Susceptibility assessment of colluvium landslides along the Changyang section of Qingjiang River using Logistic regression and random forest methods
-
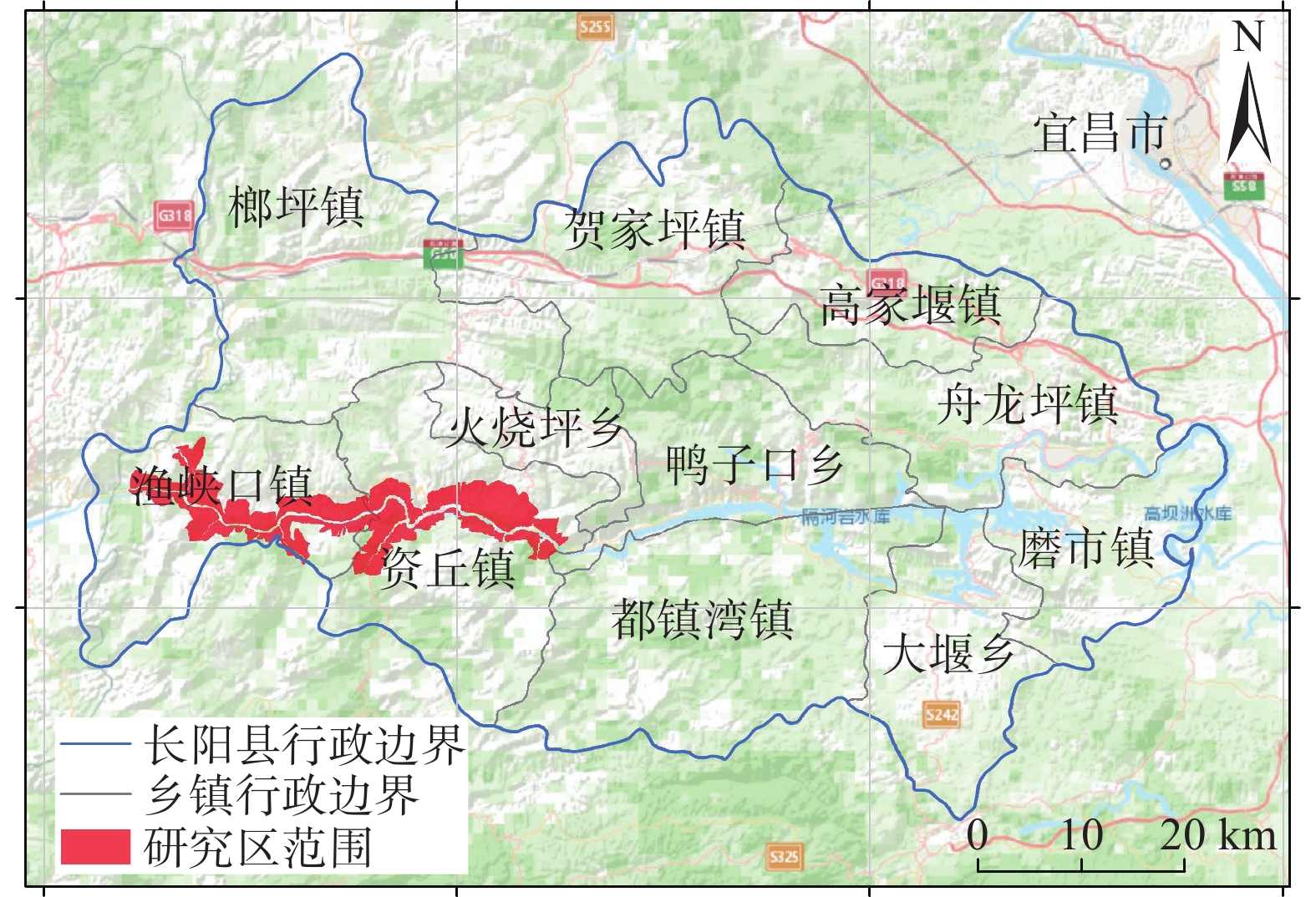
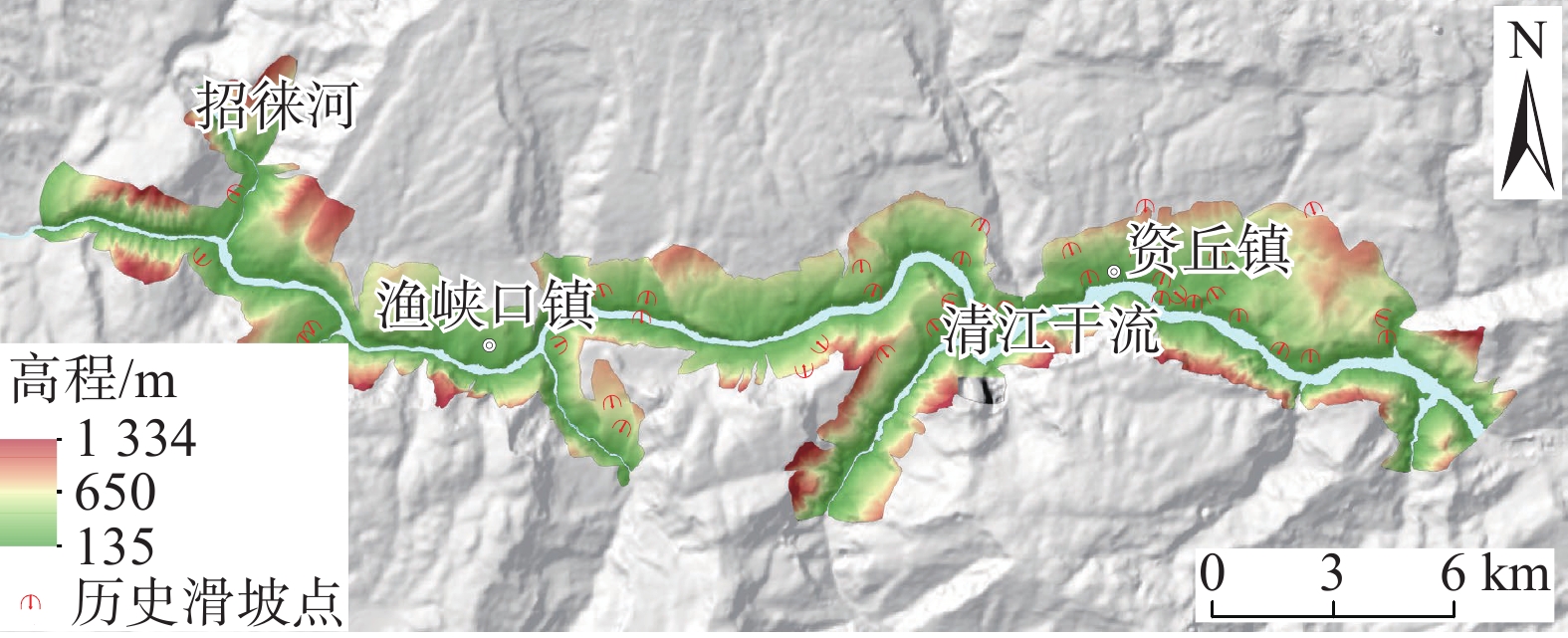
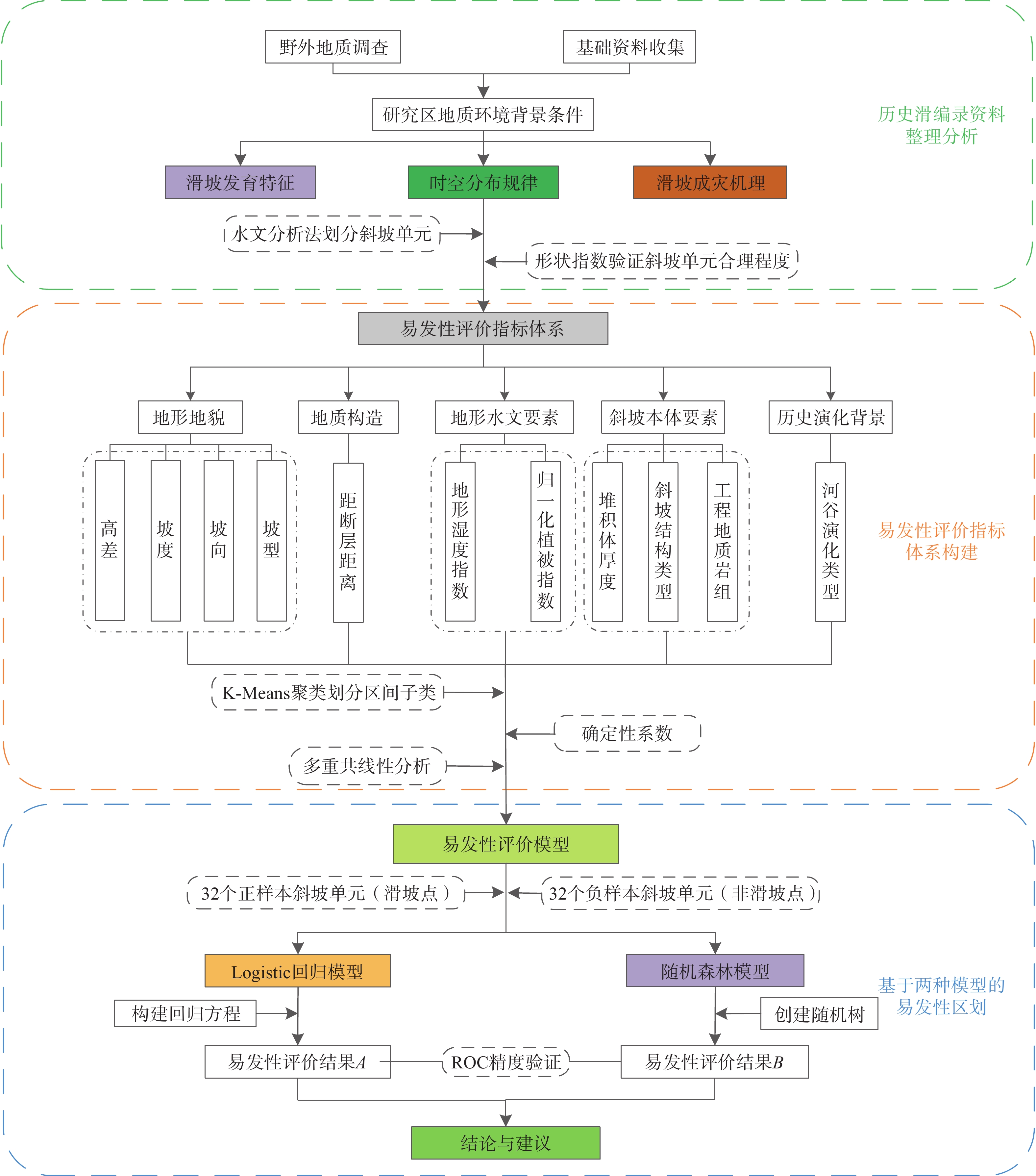
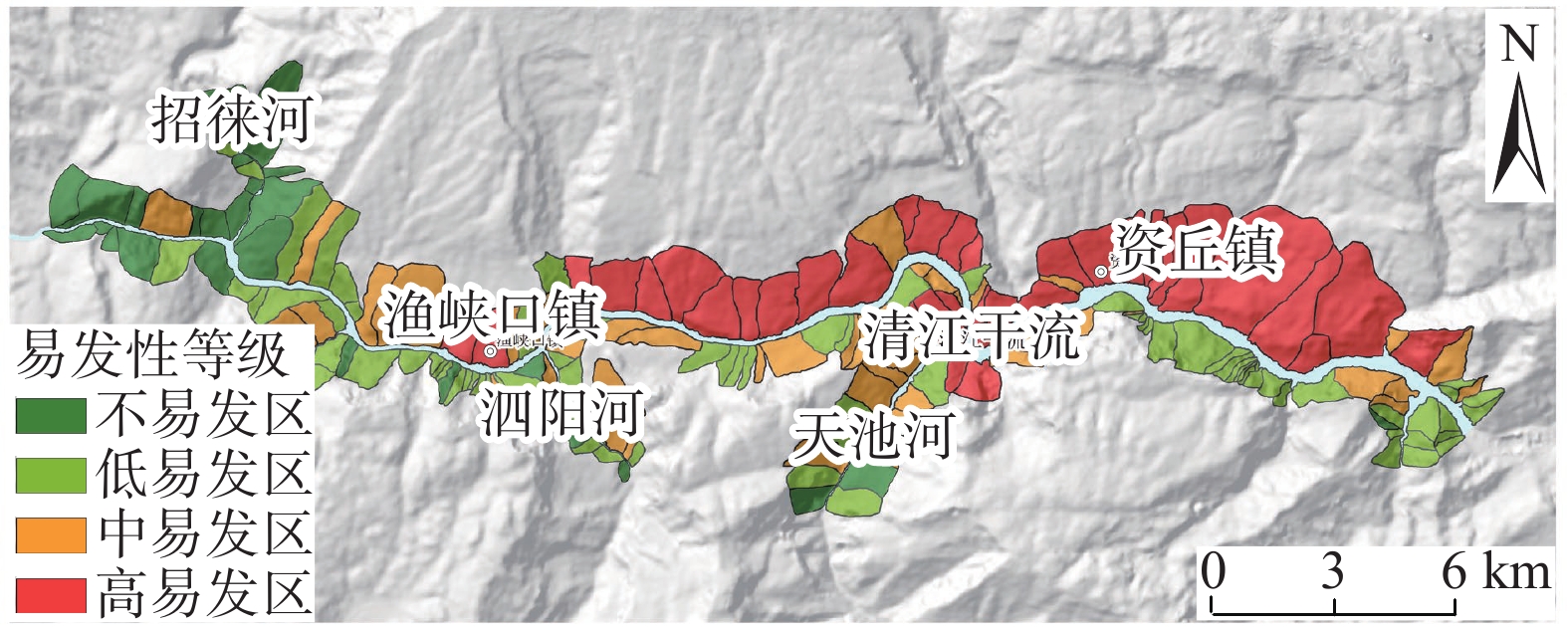
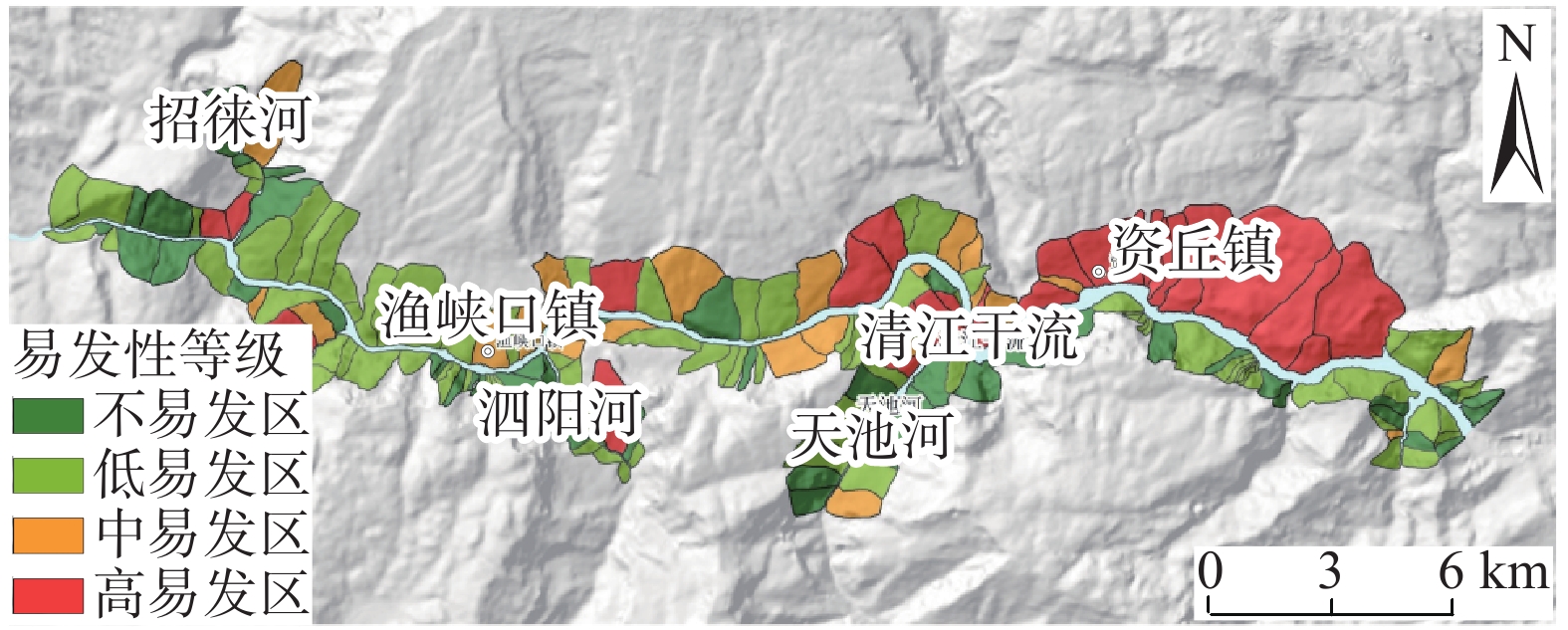
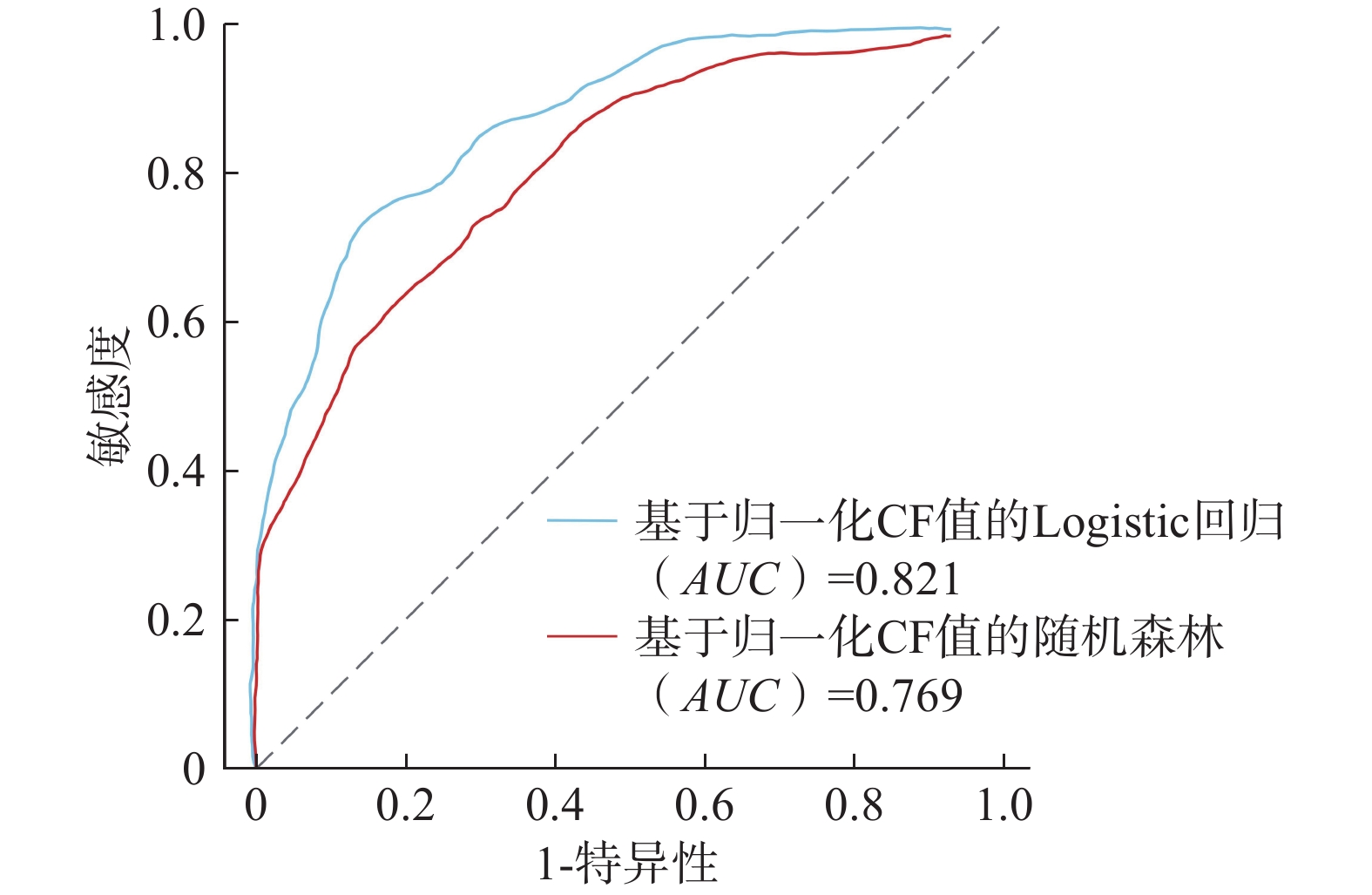
摘要: 清江流域地质环境背景条件复杂,特别是沿清江库岸地质灾害频发;而过往的地质灾害易发性评价多针对行政区域范围,鲜有针对库岸带的专门评价,并且所用评价指标体系的针对性以及评价方法的可靠性仍有进一步提升的空间。为构建一套更加符合清江流域库岸带地质灾害发育特征的易发性评价指标体系,获得更加准确、适用性强的易发性区划成果,以清江流域渔峡口—资丘段为研究区,以两岸涉水斜坡体为研究对象,以斜坡单元为评价单元,构建坡度、坡向、高差、坡型、归一化植被指数、地形湿度指数、斜坡结构类型、工程地质岩组、堆积层厚度、河谷演化类型等10个指标组成的易发性评价体系;采用基于归一化确定性系数的Logistic回归和随机森林方法构建评价模型并得到不同易发性区划成果。评价结果显示:高易发区主要分布于清江干流渔峡口东—资丘东段左岸顺向斜坡体的中−下部涉水区域,且Logistic回归模型在地形地貌复杂的库岸段的适用性要优于随机森林模型。研究表明:所选堆积层厚度及河谷演化类型指标很好地代表了清江库岸段的独特地质背景条件特点;在非行政区划范围的特定研究区且当历史滑坡样本数量有限的情况下,Logistic回归模型能够较好地学习灾害发育规律并具备可靠的易发性预测能力。
-
关键词:
- 堆积层滑坡 /
- Logistic回归 /
- 随机森林 /
- 易发性评价
Abstract: The geological and environmental background conditions of the Qingjiang River Basin are highly complex, particularly with frequent geological disasters along the Qingjiang reservoir bank. Previous susceptibility assessment for geological disasters was mostly focused on administrative areas and seldom specialized evaluations for the reservoir bank zone. Furthermore, there is still room for improvement in the evaluation index system, as well as in the pertinence and reliability of the evaluation method. To address these shortcomings, a more suitable susceptibility evaluation index system was constructed to obtain accurate and applicable susceptibility zoning results. The Yuxiakou to Ziqiu section of the Qingjiang River Basin was chosen as the research area, with the wading slope body on both sides of the river selected as the research object and the slope unit chosen as the evaluation unit. A susceptibility evaluation system composed of ten indicators, including slope, aspect, elevation range, slope type, NDVI, TWI, slope structure type, engineering geological rock formation, accumulation thickness, and valley evolution, was constructed.The logistic regression and random forest methods were used to construct the evaluation model based on the normalized certain factors, and different susceptibility zoning results were obtained. According to the evaluation results, the high-prone areas were mainly distributed in the middle to lower water wading areas of the left bank from the east of Yuxiakou to the east of Ziqiu, along the main stream of the Qingjiang River. The logistic regression model showed better applicability in the reservoir-bank section with complex topography and landforms. The research revealed that the accumulation thickness and valley evolution indicators were effective in representing the unique geological background conditions of the Qingjiang reservoir bank. The logistic regression model was able to learn the developmental law of disasters and has a reliable susceptibility prediction ability. -
《中国地质灾害与防治学报》(双月刊)是由中国地质调查局主管,中国地质环境监测院、中国地质灾害防治与生态修复协会主办,反映地质灾害学科并向国内外公开发行的学术性刊物。由于贯彻了“双百”方针,理论与实践密切结合,充分运用地质灾害防治技术,重视办刊质量,因而受到同行的好评。欢迎广大科技人员和读者积极投稿。
一. 征稿范围
主要刊登范围:重点刊登地质灾害发生发展机理、成灾模式与应急处置、地质灾害链及风险评价、调查/监测/预警与综合防治,空天地一体化早期识别和普适型监测仪器研发,重大工程沿线地质灾害研究与防治等方面的创新性研究成果。
本刊物主要面向国内工程地质学科发展、地质工程建设、技术方法创新、地质环境开发与保护等方面的院校教师、研究生及科技人员。期刊最初定位是服务于生产一线的野外工作者。是我国工程地质、环境地质、特别是地质灾害研究(地质灾害防治及地质环境保护)等领域的综合性学术理论与实践相结合的地质学类权威性刊物。
二. 征稿内容
理论研究与调查评价栏目:重点针对单体单灾分析研究与调查评价;
技术方法与防治工程栏目:技术方法,是指勘察、监测、防治等具体的技术方法,不是评价方法和研究方法,这是业界约定俗成的共识;
综合研究与区划栏目:对多灾种综合研究、区域性灾害研究和易发性、危险性和风险评价与区划。
三. 稿件要求
(一) 稿件结构要求
0 引言(Introduction)
以简短的文字介绍写作背景和目的,以及相关领域内前人所作的工作和研究的概况(即前人研究进展的综述),说明本研究与前人研究工作的关系,目前研究的热点和存在的问题;以便读者了解该文的概貌,起导读的作用。基本内容应包括:
(1)简要叙述研究此项工作的起因和目的(研究背景);(2)国内外对此项工作的研究现状和研究动态(并指出存在的问题);(3)强调此项研究工作拟解决现有研究中存在问题中的哪个问题,以及研究解决这些问题的重要性和意义;(4)适当说明研究假设。
1 材料与方法(Methods)
这是论文的重要部分。重点阐述两方面的内容,一是用什么做研究(即研究所用的材料),二是怎么做研究(从事研究所用的方法)。如果采用的方法是按照前人的,或者即使有所改进,也必须标注参考文献。
不同的课题有不同的研究方法,以试验研究方法为例,其内容应包括:(1)研究的对象及其取样;(2)仪器设备的应用;(3)相关因素和无关因素的控制;(4)操作程序与方法;(5)操作性概念的界定;(6)研究结果的统计方法。针对基于地质调查的研究论文,可将第1节设置为“研究区地质背景”,其内容包括:(1)野外调查工作和试验室测试所用的技术方法或技术手段(野外工作技术路线),开展完成的主要工作(及其量);(2)所得到第一手资料情况以及开展综合研究所应用的基础数据(包括利用前人已有数据)情况;(3)室内综合研究所用的方法(技术路线)。
2 结果(Results)
结果是论文的核心(主体部分),主要论述通过试验研究得到了什么数据、规律和发现等(可包括试验和研究的结果、数据,被确定的关系,观察或得到的效果、性能等)。
结果内容的表达:(1)数据,不用原始数据,要经统计学处理;(2)图表,用于显示规律性和对比性;(3)照片,能形象客观地表达研究结果;(4)文字,对数据、图表、照片加以说明。
结果的写作应注意:(1)按试验所得到的事实材料进行安排,可分段、分节,可加小标题;(2)解释客观结果,不要外加作者的评价、分析和推理;(3)结果要真实性,不可将不符合主观设想的数据或其它结果随意删除;(4)因图表和照片所占篇幅较大,能用文字说明的问题,尽可能少用或不用图表或照片。
3 讨论(Discussion)
讨论是论文的重要主体部分,是作者对研究得到的资料进行归纳、概括和探讨,提出自己的见解,评价其意义。
讨论的内容包括:(1)对试验观察过程中各种数据或现象的理论分析和解释;(2)评估研究方法的科学性,评估自己结果的正确性和可靠性,与他人结果比较异同,并解释其原因;(3)试验结果的理论意义及对实践的指导作用和应用价值;(4)作用机制或变化规律的探讨;(5)本研究还存在的局限性以及进一步研究的建议。
4 结论(及建议)(Conclusion)
这是论文的精髓部分。要回答研究出了什么,主要内容应包括:
(1)由研究结果所揭示的原理及其普遍性(即本研究结果说明了什么问题,得出了什么规律性的东西,解决了什么理论或实际问题);
*(2)研究中有无例外或本论文尚难解决的问题(还有哪些问题没有解决),与以前以发表论文的异同,在理论与实践上意义;
*(3)对进一步研究的建议。
需要特别注意的是,结论不是摘要的简单重复。结语部分文字要简洁,逐条写出,3~4 条为宜。
(二) 稿件内容要求
(1)论文标题需明确、精练,体现创新点。具体要求:
● 阐述具体,用语简洁。题目不足以概括论文内容时,可加副标题;
● 文题相称、确切鲜明,标题体现内容,内容说明标题;
● 重点突出、主题明确,突出论文创新点,高度概括,一目了然。
(2)基金资助的研究项目,需注明资助项目来源及编号。
(3)作者一般只列出主要参加者。第一作者和通讯作者附简介:姓名(出生年—),性别,学历,职称,主要从事工作或研究方向,E-mail。
(4)摘要应具有独立性和自明性,即通过阅读摘要就能获得必要的信息。摘要的内容包括研究目的、方法、结果和结论,也可适当增加背景和意义,500字左右。英文摘要与中文摘要内容基本一致,可以适当扩充。关键词5~8个,要严格筛选,选用实词,充分、准确、全面地反映文章的中心内容。具体要求:
● 目的(objective):阐述论文要解决的问题及其起源、由来(适当突出问题的重要性和目前存在的不足,指出你的论文工作要解决存在的不足中的什么问题);
● 方法(methods):说明论文采用的主要手段(方法),必要时介绍使用手段的方式;
● 结果(results):说明研究内容中得出的主要结果,得到了什么数据、规律和发现等;
● 结论(conclusions):说明研究结果有什么含义、影响和意义(理论意义或实用价值、推广前景等)。
(5)全文一般不超过 10 个版面(包括图、表)。
(6)论文需符合科技论文体裁,论点明确,论据充分,论述严谨,结论可信,语句通达,逻辑严密。
(7)正文采用 3 级标题,即:一级标题如“2 模型建立及计算方法”;二级标题如“2.1 模型建立”;三级标题如 “2.1.1 模型建立基本原则”或“(1)模型建立基本原则”。
(8)提供必要的图表。表格一般采用三线表,使用国家法定计量单位,采用国际标准符号。图件采用通用制图软件制作,单栏图宽不超过 8 cm,通栏图宽不超过 16 cm,图面内容主题突出、结构合理、图面清晰,图中内容要与图注和正文叙述相符。中、英文图表名齐全,图名置于图件之下,表名置于表格之上。
(9)论文要突出反映基础和试验数据,对前人研究成果及存在问题或不足要进行充分的总结、分析。
(10)参考文献遵循“最新、关键、必要和亲自阅读过”的原则,采用顺序编码制,在正文中用“[ 1 ]”或“[1-2]”在引用处标注。所有文献需用信息资源原语种著录,中文文献需列出英译文。
列出论文参考文献的目的是让读者了解论文研究命题的来龙去脉,便于查找,同时也是尊重前人劳动,对自己的工作有准确的定位。一切粗心大意、不查文献,故意不引、自鸣创新,贬低别人、抬高自己,避重就轻、故作姿态的做法都是错误的。
四. 稿件录用
(1)本刊只接收网络投稿,投稿网址为http://www.zgdzzhyfzxb.com。
(2)自收稿日起 3 个月内,编辑部通知作者稿件处理结果。退稿不附详细意见。
(3)作者收到修改通知后 2 个月内返回修改稿。逾期(特殊原因且已向编辑部说明者除外)视为自动撤稿。
(4)期刊不收取审稿费,按规定收取版面费和支付稿费(含印刷版、光盘版和网络版),每篇论文赠送当期刊物 2 本。
(5)为了保证期刊正常出版,《中国地质灾害与防治学报》收取版面费,需要由作者或其所在机构、基金资助项目等支付。如果作者确无课题经费支付版面费可申请减免。申请方式:作者提交经单位科研管理部门盖章的书面申请,并提供单位科研管理部门的联系电话,编辑部经确认后即可减免。
论文出版版面费收费标准为:每面收取300元;加急论文出版版面费收费标准为:每面收取600元。
五. 声明
作者应对所投稿件拥有无可争议的著作权,且文责自负。作者应保证稿件未一稿多投,且保证我刊的首发权。稿件一旦被本刊录用,作者即将论文整体及附属于论文的图表等可许可使用的著作权(包括但不限于复制权、发行权、信息网络传播权、翻译权、汇编权),转交给本刊。许可期限为论文著作权的法定保护期,许可地域范围为全世界。作者依著作权法行使上述权利或向第三方转让上述权利时,不得损害本刊利益,如汇编入其他论文集时,必须注明曾在本刊刊出,并注明刊载年、卷、期。
(2022 年 2 月修订)
-
表 1 评价指标来源及处理方式
Table 1 Sources and processing methods of the evaluation indicators
评价指标 来源 数据类型 子类划分方式说明 坡度 5mDEM(栅格) 连续型 (1)归一化植被指数、地形湿度指数:用K-means聚类法将指标分为5个子类区间
(2)堆积层厚度:由野外实测堆积层点数据通过经验贝叶斯克里金法插值为面数据,用K-means聚类法分为5个子类区间
(3)工程地质岩组分为6个子类区间:Ⅱ-1(坚硬−较坚硬碎屑岩)、Ⅱ-4(较坚硬碎屑岩)、Ⅲ-1(坚硬碳酸盐岩)、Ⅲ-2(坚硬碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩)、Ⅲ-3(较坚硬碳酸盐岩)、Ⅲ-4(较坚硬碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩)
(4)斜坡结构类型分为4个:顺向坡、斜向坡、横向坡、逆向坡
(5)河谷演化类型分为2个:迁移性河谷、持续性河谷
(6)坡向分为8个:北-东北-东-东南-南-西南-西-西北
(7)坡型分为3个:凸形坡、平直坡、凹形坡高差 5mDEM(栅格) 连续型 归一化植被指数 Landsat8-OLT(栅格) 连续型 地形湿度指数 5mDEM(栅格) 连续型 距断层距离 线数据(矢量) 连续型 堆积层厚度 点数据(矢量) 连续型 工程地质岩组 面数据(矢量) 分类型 斜坡结构类型 面数据(矢量) 分类型 河谷演化类型 面数据(矢量) 分类型 坡向 5mDEM(栅格) 分类型 坡型 5mDEM(栅格) 分类型 -
[1] 雷深涵,华骐,郭峰,等. 长阳县地质灾害发育特征[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2013,24(1):30 − 35. [LEI Shenhan,HUA Qi,GUO Feng,et al. Characteristics of the geological hazards in Changyang[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2013,24(1):30 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) LEI Shenhan, HUA Qi, GUO Feng, et al. Characteristics of the geological hazards in Changyang[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2013, 24(1)30-35(in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 肖尚德,李智民,刘云彪,等. 湖北省清江流域滑坡分布规律与减灾对策研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(4):514 − 521. [XIAO Shangde,LI Zhimin,LIU Yunbiao,et al. Distribution law and hazard mitigation strategies of landliides in Qingjing River valley,Hubei[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(4):514 − 521. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIAO Shangde, LI Zhimin, LIU Yunbiao, et al. Distribution law and hazard mitigation strategies of landliides in Qingjing River valley, Hubei[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(4): 514-521. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 王凯,张少杰,韦方强. 斜坡单元提取方法研究进展和展望[J]. 长江科学院院报,2020,37(6):85 − 93. [WANG Kai,ZHANG Shaojie,WEI Fangqiang. Slope unit extraction methods:advances and prospects[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2020,37(6):85 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract) Wang Kai, Zhang Shaojie, Wei Fangqiang. Slope unit extraction methods: advances and prospects[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2020, 37(6): 85-93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] ALVIOLI M,MARCHESINI I,REICHENBACH P,et al. Automatic delineation of geomorphological slope units with r. slopeunits v1.0 and their optimization for landslide susceptibility modeling[J]. Geoscientific Model Development,2016,9(11):3975 − 3991. DOI: 10.5194/gmd-9-3975-2016
[5] SUN Xiaohui,CHEN Jianping,HAN Xudong,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping along the upper Jinsha River,south-western China:A comparison of hydrological and curvature watershed methods for slope unit classification[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2020,79(9):4657 − 4670. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-020-01849-0
[6] 黄立鑫,郝君明,李旺平,等. 基于RBF神经网络−信息量耦合模型的滑坡易发性评价—以甘肃岷县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):116 − 126. [HUANG Lixin,HAO Junming,LI Wangping,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment by the coupling method of RBF neural network and information value:A case study in Min Xian,Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):116 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG Lixin, HAO Junming, LI Wangping, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment by the coupling method of RBF neural network and information value: a case study in Min Xian, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(6)116-126(in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 白光顺,杨雪梅,朱杰勇,等. 基于证据权法的昆明五华区地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(5):128 − 138. [BAI Guangshun,YANG Xuemei,ZHU Jieyong,et al. Susceptibility assessment of geological hazards in Wuhua District of Kuming, China using the weight evidence method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(5):128 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract) [BAI Guangshun, YANG Xuemei, ZHU Jieyong, et al. Susceptibility assessment of geological hazards in Wuhua District of Kuming, China using the weight evidence method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(5): 128-138.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 李光辉,铁永波,白永建,等. 则木河断裂带(普格段)地质灾害发育规律及易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):51. [LI Guanghui,TIE Yongbo,BAI Yongjian,et al. Distribution and susceptibility assessment of geological hazards in Zemuhe fault zone(Puge section)[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):51. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Guanghui, TIE Yongbo, BAI Yongjian, et al. Distribution and susceptibility assessment of geological hazards in Zemuhe fault zone(Puge section)[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3): 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王涛,刘甲美,栗泽桐,等. 中国地震滑坡危险性评估及其对国土空间规划的影响研究[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(1):21 − 39. [WANG Tao,LIU Jiamei,LI Zetong,et al. Seismic landslide hazard assessment of China and its impact on national territory spatial planning[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(1):21 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) [WANG Tao, LIU Jiamei, LI Zetong, et al. Seismic landslide hazard assessment of China and its impact on national territory spatial planning[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(1): 21-39.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] ZHAO Shuai,ZHAO Zhou. A comparative study of landslide susceptibility mapping using SVM and PSO-SVM models based on grid and slope units[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering,2021,2021:1 − 15.
[11] XIAO Ting,YIN Kunlong,YAO Tianlu,et al. Spatial prediction of landslide susceptibility using GIS-based statistical and machine learning models in Wanzhou County,Three Gorges Reservoir,China[J]. Acta Geochimica,2019,38(5):654 − 669. DOI: 10.1007/s11631-019-00341-1
[12] YU Chenglong,CHEN Jianping. Application of a GIS-based slope unit method for landslide susceptibility mapping in Helong city:comparative assessment of ICM,AHP,and RF model[J]. Symmetry,2020,12(11):1848. DOI: 10.3390/sym12111848
[13] 常宏,金维群,王世昌,等. 清江中下游岸坡稳定性对河流地貌过程的响应[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(5):756 − 763. [CHANG Hong,JIN Weiqun,WANG Shichang,et al. Slope stability response to river geomorphic process in middle and lower reaches of Qingjiang River[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(5):756 − 763. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHANG Hong, JIN Weiqun, WANG Shichang, et al. Slope stability response to river geomorphic process in middle and lower reaches of Qingjiang River[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(5): 756-763. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 常宏, 谭建民, 李明. 清江河道变迁与滑坡崩塌[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2018 CHANG Hong, TAN Jianmin, LI Ming. Changes of Qingjiang River and landslide collapse[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2018. (in Chinese)
[15] 陈伟. 山区村镇滑坡灾害风险评估研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学 CHEN Wei. Study on risk assessment of landslide disaster in mountainous villages and towns[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] GUO Zizheng. Landslide susceptibility zonation method based on C5.0 decision tree and K-means cluster algorithms to improve the efficiency of risk management[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(6):101249. DOI: 10.1016/j.gsf.2021.101249
[17] 王峰. 四川省南江县地质灾害易发性区划研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学 WANG Feng. Study on regionalization of geological disaster susceptibility in Nanjiang County, Sichuan Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 罗路广, 裴向军, 崔圣华, 等. 九寨沟地震滑坡易发性评价因子组合选取研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(11): 2306 − 2319. LUO Luguang, PEI Xiangjun, CUI Shenghua, et al. Combined selection of susceptibility assessment factors for Jiuzhaigou earthquake-induced landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(11): 2306 − 2319. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] 王锐. 基于GIS和Logistic回归模型的降雨型滑坡易发性研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学 WANG Rui. Study on the susceptibility of rainfall landslide based on GIS and Logistic regression model[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 吴润泽,胡旭东,梅红波,等. 基于随机森林的滑坡空间易发性评价—以三峡库区湖北段为例[J]. 地球科学,2021(1):321 − 330. [WU Runze,HU Xudong,MEI Hongbo,et al. Spatial susceptibility assessment of landslides based on random forest:A case study from Hubei section in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Earth Science,2021(1):321 − 330. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Runze, HU Xudong, MEI Hongbo, et al. Spatial susceptibility assessment of landslides based on random forest: a case study from Hubei section in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Earth Science, 2021(1): 321-330. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 郝国栋. 基于随机森林模型的商南县滑坡易发性评价[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2020 HAO Guodong. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in Shangnan County based on random forest model[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)




 下载:
下载:

 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS