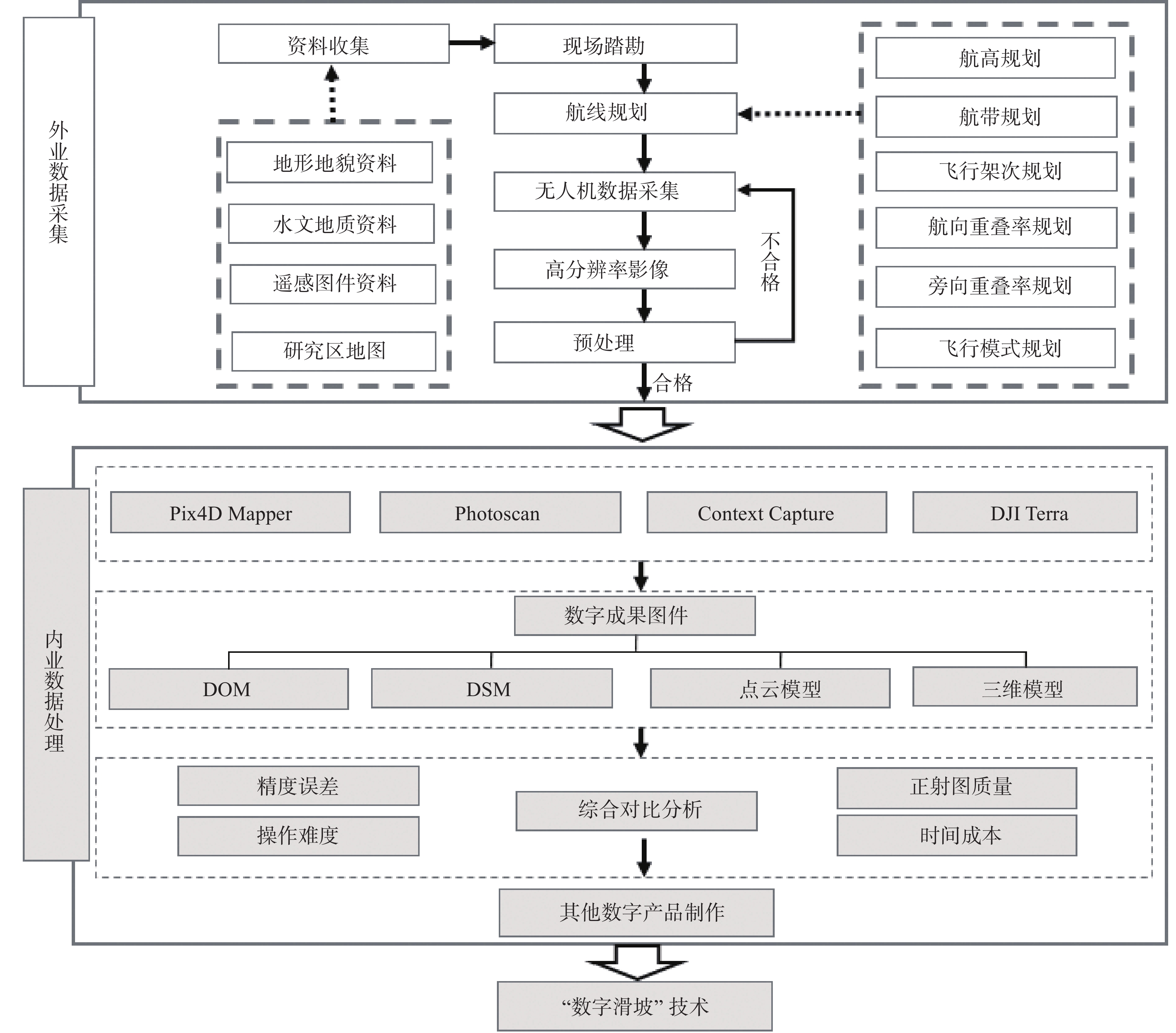
Comparison on the application of the software for image-free control UAV data processing of digital landslide: A case study of Huangtupo landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area
-
摘要:
滑坡灾害是中国最常见的地质灾害之一,高效、便捷和准确地实现数字滑坡是滑坡防灾减灾的关键环节。近年来,由于高效率和低成本等优势,免像控无人机航测技术已被逐渐应用于数字滑坡分析领域。文章探讨了基于免像控技术的各航测软件在滑坡地形处理中的优劣势,以及应用于数字滑坡技术中的可行性。选取长江三峡库区的大型黄土坡滑坡为研究对象,借助大疆Phantom 4 RTK无人机获取研究区高分辨率遥感数据,采用4款国内外常用的专业航测处理软件Pix4D Mapper、Photoscan、Context Capture以及DJI Terra分别进行数字化处理,并从正射图质量、精度误差、耗时及操作难度四个维度进行对比分析并应用。结果表明:(1)在单体滑坡航拍面积高达2.23 km2的情况下,Pix4D Mapper软件生成的正射图质量效果最好且能达到大比例尺制图要求;(2)在精度误差上,DJI Terra与Pix4D Mapper表现最好,其中20个检查点的平面中误差均未超过10 cm,垂直中误差均未超过30 cm,综合对比结果发现在较大面积的单体滑坡灾害分析中Pix4D Mapper软件最具优势。认为可基于数字滑坡图件遥感解译获取了滑坡基本数字信息并通过GIS软件将滑坡数字信息储存起来建立滑坡灾害大数据库。研究显示,免像控无人机航测技术在今后滑坡灾害大数据库的快速建立方面具有巨大优势并将成为重要的研究方向之一,可为滑坡灾害防治与应急调查快速分析提供技术与数据支撑。
Abstract:Landslide disasters are among the most prevalent geological hazards in China, which seriously threatens the safety of people's lives and property. Efficient, convenient, and accurate digital landslide analysis is crucial for landslide disaster prevention and mitigation. In recent years, image-free unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) aerial survey technology has been increasingly employed in digital landslide analysis due to its advantages of high processing efficiency and production of high-quality maps. This study aims to explore the advantages and disadvantages of various aerial survey software based on image-free control technology in landslide terrain processing, as well as their feasibility in digital landslide applications. In this paper, the Huangtupo landslide in the Three Gorges reservoir area of the Yangtze River is selected as the research object. High-resolution remote sensing data in the study area are obtained using the Dajiang PHANTOM 4RTK UAV. Four commonly used professional aerial survey processing software, namely Pix4D Mapper, Photoscan, Context Capture, and DJI Terra, are utilized for digital processing. A comparative analysis is conducted based on four aspects: orthophoto quality, accuracy error, time consumption, and operation difficulty. The research findings reveal that: (1) Under the condition of a single landslide aerial photography area of up to 2.23 km2, Pix4D Mapper software generates orthophoto maps of the highest quality that meet the requirements for large-scale mapping; (2) DJI Terra and Pix4D Mapper have the best performance in terms of accuracy error, with the mean square error of 20 inspection points in the plane and vertical axis not exceeding 10cm and 30cm, respectively. Comprehensive comparison results indicate that Pix4D Mapper software demonstrates the most advantages in analyzing large-scale individual landslide disasters; (3) Based on the remote sensing interpretation of digital landslide maps, the basic digital information of the landslide is obtained, and a comprehensive landslide disaster database is established by storing the digital landslide information using GIS software. In conclusion, image-free UAV aerial survey technology holds significant advantages in the rapid establishment of future landslide disaster databases, emerging as an important research direction that provides technical and data support for swift analysis of landslide disaster prevention and emergency investigations.
-
0. 引 言
每年由于滑坡形成的地质灾害都会给我国造成巨大的人员伤亡和财产损失。根据最新公布的《中国统计年鉴2024》统计,近5年共发生地质灾害
28109 起,其中滑坡地质灾害16290 起,占总地质灾害数量的57.67%[1],是最常见的灾害类型之一。因此,对滑坡地质灾害进行早期防控,对于减少人员伤亡和经济损失都具有十分重要的实际意义。其中,变形速率作为对滑坡地质灾害预警和防控最主要的依据之一,其预测的准确度和时效性对于滑坡地质灾害的预测和防控起着关键作用。然而,滑坡地质灾害特别是突发型滑坡在其变形过程中,可能会发生与历史变形趋势完全不符的变形趋势[2],导致现有方法在预测此类问题时产生困难。随着近年来人工智能技术的飞速发展,在线监测与深度学习相结合的超前预测逐渐成为滑坡地质灾害防控研究的热点[3 − 5]。其中,长短时记忆(long short term memory network,LSTM)神经网络由于其在处理时序数据上的优势而得到广泛关注[6 − 7]。如李丽敏等[8]将滑坡累计位移分解为趋势项与波动项,并用多项式拟合预测趋势项、LSTM网络预测波动项;张明岳等[9]预测对比了循环神经网络(recurrent neural network,RNN)和LSTM2种模型在滑坡位移预测时的精度;LI等[10]采用自回归、LSTM和支持向量机(support vector machines,SVM)建立了综合模型并分析了各模型的权重;唐宇峰等[11]采用了一种动态残差修正的LSTM进行了滑坡位移预测。然而,传统LSTM网络难以同时提取从后向前的信息,使其应用受到了一定的限制。相比于传统LSTM网络,Tengtrairat等[12]提出了一种双向长短期记忆(bi-directional long short term memory network,BiLSTM)神经网络算法,该方法采用双向重叠计算的方法,比单向LSTM可以更好地捕捉双向时序特征,因此具有更好的应用前景[13]。在滑坡领域,Cui等[14]提出一种基于语义门(semantic gate,SG)和双时长短期记忆网络(SG-BiLSTM)的方法,并识别了滑坡体图像;Wang等[15]通过BiLSTM-RNN及卷积神经网络(convolutional neural network,CNN)结合LSTM的方法,生成了基于人工智能的香港滑坡敏感性地图。Lin等[16]采用GRA-MIC融合相关计算方法选取了影响滑坡位移的因素,最后采用CNN-BiLSTM模型进行了预测。综上,BiLSTM方法在滑坡领域内已经取得许多成果。然而,对于突发型滑坡灾害,由于其在加速变形过程中的变形速率发展历程可能与历史变形速率历程完全不符,导致了现有方法在预测此类问题时存在精度及效率不足的困难。因此,建立一种动态预测且深层优化的多层耦合算法,在提高预测准确率的同时保证较快的响应速度,对于准确地进行突发型滑坡预警及增加预警后的应急响应时间是具有十分重要的实际意义的。
鉴于此,本文提出一种基于动态串联PSO- BiLSTM的滑坡变形速率预测方法,首先,通过集合经验模态分解(EEMD)将变形速率序列进行分解,得到周期项及趋势项变形速率序列;其次,设置PSO启动阈值,并分别通过多项式拟合及周期项PSO-BiLSTM预测网络,得到趋势项及周期项变形速率预测值,将预测值分别加入趋势项变形速率序列及周期项变形速率序列;再次,以趋势项变形速率序列、周期项变形速率序列及残差变形速率序列为输入,建立总PSO-BiLSTM预测网络,得到总预测变形速率,最后,由总预测变形速率和监测变形速率,相减得到下一循环计算所需的残差变形速率。通过以上方式,提高对变形速率预测的准确率及滑坡预警的响应速度,为增加滑坡预警时间提供一种新的思路。
1. PSO-BiLSTM算法理论基础
1.1 LSTM算法理论基础
LSTM神经网络是对RNN的改进算法,其工作原理见图1[17]。LSTM算法在RNN的基础上引入了单元状态c以及“门”的概念,解决了在RNN中存在的梯度消失和爆炸问题。
LSTM神经网络的基本单元称为细胞,由遗忘门、输入门及输出门构成。其中,遗忘门决定上一时刻的状态St−1保留至当前时刻的信息,其通过一个取值为0~1范围的Sigmoid函数,将输入xt与上一时刻的输出ht−1相联系来决定遗忘的信息,Sigmoid函数取0表示全部遗忘,取1代表全部记忆;输入门的作用是控制当前输入xt保存到状态单元St中的记忆量,其主要结构算法为:
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) 式中:
1.2 BiLSTM算法理论基础
BiLSTM网络是在LSTM网络基础上发展起来的,其可在不增加数据量的前提下学习序列数据和时间步长之间的双向依赖关系[12]。BiLSTM和单向LSTM最大的区别在于,前者可以同时保存过去和未来的信息,而后者只保存过去的信息,如图2所示。
1.3 PSO-BiLSTM算法
PSO常用来求解最优化问题,其基本思路是将待求解问题的解描述为粒子,每个粒子在N维解空间中可以不断寻求,其粒子极值
式中:
基于以上理论,基于PSO优化的BiLSTM网络训练流程如图3所示。
2. 动态串联PSO-BiLSTM算法
2.1 动态串联PSO-BiLSTM算法基本原理
滑坡体在随着时间的演变过程中,其滑坡变形速率趋势会呈现出“稳定型”、“渐变型”、“突发型”等不同的变化趋势。对于突发型滑坡,其从变形速率突变到产生滑坡的时间非常短(图4),现有方法在解决突变型滑坡位移预测时存在明显的精度不足、效率低下等困难。
(1)传统BiLSTM网络仅通过已有监测数据一次性建立和验证网络,并将该网络作为后续预测的依据,即“静态网络”。这种网络训练完成后不再更新,当变形速率发展趋势与前期变形速率趋势发生较大变化时,难以适应新趋势的发展,无法对变形速率进行有效预测。
(2)“动态网络”,即在每一次得到新的监测数据后对网络进行更新,可使网络具备更新后的变形速率信息,相比于静态网络可以显著提高预测精度。然而,一方面,动态BiLSTM网络预测的准确率与经验设定的网络参数有关,参数不当会严重影响其预测精度;另一方面,在变形速率产生突变时,其突变后的数据量少、突变速率变化快,动态网络的方法在预测时仍存在严重的滞后性。
(3)PSO优化可以对BiLSTM参数进行寻优从而提高准确率,但会大大增加计算成本,导致过长的预测时间而不利于工程的实际应用。
基于以上现状,本文建立了一种基于动态串联PSO-BiLSTM的滑坡变形速率预测方法。首先,设置每一次要分析的变形速率数据量N,通过“动态滑窗”方式截取待分析数据(“动态滑窗”指每获取最新一轮时序数据,将序列中最早的一轮时序数据去除,从而保持总数据量始终不变,达到减小待分析数据量和历史数据的影响的目的),并通过集合经验模态分解(EEMD)将变形速率序列进行分解,得到周期项及趋势项变形速率序列;其次,分别通过多项式拟合及周期项PSO-BiLSTM预测网络,得到趋势项及周期项变形速率预测值,并将预测值分别加入趋势项变形速率序列及周期项变形速率序列;再次,以趋势项变形速率序列、周期项变形速率序列及残差变形速率序列为输入,建立总PSO-BiLSTM预测网络,得到总预测变形速率;最后,由总预测变形速率和监测变形速率,相减得到下一循环建立总PSO-BiLSTM所需的残差变形速率。需要指出的是:(1)为提升预测效率,为PSO-BiLSTM网络仅当某一次预测的周期项残差率
通过以上方式,在动态训练网络的基础上,考虑了不同历史时刻条件下动态网络速率预测的误差,实现了不同动态网络之间的学习,且仅当预测误差过大时才启动PSO优化,因此可在提高预测准确率的前提下保证较高的计算效率。
2.2 模型性能指标
为全面评价该滑坡变形速率预测模型精度,采用平均绝对误差(mean absolute error,MAE)、绝对百分比误差(mean absolute percentage error,MAPE)、均方根误差(root mean square error,RMSE)及拟合优度R2来作为模型性能指标,如下[20]:
(7) (8) (9) (10) 式中:
3. 工程实例
3.1 滑坡变形速率实测及预处理
以四川省某滑坡体实测变形速率为例。自2020年3月14日—9月17日间对该案例进行了地表裂缝监测及降雨量监测(图6),其中每小时一组数据,共得到了
11776 组滑坡变形速率监测数据。该滑坡体在前期监测中变形一直相对稳定,自9月13日12时起,该滑坡隐患点在连日降雨影响下,其变形速率有明显突变迹象。如图7所示为9月13日前500 h内变形速率变化情况。
由图7所示, 该滑坡体在前期一直处于稳定状态,仅在突变前极短时间内变形速率发生了突变。由于本文的研究目的主要是针对变形速率产生突变情况下的预测研究,稳定期的变形速率对文章研究意义不大。因此仅选取了2020年9月12日17时—14日6时间的50 h为例进行探讨分析。
在实际工程中,存在变形速率的发展不是单向放大过程的情况,而是在某些时刻内会存在阶梯性的变化,这给变形速率的预测带来了困难。在本文中,采用“相邻极大值”方法来对数据进行预处理,即每一个时刻t的变形速率
从图8可以看出,该滑坡体的变形速率在20 h之后呈快速增加的趋势,其变化形态与历史趋势有着较大的差异,即产生了“突变”。
3.2 模型建立与参数选取
为验证本文方法的优势,分别采用动态BiLSTM网络(类型Ι)、动态PSO-BiLSTM网络(类型Ⅱ)、文中提出的动态串联PSO-BiLSTM网络在PSO启动残差率C=0(类型Ⅲ)和C=0.1(类型IV)4种情况进行预测分析。每类BiLSTM网络的输出均为一维。其中,动态BiLSTM的BiLSTM层节点数选取为50,正则化系数为0,初始学习率为0.2;PSO优化的参数为BiLSTM层节点数、初始学习率和正则化系数;PSO启动残差率C取0.1,动态滑窗截取数据为30,预测数据量为20。
3.3 预测结果及指标评价
4种类型算法均进行了3次预测,取计算结果的平均值。图9为4种方法变形速率预测结果与实测结果20轮预测对比。
其中,为获取总PSO-BiLSTM网络所需的残差变形速率,在前10个预测循环中仅采用周期项PSO-BiLSTM网络进行预测,而最后10项采用动态串联PSO-BiLSTM网络进行预测。因此,以下仅选择最后10次数据进行对比分析,如图10所示。
为进一步对比预测结果,采用MAE、MAPE、RMSE及R2共4种评价指标评价位移预测结果,表1为各模型位移预测结果的评价结果。
表 1 预测结果评价Table 1. Evaluation of prediction results预测
类型位移评价指标 计算时间/s MAE MAPE/% RMSE R2 类型Ⅰ 0.43 8.45 0.70 0.96 24.89 类型Ⅱ 0.36 7.07 0.61 0.97 294.50 类型Ⅲ 0.30 5.82 0.51 0.98 1861.87 类型Ⅳ 0.28 5.41 0.57 0.98 380.22 其中,MAE为绝对误差;MAPE为预测值与实测值的平均偏离程度,其越接近0表示效果越好;RMSE为预测值与真实值之间的偏差,越接近0表示预测值与真实值越吻合;R2越接近1说明预测越准确。
从图10及表1可以看出:(1)动态BiLSTM网络(类型Ⅰ)的绝对误差和平均偏离程度、偏差均为最大,且拟合优度R2最小,说明此时类型Ⅰ在四种类型中效果最差,但由于未采用PSO优化算法,此时拥有最佳的计算效率;(2)加入PSO算法后(类型Ⅱ),其MAE、MAPE和RMSE值相比类型Ⅰ均有明显的下降,且拟合优度上升,说明PSO优化算法对预测结果有明显的提升;(3)当加入串联算法后(类型Ⅲ和类型Ⅳ),其MAE、MAPE和RMSE值进一步下降,而拟合优度进一步提升,说明串联算法对预测精度有进一步提升;(4)类型Ⅲ与类型Ⅳ的各评价指标差距较小且各有优劣,但类型Ⅳ相比与类型Ⅲ计算效率大大提升,这对于滑坡变形速率的快速预测具有重要的实用价值。
4. 结论
(1)传统动态BiLSTM算法在进行滑坡变形速率预测时具有较高的计算效率,但在面临滑坡变形速率快速变化的情况时预测精度偏低;而相对于传统动态BiLSTM算法,PSO-BiLSTM优化算法对突发型滑坡变形速率预测结果有明显的提升。
(2)动态串联PSO-BiLSTM算法可以有效地提高突发型滑坡变形速率的预测准确率,但由于PSO优化计算时间过长,不利于工程应用;加入PSO启动机制后,其MAE、MAPE、RMSE、R2分别为0.28、5.41%、0.57、0.98,计算时间为380.22 s,在具有较高的精度的同时保证了计算效率,对于滑坡预测的快速响应、提高工程实用价值都有重要的意义。
-
表 1 各软件主要优势与数字化功能
Table 1 Key advantages and digital features of each software
软件名称 主要优势 数字化功能 其他信息 Pix4D Mapper 操作简单、界面简洁;能自动识别出照片中所对应的相机信息;兼容性强支持任意影像的数据处理,输出格式类型丰富[25] 软件可识别EXIF ID;可通过点云编辑器可实现手动选择以删除点云 瑞士Pix4D公司研发;最早于2011年推出测试 Photoscan 空三质量好;支持批量处理;支持多种文件格式;对初始数据的容错度较高;支持二次开发;支持全景拼接[26] 测量距离与坐标点信息 俄罗Agisoft公司研发;2006年开始专注于计算机视觉技术的创新与研究 Context Capture 三维建模能力强;数据源兼容性广;支持切块处理;支持生成多种三维格式[27] 提供测量功能如点坐标、线段距离以及面积与体积的计算 其前身为法国Acute3D公司,后被美国Bentley公司收购;最早于2011年发行测试版 DJI Terra 处理任务功能丰富;支持实时建模;支持集群计算;提供多种场景建模方式 支持处理生成LAS格式的点云数据 中国大疆创新公司研发;于2019年首发 表 2 无人机飞行参数表
Table 2 UAV Flight Parameters
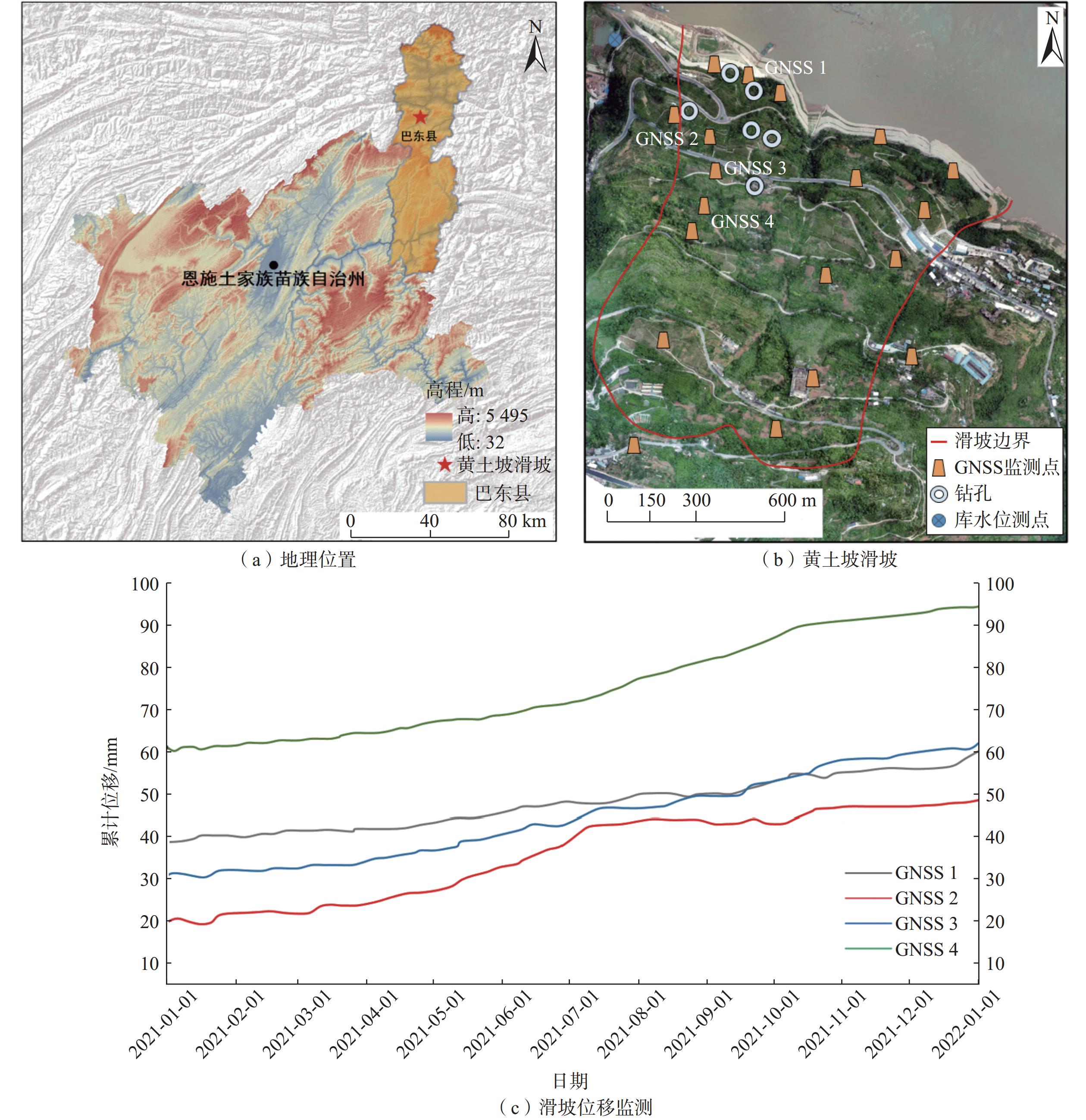
参数 信息 区域名称 巴东县新城区的黄土坡滑坡 飞行平台 大疆Phantom4 RTK 无人机GNSS精度 垂直 1.5 cm + 1 ppm(RMS);
水平 1 cm + 1 ppm(RMS)飞行器重量/kg 约1.4 相机型号 FC6310R 单次飞行时间/min 约30 min 影像分辨率/pix 5472 ×3648 像素大小/mm 13.2 航拍面积/km2 2.23 平均航高/m 120 航线数/条 43 旁向重叠度/% 70 航向重叠度/% 80 航飞路线方式 “之”字形 表 3 正射图像元大小对比表
Table 3 Comparison of orthophoto pixel sizes
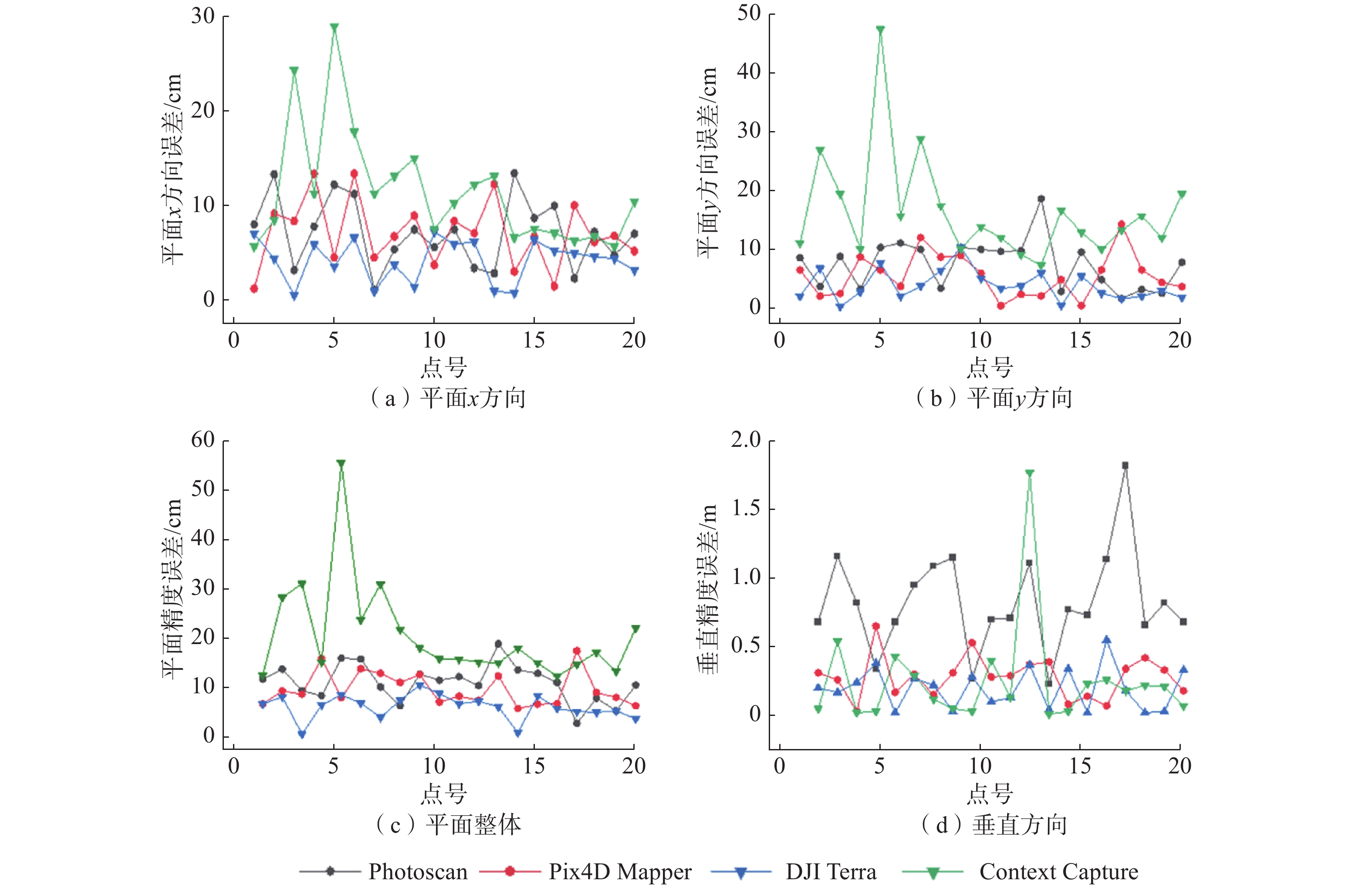
软件名称 DOM像元尺寸/cm Photoscan 7.39 DJI Terra 8.70 Context Capture 9.31 Pix4D Mapper 11.05 表 4 软件精度误差对比
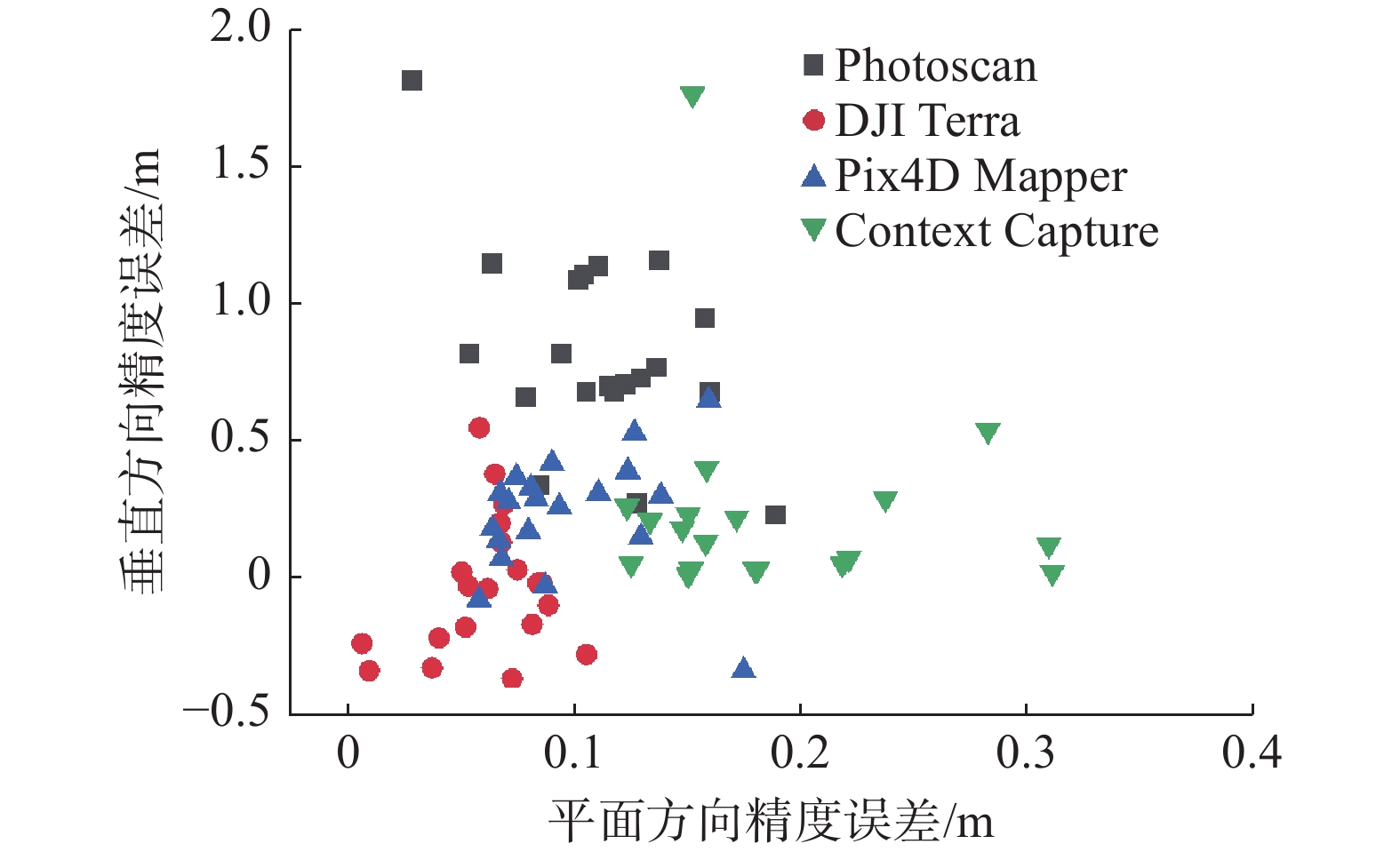
Table 4 Comparison of software precision errors
软件 Δx/m Δy/m ΔS/m Δz/m Pix4D Mapper 0.07 0.06 0.09 0.28 Photoscan 0.07 0.08 0.10 0.82 Context Capture 0.11 0.16 0.19 0.25 DJI Terra 0.04 0.04 0.06 0.19 表 5 山区摄影测量技术精度要求
Table 5 Accuracy requirements for aerial photogrammetry techniques
比例尺 正射影像图平面误差/m 数字高程模型高程误差/m 1∶500 0.4 0.5 1∶ 1000 0.8 0.7 1∶ 2000 1.6 1.2 表 6 软件耗时对比
Table 6 Comparison of processing time for software
软件 耗时/min Pix4D Mapper 725 Photoscan 4658 Context Capture 2580 DJI Terra 345 表 7 软件操作性对比
Table 7 Comparison of software usability
软件名称 操作难度 专业知识要求 Pix4D Mapper 简单 低 Context Capture 难 中等 Photoscan 中等 高 DJI Terra 简单 较低 表 8 专家评分法结果
Table 8 Results of expert rating method
指标 权数 得分 等级
(最好1.0分 / 好0.8分 / 较好0.6分 /一般0.5分 / 差0.1分)Pix4D
MapperContext
CapturePhotoscan DJI
Terra分辨率 0.1 一般
(0.05)较好
(0.06)最好
(0.1)好
(0.08)匀色、
纹理状态0.5 最好
(0.5)较好
(0.3)较好
(0.3)一般
(0.25)误差精度 0.25 好
(0.2)一般
(0.125)差
(0.025)最好
(0.25)耗时 0.15 好
(0.12)一般
(0.075)差
(0.015)最好
(0.15)合计 1.00 0.87 0.56 0.44 0.73 -
[1] 唐辉明,李长冬,龚文平,等. 滑坡演化的基本属性与研究途径[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(12):4596 − 4608. [TANG Huiming,LI Changdong,GONG Wenping,et al. Fundamental attribute and research approach of landslide evolution[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(12):4596 − 4608. (in Chinese with English abstract)] TANG Huiming, LI Changdong, GONG Wenping, et al. Fundamental attribute and research approach of landslide evolution[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(12): 4596 − 4608. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] NI Weida,ZHAO Liuyuan,ZHANG Lele,et al. Coupling progressive deep learning with the AdaBoost framework for landslide displacement rate prediction in the Baihetan Dam Reservoir,China[J]. Remote Sensing,2023,15(9):2296. DOI: 10.3390/rs15092296
[3] 窦杰,向子林,许强,等. 机器学习在滑坡智能防灾减灾中的应用与发展趋势[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(5):1657 − 1674. [DOU Jie,XIANG Zilin,XU Qiang,et al. Application and development trend of machine learning in landslide intelligent disaster prevention and mitigation[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(5):1657 − 1674. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOU Jie, XIANG Zilin, XU Qiang, et al. Application and development trend of machine learning in landslide intelligent disaster prevention and mitigation[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(5): 1657 − 1674. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 王治华. 数字滑坡技术及其应用[J]. 现代地质,2005,19(2):157 − 164. [WANG Zhihua. Progress and applications for digital landslide[J]. Geoscience,2005,19(2):157 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.02.001 WANG Zhihua. Progress and applications for digital landslide[J]. Geoscience, 2005, 19(2): 157 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.02.001
[5] 吕杰堂,王治华,周成虎. 西藏易贡滑坡堰塞湖的卫星遥感监测方法初探[J]. 地球学报,2002,23(4):363 − 368. [LYU Jietang,WANG Zhihua,ZHOU Chenghu. A tentative discussion on the monitoring of the Yigong landslide-blocked lake with satellite remote sensing technique[J]. Acta Geosicientia Sinica,2002,23(4):363 − 368. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.04.014 LYU Jietang, WANG Zhihua, ZHOU Chenghu. A tentative discussion on the monitoring of the Yigong landslide-blocked lake with satellite remote sensing technique[J]. Acta Geosicientia Sinica, 2002, 23(4): 363 − 368. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.04.014
[6] 程乙峰,刘志辉. 3S技术下滑坡危险性区划及监测[J]. 测绘科学,2016,41(8):95 − 100. [CHENG Yifeng,LIU Zhihui. Landslide hazard zoning and monitoring with 3S technology[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2016,41(8):95 − 100. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHENG Yifeng, LIU Zhihui. Landslide hazard zoning and monitoring with 3S technology[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2016, 41(8): 95 − 100. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] CHANG K T,MERGHADI A,YUNUS A P,et al. Evaluating scale effects of topographic variables in landslide susceptibility models using GIS-based machine learning techniques[J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9:12296. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-48773-2
[8] MERGHADI A,YUNUS A P,DOU Jie,et al. Machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility studies:A comparative overview of algorithm performance[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2020,207:103225. DOI: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103225
[9] EKER R,AYDINOC A,HÜBL J. Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based monitoring of a landslide:Gallenzerkogel landslide (Ybbs-Lower Austria) case study[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2018,190(1):28. DOI: 10.1007/s10661-017-6402-8
[10] DOU Jie,YUNUS A P,MERGHADI A,et al. Different sampling strategies for predicting landslide susceptibilities are deemed less consequential with deep learning[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,720:137320. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137320
[11] 丁要轩,龚文平,程展,等. 基于多期无人机影像的滑坡地表竖向变形测量模型试验与工程应用[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(2):267 − 278. [DING Yaoxuan,GONG Wenping,CHENG Zhan,et al. Model tests of the vertical ground deformation measurement of landslide based on multiple UAV images and its application[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(2):267 − 278. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DING Yaoxuan, GONG Wenping, CHENG Zhan, et al. Model tests of the vertical ground deformation measurement of landslide based on multiple UAV images and its application[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 267 − 278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 郭晨,许强,彭双麒,等. 无人机摄影测量技术在金沙江白格滑坡应急抢险中的应用[J]. 灾害学,2020,35(1):203 − 210. [GUO Chen,XU Qiang,PENG Shuangqi,et al. Application research of UAV photogrammetry technology in the emergency rescue of Baige landslide[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2020,35(1):203 − 210. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2020.01.038 GUO Chen, XU Qiang, PENG Shuangqi, et al. Application research of UAV photogrammetry technology in the emergency rescue of Baige landslide[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2020, 35(1): 203 − 210. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2020.01.038
[13] KARANTANELLIS E,MARINOS V,PAPATHANASSIOU G. Multitemporal landslide mapping and quantification of mass movement in red beach,Santorini Island using lidar and UAV platform[C]//Shakoor A,Cato K. IAEG/AEG Annual Meeting Proceedings,San Francisco,California,2018 - Volume 1. Cham:Springer,2019:163 − 169.
[14] ROSSI G,TANTERI L,TOFANI V,et al. Multitemporal UAV surveys for landslide mapping and characterization[J]. Landslides,2018,15(5):1045 − 1052. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-018-0978-0
[15] TURNER D,LUCIEER A,DE JONG S. Time series analysis of landslide dynamics using an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)[J]. Remote Sensing,2015,7(2):1736 − 1757. DOI: 10.3390/rs70201736
[16] VALKANIOTIS S,PAPATHANASSIOU G,GANAS A. Mapping an earthquake-induced landslide based on UAV imagery: Case study of the 2015 Okeanos landslide,Lefkada,Greece[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,245:141 − 152. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.08.010
[17] 周小龙,贾强,石鹏卿,等. 免像控无人机航测技术在舟曲县立节北山滑坡-泥石流灾害应急处置中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):107 − 116. [ZHOU Xiaolong,JIA Qiang,SHI Pengqing,et al. Application of image-free control UAV aerial survey technology in emergency treatment of landslide-debris flow disaster in Lijie north hill,Zhouqu County[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):107 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHOU Xiaolong, JIA Qiang, SHI Pengqing, et al. Application of image-free control UAV aerial survey technology in emergency treatment of landslide-debris flow disaster in Lijie north hill, Zhouqu County[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(1): 107 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 陈巧,袁飞云,付霞,等. 无人机摄影测量技术在阿娘寨滑坡应急调查中的应用[J]. 测绘通报,2023(1):77 − 83. [CHEN Qiao,YUAN Feiyun,FU Xia,et al. Application of UAV photogrammetry technology in emergency investigation of Aniangzhai landslide[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2023(1):77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2023.0013 CHEN Qiao, YUAN Feiyun, FU Xia, et al. Application of UAV photogrammetry technology in emergency investigation of Aniangzhai landslide[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2023(1): 77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2023.0013
[19] LI CHANGCHUN1 Z G, CHANGE 2 E, NATURAL DISASTER M O E, et al. Quick image-processing method of UAV without control points data in earthquake disaster area[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011(Sup 3): 523 − 528. LI CHANGCHUN1 Z G,CHANGE 2 E,NATURAL DISASTER M O E,et al. Quick image-processing method of UAV without control points data in earthquake disaster area[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2011(Sup 3):523 − 528.
[20] 金鼎坚,支晓栋,王建超,等. 面向地质灾害调查的无人机遥感影像处理软件比较[J]. 国土资源遥感,2016,28(1):183 − 189. [JIN Dingjian,ZHI Xiaodong,WANG Jianchao,et al. Comparison of UAV remote sensing image processing software for geological disasters monitoring[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources,2016,28(1):183 − 189. (in Chinese with English abstract)] JIN Dingjian, ZHI Xiaodong, WANG Jianchao, et al. Comparison of UAV remote sensing image processing software for geological disasters monitoring[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2016, 28(1): 183 − 189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 孙姣姣,王琦,郑洁,等. 基于DOM成果的航测软件对比分析[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息,2021,44(8):71 − 74. [SUN Jiaojiao,WANG Qi,ZHENG Jie,et al. Comparative analysis of aerial survey software based on DOM results[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology,2021,44(8):71 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)] SUN Jiaojiao, WANG Qi, ZHENG Jie, et al. Comparative analysis of aerial survey software based on DOM results[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2021, 44(8): 71 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 马旭文,徐柳华. 基于倾斜摄影三维模型的大比例尺地形图测图软件比较与分析[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息,2020,43(2):57 − 59. [MA Xuwen,XU Liuhua. Comparison and analysis of large-scale topographic mapping software based on oblique photography 3D model[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology,2020,43(2):57 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)] MA Xuwen, XU Liuhua. Comparison and analysis of large-scale topographic mapping software based on oblique photography 3D model[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2020, 43(2): 57 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] KAIMARIS D,PATIAS P,SIFNAIOU M. UAV and the comparison of image processing software[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Unmanned Systems,2017,5(1):18 − 27. DOI: 10.1108/IJIUS-12-2016-0009
[24] JIN D,LI J,GONG J,et al. Shipborne mobile photogrammetry for 3D mapping and landslide detection of the water-level fluctuation zone in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China[J]. [J]. Remote Sensing,2021,13:1007.
[25] 王浩舟,常雅荃,李川,等. 无人机影像处理软件Pix4Dmapper与 Photoscan在资源普查中的成像性能分析[J]. 甘肃科技,2017,33(22):46 − 51. [WANG Haozhou,CHANG Yaquan,LI Chuan,et al. Imaging performance analysis of UAV image processing software Pix4Dmapper and Photoscan in resource survey[J]. Gansu Science and Technology,2017,33(22):46 − 51. (in Chinese)] WANG Haozhou, CHANG Yaquan, LI Chuan, et al. Imaging performance analysis of UAV image processing software Pix4Dmapper and Photoscan in resource survey[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 2017, 33(22): 46 − 51. (in Chinese)
[26] 赵明. Agisoft PhotoScan Professional软件在无人机航空摄影数据处理中的应用[J]. 水电站设计,2017,33(2):44 − 46. [ZHAO Ming. Application of agisoft PhotoScan professional software in UAV aerial photography data processing[J]. Design of Hydroelectric Power Station,2017,33(2):44 − 46. (in Chinese)] ZHAO Ming. Application of agisoft PhotoScan professional software in UAV aerial photography data processing[J]. Design of Hydroelectric Power Station, 2017, 33(2): 44 − 46. (in Chinese)
[27] 王文敏,王晓东. 基于ContextCapture Center平台的城市级实景三维建模技术研究[J]. 测绘通报,2019(增刊1):126 − 128. [WANG Wenmin,WANG Xiaodong. Study of city real 3D modeling technology based on ContextCapture Center[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2019(Sup 1):126 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Wenmin, WANG Xiaodong. Study of city real 3D modeling technology based on ContextCapture Center[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2019(Sup 1): 126 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] TANG Huiming,LI Changdong,HU Xinli,et al. Evolution characteristics of the Huangtupo landslide based on in situ tunneling and monitoring[J]. Landslides,2015,12(3):511 − 521. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-014-0500-2
[29] 唐辉明,李长冬,胡伟,等. 重大滑坡启滑的物理机制是什么?[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(10):3902 − 3903. [TANG Huiming,LI Changdong,HU Wei,et al. What is the physical mechanism of major landslides? [J]. Earth Science,2022,47(10):3902 − 3903. (in Chinese)] TANG Huiming, LI Changdong, HU Wei, et al. What is the physical mechanism of major landslides? [J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(10): 3902 − 3903. (in Chinese)
[30] 管建军,王俊豪,王双亭,等. 无人机倾斜摄影在黄土地区泥石流灾害调查与评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(4):137 − 145. [GUAN Jianjun,WANG Junhao,WANG Shuangting,et al. Application of UAV oblique photography in investigation and evaluation of debris flow disasters in loess area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(4):137 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)] GUAN Jianjun, WANG Junhao, WANG Shuangting, et al. Application of UAV oblique photography in investigation and evaluation of debris flow disasters in loess area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2017, 28(4): 137 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] DOU Jie,YUNUS A P,BUI D T,et al. Improved landslide assessment using support vector machine with bagging,boosting,and stacking ensemble machine learning framework in a mountainous watershed,Japan[J]. Landslides,2020,17(3):641 − 658. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-019-01286-5
[32] 贾伟洁,王治华. 基于高分辨率遥感影像的滑坡活动特征及稳定性分析——以东苗家滑坡为例[J]. 国土资源遥感,2019,31(4):174 − 181. [JIA Weijie,WANG Zhihua. Landslide activity characteristics and stability analysis based on high-resolution remote sensing image:A case study of Dongmiaojia landslide[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources,2019,31(4):174 − 181. (in Chinese with English abstract)] JIA Weijie, WANG Zhihua. Landslide activity characteristics and stability analysis based on high-resolution remote sensing image: A case study of Dongmiaojia landslide[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2019, 31(4): 174 − 181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 刘路路,宋亮,焦玉勇,等. 库水位波动条件下黄土坡临江1#崩滑堆积体稳定性研究[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(增刊1):359 − 366. [LIU Lulu,SONG Liang,JIAO Yuyong,et al. Study of stability of Huangtupo riverside slumping mass #1 under reservoir water level fluctuations[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(Sup 1):359 − 366. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Lulu, SONG Liang, JIAO Yuyong, et al. Study of stability of Huangtupo riverside slumping mass #1 under reservoir water level fluctuations[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(Sup 1): 359 − 366. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 蔡小东. 暴雨条件下赣南山区高速公路高边坡稳定性研究. 价值工程. 2025(04): 139-141 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赖波,江金进,江山,江宁,赵风顺. 珠海市南水镇金龙边坡变形破坏特征及稳定性评价. 城市地质. 2024(01): 20-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王玉刚,袁伟. 基于遗传算法的地下暗挖工程边坡稳定性分析. 大众标准化. 2023(15): 103-105 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 林逸晖,李广涛,杨天雨,乔登攀,王俊,张希,赵怀军. 基于PCA-RF的边坡稳定性预测. 化工矿物与加工. 2023(12): 59-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王猛,何德伟,贾志宏,胡至华. 基于多源遥感数据的高位滑坡特征分析——以广元市利州区荣山镇岩窝村滑坡为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(06): 57-68 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 刘顺青,蔡宇宸,程涛,周萍,王旭畅. 降雨入渗条件下下蜀土边坡稳定性分析. 地质灾害与环境保护. 2022(02): 32-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 郭世兴. 关于崩滑地质灾害抢险治理工程的斜坡稳定性分析. 世界有色金属. 2021(21): 203-204 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:













 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS