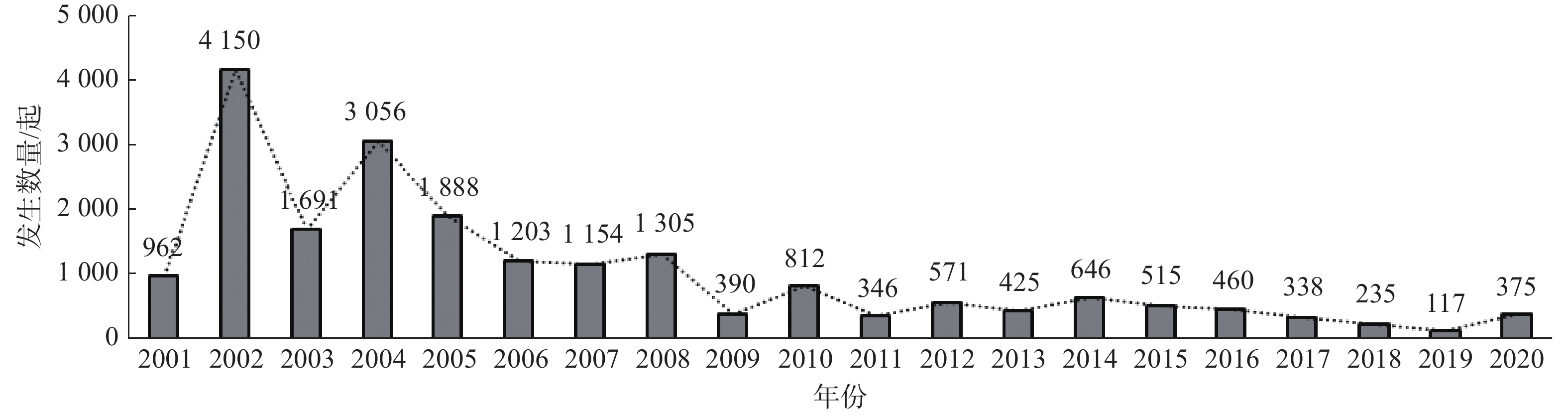
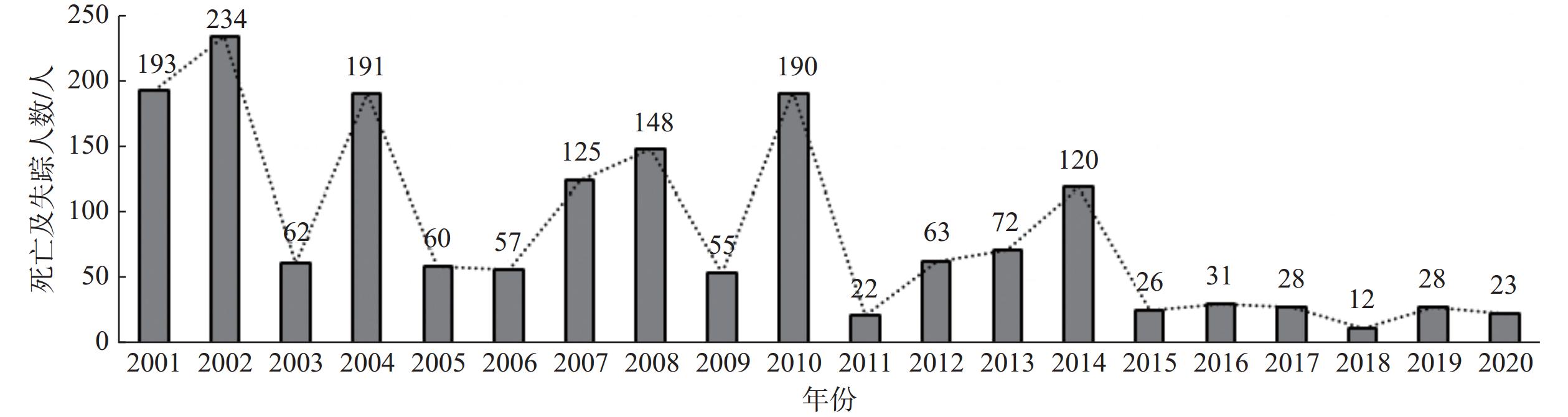
摘要: 云南省地质灾害综合防治体系建设是国内规模最大、最广泛的地质灾害防治专项,其实施使全省地质灾害发生数量大幅减少,因灾死亡及失踪人数明显递减,防灾减灾成效显著。文章依据12项系列专题研究成果,综述了体系建设实施概况及防灾减灾成效,归纳评述了取得的主要科技成果,重点对高原地质灾害成因、规律认识、特殊岩土控灾机制、易发性分区评价、隐患综合遥感识别、自动化监测预警及信息标准体系建设进展进行了总结,成果可为云南省地质灾害综合防治提供经验借鉴。Abstract: The establishment of the comprehensive geological disaster prevention and control system in Yunnan province stands as China’s most extensive and grand-scale endeavor in safeguarding the prevention and control of geological disasters in China. Its implementation has led to a significant reduction in the occurrence of geological disasters, resulting in a substantial decrease in both casualties and missing persons affected by such disasters. This accomplishment has yielded remarkable outcomes in disaster prevention and mitigation. Based on the results of 12 series monographic studies, this paper provides an overview of the implementation of the system and its disaster prevention and mitigation effects. It summarizes the main scientific and technological achievements, with a particular focus on the causes and patterns of plateau geological disasters, understanding of special rock and soil disaster control mechanisms, susceptibility zoning evaluation, comprehensive remote sensing identification of geological hazards, progress in automated monitoring and early warning, and the development of geological environment information standard system. These achievements can provide valuable insights for the comprehensive geological disaster prevention and control in Yunnan Province.
-
0. 引 言
据不完全统计我国共有露天煤矿约300座(不含井露联合开采煤矿),产能达7.5908×108 t/a[1]。露天矿山边坡失稳滑坡会直接威胁到矿山工作者的生命和财产安全[2],由若干台阶构成的边坡也是露天矿山生产运输的主要依托对象,露天边坡稳定性直接影响到露天矿山的建设和生产。露天矿边坡稳定性分析一直是岩土工程领域研究的热点问题,一方面,露天矿边坡往往受多种影响因素共同作用,关系复杂[3]。另一方面,试验室难以还原现场地质条件及其他因素的影响,试验室岩样数据往往不能直接用于矿山边坡稳定性分析,所以作为露天矿边坡稳定性计算及数值模拟中岩(土)体的参数取值具有很大的模糊性,导致露天矿边坡是一个不确定性的系统,其稳定性评价也是一个不确定、多因素、非线性问题[4]。
针对露天矿边坡稳定性评价问题的不确定性、复杂性,一些学者将模糊评价理论等不确定性分析方法应用到边坡稳定性分析中。蒋中明[5]通过对边坡刚体极限平衡分析中模糊因素的分析, 提出了一种使用模糊集理论计算工程边坡稳定性的方法。丁浩江等[6]、王华俊等[7]分别运用模糊综合评价模型对澜沧江某水电站泄洪洞出口边坡和宁波市国省道公路岩质边坡进行了稳定性评价,评价结果均与实际情况吻合较好,验证了模糊综合评价方法运用于边坡稳定性分析的有效性。由于不同影响因素对边坡稳定性的影响不同,模糊综合评价方法中边坡影响因素权重的确定存在主观性,因此先采用层次分析法客观确定不同因素对边坡稳定性的影响权重进而采用模糊综合评价法对边坡稳定性进行评价效果会更好[8 − 9]。但是目前边坡稳定性分析的层次分析-模糊综合评价模型的评价指标主要来自边坡地质调查和边坡基本形态。已有研究中,将边坡变形监测信息作为评价指标纳入到该模型中的研究相对较少;此外已有研究主要通过现场观察边坡是否稳定来验证模型,这种模型验证方法存在一定的主观性。
基于此,本文建立了考虑边坡监测信息的层次分析-模糊综合评价模型,首先对边坡监测数据进行分析,然后将边坡监测信息纳入边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型中,同边坡几何形态、边坡地质信息、气象水文信息等构成边坡系统的评价指标,然后基于层次分析法确定边坡稳定性评价指标的权重,最后基于隶属度最大原则确定边坡稳定性状态。将建立的层次分析-模糊综合评价模型应用于扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡稳定性评价,综合得出北帮边坡稳定性状况,最后通过数值模拟求解边坡安全系数对模型评价结果进行验证。
1. 边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型
模糊综合评价法对于复杂及不确定系统的评价具有明显的优势,将模糊综合评价法应用于边坡稳定性分析中首先需要确定边坡模糊指标集和评价集,然后根据隶属度函数确定单因子评价矩阵,根据边坡指标权重进行赋值,最后将权重向量与评价矩阵相结合根据隶属度最大原则得到最终的边坡稳定性评价结果[10 − 12]。
1.1 边坡模糊综合评价指标体系
根据相关规范[12],边坡的稳定性可以分为稳定、基本稳定、欠稳定、不稳定4个级别,同时建立边坡几何形态、边坡地质信息、边坡气象水文信息、边坡监测信息等四类边坡一级影响指标。边坡几何形态包括边坡坡高、边坡坡度、边坡结构类型3类指标;边坡地质信息包括边坡岩性、边坡弱层2项评价指标,边坡气象水文信息包括地下水影响、年平均降雨量2项评价指标;边坡监测信息主要包括地面变形情况、边坡变形速率等评价指标。边坡评价指标共9项,其中定量指标4项,定性指标5项。参考规范及已有研究[12 − 13]确定影响等级如表1和表2所示。
表 1 连续型指标影响等级划分Table 1. Classification of impact levels for continuous influencing indicators稳定性 坡高/m 坡度/(°) 年均降雨量/mm 地表变形
速率/(mm·d−1)稳定 0~100 0~15 0~500 5 基本稳定 >100~200 >15~30 >500~800 >5~30 欠稳定 >200~300 >30~50 >800~1200 >30~80 不稳定 >300 >50 >1200 >80 表 2 离散型指标影响等级划分Table 2. Classification of impact levels for discrete influencing indicators稳定性 岩性 结构类型 弱层 地面变形 地下水影响 稳定 坚硬岩体 均质/反倾 无 无 很弱 基本稳定 中等坚硬 斜交/横坡 反倾夹层 弱 较弱 欠稳定 软弱岩体 近水平坡 顺倾夹层、
反倾基岩中等 较强 不稳定 松散体 顺向坡 顺倾基岩 强烈 很强 1.2 层次分析法
对于露天矿边坡而言,各评价指标对边坡稳定性评价的贡献度是不同的,因此有必要利用层次分析法确定边坡各评价指标的影响因子[14]。通过标度方法,将影响因子的重要程度定量化[15]。如表3所示,通过指标两两比较后得出最终的边坡评价指标排序,表3中
标度 含义 1 3 5 7 9 2,4,6,8 介于以上两种比较之间的标度值 倒数 1.3 模型隶属度函数
隶属函数的确定对于边坡模糊综合评价具有重要的意义,隶属函数值即隶属度是表征边坡评价因子隶属于某个评价等级的程度。对于定量因素采用三角隶属度分布函数,本文采用的三角隶属度函数式(1)—(3)[17 − 18]。离散型指标隶属度的确定取值见表4[9, 13]。考虑到各个评价指标在边坡稳定性评价中的贡献不同,采用层次分析法将各项评价指标赋予一定的权重值,通过标度方法,将评价因子的重要程度定量化。
表 4 离散型指标评价隶属度表Table 4. Discrete index evaluation membership degree离散型指标 具体指标 离散型指标评价隶属度 稳定 基本稳定 欠稳定 不稳定 岩性 坚硬岩体 0.8 0.2 0 0 中等坚硬 0.4 0.5 0.1 0 软弱岩体 0 0.2 0.5 0.3 松散体 0 0 0.2 0.8 结构类型 顺向坡 0 0 0.2 0.8 近水平坡 0.1 0.2 0.7 0 斜交/横坡 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 均质/反倾 0.8 0.2 0 0 弱层 无 1 0 0 0 反倾夹层 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 顺倾夹层、反倾基岩 0 0.1 0.7 0.2 顺倾基岩 0 0 0.2 0.8 地面变形 无 0.8 0.2 0 0 弱 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 中等 0 0.1 0.7 0.2 强烈 0 0 0.2 0.8 地下水影响 很弱 0.55 0.30 0.10 0.05 较弱 0.25 0.50 0.15 0.10 较强 0.05 0.10 0.30 0.55 很强 0.05 0.15 0.10 0.70 (1) (2) (3) 式中:
2. 层次分析-模糊综合评价模型应用
2.1 工程概况
扎哈淖尔露天煤矿位于内蒙古自治区通辽市西北端,露天矿北帮于2020年5月出现明显的变形现象,边坡上部940水平及920水平出现明显裂隙,采场下部边坡850水平出现明显的大块岩体剪出现象,图1为扎哈淖尔露天矿的俯瞰图及现场图。沿边坡倾向方向选取研究剖面(图2),NO.1和NO.2为布置在剖面上的微变监测雷达监测特征点,露天矿北帮岩(土)层剖面如图3所示,北帮岩体整体倾向为逆倾、倾角5°~13°,边坡高度为234 m,坡度为16°,自上而下依次为第四系岩层、新近系和古近系岩层、泥岩、泥砂岩互层及煤层。经过现场勘探北帮850水平存在一层弱层,弱层厚度在1~2 m,钻孔岩芯(图4)显示弱层附近岩体较破碎。同时北帮边坡泥岩和第四系黏土中有出水点[20 − 21]。
2.2 基于层次分析-模糊综合评价模型的边坡稳定性评价
根据现场勘察及收集已有的矿山地质资料,确定边坡高度为234 m,坡度为16°,年平均降雨量为354.3 mm,边坡变形速率取目前NO.1点和NO.2点监测数据的平均值,根据现场监测取值为24 mm/d,对于折减系数的取值,基于安全的角度,边坡模糊综合评价中的折减系数选取数值计算所得的较低值(1.121),定量指标采用三角形隶属度函数确定(表5)。定性指标隶属度参考相关文献确定(表6)最后得到边坡模糊综合评价矩阵R,进一步利用层次分析法确定了扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡模糊评价指标的权重矩阵M,并进行一致性检验[22 − 24]。
表 5 北帮边坡定量指标隶属度Table 5. Membership degree of quantitative indexes for the northern slope稳定性 坡高隶属度 坡度隶属度 年均降雨量
隶属度地表变形速率
隶属度稳定 0 0.86 1 0 基本稳定 0.16 0.14 0 0.83 欠稳定 0.84 0 0 0.17 不稳定 0 0 0 0 表 6 北帮边坡定性指标隶属度Table 6. Membership degrees of qualitative indexes for the northern slope稳定性 岩性隶属度 结构类型
隶属度弱层隶属度 地面变形
隶属度地下水影响
隶属度稳定 0 0.80 0.20 0 0.05 基本稳定 0.20 0.20 0.70 0 0.10 欠稳定 0.50 0 0.10 0.20 0.30 不稳定 0.30 0 0 0.80 0.55 边坡地表变形监测主要分析微变监测雷达系统于2020年4月26日—2021年6月14日NO.1点位和NO.2点位的微变监测雷达监测数据,将监测点的变形速率用不同的点线图来表示(图5),由图5可见边坡最初变形速率较快,后期变形速率逐渐趋于稳定。
由模糊综合评价法确定的模糊综合评价矩阵以及通过层次分析法确定的影响因子矩阵,确定扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡评价矩阵,北帮边坡为稳定状态、基本稳定状态、欠稳定状态、不稳定状态的隶属度分别为0.27545,0.43196,0.19304,0.09955,最大隶属度原则是得到边坡稳定性最常用的方法,但是如果第二大隶属度与最大隶属度值很接近的话,得到的评价结果准确度降低,基于此,首先对隶属度矩阵进行有效性检验。最大隶属度有效性验证公式如下[25]:
(4) 式中:
经过计算,扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型所得的隶属度矩阵有效度为0.65521,属于比较有效,说明评价结果是稳定的,根据隶属度最大原则判定北帮边坡属于基本稳定状态。
2.3 模型检验
本研究通过数值模拟对层次分析-模糊综合评价模型得到的北帮边坡稳定性结果进行检验,根据北帮研究区剖面(图2)建立数值计算模型(图6),模型计算选取的坐标系为边坡临空面方向为X正方向,竖直向上为Z正方向。模型的左右边界(南北)、前后边界(东西)和底部边界分别以水平和垂直方向的位移约束,顶面设定为自由面,采用摩尔-库仑弹塑性本构模型进行求解,岩土体力学参数采用Hoek-Brown岩体强度方法并结合现场研究报告综合确定岩土体力学参数如表7所示[26 − 27]。
表 7 岩层物理力学参数表Table 7. Physico-mechanical parameters of strata岩层 重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 排弃物料 17.70 10.0 20.0 第四系地层 17.90 17.0 11.7 弱层 17.90 8.0 5.7 新近系和古近系地层 17.90 14.0 13.0 泥岩层 20.20 33.7 15.4 砂岩层 24.40 40.0 28.0 泥砂岩互层 23.45 35.0 24.6 煤层 12.70 24.5 21.0 采用人为定义边坡折减强度上下限的方法确定边坡的折减系数,首先初步确定边坡折减系数的范围,然后以0.001为一个梯度进行折减计算,通常数值模拟对岩土体强度的折减是针对整个边坡区域进行折减,不能计算边坡内部多级滑动面。而对于多台阶边坡而言,每级台阶的折减系数和潜在滑移面都是值得关注的。因此在模拟过程中只折减850水平以上岩层和煤层的黏聚力和摩擦角[28 − 29]。模拟结果如图7所示,850水平之上形成潜在滑坡面,边坡剪切变形相对集中于局部化变形区域内,而区域外的变形相当于卸载后的刚体运动,潜在滑坡体将沿该滑动面滑动,滑动面两侧沿滑动面方向的位移相差明显,存在较大的变形梯度。通过监测边坡表面各测点位移可发现随着监测点高程增大其位移量减小,边坡内部形成潜在滑坡面,滑移面安全系数为1.121。
基于强度折减法得到北帮潜在滑移面安全系数分别为1.121(850水平以上),根据相关规范边坡稳定性划分表(表8)[12],北帮850水平上部边坡属于基本稳定边坡,层次分析-模糊综合评价模型得到的边坡稳定性状态与数值模拟强度折减法得到的边坡稳定性状态相一致,验证了模型的准确性。
表 8 边坡稳定性状态划分Table 8. Classification of slope stability states边坡安全系数 F<1.00 1.00≤F<1.05 1.05≤F<1.20 F≥1.20 边坡稳定状态 不稳定 欠稳定 基本稳定 稳定 3. 结论
(1)在监测数据分析和数值模拟的基础上,建立了考虑监测信息的边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型,该模型充分融合了边坡几何形态、边坡地质信息、气象水文信息、现场监测信息等多种信息。
(2)北帮边坡稳定性状态为稳定、基本稳定、欠稳定、不稳定,隶属度分别为0.27545,0.43196,0.19304,0.09955,根据隶属度最大原则得出北帮边坡目前处于基本稳定状态。
(3)通过数值模拟求解得北帮边坡滑移面安全系数为1.121,属于基本稳定边坡,强度折减法结果与所建立的边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型得到的边坡稳定性状态一致,验证了模型的有效性。
-
表 1 研究专题设置情况
Table 1 The research topic setting fact sheet
编号 专题名称 牵头单位/协作单位 1 云南高原地质环境特征与地质灾害发育规律研究 云南省地质环境监测院/昆明理工大学 2 云南高原山区地质灾害应急技术支撑体系研究 云南省地质环境监测院 3 云南高原山区崩滑流地质灾害自动化监测预警技术方法研究 云南省地质环境监测院 4 云南高原山区地质灾害隐患综合遥感识别技术研究 云南省地质环境监测院/中国自然资源航空物探遥感中心、中南大学 5 面向降雨型滑坡时空信息服务关键技术应用研究 云南省自然资源厅国土资源信息中心/云南省地质环境监测院、
中国地质大学(武汉)6 高原山区复杂环境条件地质灾害综合防治新型工程技术体系研究 云南地质工程勘察设计研究院 7 高原环境特殊岩土体地质灾害成因机制及防治工程技术研究 云南地质工程第二勘察院 8 高原岩溶场地塌陷隐患勘测识别及防治技术研究 中国有色金属工业昆明勘察设计研究院 9 云南高原深切峡谷区水利水电工程地质灾害问题及防治措施研究 云南华昆国电工程勘察有限公司/中国电建集团昆明勘测设计研究院、
昆明理工大学10 云南高原公路工程重大地质灾害成因机制及防治技术研究 云南省交通规划设计研究院 11 云南高原采矿沉陷区次生地质灾害隐患识别及防治对策研究 昆明煤炭设计研究院/昆明理工大学 12 云南高原地质灾害发育规律及防治技术序列研究 云南省地质调查局/云南省地质环境监测院、云南地质工程勘察设计研究院 13 《云南省地质灾害防治与地质环境保护研究论文集》选辑 云南省地质灾害研究会 表 2 云南省地质环境条件分区表
Table 2 Zoning of geological environmental conditions in Yunnan Province
地质环境条件等级 分区代号 分区名称 面积/km2 占全省面积/% 差 Ⅰ1 金沙江上游碎屑岩高山峡谷区 20 263.08 5.14 Ⅰ2 怒江流域中上游花岗岩变质岩高山峡谷区 18 525.07 4.70 Ⅰ3 金沙江北段碎屑岩玄武岩中山峡谷区 21 715.10 5.51 Ⅰ4 金沙江中段碎屑岩红层区 12 019.53 3.05 Ⅰ5 金沙江下游玄武岩碎屑岩深切割中山峡谷区 15 523.85 3.94 Ⅰ6 哀牢山变质岩中山峡谷区 28 561.80 7.25 较差 Ⅱ1 兰坪漾濞碎屑岩变质岩高山峡谷区 13 288.97 3.37 Ⅱ2 怒江流域中下游碎屑岩花岗岩宽谷区 31 892.84 8.09 Ⅱ3 景东镇沅变质岩深切山区 16 379.76 4.16 Ⅱ4 澜沧江中下游花岗岩中山宽谷区 22 130.89 5.61 中等 Ⅲ1 滇西花岗岩宽谷盆地区 16 133.86 4.09 Ⅲ2 丽江大理碎屑岩高原湖盆区 13 610.39 3.45 Ⅲ3 滇中碎屑岩红层高原区 25 383.59 6.44 Ⅲ4 威信镇雄碎屑岩碳酸盐岩褶皱山区 6 260.75 1.59 Ⅲ5 滇东碳酸盐岩碎屑岩山区 6 376.07 1.62 Ⅲ6 红河小江流域碳酸盐岩山区 5 474.41 1.39 Ⅲ7 富宁麻栗坡碎屑岩裂陷山区 7 404.82 1.88 Ⅲ8 澜沧江下游花岗岩变质岩宽谷区 21 476.98 5.45 较好 Ⅳ1 香格里拉松散层高原剥夷面 2 237.94 0.57 Ⅳ2 昭通鲁甸碎屑岩高原盆地区 2 544.78 0.65 Ⅳ3 滇东碳酸盐岩高原湖盆区 45 164.68 11.46 Ⅳ4 滇东南碳酸盐岩岩溶丘峰区 24 247.46 6.15 Ⅳ5 滇南碎屑岩低中山区 17 522.38 4.45 好 区域分布面积小且比较分散,不单独划区 表 3 怒江流域北段高山峡谷区地质灾害激发雨强预警判据
Table 3 Criteria for early warning of geological disasters in the alpine valley area of the northern section of the Nujiang River Basin
预警等级 预警时效/h 预警判据/mm 崩塌 滑坡 泥石流 一级 1 6 9 20 二级 6 8 三级 4.5 5 一级 24 80 110 120 二级 60 70 90 三级 35 45 60 -
[1] 王宇,杨迎冬,晏祥省,等. 云南鲁甸6·5级地震次生特大地质灾害的特征及原因[J]. 灾害学,2016,31(1):83 − 86. [WANG Yu,YANG Yingdong,YAN Xiangsheng,et al. Characteristics and causes of super-huge secondary geological hazards induced by M6.5 Ludian earthquake in Yunnan[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2016,31(1):83 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Yu, YANG Yingdong, YAN Xiangsheng, et al . Characteristics and causes of super-huge secondary geological hazards induced by M6.5 Ludian earthquake in Yunnan[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2016 ,31 (1 ):83 −86 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 韩俊,王保云. 基于原型网络的云南怒江州泥石流灾害易发性评价与区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(5):117 − 129. [HAN Jun,WANG Baoyun. A case study on the susceptibility assessment of debris flows disasters based on prototype network in Nujiang Prefecture, Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,34(5):117 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN Jun, WANG Baoyun . A case study on the susceptibility assessment of debris flows disasters based on prototype network in Nujiang Prefecture, Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020 ,34 (5 ):117 −129 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 杨得虎,朱杰勇,刘帅,等. 基于信息量、加权信息量与逻辑回归耦合模型的云南罗平县崩滑灾害易发性评价对比分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(5):43 − 53. [YANG Dehu,ZHU Jieyong,LIU Shuai,et al. Comparative analyses of susceptibility assessment for landslide disasters based on information value, weighted information value and logistic regression coupled model in Luoping County, Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(5):43 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Dehu, ZHU Jieyong, LIU Shuai, et al . Comparative analyses of susceptibility assessment for landslide disasters based on information value, weighted information value and logistic regression coupled model in Luoping County, Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (5 ):43 −53 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[4] 杨迎冬,汤沛,肖华宗,等. 云南省地质灾害与水系关系初步分析[J]. 灾害学,2017,32(3):36 − 39. [YANG Yingdong,TANG Pei,XIAO Huazong,et al. Preliminary analysis on relationships between geo-hazards and river systems of Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2017,32(3):36 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Yingdong, TANG Pei, XIAO Huazong, et al . Preliminary analysis on relationships between geo-hazards and river systems of Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2017 ,32 (3 ):36 −39 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 王宇. 云南省地质灾害防治与研究历史评述[J]. 灾害学,2019,34(3):134 − 139. [WANG Yu. Historical review of geological disaster prevention and research in Yunnan Province,China[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2019,34(3):134 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2019.03.025 WANG Yu . Historical review of geological disaster prevention and research in Yunnan Province, China[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2019 ,34 (3 ):134 −139 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2019.03.025[6] 王宇,祝传兵,张杰,等. 云南省地质灾害应急监测预警及处置措施研究[R]. 昆明:云南省地质调查局,2020. [WANG Yu,ZHU Chuanbing,ZHANG Jie,et al. Research on emergency monitoring and warning and disposal measures of geological disasters in Yunnan Province [R]. Kunming:Yunnan Geological Survey,2020. (in Chinese) WANG Yu, ZHU Chuanbing, ZHANG Jie, et al. Research on emergency monitoring and warning and disposal measures of geological disasters in Yunnan Province [R]. Kunming: Yunnan Geological Survey, 2020. (in Chinese)
[7] 王宇,黄成,周翠琼,等. 山区地质灾害应急调查的内涵及方法分析评述[J]. 中国岩溶,2020,39(4):492 − 499. [WANG Yu,HUANG Cheng,ZHOU Cuiqiong,et al. Review on the connotation and methods of emergency investigations to geological hazards in mountainous area[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2020,39(4):492 − 499. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Yu, HUANG Cheng, ZHOU Cuiqiong, et al . Review on the connotation and methods of emergency investigations to geological hazards in mountainous area[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2020 ,39 (4 ):492 −499 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 宋昭富,张勇,佘涛,等. 基于易发性分区的区域滑坡降雨预警阈值确定——以云南龙陵县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(4):22 − 29. [SONG Zhaofu,ZHANG Yong,SHE Tao,et al. Determination of regional landslide rainfall warning threshold based on susceptibility zoning: A case study in Longling County of Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(4):22 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) SONG Zhaofu, ZHANG Yong, SHE Tao, et al . Determination of regional landslide rainfall warning threshold based on susceptibility zoning: A case study in Longling County of Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (4 ):22 −29 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 王宇,康晓波,柴金龙,等. 云南高原地质灾害发育规律及防治技术序列研究报告[R]. 昆明:云南省地质调查局. 2022. [WANG Yu,KANG Xiaobo,CHAI Jinlong,et al. Research report on the development law and control technology sequence of geological hazards in Yunnan Plateau[R]. Kunming:Yunnan Geological Survey,2022. (in Chinese) WANG Yu, KANG Xiaobo, CHAI Jinlong, et al. Research report on the development law and control technology sequence of geological hazards in Yunnan Plateau[R]. Kunming: Yunnan Geological Survey, 2022. (in Chinese)
[10] 张奇林,赫念学,黄兴章,等. 高原山区复杂环境条件地质灾害综合防治新型工程技术体系研究专题研究报告[R]. 昆明:云南地质工程勘察设计研究院有限公司. 2021. [ZHANG Qilin,HE Nianxue,HUANG Xingzhang,et al. Research report on new engineering technology system of comprehensive prevention and control of geological disasters under complex environmental conditions in Plateau mountainous areas [R]. Kunming:Yunnan Geological Engineering Survey and Design Research Institute Limited Company,2021. (in Chinese) ZHANG Qilin, HE Nianxue, HUANG Xingzhang, et al. Research report on new engineering technology system of comprehensive prevention and control of geological disasters under complex environmental conditions in Plateau mountainous areas [R]. Kunming: Yunnan Geological Engineering Survey and Design Research Institute Limited Company, 2021. (in Chinese)
[11] 杨迎冬,晏祥省,王宇,等. 云南省地质灾害特征及形成规律研究[J]. 灾害学,2021,36(3):131 − 139. [YANG Yingdong,YAN Xiangsheng,WANG Yu,et al. The characteristics and formation of geological hazards in Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021,36(3):131 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2021.03.023 YANG Yingdong, YAN Xiangsheng, WANG Yu, et al . The characteristics and formation of geological hazards in Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021 ,36 (3 ):131 −139 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2021.03.023[12] 李强,刘珍,尹博,等. 高原环境特殊岩土体地质灾害成因机制及防治工程技术专题研究报告[R]. 昆明:云南地质工程第二勘察院有限公司. 2021. [LI Qiang,LIU Zhen,YIN Bo,et al. Research report on the cause mechanism and control engineering technology of geological disasters of special rock and soil mass in plateau environment [R]. Kunming:Yunnan Geological Engineering the Second Investigation Institute Limited Company,2021. (in Chinese) LI Qiang, LIU Zhen, YIN Bo, et al. Research report on the cause mechanism and control engineering technology of geological disasters of special rock and soil mass in plateau environment [R]. Kunming: Yunnan Geological Engineering the Second Investigation Institute Limited Company, 2021. (in Chinese)
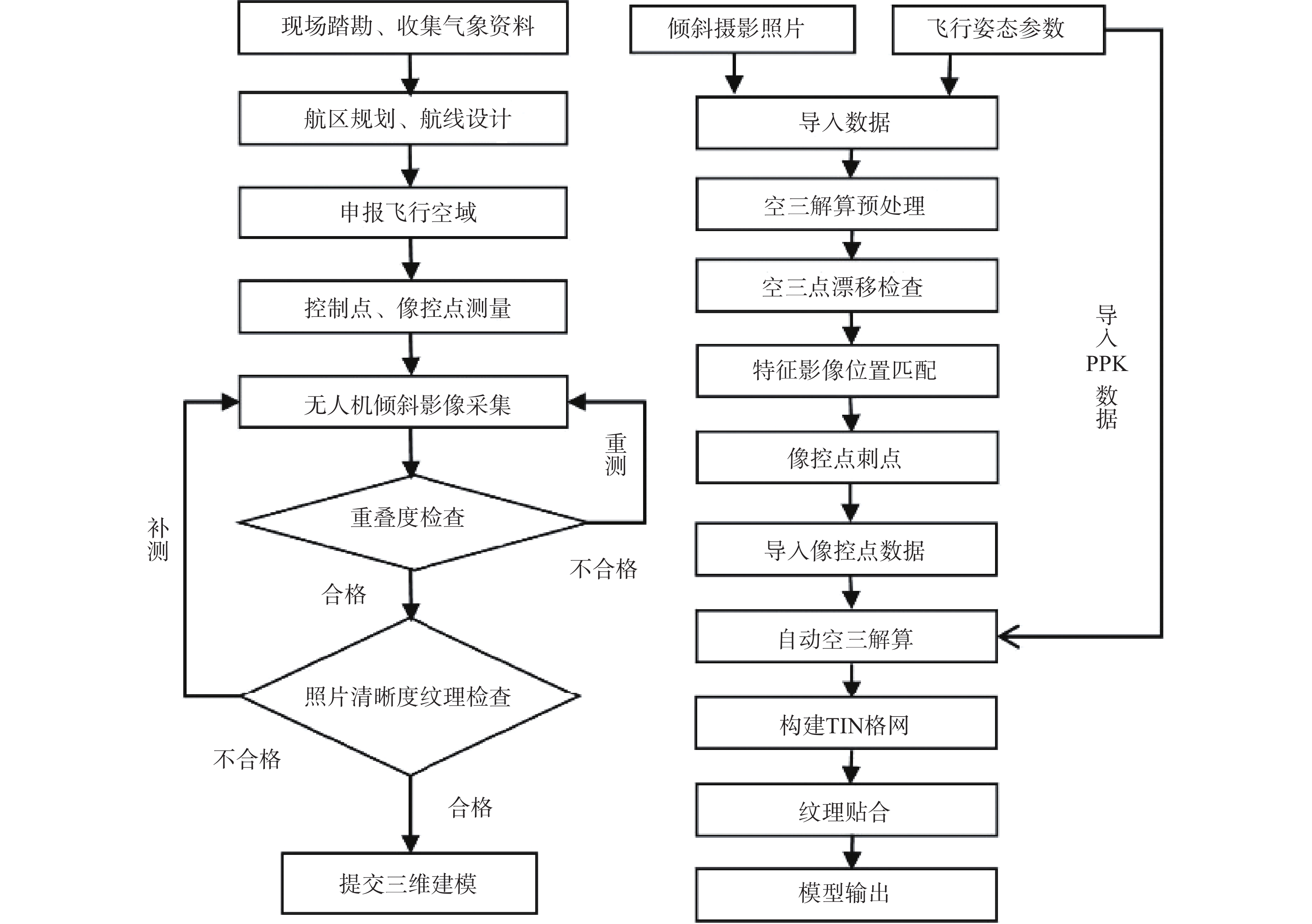
[13] 康晓波,王宇,张华,等. 云南高原岩溶塌陷发育特征及成因机制[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(5):50 − 58. [KANG Xiaobo,WANG Yu,ZHANG Hua,et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of karst collapse in Yunnan Plateau[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(5):50 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract) KANG Xiaobo, WANG Yu, ZHANG Hua, et al . Characteristics and formation mechanism of karst collapse in Yunnan Plateau[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (5 ):50 −58 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 李星宇,赫念学,魏英波,等. 复杂环境倾斜摄影与实景三维建模技术应用[J]. 测绘通报,2021(增刊1):20-24. [LI Xingyu,HE Nianxue,WEI Yingbo,et al. Application of tilt photography and real 3D modeling technology in complex environment[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2021(Sup 1):20-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Xingyu, HE Nianxue, WEI Yingbo, et al. Application of tilt photography and real 3D modeling technology in complex environment[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2021(Sup 1): 20-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 刘文连,徐鹏飞,眭素刚,等. 高原岩溶场地塌陷隐患勘测识别及防治技术研究专题研究报告[R]. 昆明:中国有色金属工业昆明勘察设计研究院有限公司. 2021. [LIU Wenlian,XU Pengfei,SUI Sugang,et al. Research report on the investigation,identification and prevention technology of plateau karst site collapse hazards [R]. Kunming:China Nonferrous Metal Industry Kunming Survey Design Institute Limited Company,2021. (in Chinese) LIU Wenlian, XU Pengfei, SUI Sugang, et al. Research report on the investigation, identification and prevention technology of plateau karst site collapse hazards [R]. Kunming: China Nonferrous Metal Industry Kunming Survey Design Institute Limited Company, 2021. (in Chinese)
[16] 张黎明,曹国献,许万忠,等. 云南高原采矿沉陷区次生地质灾害隐患识别及防治对策专题研究报告[R]. 昆明:昆明煤炭设计研究院有限公司. 2021. [ZHANG Liming,CAO Guoxian,XU Wanzhong,et al. Research report on the identification and prevention of secondary geological hazards in mining subsidence area of Yunnan Plateau[R]. Kunming:Kunming Coal Design & Research Institute Limited Company,2021. (in Chinese) ZHANG Liming, CAO Guoxian, XU Wanzhong, et al. Research report on the identification and prevention of secondary geological hazards in mining subsidence area of Yunnan Plateau[R]. Kunming: Kunming Coal Design & Research Institute Limited Company, 2021. (in Chinese)
[17] 王文,张志,张岩,等. 自然灾害综合监测预警系统建设研究[J]. 灾害学,2022,37(2):229 − 234. [WANG Wen,ZHANG Zhi,ZHANG Yan,et al. Research on the construction of comprehensive monitoring and early warning system for natural disasters[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2022,37(2):229 − 234. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Wen, ZHANG Zhi, ZHANG Yan, et al . Research on the construction of comprehensive monitoring and early warning system for natural disasters[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2022 ,37 (2 ):229 −234 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 李傲雯,李永红,姚超伟,等. 几种地质灾害监测预警和成功预报的模式[J]. 灾害学,2020,35(1):222 − 229. [LI Aowen,LI Yonghong,YAO Chaowei,et al. Several modes of geological disasters monitoring,early warning and successful predicting[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2020,35(1):222 − 229. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Aowen, LI Yonghong, YAO Chaowei, et al . Several modes of geological disasters monitoring, early warning and successful predicting[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2020 ,35 (1 ):222 −229 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] 杨江涛,李波,李伯宣,等. 自贡市地质灾害专群结合监测预警模式升级与实践[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):130 − 134. [YANG Jiangtao,LI Bo,LI Boxuan,et al. Upgrading and practice of early warning mode of geological disaster special group combination in Zigong City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):130 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Jiangtao, LI Bo, LI Boxuan, et al . Upgrading and practice of early warning mode of geological disaster special group combination in Zigong City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020 ,31 (6 ):130 −134 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[20] 黄成,赵鹏,朱广毅,等. 云南省地质环境信息发布系统:中国,2021SR0986009[P]. 2018-03-05. [HUANG Cheng,ZHAO Peng,ZHU Guangyi,et al. Yunnan Province geological environment information release system:China,2021SR0986009[P]. 2018-03-05. (in Chinese) HUANG Cheng, ZHAO Peng, ZHU Guangyi, et al. Yunnan Province geological environment information release system: China, 2021SR0986009[P]. 2018-03-05. (in Chinese)
[21] 黄成,杨迎冬,晏祥省,等. 云南省地质环境一张图系统:中国,2021SR0794747[P]. 2018-04-16. [HUANG Cheng,YANG Yingdong,YAN Xiangsheng,et al. A map system of geological environment in Yunnan Province:China,2021SR0794747[P]. 2018-04-16. (in Chinese) HUANG Cheng, YANG Yingdong, YAN Xiangsheng, et al. A map system of geological environment in Yunnan Province: China, 2021SR0794747[P]. 2018-04-16. (in Chinese)
[22] 黄成,杨迎冬,晏祥省,等. 云南省地质灾害综合管理系统:中国,2021SR0803964[P]. 2021-04-25. [HUANG Cheng,YANG Yingdong,YAN Xiangsheng,et al. Integrated geological hazard management system of Yunnan Province:China,2021SR0803964[P]. 2021-04-25. (in Chinese) HUANG Cheng, YANG Yingdong, YAN Xiangsheng, et al. Integrated geological hazard management system of Yunnan Province: China, 2021SR0803964[P]. 2021-04-25. (in Chinese)
[23] 黄成,杨迎冬,晏祥省,等. 云南省地质灾害风险调查野外实时采集系统:中国,2021SR0944823[P]. 2021-05-13. [HUANG Cheng,YANG Yingdong,YAN Xiangsheng,et al. Field real-time acquisition system for geological disaster risk investigation in Yunnan Province:China,2021SR0944823[P]. 2021-05-13.(in Chinese) HUANG Cheng, YANG Yingdong, YAN Xiangsheng, et al. Field real-time acquisition system for geological disaster risk investigation in Yunnan Province: China, 2021SR0944823[P]. 2021-05-13.(in Chinese)
[24] 黄成,杨迎冬,赵鹏,等. 云南省地质灾害精细化调查野外实时采集系统:中国,2021SR0944822[P]. 2021-05-25. [HUANG Cheng,YANG Yingdong,ZHAO Peng,et al. A real-time field collection system for geological hazard investigation in Yunnan Province:China,2021SR0944822[P]. 2021-05-25. (in Chinese) HUANG Cheng, YANG Yingdong, ZHAO Peng, et al. A real-time field collection system for geological hazard investigation in Yunnan Province: China, 2021SR0944822[P]. 2021-05-25. (in Chinese)
[25] 黄成,赵鹏,晏祥省,等. 云南省小型无人机航测数据管理系统:中国,2022SR0334223[P]. 2021-10-22. [HUANG Cheng,ZHAO Peng,YAN Xiangsheng,et al. Yunnan Province small UAV aerial survey data management system:China,2022SR0334223[P]. 2021-10-22. (in Chinese) HUANG Cheng, ZHAO Peng, YAN Xiangsheng, et al. Yunnan Province small UAV aerial survey data management system: China, 2022SR0334223[P]. 2021-10-22. (in Chinese)
[26] 黄成,魏蕾,杨迎冬,等. 云南省地质灾害风险区划计算系统:中国,2022SR0334222[P]. 2021-11-09. [HUANG Cheng,WEI Lei,YANG Yingdong,et al. Geological disaster risk regionalization calculation system of Yunnan Province:China,2022SR0334222[P]. 2021-11-09. (in Chinese) HUANG Cheng, WEI Lei, YANG Yingdong, et al. Geological disaster risk regionalization calculation system of Yunnan Province: China, 2022SR0334222[P]. 2021-11-09. (in Chinese)
[27] 刘文连,李泽,眭素刚,等. 一种溶洞覆盖层表面极限均布荷载的计算方法:CN112541216B[P]. 2023-02-03. [LIU Wenlian,LI Ze,SUI Sugang,et al. Method for calculating ultimate uniform load on surface of karst cave covering layer: CN112541216B[P]. 2023-02-03.(in Chinese) LIU Wenlian, LI Ze, SUI Sugang, et al. Method for calculating ultimate uniform load on surface of karst cave covering layer: CN112541216B[P]. 2023-02-03.(in Chinese)
[28] 刘文连,李泽,眭素刚,等. 一种岩溶地基稳定性计算方法:CN202011422482.1[P]. 2021-03-16. [LIU Wenlian,LI Ze,SUI Sugang,et al. A method for calculating the stability of karst foundation:CN202011422482.1[P]. 2021-03-16. (in Chinese) LIU Wenlian, LI Ze, SUI Sugang, et al. A method for calculating the stability of karst foundation: CN202011422482.1[P]. 2021-03-16. (in Chinese)
[29] 刘文连,李泽,眭素刚,等. 一种岩溶桩基础地基溶洞顶板最小厚度的计算方法:CN112507435B[P]. 2022-12-06. [LIU Wenlian,LI Ze,SUI Sugang,et al. Method for calculating minimum thickness of karst cave top plate of karst pile foundation:CN112507435B[P]. 2022-12-06. (in Chinese) LIU Wenlian, LI Ze, SUI Sugang, et al. Method for calculating minimum thickness of karst cave top plate of karst pile foundation: CN112507435B[P]. 2022-12-06. (in Chinese)
[30] 王自高,钟延江,王昆,等. 云南高原深切峡谷区水利水电工程地质灾害问题及防治措施研究报告[R]. 昆明:云南华昆国电工程勘察有限公司. 2021. [WANG Zigao,ZHONG Yanjiang,WANG Kun,et al. Research report on geological hazards and prevention measures of water conservancy and hydropower engineering in Deep Gorge area of Yunnan Plateau [R]. Kunming:Yunnan Huakun Guodian Engineering Survey Limited Company,2021. (in Chinese) WANG Zigao, ZHONG Yanjiang, WANG Kun, et al. Research report on geological hazards and prevention measures of water conservancy and hydropower engineering in Deep Gorge area of Yunnan Plateau [R]. Kunming: Yunnan Huakun Guodian Engineering Survey Limited Company, 2021. (in Chinese)
[31] 李果,陈贺,尹浩,等. 云南高原公路工程重大地质灾害成因机制及防治技术研究专题研究报告[R]. 昆明:云南省交通规划设计研究院有限公司. 2021. [LI Guo,CHEN He,YIN Hao,et al. Research report on the cause mechanism and prevention Technology of major geological disasters in highway engineering of Yunnan Plateau[R]. Kunming:Yunnan Institute of Transportation Planning and Design Limited Company,2021. (in Chinese) LI Guo, CHEN He, YIN Hao, et al. Research report on the cause mechanism and prevention Technology of major geological disasters in highway engineering of Yunnan Plateau[R]. Kunming: Yunnan Institute of Transportation Planning and Design Limited Company, 2021. (in Chinese)
[32] 王宇. 云南省崩塌滑坡泥石流灾害及防治[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,1998,9(4):38 − 41. [WANG Yu. Hazards collapse landslide and debris flow in Yunnan and their control[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,1998,9(4):38 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Yu . Hazards collapse landslide and debris flow in Yunnan and their control[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,1998 ,9 (4 ):38 −41 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[33] 姚超伟,王念秦,李永红,等. 地质灾害防治行业信用体系建设探讨[J]. 灾害学,2021,36(2):24 − 29. [YAO Chaowei,WANG Nianqin,LI Yonghong,et al. Discussion on the construction of credit system in the industry of geological disaster prevention[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021,36(2):24 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAO Chaowei, WANG Nianqin, LI Yonghong, et al . Discussion on the construction of credit system in the industry of geological disaster prevention[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021 ,36 (2 ):24 −29 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[34] 陈洪凯. 生态文明视角下地质灾害防治新常态[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版),2020,37(4):51 − 56. [CHEN Hongkai. The new normalcy of geological disasters control under the vision of ecological civilization[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science),2020,37(4):51 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Hongkai . The new normalcy of geological disasters control under the vision of ecological civilization[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science),2020 ,37 (4 ):51 −56 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[35] 刘传正,陈春利. 中国地质灾害防治成效与问题对策[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):375 − 383. [LIU Chuanzheng,CHEN Chunli. Achievements and countermeasures in risk reduction of geological disasters in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):375 − 383. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Chuanzheng, CHEN Chunli . Achievements and countermeasures in risk reduction of geological disasters in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020 ,28 (2 ):375 −383 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[36] 殷跃平. 地质灾害风险调查评价方法与应用实践[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):5 − 6. [YIN Yueping. Geological hazard risk investigation and evaluation method and its application practice[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):5 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) YIN Yueping . Geological hazard risk investigation and evaluation method and its application practice[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (4 ):5 −6 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[37] 刘传正,刘秋强,吕杰堂. 地质灾害防治规划编制研究[J]. 灾害学,2020,35(1):1 − 5. [LIU Chuanzheng,LIU Qiuqiang,LYU Jietang. Research on compiling methods of mitigation planning in geological hazards[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2020,35(1):1 − 5.(in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Chuanzheng, LIU Qiuqiang, LYU Jietang . Research on compiling methods of mitigation planning in geological hazards[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2020 ,35 (1 ):1 −5 .(in Chinese with English abstract)[38] 王兆丰,肖建兵,段君君,等. 新形势下加强地质灾害防治资质管理的思考与建议[J]. 中国矿业,2019,28(4):31 − 33. [WANG Zhaofeng,XIAO Jianbing,DUAN Junjun,et al. Thoughts and suggestions on strengthening the qualification management of geological disasters prevention and control under the new situation[J]. China Mining Magazine,2019,28(4):31 − 33.(in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Zhaofeng, XIAO Jianbing, DUAN Junjun, et al . Thoughts and suggestions on strengthening the qualification management of geological disasters prevention and control under the new situation[J]. China Mining Magazine,2019 ,28 (4 ):31 −33 .(in Chinese with English abstract) -
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 何胜庆,郑达,张文. 高海拔地区宽级配泥石流冲击拦砂坝试验研究. 水文地质工程地质. 2024(01): 123-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 沈凌铠,周保,魏刚,魏赛拉加,常文斌,张明哲,邢爱国. 气温变化对多年冻土斜坡稳定性的影响——以青海省浅层冻土滑坡为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(01): 8-16 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 苏晓军,孟兴民,张毅,岳东霞,周自强,郭富赟. 中巴经济走廊地质灾害研究进展与展望. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(05): 694-710 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 彭帅英,李霄琳,牛岑岑,乔双双. 泥石流模拟实验装置及虚拟仿真平台设计与应用. 实验技术与管理. 2023(10): 153-158 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 文强,胡卸文,刘波,席传杰,何坤. 四川丹巴梅龙沟“6·17”泥石流成灾机理分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(03): 23-30 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 胡艳香,朱厚影,陈昊,薛凯喜,韩静云,梁海安. 贺兰山苏峪口泥石流物源启动模型试验分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(06): 44-52 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载:


























 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS