Deformation characteristics and engineering effect evaluation of a sandstone bedding excavation high slope treatment project during construction
-
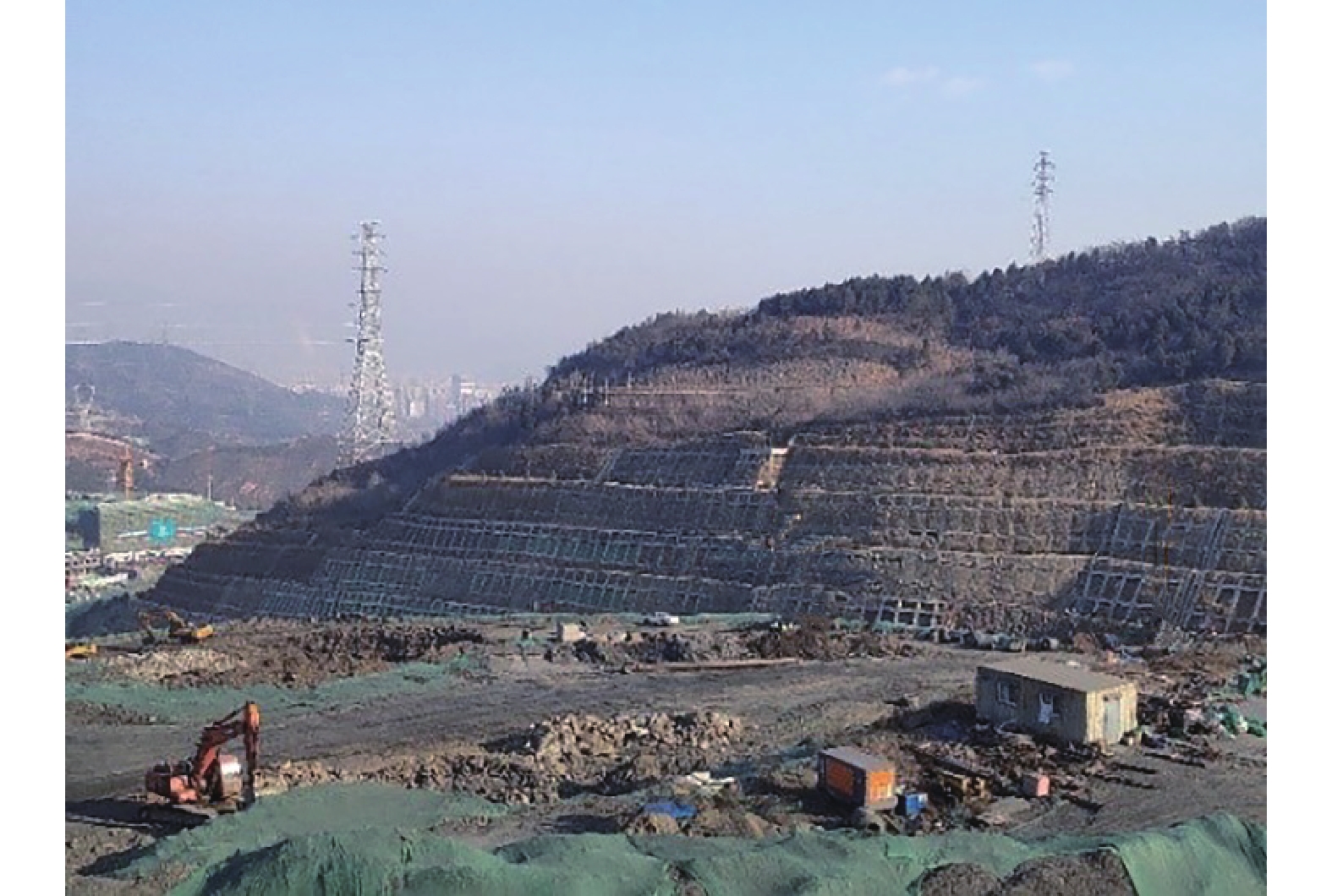
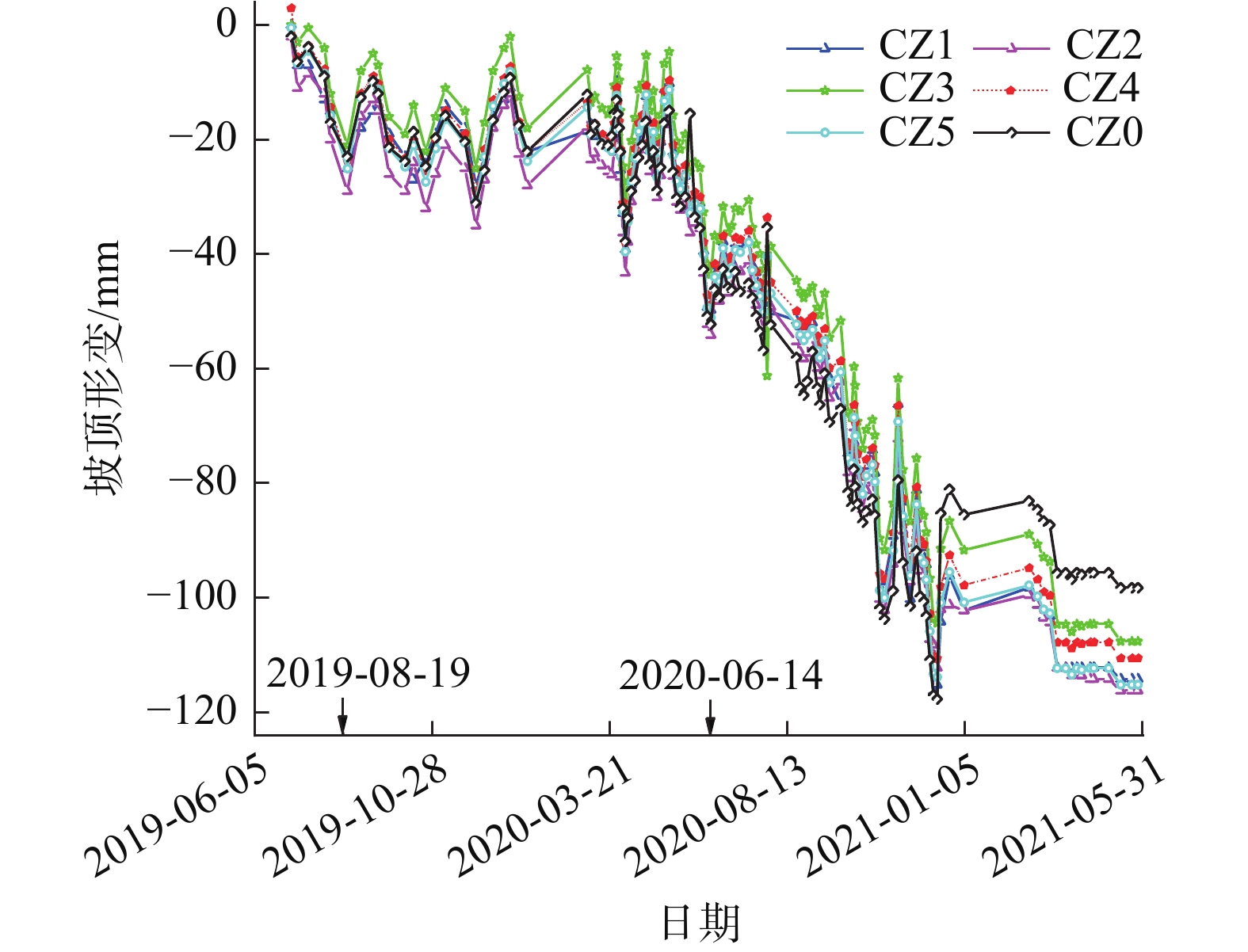
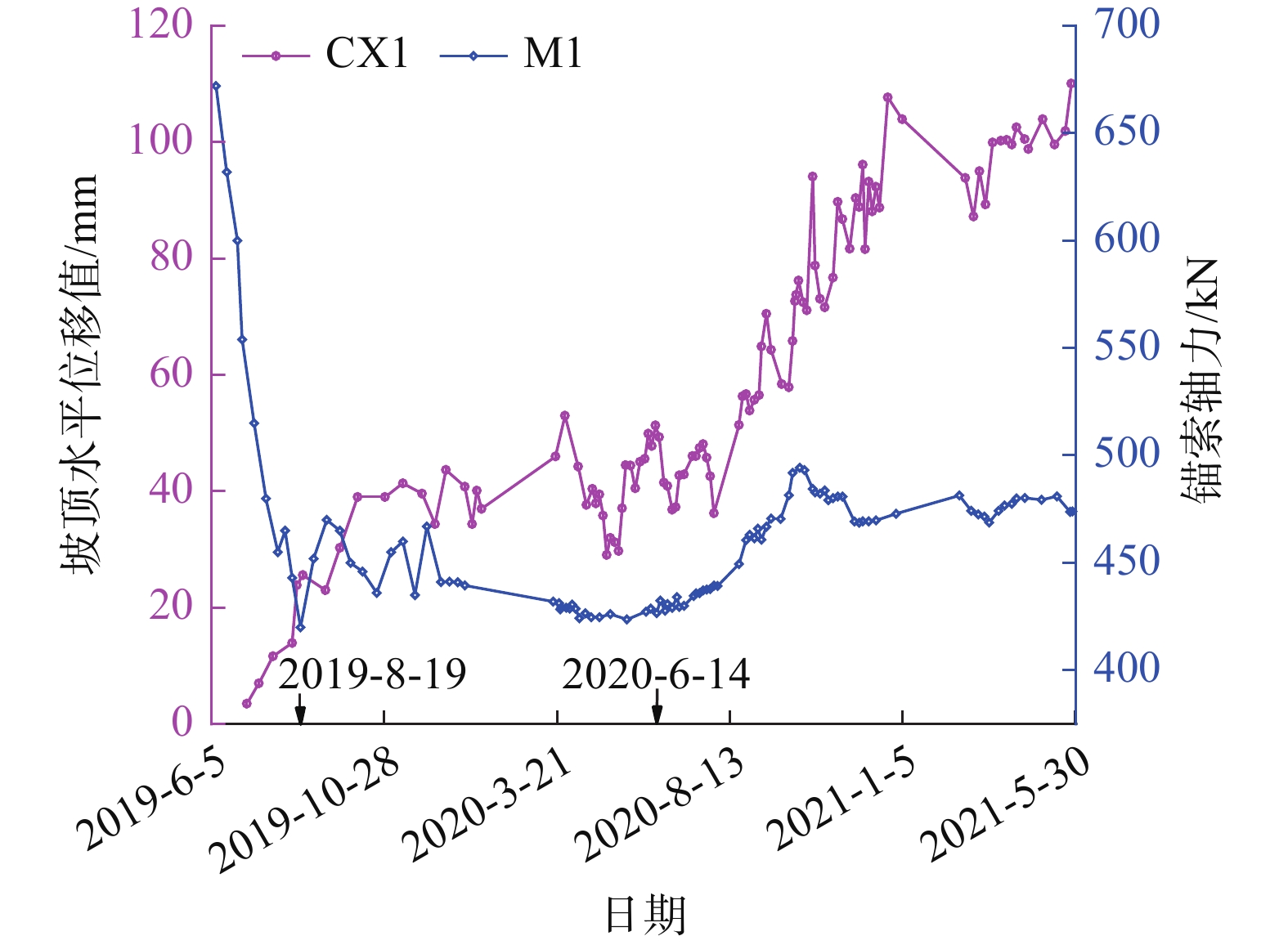
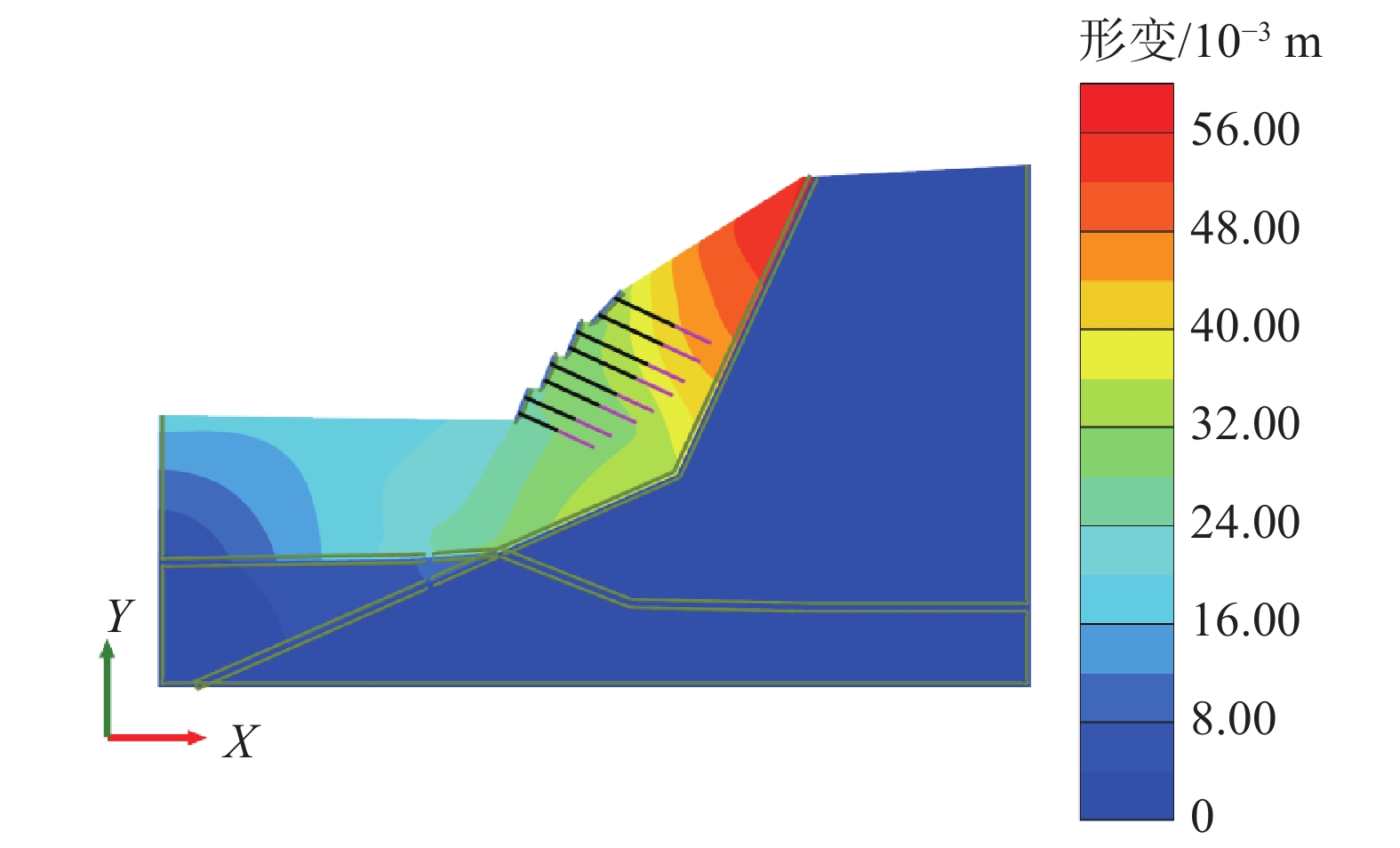
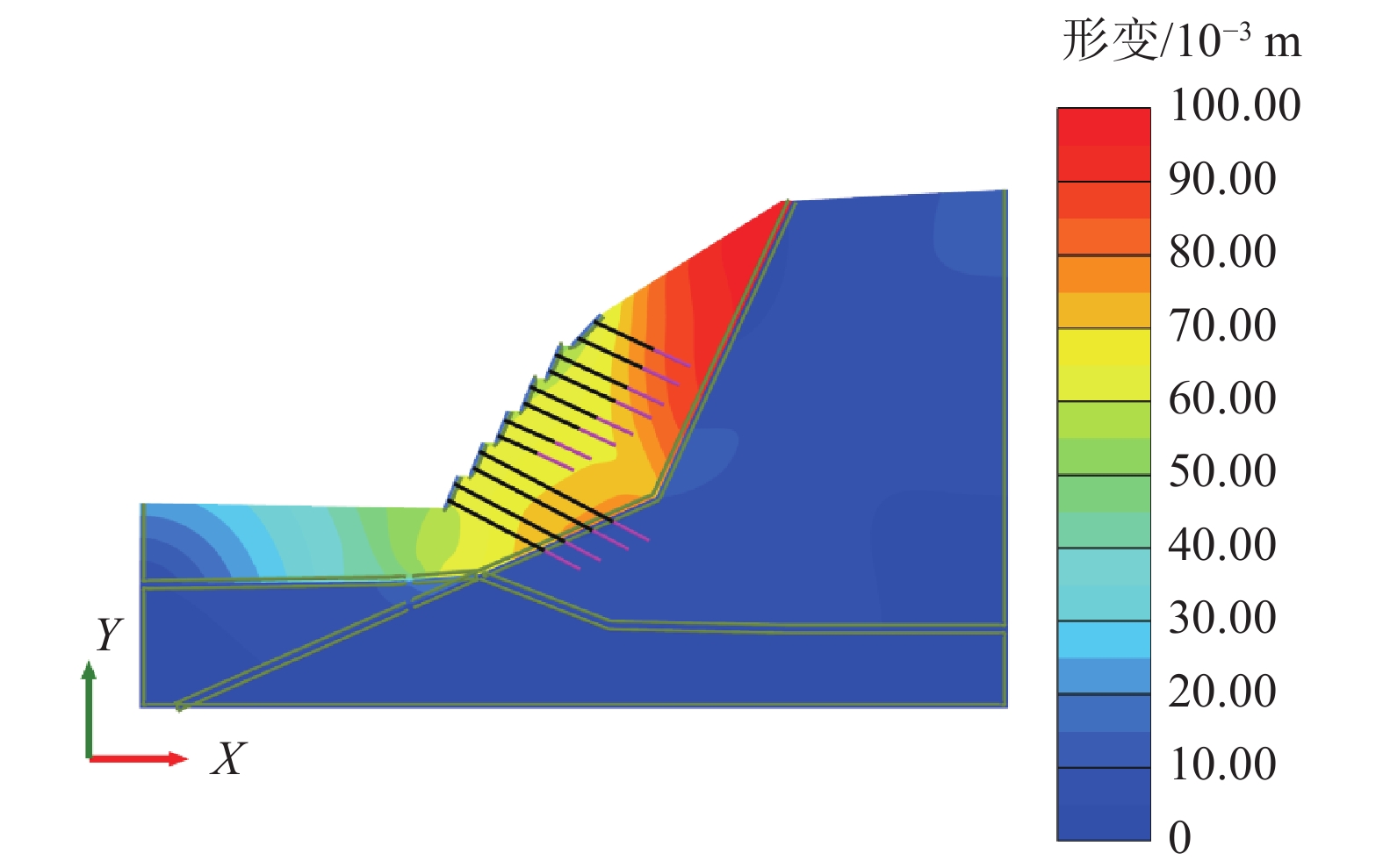
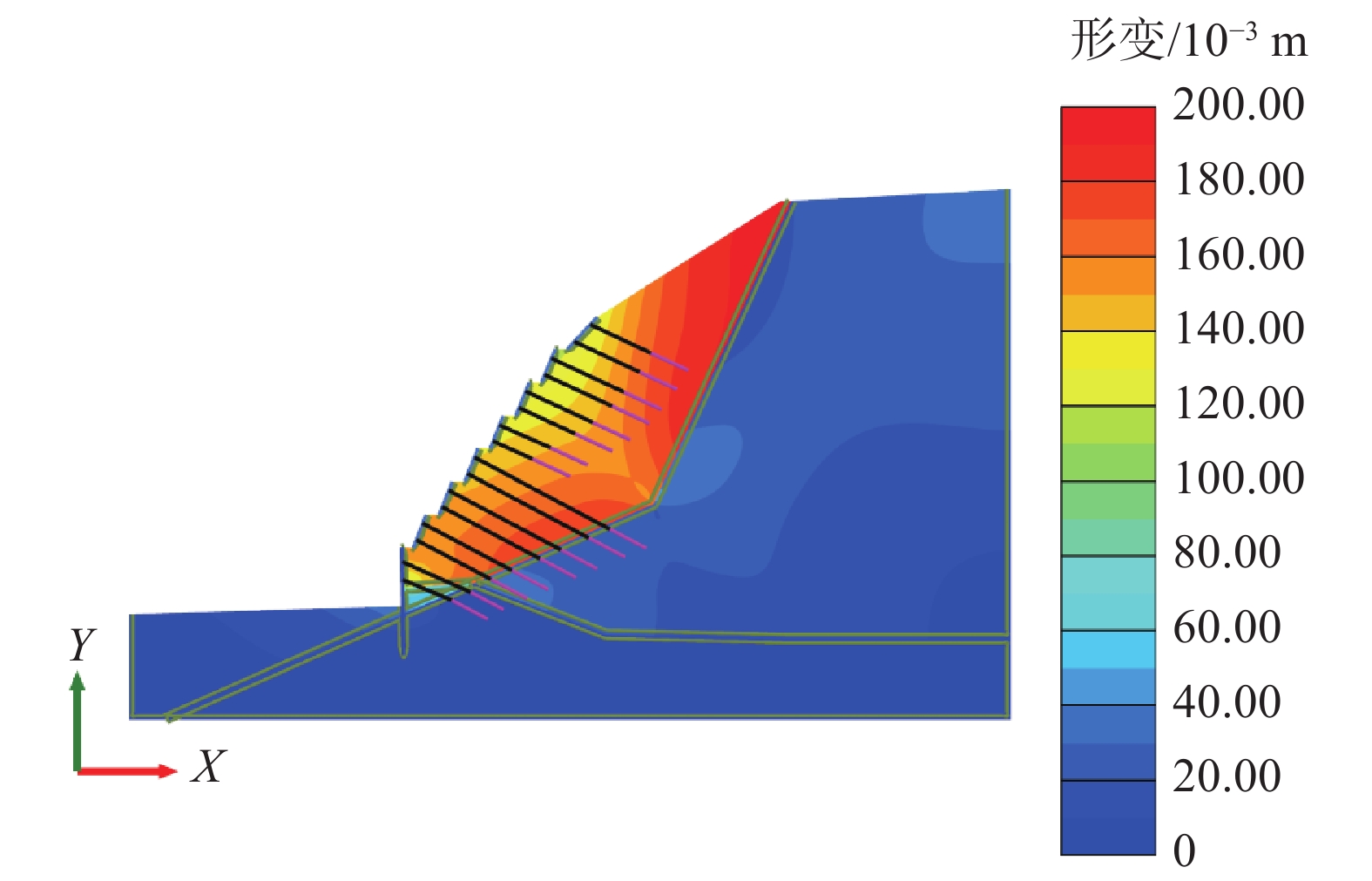
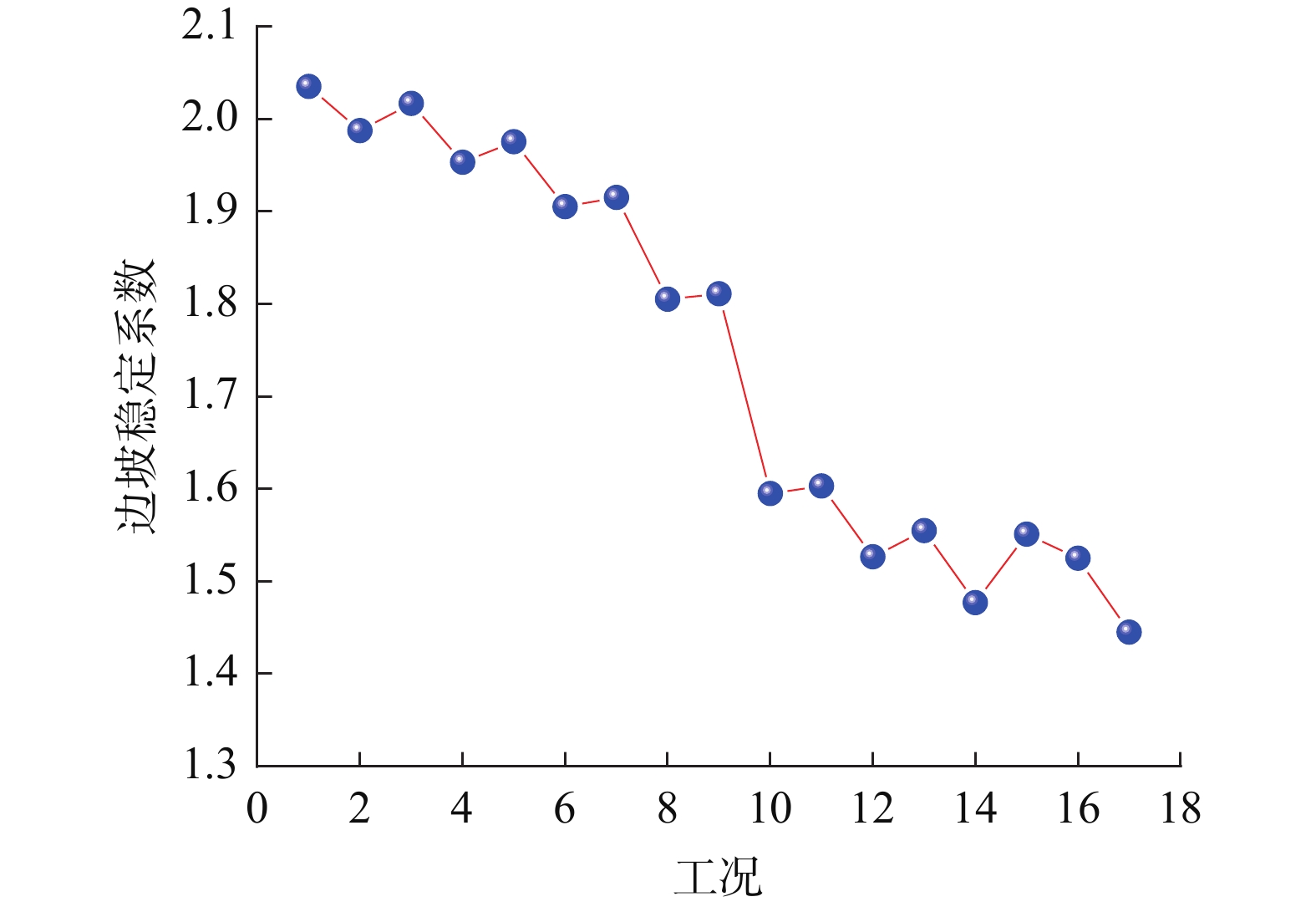
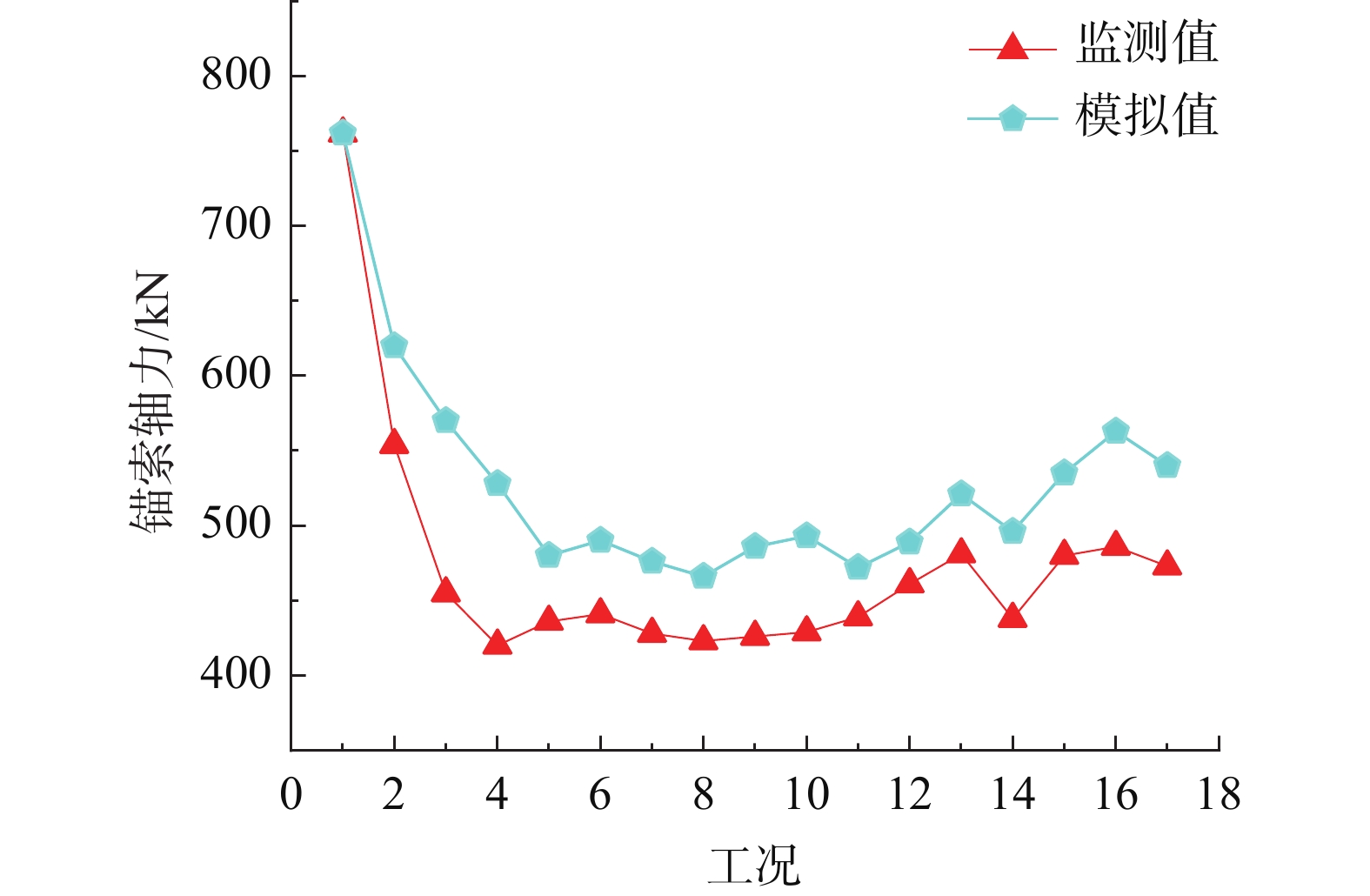
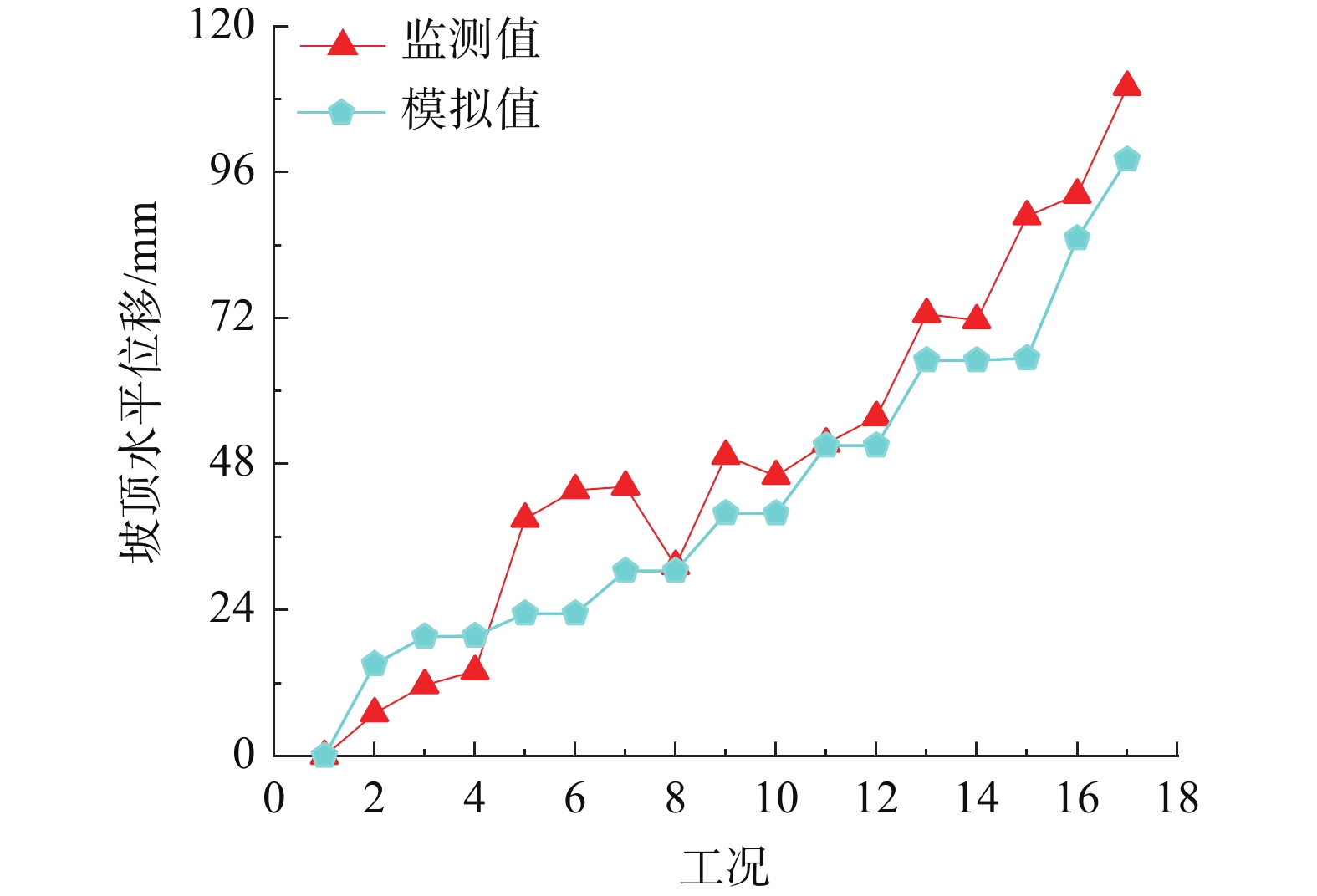
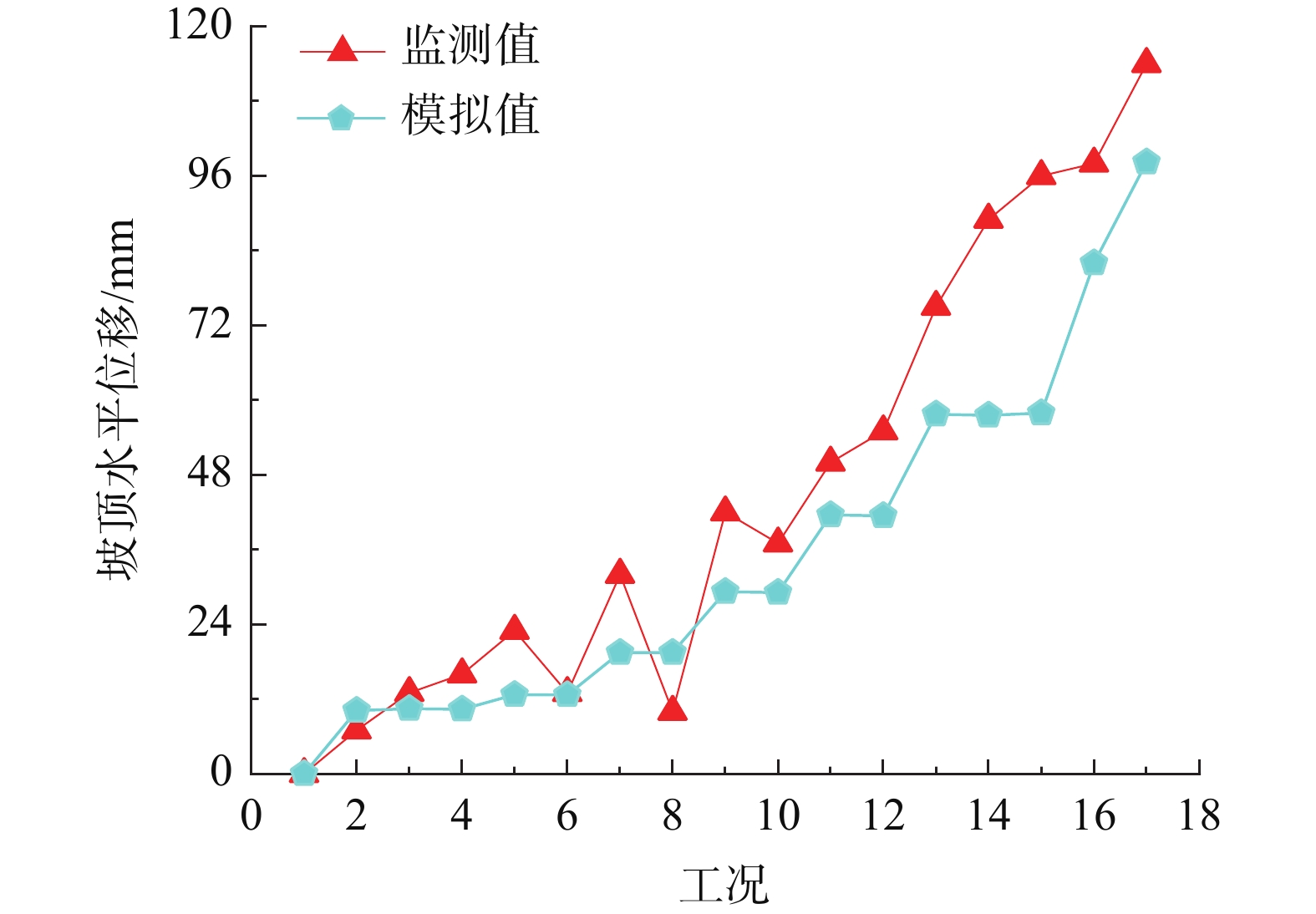
摘要: 为了研究砂岩顺层挖方高边坡支护工程施工期间及施工后的边坡变形规律和治理工程效果,文章依托北京某边坡支护项目,对边坡在施工过程中的锚索轴力及边坡位移进行监测分析,结果表明:锚索轴力变化主要分为加速损失阶段、波动阶段以及持续稳定趋变阶段;锚索轴力变化可以很好地反映坡体内力的变化情况;坡顶水平位移和竖向沉降的变化,可以反映边坡深层位移的变化规律和边坡的稳定性;框架预应力锚索抗滑桩组合支护体系应用于砂岩顺层挖方高边坡的支护时,具有较好的支护效果。采用有限元分析软件,模拟该砂岩顺层挖方高边坡的开挖支护过程发现:随着边坡的开挖,坡体位移沿着软弱滑动面向坡角发展,边坡稳定性降低。将监测结果与模拟结果对比分析,发现二者的变化趋势基本一致,证明了该边坡的支护体系能有效地控制边坡的变形。研究成果能为以后类似边坡的设计施工提供参考。Abstract: In order to study the slope deformation law during and after the construction of the sandstone bed-cut high slope support project and the effect of the treatment project, this paper relies on a slope support project in Beijing to analyze the axial force of the anchor cable and the slope during the construction process. The slope displacement is monitored and analyzed, and the results show that the change of the axial force of the anchor cable is mainly divided into the acceleration loss stage, the fluctuation stage and the continuous stable trend stage; the change of the axial force of the anchor cable can well reflect the change of the internal force of the slope; the change of horizontal displacement and vertical settlement can reflect the change law of the deep displacement of the slope and the stability of the slope, has a better support effect. The finite element analysis software was used to simulate the excavation and support process of the sandstone-layered high slope. It was found that with the excavation of the slope, the displacement of the slope developed along the slope angle of the weak sliding surface, and the stability of the slope decreased. The monitoring results and the simulation results are compared and analyzed, and it is found that the change trends of the two are basically the same, which proves that the slope support system can effectively control the deformation of the slope. The research results can provide reference for the design and construction of similar slopes in the future.
-
-
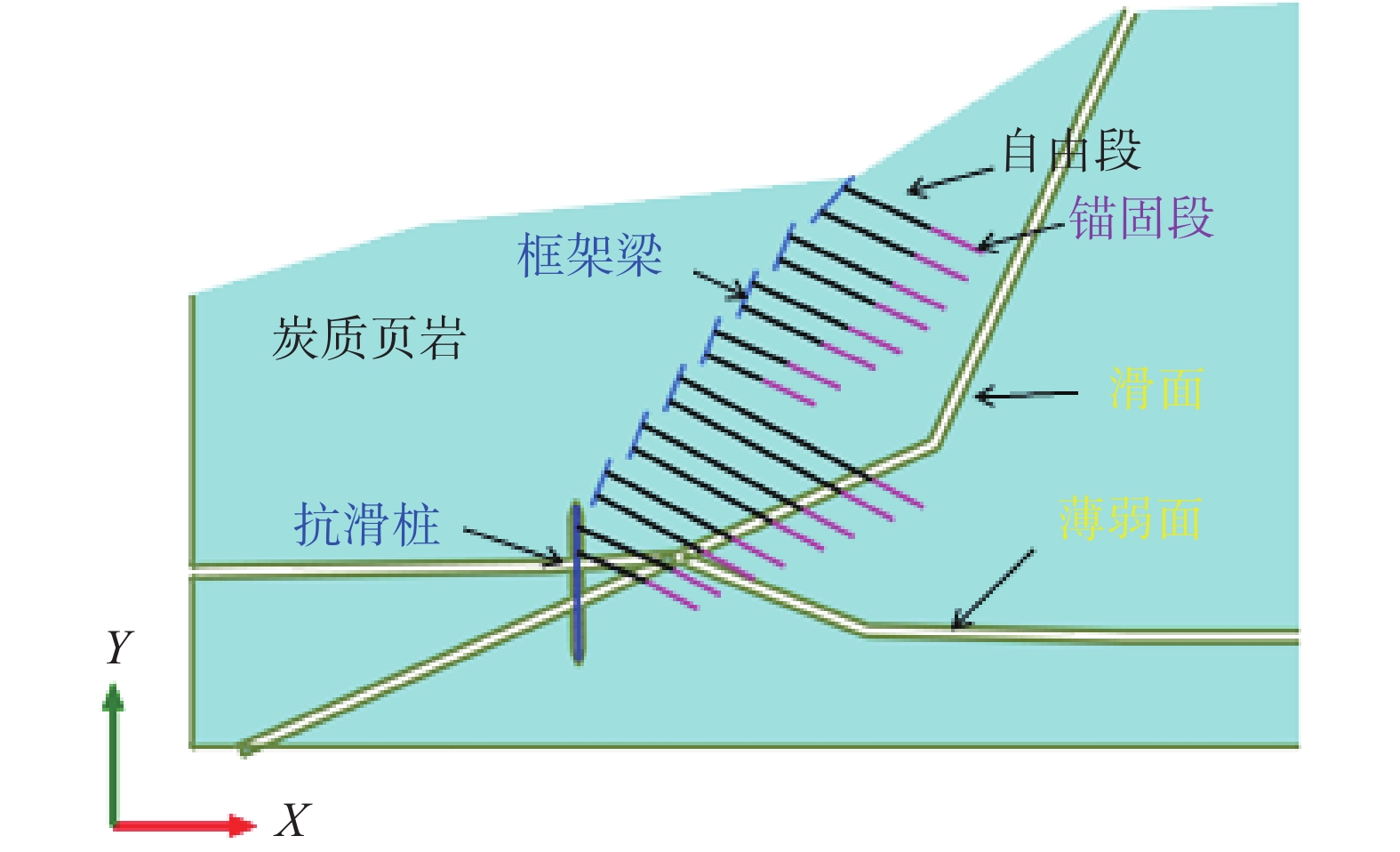
表 1 支护参数及说明
Table 1 Support parameters and description
坡级 锚索支护参数 八级坡 6Φ15.2,l=26 m,l锚=10 m,设计轴力672 kN 七级坡 6Φ15.2,l=28 m,l锚=10 m,设计轴力672 kN 六级坡 6Φ15.2, l=27 m,l锚=10 m,设计轴力672 kN 五级坡 6Φ15.2,l=22 m,l锚=10 m,设计轴力672 kN 四级坡 8Φ15.2,l=47.5 m, l锚=10 m,设计轴力672 kN 三级坡 8Φ15.2,l=34.5 m,l锚=10 m,设计轴力672 kN 二级坡 8Φ15.2,l=31 m,l锚=10 m,设计轴力672 kN 抗滑桩 8Φ15.2,l=41 m,l锚=10 m,设计轴力672 kN 表 2 场地土层主要物理力学参数
Table 2 The main physical and mechanical parameters of the soil layer of the site
材料名称 厚度
/m重度
/(kN·m−3)泊松比 黏聚力
/kPa内摩擦角
/(°)碳质砂岩 >80 27.2 0.25 18.0 38.0 滑面 / 24.5 0.30 11.0 28.0 薄弱面 / 20.0 0.25 12.0 30.0 表 3 结构主要计算参数表
Table 3 Structure main calculation parameter table
参数 抗滑桩 自由段 锚固段 框架梁 重度
/(kN·m−3)25 67.60×106 39×106 25 弹性模量
/(kN·m−2)3.25×107 弹性模量与
截面的乘积为
1.42×105 kN2.06×108 3.25×107 尺寸 3 m×2 m 直径0.13 m 0.18 m×0.16 m 表 4 具体施工步骤
Table 4 Specific construction steps
步骤 说明 工况1 初始地应力分析 工况2 八级坡开挖 工况3 八级坡施工框架预应力锚索 工况4 七级坡开挖 工况5 七级坡施工框架预应力锚索 工况6 六级坡开挖 工况7 六级坡施工框架预应力锚索 工况8 五级坡开挖 工况9 五级坡施工框架预应力锚索 工况10 四级坡开挖 工况11 四级坡施工框架预应力锚索 工况12 三级坡开挖 工况13 三级坡施工框架预应力锚索 工况14 二级坡开挖 工况15 二级坡施工框架预应力锚索抗滑桩施工 工况16 施工抗滑桩预应力锚索 工况17 开挖到坡底 -
[1] 宛良朋, 汤开宇, 李建林, 等. 深部软弱岩体置换体对岩质边坡支护效果分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(增刊1): 476 − 480 WAN Liangpeng, TANG Kaiyu, LI Jianlin, et al. Supporting effect analysis of deep weak rock mass replacement for rock slope[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(Sup 1): 476 − 480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 邓安. 多锚点抗滑桩在北京戒台寺滑坡治理工程中的应用研究[D]. 北京: 铁道部科学研究院, 2007 DENG An. Application of multi anchor-points anti-slide pile in controlling jietaisi temple landslide in Beijing[D]. Beijing: Academy of Sciences of the Ministry of Railways, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 朱志刚. 北京双大路碎裂岩质滑坡灾变机理及控制技术[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012 ZHU Zhigang. Mechanism and controlling techniques of landslide in cataclastic rock mass of shuangda road in Beijing[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 成永刚. 滑坡的区域性分布规律与防治方案研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2013 CHENG Yonggang. Study on regional distribution discipline of landslides and prevention programme[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 蒲凯超. 某顺层岩质边坡开挖支护过程及其稳定性响应[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2020 PU Kaichao. The excavation and support process of a bedding rock slope and its stability response[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 廖海军,祁生文,杨存进,等. 北京市戒台寺滑坡发生发展机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2007,15(5):585 − 592. [LIAO Haijun,QI Shengwen,YANG Cunjin,et al. Mechanism for initiation and development of Jietai temple landslide in Beijing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2007,15(5):585 − 592. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.05.002 [7] 汪维. 门头沟深挖顺层软岩高边坡支护结构多目标优化设计研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2020 WANG Wei. Research on multi-objective optimization design of support structure of high soft rock slope in Mentougou deep excavation[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 孟祥铭. 现代监测手段在黑岱沟露天矿边坡中的应用研究[D]. 包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2012 MENG Xiangming. Research on modern monitoring means and its application for Heidaigou open pit slope[D]. Baotou: Inner Mongolia University of Science & Technology, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 黄秋香, 汪家林, 邓建辉. 基于多点位移计监测成果的坡体变形特征分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(增刊1): 2667 − 2673 HUANG Qiuxiang, WANG Jialin, DENG Jianhui. Slope deformation character analysis based on monitoring results of multiple multi-point borehole extensometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(Sup 1): 2667 − 2673. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李京榜, 朱彦鹏, 叶帅华, 等. 某二级高边坡健康监测试验研究与分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(增刊1): 129 − 134 LI Jingbang, ZHU Yanpeng, YE Shuaihua, et al. Health monitoring tests on a secondary high slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(Sup 1): 129 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 朱彦鹏, 李京榜, 叶帅华, 等. 基于锚索格构梁支护结构的高边坡健康监测研究与分析[J]. 工程力学, 2015, 32(增刊1): 271 − 276 ZHU Yanpeng, LI Jingbang, YE Shuaihua, et al. Health monitoring and analysis on high slope anchor lattice beam supporting structure[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 32(Sup 1): 271 − 276. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 高大水,曾勇. 三峡永久船闸高边坡锚索预应力状态监测分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2001,20(5):653 − 656. [GAO Dashui,ZENG Yong. Monitoring analysis on prestress state of anchor cable of high slope of the tgp permanent shiplocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2001,20(5):653 − 656. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2001.05.010 [13] 王旭日. 某泥岩砂岩互层高边坡监测与稳定性分析[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2016 WANG Xuri. The monitoring and stability analysis of a interbedding high slope of mudstone and sandstone[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 关松,谭运坤,赵娜. 锦屏一级电站高陡顺层边坡支护内部安全监测分析[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版),2013,35(2):16 − 19. [GUAN Song,TAN Yunkun,ZHAO Na. Monitoring analysis of internal safety for high-steep bedding slope supporting in Jinping I hydropower station[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences),2013,35(2):16 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 周勇,王旭日,朱彦鹏,等. 强风化软硬互层岩质高边坡监测与数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(6):2249 − 2258. [ZHOU Yong,WANG Xuri,ZHU Yanpeng,et al. Monitoring and numerical simulation of an interbedding high slope composed of soft and hard strong-weathered rock[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(6):2249 − 2258. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2016.2026 [16] 陶志刚,罗森林,朱淳,等. 滑坡动态力学监测及破坏过程案例分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(1):177 − 186. [TAO Zhigang,LUO Senlin,ZHU Chun,et al. Dynamic mechanical monitoring of landslide and case analysis of failure process[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(1):177 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0027 [17] 何满潮. 滑坡地质灾害远程监测预报系统及其工程应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(6):1081 − 1090. [HE Manchao. Real-time remote monitoring and forecasting system for geological disasters of landslides and its engineering application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(6):1081 − 1090. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.06.001 [18] 刘志祥, 张海清. PLAXIS 3D基础教程[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2015 LIU Zhixiang, ZHANG Haiqing. PLAXIS 3D basic course[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
[19] 米海珍, 胡燕妮, 李春燕. 土木工程专业本科系列教材 弹性力学 (第2版)[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004. MI Haizhen, HU Yanni, LI Chunyan. A series of undergraduate textbooks for civil engineeringElastic mechanics (2nd Edition), [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 贾丽娜,李瑞冬,魏新平. 基于InSAR技术的黄土滑坡及周边斜坡变形识别. 地下水. 2023(02): 121-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何丽,吴先谭,陈欣,罗芳,何政伟,薛东剑,白文倩,康桂川,张雨祥. 基于SBAS-InSAR的西宁市滑坡识别和形变监测分析. 物探化探计算技术. 2023(06): 812-823 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 裴小龙,杨瀚文,宋东阳,杨斌,田野. 雅砻江中游楞古水电站夏日滑坡发育特征及稳定性分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(01): 75-82 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 吴明辕,罗明,刘岁海. 基于光学遥感与InSAR技术的潜在滑坡与老滑坡综合识别——以滇西北地区为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(03): 84-93 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 郭富赟,周小龙,火飞飙,张毅. 舟曲断裂带滑坡灾害效应与防治对策研究. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(06): 80-89 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 蒲虹宇,张立峰,何毅,陈宝山,陈毅,何旭. 甘肃通渭黄土滑坡二维形变时序监测. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(06): 114-124 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 戴嵩,魏冠军,梁斌. 控制点布设方案对无人机精度测量的影响及其应用——以西北地区某尾矿坝地表沉降监测为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2021(05): 113-120 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:

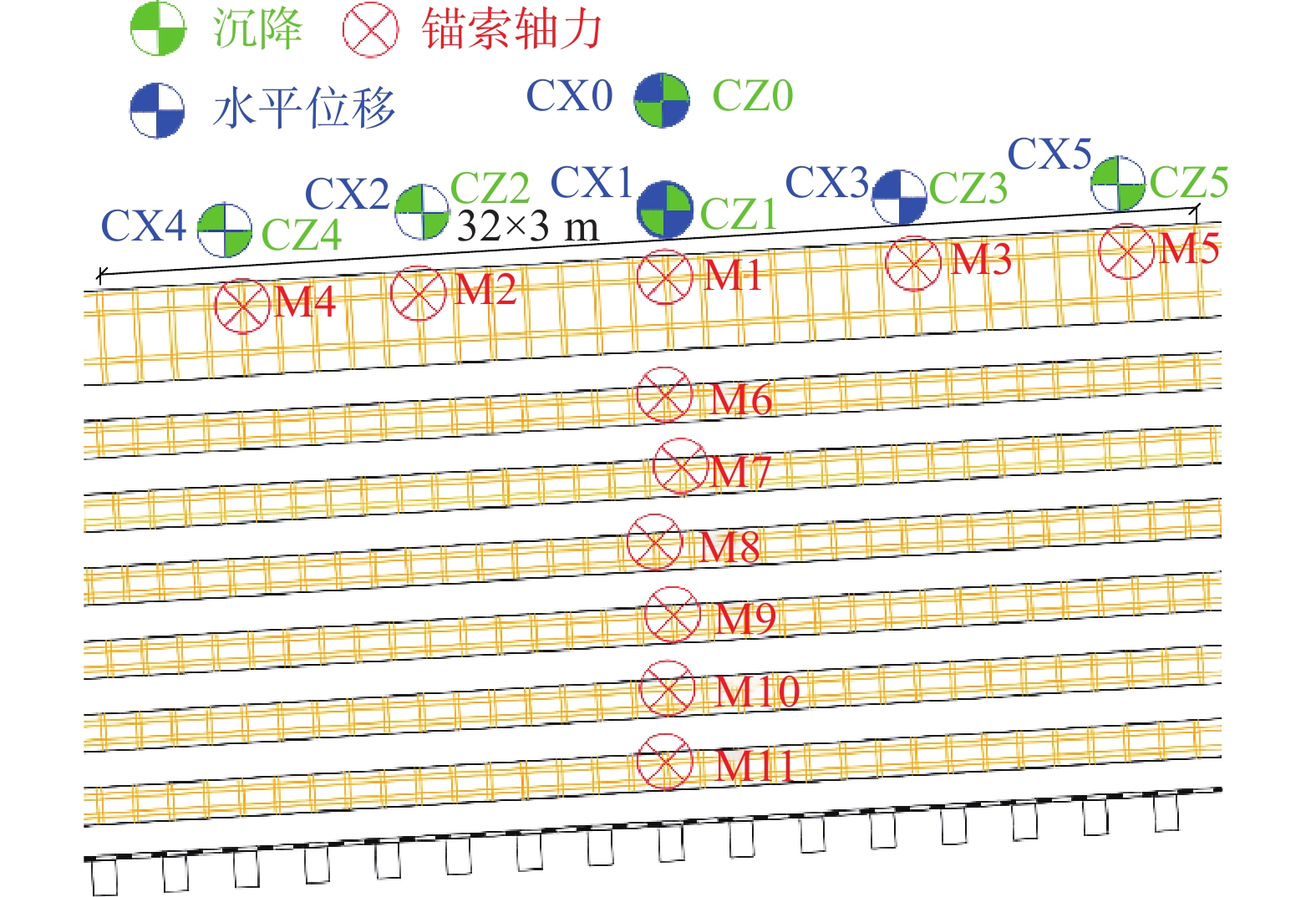
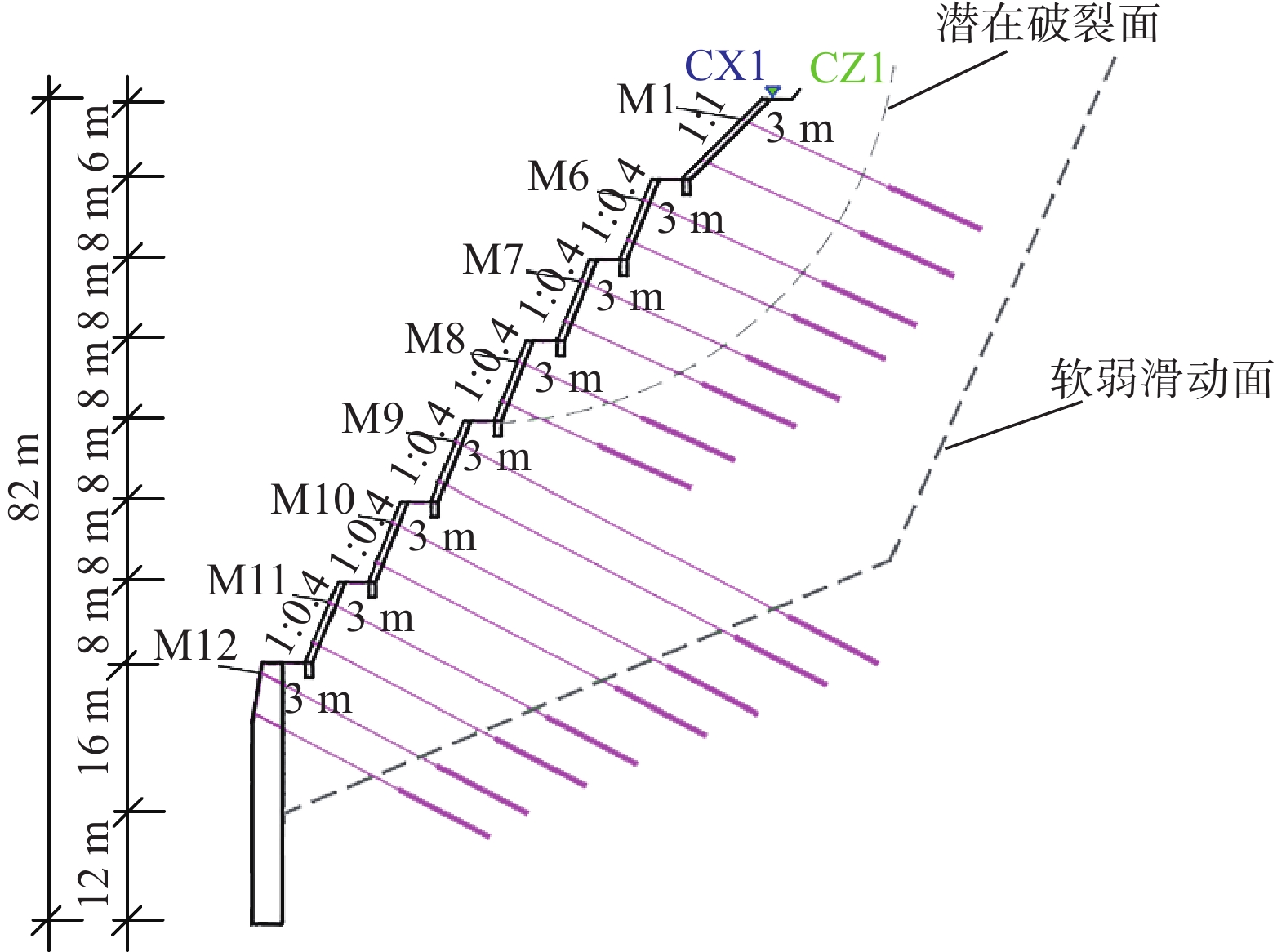
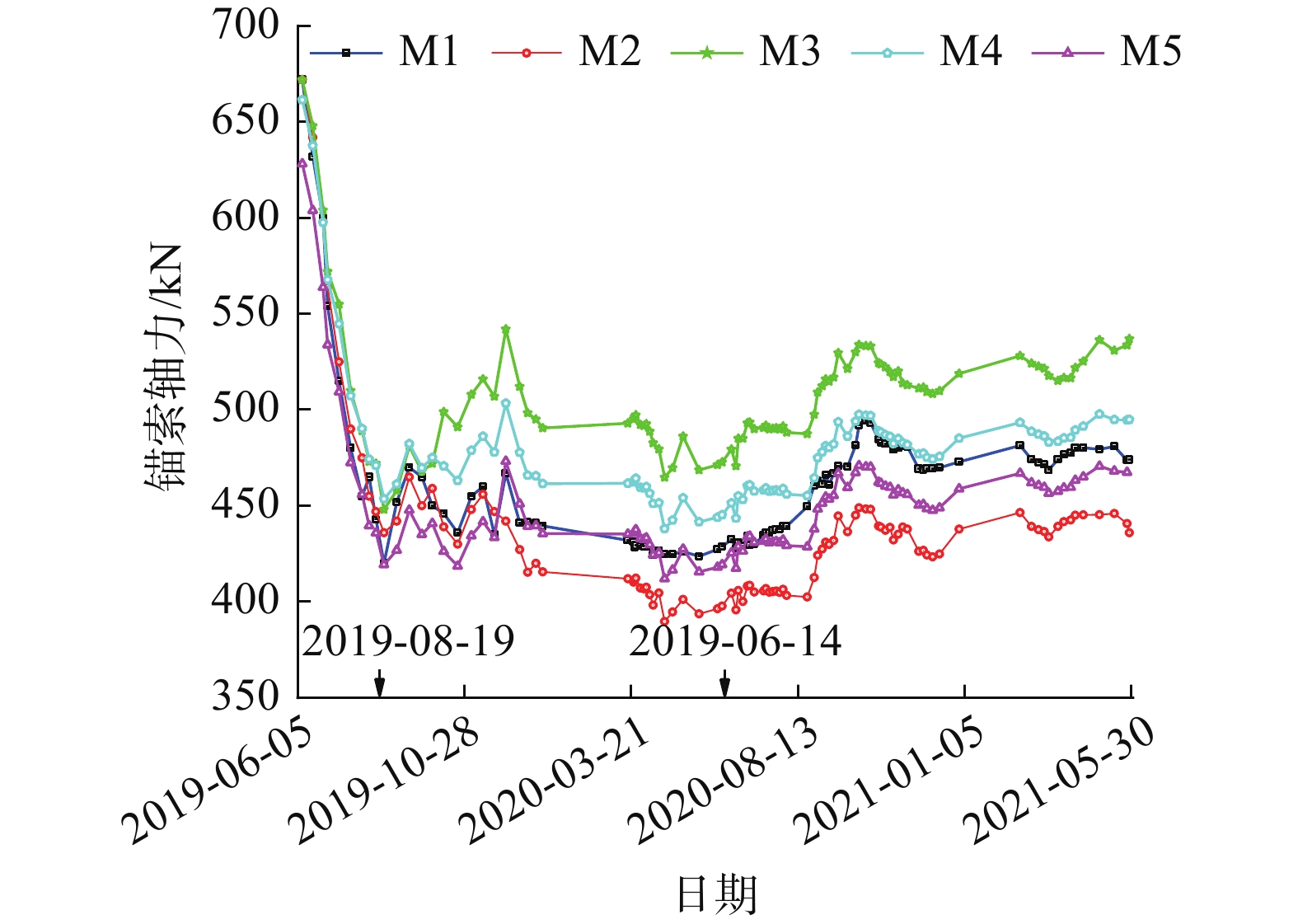
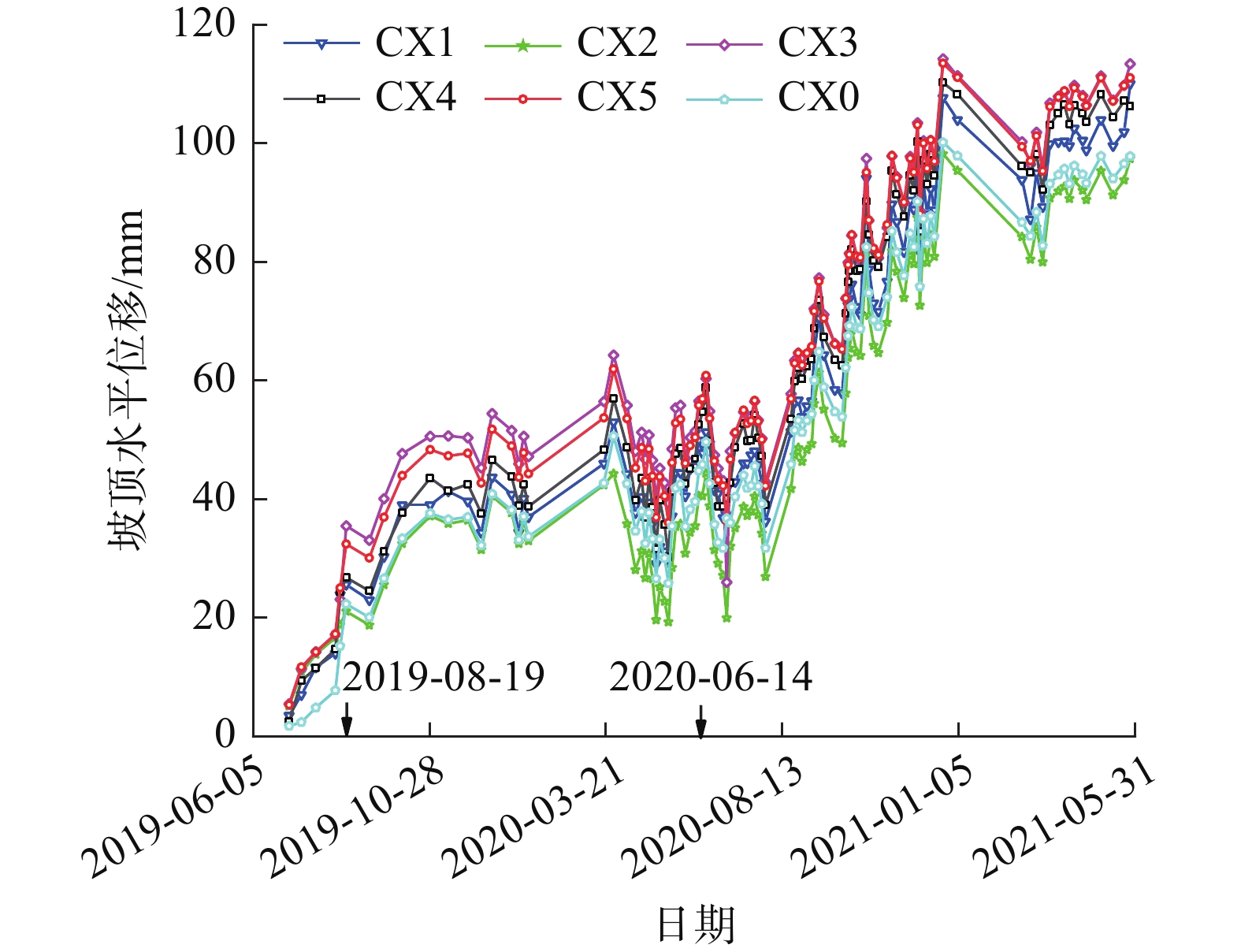
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS