Assessment of landslide susceptibility mapping based on XGBoost model: A case study of Yanshan Township
-
摘要: 滑坡易发性评价是精细化滑坡灾害风险评价的基础。为了提升滑坡易发性评价模型的精度和稳健性,以三峡库区万州区燕山乡为例,选取工程地质岩组、堆积层厚度等九个影响因子构建滑坡易发性评价指标体系,应用信息量模型定量分析滑坡发育与指标之间的关系。在此基础上,随机选取70%/30%的滑坡样本作为训练/验证数据集,应用极致梯度提升模型(extreme gradient boosting, XGBoost)开展易发性评价。随后从模型预测精度和模型稳定性两方面将其与决策树模型(decision tree, DT)和梯度提升树模型(gradient boosting decision tree, GBDT)进行对比。结果表明:研究区堆积层滑坡主要受长江水系、堆积层厚度和工程地质岩组影响。XGBoost模型具有最高的准确率(94.3%)和预测精度(97.3%)。在模型稳定性验证中,平均预测精度最高(97.3%),优于DT(91.3%)和GBDT(95.7%),模型标准差和变异系数均为0.01,低于其余两种模型。XGBoost在区域滑坡易发性评价与制图中得到了可靠的结果,为滑坡灾害空间预测提供了新的技术支撑。Abstract: Landslide susceptibility assessment forms the foundation for precise evaluation of landslide risk. To enhance the accuracy and robustness of landslide susceptibility mapping, a state-of-art machine learning algorithm named the extreme gradient boosting model (XGBoost) was introduced to this study. Yanshan Town in Wanzhou district, Three Gorges reservoir, was chosen as a case study. Nine influencing factors, including engineering geological lithology and thickness of deposit layer, were selected to construct the landslide susceptibility evaluation index system. The relationship between landslide development and these indicators is quantitatively analyzed using the information value model. Subsequently, 70% of landslide samples were randomly assigned for training, while the remaining 30% were used for validation. The XGBoost model was then employed for landslide susceptibility mapping. The output were compared with those of the decision tree model (DT) and gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT) in terms of prediction accuracy and model stability. The findings revealed that distance to the Yangtze River, soil thickness, and lithology were the primary factors influencing landslide development. The XGBoost model demonstrated the highest average prediction accuracy (97.3%) in 100 repeated trials, surpassing the DT (91.3%) and GBDT models. Moreover, the XGBoost model exhibited superior robustness with a standard deviation and coefficient of variation of 0.01, lower than the other two models. It also achieved the highest accuracy (94.3%) and prediction accuracy (97.3%) in the validation process. The proposed XGBoost model serves as a reliable assessment method and yields optimal results in regional landslide susceptibility mapping.
-
0. 引言
滑坡作为我国主要的地质灾害类型,具有分布地区广、发生次数多、威胁严重等特点[1],对国民经济建设和自然资源可持续利用造成了不可估量的破坏。由于复杂脆弱的地质环境,三峡库区是全国滑坡发生最多、经济损失最为严重的地区之一[2]。自2003年蓄水以来,三峡库区新滑坡的发生和老滑坡的复活明显增多[3 − 4]。目前,库区内共有滑坡4, 664个,其中674个有明显变形特征[5]。因此开展定量化的滑坡灾害空间预测与精细化风险评价研究十分必要。
滑坡易发性建模的本质是研究滑坡灾害在地质、环境及人类工程活动等因素影响下发生的空间概率[6],准确、可靠的评价结果能为风险防控措施的制定提供可靠的科学依据。近几十年来,国内外学者开展了大量滑坡易发性建模研究,主要包括知识驱动模型和数据驱动模型[7 − 11]。随着对地观测技术的发展,高质量的区域滑坡数据获取成为可能。由于相对简单的操作和可靠的性能,数据驱动模型逐渐在滑坡易发性评价中受到欢迎,主要可以分为数理统计模型[12 − 14]和机器学习模型[15 − 16]两类。由于具有更强的非线性预测能力,机器学习模型在易发性建模中表现出更高的预测精度,常用的算法有人工神经网络[17 − 18]、支持向量机[19 − 20]、决策树(decision tree, DT)[21 − 22]等。
DT是一种经典的树型结构分类算法,由于计算速度快、训练简单、便于理解和解释性好等优点被广泛运用,但在训练过程中易产生较复杂的模型,导致数据泛化能力差,出现过拟合情况,甚至微小的数据变化也会导致预测结果出现较大偏差。相比而言,基于DT和Boosting集成的梯度提升树模型(gradient boosting decision tree, GBDT)引入随机性,降低模型过度训练的可能性,能够较好地拟合多维复杂数据,并在相对短的时间内对海量数据得出较好的结果[23],但模型仍存在损失函数难收敛和难以处理特征缺失样本等问题。极致梯度提升模型(extreme gradient boosting, XGBoost)是在GBDT基础上进行优化得到,通过在GBDT损失函数中加上正则项和二阶导数来降低模型运行复杂度以及权衡模型方差,从而学习出更简单的模型,并进一步防止模型过拟合。在处理特征值有缺失的训练样本时,XGBoost还可以自动学习并拟合出数据的分裂方向。由于XGBoost具备预测精度高、稳定性好等特点,现已被广泛地应用到医学预测、电力估计等领域[24 − 27],而在滑坡易发性评价领域运用较少。
本文以三峡库区万州区燕山乡为研究区,选取坡度、工程地质岩组、堆积层厚度等九个指标因子构建易发性指标体系,应用信息量模型定量分析各指标与滑坡发育关系;分别采用XGBoost、GBDT和DT对研究区开展易发性评价研究,并从预测精度和稳健性方面对模型性能进行综合对比分析。
1. 方法原理
1.1 决策树模型
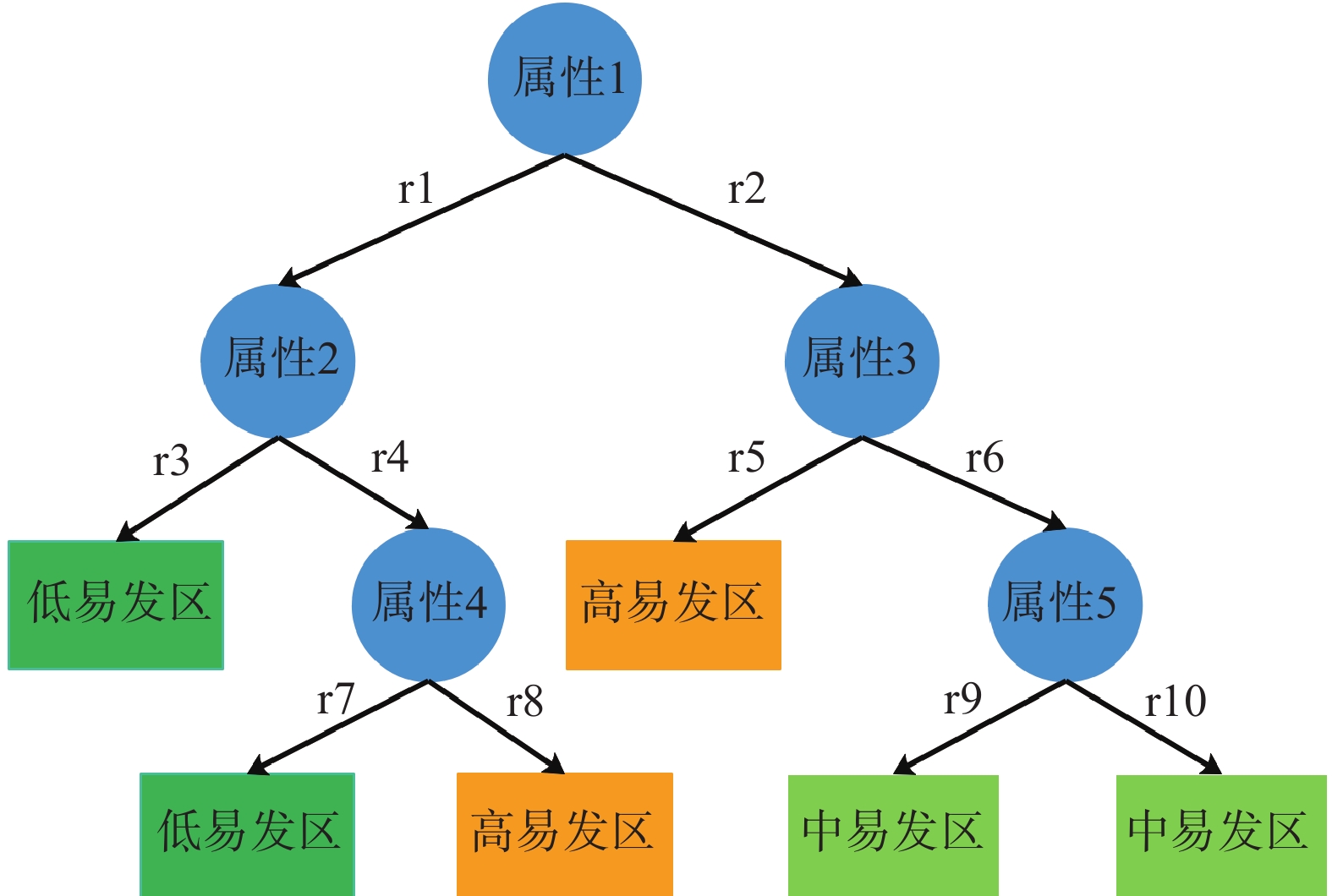
决策树模型是一种对实例进行分类的树形结构,决策树由节点和有向边组成,其中内部节点代表一个特征或者一种属性,叶节点代表类别[28]。在模型运算过程中,首先将实例从根节点开始排列,然后将属性和特征在中间节点根据特定规则分割为两个子集,直到在叶节点得到两个分类结果(图1)。其中基尼系数构成根节点到叶子节点的分类规则序列,基尼系数值越小,代表构建分类标准越好,最终的分类结果精度越高。
1.2 梯度提升树模型
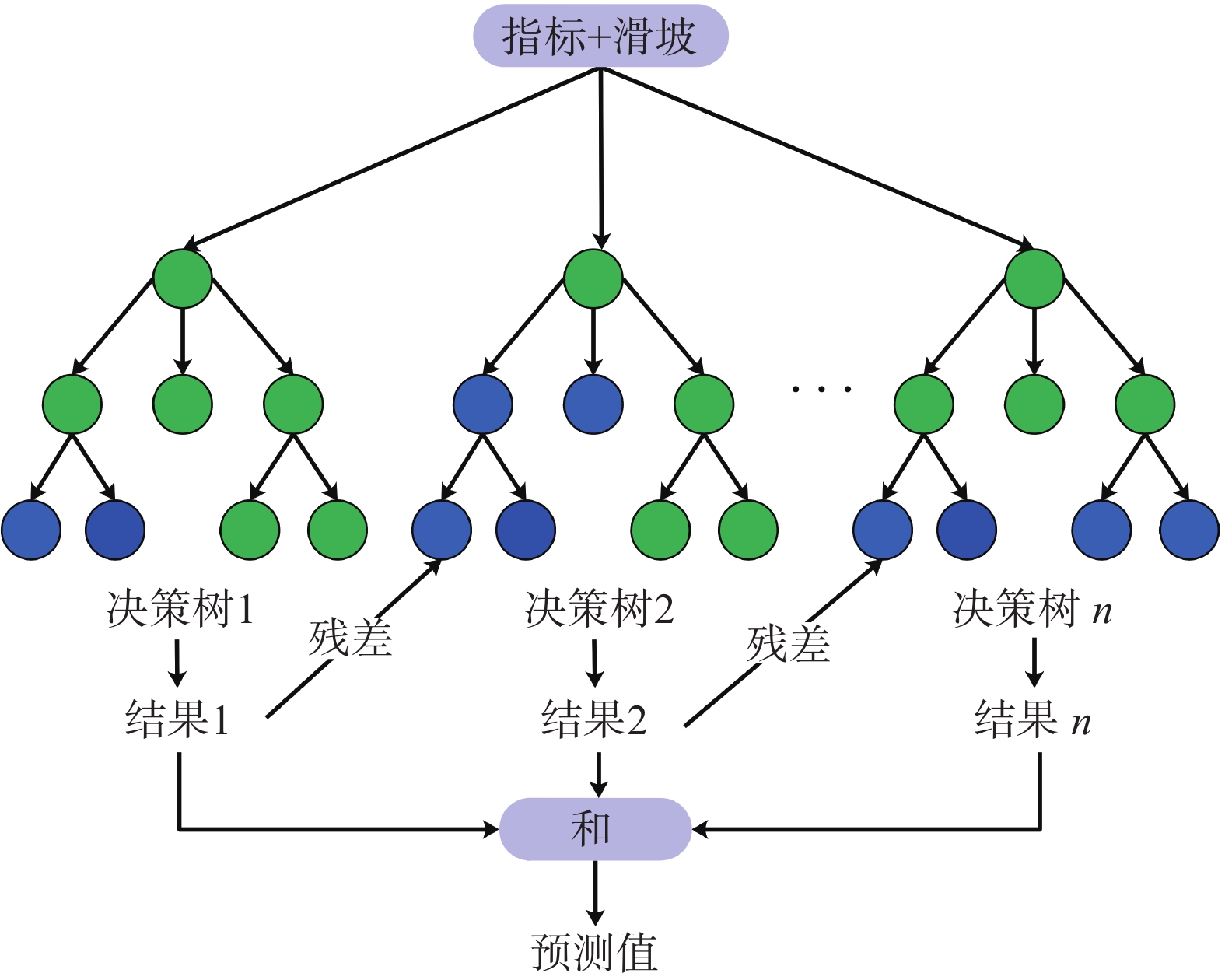
梯度提升树模型是一种常用的树形模型,采用Boosting方法将多颗决策树进行关联,新决策树的生成是在上一棵树损失函数的梯度下降方向,通过不断迭代来优化模型[29](图2)。
设训练样本为
${x_i}$ ,初始损失函数${F_0}$ 为:$$ {F_0}({x_i}) = \mathop {\arg \min } \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n L \left( {{y_i},c} \right) $$ (1) 式中:xi——训练样本。
利用生成的决策树
${h_j}\left( {{x_i}} \right)$ 去拟合损失函数的梯度下降方向,使损失函数得到第j轮的最佳拟合值${r_j}$ :$$ {r_j} = \mathop {\arg \min }\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n L \left( {y,{F_{j - 1}}(x) + {h_j}\left( {{x_i}} \right)} \right) $$ (2) 并利用损失函数对模型进行更新,得到最终预测结果计算函数为:
$$ {F_M}(x) = \sum\limits_{j = 1}^m {{F_{j - 1}}} (x) $$ (3) ${F_M}$ 为单颗决策树预测结果,将多棵决策树预测结果求和可得到梯度提升树模型最终预测结果。1.3 极致梯度提升模型
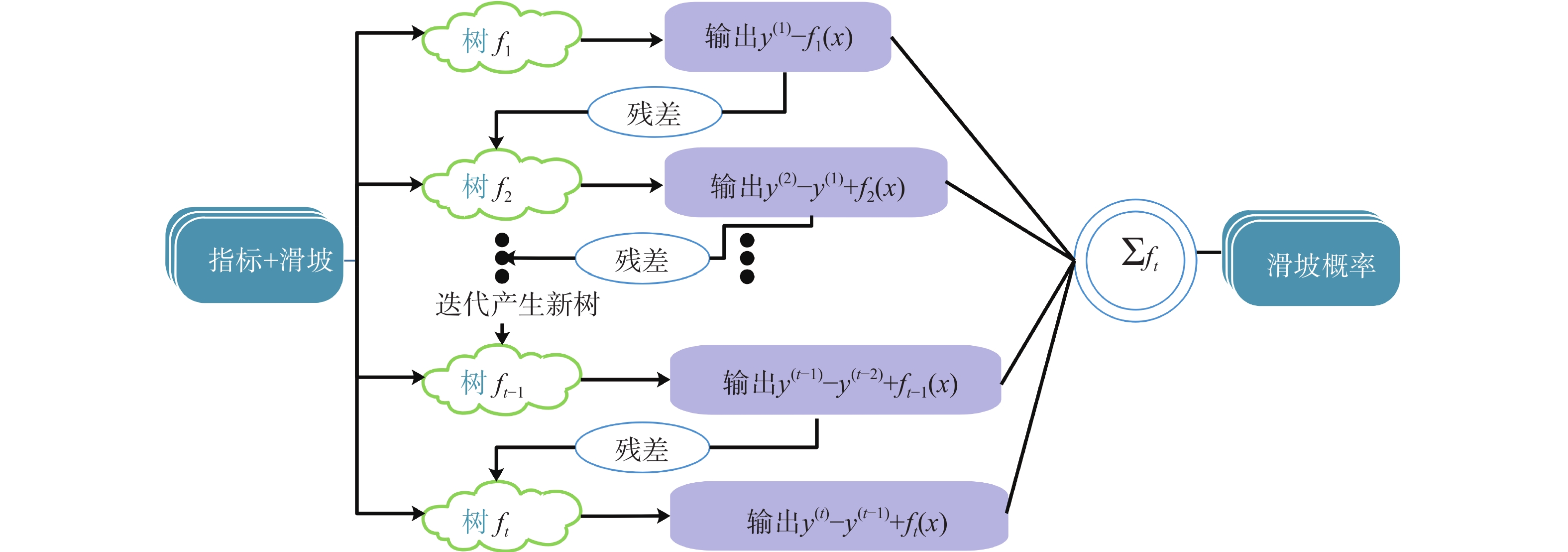
XGBoost是一种基于GBDT的模型,其模型结构与GBDT类似,都是以决策树为基础,通过不断迭代,集成弱分类器为强分类器。随着模型迭代次数的增多,预测精度也会不断提高,计算流程如图3所示。与GBDT不同的是它在损失函数中加入了二阶导数
${h_i}$ 和正则项$ {{\Omega }}\left( {{{{f}}_{{k}}}} \right) $ 来对每一轮的目标函数进行优化,目标函数值越小,则树结构越好[30 − 31]。为了求得最小化目标函数,分别进行二阶泰勒展开、正则化项展开来合并一次项系数和二次项系数,经过多轮迭代后得到最终预测结果计算公式为:
$$ Obj = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\left[ {l\left( {{y_i},\hat y_i^{(t - 1)}} \right) + {g_i}{f_t}\left( {{x_i}} \right) + \frac{1}{2}{h_i}f_t^2\left( {{x_i}} \right)} \right]} + \sum\limits_k \Omega \left( {{f_k}} \right) $$ (4) 式中:
$\hat y_i^{(t - 1)} $ ——前t−1轮模型预测值;$l\left( {{y_i},\hat y_i^{(t - 1)}} \right) $ ——样本xi的训练误差;$f(x) $ ——其中一棵回归树;$\Omega \left( {{f_k}} \right) $ ——第k棵树的正则项。2. 研究区概况与数据准备
2.1 基本概况
燕山乡位于三峡库区万州区西南部长江右岸,面积约56.93 km²。燕山乡属构造剥蚀中浅切割丘陵河流地貌,地势东高西低,海拔范围在120~1430 m。区内地形总体向西倾向长江,多形成单倾斜坡地形,长年受雨水冲刷切割形成纵向凹槽、冲沟、溪流,汇集于长江。燕山乡年平均降雨量为1193.3 mm,日最大降雨为243 mm,最大连续降雨量为488.7 mm,夏季大雨、暴雨频繁,极易诱发滑坡灾害。区内共发育滑坡灾害33处,其中小型滑坡6处,中型滑坡22处,大型滑坡5处。研究区地理位置及滑坡分布如图4所示。
研究区位于方斗山背斜西侧,区内地层岩性复杂,主要出露地层为侏罗系新田沟组、自流井组、珍珠冲组和三叠系巴东组、嘉陵江组、大冶组,岩性为砂岩夹泥岩、泥岩、页岩和灰岩等。区内堆积层整体较薄,多分布于河谷斜坡、山顶侵蚀平台之上。河谷地带多为冲洪积亚黏土、砂土、含土卵砾石等,局部具二元结构,而山间斜坡地带主要为残积、坡积、崩积等重力堆积的含碎石土,总体上,区内堆积体结构松散,孔隙发育,为堆积层滑坡发育提供充分条件。随着社会经济的快速发展,频繁的人类工程活动(如G69高速公路等)对周边自然环境造成了影响,特别是三峡库区周期性蓄降水,造成了许多老滑坡的复活及稳定斜坡的变形。
2.2 滑坡编录数据
基于历史滑坡编录数据、影像信息和野外实地调查建立研究区滑坡灾害编录数据库。根据野外实际调研结果,研究区滑坡主要诱发因素有大气降雨、人类工程活动、水库蓄水等。其中沙榜咀滑坡在暴雨和连续强降雨下发生变形,大量雨水汇集,一方面加强了地下水入渗,使滑体本身的重量变大,另一方面当雨水入渗到滑动面,也减弱了滑带土的抗剪强度,增加了滑体的下滑力。桐子林滑坡滑体物质为大量后期人工生活及建筑堆积物和崩积含碎块石粉质黏土;五尺坝滑坡为区内典型的受库水位影响的库岸滑坡,其中前缘以滑塌变形为主,受到库水位浸泡和侧向冲刷是诱发滑坡前缘变形的主要原因。研究区滑坡从发育平面形态特征来看,共发育舌形滑坡16个,箕形滑坡7个,扇形滑坡5个,横长形滑坡3个,不规则长条形滑坡2个。从发育剖面形态特征来看,直线形所占比例最大,其比例为91%,圆弧形较少分布,其比例为9%。整体来看,研究区滑坡在东西方向数量分布存在明显差异,且东西方向上堆积层厚度、坡度、工程地质岩组等指标存在明显差异,根据主要诱发因可分为受水库波动影响较大的缓倾角堆积层滑坡和受降雨影响较大的陡倾角堆积层滑坡(图5)。
2.3 易发性评价指标体系
影响滑坡发育的指标因子主要包括有地形地貌、地质条件和人类工程活动等[32]。在前人对万州区进行滑坡易发性评价基础上[33 − 35],考虑研究区地质背景、滑坡形成条件及其发育特征,并根据野外实际调研中,研究区东西方向地理条件差异鲜明情况,选取土地利用、斜坡结构、岩组、坡度、距长江距离、堆积层厚度、植被归一化指数、斜坡形态、汇水面积九个指标因子构建研究区易发性评价指标体系。为了判别指标之间相关性密切程度,利用ArcGIS中波段集统计工具检验各指标因子之间的相关性,结果显示各指标因子之间相关性皆小于0.4,表明指标因子之间呈弱相关性或不相关(图6),可用作研究区滑坡易发性评价建模,各因子指标分级情况如图7所示。
3. 滑坡易发性建模
3.1 模型建立
将指标因子作为模型输入数据,滑坡预测相对概率作为模型输出进行易发性建模。随机选择70%的滑坡和相同数量的非滑坡数据作为训练数据,剩余30%滑坡数据则作为验证数据[36]。
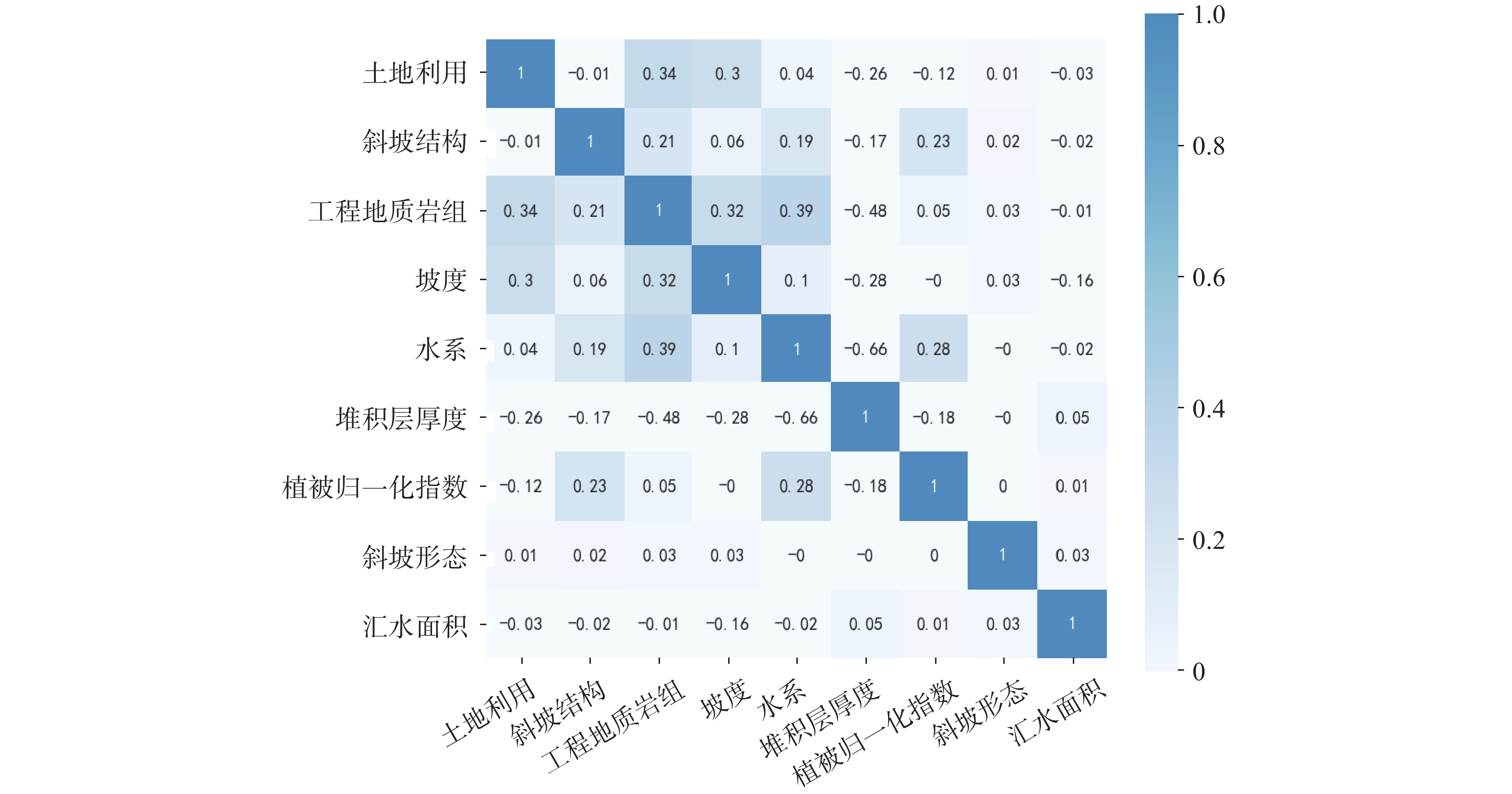
为了保证模型在对比时达到一个较优的状态,需要对各个模型进行调参。最大叶子节点数是决策树模型主要影响参数,通过试算法确定叶节点个数。如图8(a)所示,DT模型的预测精度随着最大叶子节点数的增大呈现出上升趋势,当叶子节点数目达到160时,预测精度达到峰值,呈稳定状态,因此设置决策树模型最大叶子节点数目为160。
GBDT和XGBoost为集成树模型,主要通过创建新决策树,由多颗决策树的预测值得到最终结果,而影响集成树模型精度的主要参数为决策树数量。一般来说,模型决策树数量较小时,容易欠拟合,而决策树数量过多,计算量快速增加,且决策树数量增加到一定时,模型逐渐趋于稳定,预测精度不会随决策树数量增加出现大幅度变动[37]。同样采用试算法来确定适合模型的决策树数量,GBDT和XGBoost模型中决策树数量和预测精度的关系曲线分布如图8(b)和图8(c)所示。可以看出GBDT和XGBoost在决策树数量分别大于145和大于75预测精度无明显提升,且趋于稳定,因此设置GBDT和XGBoost决策树数量分别为145和75,此时最大决策树深度为7,能够最多生成的叶子结点数为49。此外,设置XGBoost学习率、L1和L2正则项权重分别为0.1、0和1。
将评价指标输入到训练好的DT、GBDT和XGBoost模型中,计算研究区滑坡易发性相对概率值,并分为四个易发性等级区间,分别为低(77%)、中(7%)、高(7%)和极高(9%)。结果如图9所示。
3.2 结果对比与分析
3.2.1 滑坡空间发育规律分析
信息量模型是一种二变量统计方法,统计结果能够很好地表征影响因素对滑坡空间发育的影响作用与程度。信息量值为正,说明指标对滑坡发育有促进作用;信息量值为负,则说明有抑制作用,且绝对值越大表明作用越强,各评价指标的信息量计算结果如表1所示。影响区内滑坡发育的主要指标有距长江距离(0~400 m)、堆积层厚度(>2.4 m)和工程地质岩组(砂岩夹泥岩和砂岩),信息量值分别为2.96、2.54和1.58。受三峡水库蓄降水的影响,研究区长江沿岸滑坡面积约占总滑坡面积的53%,并且长江支流附近水系发育,受各类水流的长期侵蚀和冲刷,斜坡整体稳定性低;研究区第四系堆积层厚度大于2.4 m的区域主要在冲沟和长江沿岸,此类斜坡土体结构松散,吸水能力较强且持水能力差,在降雨诱发下快速形成暂时的饱水带,易失稳滑动;区内泥岩风化程度高,结构破碎,在降雨等不利条件下极易失稳滑动。
表 1 各因素状态信息量表Table 1. The weighted information values of each factor state指标 分级 信息量 指标 分级 信息量 指标 分级 信息量 坡度/(°) 0~9 1.28 工程地质岩组 砂岩夹泥岩、砂岩 1.58 斜坡结构 顺向伏倾坡、顺向飘倾坡 0.75 9~21 0.75 砂泥岩互层 0.59 顺斜坡 −0.99 21~33 −0.83 泥岩夹砂岩、泥岩 1.46 横向坡、逆斜坡、逆向坡 −0.96 33~45 −3.28 页岩夹灰岩、灰岩 −1.79 斜坡形态 内向凸形坡 0.31 >45 −9.32 距长江距离/m 0-400 2.96 直线凸形坡、外向凸形坡 −0.21 植被归一化指数 <0.15 1.07 400~700 −0.46 内向直坡、直线直坡 −1.79 0.15~0.25 −0.30 700~1400 0.72 外向直坡、内向凹坡 −0.82 >0.25 −0.70 >1400 −1.84 直线凹坡、外向凹坡 −0.99 坡向/(°) 0~180 −1.33 地形湿度指数 0~6 −0.35 堆积层厚度/m 0~0.8 −9.98 180~234 0.01 6~12 0.83 0.8~1.6 −3.35 234~252 −0.13 12~18 0.23 1.6~2.4 −1.04 252~342 0.58 >18 −1.24 >2.4 2.54 342~360 −0.60 3.2.2 模型性能分析
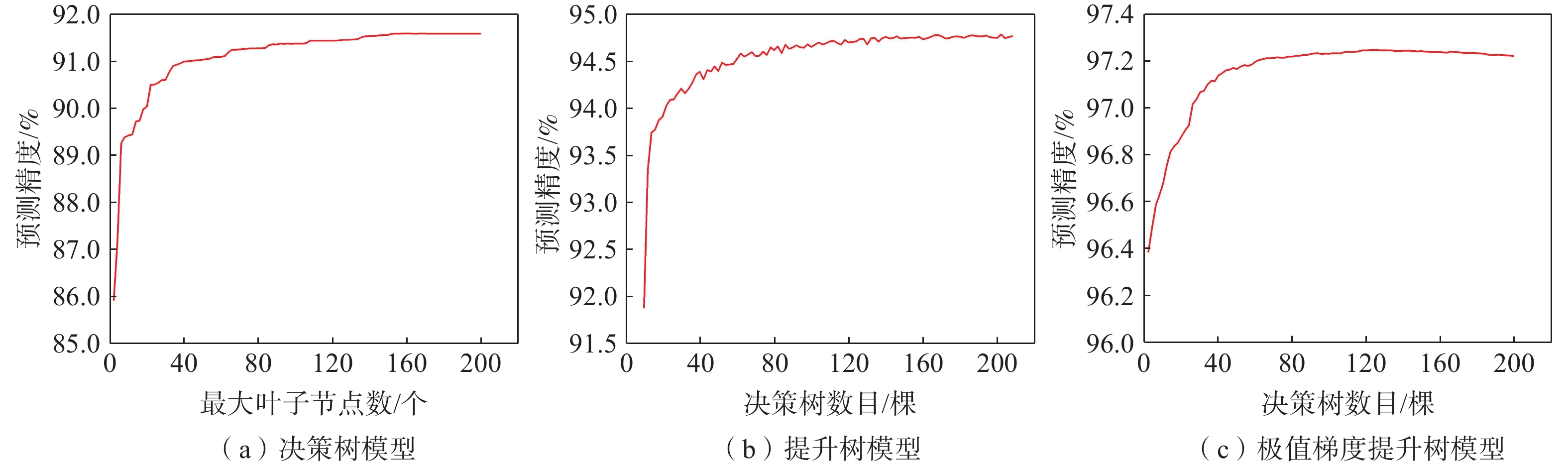
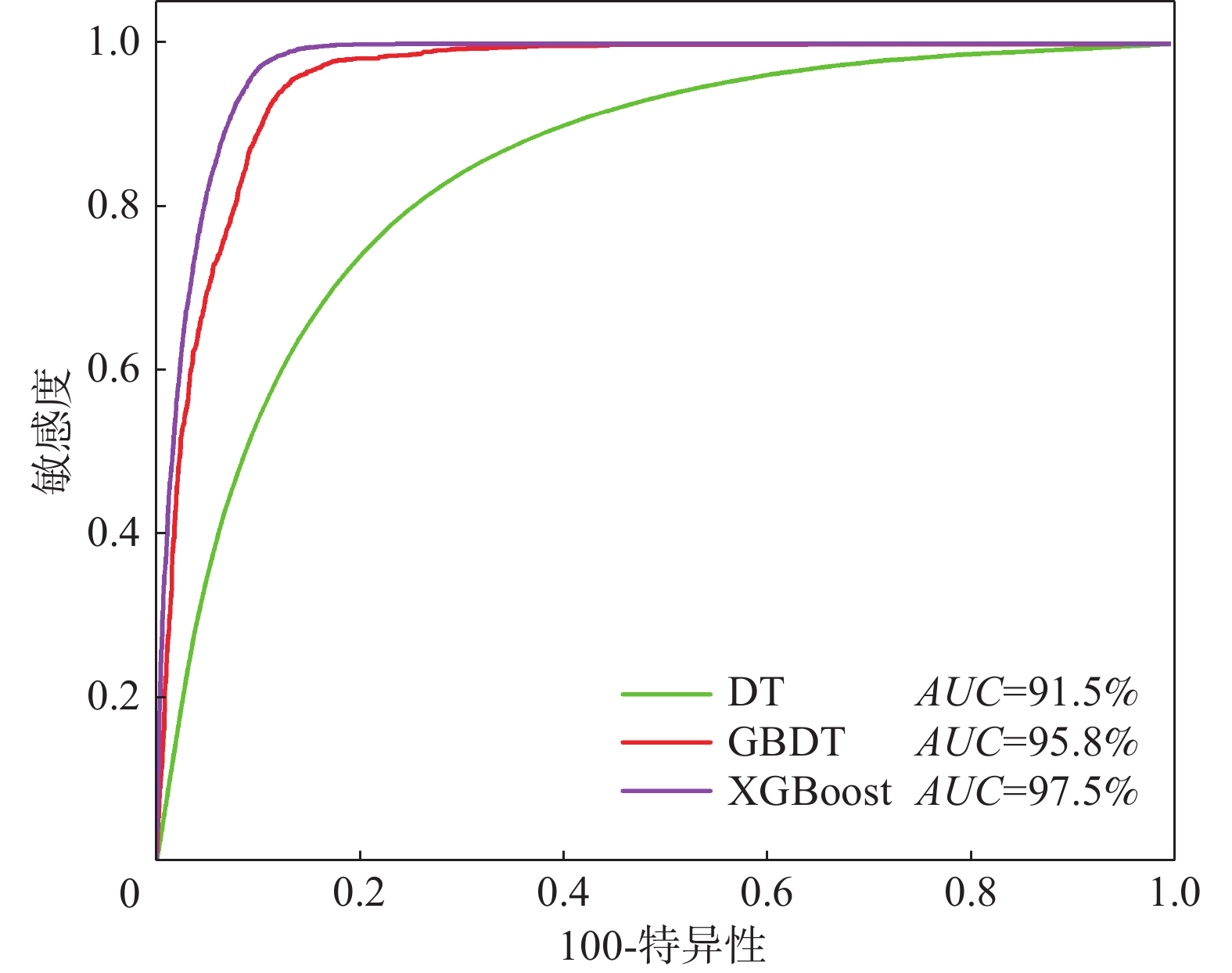
滑坡比率为该易发性等级滑坡栅格点数量占总滑坡栅格点数量之比与分级栅格数占研究区栅格数之比的比值。统计各模型滑坡比率,各模型滑坡比率皆是从低易发性到极高易发性依次增大,且在极高易发区滑坡比率最高。XGBoost极高易发性等级的滑坡比率分别10.19,高于为DT和GBDT的8.07、8.59。准确率为分类正确的滑坡样本个数占总滑坡样本个数的比例[38],通过计算得到各模型准确率分别为92.63%、93.13%和94.32%,表明XGBoost预测结果准确性最高,优于DT和GBDT(图10)。绘制全区受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC)[39](图11),可以看出XGBoost全区预测精度为0.973,优于DT和GBDT。
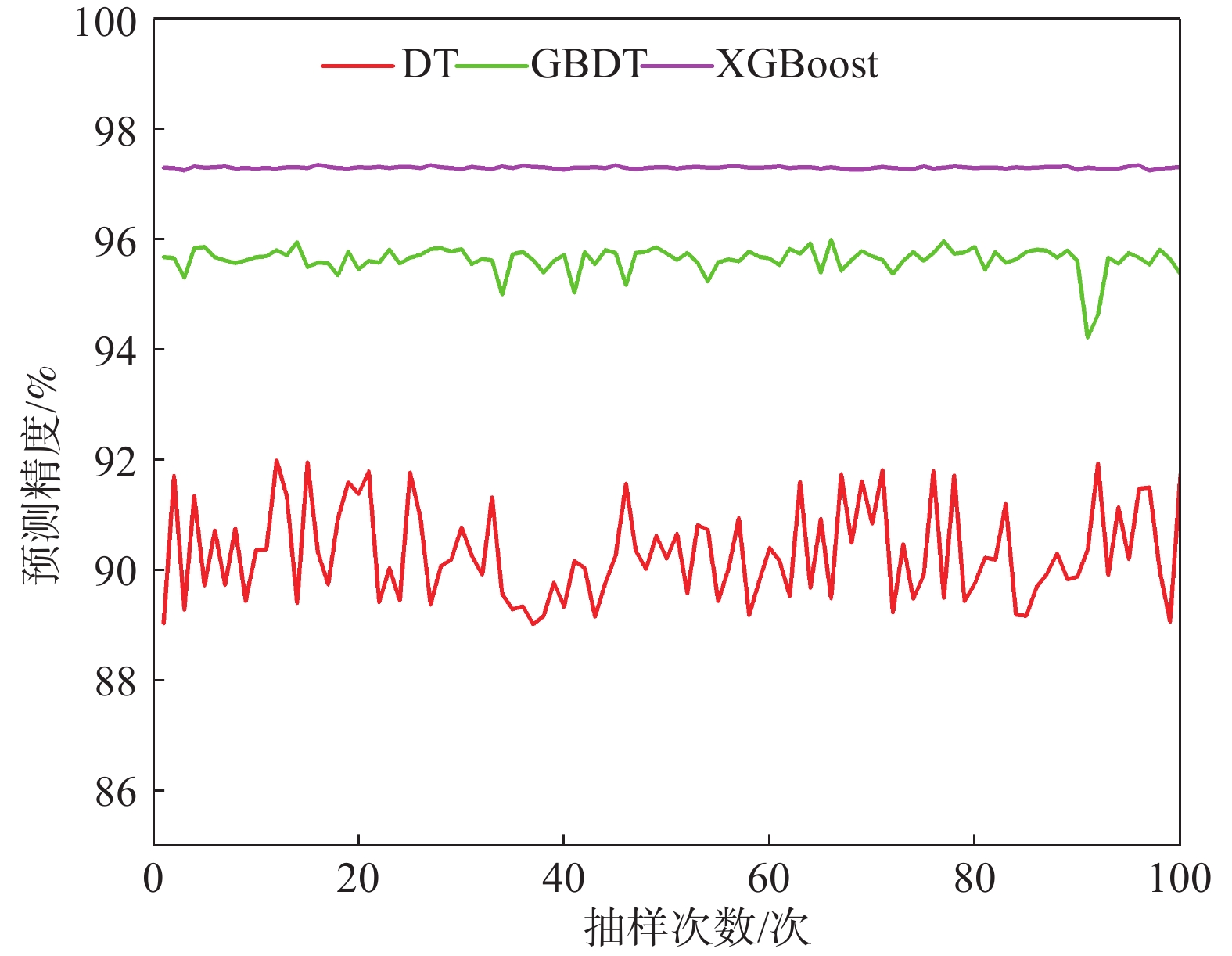
为进一步探究模型预测的稳健性,随机生成100组试验数据进行滑坡易发性预测,得到预测精度和抽样次数关系曲线、标准差和变异系数如图12和表2所示。
表 2 标准差和变异系数Table 2. Standard deviation and coefficient of variation模型 平均数 标准差 变异系数 95%置信区间下限 95%置信区间上限 DT 90.304 0.734 0.813 90.160 90.448 GBDT 95.612 0.062 0.065 95.600 95.624 XGBoost 97.281 0.010 0.010 97.279 97.283 在多组抽样数据下,XGBoost拥有最好的预测精度,且预测精度上下起伏不大,稳定性较好,预测精度平均值为97.28%,优于GBDT(95.61%)和DT(90.30%),其标准差为0.010,小于GBDT(0.062)和DT(0.734),变异系数为0.010,小于GBDT(0.065)和DT(0.813)。
4. 结论
以燕山乡为例,选取坡度、工程地质岩组、堆积层厚度等九个影响因子构建易发性评价指标体系,应用信息量模型分析滑坡发育与指标之间的关系。研究结果发现:距长江距离(0~400 m)、工程地质岩组(砂岩夹泥岩、砂岩和泥岩夹砂岩、泥岩)和堆积层厚度(>2.4 m)是研究区滑坡空间发育的主要控制因素;燕山乡东部出露抗风化能力较强的灰岩且基本无第四系堆积物,不具备发育滑坡的条件,研究区西部长期受到库水位压力变化,斜坡失稳概率极大。因此研究区东部与西部地区之间滑坡易发性评价结果有明显的差异,与野外实际勘察情况一致。
通过对100组训练/验证数据集开展易发性评价探究模型预测准确性、稳定性。结果表明XGBoost模型的标准差和变异系数均为0.01,优于GBDT和DT,说明该模型在多次重复中具有较好的稳健性。对评价结果进行验证得到准确率和预测精度分别为94.3%和97.3%,优于GBDT和DT。DT是一个训练简单、可理解性好的模型,但模型易过拟合且预测精度不高,通过模型集成的方法可以解决DT易过拟合的不足;将DT和Boosting集成的GBDT能够较好地拟合多维复杂数据并降低模型过拟合可能。为解决损失函数难收敛问题,在GBDT基础上添加正则项和二阶导数的XGBoost拥有模型稳定性和预测准确性。XGBoost是一种优秀的滑坡易发性预测模型,具有较高的预测精度,并能为后续滑坡风险评价和分析提供技术支撑。
-
表 1 各因素状态信息量表
Table 1 The weighted information values of each factor state
指标 分级 信息量 指标 分级 信息量 指标 分级 信息量 坡度/(°) 0~9 1.28 工程地质岩组 砂岩夹泥岩、砂岩 1.58 斜坡结构 顺向伏倾坡、顺向飘倾坡 0.75 9~21 0.75 砂泥岩互层 0.59 顺斜坡 −0.99 21~33 −0.83 泥岩夹砂岩、泥岩 1.46 横向坡、逆斜坡、逆向坡 −0.96 33~45 −3.28 页岩夹灰岩、灰岩 −1.79 斜坡形态 内向凸形坡 0.31 >45 −9.32 距长江距离/m 0-400 2.96 直线凸形坡、外向凸形坡 −0.21 植被归一化指数 <0.15 1.07 400~700 −0.46 内向直坡、直线直坡 −1.79 0.15~0.25 −0.30 700~1400 0.72 外向直坡、内向凹坡 −0.82 >0.25 −0.70 >1400 −1.84 直线凹坡、外向凹坡 −0.99 坡向/(°) 0~180 −1.33 地形湿度指数 0~6 −0.35 堆积层厚度/m 0~0.8 −9.98 180~234 0.01 6~12 0.83 0.8~1.6 −3.35 234~252 −0.13 12~18 0.23 1.6~2.4 −1.04 252~342 0.58 >18 −1.24 >2.4 2.54 342~360 −0.60 表 2 标准差和变异系数
Table 2 Standard deviation and coefficient of variation
模型 平均数 标准差 变异系数 95%置信区间下限 95%置信区间上限 DT 90.304 0.734 0.813 90.160 90.448 GBDT 95.612 0.062 0.065 95.600 95.624 XGBoost 97.281 0.010 0.010 97.279 97.283 -
[1] 武雪玲,沈少青,牛瑞卿. GIS支持下应用PSO-SVM模型预测滑坡易发性[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2016,41(5):665 − 671. [WU Xueling,SHEN Shaoqing,NIU Ruiqing. Landslide susceptibility prediction using GIS and PSO-SVM[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2016,41(5):665 − 671. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Xueling, SHEN Shaoqing, NIU Ruiqing. Landslide susceptibility prediction using GIS and PSO-SVM[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2016, 41(5)665-671(in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 殷跃平,张晨阳,闫慧,等. 三峡水库蓄水运行滑坡渗流稳定和防治设计研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(4):649 − 659. [YIN Yueping, ZHANG Chenyang, YAN Hui, et al. Research on seepage stability and prevention design of landslides during impoundment operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2022,41(4):649 − 659. (in Chinese with English abstract) Yin Yueping, Zhang Chenyang, Yan Hui, et al. Research on seepage stability and prevention design of landslides during impoundment operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(4): 649-659.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 杨何,汤明高,许强,等. 长江三峡库区滑坡变形统计特征研究[J]. 灾害学,2021,36(2):37 − 42. [YANG He,TANG Minggao,XU Qiang,et al. Research of statistical characteristics of deformation of landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area of the Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2021,36(2):37 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG He, TANG Minggao, XU Qiang, et al. Research of statistical characteristics of deformation of landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area of the Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2021, 36(2)37-42(in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 朱宇航,黄海峰,殷坤龙,等. 基于滑坡破坏模式分析的易发性评价—以三峡库区首段泄滩河左岸为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(2):156 − 166. [ZHU Yuhang, HUANG Haifeng, YIN Kunlong, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide failure mode analysis: A case study of the left bank of Xietan River in the first section of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(2):156 − 166. (in Chinese with English abstract) [ZHU Yuhang, HUANG Haifeng, YIN Kunlong, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide failure mode analysis: a case study of the left bank of Xietan River in the first section of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(2)156-166(in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 许嘉慧,张虹,文海家,等. 基于逻辑回归的巫山县滑坡易发性区划研究[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021,38(2):48 − 56. [XU Jiahui,ZHANG Hong,WEN Haijia,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on logistic regression in Wushan County[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science),2021,38(2):48 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) Xu Jiahui, Zhang Hong, Wen Haijia, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on logistic regression in Wushan County[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science), 2021, 38(2): 48-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 陈丽霞, 徐勇, 李德营. 武陵山区城镇地质灾害风险评估技术指南及案例分析[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2019 CHEN Lixia, XU Yong, LI Deying. Guidelines and applications for geohazard risk assessment of urban areas in Wuling Mountain region[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[7] BAI Shibiao,WANG Jian,LÜ Guonian,et al. GIS-based logistic regression for landslide susceptibility mapping of the Zhongxian segment in the Three Gorges area,China[J]. Geomorphology,2010,115(1/2):23 − 31.
[8] LONG Jingjing,LIU Yong,LI Changdong,et al. A novel model for regional susceptibility mapping of rainfall-reservoir induced landslides in Jurassic slide-prone strata of western Hubei Province,Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment,2021,35(7):1403 − 1426. DOI: 10.1007/s00477-020-01892-z
[9] 周超,殷坤龙,曹颖,等. 基于集成学习与径向基神经网络耦合模型的三峡库区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(6):1865 − 1876. [ZHOU Chao,YIN Kunlong,CAO Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment by applying the coupling method of radial basis neural network and adaboost:a case study from the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(6):1865 − 1876. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU Chao, YIN Kunlong, CAO Ying, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment by applying the coupling method of radial basis neural network and adaboost: a case study from the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(6): 1865-1876. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 田乃满,兰恒星,伍宇明,等. 人工神经网络和决策树模型在滑坡易发性分析中的性能对比[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2020,22(12):2304 − 2316. [TIAN Naiman,LAN Hengxing,WU Yuming,et al. Performance comparison of BP artificial neural network and CART decision tree model in landslide susceptibility prediction[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2020,22(12):2304 − 2316. (in Chinese with English abstract) TIAN Naiman, LAN Hengxing, WU Yuming, et al. Performance comparison of BP artificial neural network and CART decision tree model in landslide susceptibility prediction[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2020, 22(12): 2304-2316. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] REGMI N R,GIARDINO J R,VITEK J D. Assessing susceptibility to landslides:using models to understand observed changes in slopes[J]. Geomorphology,2010,122(1/2):25 − 38.
[12] 王佳佳,殷坤龙,肖莉丽. 基于GIS和信息量的滑坡灾害易发性评价—以三峡库区万州区为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(4):797 − 808. [WANG Jiajia,YIN Kunlong,XIAO Lili. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on GIS and weighted information value:A case study of Wanzhou district,Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(4):797 − 808. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Jiajia, YIN Kunlong, XIAO Lili. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on GIS and weighted information value: a case study of Wanzhou district, Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(4): 797-808. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 周超,殷坤龙,向章波,等. 基于GIS的淳安县滑坡易发性定量评价[J]. 安全与环境工程,2015,22(1):45 − 50. [ZHOU Chao,YIN Kunlong,XIANG Zhangbo,et al. Quantitative evaluation of the landslide susceptibility in Chun'an County based on GIS[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2015,22(1):45 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU Chao, YIN Kunlong, XIANG Zhangbo, et al. Quantitative evaluation of the landslide susceptibility in Chun'an County based on GIS[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2015, 22(1): 45-50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 张林梵,王佳运,张茂省,等. 基于BP神经网络的区域滑坡易发性评价[J]. 西北地质,2022,55(2):260 − 270. [ZHANG Linfan, WANG Jiayun, ZHANG Maosheng, et al. Evaluation of regional landslide susceptibility assessment based on BP neural network[J]. Northwestern Geology,2022,55(2):260 − 270. (in Chinese with English abstract) [ZHANG Linfan, WANG Jiayun, ZHANG Maosheng, et al. Evaluation of regional landslide susceptibility assessment based on BP neural network[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(2): 260-270.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 许冲,徐锡伟. 基于GIS与ANN模型的地震滑坡易发性区划[J]. 地质科技情报,2012,31(3):116 − 121. [XU Chong,XU Xiwei. GIS and ANN model for earthquake triggered landslides susceptibility zonation[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2012,31(3):116 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Chong, XU Xiwei. GIS and ANN model for earthquake triggered landslides susceptibility zonation[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(3): 116-121. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] BRAGAGNOLO L,DA SILVA R V,GRZYBOWSKI J M V. Artificial neural network ensembles applied to the mapping of landslide susceptibility[J]. CATENA,2020,184:104240. DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.104240
[17] 陈飞,蔡超,李小双,等. 基于信息量与神经网络模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(S01):2859 − 2870. [CHEN Fei,CAI Chao,LI Xiaoshuang,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on information volume and neural network model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(S01):2859 − 2870. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Fei, CAI Chao, LI Xiaoshuang, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on information volume and neural network model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(S01): 2859-2870. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] YU Chenglong,CHEN Jianping. Landslide susceptibility mapping using the slope unit for southeastern Helong city,Jilin Province,China:a comparison of ANN and SVM[J]. Symmetry,2020,12(6):1047. DOI: 10.3390/sym12061047
[19] ZHAO Shuai,ZHAO Zhou. A comparative study of landslide susceptibility mapping using SVM and PSO-SVM models based on grid and slope units[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering,2021,2021:1 − 15.
[20] LEE S,HONG S M,JUNG H S. A support vector machine for landslide susceptibility mapping in gangwon Province,Korea[J]. Sustainability,2017,9(1):48. DOI: 10.3390/su9010048
[21] PRADHAN B. A comparative study on the predictive ability of the decision tree,support vector machine and neuro-fuzzy models in landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2013,51:350 − 365.
[22] PARK S,HAMM S Y,KIM J. Performance evaluation of the GIS-based data-mining techniques decision tree,random forest,and rotation forest for landslide susceptibility modeling[J]. Sustainability,2019,11(20):5659. DOI: 10.3390/su11205659
[23] SONG Yingxu,NIU Ruiqing,XU Shiluo,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on weighted gradient boosting decision tree in Wanzhou section of the Three Gorges Reservoir area (China)[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information,2018,8(1):4. DOI: 10.3390/ijgi8010004
[24] YANG Yanguo, YU Jiaqi, FU Yubin, et al. Research on geological hazard risk assessment based on the cloud fuzzy clustering algorithm[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems,2019,37(4):4763 − 4770.
[25] SRIKANTH B,LAKSHMI V PAPINENI S,SRIDEVI G,et al. Adaptive XGBOOST hyper tuned meta classifier for prediction of churn customers[J]. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing,2022,33(1):21 − 34.
[26] TEHRANY M S,PRADHAN B,MANSOR S,et al. Flood susceptibility assessment using GIS-based support vector machine model with different kernel types[J]. CATENA,2015,125:91 − 101. DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2014.10.017
[27] WU Yuanyuan,WU Li,ZHU Huacheng,et al. Design of high temperature complex dielectric properties measuring system based on XGBoost algorithm[J]. Materials,2020,13(6):1419. DOI: 10.3390/ma13061419
[28] 赵建华,陈汉林,杨树锋,等. 基于决策树算法的滑坡危险性区划评价[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版),2004,31(4):465 − 470. [ZHAO Jianhua,CHEN Hanlin,YANG Shufeng,et al. Landslide risk assessment based on decision tree arithmetic[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition),2004,31(4):465 − 470. (in Chinese with English abstract) Zhao Jianhua, Chen Hanlin, Yang Shufeng, et al. Landslide risk assessment based on decision tree arithmetic[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 2004, 31(4): 465-470. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 蔡文学,罗永豪,张冠湘,等. 基于GBDT与Logistic回归融合的个人信贷风险评估模型及实证分析[J]. 管理现代化,2017,37(2):1 − 4. [CAI Wenxue, LUO Yonghao, ZHANG Guanxiang, et al. Personal credit risk assessment model and empirical analysis based on the fusion of GBDT and logistic regression[J]. Modernization of Management,2017,37(2):1 − 4. (in Chinese with English abstract) [Cai Wenxue, Luo Yonghao, Zhang Guanxiang, et al. Personal credit risk assessment model and empirical analysis based on the fusion of GBDT and logistic regression[J]. Modernization of Management, 2017, 37(2(in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] CHEN Tianqi, GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. August 13 – 17, 2016, San Francisco, California, USA. New York: ACM, 2016: 785 – 794.
[31] ZHONG Jiancheng,SUN Yusui,PENG Wei,et al. XGBFEMF:an XGBoost-based framework for essential protein prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience,2018,17(3):243 − 250. DOI: 10.1109/TNB.2018.2842219
[32] 黄发明,殷坤龙,蒋水华,等. 基于聚类分析和支持向量机的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(1):156 − 167. [HUANG Faming,YIN Kunlong,JIANG Shuihua,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on clustering analysis and support vector machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(1):156 − 167. (in Chinese with English abstract) Huang Faming, Yin Kunlong, Jiang Shuihua, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on clustering analysis and support vector machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(1): 156-167. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 张俊,殷坤龙,王佳佳,等. 三峡库区万州区滑坡灾害易发性评价研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(2):284 − 296. [ZHANG Jun,YIN Kunlong,WANG Jiajia,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou District of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(2):284 − 296. (in Chinese with English abstract) Zhang Jun, Yin Kunlong, Wang Jiajia, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou district of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(2): 284-296. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 王芳,殷坤龙,桂蕾,等. 不同日降雨工况下万州区滑坡灾害危险性分析[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(1):190 − 195. [WANG Fang,YIN Kunlong,GUI Lei,et al. Landslide hazard analysis under different daily rainfall conditions in Wanzhou district[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(1):190 − 195. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Fang, YIN Kunlong, GUI Lei, et al. Landslide hazard analysis under different daily rainfall conditions in Wanzhou district[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(1): 190-195. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 刘渊博,牛瑞卿,于宪煜,等. 旋转森林模型在滑坡易发性评价中的应用研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2018,43(6):959 − 964. [LIU Yuanbo,NIU Ruiqing,YU Xianyu,et al. Application of the rotation forest model in landslide susceptibility assessment[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2018,43(6):959 − 964. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Yuanbo, NIU Ruiqing, YU Xianyu, et al. Application of the rotation forest model in landslide susceptibility assessment[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(6): 959-964. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] BASHEER I A,HAJMEER M. Artificial neural networks:fundamentals,computing,design,and application[J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods,2000,43(1):3 − 31. DOI: 10.1016/S0167-7012(00)00201-3
[37] TIAN Liwei,FENG Li,SUN Yu,et al. Forecast of LSTM-XGBoost in stock price based on Bayesian optimization[J]. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing,2021,29(3):855 − 868.
[38] CHEN Yu,WEI Yongming,WANG Qinjun,et al. Mapping post-earthquake landslide susceptibility:A U-net like approach[J]. Remote Sensing,2020,12(17):2767. DOI: 10.3390/rs12172767
[39] ZHANG Kaixiang,WU Xueling,NIU Ruiqing,et al. The assessment of landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest and decision tree methods in the Three Gorges Reservoir area,China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2017,76(11):405. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-017-6731-5
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 刘娟,王宇栋,李晓丽,林静. 基于WOE-CatBoost耦合模型的滑坡灾害易发性评价. 地质灾害与环境保护. 2025(01): 6-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孔雅茜,肖正辉,黄炜敏,罗伟奇,肖巍峰,曹运江,罗路广,唐豪. 极端降雨背景下滑坡易发性评估模型集成及关键因素分析. 国土资源导刊. 2025(01): 89-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郑德凤,潘美伊,高敏,闫成林,李媛媛,年廷凯. 集中降雨影响下辽南仙人洞国家级自然保护区滑坡灾害多因子风险评价. 地质科技通报. 2025(02): 48-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王秀英,杨红娟,贾一凡,张少杰,宋建洋,田华. 利用MIA-HSU方法划分斜坡单元的奉节县滑坡易发性评价. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2025(02): 152-161 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 黄远东,许冲,刘毅,何祥丽,邵霄怡,赵斌滨,孔小昂. 2024年4月广东韶关暴雨诱发的浅层滑坡编目与滑坡分布特征分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2025(02): 28-42 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 安雪莲,密长林,孙德亮,文海家,李晓琴,辜庆渝,丁悦凯. 基于不同评价单元的三峡库区滑坡易发性对比——以重庆市云阳县为例. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2024(05): 1629-1644 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 李瑞晨,侯木舟,孔梦麟,谢昊含. 基于VMD-SegSigmoid-XGBoost-ClusterLSTM算法的山体滑坡表面位移预测. 科技通报. 2024(09): 111-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 周鹏飞,王艳霞. 应用机器学习算法分析广西林火发生驱动因素及林火预测. 东北林业大学学报. 2024(11): 72-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张锦瑞,汪洋,冯霄,李远耀,金必晶,周超,张鑫,邓扬. 考虑地表形变和土地利用变更的滑坡时空易发性差异分析. 地质科技通报. 2024(06): 184-195 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 马祥龙,文海家,张廷斌,孙德亮,潘明辰. 自动可解释机器学习滑坡易发性评价模型. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(06): 806-818 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(10)



 下载:
下载:

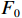
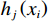
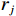
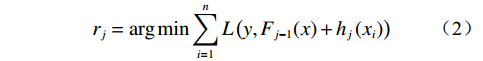
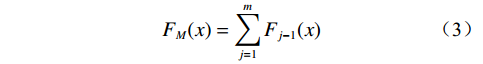
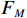
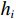
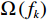
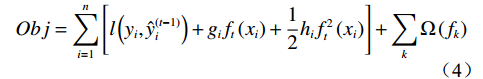
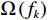




 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS