Influences of stone content on stability of gravel soil slope based on DIC analysis
-
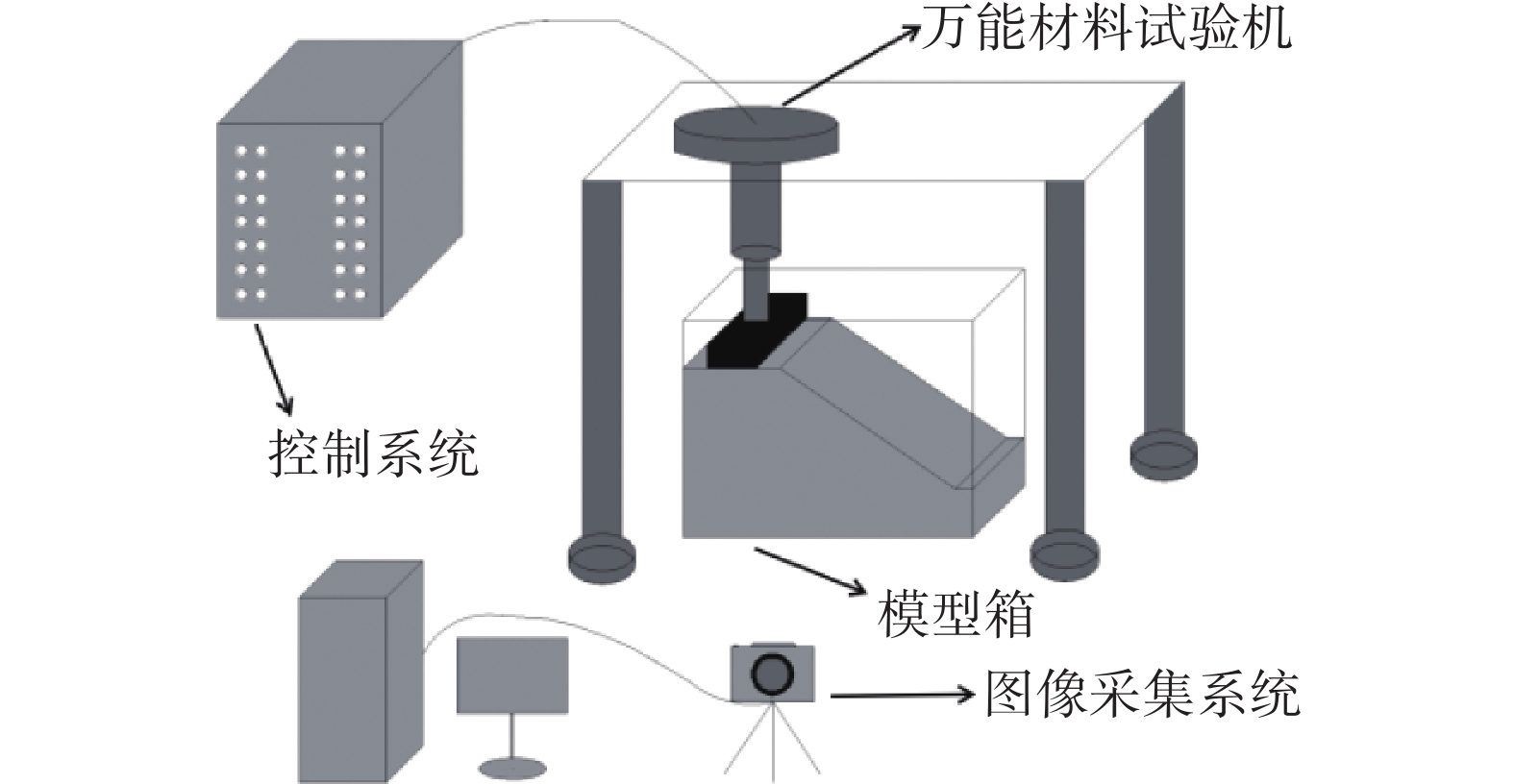
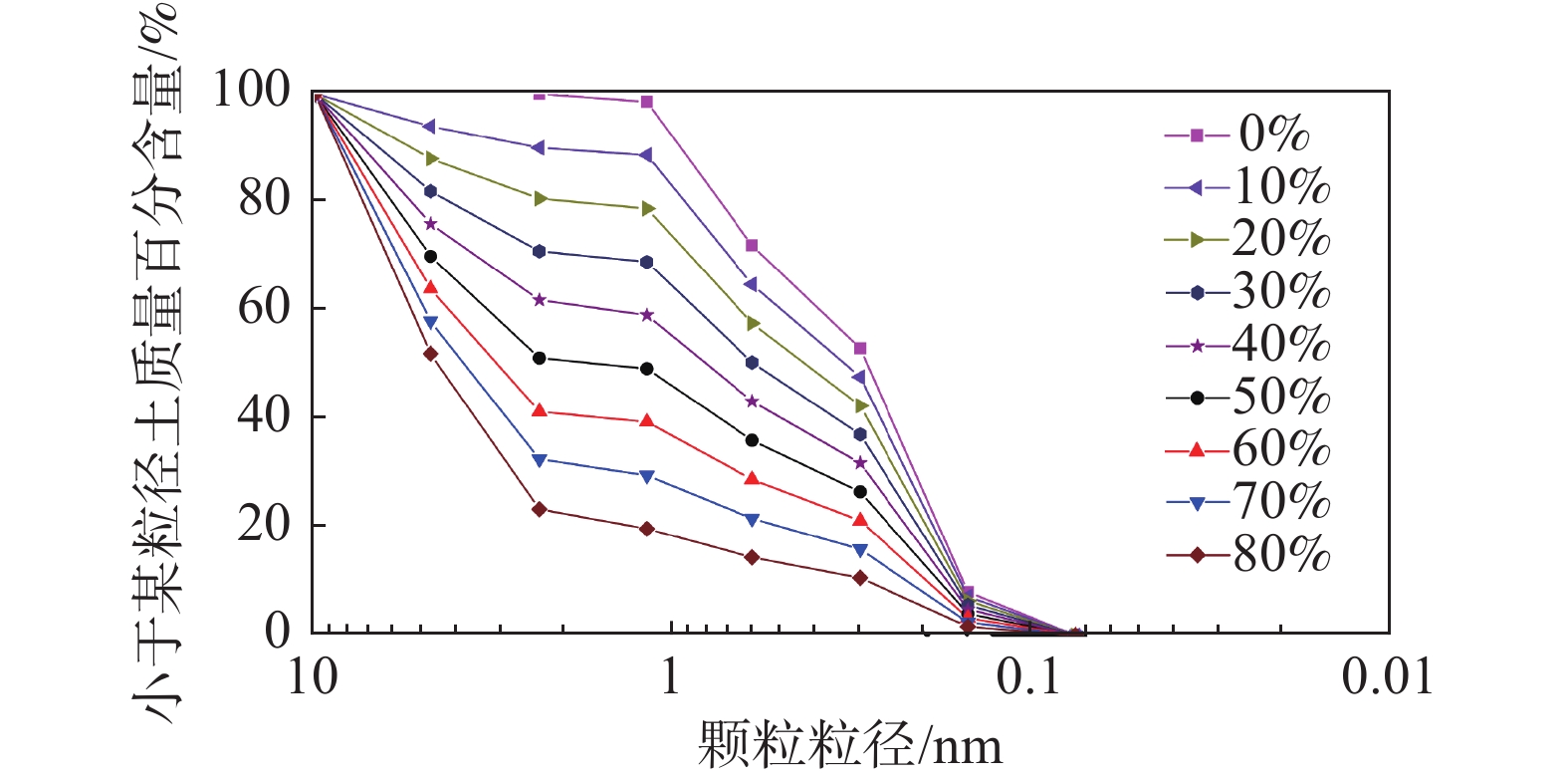
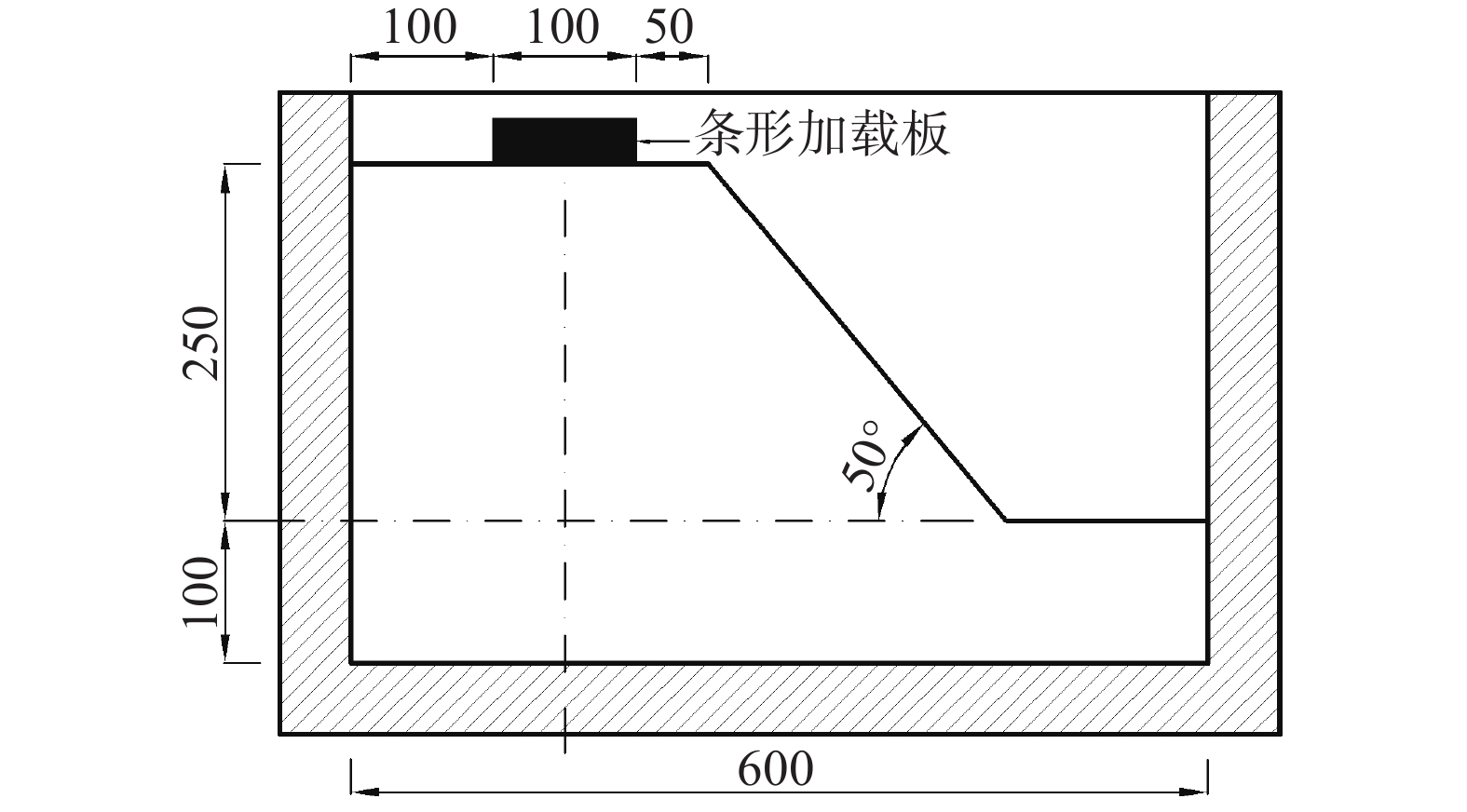
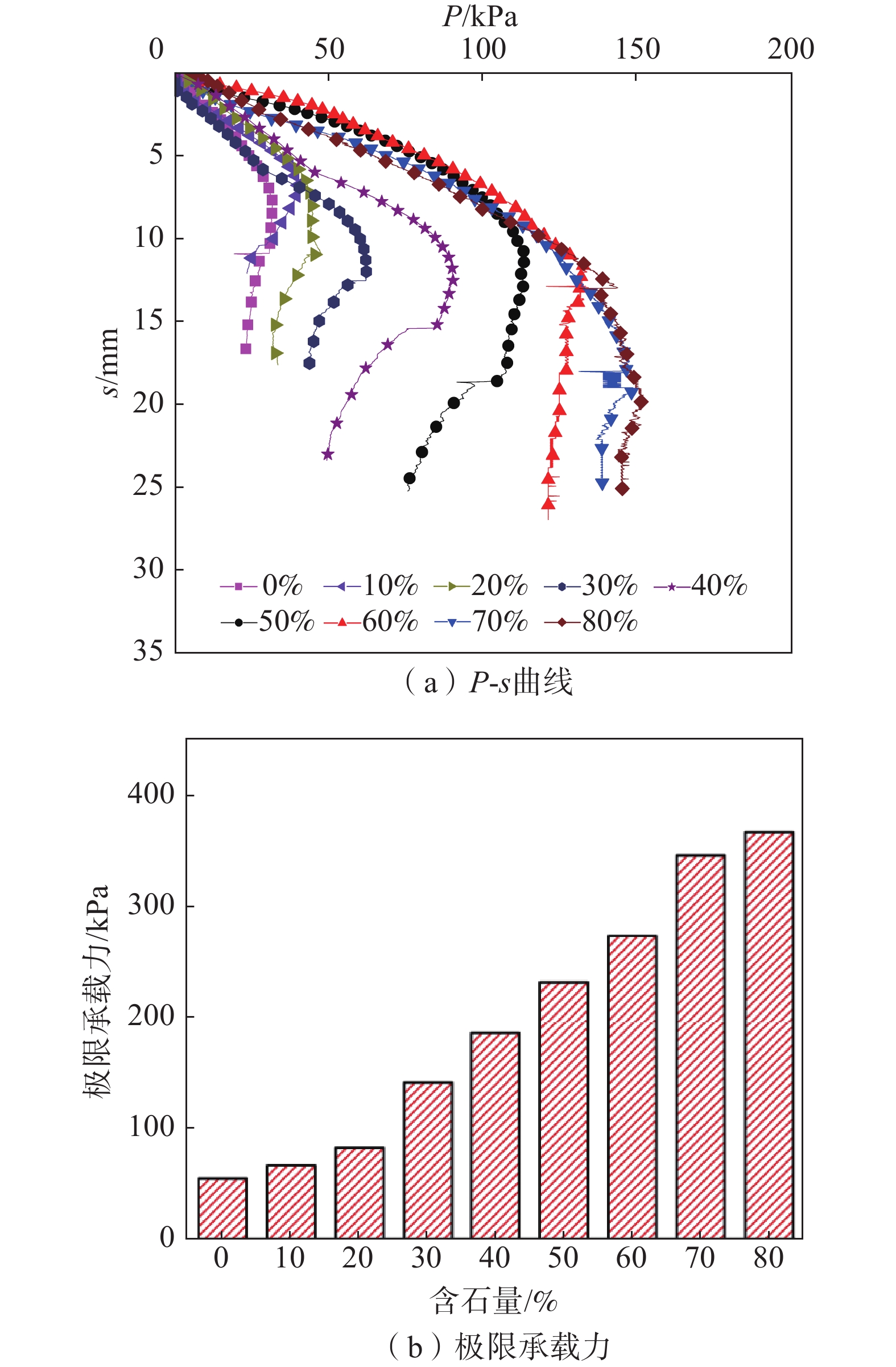
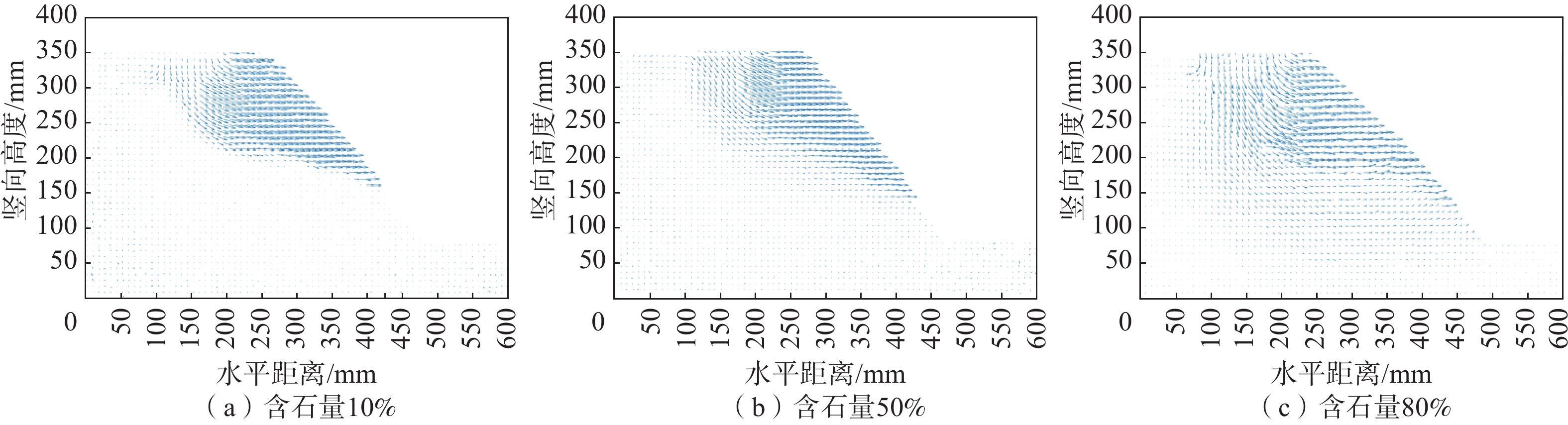
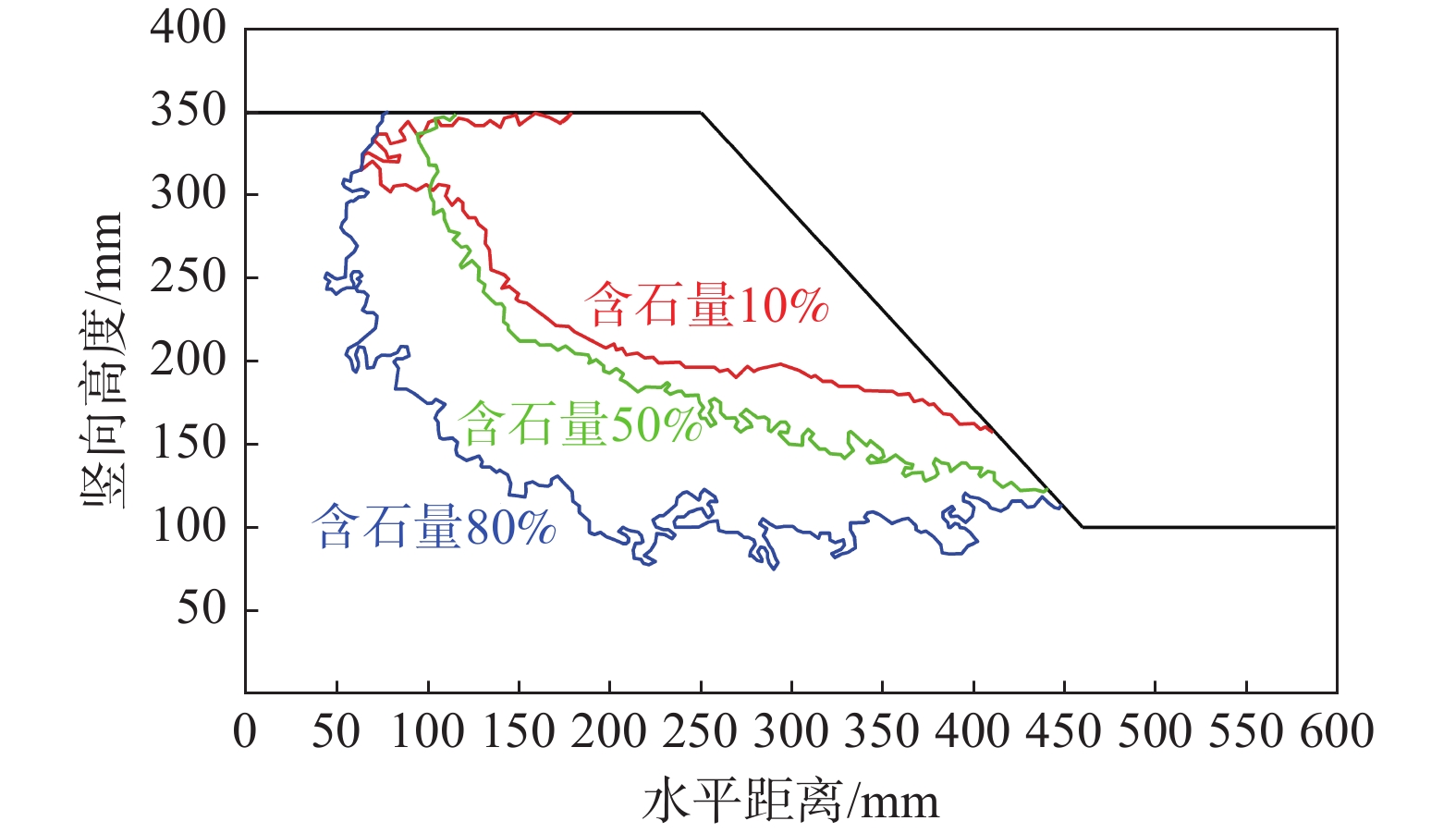
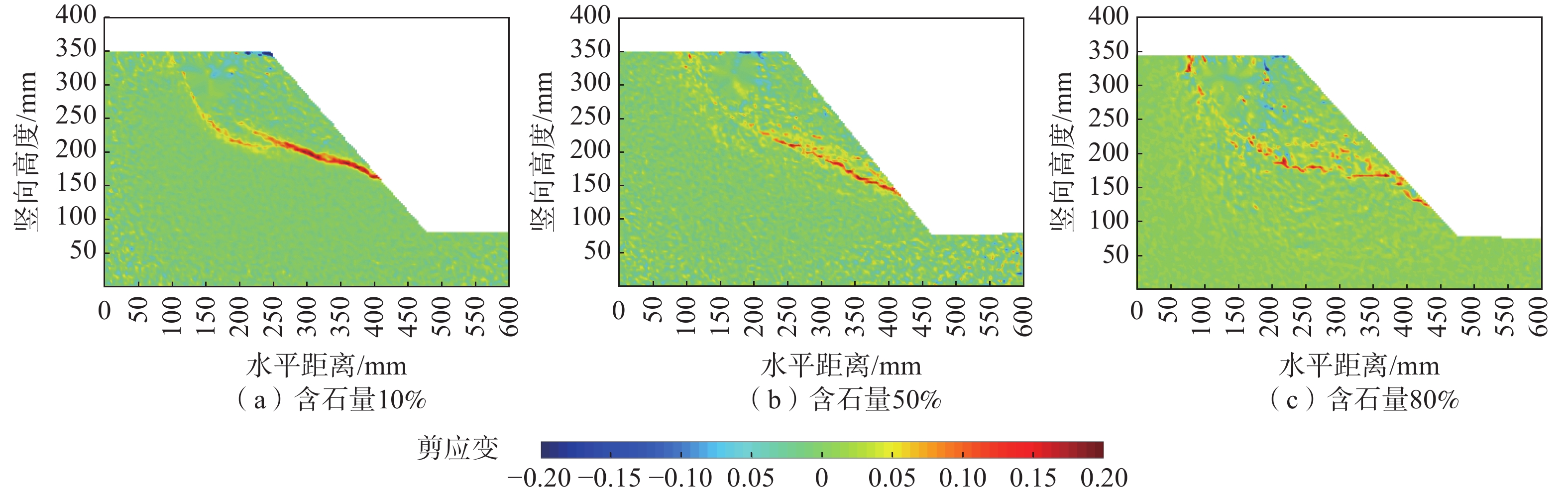
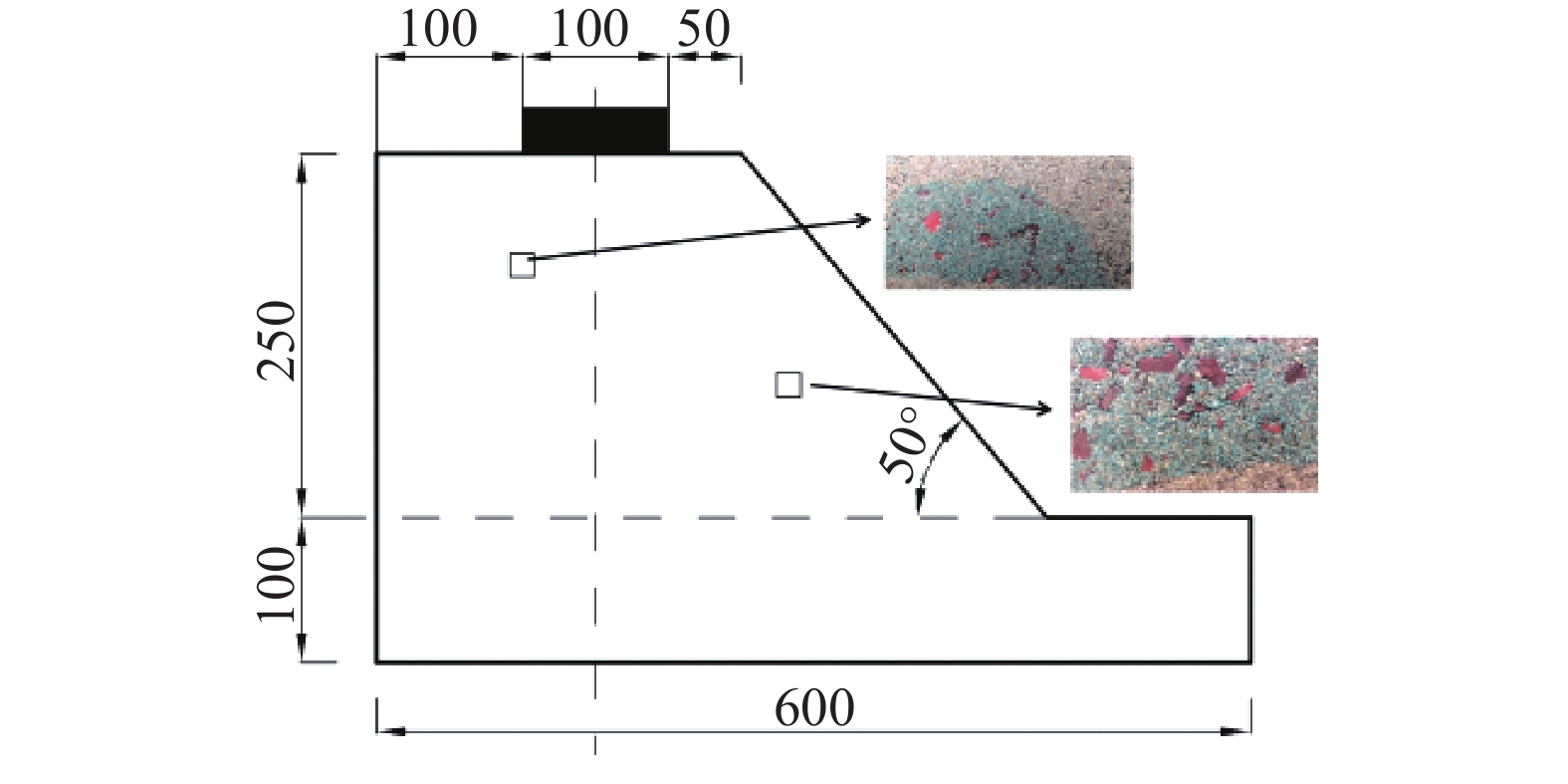
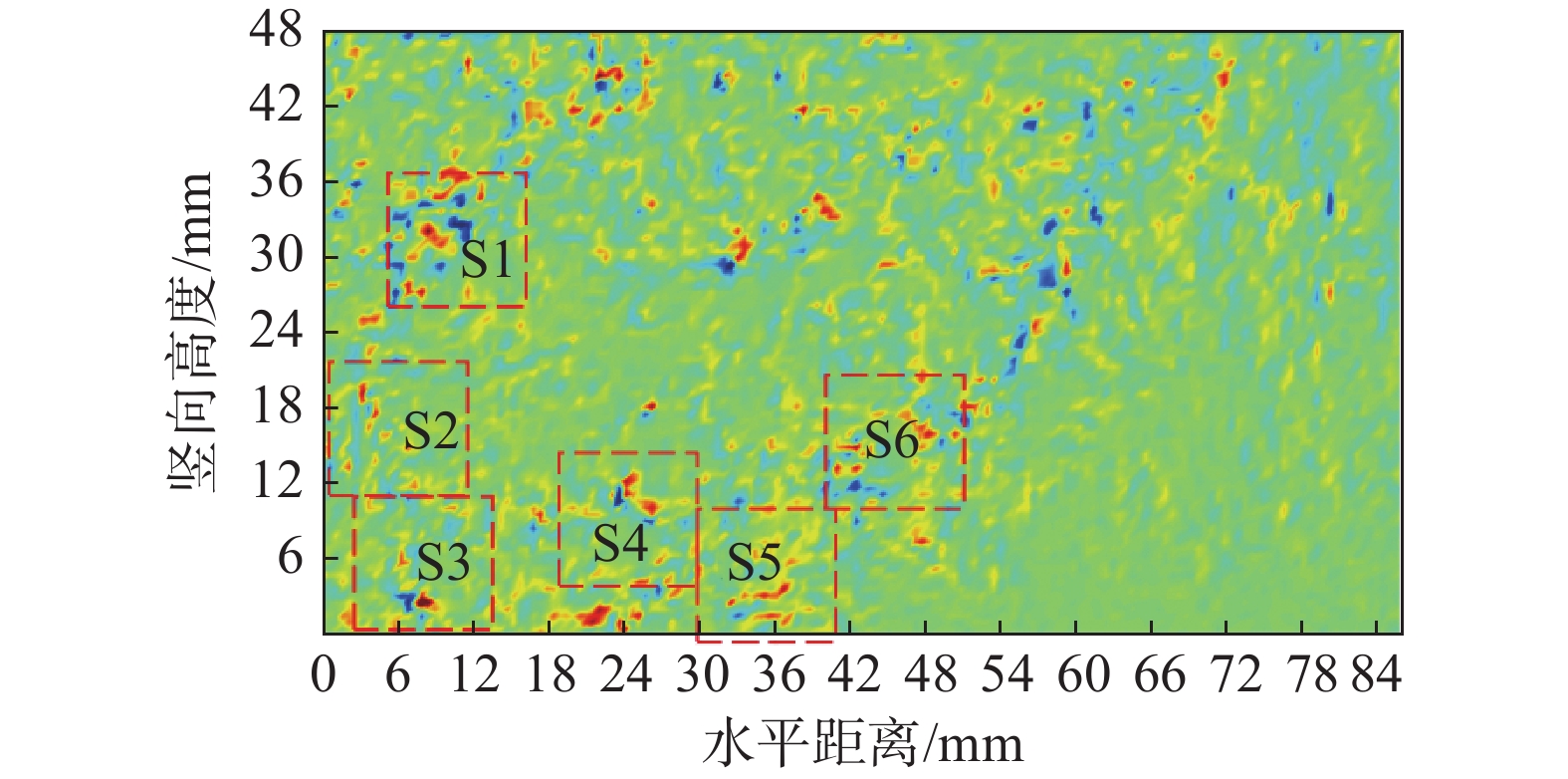
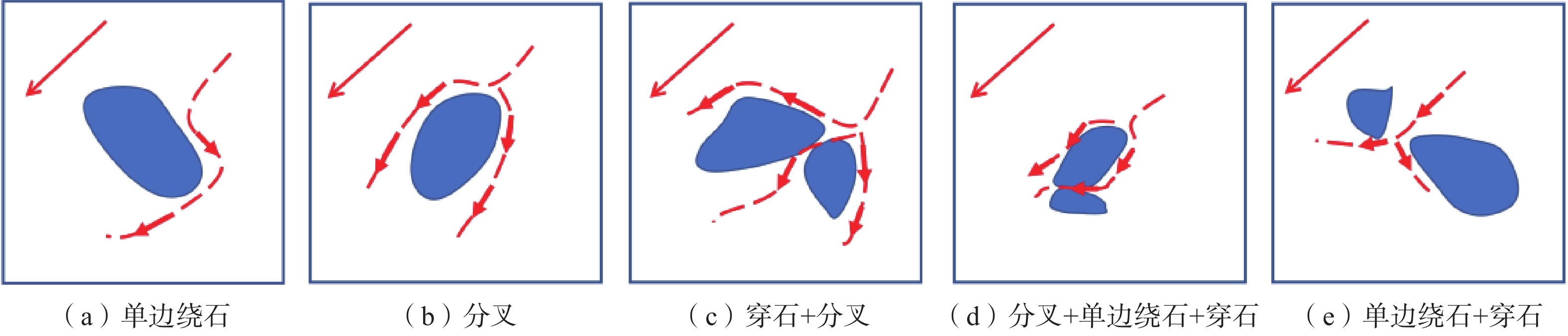
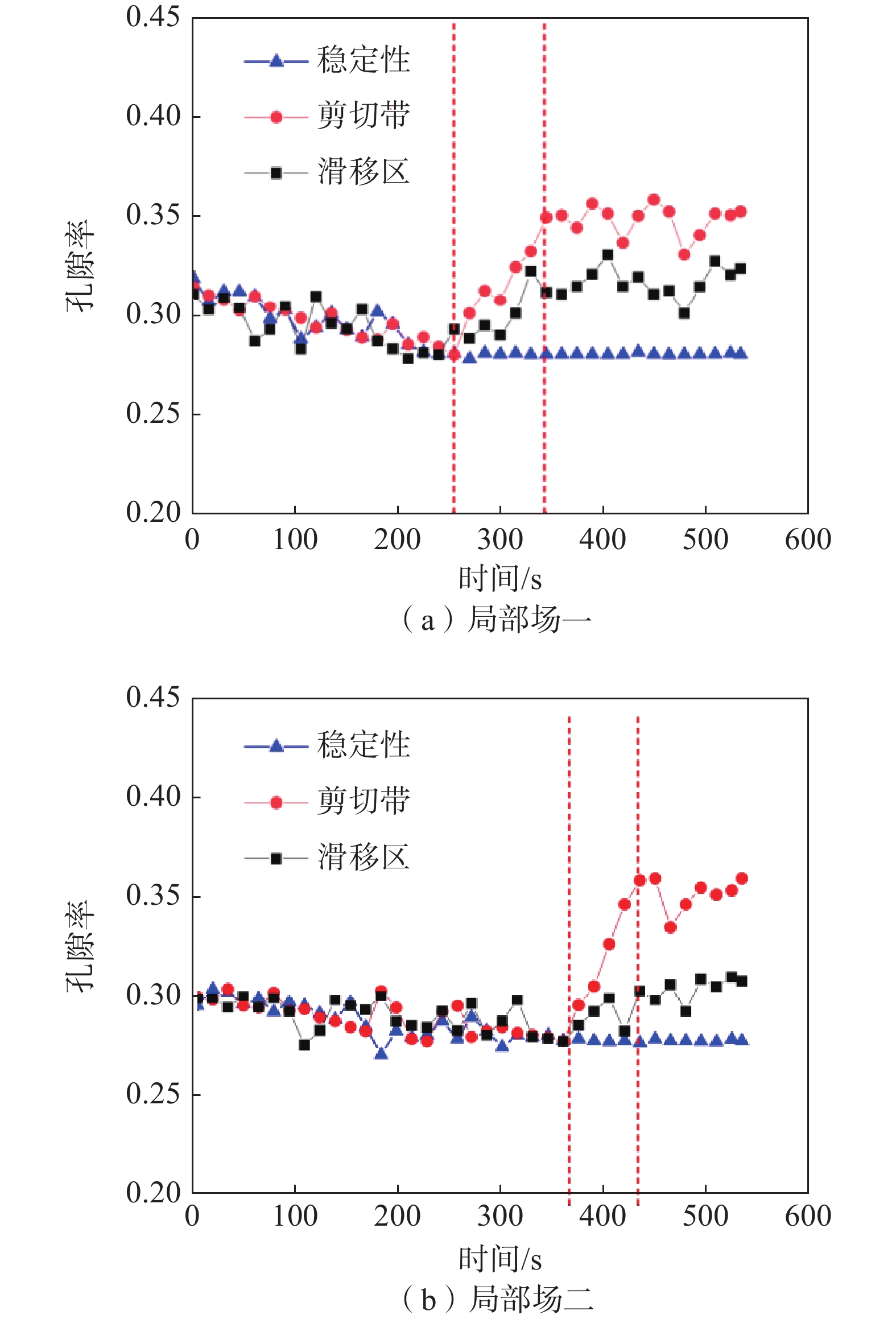
摘要: 为了研究含石量对碎石土边坡稳定性的影响,对不同含石量的边坡进行了模型试验。模型试验中结合数字图像关联技术DIC,分析了边坡全场和局部场的土体变形。研究发现含石量对碎石土边坡的承载力和变形特性具有显著的控制效果,并且根据极限承载力发现含石量存在两个阈值,分别为20%和70%。对局部土体的变形规律和碎石的运动行为进行分析,发现在剪切过程中,局部土体出现剪胀效应,剪切带内孔隙率会明显增加。通过对局部土体中碎石及其周边砂颗粒的追踪,发现碎石会影响剪切带的发展,从而总结出5种剪切带绕石模式:单边绕石模式、分叉模式、穿石和分叉复合模式、分叉和单边绕石及穿石复合模式、单边绕石和穿石复合模式。研究成果可为进一步了解碎石土边坡失稳的内在机理提供相关参考。Abstract: To study the influence of stone content on the stability of gravel soil slopes, static overload tests were carried out on slopes with different stone contents. By combining model tests combined with digital image correlation (DIC) technology, the deformation of the soil body in both the whole field and local field of the slope was analyzed. The findings indicated that the stone content had a significant controlling effect on the bearing capacity and deformation characteristics of gravel soil slope, and two threshold values of stone content, i.e. 20% and 70% were found based on the ultimate bearing capacity. Further analysis was conducted at the meso-scale to understand the deformation behaviour of local soil and the movement of gravel during the shearing process. The local soil was found to exhibit the shear dilatancy effect, resulting in a significant increase in porosity in the shear zone. By tracing the movement of gravel and its surrounding sand particles in the local soil, it was found that the gravel can affect the development of shear zone, and five modes of shear zone surrounding stone were summarized: unilateral rock bypass mode, bifurcation mode, crossing rock and bifurcation composite mode, bifurcation and unilateral rock bypass and crossing rock composite mode, and unilateral rock bypass and crossing rock composite mode. The research results provided a reference for further understanding the inherent mechanism of gravel soil slope instability.
-
Keywords:
- digital image correlation technology /
- stone content /
- model test /
- gravel soil /
- porosity
-
-
表 1 不同含石量碎石土边坡总时间(T)
Table 1 Time of gravel soil slope with different stone contents
含石量/% T/s 含石量/% T/s 0 150 50 535 10 189 60 624 20 224 70 700 30 295 80 715 40 426 表 2 颗粒位移和旋转角度
Table 2 Summary table of the particle displacement and rotation angle
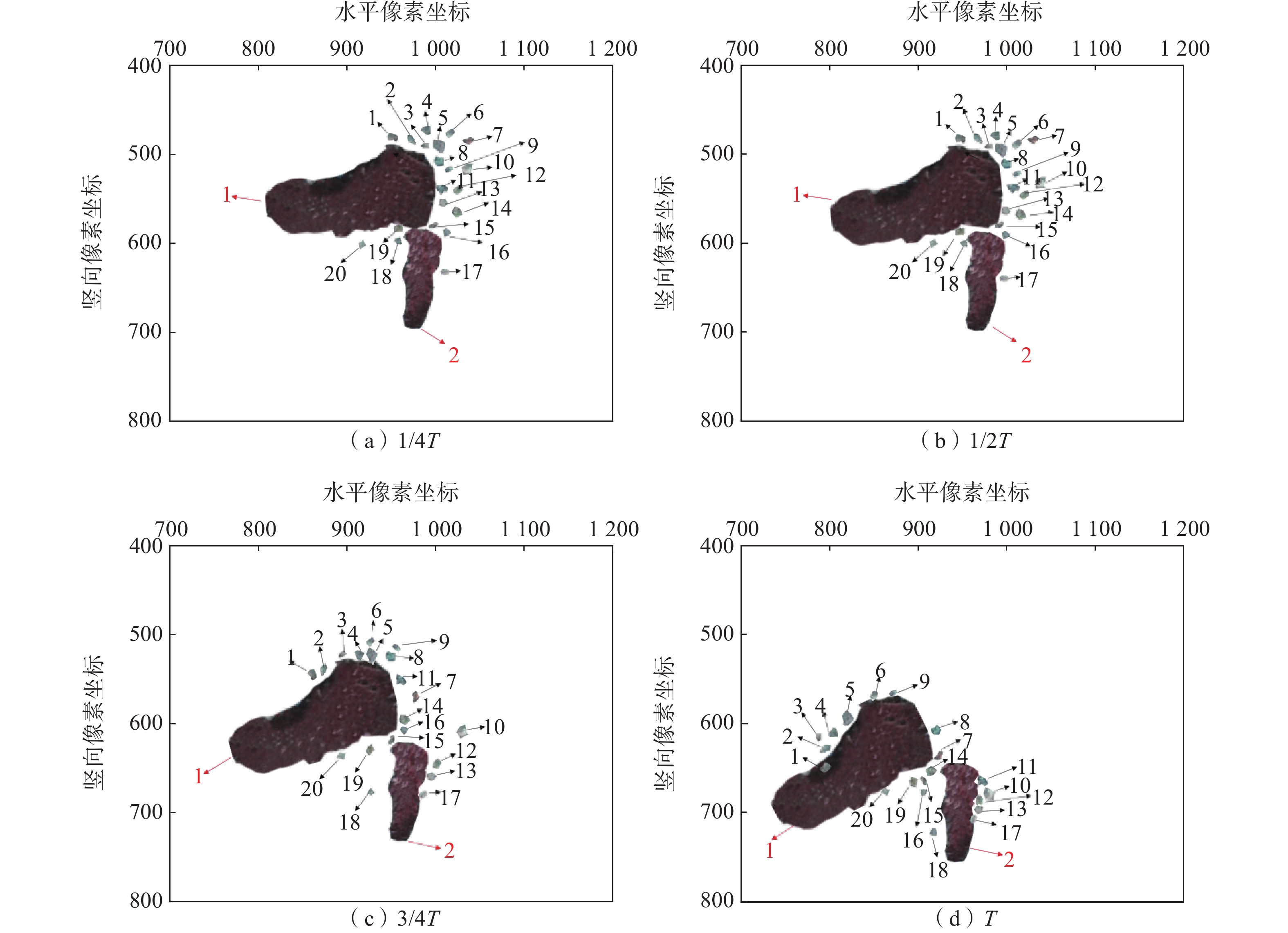
颗粒 水平位移/mm 竖直位移/mm 旋转角度/(°) 颗粒 水平位移/mm 竖直位移/mm 旋转角度/(°) 碎石1 3.87 5.17 16 砂颗粒10 2.75 8.25 −36 碎石2 1.75 3.01 1 砂颗粒11 1.78 5.93 −20 砂颗粒1 7.88 8.54 122 砂颗粒12 2.84 7.40 −25 砂颗粒2 8.90 7.30 110 砂颗粒13 2.04 7.20 −94 砂颗粒3 10.19 5.68 90 砂颗粒14 5.55 4.69 −80 砂颗粒4 9.41 6.94 114 砂颗粒15 4.69 4.28 117 砂颗粒5 9.25 5.98 50 砂颗粒16 5.41 4.62 56 砂颗粒6 8.39 4.31 52 砂颗粒17 2.41 3.91 77 砂颗粒7 5.74 7.67 22 砂颗粒18 2.14 6.35 −22 砂颗粒8 4.26 4.5 160 砂颗粒19 3.31 4.24 30 砂颗粒9 7.23 1.71 10 砂颗粒20 2.70 3.92 −45 -
[1] 彭成,邓沛宇,范子坚,等. 含石率对石英砂岩类碎石土力学特性的影响研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2021,18(2):375 − 382. [PENG Cheng,DENG Peiyu,FAN Zijian,et al. Study on the influence of gravel content on the mechanical properties of crushed aggregates containing quartz and sandstone[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2021,18(2):375 − 382. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.T20200331 PENG Cheng, DENG Peiyu, FAN Zijian, et al. Study on the influence of gravel content on the mechanical properties of crushed aggregates containing quartz and sandstone[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(2)375-382(in Chinese) DOI: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.T20200331
[2] 汪美华, 李勇, 裴叶青. 甘肃临夏盆地韩集北山滑坡群致灾特征与稳定性评价[J]. 地质通报, 2023, 42(2/3): 460 − 468. WANG Meihua, LI Yong, PEI Yeqing. Disaster characteristics and stability evaluation of the Hanjin Beishan landslide group in Linxia Basin, Gansu Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(2/3): 460 − 468. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 梁雄,阳军生,谢亦朋,等. 土石堆积体精细化模型构建及力学特性数值试验[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2021,18(3):710 − 719. [LIANG Xiong,YANG Junsheng,XIE Yipeng,et al. Refined model construction and experimental simulation on mechanical characteristics of accumulation body[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2021,18(3):710 − 719. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.T20200461 LIANG Xiong, YANG Junsheng, XIE Yipeng, et al. Refined model construction and experimental simulation on mechanical characteristics of accumulation body[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(3)710-719(in Chinese) DOI: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.T20200461
[4] 孟佳佳, 吴益平, 柯超, 等. 滑坡多发区第四系堆积层厚度智能预测与影响因素分析—以重庆万州铁峰乡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(1):1 − 10. [MENG Jiajia, WU Yiping, KE Chao, et al. Intelligent prediction and analysis of influencing factors of Quaternary accumulation layer thickness in landslide-prone areas:A case study in the Tiefeng area of Wanzhou District, Chongqing City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(1):1 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) [MENG Jiajia, WU Yiping, KE Chao, et al. Intelligent prediction and analysis of influencing factors of Quaternary accumulation layer thickness in landslide-prone areas: a case study in the Tiefeng area of Wanzhou District, Chongqing City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(2): 1-10.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] WENJIE,XU. Discrete element modelling of a soil-rock mixture used in an embankment dam[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2016,86:141 − 156. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.04.004
[6] COLI N,BERRY P,BOLDINI D. In situ non-conventional shear tests for the mechanical characterisation of a bimrock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2011,48(1):95 − 102. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.09.012
[7] 许旭堂, 鲜振兴, 杨枫, 等. 水-力耦合及干湿循环效应对浅层残积土斜坡稳定性的影响[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):28 − 36. [XU Xutang, XIAN Zhenxing, YANG Feng, et al. Influence of hydraulic-mechanical coupling and dry-wet cycle effect on surficial layer stability of residual soil slopes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):28 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract) [XU Xutang, XIAN Zhenxing, YANG Feng, et al. Influence of hydraulic-mechanical coupling and dry-wet cycle effect on surficial layer stability of residual soil slopes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 28-36.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 陈文胜,蒋茂林,周伟,等. 反坡对边坡稳定性分析的影响探讨[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2021,18(7):1756 − 1763. [CHEN Wensheng,JIANG Maolin,ZHOU Wei,et al. Discussion on the influence of reverse slope on slope stability analysis[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2021,18(7):1756 − 1763. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.T20200882 CHEN Wensheng, JIANG Maolin, ZHOU Wei, et al. Discussion on the influence of reverse slope on slope stability analysis[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(7)1756-1763(in Chinese) DOI: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.T20200882
[9] 宋宜祥, 尹子航, 黄达. 基于Green-Ampt模型的多层结构边坡降雨入渗改进计算方法及稳定性影响研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):162 − 170. [SONG Yixiang, YIN Zihang, HUANG Da. Rainfall infiltration process of multi-layer slope based on improved Green-Ampt model stability analysis[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):162 − 170. (in Chinese with English abstract) [SONG Yixiang, YIN Zihang, HUANG Da. Rainfall infiltration process of multi-layer slope based on improved Green-Ampt model stability analysis[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 162-170.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] SRIKRISHNAN,SUBRAMANIAN S,. Stability assessment approach for soil slopes in seasonal cold regions[J]. Engineering Geology,2017,221:154 − 169. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.008
[11] NAPOLI M L,BARBERO M,RAVERA E,et al. A stochastic approach to slope stability analysis in bimrocks[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2018,101:41 − 49. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.11.009
[12] 庄锦亮,孔思丽,宋鑫华. 基于FLAC3D和极限平衡法土质边坡稳定性分析与影响因素的探讨[J]. 人民珠江,2016,37(3):42 − 45. [ZHUANG Jinliang,KONG Sili,SONG Xinhua. Analysis of soil slope stability and influential factors with FLAC3D and limit equilibrium method[J]. Pearl River,2016,37(3):42 − 45. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2016.03.010 ZHUANG Jinliang, KONG Sili, SONG Xinhua. Analysis of soil slope stability and influential factors with FLAC3D and limit equilibrium method[J]. Pearl River, 2016, 37(3)42-45(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2016.03.010
[13] 李存柱,盛俭,周正华,等. 粗粒料颗粒形状对材料宏观力学性能的影响[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2020,40(2):222 − 228. [LI Cunzhu,SHENG Jian,ZHOU Zhenghua,et al. Influence of particle shape on the macroscopic mechanical properties of coarse aggregate[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2020,40(2):222 − 228. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Cunzhu, SHENG Jian, ZHOU Zhenghua, et al. Influence of particle shape on the macroscopic mechanical properties of coarse aggregate[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2020, 40(2): 222-228. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] YE LU. Stability analyses on slopes of clay-rock mixtures using discrete element method[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,244:116 − 124. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.07.021
[15] 彭东黎,李志勇. 堆积体边坡碎石土抗剪强度试验研究[J]. 公路工程,2014,39(2):254 − 257. [PENG Dongli,LI Zhiyong. Experimental study on shear strength of rock-soil aggregates in accumulation slope[J]. Highway Engineering,2014,39(2):254 − 257. (in Chinese with English abstract) PENG Dongli, LI Zhiyong. Experimental study on shear strength of rock-soil aggregates in accumulation slope[J]. Highway Engineering, 2014, 39(2): 254-257. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] Y WANG. Use of X-ray computed tomography to investigate the effect of rock blocks on meso-structural changes in soil-rock mixture under triaxial deformation[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,164:386 − 399. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.173
[17] 王腾,胡岱松,张嘎. 土石混合料力学特性的试验研究[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2018,58(5):456 − 460. [WANG Teng,HU Daisong,ZHANG Ga. Experimental study of the behavior of soil-gravel mixtures[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology),2018,58(5):456 − 460. (in Chinese with English abstract) Wang Teng, Hu Daisong, Zhang Ga. Experimental study of the behavior of soil-gravel mixtures[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2018, 58(5): 456-460. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 贾丽娜,李瑞冬,魏新平. 基于InSAR技术的黄土滑坡及周边斜坡变形识别. 地下水. 2023(02): 121-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何丽,吴先谭,陈欣,罗芳,何政伟,薛东剑,白文倩,康桂川,张雨祥. 基于SBAS-InSAR的西宁市滑坡识别和形变监测分析. 物探化探计算技术. 2023(06): 812-823 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 裴小龙,杨瀚文,宋东阳,杨斌,田野. 雅砻江中游楞古水电站夏日滑坡发育特征及稳定性分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(01): 75-82 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 吴明辕,罗明,刘岁海. 基于光学遥感与InSAR技术的潜在滑坡与老滑坡综合识别——以滇西北地区为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(03): 84-93 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 郭富赟,周小龙,火飞飙,张毅. 舟曲断裂带滑坡灾害效应与防治对策研究. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(06): 80-89 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 蒲虹宇,张立峰,何毅,陈宝山,陈毅,何旭. 甘肃通渭黄土滑坡二维形变时序监测. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(06): 114-124 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 戴嵩,魏冠军,梁斌. 控制点布设方案对无人机精度测量的影响及其应用——以西北地区某尾矿坝地表沉降监测为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2021(05): 113-120 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载:


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS