Multi-wave joint detection of unfavorable geological bodies in coal mining face
-
摘要: 影响岳南煤矿工作面回采速度的主要因素为煤层上方灰岩富水区域和内部地质隐伏构造。通过采用瞬变电磁法、无线电波透视、槽波地震多种物探方法可以对回采工作面进行透明化探测。探测过程中发现:瞬变电磁法二次波场接收到的感应电压对富水低阻区域较为敏感;观测无线电波透视发射、接收的能量衰减可识别煤层变化区域横向情况;槽波地震的包络振幅、频谱分析与频散曲线综合分析成像,对判别断层走向有良好效果。通过多波场中感应因子对异常区域综合响应特征的识别,并依据多源波场圈定的异常区域进行平面图叠加和综合显现,可有效识别工作面顶板富水区域与煤层内部构造区域的关联情况,清晰判断导水通道情况。试验结果表明,多种物探方法可探明回采工作面内部异常区域并提前预测预报,对今后类似地质条件的探测提供了借鉴依据。Abstract: The main factors restricting the mining speed of the working face in Yuenan Coal Mine are the water-rich area of limestone above the coal seam and the internal geological concealed structure. The transparent detection of the working face is carried out by using transient electromagnetic method, radio wave perspective and slot wave seismic geophysical methods. In the process of detection, it is found that the induced voltage received by the secondary wave field of transient electromagnetic method is more sensitive to the area of rich water and low resistance, and the lateral situation of coal seam can be identified by observing the energy attenuation emitted and received by radio wave perspective. The integrated analysis of envelope amplitude, spectrum and dispersion curve of in-seam wave seismic imaging has good effect on identifying fault strike. Through the identification of the comprehensive response characteristics of the abnormal region by the induction factor in the multi-wave field, the plane map is superimposed according to the abnormal area delineated by the multi-source wave field, and a variety of abnormal characteristics are shown synthetically, which can effectively identify the correlation between the water-rich area of the roof of the working face and the internal structural area of the coal seam, and clearly judge the existence of the water channel. The test results show that the geophysical method can find out the internal abnormal area of the mining face and predict in advance, and the combined detection of various geophysical methods can provide a reference basis for similar geological conditions in the future.
-
0. 引言
强降雨多发生在每年7—8月,降雨因素为该时间段地质灾害发生的主要影响因素。据历史数据统计,中国约60%的突发地质灾害的发生与降雨强度及累计降雨量密切相关,突发地质灾害集中发生在每年暴雨多发的汛期[1]。
降雨型滑坡预测预报研究一直以来受到国内外学者的关注,研究方向可分为滑坡破坏机理分析和预警预报研究两方面。降雨型滑坡预警预报研究方法包括试验分析法、数值模拟法和数学统计法。黄润秋等[2]通过室内模型试验揭示了降雨型滑坡随着降雨量的增大,滑坡岩土体孔隙水压力逐渐升高,最终形成滑坡,揭示了降雨型滑坡存在降雨阈值的根本原因。Guzzetti等[3]、Sharir等[4]认为降雨型滑坡的发生通常与临界降雨量有关,若超过此雨量界限,可能会发生滑坡。
根据分析对象不同,数学统计法又分为滑坡位移与降雨相关性分析法[5]、滑坡结构与降雨相关性分析法[6]、经验统计模型法[7]。甘肃省地质构造复杂,崩塌、滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害非常发育。按年度统计,降雨引发的地质灾害占比约60%以上,最高可达99%(图1)。甘肃省以区域降雨统计模型、滑坡24 h趋势预警模型、泥石流预警模型均属于以数学统计为主的第一代预警模型,在地质灾害气象风险预警中发挥了重要作用[8 − 10]。
目前,甘肃省的地质灾害气象风险预警模型研究仍处于第一代隐式统计模型向第二代显示统计模型的过渡阶段[11],预警模型研究及应用相对滞后,精度有待提高。近年来,甘肃省地质灾害气象风险预警模型研究主要集中在地质灾害高发、频发的白龙江流域,且以泥石流灾害预警模型研究为主。比如王高峰等[12]选取泥石流危险性评价因子:泥石流沟的规模、主沟纵比降、沟谷发育密度、物源区沟道纵比降,通过综合分析研究,得出了自然沟谷发生泥石流灾害的定量评价模型,为中小型泥石流预警预报提供思路,而针对斜坡类灾害的预警模型研究相对较少。
本文以白龙江流域降雨型滑坡为研究对象,针对不同岩性特征的滑坡,建立了不同概率等级下的滑坡发生时事件降雨量(event rainfall)与降雨历时(duration of rainfall)之间的关系模型,以下简称ED模型,为不同岩性类型的斜坡在降雨作用下发生滑坡的阈值研究提供新思路。
1. 白龙江流域灾害概况
1.1 地质灾害发育特征
白龙江流域甘肃段包含5个县(区),位于长江上游,区内植被发育,受新生代印度—亚洲板块挤压作用影响,断裂构造变形明显[13]。区内山大沟深,地形地貌复杂、岩土体类型多样、新构造活动强烈、生态环境脆弱,加之地震活动频繁、降雨集中、暴雨频发,建设用地紧张、发展与环境保护矛盾突出。滑坡、泥石流灾害的暴发,不仅严重威胁当地人民的生命财产,也严重制约社会经济发展。
研究区是中国滑坡、泥石流四大高易发区之一,开展区内降雨引发滑坡灾害预警模型研究意义重大。据统计,截至2023年底,研究区共发育地质灾害隐患点5035处,占当年全省隐患点总数的22.97%,隐患点密度为0.24处/km2;按类型划分,滑坡2776处,崩塌910处,泥石流1341处,地裂缝1处,地面塌陷7处;按行政区划分,宕昌380处,武都2251处,文县1530处,迭部401处,舟曲473处。
1.2 降雨型滑坡界定
本研究以2000—2019年研究区发生的滑坡灾害数据为基础。结合自然资源部门地质灾害隐患点台账、县(区)地质灾害区划报告资料、地质灾害调查报告、县志等资料,同时采用多期遥感数据对比分析、室内解译、野外调查、访问、取样、测试等手段,修正补充已有的滑坡灾害台账数据,结合前期降雨事件分析比对,最终整理形成128个因降雨引发滑坡的记录,资料详细记录了滑坡事件发生的地点、时间、类型、成因等,数据较为可靠,成为本次研究的对象。经分析,该类滑坡主要分布在白龙江两岸的山坡地带,在6—9月多发,占比为74%,7月下旬及8月上旬,滑坡发生数量达到峰值,其余月份滑坡发生的数量较少,滑坡的发生数量与降雨量和降雨强度基本吻合[14],与当地灾害发生的规律相符(图2—3)。
2. 研究方法
按照滑坡岩性特征将滑坡分为较硬、极软、软硬相间三种类型。对于每种类型的滑坡,采用频数法,分别计算不同降雨事件下滑坡发生的概率,即不同岩性类型的滑坡发生前的事件雨量和降雨历时关系,基于频率法分别获得不同概率条件下ED降雨阈值曲线[15 − 16],建成滑坡发生概率预警模型。
2010年Brunetti等[15]发表的论文中指出基于频率法的ED降雨阈值符合幂律法则:
式中:E——事件雨量/mm;
D——降雨持续时间/d;
α——截距,Δα为与α相关的变量;
γ——指数,Δγ为与γ相关的变量。
假设选择一组滑坡数据,以滑坡发生的概率为5%、20%和50% 3种情况下,获得对应的截距和指数,绘制3条曲线,将滑坡事件分为4个区间。即,位于5%概率线以下的点表示该降雨事件下的雨量及降雨历时引发滑坡的概率小于5%。如图4所示,通过对滑坡降雨事件数据统计分析,分别获取滑坡发生概率为5%、20%和50%的ED关系曲线,其中,RLs为诱发滑坡的降雨事件,NRLs为未诱发滑坡的降雨事件。根据样本数据中滑坡发生概率,采用数据拟合方法,计算获得截距和指数γ±Δγ取0.64±0.09,概率为5%的直线关系(T5)为E=(5.01±0.06)·D(0.64±0.09),概率为20%的直线关系为(T20)E=(7.08±0.67)·D(0.64±0.09),概率为50%的直线关系(T50)为E=(15.14±1.15)·D(0.64±0.09)。ɑ取值介于2.07~16.29,D取值介于1~40 d,随着滑坡事件概率的增大,相对不确定性增加,ED之间的关系趋于离散[17]。通过对本次研究中数据的分析,在概率为50%的直线关系中,其相对不确定度为7.6%;在概率为20%的直线关系中,其相对不确定度为9.5%;在概率为5%的直线关系中,其相对不确定度为1.2%。从图2中可以看出,概率为50%的曲线关系中,其相对不确定度较低,说明数据较为集中[18]。
3. 不同岩性滑坡的降雨阈值
根据地层年代、岩体工程性质特征等因素综合考虑,将区域内地层岩性按照软弱程度进行分类,分类标准详见表1。通过岩性分类结果与128处滑坡样本空间分布进行对比,得出松散物质、软硬相间、极软三种类型的岩性中滑坡灾害多发,其中,有72起滑坡分布在松散层内,岩土体类型主要为第四系残坡积碎石土、粉质黏土、强风化千枚岩、砾石,占比约56.25%;有37起滑坡分布在软硬相间的岩性中,岩体类型主要有板岩、千枚岩、浅变质砂岩、砂岩与千枚岩互层岩体,占比约28.91%;有12起滑坡分布极软的岩组中,岩性主要是新近系砾岩、页岩、泥质砂岩等,占比9.38%[19 − 20]。而坚硬、较软、较硬三种岩性类型中滑坡分布数量为7起,数量较少,滑坡降雨阈值曲线的拟合效果差,因此此处不做分析(图5)。
表 1 岩性类型的划分标准Table 1. Classification Standards for Lithological Types软硬类型 主要岩性类型 极软 层状碎屑岩:古近系砾岩;新近系砾岩、页岩、泥质砂岩 坚硬 块状岩浆岩:花岗岩、辉绿岩、辉长岩、闪长岩、
闪长玢岩、闪斜煌斑岩等较软 层状碎屑岩:白垩系砾岩、砂岩、泥岩 较硬 层状碳酸盐岩:三叠系、二叠系灰岩、砂岩、页岩等
泥盆系板岩、砂岩、页岩、灰岩等软硬相间 ①层状变质岩:二叠系砂岩、砂质板岩、凝灰岩、千枚岩;
志留系砂岩、石灰岩、千枚岩、板岩
②层状碳酸盐岩:泥盆系板岩、千枚岩、灰岩
③层状碎屑岩:侏罗系砂岩、泥岩、砾岩、页岩松散物质 第四系残坡积碎石土、粉质黏土、强风化千枚岩、砾石 采用频数法对不同岩体类型的滑坡进行分析,得到概率分别为15%(低)、25%(中)、40%(高)、60%(极高)时,降雨ED曲线(图6),以曲线为下限,将曲线上部4个区间自下而上依次对应定义为低风险区、中风险区、高风险区、极高风险区4个预警等级,即降雨事件雨量与降雨历时所对应的点落入4个区间中的某一个,即判定该滑坡的风险等级为该区间的风险等级。
3种岩性类型的滑坡不同预警等级下限的降雨阈值曲线分别如下:
松散物质:E=6.43D0.72(P=15%,蓝色预警)、E=7.94D0.72(P=25%,黄色预警)、E=10.91D0.72(P=40%,橙色预警)、E=18.79D0.72(P=60%,红色预警)。
极软岩类:E=9.25D0.54(P=15%,蓝色预警)、E=12.30D0.54(P=25%,黄色预警)、E=18.88D0.54(P=40%,橙色预警)、E=31.48D0.54(P=60%,红色预警)。
软硬相间:E=9.79D0.46 (P=15%,蓝色预警)、E=11.16D0.54(P=25%,黄色预警)、E=15.00D0.46(P=40%,橙色预警)、E=21.09D0.46(P=60%,红色预警)。
从图6中可知,松散层滑坡降雨阈值曲线的间距较小,不同预警等级临界累计降雨量差值最小,降雨量对松散层滑坡作用较快。极软岩类滑坡降雨阈值曲线的间距较大,不同预警等级临界累计降雨量差值较大,降雨量对滑坡发生反映慢。软硬相间岩类滑坡降雨阈值曲线的间距中等,不同预警等级临界累计降雨量差值中等,降雨量对滑坡发生反映中等。按照12 d降雨历时,计算得不同岩性类型斜坡分别在4种预警等级下的下限临界累计雨量值(表2)。
表 2 不同岩性类型的斜坡在各预警等级下发生滑坡前不同降雨历时下的累计雨量Table 2. Duration and cumulative rainfall before landslides occur on slopes of different rock types at different warning levels/mm 滑坡类型 预警等级 降雨历时/d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 松散物质 低(P=15%) 6.43 10.59 14.18 17.45 20.49 23.36 26.10 28.74 31.28 33.75 36.14 38.48 中(P=25%) 7.94 13.08 17.51 21.54 25.30 28.85 32.23 35.49 38.63 41.67 44.63 47.52 高(P=40%) 10.91 17.97 24.06 29.60 34.76 39.64 44.29 48.76 53.07 57.26 61.32 65.29 极高(P=60%) 18.79 30.95 41.44 50.98 59.87 68.26 76.28 83.98 91.41 98.61 105.62 112.44 极软岩类 低(P=15%) 9.25 13.45 16.74 19.55 22.06 24.34 26.45 28.43 30.30 32.07 33.77 35.39 中(P=25%) 12.30 17.88 22.26 26.00 29.33 32.37 35.18 37.81 40.29 42.65 44.90 47.06 高(P=40%) 18.88 27.45 34.17 39.91 45.02 49.68 54.00 58.03 61.84 65.46 68.92 72.24 极高(P=60%) 31.48 45.77 56.97 66.55 75.07 82.84 90.03 96.76 103.12 109.15 114.92 120.45 软硬相间 低(P=15%) 9.79 13.47 16.23 18.52 20.53 22.32 23.96 25.48 26.90 28.23 29.50 30.70 中(P=25%) 11.61 15.97 19.24 21.97 24.34 26.47 28.42 30.22 31.90 33.48 34.98 36.41 高(P=40%) 15.00 20.63 24.86 28.38 31.45 34.20 36.71 39.04 41.21 43.26 45.20 47.05 极高(P=60%) 21.09 29.01 34.96 39.90 44.22 48.09 51.62 54.89 57.95 60.82 63.55 66.15 4. 预警模型检验
本文收集了2020年陇南“8•17”暴洪灾害期间59起滑坡信息及前期降雨资料,其中,滑坡发生与8月11—17日,降雨数据为滑坡附近雨量站点8月5—18日逐日累计降雨数据,共计372条。按照3种岩性类型,分别与上述不同预警等级的降雨阈值曲线对比分析,检验模型的准确性。
根据滑坡事件分析,滑坡多在降雨持续6 d后集中暴发。松散物质类滑坡共计38起,其中,25起滑坡发生前降雨事件位于极高风险区,占比约65.79%;10起位于高风险区(40%≤P<60%),占比约7.89%;3起位于中风险区(25%≤P<40%),占比约0。极软岩类滑坡事件共计9起,其中,8起滑坡时降雨事件位于极高风险区(P≥60%),占比约88.89%;1起位于高风险区(40%≤P<60%),占比约11.11%;中、低风险区(P<40%)无滑坡发生。软硬相间滑坡事件共计12起,其中,10起滑坡降雨事件位于极高风险区(P≥60%),占比约83.33%;1起位于高风险区(40%≤P<60%),占比约8.33%;1起位于低风险区(40%≤P<60%),占比约8.33%;中风险区无滑坡发生(表3、图7)。
表 3 不同岩性类型滑坡事件对应的预警等级Table 3. Warning levels corresponding to landslide events of various lithologic types滑坡类型 预警等级 滑坡/处 事件比例/% 松散物质 低(P<25%) 0 0 中(25%≤P<40%) 3 7.89 高(40%≤P<60%) 10 26.32 极高(P≥60%) 25 65.79 极软岩类 低(P<25%) 0 0 中(25%≤P<40%) 0 0 高(40%≤P<60%) 1 11.11 极高(P≥60%) 8 88.89 软硬相间 低(P<25%) 1 8.33 中(25%≤P<40%) 0 0 高(40%≤P<60%) 1 8.33 极高(P≥60%) 10 83.33 综上所述,位于极高风险预区的降雨事件,比例最低的为松散物质类滑坡,占比65.79%,其次为软硬相间滑坡,占比83.33%,最高为极软岩类滑坡,占比88.89%,但都大于60%,因此,极高风险阈值曲线基本准确。
5. 结论
(1)白龙江流域甘肃段地质灾害数量多,严重威胁当地群众的生命财产安全,制约社会经济发展,针对降雨引发斜坡类灾害研究较少,本文为开展该区地质灾害预警预报模型研究提供了新思路。
(2)基于频率法建立了白龙江流域不同岩性特征的滑坡降雨阈值ED模型,并给出了累计雨量下限阈值,对白龙江流域斜坡类灾害预警预报具有指导意义。
(3)通过2020年陇南“8•17”暴洪灾害期间,降雨引发的59起滑坡事件前期降雨量分析对比,引发滑坡的降雨事件约65.79%以上均位于极高风险预警区,与极高风险(P>60%)阈值曲线一致。
(4)本文获取的滑坡下限降雨预警曲线,只能通过已发生的滑坡灾害结合前期降雨事件来验证模型准确性,对滑坡发生前的预警曲线校验存在困难,下一步研究中应考虑滑坡发生前不同风险等级预警模型或阈值,为斜坡类地质灾害降雨预警预报提供依据。
-
表 1 物探异常推断分析表
Table 1 Geophysical anomaly inference analysis
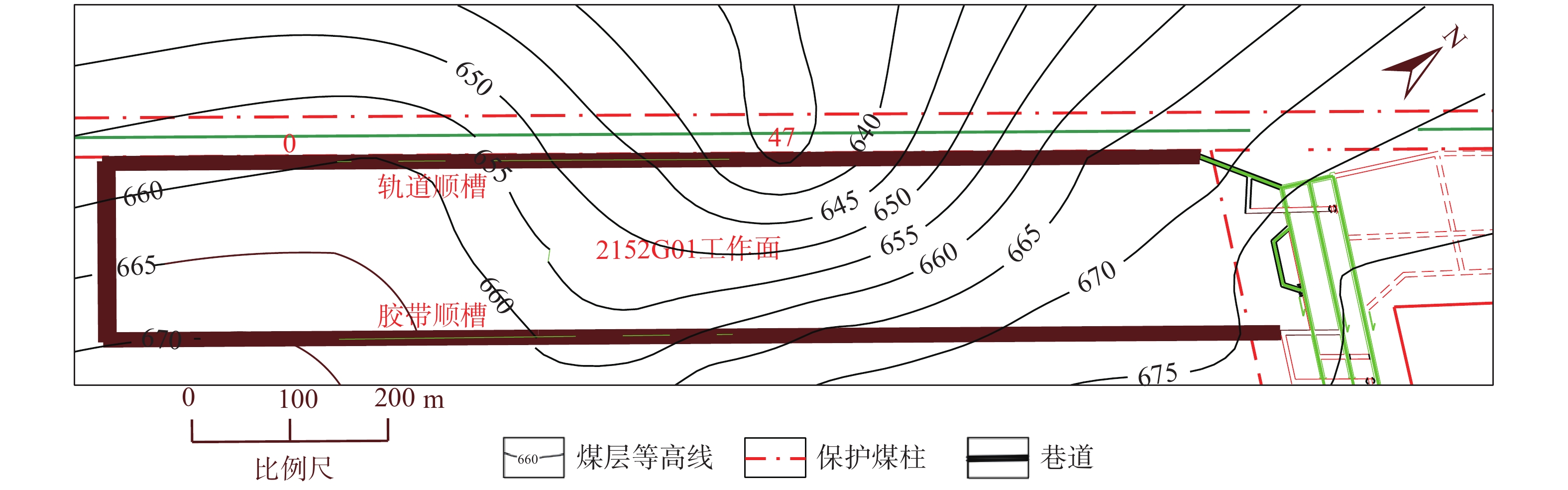
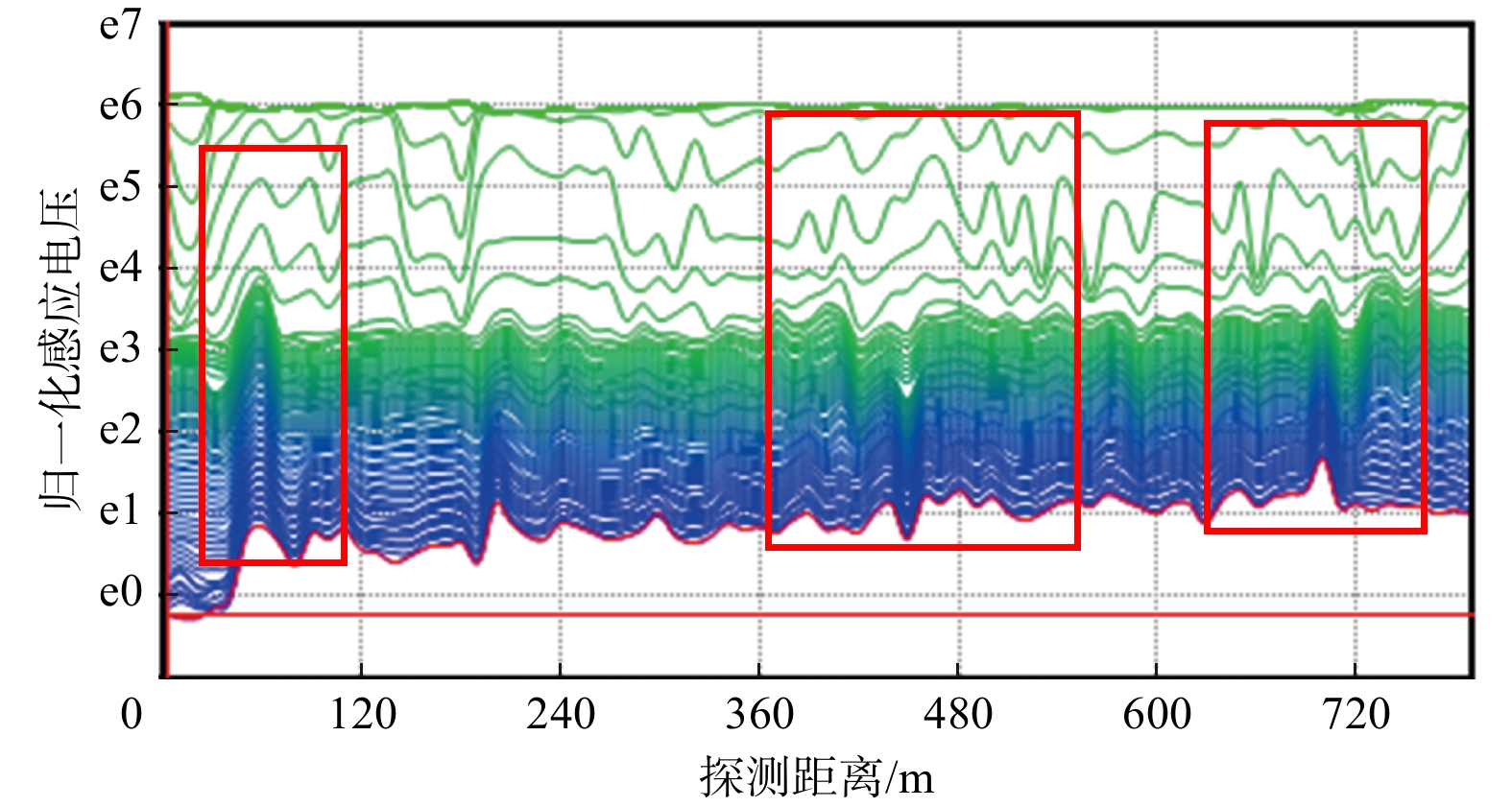
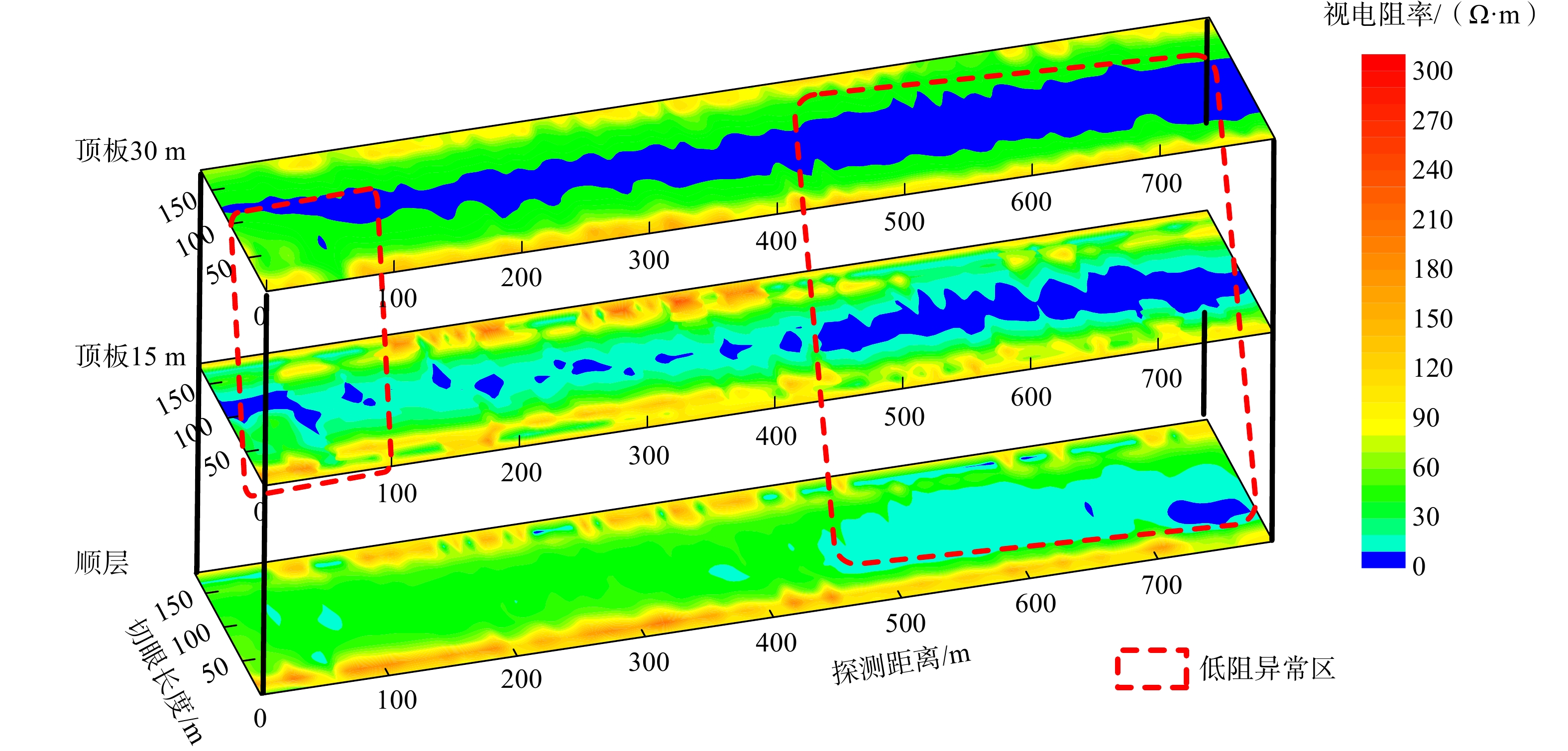
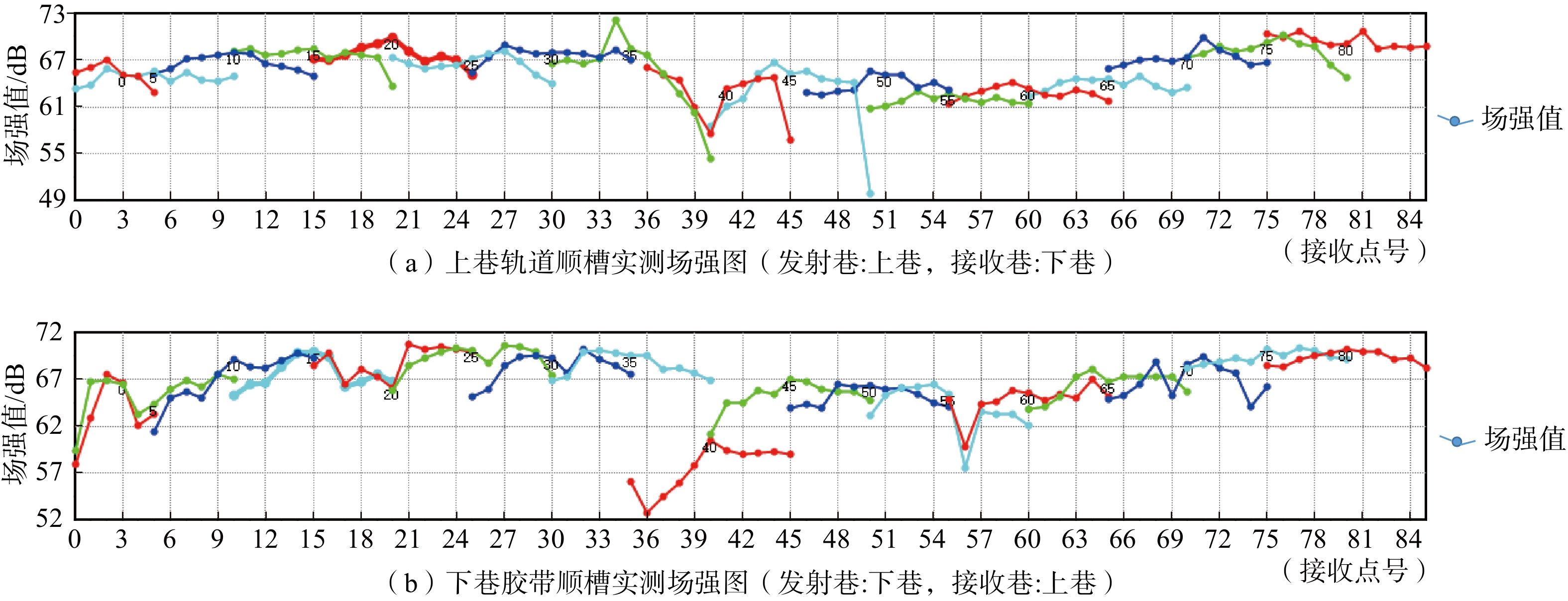
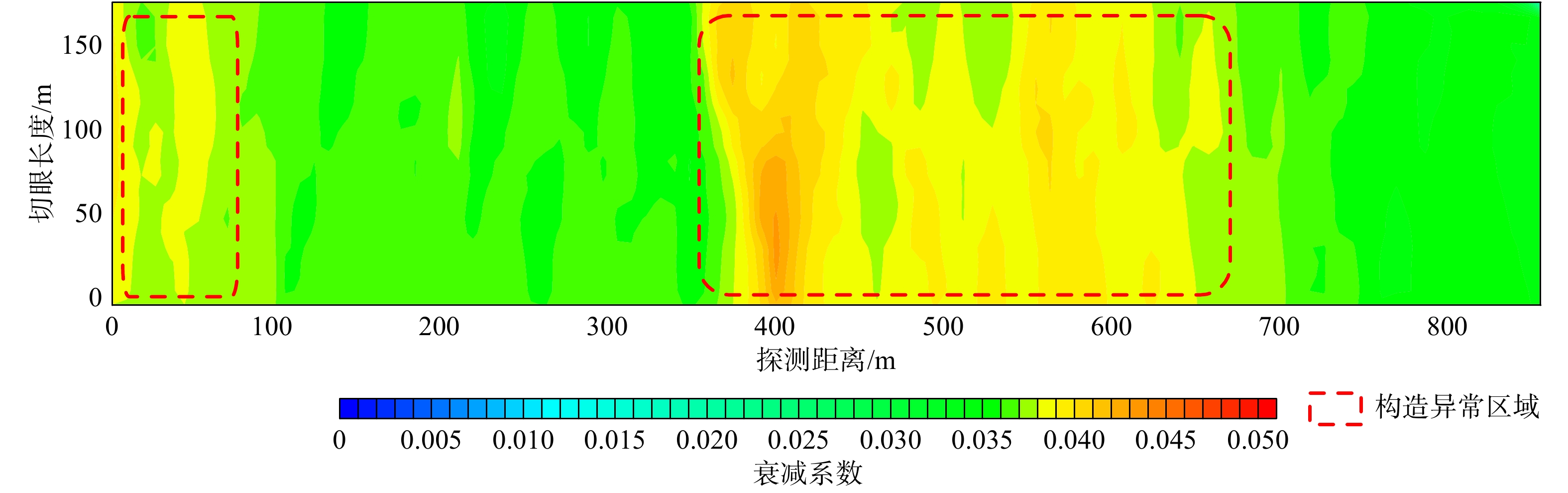
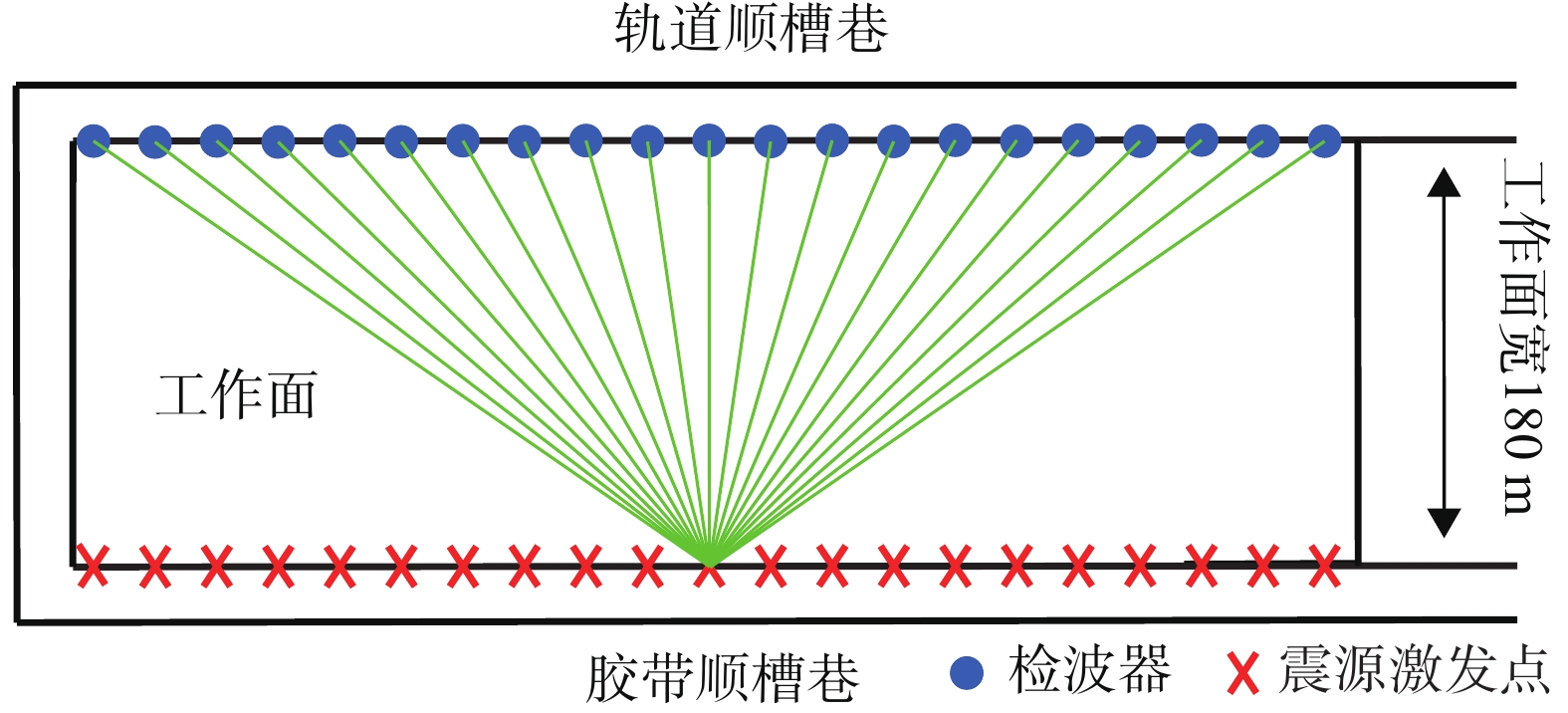
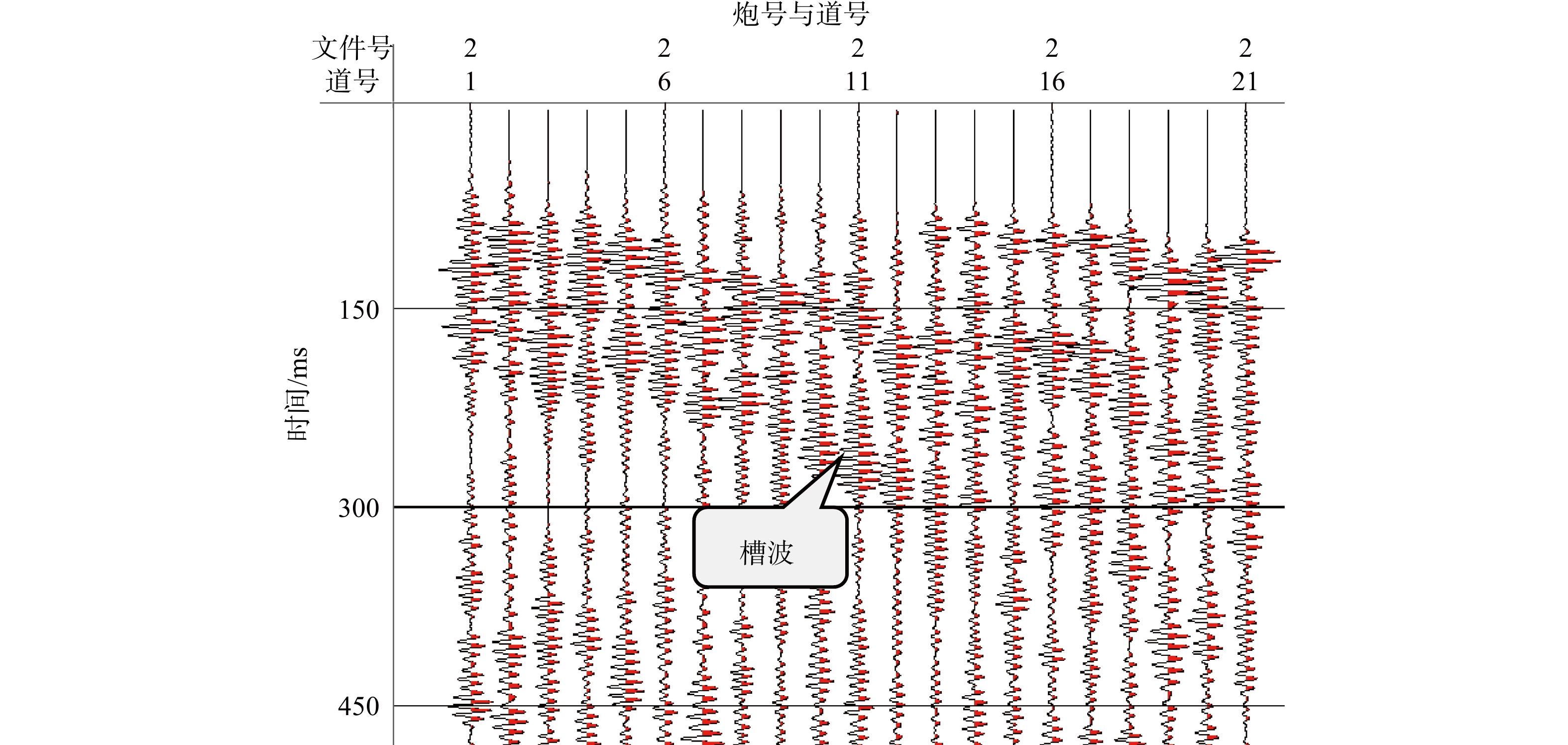
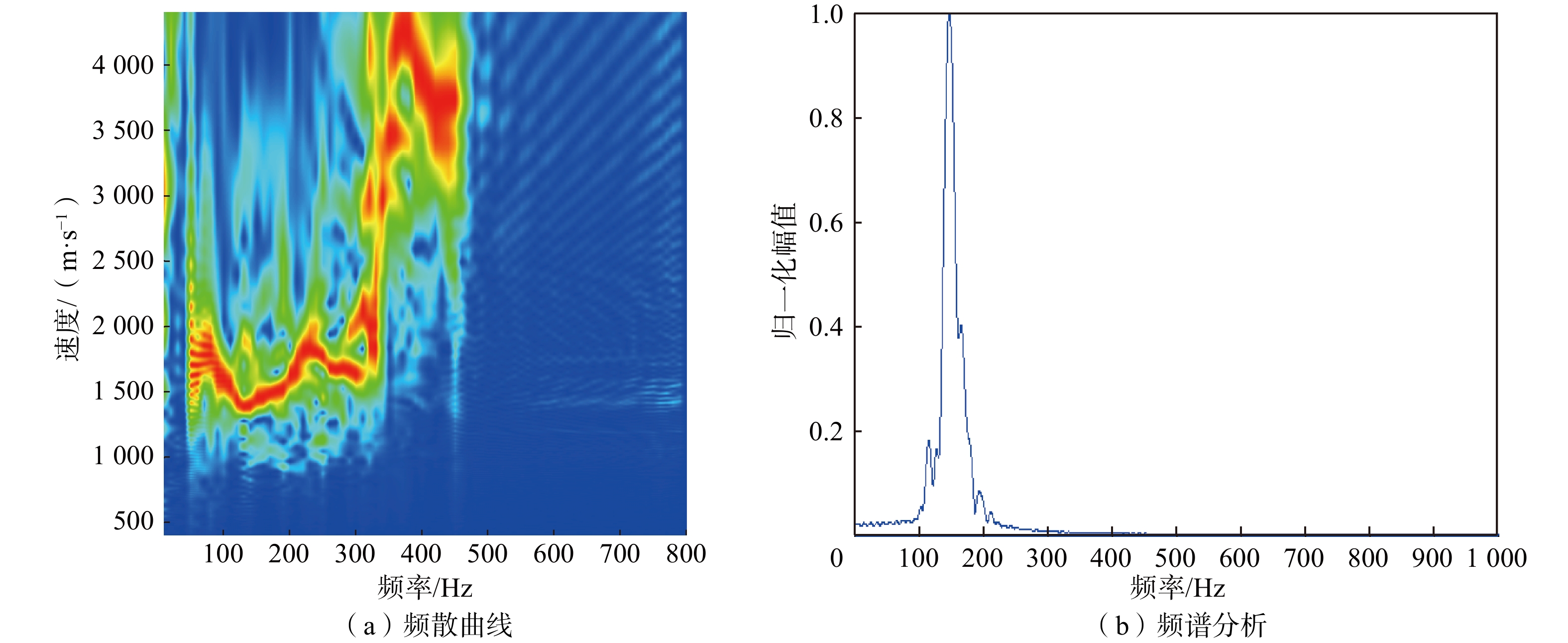
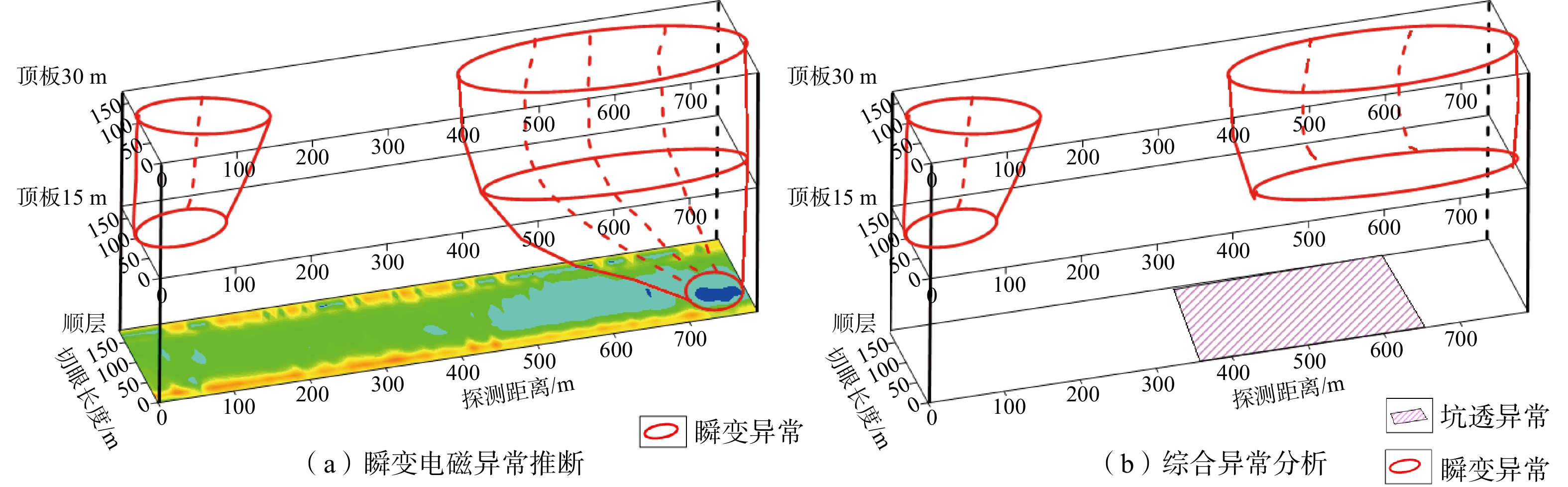
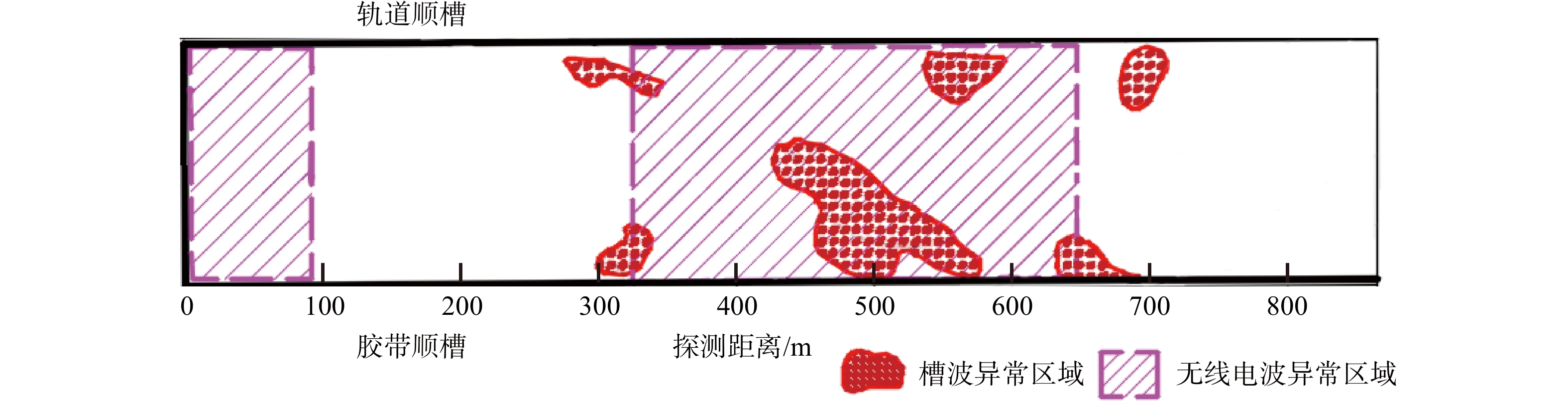
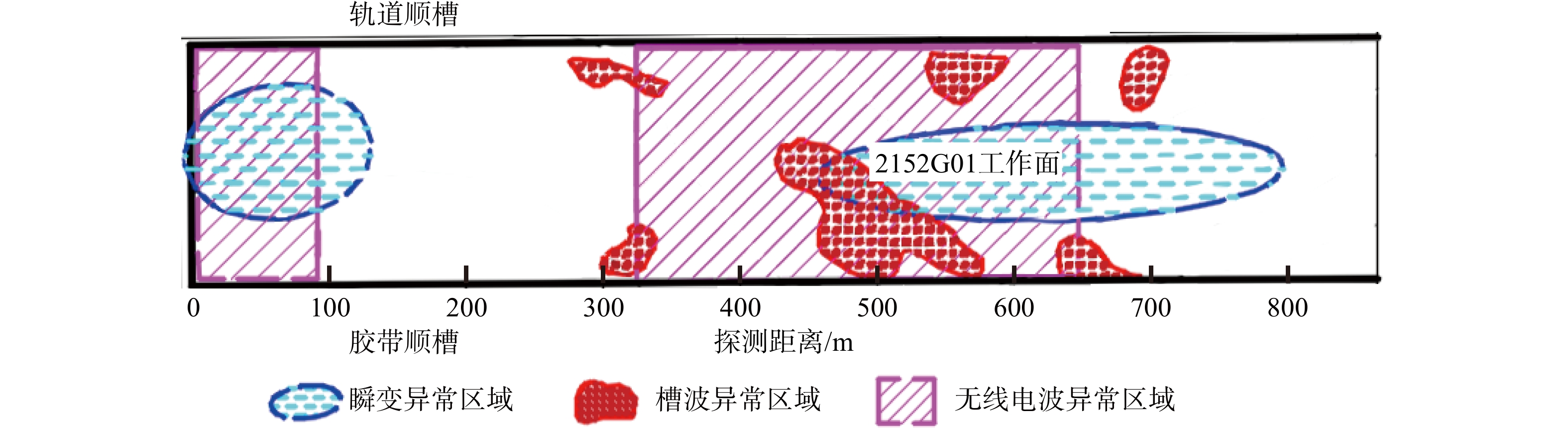
物探方法 异常区域/m 异常推断 导水程度 回采影响 瞬变电磁 0~100 富水区域 弱 一般 500~650 富水区域 强 重大 650~800 富水区域 弱 一般 无线电波 0~80 煤层变化 弱 较大 350~650 地质构造 强 重大 槽波地震 300 地质构造 弱 较大 420~650 地质构造 强 重大 700 地质构造 弱 较大 -
[1] 李江华,廉玉广,焦阳,等. 综合物探技术在工作面导水构造探测中的应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2018,49(3):129 − 132. [LI Jianghua,LIAN Yuguang,JIAO Yang,et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical exploration technique in exploration of water conductive structures in working face[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2018,49(3):129 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Jianghua, LIAN Yuguang, JIAO Yang, et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical exploration technique in exploration of water conductive structures in working face[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2018, 49(3): 129-132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 张平松,胡泽安,吴荣新,等. 煤层工作面地质构造及异常透射CT综合成像方法与应用[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2017,29(9):49 − 52. [ZHANG Pingsong,HU Zean,WU Rongxin,et al. Coal face geological structure and application of anomalous body transmitting CT integrated imaging[J]. Coal Geology of China,2017,29(9):49 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2017.09.10 ZHANG Pingsong, HU Zean, WU Rongxin, et al. Coal face geological structure and application of anomalous body transmitting CT integrated imaging[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2017, 29(9): 49-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2017.09.10
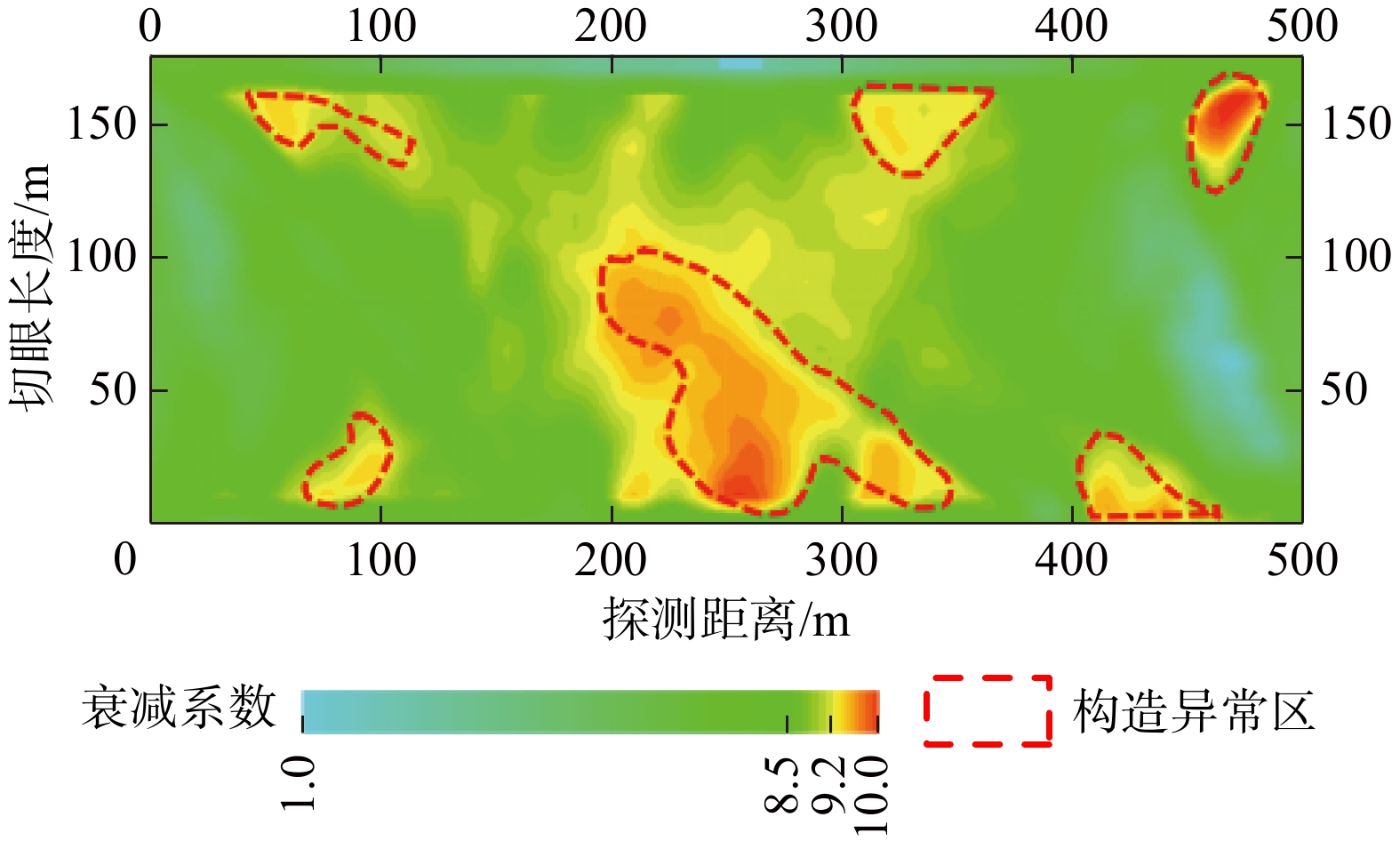
[3] 马志超,杨高峰,王克南. 利用透射槽波衰减系数探查煤层内部的断层响应特征研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2021,40(3):49 − 51. [MA Zhichao,YANG Gaofeng,WANG Kenan. Fault response characteristics of coal seam are investigated by using attenuation coefficient of transmitted in-seam wave[J]. Coal Technology,2021,40(3):49 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA Zhichao, YANG Gaofeng, WANG Kenan. Fault response characteristics of coal seam are investigated by using attenuation coefficient of transmitted In-seam wave[J]. Coal Technology, 2021, 40(3): 49-51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 辛光明,邢文彬,武凯,等. 阳城煤矿断层导水灾害“挡-堵”多体系防治技术[J]. 煤矿安全,2019,50(5):91 − 94. [XIN Guangming,XING Wenbin,WU Kai,et al. Multi-system prevention and control technology of “blocking-plugging” in fault water guiding disaster of Yangcheng coal mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2019,50(5):91 − 94. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIN Guangming, XING Wenbin, WU Kai, et al. Multi-system prevention and control technology of “blocking-plugging” in fault water guiding disaster of Yangcheng coal mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50(5): 91-94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 牟义,李江华,徐慧,等. 矿井瞬变电磁法参数优化试验及超前探测应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(6):184 − 190. [MU Yi,LI Jianghua,XU Hui,et al. Parameters optimization test of mine transient electromagnetic method and application of advanced detection[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(6):184 − 190. (in Chinese with English abstract) MU Yi, LI Jianghua, XU Hui, et al. Parameters optimization test of mine transient electromagnetic method and application of advanced detection[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(6): 184-190. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李宏杰,黎灵,李健,等. 采动覆岩导水断裂带发育高度研究方法探讨[J]. 金属矿山,2015(4):1 − 6. [LI Hongjie,LI Ling,LI Jian,et al. Discussion on the methods for determining the height of fractured water-conducting zone[J]. Metal Mine,2015(4):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Hongjie, LI Ling, LI Jian, et al. Discussion on the methods for determining the height of fractured water-conducting zone[J]. Metal Mine, 2015(4): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李宏杰,马君,姜鹏,等. 准格尔煤田岩溶水文地质特征及水害防治技术[J]. 煤矿安全,2018,49(9):246 − 251. [LI Hongjie,MA Jun,JIANG Peng,et al. Karst hydrogeological characteristics and prevention and control technology for water damage in Zhungar coalfield[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2018,49(9):246 − 251. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Hongjie, MA Jun, JIANG Peng, et al. Karst hydrogeological characteristics and prevention and control technology for water damage in zhungar coalfield[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2018, 49(9): 246-251. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 牟义,邱浩,牛超,等. 多源干扰条件下瞬变电磁法电性响应规律研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2019,34(6):2493 − 2502. [MU Yi,QIU Hao,NIU Chao,et al. Study on the electrical response law of transient electromagnetic method under multi-source interference conditions[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2019,34(6):2493 − 2502. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.6038/pg2019CC0434 MU Yi, QIU Hao, NIU Chao, et al. Study on the electrical response law of transient electromagnetic method under multi-source interference conditions[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(6): 2493-2502. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.6038/pg2019CC0434
[9] 牟义,徐慧,马志超,等. 带压综采工作面矿井综合物探及安全性评价研究[J]. 重庆大学学报,2019,42(12):41 − 49. [MU Yi,XU Hui,MA Zhichao,et al. Comprehensive geophysical exploration and safety evaluation of the mine with a fully mechanized pressurized mining face[J]. Journal of Chongqing University,2019,42(12):41 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2019.12.005 MU Yi, XU Hui, MA Zhichao, et al. Comprehensive geophysical exploration and safety evaluation of the mine with a fully mechanized pressurized mining face[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2019, 42(12): 41-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2019.12.005
[10] 李文,牟义,邱浩. 煤矿含水异常体矿井综合物探方法及应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2017,48(7):208 − 211. [LI Wen,MU Yi,QIU Hao. Application of mine comprehensive geophysical detection methods on water bearing abnormal bodies[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2017,48(7):208 − 211. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Wen, MU Yi, QIU Hao. Application of mine comprehensive geophysical detection methods on water bearing abnormal bodies[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2017, 48(7): 208-211. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 牟义. 切片技术在煤矿回采工作面瞬变电磁法探测中的研究与应用[J]. 中国煤炭,2014,40(3):35 − 39. [MU Yi. Research and application of slicing technology in transient electromagnetic detection in coal mining face[J]. China Coal,2014,40(3):35 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.19880/j.cnki.ccm.2014.03.008 MU Yi. Research and application of slicing technology in transient electromagnetic detection in coal mining face[J]. China Coal, 2014, 40(3): 35-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.19880/j.cnki.ccm.2014.03.008
[12] 马志超,廉玉广,牟义,等. 煤矿井下探测中影响不含水断层视电阻率变化的单一主控因素分析[J]. 能源与环保,2020,42(12):106 − 111. [MA Zhichao,LIAN Yuguang,MU Yi,et al. Analysis of single main controlling factor affecting change of apparent resistivity of water-free faults in underground coal mine exploration[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection,2020,42(12):106 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA Zhichao, LIAN Yuguang, MU Yi, et al. Analysis of single main controlling factor affecting change of apparent resistivity of water-free faults in underground coal mine exploration[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2020, 42(12): 106-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 廉玉广,马志超,李江华,等. 岩石单轴加载破坏全过程波速变化特征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(8):64 − 69. [LIAN Yuguang,MA Zhichao,LI Jianghua,et al. Study on variation characteristics of wave velocity in whole process of rock uniaxial loading failure[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(8):64 − 69. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIAN Yuguang, MA Zhichao, LI Jianghua, et al. Study on variation characteristics of wave velocity in whole process of rock uniaxial loading failure[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(8): 64-69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李江华,廉玉广,马志超. 受载岩体破坏全过程声波响应特征及工程意义[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(2):106 − 112. [LI Jianghua,LIAN Yuguang,MA Zhichao. Acoustic response characteristics and engineering significance of loaded rock during failure process[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(2):106 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Jianghua, LIAN Yuguang, MA Zhichao. Acoustic response characteristics and engineering significance of loaded rock during failure process[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(2): 106-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 焦阳,廉玉广,李梓毓,等. 综合矿井物探技术在陷落柱探测中的应用[J]. 煤矿开采,2018,23(6):16 − 18. [JIAO Yang,LIAN Yuguang,LI Ziyu,et al. Application of integrated geophysical techniques in collapse column exploring[J]. Coal Mining Technology,2018,23(6):16 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIAO Yang, LIAN Yuguang, LI Ziyu, et al. Application of integrated geophysical techniques in collapse column exploring[J]. Coal Mining Technology, 2018, 23(6): 16-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 李忠华,梁影,包思远,等. 断层冲击地压的影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):126 − 131. [LI Zhonghua,LIANG Ying,BAO Siyuan,et al. Analysis on influence factors of the fault rock burst[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):126 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Zhonghua, LIANG Ying, BAO Siyuan, et al. Analysis on influence factors of the fault rock burst[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(3): 126-131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张平松,欧元超,李圣林. 我国矿井物探技术及装备的发展现状与思考[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(7):1 − 15. [ZHANG Pingsong,OU Yuanchao,LI Shenglin. Development quo-status and thinking of mine geophysical prospecting technology and equipment in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(7):1 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.07.001 ZHANG Pingsong, OU Yuanchao, LI Shenglin. Development quo-status and thinking of mine geophysical prospecting technology and equipment in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(7): 1-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.07.001
[18] 赵虎,张泉,谭建秋,等. 基于综合物探方法的公路不稳定边坡潜在滑面探测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):117 − 122. [ZHAO Hu,ZHANG Quan,TAN Jianqiu,et al. Detection of the potential failure zones of the unstable slopes along highway using comprehensive geophysical methods[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):117 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.01-14 ZHAO Hu, ZHANG Quan, TAN Jianqiu, et al. Detection of the potential failure zones of the unstable slopes along highway using comprehensive geophysical methods[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(1): 117-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.01-14
[19] 王瑞丰,温来福,程久龙,等. 高密度电法与瞬变电磁法联合勘查河北承德地区基岩裂隙水[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2020,42(6):784 − 790. [WANG Ruifeng,WEN Laifu,CHENG Jiulong,et al. Joint detection of bedrock fissure water using high-density electrical method and transient electromagnetic method in Chengde area of Hebei,China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2020,42(6):784 − 790. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Ruifeng, WEN Laifu, CHENG Jiulong, et al. Joint detection of bedrock fissure water using high-density electrical method and transient electromagnetic method in Chengde area of Hebei, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2020, 42(6): 784-790. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 邓凤茹,赵艳. 基于无线电波坑道透视算法数学模型的研究[J]. 北华航天工业学院学报,2012,22(3):12 − 13. [DENG Fengru,ZHAO Yan. Study of mathematical model based on the algorithm of radio waves tunnels perspective[J]. Journal of North China Institute of Aerospace Engineering,2012,22(3):12 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) DENG Fengru, ZHAO Yan. Study of mathematical model based on the algorithm of radio waves tunnels perspective[J]. Journal of North China Institute of Aerospace Engineering, 2012, 22(3): 12-13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 王启浩,吕亚斌,张德栋. 甘肃省白龙江流域泥沙时空变化特征及演变趋势研究. 江西水利科技. 2025(01): 32-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 龙宇飞. 黄河兰州段白塔山地质灾害现状及生态环境治理探讨. 资源信息与工程. 2025(02): 91-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 曾新雄,刘佳,赖波,赵风顺,江山. 广东珠海市降雨型崩塌滑坡预警阈值研究. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 141-150 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 刘强. 浙江省兰溪市地质灾害致灾雨量阈值分析. 工程技术研究. 2024(23): 45-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:









 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS