Analysis of sliding mechanism of the cut slopes with multi-weak interlayers under rainfall
-
摘要:
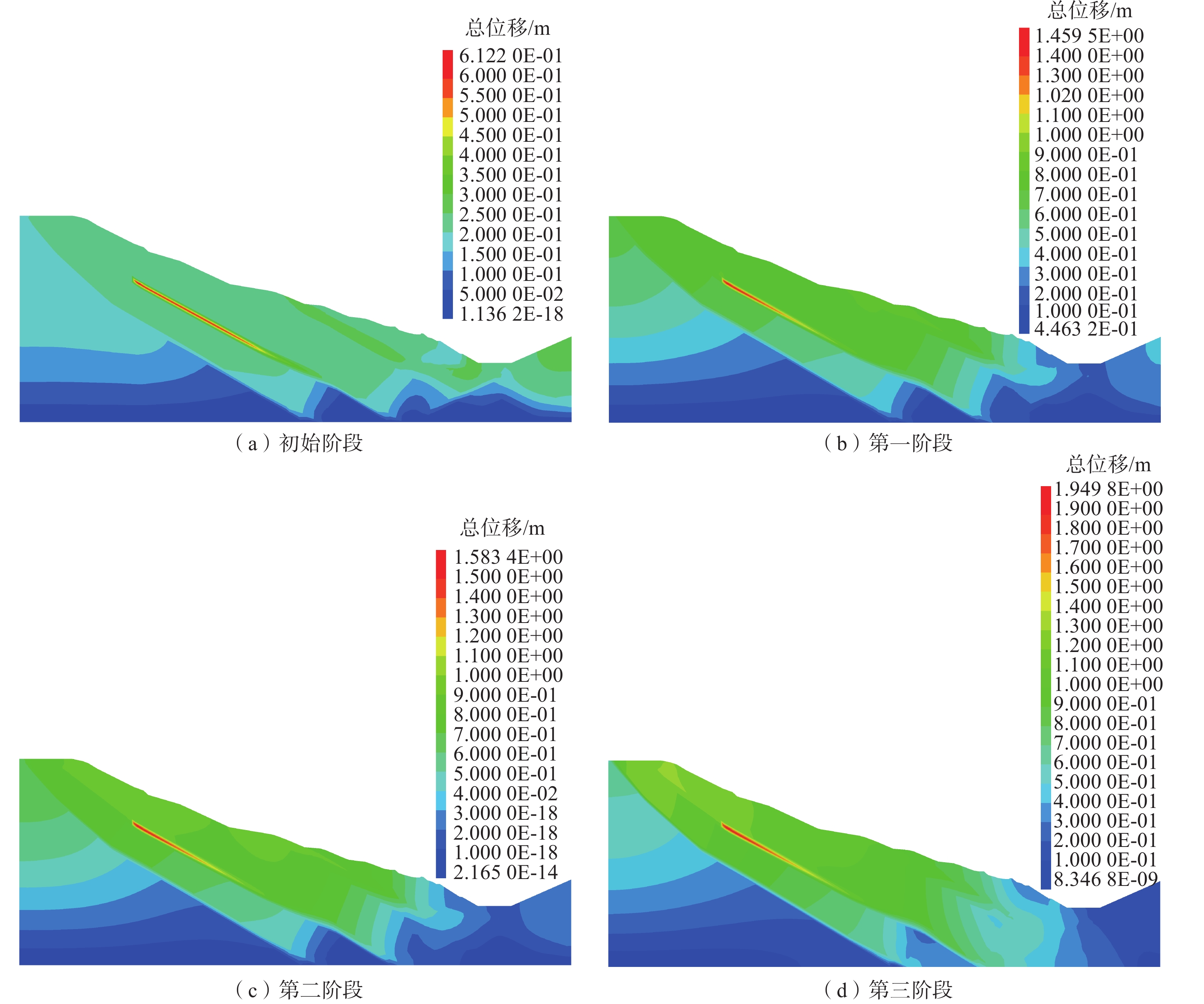
文章基于抚顺西露天矿南帮滑坡工程实例,分析地下水及降雨入渗作用下顺倾软弱夹层边坡失稳的水力学模式,采用FLAC3D软件对抚顺西露天矿南帮边坡在地下水及降雨入渗作用下边坡变形的演化过程进行数值模拟分析,总结地下水及降雨入渗作用下顺倾多软弱夹层边坡的滑动规律。结果表明:降雨入渗和地下水的流动对坡体产生渗透压力,坡体破裂面大量发育,最大总位移约为1.27 m,形成多阶段滑坡,整体呈现混合式滑坡;边坡变形破坏期间,坡顶附近易沿弱层产生拉张破坏,为地表水渗透和地下水的运移提供通道,并呈现多滑面的特点,形成贯通的剪切破坏面,进一步导致边坡的多段变形;在地下水及降雨入渗影响下,边坡弱层含水率累积增加,损伤破裂,体积应变增量降低,有效应力降低,孔压累积上升,抗剪强度减低,从而诱发滑坡。相比降雨工况下,采用不同坡高高度回填压脚防护的边坡具有较高的安全系数,考虑工程实际综合比较不同防治方案,在降雨影响下,回填压脚至1/2坡高高度防治效果更好,边坡较稳定。
Abstract:This paper presents an analysis of the hydraulic model of the slope instability of a down-dipping soft sandwich slope, focusing on the southern slope landslide project of Fushun west open pit mine. The study investigates the effects of groundwater and rainfall infiltration on the slope deformation evolution process using numerical simulation analysis with FLAC3D software. The sliding law of the slope with soft interlayer under the action of groundwater and rainfall infiltration is summarized. The results show that rainfall infiltration and groundwater flow produce osmotic pressure on the slope, causing the development of a large number of rupture surfaces on the slope. The maximum cumulative displacement is about 1.27 m resulting in a multi-stage landslide with a mixed landslide type. During the deformation and failure of the slope, tension failure is prone to occur along the weak layer near the slope top, providing a channel for surface water infiltration and groundwater migration, and showing the characteristics of multiple sliding surface, forming a continuous shear failure surface, which further leads to the multi-stage deformation of the slope. Under the influence of groundwater and rainfall infiltration, the water content in the weak layer of slope accumulates, resulting in damage and rupture, reducing the volume strain increment, lowering the effective stress, increasing the pore pressure, and reduing the shear strength, thereby inducing landslide. To improve the stability of the slope, the study compares different prevention and control schemes, including backfilling presser foot with different slope heights. The study finds that compared with the rainfall condition, the slope protected by backfilling presser foot with different slope heights has a higher safety factor. Considering the engineering practice, the backfilling and pressure protection up to half of the slope height has a better effect on preventing and controlling the slope, and the slope is more stable.
-
Keywords:
- groundwater /
- rainfall infiltration /
- weak interlayer /
- slope /
- numerical simulation /
- Fushun west open pit mine
-
0. 引 言
据不完全统计我国共有露天煤矿约300座(不含井露联合开采煤矿),产能达7.5908×108 t/a[1]。露天矿山边坡失稳滑坡会直接威胁到矿山工作者的生命和财产安全[2],由若干台阶构成的边坡也是露天矿山生产运输的主要依托对象,露天边坡稳定性直接影响到露天矿山的建设和生产。露天矿边坡稳定性分析一直是岩土工程领域研究的热点问题,一方面,露天矿边坡往往受多种影响因素共同作用,关系复杂[3]。另一方面,试验室难以还原现场地质条件及其他因素的影响,试验室岩样数据往往不能直接用于矿山边坡稳定性分析,所以作为露天矿边坡稳定性计算及数值模拟中岩(土)体的参数取值具有很大的模糊性,导致露天矿边坡是一个不确定性的系统,其稳定性评价也是一个不确定、多因素、非线性问题[4]。
针对露天矿边坡稳定性评价问题的不确定性、复杂性,一些学者将模糊评价理论等不确定性分析方法应用到边坡稳定性分析中。蒋中明[5]通过对边坡刚体极限平衡分析中模糊因素的分析, 提出了一种使用模糊集理论计算工程边坡稳定性的方法。丁浩江等[6]、王华俊等[7]分别运用模糊综合评价模型对澜沧江某水电站泄洪洞出口边坡和宁波市国省道公路岩质边坡进行了稳定性评价,评价结果均与实际情况吻合较好,验证了模糊综合评价方法运用于边坡稳定性分析的有效性。由于不同影响因素对边坡稳定性的影响不同,模糊综合评价方法中边坡影响因素权重的确定存在主观性,因此先采用层次分析法客观确定不同因素对边坡稳定性的影响权重进而采用模糊综合评价法对边坡稳定性进行评价效果会更好[8 − 9]。但是目前边坡稳定性分析的层次分析-模糊综合评价模型的评价指标主要来自边坡地质调查和边坡基本形态。已有研究中,将边坡变形监测信息作为评价指标纳入到该模型中的研究相对较少;此外已有研究主要通过现场观察边坡是否稳定来验证模型,这种模型验证方法存在一定的主观性。
基于此,本文建立了考虑边坡监测信息的层次分析-模糊综合评价模型,首先对边坡监测数据进行分析,然后将边坡监测信息纳入边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型中,同边坡几何形态、边坡地质信息、气象水文信息等构成边坡系统的评价指标,然后基于层次分析法确定边坡稳定性评价指标的权重,最后基于隶属度最大原则确定边坡稳定性状态。将建立的层次分析-模糊综合评价模型应用于扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡稳定性评价,综合得出北帮边坡稳定性状况,最后通过数值模拟求解边坡安全系数对模型评价结果进行验证。
1. 边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型
模糊综合评价法对于复杂及不确定系统的评价具有明显的优势,将模糊综合评价法应用于边坡稳定性分析中首先需要确定边坡模糊指标集和评价集,然后根据隶属度函数确定单因子评价矩阵,根据边坡指标权重进行赋值,最后将权重向量与评价矩阵相结合根据隶属度最大原则得到最终的边坡稳定性评价结果[10 − 12]。
1.1 边坡模糊综合评价指标体系
根据相关规范[12],边坡的稳定性可以分为稳定、基本稳定、欠稳定、不稳定4个级别,同时建立边坡几何形态、边坡地质信息、边坡气象水文信息、边坡监测信息等四类边坡一级影响指标。边坡几何形态包括边坡坡高、边坡坡度、边坡结构类型3类指标;边坡地质信息包括边坡岩性、边坡弱层2项评价指标,边坡气象水文信息包括地下水影响、年平均降雨量2项评价指标;边坡监测信息主要包括地面变形情况、边坡变形速率等评价指标。边坡评价指标共9项,其中定量指标4项,定性指标5项。参考规范及已有研究[12 − 13]确定影响等级如表1和表2所示。
表 1 连续型指标影响等级划分Table 1. Classification of impact levels for continuous influencing indicators稳定性 坡高/m 坡度/(°) 年均降雨量/mm 地表变形
速率/(mm·d−1)稳定 0~100 0~15 0~500 5 基本稳定 >100~200 >15~30 >500~800 >5~30 欠稳定 >200~300 >30~50 >800~1200 >30~80 不稳定 >300 >50 >1200 >80 表 2 离散型指标影响等级划分Table 2. Classification of impact levels for discrete influencing indicators稳定性 岩性 结构类型 弱层 地面变形 地下水影响 稳定 坚硬岩体 均质/反倾 无 无 很弱 基本稳定 中等坚硬 斜交/横坡 反倾夹层 弱 较弱 欠稳定 软弱岩体 近水平坡 顺倾夹层、
反倾基岩中等 较强 不稳定 松散体 顺向坡 顺倾基岩 强烈 很强 1.2 层次分析法
对于露天矿边坡而言,各评价指标对边坡稳定性评价的贡献度是不同的,因此有必要利用层次分析法确定边坡各评价指标的影响因子[14]。通过标度方法,将影响因子的重要程度定量化[15]。如表3所示,通过指标两两比较后得出最终的边坡评价指标排序,表3中
标度 含义 1 3 5 7 9 2,4,6,8 介于以上两种比较之间的标度值 倒数 1.3 模型隶属度函数
隶属函数的确定对于边坡模糊综合评价具有重要的意义,隶属函数值即隶属度是表征边坡评价因子隶属于某个评价等级的程度。对于定量因素采用三角隶属度分布函数,本文采用的三角隶属度函数式(1)—(3)[17 − 18]。离散型指标隶属度的确定取值见表4[9, 13]。考虑到各个评价指标在边坡稳定性评价中的贡献不同,采用层次分析法将各项评价指标赋予一定的权重值,通过标度方法,将评价因子的重要程度定量化。
表 4 离散型指标评价隶属度表Table 4. Discrete index evaluation membership degree离散型指标 具体指标 离散型指标评价隶属度 稳定 基本稳定 欠稳定 不稳定 岩性 坚硬岩体 0.8 0.2 0 0 中等坚硬 0.4 0.5 0.1 0 软弱岩体 0 0.2 0.5 0.3 松散体 0 0 0.2 0.8 结构类型 顺向坡 0 0 0.2 0.8 近水平坡 0.1 0.2 0.7 0 斜交/横坡 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 均质/反倾 0.8 0.2 0 0 弱层 无 1 0 0 0 反倾夹层 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 顺倾夹层、反倾基岩 0 0.1 0.7 0.2 顺倾基岩 0 0 0.2 0.8 地面变形 无 0.8 0.2 0 0 弱 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 中等 0 0.1 0.7 0.2 强烈 0 0 0.2 0.8 地下水影响 很弱 0.55 0.30 0.10 0.05 较弱 0.25 0.50 0.15 0.10 较强 0.05 0.10 0.30 0.55 很强 0.05 0.15 0.10 0.70 (1) (2) (3) 式中:
2. 层次分析-模糊综合评价模型应用
2.1 工程概况
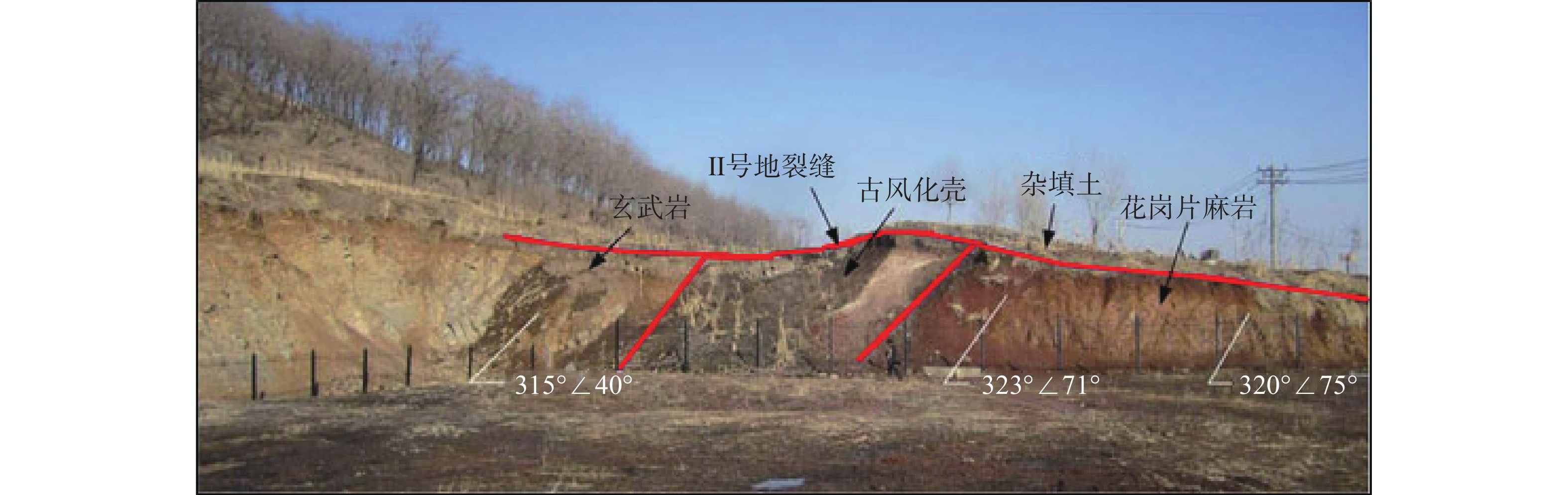
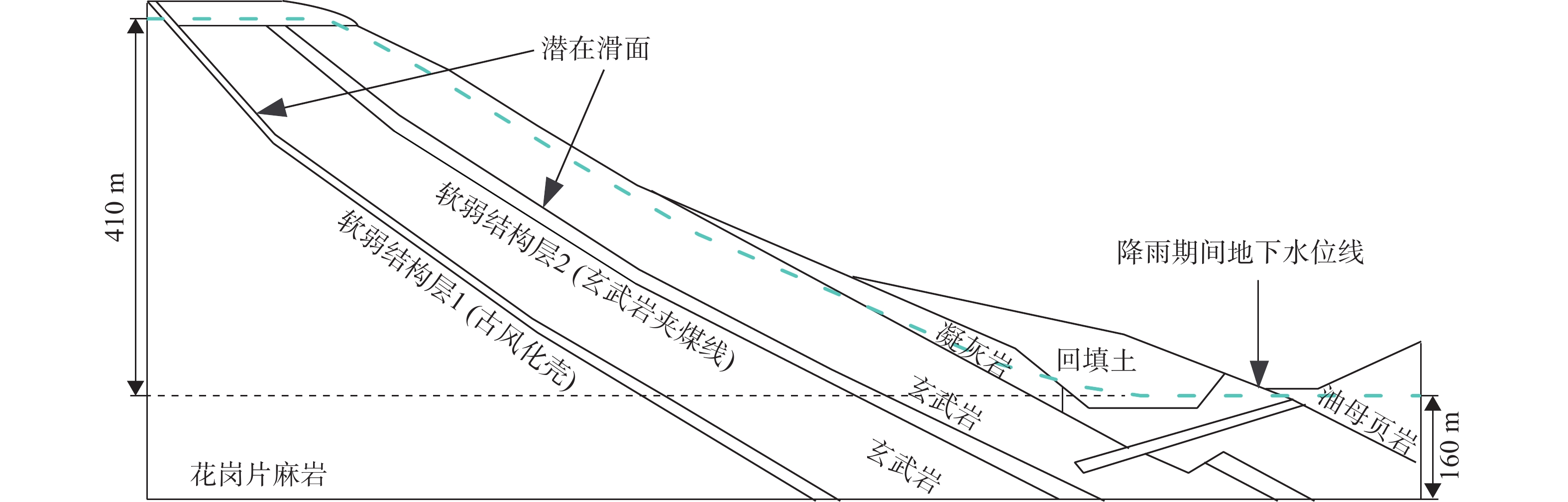
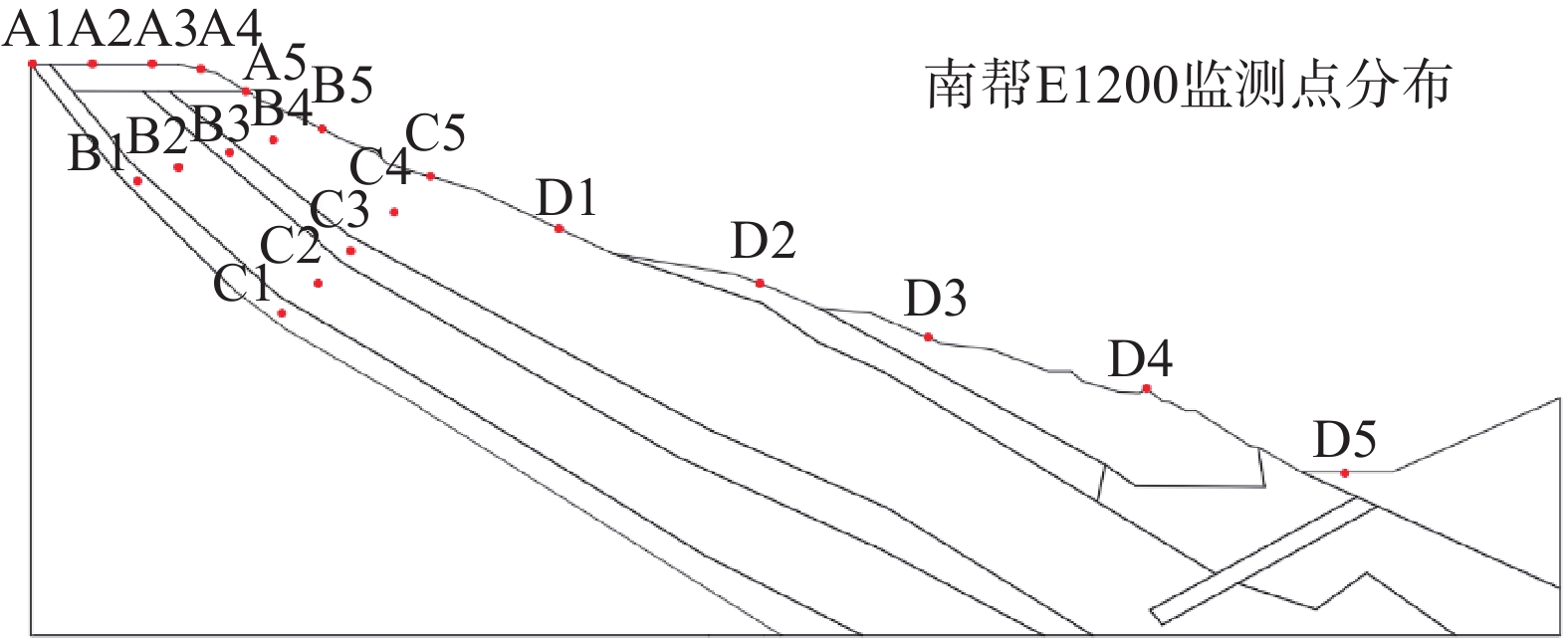
扎哈淖尔露天煤矿位于内蒙古自治区通辽市西北端,露天矿北帮于2020年5月出现明显的变形现象,边坡上部940水平及920水平出现明显裂隙,采场下部边坡850水平出现明显的大块岩体剪出现象,图1为扎哈淖尔露天矿的俯瞰图及现场图。沿边坡倾向方向选取研究剖面(图2),NO.1和NO.2为布置在剖面上的微变监测雷达监测特征点,露天矿北帮岩(土)层剖面如图3所示,北帮岩体整体倾向为逆倾、倾角5°~13°,边坡高度为234 m,坡度为16°,自上而下依次为第四系岩层、新近系和古近系岩层、泥岩、泥砂岩互层及煤层。经过现场勘探北帮850水平存在一层弱层,弱层厚度在1~2 m,钻孔岩芯(图4)显示弱层附近岩体较破碎。同时北帮边坡泥岩和第四系黏土中有出水点[20 − 21]。
2.2 基于层次分析-模糊综合评价模型的边坡稳定性评价
根据现场勘察及收集已有的矿山地质资料,确定边坡高度为234 m,坡度为16°,年平均降雨量为354.3 mm,边坡变形速率取目前NO.1点和NO.2点监测数据的平均值,根据现场监测取值为24 mm/d,对于折减系数的取值,基于安全的角度,边坡模糊综合评价中的折减系数选取数值计算所得的较低值(1.121),定量指标采用三角形隶属度函数确定(表5)。定性指标隶属度参考相关文献确定(表6)最后得到边坡模糊综合评价矩阵R,进一步利用层次分析法确定了扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡模糊评价指标的权重矩阵M,并进行一致性检验[22 − 24]。
表 5 北帮边坡定量指标隶属度Table 5. Membership degree of quantitative indexes for the northern slope稳定性 坡高隶属度 坡度隶属度 年均降雨量
隶属度地表变形速率
隶属度稳定 0 0.86 1 0 基本稳定 0.16 0.14 0 0.83 欠稳定 0.84 0 0 0.17 不稳定 0 0 0 0 表 6 北帮边坡定性指标隶属度Table 6. Membership degrees of qualitative indexes for the northern slope稳定性 岩性隶属度 结构类型
隶属度弱层隶属度 地面变形
隶属度地下水影响
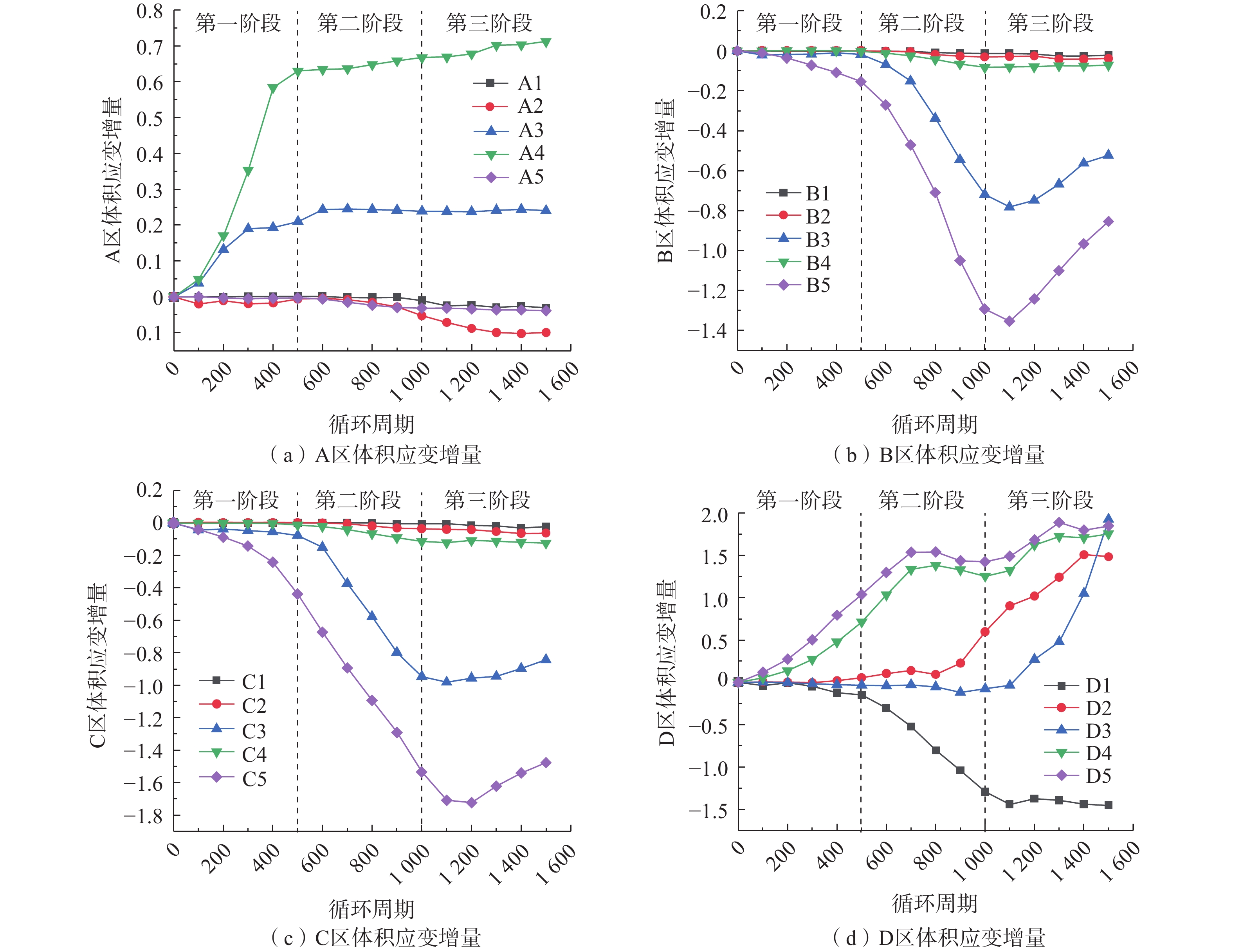
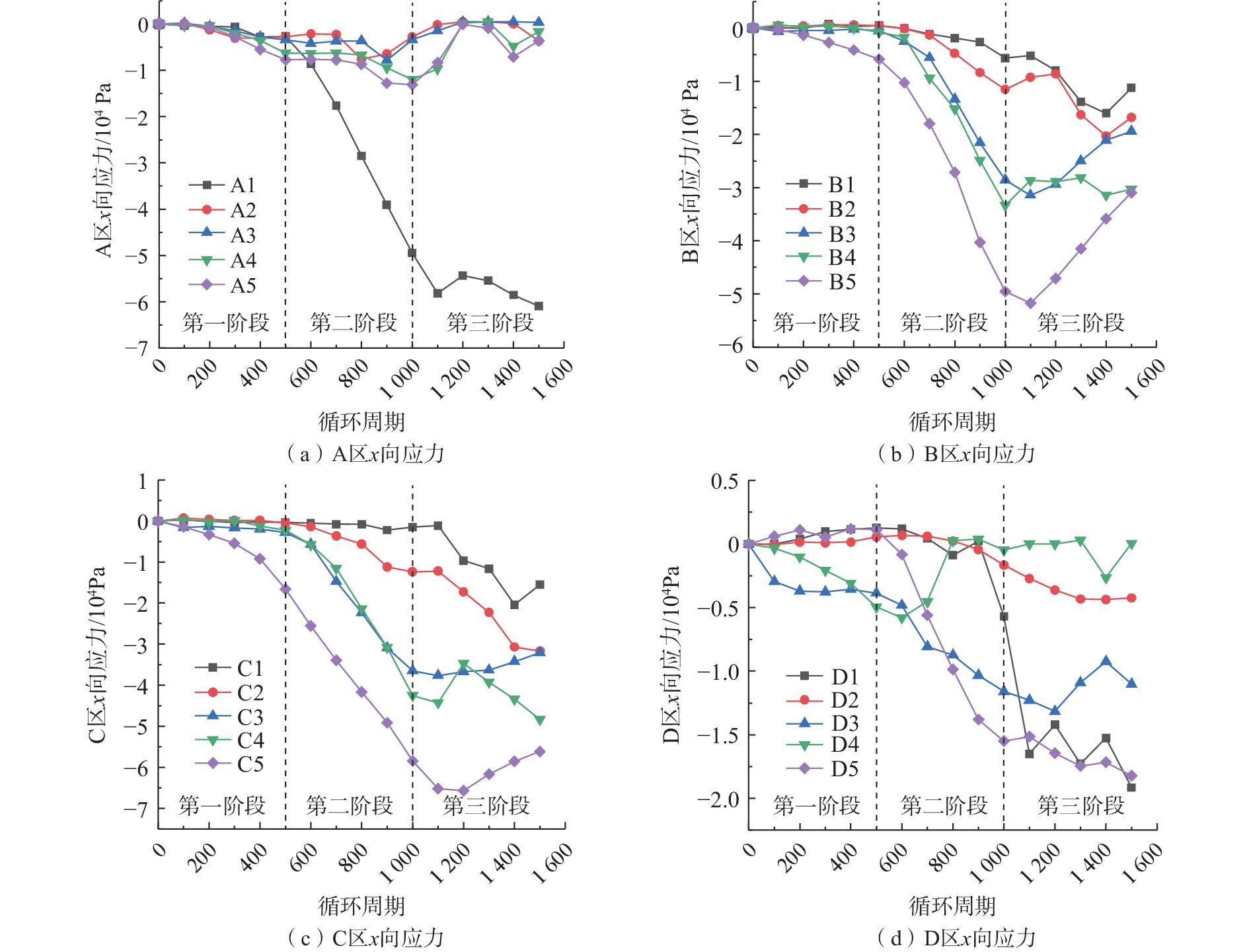
隶属度稳定 0 0.80 0.20 0 0.05 基本稳定 0.20 0.20 0.70 0 0.10 欠稳定 0.50 0 0.10 0.20 0.30 不稳定 0.30 0 0 0.80 0.55 边坡地表变形监测主要分析微变监测雷达系统于2020年4月26日—2021年6月14日NO.1点位和NO.2点位的微变监测雷达监测数据,将监测点的变形速率用不同的点线图来表示(图5),由图5可见边坡最初变形速率较快,后期变形速率逐渐趋于稳定。
由模糊综合评价法确定的模糊综合评价矩阵以及通过层次分析法确定的影响因子矩阵,确定扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡评价矩阵,北帮边坡为稳定状态、基本稳定状态、欠稳定状态、不稳定状态的隶属度分别为0.27545,0.43196,0.19304,0.09955,最大隶属度原则是得到边坡稳定性最常用的方法,但是如果第二大隶属度与最大隶属度值很接近的话,得到的评价结果准确度降低,基于此,首先对隶属度矩阵进行有效性检验。最大隶属度有效性验证公式如下[25]:
(4) 式中:
经过计算,扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型所得的隶属度矩阵有效度为0.65521,属于比较有效,说明评价结果是稳定的,根据隶属度最大原则判定北帮边坡属于基本稳定状态。
2.3 模型检验
本研究通过数值模拟对层次分析-模糊综合评价模型得到的北帮边坡稳定性结果进行检验,根据北帮研究区剖面(图2)建立数值计算模型(图6),模型计算选取的坐标系为边坡临空面方向为X正方向,竖直向上为Z正方向。模型的左右边界(南北)、前后边界(东西)和底部边界分别以水平和垂直方向的位移约束,顶面设定为自由面,采用摩尔-库仑弹塑性本构模型进行求解,岩土体力学参数采用Hoek-Brown岩体强度方法并结合现场研究报告综合确定岩土体力学参数如表7所示[26 − 27]。
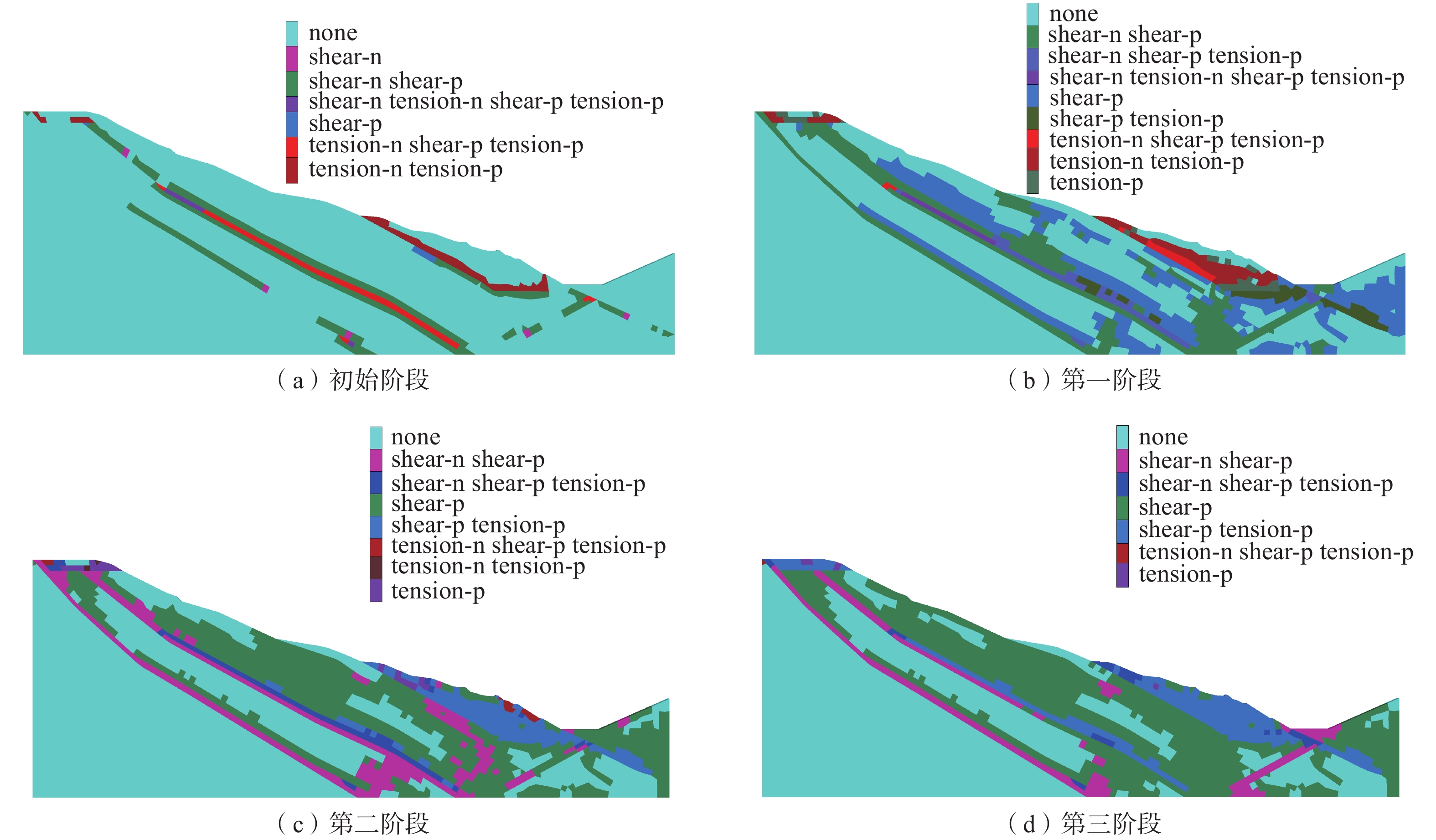
表 7 岩层物理力学参数表Table 7. Physico-mechanical parameters of strata岩层 重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 排弃物料 17.70 10.0 20.0 第四系地层 17.90 17.0 11.7 弱层 17.90 8.0 5.7 新近系和古近系地层 17.90 14.0 13.0 泥岩层 20.20 33.7 15.4 砂岩层 24.40 40.0 28.0 泥砂岩互层 23.45 35.0 24.6 煤层 12.70 24.5 21.0 采用人为定义边坡折减强度上下限的方法确定边坡的折减系数,首先初步确定边坡折减系数的范围,然后以0.001为一个梯度进行折减计算,通常数值模拟对岩土体强度的折减是针对整个边坡区域进行折减,不能计算边坡内部多级滑动面。而对于多台阶边坡而言,每级台阶的折减系数和潜在滑移面都是值得关注的。因此在模拟过程中只折减850水平以上岩层和煤层的黏聚力和摩擦角[28 − 29]。模拟结果如图7所示,850水平之上形成潜在滑坡面,边坡剪切变形相对集中于局部化变形区域内,而区域外的变形相当于卸载后的刚体运动,潜在滑坡体将沿该滑动面滑动,滑动面两侧沿滑动面方向的位移相差明显,存在较大的变形梯度。通过监测边坡表面各测点位移可发现随着监测点高程增大其位移量减小,边坡内部形成潜在滑坡面,滑移面安全系数为1.121。
基于强度折减法得到北帮潜在滑移面安全系数分别为1.121(850水平以上),根据相关规范边坡稳定性划分表(表8)[12],北帮850水平上部边坡属于基本稳定边坡,层次分析-模糊综合评价模型得到的边坡稳定性状态与数值模拟强度折减法得到的边坡稳定性状态相一致,验证了模型的准确性。
表 8 边坡稳定性状态划分Table 8. Classification of slope stability states边坡安全系数 F<1.00 1.00≤F<1.05 1.05≤F<1.20 F≥1.20 边坡稳定状态 不稳定 欠稳定 基本稳定 稳定 3. 结论
(1)在监测数据分析和数值模拟的基础上,建立了考虑监测信息的边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型,该模型充分融合了边坡几何形态、边坡地质信息、气象水文信息、现场监测信息等多种信息。
(2)北帮边坡稳定性状态为稳定、基本稳定、欠稳定、不稳定,隶属度分别为0.27545,0.43196,0.19304,0.09955,根据隶属度最大原则得出北帮边坡目前处于基本稳定状态。
(3)通过数值模拟求解得北帮边坡滑移面安全系数为1.121,属于基本稳定边坡,强度折减法结果与所建立的边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型得到的边坡稳定性状态一致,验证了模型的有效性。
-
地层岩性 密度
/(kg·m−3)弹性模量
/GPa泊松比 黏聚力
/MPa抗拉强度
/MPa内摩擦角/(°) 渗透系数
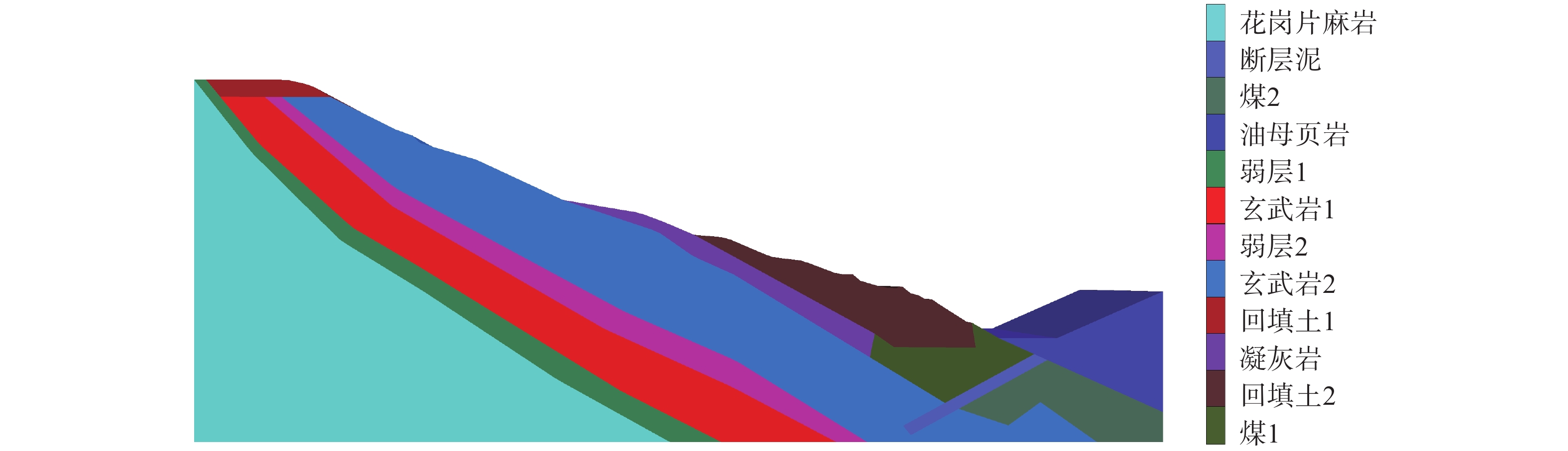
/(m2·Pa−1·s−1)凝灰岩 2590 10 0.24 3 2 45 9E-10 凝灰岩(弱化) 2590 1 0.24 0.3 0.2 40 9E-10 玄武岩 2800 25 0.23 3 2 40 9E-10 玄武岩(弱化) 2800 2.5 0.23 0.3 0.2 35 9E-10 煤 1400 1.2 0.24 0.45 0.15 30 9E-10 煤(弱化) 1400 1.2 0.24 0.45 0.24 35 3E-9 弱层 2100 15 0.24 2.5 1.75 48 9E-10 弱层(弱化) 2100 0.018 0.4 0.003 0.01 10 9E-10 花岗片麻岩 2800 35 0.22 4 3 45 8E-9 回填土 1860 0.27 0.3 0.2 0.1 25 9E-10 回填土(弱化) 1860 0.027 0.3 0.02 0.01 20 9E-10 断层泥 1800 0.01 0.4 0.18 0.2 7 3E-9 油页岩 2550 5 0.22 0.15 0.35 35 9E-10 表 2 边坡防治方案稳定性评价结果
Table 2 Stability evaluation results of slope control scheme
工况 防治方案剖面图 边坡总位移变化云图 安全系数 稳定性分析 现状 

1.22 稳定 降雨 

0.71 不稳定 回填1/10
坡高

0.89 不稳定 回填1/5
坡高

0.96 不稳定 回填1/4
坡高

1.02 欠稳定 回填1/3
坡高

1.08 欠稳定 回填1/2
坡高

1.15 稳定 回填3/5
坡高

1.21 稳定 回填2/3
坡高

1.42 稳定 回填3/4
坡高

1.36 稳定 -
[1] 李安洪, 周德培, 冯君. 顺层岩质边坡稳定性分析与支挡防护设计[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2011 LI Anhong, ZHOU Depei, FENG Jun. Stability analysis and retaining protection design of bedding rock slope[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2011. (in Chinese)
[2] 蒋先念,张晨阳. 三峡库区典型顺斜向岩质滑坡变形破坏特征及失稳机制分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):36 − 42. [JIANG Xiannian,ZHANG Chenyang. Deformation characteristics and failure mechanism of large-scale obliquely dip rock landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):36 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIANG Xiannian, ZHANG Chenyang. Deformation characteristics and failure mechanism of large-scale obliquely dip rock landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(2): 36-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 李守定,李晓,吴疆,等. 大型基岩顺层滑坡滑带形成演化过程与模式[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(12):2473 − 2480. [LI Shouding,LI Xiao,WU Jiang,et al. Evolution process and pattern of sliding zone in large consequent bedding rock landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(12):2473 − 2480. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.12.012 LI Shouding, LI Xiao, WU Jiang, et al. Evolution process and pattern of sliding zone in large consequent bedding rock landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(12): 2473-2480. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.12.012
[4] 张璟,陈文胜,蒋茂林. 等厚顺层岩质边坡稳定性的模型试验研究及数值验证[J]. 北方交通,2020,378(10):40 − 44. [ZHANG Jing,CHEN Wensheng,JIANG Maolin. Model test study and numerical verification of stability of bedding rock slope with equal thickness[J]. Northern Communications,2020,378(10):40 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Jing, CHEN Wensheng, JIANG Maolin. Model test study and numerical verification of stability of bedding rock slope with equal thickness[J]. Northern Communications, 2020, 378(10): 40-44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 贺小黑,彭鑫,谭建民,等. 地下水渗流对崩坡积滑坡稳定性和变形的影响—以湖南安化春风滑坡群为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):96 − 103. [HE Xiaohei,PENG Xin,TAN Jianmin,et al. Influence of groundwater seepage on stability and deformation of colluvial deposit landslide:Taking Chunfeng landslide group in Anhua County of Hunan Province as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE Xiaohei, PENG Xin, TAN Jianmin, et al. Influence of groundwater seepage on stability and deformation of colluvial deposit landslide: taking Chunfeng landslide group in Anhua County of Hunan Province as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 96-103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 陈林万,张晓超,裴向军,等. 降雨诱发直线型黄土填方边坡失稳模型试验[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):151 − 160. [CHEN Linwan,ZHANG Xiaochao,PEI Xiangjun,et al. Model test of the linear loess fill slope instability induced by rainfall[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):151 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202010041 CHEN Linwan, ZHANG Xiaochao, PEI Xiangjun, et al. Model test of the linear loess fill slope instability induced by rainfall[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(6): 151-160. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202010041
[7] 王智德,夏元友,夏国邦,等. 顺层岩质边坡稳定性极限分析上限法[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(2):576 − 583. [WANG Zhide,XIA Yuanyou,XIA Guobang,et al. Upper bound limit analysis method for stability analysis of bedding rock slopes[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(2):576 − 583. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Zhide, XIA Yuanyou, XIA Guobang, et al. Upper bound limit analysis method for stability analysis of bedding rock slopes[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(2): 576-583. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 冯君,周德培,李安洪. 顺层岩质边坡开挖稳定性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(9):1474 − 1478. [FENG Jun,ZHOU Depei,LI Anhong. Research on stability of rock bedded slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(9):1474 − 1478. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.09.003 FENG Jun, ZHOU Depei, LI Anhong. Research on stability of rock bedded slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(9): 1474-1478. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.09.003
[9] 陈从新,黄平路,卢增木. 岩层倾角影响顺层岩石边坡稳定性的模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(3):476 − 481. [CHEN Congxin,HUANG Pinglu,LU Zengmu. Study on correlation between stability of consequent rock slope and obliquity of rock layer by simulation experiment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2007,28(3):476 − 481. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.03.009 CHEN Congxin, HUANG Pinglu, LU Zengmu. Study on correlation between stability of consequent rock slope and obliquity of rock layer by simulation experiment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(3): 476-481. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.03.009
[10] HART M W. Bedding-parallel shear zones as landslide mechanisms in horizontal sedimentary rocks[J]. Environmental and Engineering Geoscience,2000,6(2):95 − 113. DOI: 10.2113/gseegeosci.6.2.95
[11] 舒继森,唐震,才庆祥. 水力学作用下顺层岩质边坡稳定性研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2012,41(4):521 − 525. [SHU Jisen,TANG Zhen,CAI Qingxiang. Research on stability of bedding rock slopes under hydraulic pressure[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2012,41(4):521 − 525. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHU Jisen, TANG Zhen, CAI Qingxiang. Research on stability of bedding rock slopes under hydraulic pressure[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2012, 41(4): 521-525. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 魏刚,殷志强,罗银飞,等. 黄河上游康杨滑坡堆积体特征及形成机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):1 − 8. [WEI Gang,YIN Zhiqiang,LUO Yinfei,et al. Analysis on the accumulation deposits characteristics and formation mechanism of Kangyang landslide in the upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.02-01 WEI Gang, YIN Zhiqiang, LUO Yinfei, et al. Analysis on the accumulation deposits characteristics and formation mechanism of Kangyang landslide in the upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.02-01
[13] HOEK E, BRAY J. Rock slope engineering, 3rd ed[M]. London: [s.n.], 1981.
[14] 赵磊,付昱凯,陈春利,等. 青川浅层滑坡降雨入渗及稳定性研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2022,36(1):111 − 119. [ZHAO Lei,FU Yukai,CHEN Chunli,et al. Study on rainfall infiltration and stability of Qingchuan shallow landslide[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2022,36(1):111 − 119. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2022.015 ZHAO Lei, FU Yukai, CHEN Chunli, et al. Study on rainfall infiltration and stability of Qingchuan shallow landslide[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2022, 36(1): 111-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2022.015
[15] 聂永鹏,倪万魁,刘魁,等. 陕西延安某老滑坡场地上建筑物破坏机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(2):43 − 50. [NIE Yongpeng,NI Wankui,LIU Kui,et al. Damage mechanism of buildings on an old landslide in Yan’an City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(2):43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.02.06 NIE Yongpeng, NI Wankui, LIU Kui, et al. Damage mechanism of buildings on an old landslide in Yan'an City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(2): 43-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.02.06
[16] 田辽西,赵玉苹,赵伟. 降雨入渗对某滑坡地下水渗流及滑坡稳定性影响[J]. 科学技术创新,2022(20):125 − 128. [TIAN Liaoxi,ZHAO Yuping,ZHAO Wei. Influence of rainfall infiltration on groundwater seepage and landslide stability of a landslide[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation,2022(20):125 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2022.20.032 TIAN Liaoxi, ZHAO Yuping, ZHAO Wei. Influence of rainfall infiltration on groundwater seepage and landslide stability of a landslide[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation, 2022(20): 125-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2022.20.032
[17] 刘艳辉,刘丽楠. 基于诱发机理的降雨型滑坡预警研究—以花岗岩风化壳二元结构斜坡为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(4):542 − 549. [LIU Yanhui,LIU Linan. Rainfall-induced mechanism based early warning model for slopes of dualistic layers in weathered granitic area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(4):542 − 549. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Yanhui, LIU Linan. Rainfall-induced mechanism based early warning model for slopes of dualistic layers in weathered granitic area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(4): 542-549. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] RICHARDS L A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums[J]. Physics,1931,1(5):318 − 333. DOI: 10.1063/1.1745010
[19] FREDLUND D G,XING A Q. Equations for the soil-water characteristic curve[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1994,31(4):521 − 532. DOI: 10.1139/t94-061
[20] 黄润秋,徐则民,许模. 地下水的致灾效应及异常地下水流诱发地质灾害[J]. 地球与环境,2005,33(3):1 − 9. [HUANG Runqiu,XU Zemin,XU Mo. Hazardous effects of underground water and extraordinary water flow-induced geohazards[J]. Geology-geochemistry,2005,33(3):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2005.03.001 HUANG Runqiu, XU Zemin, XU Mo. Hazardous effects of underground water and extraordinary water flow-induced geohazards[J]. Geology-geochemistry, 2005, 33(3): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2005.03.001
[21] 郭子钰,刘向峰,王来贵,等. 抚顺西露天矿开挖作用下边坡变形破坏滑动规律研究[J]. 金属矿山,2021(12):190 − 199. [GUO Ziyu,LIU Xiangfeng,WANG Laigui,et al. Study on the slope deformation and failure sliding law under the excavation of Fushun west open-pit mine[J]. Metal Mine,2021(12):190 − 199. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO Ziyu, LIU Xiangfeng, WANG Laigui, et al. Study on the slope deformation and failure sliding law under the excavation of Fushun west open-pit mine[J]. Metal Mine, 2021(12): 190-199. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 郭子钰. 露天煤矿边坡变形破坏滑动全过程研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2021 GUO Ziyu. Study on the whole process of slope deformation, failure and sliding in open-pit coal mine[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 缪海宾. 抚顺西露天矿高陡边坡蠕变-大变形综合预警及防治技术研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2020 MIAO Haibin. Research on comprehensive early warning and prevention technology of creep-large deformation in high and steep slope of Fushun west open-pit mine[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 崔原. 抚顺西露天矿南帮滑坡地质特征与机理分析[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018 CUI Yuan. Geological characteristics and mechanism analysis of south slope landslide in Fushun west open pit mine[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 李超. 抚顺西露天矿南帮边坡稳定性分析[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2013 LI Chao. Stability analysis of south slope of Fushun west open pit mine[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 郭富赟,周小龙,火飞飙,等. 舟曲断裂带滑坡灾害效应与防治对策研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):80 − 89. [GUO Fuyun,ZHOU Xiaolong,HUO Feibiao,et al. Study on landslide disaster effect and prevention countermeasures in Zhouqu fault zone[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):80 − 89. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO Fuyun, ZHOU Xiaolong, HUO Feibiao, et al. Study on landslide disaster effect and prevention countermeasures in Zhouqu fault zone[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(6): 80-89. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 马海涛,于正兴,蓝永建. 冻融作用对露天矿山边坡稳定性的影响分析研究. 矿产勘查. 2024(S1): 56-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李刚. 基于可变模糊评价模型的黄土边坡稳定性研究. 公路. 2023(08): 75-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 孙杰龙,王弘起,李盛斌,李大卫,邱明明. 冻融作用下高填方黄土抗剪强度劣化特性分析. 岩土工程技术. 2023(05): 609-613 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 安宁,万宝峰,侯云龙,姜钰泉. 冻融作用对中俄东线天然气管道工程过境段边坡影响. 科学技术与工程. 2023(33): 14211-14219 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 黄文强. 冻融循环作用下黄土边坡的浅层滑动探讨. 科学技术与工程. 2022(04): 1558-1565 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨鑫光,李希来,王克宙,李志炜,马盼盼. 煤矸石山生态恢复的主要路径. 生态学报. 2022(19): 7740-7751 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王延寿. 农业灌溉作用下黄土边坡失稳引起耕地流失分析. 中国农学通报. 2022(36): 88-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李广,张明礼,叶伟林,王得楷,马昭,安亚鹏. 甘肃黑方台坡面冻融特征及冻结滞水效应分析. 干旱区资源与环境. 2021(06): 117-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 佘长超,陈涛,韩流,宋仁忠,韩兴,闫石. 冻融循环下排土场软岩边坡抗剪特性及时效性研究. 煤炭科学技术. 2021(10): 50-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 闫茂华,魏云杰,李亚民,刘明学,王文沛,王俊豪,曹峰. 云南德钦日因卡滑坡孕灾背景及形成机理. 地质通报. 2020(12): 1971-1980 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 姜成潼,王亚军,李元松,司马丹琪,何泉. 基于多判据的“三高”地区公路边坡稳定性的综合评价. 武汉工程大学学报. 2018(04): 419-424 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 边晓亚,白俊龙,张军. 冻融对黄土边坡稳定性的影响. 武汉工程大学学报. 2018(04): 425-429 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 许健,郑翔,张辉. 黄土地区边坡冻融剥落病害机理及稳定性分析. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2018(04): 477-484 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 黄明,张瑾璇,靳贵晓,蒋宇静,邱继业,龚豪,郭珅. 残积土MICP灌浆结石体冻融损伤的核磁共振特性试验研究. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2018(12): 2846-2855 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 陈静茹,李宝平,杨帆,王元戎. 冻融循环条件下重塑黄土水分迁移及其对力学性质影响. 科学技术与工程. 2018(34): 226-230 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 魏云杰,邵海,朱赛楠,黄喆,王文沛,石爱军,庄茂国. 新疆伊宁县皮里青河滑坡成灾机理分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2017(04): 22-26 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(16)




 下载:
下载:

























 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS