Assessment of landslide hazard risk in Kenya based on different statistical models
-
摘要: 肯尼亚是我国“一带一路”倡议在东非重要支点。受高原裂谷地形和显著的雨旱季节影响,肯尼亚地质灾害频发。本文以肯尼亚的历史滑坡数据为样本,选取高度、坡度、坡向、地貌、平面曲率、土壤类型、年平均降雨量、水流强度指数、地形湿度指数及土地利用类型作为评价指标,分别基于信息量模型(IV)、逻辑回归模型(LR)和极限学习机模型(ELM)对肯尼亚滑坡灾害进行危险性区划,其中ELM分别考虑了sigmoid 函数、正弦函数和对称阈值型传输函数作为激活函数进行讨论。主要结论如下:(1)肯尼亚滑坡灾害高危险性及以上等级区域集中分布在西南部的高原和高原—裂谷过渡地带;(2)采用ROC曲线对模型精度进行评价,各模型的AUC值分别为0.977(IV)、0.965(LR)、0.859(ELM-SIG)、0.900(ELM-SIN)、0.941(ELM-HARDLIM),评价结果有效;(3)综合PR曲线结果判定,LR模型的召回率和精确率都处于较高的水平,优于其他模型;(4)肯尼亚内罗毕省(Nairobi)、中部省(Central)、尼扬扎省(Nyanza)和西部省(Western)四个省份高危险性区域占比较大。Abstract: Kenya is an important fulcrum of China's Belt and Road initiative in east Africa. However, due to its plateau rift terrain and aboriginal rain and drought season, geological disasters occur frequently in Kenya. The study used historical landslide data in Kenya as samples and selected several evaluation indexes, including elevation, slope, aspect, landform, plane curvature, soil type, annual average rainfall, stream power index, terrain witness index, and land use type. The landslide risk in Kenya was evaluated based on the information value model (IV), logistic regression model (LR), and extreme learning machine model (ELM), with the ELM model considering SIG, SIN, and HARDLIM functions as activation functions for discussion. The main findings are as follows: (1) The high-risk and above-grade areas of landslide disasters in Kenya are mainly concentrated in the plateau and plateau-rift transition zone in the southwest. (2) The ROC curve was used to evaluate the accuracy of the models, and the AUC values of the 0.977(IV), 0.965(LR), 0.859(ELM-SIG), 0.900(ELM-SIN), and 0.941(ELM-HARDLIM) models illustrate their validity. (3) Considering the PR curve results comprehensively, the recall rate and precision rate of the LR model are at a high level, marking it better than other models. (4) Nairobi, Central, Nyanza and Western provinces in Kenya account for a significant proportion of the high-risk and above-grade areas of landslide disasters.
-
Keywords:
- Kenya /
- risk /
- information value /
- logistic regression /
- machine learning
-
0. 引言
肯尼亚位于非洲东部,是我国“一带一路”倡议的重要沿线国家,地形以高原山地为主,东非大裂谷纵贯南北。肯尼亚大部分地区分布在赤道附近,以热带草原性气候为主,降水分为明显的旱雨两季,受地形和雨季气候影响,境内滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害频发[1]。
国内外学者在地质灾害风险评估方面开展了一系列研究。早在18世纪70年代,如Coulomb等[2],Terzaghi等[3],Janbu等[4]最先基于极限平衡方法对边坡的稳定性问题进行了探索。自20世纪60年代以来,借助计算机技术,以有限元法[5]为代表的数值分析方法在边坡稳定性分析中得到广泛应用。然而,这类方法严重依赖于详细的边坡物理力学参数,且计算过程非常耗时。因此,虽然二者在分析边坡时具有明确的物理意义,但多用于单个边坡的详细分析。随着计算机技术的进一步发展,Roger等[6]于1962年首次提出了“地理信息系统”(GIS)概念,在此基础上,频率比[7]、逻辑回归[8]、神经网络[9]、支持向量机[10]、层次分析法[11-12]等方法逐渐被应用于区域尺度上的地质灾害风险评价研究中。如张俊等[13]以重庆市万州区为研究对象,建立了信息量和逻辑回归的组合模型并得到了全区滑坡易发性区划图;Chen等[14]以宝鸡市的滑坡灾害为分析对象建立了确定性系数和层次分析法的组合模型,从灾害分布等角度出发对模型效果进行了论证;刘璐瑶等[15]建立了确定性系数和逻辑回归的组合模型并对永嘉县滑坡灾害易发性进行了评价,从准确率等角度出发验证了组合模型的优越性;我国《地质灾害危险性评估规范》(GB/T 40112—2021)[16]中根据项目重要性和地质复杂程度针对建设场地范围内不同种类的地质灾害的防治对策进行了划分,建议采用定性和半定量组合的方法进行地质灾害危险性评价。尽管相关研究已经形成了丰硕成果,但在分析方法上多从参数优化、模型组合的角度进行考虑,对不同统计模型间对比研究的关注则相对较少,同时研究对象常选取为经济较发达的地区。像肯尼亚这类落后发展中国家的地质灾害防治工作往往很少得到学者关注。近年来,我国在肯尼亚援建了“蒙内铁路”、“内马铁路”等多项重大工程。随着肯尼亚基础设施建设的大力开展,人工对山体的扰动逐渐加剧,滑坡等地质灾害发生风险也逐渐上升,给肯尼亚人民的生命财产安全造成严重威胁的同时也直接影响我国“一带一路”战略的顺利开展。
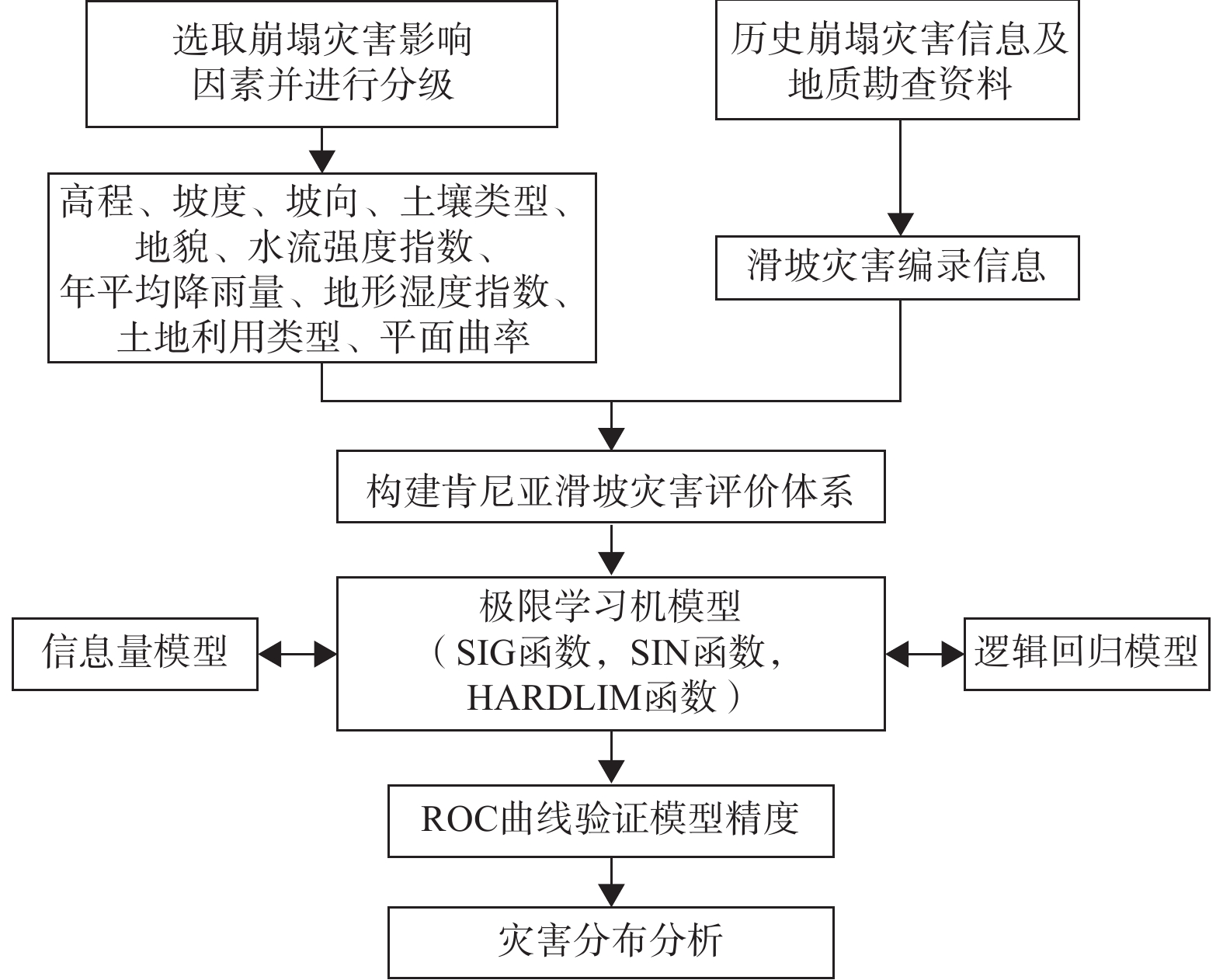
基于此,本文以肯尼亚地区为研究对象,以历史滑坡数据为样本,分别运用信息量(双变量模型)、逻辑回归(多变量模型)、和极限学习机(机器学习模型)对肯尼亚滑坡灾害进行危险性评价,并依据ROC曲线和PR曲线对评价效果进行讨论。
1. 研究区域概况
肯尼亚地处东非地区,陆地面积约58.26×104 km2,东部地区以平原地形为主,而西部尤其是西南部地区主要为高原山地地带,同时夹杂着裂谷等其他复杂地貌。北部地区同样以海拔较低的平原为主,其中沙漠和半沙漠覆盖面积广,约占肯尼亚国土面积的一半左右。区内东非大裂谷控制了全区的地形走势,山脉主要展布方向为南—北和西北—东南走向,在山脉之间和沿海地带分布着大量高原和荒漠,地势由内陆山地向沿海地带倾斜,西高东低,地形起伏大,地貌类型复杂(图1)。肯尼亚地处赤道附近的沿海地带,大部分地区属于热带草原性气候,降水分为明显的干湿两季,年降雨量1400~2200 mm,且降水多集中于3—5月及10—12月[17]。受地形和降水影响,区内河流和湖泊众多,但流域面积较为有限,长度很少超过200 km。肯尼亚位于非洲板块和印度洋板块的交接地区,受地质构造运动影响,发育着大量呈南北方向展布的多期构造,区内断裂和褶皱分布较广。肯尼亚地层发育较为齐全,主要由沉积地层与火成岩地层组成﹐其中沉积地层自太古代至第四系均有不同程度的出露,火成岩地层则主要分布于东非大裂谷附近的火山地区。复杂的地质条件和雨季的大量降水为肯尼亚滑坡灾害的发生创造了客观条件[18]。肯尼亚地形分布情况如图1所示。
2. 评价模型及指标
2.1 数据来源
本文以肯尼亚滑坡灾害为研究对象,采用50 m×50 m分辨率的基本评价单元。主要的数据来源包括:(1)肯尼亚历史滑坡数据集共包含425处历史滑坡,其中滑坡数据集1来源于肯尼亚信息、通信和技术部的公开数据[19],包含肯尼亚1999—2013年间的39次滑坡。滑坡数据集2来自全球毁灭性滑坡数据集库[20],包含63处滑坡。滑坡数据集3由Broeckx等[21]编制的非洲滑坡列表中提取获得,共包含323处滑坡。(2)数据高程模型(DEM)数据来自ASTERGDEMV2卫星的全球高程数据[22],坡度、平面曲率提取于DEM数据;年平均降雨量、土地利用类型、地貌等其他数据来自开放非洲资源库[23]和世界资源研究所[24]。肯尼亚历史滑坡灾害分布情况如图1所示。
由图1可知,肯尼亚的历史滑坡灾害点主要分布在西南部的高原山地地区,尤其是在东非大裂谷附近,而东部和南部的平原地区相对分布较少,侧面说明了地形地貌对肯尼亚滑坡灾害的发生具有重大影响。杨先全等[17]对肯尼亚地区的灾害记录进行了分析并采用层次分析法进行了易发性区划,发现洪水、极端降雨和滑坡是肯尼亚的主要灾害类型,且当地的自然灾害主要发生在每年的雨季期间(3—5月及10—12月),但其评价方法较为主观,且灾害样本数量较少(39例)。
2.2 评价指标
地质灾害是在一定的地质环境的条件下发生的。在进行地质灾害风险研究之前,有必要对研究区域内所有可能影响地质灾害发生的地理信息数据进行收集、整理和分类。在广泛阅读相关文献的基础上,基于数据的可用性、研究区域的特征等因素,共选取高度、坡度、坡向、地貌、平面曲率、土壤类型、年平均降雨量、水流强度指数、地形湿度指数及土地利用类型共10个因素作为分析的评价指标对模型进行讨论,评价因子概况如图2所示。
2.2.1 高程
高程即某点沿垂直方向至某点的绝对距离,是影响滑坡等地质灾害发生、发展及其形态特征的重要因素之一。肯尼亚地势西高东低,东部为广阔的沿海平原,而西部地区受板块构造活动影响,平均海拔在1500 m以上。在不同的高程范围内,地区的植被覆盖率、降雨量、水热条件、温差变化及人类工程活动强度均具有明显差异性,而这些因素也会直接或间接地影响着地质灾害的发生。肯尼亚高程数据分布如图2(a)所示。
2.2.2 坡度
坡度表征了崩塌灾害点和潜在危险边坡的地表陡缓程度,一般以坡面某点到坡脚的垂直距离和水平距离之比来表示。坡度越陡,其坡内水分和可溶性盐会逐渐向下方堆积,会直接影响坡面植被分布。不同坡度位置,其坡体内水分的运动、坡面岩土体的剥蚀作用和物质分布、坡体内部的应力特征等情况也会有所不同,发生滑坡的概率也会随之变化。肯尼亚坡度数据的分布如图2(b)所示。
2.2.3 坡向
坡向表示为坡面法线方向在平面上的投影和正北方向的夹角。坡向对坡体所受的日照天数和总辐射量都有影响,尤其是在肯尼亚这类热带草原气候影响强烈的区域。由于所得到的太阳辐射量有所差异,不同坡向的坡体表面水分蒸发、坡面植物分布、孔隙水压力和坡体的干湿循环周期也会有所不同。肯尼亚坡向数据的分布如图2(c)所示。
2.2.4 地貌
地貌是地形因素的最直观表现,是影响坡体稳定性的另一个重要指标。不同地貌的坡体在临空面、植被覆盖率、受日照和风化程度以及人类活动影响等方面都具有一定的差异,是一个综合性的滑坡影响因子。肯尼亚境内涵盖着丰富的地貌类型,包含洼地、山麓、高原、平原等等。复杂的地形条件为肯尼亚地质灾害的发生提供更大的可能性。肯尼亚地形分布如图2(d)所示。
2.2.5 曲率
曲率表现为坡体表面的凹凸状况。曲率对坡体表面的风化剥蚀和地表径流都有影响,是坡体临空面最直观的体现。相对于其他曲率的斜坡体而言,平坦地区的斜坡体要更加稳定。肯尼亚曲率分布如图2(e)所示。
2.2.6 土壤类型
依据土壤的各成分的含量不同,肯尼亚境内的土壤可分为黏土、壤土等类型。其中砂土砂粒含量高,颗粒间的空隙率较大,渗透性较强;黏土主要由黏粒构成,颗粒间的空隙率较小,保水能力强;壤土中砂粒、粉粒以及黏粒的比例相当,物理力学性质也介于黏土和砂土之间。肯尼亚境内存在大量的黏土,许多地区黏土中黏粒的含量更是超过60%,被划分为高含量黏土。肯尼亚土壤分布如图2(f)所示。
2.2.7 年平均降雨量
肯尼亚的气候属于热带季风气候,降水具有明显的季风气候特点,每年的2到5月为大雨季,10到12月为小雨季,其余则为旱季。雨季期间,丰富的降水可以给地表径流带来了大量水源补充,同时也提高了坡体的含水率,劣化了其物理力学指标,滑坡等地质灾害发生的概率也会随之升高。肯尼亚年平均降雨量空间分布情况如图2(g)所示。
2.2.8 水流能力指数及地形湿度指数
水体的存在会对沿岸的岩土体产生相当大的侵蚀。土体的含水率越高,其抗剪强度就越低,在自然营力作用下的稳定性也就越差,会更易发生滑坡等地质灾害。水流能力指数(stream power index,SPI)和地形湿度指数(topographic wetness index,TWI)是衡量岩土体受水体影响程度的重要指标,其计算公式如下:
(1) (2) 式中:
肯尼亚TWI和SPI分布情况如图2(h)和(i)所示。
2.2.9 土地利用类型
肯尼亚的土地利用类型包含农业用地、荒地、灌木丛、林地、草地、沼泽、城镇用地,其他部分则为水体(湖泊等)。一方面,土地利用类型能反映出人类活动的影响程度,人类活动影响越强的地方对地质灾害发生所造成的直接损失可能越严重,且人类活动的影响在一定程度会影响到岩土体稳定性。另一方面,土地利用类型也会影响当地的植被分布,而植被分布对滑坡等灾害具有明显的防护作用。肯尼亚土地利用类型分布如图2(j)所示。
2.3 评价模型
根据计算方式的不同,滑坡等地质灾害的评价方法可分为定性和定量两种,其中定性分析方法模型建立较为简便,计算过程相对简单,但其主要根据专家的经验打分确定权重,主观性较强;定量分析方法依据客观数据进行计算,不受决策者主观因素的影响,在实践中得到了广泛应用。根据分析模型的不同,定量分析方法可进一步划分为双变量模型、多变量模型及机器学习模型等,其中双变量模型着重于分析单个评价因素和目标变量之间的关系,侧重单因素对目标变量的解释能力。多变量模型则涉及研究两个或两个以上评价因素对目标变量的影响,可反映目标变量对多种评价因素的变动规律。机器学习是一门多领域交叉学科确定的计算方法,调节过程依靠程序驱动,可根据评价结果不断改善自身的性能。尽管国内外已经对区域性地质灾害危险性问题做出过大量探索,但对于不同模型的对比研究相对较少。基于此,本文结合收集到的历史灾害记录和矢量数据,选取信息量(双变量模型)、逻辑回归(多变量模型)、极限学习机(机器学习模型)分别对肯尼亚滑坡灾害进行危险性评价。
2.3.1 信息量模型
信息量(information value,IV)模型是描述目标变量和单个影响因素之间相关程度的定量分析方法。IV可以基于灾害点在因素各分级区间的分布比例,分别计算各区间的信息量,进而对肯尼亚滑坡灾害危险性做出评价。各分级区间的信息量是由滑坡灾害点在区间的分布情况确定的,具体计算公式如下:
(3) 式中:
2.3.2 逻辑回归模型
逻辑回归(logistic regression,LR)模型是一种广义的线性回归预测方法,可用于分析目标变量和多个影响因素之间的具体数值关系,进而对滑坡灾害的危险性做出评价。LR模型各因素的权重主要由其对目标变量的影响程度确定,训练速度较快,可解释性好,非常适用于危险性评价等二分类问题。LR模型表达式如下:
(4) 式中:
2.3.3 极限学习机模型
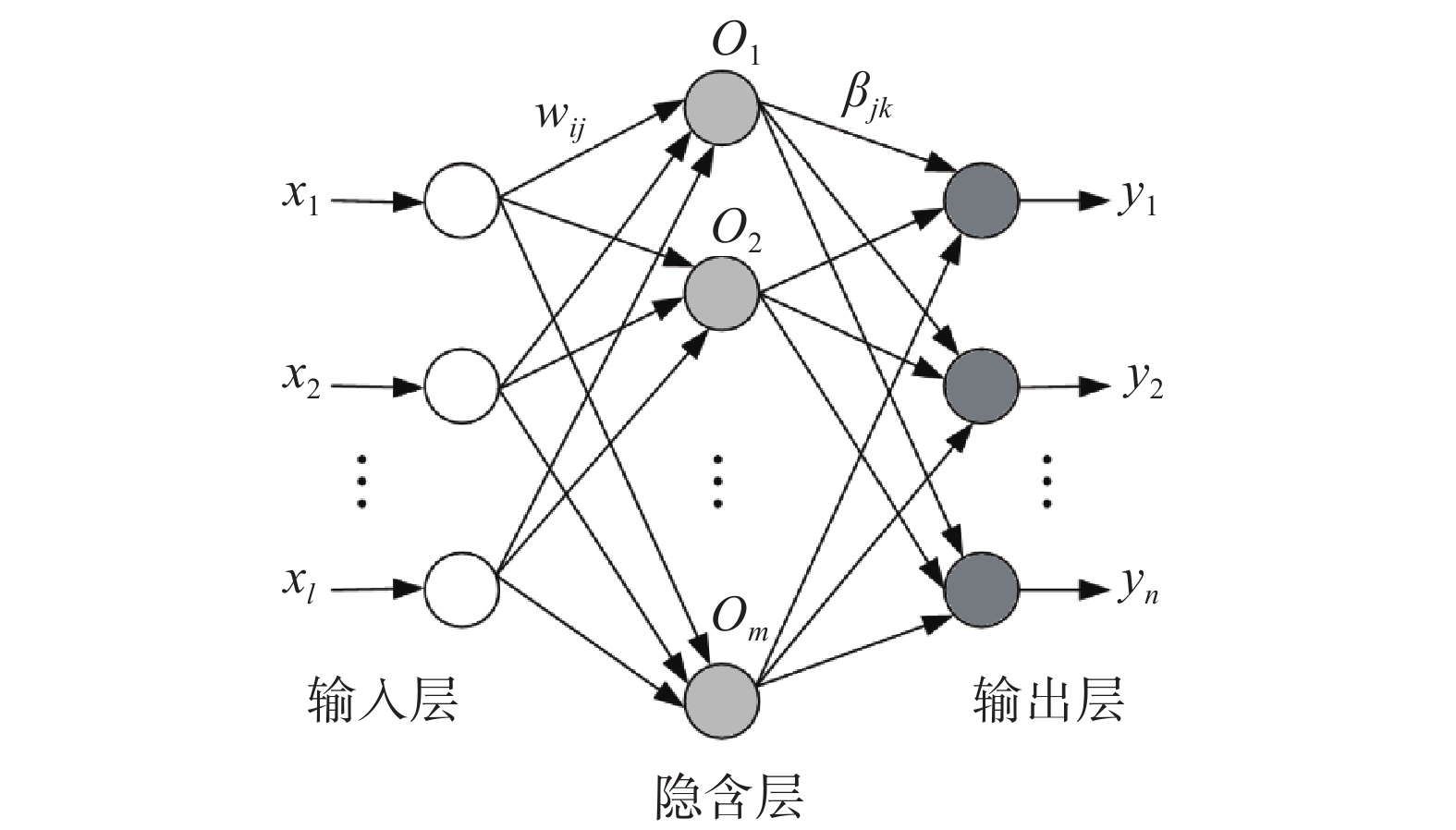
极限学习机(extreme learning machine,ELM)是一种机器学习领域的神经网络模型。ELM的结构包含输入层、隐含层和输出层3个部分,各层之间依靠神经元联系,其结构如图3所示。与传统的前馈神经网络模型不同,极限学习机模型不涉及到隐含层各个节点的改变和调试,输入层与隐含层之间的连接权重、隐含神经元的阈值等参数都是采取随机的方式进行设置。
对于有
(5) 式中:
为了处理一些非线性的数据集,可以使用一些激活函数为原数据集进行换算,来让数据集变得线性可分离,不同的激活函数可以对原数据集达成不同的操作。在分析时分别选取sigmoid函数(SIG)、正弦函数(SIN)和对称阈值型传输函数(HARDLIM)作为激活函数对极限学习机模型进行讨论。评价流程如图4所示。
3. 结果分析和精度评价
3.1 结果分析
将历史滑坡点和随机选取的相同数量的非灾害点进行组合,形成评价数据集,随机抽取70%的样本作为训练集,剩下30%的样本作为测试集进行评价。LR和IV模型系数结果如表1和表2所示。信息量可以表征评价因素不同分级区间对滑坡灾害的影响程度,其值越大,说明在该区间下发生滑坡的概率越高。如果某个分级区间对应的频率值为0,则可说明在该区间内没有灾害记录,滑坡灾害的发生和该因素区间无关,该区间对滑坡灾害的发生没有影响。由表1中可知,高程在>2000 m、坡度在>45°时的区间信息量最高,且信息量随着分区等级的上升呈递增趋势,表明在高程和坡度因子对滑坡灾害具有明显的正相关性;坡向对滑坡的影响主要体现在东北方位(22.5°~67.5°);土壤类型为高含量黏土时对滑坡影响最大,也印证了CHENG等[25]的研究结论;年平均降雨量在1200~1600 mm,地形湿度指数在7~12,水流能力指数在9~12时的信息量最高,对滑坡的影响表现在一定的范围内,但其也保持了一定程度的正相关性;其余因子中,地貌为山谷、平面曲率为凹、土地利用类型为城镇时的要素单元和滑坡的相关性最高。逻辑回归系数代表了因素对滑坡灾害发生的影响程度,其值越大,说明该因素对滑坡危险性的影响越大。由表2可知,高程、水流能力指数、年平均降雨量、地形湿度指数等因素对肯尼亚滑坡灾害发生的影响程度较大(权重>1),而土壤类型、平面曲率和土地利用类型等因素影响程度较小(权重<0.05)。相关研究中[8-11,13-15],为进一步对地质灾害危险性进行细致划分,主要将危险性划分为5类进行分析,本文参考相关文献进行划分,利用自然间断法对各模型的计算结果进行划分可得到肯尼亚滑坡危险性分区图,如图5所示。
表 1 信息量模型系数Table 1. Summary table for coefficients of the IV model因素 因子分级 信息量 因素 因子分级 信息量 高程
/m0~50 −1.341 坡度/(°) 0~5 −2.212 50~200 0.000 5~15 0.315 200~500 −1.941 15~25 1.552 500~1000 −2.813 25~35 3.671 1000~2000 0.452 35~45 4.889 >2000 2.316 >45 5.356 坡向 平 0.000 地貌 洼地 1.547 北 0.282 山麓 0.340 东北 0.322 高原 1.389 东北 0.183 平原 −2.277 东南 −0.032 谷底 0.000 南 −0.215 悬崖 1.062 西南 −0.707 丘陵 0.913 西 −0.089 山谷 2.353 西北 0.052 山脊 1.476 土壤
类型黏土 −0.124 水体 0.000 壤土 0.115 年平均
降雨量
/mm<400 −1.762 砂土 −1.948 400~800 −0.729 高含量黏土 0.450 800~1200 0.850 地形
湿度
指数7~12 1.666 1200~1600 2.240 12~14 −1.423 1600~2000 0.503 14−16 −2.041 2000~2400 0.607 16~20 −1.785 >2400 0.000 20~32 −2.319 水流
能力
指数2~5 −2.889 土地
利用
类型农业用地 0.800 5~7 −1.562 荒地 −1.365 7~9 0.972 灌木丛 −1.570 9~12 1.107 林地 2.043 12~23 0.250 草地 0.000 平面
曲率凸 −0.089 沼泽 0.000 平 −1.026 城镇 2.148 凹 0.187 表 2 逻辑回归模型系数Table 2. Summary table for coefficients of the LR model因素 系数 因素 系数 高程 1.683 土壤类型 −0.048 坡度 0.754 地形湿度指数 −1.125 坡向 −0.097 水流能力指数 1.481 地貌 0.229 年平均降雨量 1.466 平面曲率 0.047 土地利用类型 0.026 3.2 精度评价
结合受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)对各模型计算结果进行精度验证。ROC曲线以假阴性率(false positive rate,FPR,又称特异性)为横轴,以真阳性率(true positive rate,TPR,又称敏感性)为纵轴,其中TPR为正样本中预测正确的比率,FPR为负样本中预测错误的比率。ROC曲线和
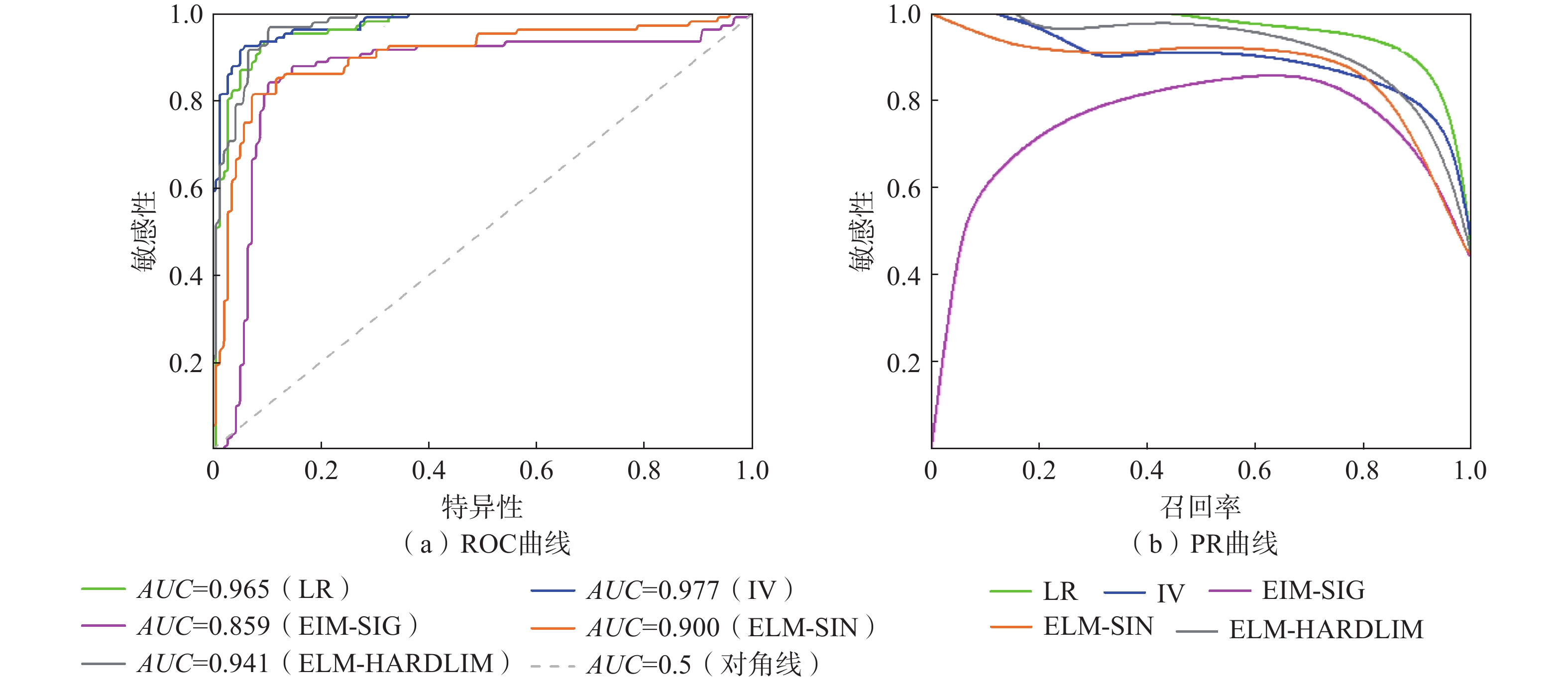
由图6(a)可知,不同模型下的AUC面积分别为:0.965(LR)、0.977(IV)、0.859(ELM-SIG)、0.900(ELM-SIN)、0.941(ELM-HARDLIM),除了ELM-SIG方法以外,其他模型的AUC面积均大于0.9,各模型评价结果有效。PR曲线即精确-召回曲线(precision recall,PR),同样是评价模型效果的常用检验依据之一。PR曲线以召回率为横轴,精确率为纵轴,其中召回率是指正样本中被正确预测比率,其计算方式和真阳性率相同。精确率是指预测为正的样本中真正正样本所占的比率。理想情况下,精确率和召回率越高,PR曲线越靠近右上角,则表征模型评价效果越好。各模型的PR曲线如图6(b)所示。
从图中可以看出,除ELM-SIG的评价结果以外,其他方法的PR曲线均靠近右上角。LR模型的召回率和精确率都处于较高的水平,虽然IV模型AUC面积最大,但是从PR曲线来看评价效果要略低于LR模型。综合考虑ROC曲线和PR曲线的对比结果,相对于其他模型而言,LR模型具有更高的评价精度。由图5中LR模型的评价结果可以看出,肯尼亚高危险性及极高危险性区域集中分布在肯尼亚西南部的高原和高原-裂谷过渡地带,尤其是靠近东非大裂谷附近,这与肯尼亚历史滑坡数据的分布情况相吻合;高原外侧向平原的过渡地区是中危险性区域的集中地带;而东部、南部地区则以低危险性和极低危险性区域为主。
统计各个模型危险性分区的面积占比和滑坡灾害数量如表3所示。其中,灾害比重表示为发生在该危险性分区滑坡数量占比和分区面积占比之间的比值。由表3可知,随着分区等级的上升,各模型分区下的灾害比重总体上在逐渐增大,且主要分布在高危险性及极高危险性区域,说明各模型的分区效果良好。但对于ELM模型而言,SIG函数下的结果相对欠缺客观性,大量的滑坡点都分布在中危险性分区,在灾害比重上存在“中间高,两边低”的现象,虽然其ROC曲线和PR曲线结果较为合理,但是实用性仍有待讨论。
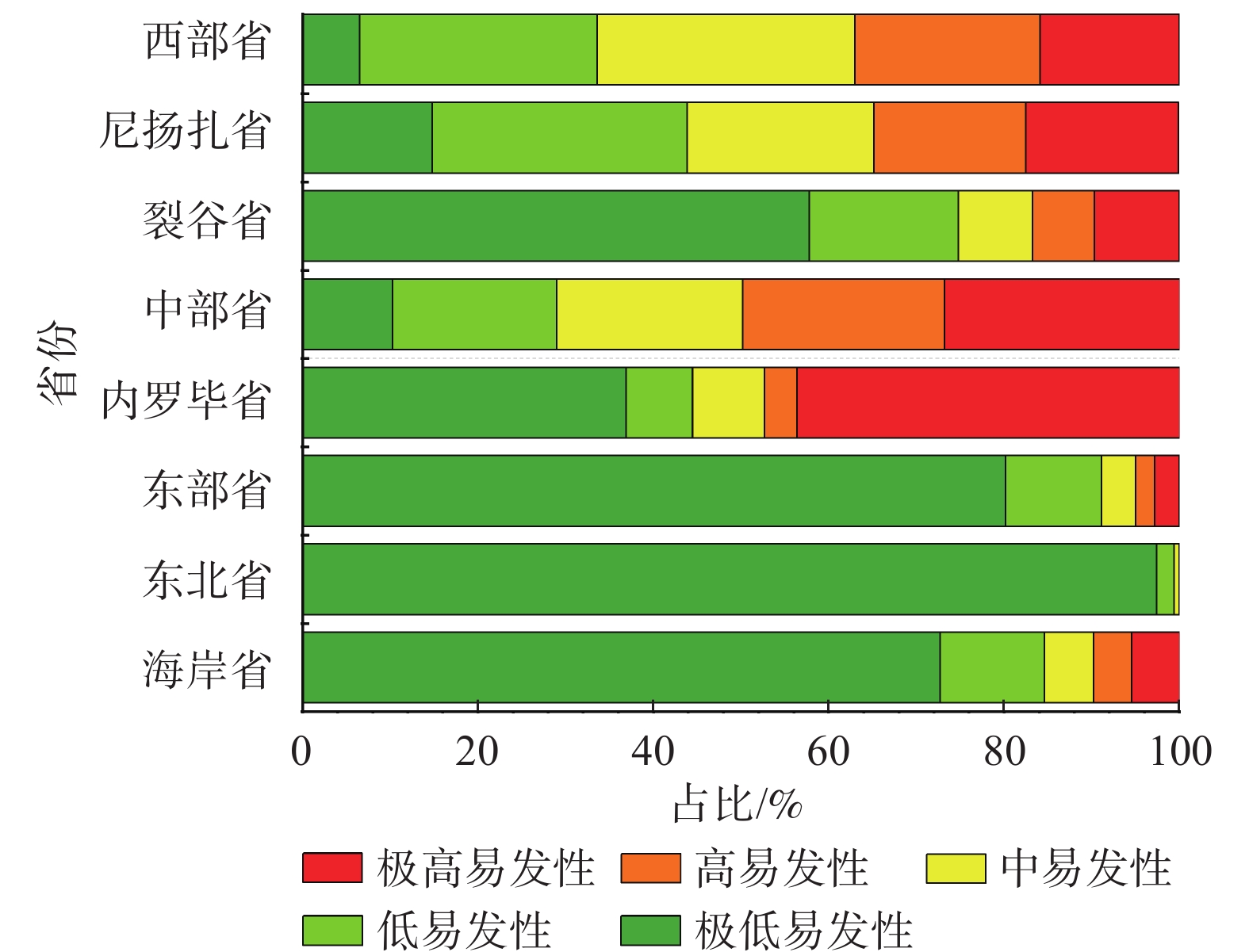
表 3 不同模型灾害分布统计结果Table 3. Statistical results of disasters distribution for different models危险性分区评估模型 极低危险性 低危险性 中危险性 高危险性 极高危险性 LR模型 面积占比/% 72.700 11.900 5.500 4.400 5.400 数量占比/% 2.570 0.930 1.170 10.510 84.810 灾害比重 0.035 0.078 0.213 2.389 15.705 IV模型 面积占比/% 35.300 29.800 16.9000 11.000 6.900 数量占比/% 0.930 0.930 2.8000 17.520 77.800 灾害比重 0.026 0.031 0.1657 1.593 11.275 ELM-SIG 面积占比/% 1.300 76.300 19.400 1.100 1.900 数量占比/% 1.870 8.410 88.080 1.170 0.470 灾害比重 1.438 0.110 4.540 1.064 0.247 ELM-SIN 面积占比/% 1.100 38.300 43.600 12.800 4.200 数量占比/% 0.700 2.800 9.110 33.880 53.500 灾害比重 0.636 0.073 0.208 2.647 12.738 ELM-HARDLIM 面积占比/% 5.200 34.300 34.500 18.000 8.000 数量占比/% 0.930 0.930 2.800 17.520 77.800 灾害比重 0.178 0.027 0.081 0.973 9.725 在LR模型评价结果基础上,依据肯尼亚的省级行政区划对模型评价结果进一步划分,统计肯尼亚各省份的危险性分区面积占比,如图7所示。
可以看出,肯尼亚境内内罗毕省(Nairobi)和中部省(Central)分别有47.40%和49.90%位于高危险性及以上分区,其次是尼扬扎省(Nyanzs)和西部省(Western),高危险性及以上分区占比分别为34.70%和37.00%,其余省份的占比都位于20%以下。依据评价结果,建议相关部门将内罗毕省、中部省、尼扬扎省和西部省作为肯尼亚滑坡灾害防治的重点,同时在肯尼亚雨季期间(3—5月及10—12月)做好相关区域的灾害预警工作,减少滑坡灾害可能造成的损失。
4. 结论
本文以肯尼亚地区为研究对象,以历史滑坡数据为样本,选取高度、坡度、坡向、地貌、平面曲率、土壤类型、年平均降雨量、水流能力指数、地形湿度指数和土地利用类型作为评价指标,分别采用IV、LR和ELM模型对肯尼亚滑坡灾害进行危险性评价,主要结论如下:
(1) 高程>2000 m、坡度在>45°、坡向为东北(22.5°~67.5°)、土壤类型为高含量黏土、平面曲率为凹、年平均降雨量在1200~1600 mm、地形湿度指数在7~12、地貌为山谷、水流能力指数在9~12、土地利用类型为城镇时的要素单元和滑坡的相关性最高;高程、水流能力指数、年平均降雨量、地形湿度指数等因素对肯尼亚滑坡灾害发生影响程度较大,而土壤类型、平面曲率和土地利用类型等因素影响程度较小。
(2) 各模型的AUC面积分别为0.977(IV)、0.965(LR)、0.859(ELM-SIG)、0.900(ELM-SIN)、0.941(ELM-HARDLIM),而结合PR曲线结果综合考虑,相对于其他模型而言,LR模型评价效果较好;随着危险区等级的上升,各模型分区下的灾害比重总体上在逐渐增加,说明各模型的分区效果良好;但对于ELM模型而言,SIG激活函数下的结果在灾害比重上存在“中间高,两边低”的现象,实用性仍有待讨论。
(3) 肯尼亚高危险性及极高危险性区域集中分布在肯尼亚西南部的高原和高原-裂谷过渡地带,尤其是靠近东非大裂谷附近,这与肯尼亚历史滑坡数据的分布情况相吻合;高原外侧向平原的过渡地区是中危险性区域的集中地带,而东部、南部地区则以低危险性和极低危险性区域为主;将肯尼亚各个省份在LR模型下的滑坡危险性区域分布情况进行统计,发现内罗毕省、中部省、尼扬扎省和西部省在高危险性及以上分区占比较多。
限于数据获取的难度和评价因素的可用性,本文的评价过程仍然存在部分不足。在评估滑坡灾害时,搜集了425例历史地质灾害点,尽管从数量上看已经较为充足,但实际上其基本信息未提及滑坡发生的时间和滑体类型等信息,导致对肯尼亚滑坡灾害概括的普遍性相对不足。此外,虽然本文选取的因素有一定的代表性,但在评估时并未考虑可能影响地质灾害发生的其他因素(如构造、岩性等),而这种忽视实际上和现实之间仍存在偏离,因此有赖于进行更深一步的研究。
-
表 1 信息量模型系数
Table 1 Summary table for coefficients of the IV model
因素 因子分级 信息量 因素 因子分级 信息量 高程
/m0~50 −1.341 坡度/(°) 0~5 −2.212 50~200 0.000 5~15 0.315 200~500 −1.941 15~25 1.552 500~1000 −2.813 25~35 3.671 1000~2000 0.452 35~45 4.889 >2000 2.316 >45 5.356 坡向 平 0.000 地貌 洼地 1.547 北 0.282 山麓 0.340 东北 0.322 高原 1.389 东北 0.183 平原 −2.277 东南 −0.032 谷底 0.000 南 −0.215 悬崖 1.062 西南 −0.707 丘陵 0.913 西 −0.089 山谷 2.353 西北 0.052 山脊 1.476 土壤
类型黏土 −0.124 水体 0.000 壤土 0.115 年平均
降雨量
/mm<400 −1.762 砂土 −1.948 400~800 −0.729 高含量黏土 0.450 800~1200 0.850 地形
湿度
指数7~12 1.666 1200~1600 2.240 12~14 −1.423 1600~2000 0.503 14−16 −2.041 2000~2400 0.607 16~20 −1.785 >2400 0.000 20~32 −2.319 水流
能力
指数2~5 −2.889 土地
利用
类型农业用地 0.800 5~7 −1.562 荒地 −1.365 7~9 0.972 灌木丛 −1.570 9~12 1.107 林地 2.043 12~23 0.250 草地 0.000 平面
曲率凸 −0.089 沼泽 0.000 平 −1.026 城镇 2.148 凹 0.187 表 2 逻辑回归模型系数
Table 2 Summary table for coefficients of the LR model
因素 系数 因素 系数 高程 1.683 土壤类型 −0.048 坡度 0.754 地形湿度指数 −1.125 坡向 −0.097 水流能力指数 1.481 地貌 0.229 年平均降雨量 1.466 平面曲率 0.047 土地利用类型 0.026 表 3 不同模型灾害分布统计结果
Table 3 Statistical results of disasters distribution for different models
危险性分区评估模型 极低危险性 低危险性 中危险性 高危险性 极高危险性 LR模型 面积占比/% 72.700 11.900 5.500 4.400 5.400 数量占比/% 2.570 0.930 1.170 10.510 84.810 灾害比重 0.035 0.078 0.213 2.389 15.705 IV模型 面积占比/% 35.300 29.800 16.9000 11.000 6.900 数量占比/% 0.930 0.930 2.8000 17.520 77.800 灾害比重 0.026 0.031 0.1657 1.593 11.275 ELM-SIG 面积占比/% 1.300 76.300 19.400 1.100 1.900 数量占比/% 1.870 8.410 88.080 1.170 0.470 灾害比重 1.438 0.110 4.540 1.064 0.247 ELM-SIN 面积占比/% 1.100 38.300 43.600 12.800 4.200 数量占比/% 0.700 2.800 9.110 33.880 53.500 灾害比重 0.636 0.073 0.208 2.647 12.738 ELM-HARDLIM 面积占比/% 5.200 34.300 34.500 18.000 8.000 数量占比/% 0.930 0.930 2.800 17.520 77.800 灾害比重 0.178 0.027 0.081 0.973 9.725 -
[1] BATALA L K,YU Wangxing,KHAN A,et al. Natural disasters' influence on industrial growth,foreign direct investment,and export performance in the South Asian region of Belt and road initiative[J]. Natural Hazards,2021,108(2):1853 − 1876. DOI: 10.1007/s11069-021-04759-w
[2] BAI Yuanli,WIERZBICKI T. Application of extended Mohr-Coulomb criterion to ductile fracture[J]. International Journal of Fracture,2010,161(1):1 − 20. DOI: 10.1007/s10704-009-9422-8
[3] ROGERS J D,CHUNG J. Applying Terzaghi’s method of slope characterization to the recognition of Holocene land slippage[J]. Geomorphology,2016,265:24 − 44. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.04.020
[4] AHMED A,UGAI K,YANG Qing qing. Assessment of 3D slope stability analysis methods based on 3D simplified janbu and hovland methods[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics,2012,12(2):81 − 89. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000117
[5] WANG Chun ming,LIU Chun yuan,WU Mai,et al. Research on soil-like slope instability based on FEM strength reduction[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials,2013,438/439:1244 − 1248. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.438-439.1244
[6] 吴信才,白玉琪,郭玲玲. 地理信息系统(GIS)发展现状及展望[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2000,36(4):8 − 9. [WU Xincai,BAI Yuqi,GUO Lingling. Development and prospect of geographic information system[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications,2000,36(4):8 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Xincai, BAI Yuqi, GUO Lingling. Development and prospect of geographic information system[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2000, 36(4): 8-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] SON J,SUH J,PARK H D. GIS-based landslide susceptibility assessment in Seoul,South Korea,applying the radius of influence to frequency ratio analysis[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(4):310. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-015-5149-1
[8] 屠水云,张钟远,付弘流,等. 基于CF与CF-LR模型的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):96 − 104. [TU Shuiyun,ZHANG Zhongyuan,FU Hongliu,et al. Geological hazard susceptibility evaluation based on CF and CF-LR model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):96 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) TU Shuiyun, ZHANG Zhongyuan, FU Hongliu, et al. Geological hazard susceptibility evaluation based on CF and CF-LR model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 96-104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 刘福臻,王灵,肖东升. 机器学习模型在滑坡易发性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):98 − 106. [LIU Fuzhen,WANG Ling,XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):98 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Fuzhen, WANG Ling, XIAO Dongsheng. Application of machine learning model in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6)98-106(in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] LIU Rui,LI Luyao,PIRASTEH S,et al. The performance quality of LR,SVM,and RF for earthquake-induced landslides susceptibility mapping incorporating remote sensing imagery[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2021,14(4):1 − 15.
[11] WANG Xi,WANG Shuangyin,QI Jiashuo. Open-channel landslide hazard assessment based on AHP and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Water Supply,2020,20(8):3687 − 3696. DOI: 10.2166/ws.2020.176
[12] 商冬凡,唐梦芸,苗雷强,等. 城市道路空洞隐患风险评估方法应用研究[J]. 市政技术,2022,40(11):37 − 42. [SHANG Dongfan,TANG Mengyun,MIAO Leiqiang,et al. Risk Assessment of Operation and Maintenance Stage of Utility Tunnel based on Combination Weighting-Improved Risk Matrix Method[J]. Journal of Municipal Technology,2022,40(11):37 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract) [Shang Dongfan, Tang Mengyun, Miao Leiqiang, Shi Jiahao, Zhou Siqing. Risk Assessment of Operation and Maintenance Stage of Utility Tunnel based on Combination Weighting-Improved Risk Matrix Method [J]. Journal of Municipal Technology, 2022,40(11): 37-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 张俊,殷坤龙,王佳佳,等. 三峡库区万州区滑坡灾害易发性评价研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(2):284 − 296. [ZHANG Jun,YIN Kunlong,WANG Jiajia,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou district of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(2):284 − 296. (in Chinese with English abstract) Zhang Jun, Yin Kunlong, Wang Jiajia, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou district of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(2): 284-296. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] CHEN Wei,LI Wenping,CHAI Huichan,et al. GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and certainty factor (CF) models for the Baozhong region of Baoji City,China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(1):63. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-015-4795-7
[15] 刘璐瑶,高惠瑛,李照. 基于CF与Logistic回归模型耦合的永嘉县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2021,51(10):121 − 129. [LIU Luyao,GAO Huiying,LI Zhao. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on coupling of CF model and logistic regression model in Yongjia County[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China,2021,51(10):121 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Luyao, GAO Huiying, LI Zhao. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on coupling of CF model and logistic regression model in Yongjia County[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(10)121-129(in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 地质灾害危险性评估规范: GB/T 40112—2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021 Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Specifications for risk assessment of geological hazard: GB/T 40112—2021[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2021. (in Chinese)
[17] 杨先全,周苏华,邢静康,等. 肯尼亚滑坡灾害分布特征及敏感性区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):65 − 74. [YANG Xianquan,ZHOU Suhua,XING Jingkang,et al. Distribution patterns and susceptibility mapping of landslides in Kenya[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):65 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Xianquan, ZHOU Suhua, XING Jingkang, et al. Distribution patterns and susceptibility mapping of landslides in Kenya[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(5)65-74(in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 朱丛瑞. 肯尼亚建国后的环境问题研究[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2021 ZHU Congrui. Research on environmental problems after the founding of Kenya[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 肯尼亚信息、通信和技术部.滑坡统计资料[M/OL]. [2015-5-18]. https://www.ict.go.ke/wp-content/uploadsKenya. Ministry of Information, Communication and Technology of Kenya. Landslide Statistics[M/OL]. [2015-5-18]. (in Chinese)
[20] 全球毁灭性滑坡数据库.肯尼亚地区滑坡数据[M/OL]. [2019-6-18]. https://blogs.agu.org/landslideblog/. Global Database of Fatal Landslides.Kenya Historical Landslide Data[M/OL]. [2019-6-18]. (in Chinese)
[21] BROECKX J,VANMAERCKE M,DUCHATEAU R,et al. A data-based landslide susceptibility map of Africa[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2018,185:102 − 121. DOI: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.002
[22] NASA 地球公开数据. ASTERGDEMV2卫星全球高程公开共享数据[M/OL]. [2013-11-30].https://visibleearth.nasa.gov/. NASA Earth Open Data. ASTERGDEMV2 satellite global elevation data[M/OL]. [2013-11-30]. (in Chinese)
[23] 开放非洲数据库. 肯尼亚地区地表径流、地貌、年降雨量等共享数据[M/OL]. [2014-1-20]. www.Openafrica.org Open Africa Database. Shared data on surface runoff, landforms, and annual rainfall in Kenya [M/OL]. [2014-1-20]. (in Chinese)
[24] 世界资源研究所公开数据. 肯尼亚地区土地利用类型共享数据[M/OL]. [2014-1-20]. www.wri.org. World Resources Institute Open Data. Shared data on land use types in Kenya[M/OL]. [2014-1-20]. (in Chinese)
[25] CHENG Yongzhen,HUANG Xiaoming. Effect of mineral additives on the behavior of an expansive soil for use in highway subgrade soils[J]. Applied Sciences,2018,9(1):30. DOI: 10.3390/app9010030
[26] SWETS J A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems[J]. Science,1988,240(4857):1285 − 1293. DOI: 10.1126/science.3287615
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 谷牧. 铁路边坡变形在线监测数据处理方法及其应用——以朔黄铁路为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2025(01): 101-107 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 殷玮民,李远耀,李星,李明,居乐,谢藕. 考虑岩土体物理力学参数空间校准分区的滑坡危险性评价. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2025(02): 162-174 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 王雅丽,王平,王会娟,许书雅,于浩然,张兴富. 耦合统计与机器学习模型的黄土地震滑坡危险性评价. 地震工程学报. 2025(04): 864-875+900 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 桂富羽,史正涛,喜文飞,付尧,郭峻杞. 基于证据权模型的滑坡灾害易发性评价研究——以普洱市为例. 城市勘测. 2024(05): 188-193+198 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨得虎,朱杰勇,刘帅,马博,代旭升. 基于信息量、加权信息量与逻辑回归耦合模型的云南罗平县崩滑灾害易发性评价对比分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(05): 43-53 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 徐春,刘迪,沈琪. 基于机器学习的高精度无人机影像滑坡自动识别研究. 云南电力技术. 2023(05): 46-50+60 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:

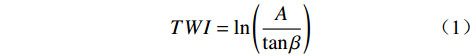
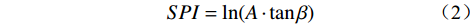
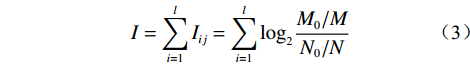
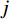
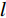
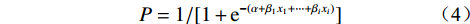
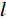
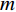
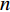
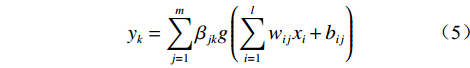
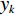
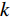
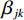
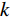
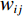
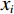
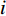
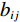

 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS