Open-pit mine slopes stability analysis based on analytic hierarchy process-fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model
-
摘要:
露天煤矿台阶所构成的边坡对矿山资源生产及运输发挥着重要的作用,也承载着煤炭外运的任务,其稳定性对矿山连续生产具有重要意义。文章在边坡地质调查和监测信息分析的基础上,充分考虑边坡几何形态、地质信息、气象水文信息、现场监测信息等指标,以层次分析法确定边坡稳定性分析的指标权重,基于隶属度最大原则确定边坡稳定性状态,建立了多源信息融合的边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型。将该模型应用于扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡稳定性分析中,最后基于数值模拟对模型进行了验证。研究表明,北帮边坡基本稳定,基于数值模拟得出扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡滑移面安全系数为1.121,模型结果与数值模拟结果所得到的边坡稳定性状态吻合度较好,验证了模型的有效性。该模型可以充分考虑多重信息对边坡稳定性分析的贡献,从而更全面准确分析边坡稳定性。
Abstract:The bench slope within an open-pit coal mine plays an important supporting role for coal resource production and transportation. The stability evaluation of the slope is of great significance in guiding continuous mining operations within the mine. This study leverages monitoring data and geological surveys of the slope, employing the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) to assign weights to slope stability analysis factors. Additionally, it employs the principle of maximum membership degree, taking into account various parameters such as slope geometry, geological data, meteorological and hydrological information, and field monitoring data. This paper establishes an analytic hierarchy process - fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model for slope stability assessment. Subsequently, the model is applied to analyze the stability of the north slope at the Zhahanao’er open-pit coal mine. The research indicates that, accordingly to the established slope analytic hierarchy process - fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model, the northern slope is deemed to be fundamentally stable. The numerical simulated FOS (factor of safety) of 1.121 aligns remarkably well with model results. It is comprehensive and accurate since the model can fully consider the contribution of multiple information to the stability of slope.
-
0. 引 言
据不完全统计我国共有露天煤矿约300座(不含井露联合开采煤矿),产能达7.5908×108 t/a[1]。露天矿山边坡失稳滑坡会直接威胁到矿山工作者的生命和财产安全[2],由若干台阶构成的边坡也是露天矿山生产运输的主要依托对象,露天边坡稳定性直接影响到露天矿山的建设和生产。露天矿边坡稳定性分析一直是岩土工程领域研究的热点问题,一方面,露天矿边坡往往受多种影响因素共同作用,关系复杂[3]。另一方面,试验室难以还原现场地质条件及其他因素的影响,试验室岩样数据往往不能直接用于矿山边坡稳定性分析,所以作为露天矿边坡稳定性计算及数值模拟中岩(土)体的参数取值具有很大的模糊性,导致露天矿边坡是一个不确定性的系统,其稳定性评价也是一个不确定、多因素、非线性问题[4]。
针对露天矿边坡稳定性评价问题的不确定性、复杂性,一些学者将模糊评价理论等不确定性分析方法应用到边坡稳定性分析中。蒋中明[5]通过对边坡刚体极限平衡分析中模糊因素的分析, 提出了一种使用模糊集理论计算工程边坡稳定性的方法。丁浩江等[6]、王华俊等[7]分别运用模糊综合评价模型对澜沧江某水电站泄洪洞出口边坡和宁波市国省道公路岩质边坡进行了稳定性评价,评价结果均与实际情况吻合较好,验证了模糊综合评价方法运用于边坡稳定性分析的有效性。由于不同影响因素对边坡稳定性的影响不同,模糊综合评价方法中边坡影响因素权重的确定存在主观性,因此先采用层次分析法客观确定不同因素对边坡稳定性的影响权重进而采用模糊综合评价法对边坡稳定性进行评价效果会更好[8 − 9]。但是目前边坡稳定性分析的层次分析-模糊综合评价模型的评价指标主要来自边坡地质调查和边坡基本形态。已有研究中,将边坡变形监测信息作为评价指标纳入到该模型中的研究相对较少;此外已有研究主要通过现场观察边坡是否稳定来验证模型,这种模型验证方法存在一定的主观性。
基于此,本文建立了考虑边坡监测信息的层次分析-模糊综合评价模型,首先对边坡监测数据进行分析,然后将边坡监测信息纳入边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型中,同边坡几何形态、边坡地质信息、气象水文信息等构成边坡系统的评价指标,然后基于层次分析法确定边坡稳定性评价指标的权重,最后基于隶属度最大原则确定边坡稳定性状态。将建立的层次分析-模糊综合评价模型应用于扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡稳定性评价,综合得出北帮边坡稳定性状况,最后通过数值模拟求解边坡安全系数对模型评价结果进行验证。
1. 边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型
模糊综合评价法对于复杂及不确定系统的评价具有明显的优势,将模糊综合评价法应用于边坡稳定性分析中首先需要确定边坡模糊指标集和评价集,然后根据隶属度函数确定单因子评价矩阵,根据边坡指标权重进行赋值,最后将权重向量与评价矩阵相结合根据隶属度最大原则得到最终的边坡稳定性评价结果[10 − 12]。
1.1 边坡模糊综合评价指标体系
根据相关规范[12],边坡的稳定性可以分为稳定、基本稳定、欠稳定、不稳定4个级别,同时建立边坡几何形态、边坡地质信息、边坡气象水文信息、边坡监测信息等四类边坡一级影响指标。边坡几何形态包括边坡坡高、边坡坡度、边坡结构类型3类指标;边坡地质信息包括边坡岩性、边坡弱层2项评价指标,边坡气象水文信息包括地下水影响、年平均降雨量2项评价指标;边坡监测信息主要包括地面变形情况、边坡变形速率等评价指标。边坡评价指标共9项,其中定量指标4项,定性指标5项。参考规范及已有研究[12 − 13]确定影响等级如表1和表2所示。
表 1 连续型指标影响等级划分Table 1. Classification of impact levels for continuous influencing indicators稳定性 坡高/m 坡度/(°) 年均降雨量/mm 地表变形
速率/(mm·d−1)稳定 0~100 0~15 0~500 5 基本稳定 >100~200 >15~30 >500~800 >5~30 欠稳定 >200~300 >30~50 >800~1200 >30~80 不稳定 >300 >50 >1200 >80 表 2 离散型指标影响等级划分Table 2. Classification of impact levels for discrete influencing indicators稳定性 岩性 结构类型 弱层 地面变形 地下水影响 稳定 坚硬岩体 均质/反倾 无 无 很弱 基本稳定 中等坚硬 斜交/横坡 反倾夹层 弱 较弱 欠稳定 软弱岩体 近水平坡 顺倾夹层、
反倾基岩中等 较强 不稳定 松散体 顺向坡 顺倾基岩 强烈 很强 1.2 层次分析法
对于露天矿边坡而言,各评价指标对边坡稳定性评价的贡献度是不同的,因此有必要利用层次分析法确定边坡各评价指标的影响因子[14]。通过标度方法,将影响因子的重要程度定量化[15]。如表3所示,通过指标两两比较后得出最终的边坡评价指标排序,表3中
${u_i}$ 、${u_j}$ 分别代表不同的评价指标[16]。表 3 层次分析法(AHP)影响因子标度Table 3. Analytic hierarchy process (AHP) influence factor scale标度 含义 1 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标影响程度相同 3 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标影响程度相比,一个比另一个稍微重要 5 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标影响程度相比,一个比另一个明显重要 7 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标影响程度相比,一个比另一个强烈重要 9 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标影响程度相比,一个比另一个极端重要 2,4,6,8 介于以上两种比较之间的标度值 倒数 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标之间判断${b_{ij}}$,${u_j}$和${u_i}$指标之间判断${1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 {{b_{ij}}}}} \right. } {{b_{ij}}}}$ 1.3 模型隶属度函数
隶属函数的确定对于边坡模糊综合评价具有重要的意义,隶属函数值即隶属度是表征边坡评价因子隶属于某个评价等级的程度。对于定量因素采用三角隶属度分布函数,本文采用的三角隶属度函数式(1)—(3)[17 − 18]。离散型指标隶属度的确定取值见表4[9, 13]。考虑到各个评价指标在边坡稳定性评价中的贡献不同,采用层次分析法将各项评价指标赋予一定的权重值,通过标度方法,将评价因子的重要程度定量化。
表 4 离散型指标评价隶属度表Table 4. Discrete index evaluation membership degree离散型指标 具体指标 离散型指标评价隶属度 稳定 基本稳定 欠稳定 不稳定 岩性 坚硬岩体 0.8 0.2 0 0 中等坚硬 0.4 0.5 0.1 0 软弱岩体 0 0.2 0.5 0.3 松散体 0 0 0.2 0.8 结构类型 顺向坡 0 0 0.2 0.8 近水平坡 0.1 0.2 0.7 0 斜交/横坡 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 均质/反倾 0.8 0.2 0 0 弱层 无 1 0 0 0 反倾夹层 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 顺倾夹层、反倾基岩 0 0.1 0.7 0.2 顺倾基岩 0 0 0.2 0.8 地面变形 无 0.8 0.2 0 0 弱 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 中等 0 0.1 0.7 0.2 强烈 0 0 0.2 0.8 地下水影响 很弱 0.55 0.30 0.10 0.05 较弱 0.25 0.50 0.15 0.10 较强 0.05 0.10 0.30 0.55 很强 0.05 0.15 0.10 0.70 $$ {V_{i1}}\left( {{x_i}} \right) = \left\{ {\begin{split} & 1 \quad\quad\quad\;\;\;{{x_i} \leqslant {a_{i1}}} \\ & {\frac{{{a_{i2}} - {x_i}}}{{{a_{i2}} - {a_{i1}}}}}\quad{{a_{i1}} < {x_i} \leqslant {a_{i2}}} \\ &0\quad\quad\quad\;\;\;{{x_i} > {a_{i2}}} \end{split}} \right. $$ (1) $$ V_{ij}\left(x_i\right)=\left\{\begin{split} & \frac{x_i-a_{ij-1}}{a_{ij}-a_{ij-1}}\quad a_{ij-1} < x_i\leqslant a_{ij} \\ & 0\quad\quad\quad\quad\; x_i\leqslant a_{ij-1}或x_i > a_{ij+1} \\ & \frac{a_{ij+1}-x_i}{a_{ij+1}-a_{ij}}\quad a_{ij} < x_i\leqslant a_{ij+1} \end{split} \right. $$ (2) $$ {V_{i1}}\left( {{x_i}} \right) = \left\{ {\begin{split} &1\quad\quad\quad\;\;\;{{x_i} \geqslant {a_{i5}}} \\ &{\frac{{{x_i} - {a_{i4}}}}{{{a_{i5}} - {a_{i4}}}}}\quad{{a_{i4}} \leqslant {x_i} < {a_{i5}}} \\ & 0\quad\quad\quad\;\;\;{{x_i} < {a_{i4}}} \end{split}} \right. $$ (3) 式中:
${x_i}$ ——连续变量指标值$\left( {i = 1,2 \cdots n} \right) $ ;${V_{ij}}$ ——${x_i}$ 对应4个危险等级隶属度(j=1, 2, 3, 4);${a_{ij}}$ ——风险等级划分标准值[19](j=1, 2, 3, 4)。2. 层次分析-模糊综合评价模型应用
2.1 工程概况
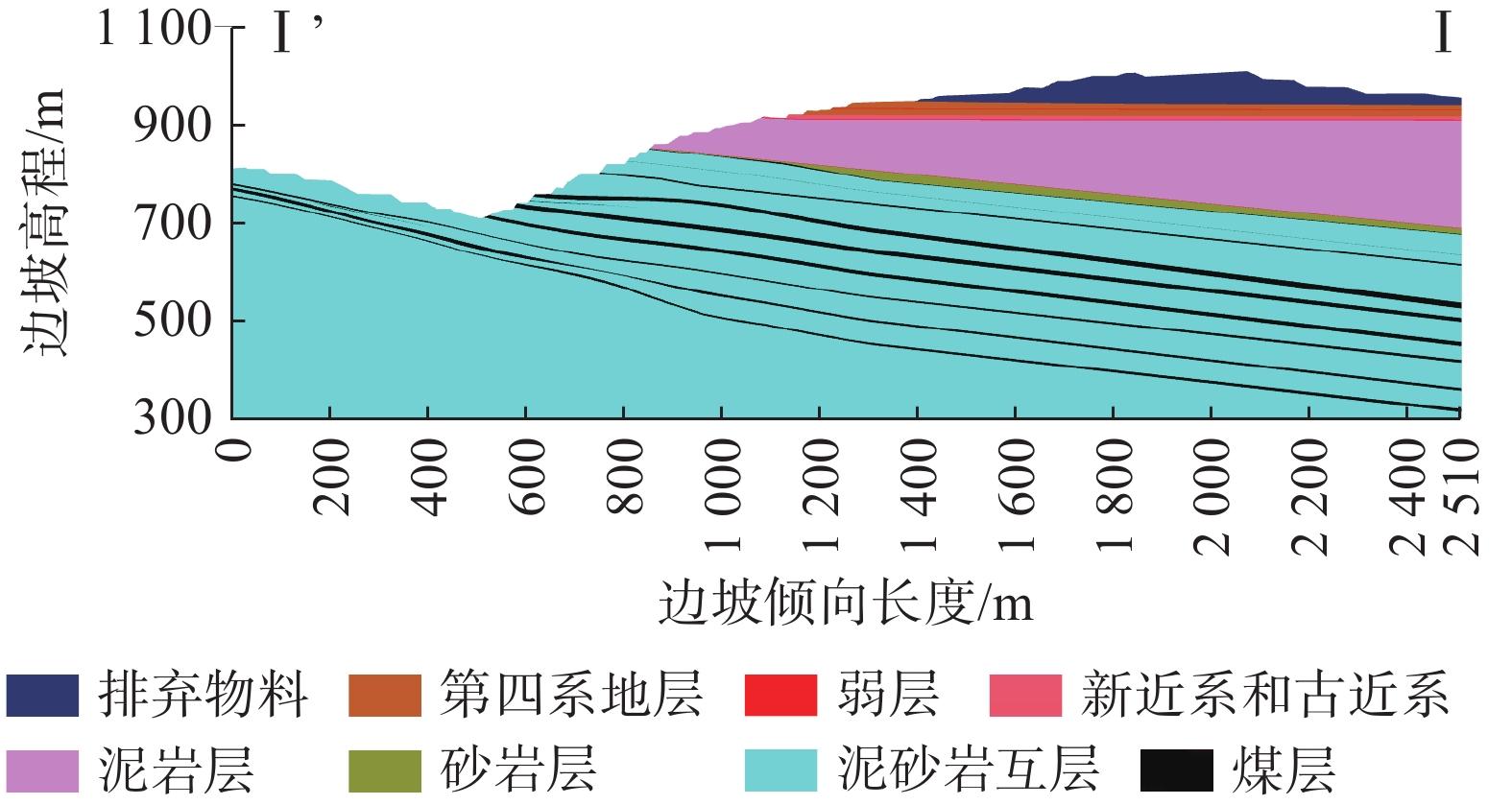
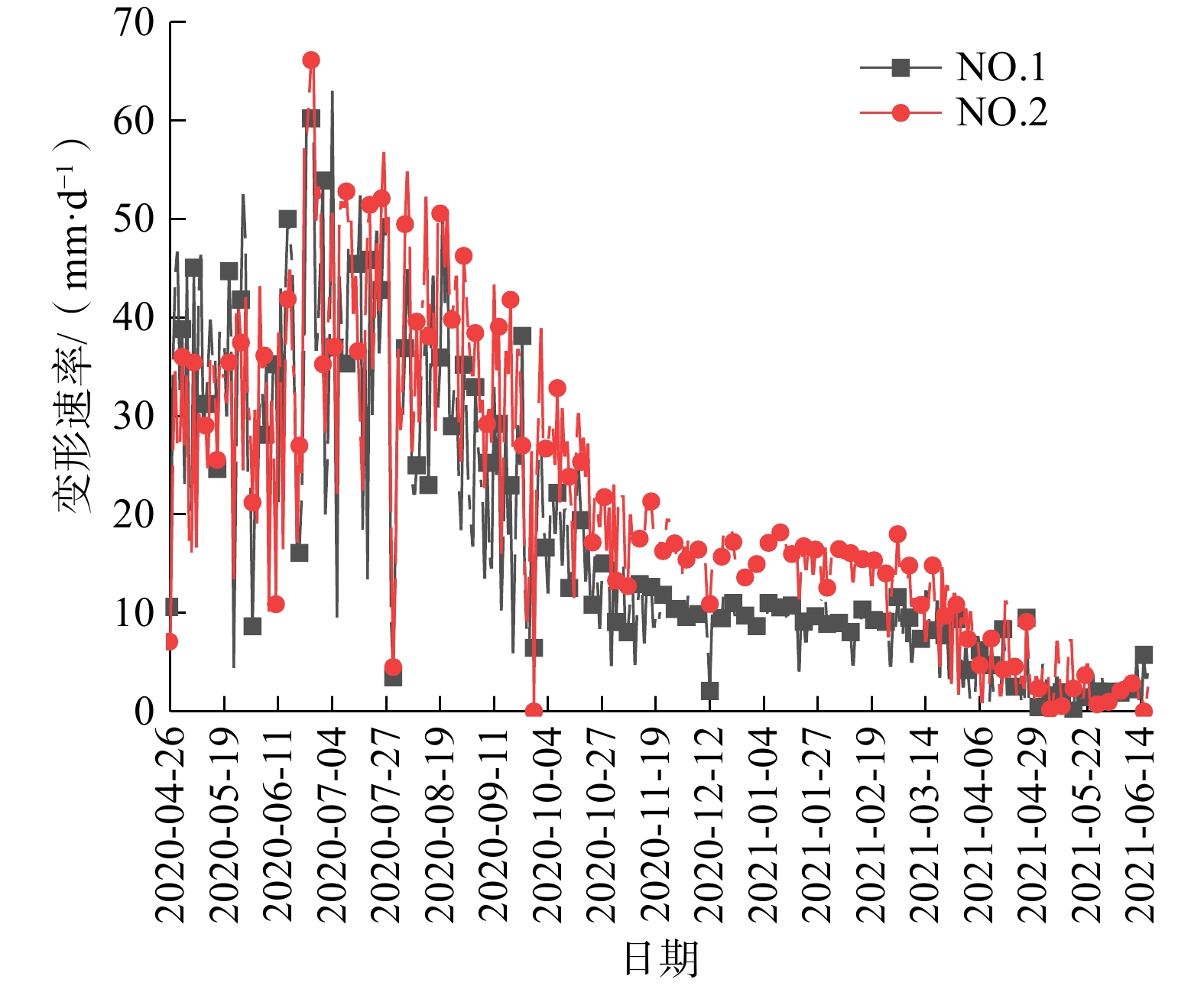
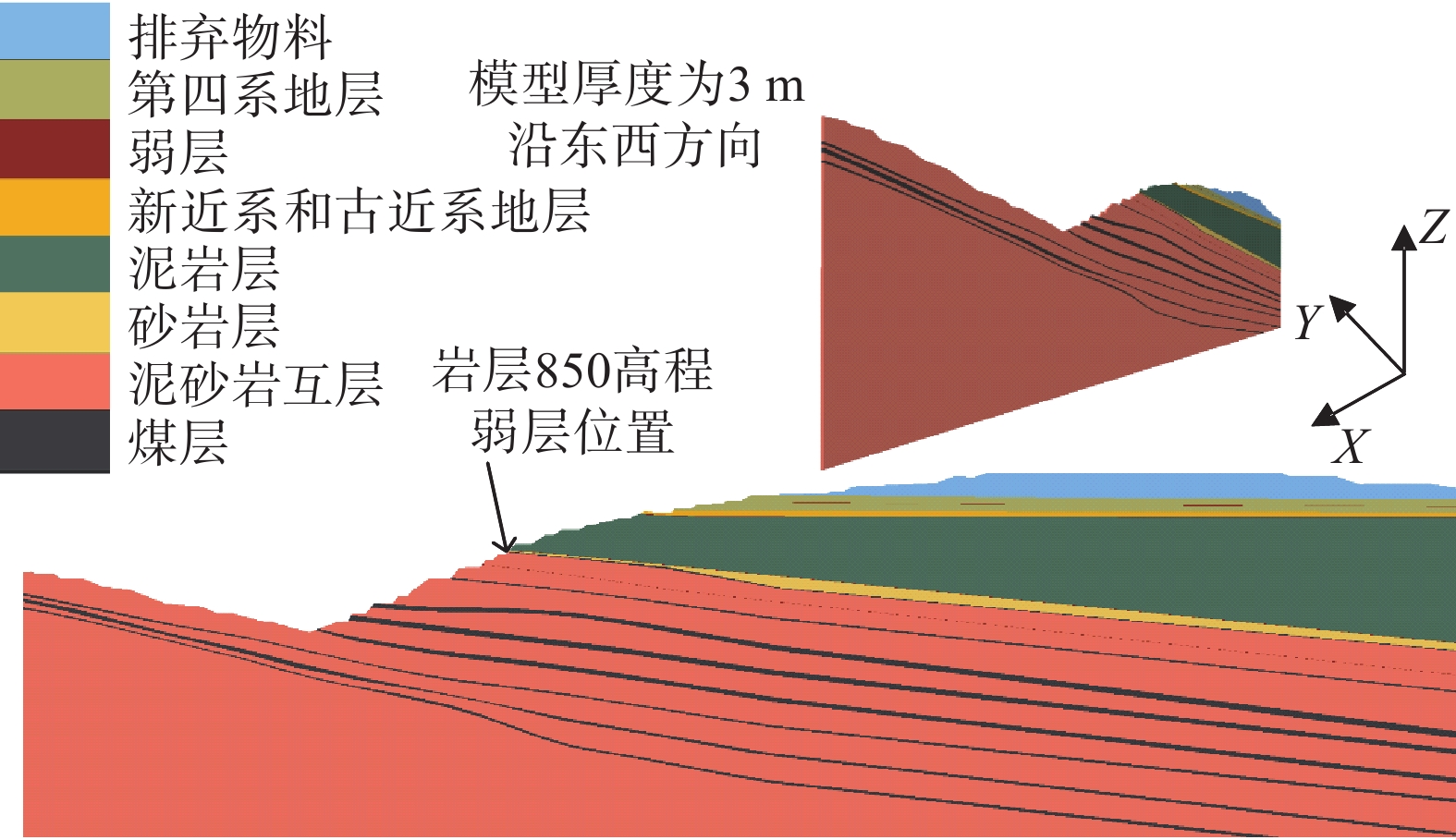
扎哈淖尔露天煤矿位于内蒙古自治区通辽市西北端,露天矿北帮于2020年5月出现明显的变形现象,边坡上部940水平及920水平出现明显裂隙,采场下部边坡850水平出现明显的大块岩体剪出现象,图1为扎哈淖尔露天矿的俯瞰图及现场图。沿边坡倾向方向选取研究剖面(图2),NO.1和NO.2为布置在剖面上的微变监测雷达监测特征点,露天矿北帮岩(土)层剖面如图3所示,北帮岩体整体倾向为逆倾、倾角5°~13°,边坡高度为234 m,坡度为16°,自上而下依次为第四系岩层、新近系和古近系岩层、泥岩、泥砂岩互层及煤层。经过现场勘探北帮850水平存在一层弱层,弱层厚度在1~2 m,钻孔岩芯(图4)显示弱层附近岩体较破碎。同时北帮边坡泥岩和第四系黏土中有出水点[20 − 21]。
2.2 基于层次分析-模糊综合评价模型的边坡稳定性评价
根据现场勘察及收集已有的矿山地质资料,确定边坡高度为234 m,坡度为16°,年平均降雨量为354.3 mm,边坡变形速率取目前NO.1点和NO.2点监测数据的平均值,根据现场监测取值为24 mm/d,对于折减系数的取值,基于安全的角度,边坡模糊综合评价中的折减系数选取数值计算所得的较低值(1.121),定量指标采用三角形隶属度函数确定(表5)。定性指标隶属度参考相关文献确定(表6)最后得到边坡模糊综合评价矩阵R,进一步利用层次分析法确定了扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡模糊评价指标的权重矩阵M,并进行一致性检验[22 − 24]。
表 5 北帮边坡定量指标隶属度Table 5. Membership degree of quantitative indexes for the northern slope稳定性 坡高隶属度 坡度隶属度 年均降雨量
隶属度地表变形速率
隶属度稳定 0 0.86 1 0 基本稳定 0.16 0.14 0 0.83 欠稳定 0.84 0 0 0.17 不稳定 0 0 0 0 表 6 北帮边坡定性指标隶属度Table 6. Membership degrees of qualitative indexes for the northern slope稳定性 岩性隶属度 结构类型
隶属度弱层隶属度 地面变形
隶属度地下水影响
隶属度稳定 0 0.80 0.20 0 0.05 基本稳定 0.20 0.20 0.70 0 0.10 欠稳定 0.50 0 0.10 0.20 0.30 不稳定 0.30 0 0 0.80 0.55 边坡地表变形监测主要分析微变监测雷达系统于2020年4月26日—2021年6月14日NO.1点位和NO.2点位的微变监测雷达监测数据,将监测点的变形速率用不同的点线图来表示(图5),由图5可见边坡最初变形速率较快,后期变形速率逐渐趋于稳定。
$$ {\boldsymbol{R}}{\text{ = }}\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {0.00}&{0.16}&{0.84}&{0.00} \\ {0.86}&{0.14}&{0.00}&{0.00} \\ {1.00}&{0.00}&{0.00}&{0.00} \\ {0.00}&{0.83}&{0.17}&{0.00} \\ {0.00}&{0.20}&{0.50}&{0.30} \\ {0.80}&{0.20}&{0.00}&{0.00} \\ {0.20}&{0.70}&{0.10}&{0.00} \\ {0.00}&{0.00}&{0.20}&{0.80} \\ {0.05}&{0.10}&{0.30}&{0.55} \end{array}} \right] $$ $$ \begin{split} {\boldsymbol{M }}= &( {0.042}\;\;{0.145}\;\;{0.015}\;\;{0.288}\;\;{0.133}\;\\ &{0.127}\;\;{0.152}\;\;{0.023}\;\;{0.075} ) \end{split}$$ 由模糊综合评价法确定的模糊综合评价矩阵以及通过层次分析法确定的影响因子矩阵,确定扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡评价矩阵,北帮边坡为稳定状态、基本稳定状态、欠稳定状态、不稳定状态的隶属度分别为0.27545,0.43196,0.19304,0.09955,最大隶属度原则是得到边坡稳定性最常用的方法,但是如果第二大隶属度与最大隶属度值很接近的话,得到的评价结果准确度降低,基于此,首先对隶属度矩阵进行有效性检验。最大隶属度有效性验证公式如下[25]:
$$ a = \frac{{n\beta - 1}}{{2\gamma \left( {n - 1} \right)}} $$ (4) 式中:
$a$ ——有效度;$n$ ——评价集中的元素个数;$\beta $ ——目标评价向量中最大隶属度;$\gamma $ ——目标评价向量中的第二大隶属度。经过计算,扎哈淖尔露天煤矿北帮边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型所得的隶属度矩阵有效度为0.65521,属于比较有效,说明评价结果是稳定的,根据隶属度最大原则判定北帮边坡属于基本稳定状态。
2.3 模型检验
本研究通过数值模拟对层次分析-模糊综合评价模型得到的北帮边坡稳定性结果进行检验,根据北帮研究区剖面(图2)建立数值计算模型(图6),模型计算选取的坐标系为边坡临空面方向为X正方向,竖直向上为Z正方向。模型的左右边界(南北)、前后边界(东西)和底部边界分别以水平和垂直方向的位移约束,顶面设定为自由面,采用摩尔-库仑弹塑性本构模型进行求解,岩土体力学参数采用Hoek-Brown岩体强度方法并结合现场研究报告综合确定岩土体力学参数如表7所示[26 − 27]。
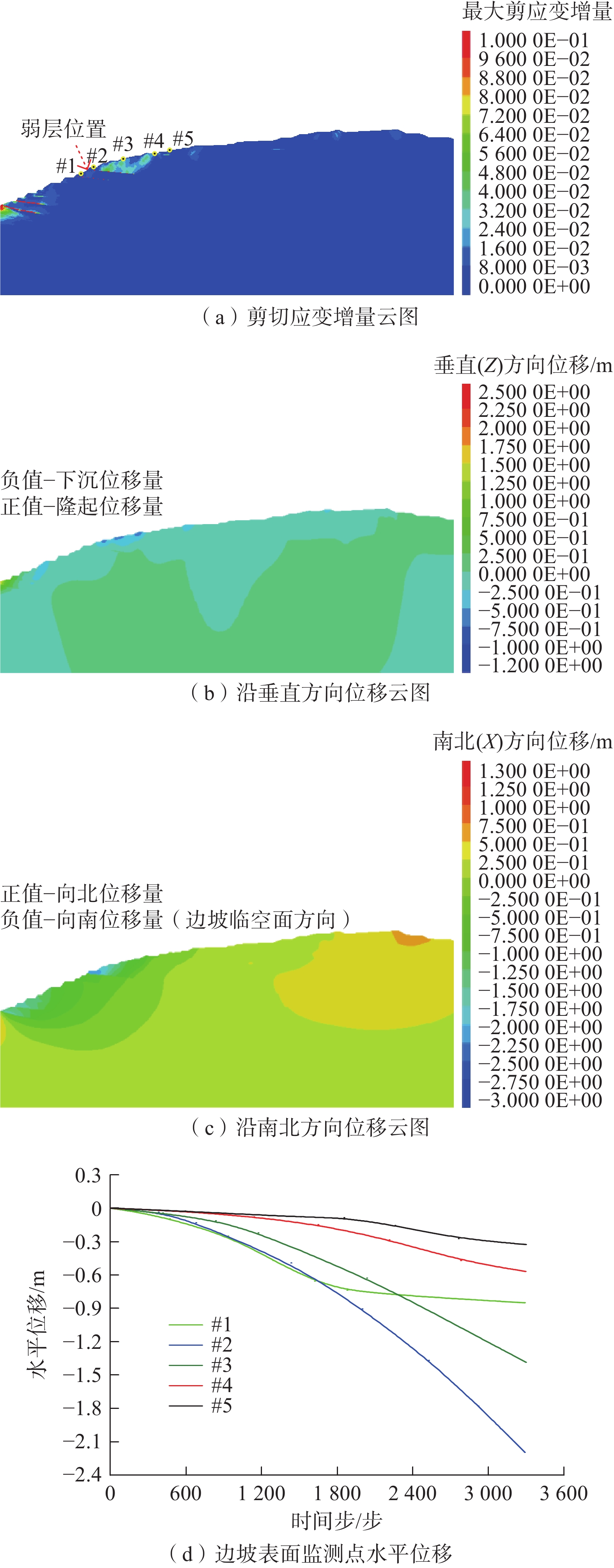
表 7 岩层物理力学参数表Table 7. Physico-mechanical parameters of strata岩层 重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 排弃物料 17.70 10.0 20.0 第四系地层 17.90 17.0 11.7 弱层 17.90 8.0 5.7 新近系和古近系地层 17.90 14.0 13.0 泥岩层 20.20 33.7 15.4 砂岩层 24.40 40.0 28.0 泥砂岩互层 23.45 35.0 24.6 煤层 12.70 24.5 21.0 采用人为定义边坡折减强度上下限的方法确定边坡的折减系数,首先初步确定边坡折减系数的范围,然后以0.001为一个梯度进行折减计算,通常数值模拟对岩土体强度的折减是针对整个边坡区域进行折减,不能计算边坡内部多级滑动面。而对于多台阶边坡而言,每级台阶的折减系数和潜在滑移面都是值得关注的。因此在模拟过程中只折减850水平以上岩层和煤层的黏聚力和摩擦角[28 − 29]。模拟结果如图7所示,850水平之上形成潜在滑坡面,边坡剪切变形相对集中于局部化变形区域内,而区域外的变形相当于卸载后的刚体运动,潜在滑坡体将沿该滑动面滑动,滑动面两侧沿滑动面方向的位移相差明显,存在较大的变形梯度。通过监测边坡表面各测点位移可发现随着监测点高程增大其位移量减小,边坡内部形成潜在滑坡面,滑移面安全系数为1.121。
基于强度折减法得到北帮潜在滑移面安全系数分别为1.121(850水平以上),根据相关规范边坡稳定性划分表(表8)[12],北帮850水平上部边坡属于基本稳定边坡,层次分析-模糊综合评价模型得到的边坡稳定性状态与数值模拟强度折减法得到的边坡稳定性状态相一致,验证了模型的准确性。
表 8 边坡稳定性状态划分Table 8. Classification of slope stability states边坡安全系数 F<1.00 1.00≤F<1.05 1.05≤F<1.20 F≥1.20 边坡稳定状态 不稳定 欠稳定 基本稳定 稳定 3. 结论
(1)在监测数据分析和数值模拟的基础上,建立了考虑监测信息的边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型,该模型充分融合了边坡几何形态、边坡地质信息、气象水文信息、现场监测信息等多种信息。
(2)北帮边坡稳定性状态为稳定、基本稳定、欠稳定、不稳定,隶属度分别为0.27545,0.43196,0.19304,0.09955,根据隶属度最大原则得出北帮边坡目前处于基本稳定状态。
(3)通过数值模拟求解得北帮边坡滑移面安全系数为1.121,属于基本稳定边坡,强度折减法结果与所建立的边坡层次分析-模糊综合评价模型得到的边坡稳定性状态一致,验证了模型的有效性。
-
表 1 连续型指标影响等级划分
Table 1 Classification of impact levels for continuous influencing indicators
稳定性 坡高/m 坡度/(°) 年均降雨量/mm 地表变形
速率/(mm·d−1)稳定 0~100 0~15 0~500 5 基本稳定 >100~200 >15~30 >500~800 >5~30 欠稳定 >200~300 >30~50 >800~1200 >30~80 不稳定 >300 >50 >1200 >80 表 2 离散型指标影响等级划分
Table 2 Classification of impact levels for discrete influencing indicators
稳定性 岩性 结构类型 弱层 地面变形 地下水影响 稳定 坚硬岩体 均质/反倾 无 无 很弱 基本稳定 中等坚硬 斜交/横坡 反倾夹层 弱 较弱 欠稳定 软弱岩体 近水平坡 顺倾夹层、
反倾基岩中等 较强 不稳定 松散体 顺向坡 顺倾基岩 强烈 很强 表 3 层次分析法(AHP)影响因子标度
Table 3 Analytic hierarchy process (AHP) influence factor scale
标度 含义 1 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标影响程度相同 3 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标影响程度相比,一个比另一个稍微重要 5 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标影响程度相比,一个比另一个明显重要 7 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标影响程度相比,一个比另一个强烈重要 9 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标影响程度相比,一个比另一个极端重要 2,4,6,8 介于以上两种比较之间的标度值 倒数 ${u_i}$和${u_j}$指标之间判断${b_{ij}}$,${u_j}$和${u_i}$指标之间判断${1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 {{b_{ij}}}}} \right. } {{b_{ij}}}}$ 表 4 离散型指标评价隶属度表
Table 4 Discrete index evaluation membership degree
离散型指标 具体指标 离散型指标评价隶属度 稳定 基本稳定 欠稳定 不稳定 岩性 坚硬岩体 0.8 0.2 0 0 中等坚硬 0.4 0.5 0.1 0 软弱岩体 0 0.2 0.5 0.3 松散体 0 0 0.2 0.8 结构类型 顺向坡 0 0 0.2 0.8 近水平坡 0.1 0.2 0.7 0 斜交/横坡 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 均质/反倾 0.8 0.2 0 0 弱层 无 1 0 0 0 反倾夹层 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 顺倾夹层、反倾基岩 0 0.1 0.7 0.2 顺倾基岩 0 0 0.2 0.8 地面变形 无 0.8 0.2 0 0 弱 0.2 0.7 0.1 0 中等 0 0.1 0.7 0.2 强烈 0 0 0.2 0.8 地下水影响 很弱 0.55 0.30 0.10 0.05 较弱 0.25 0.50 0.15 0.10 较强 0.05 0.10 0.30 0.55 很强 0.05 0.15 0.10 0.70 表 5 北帮边坡定量指标隶属度
Table 5 Membership degree of quantitative indexes for the northern slope
稳定性 坡高隶属度 坡度隶属度 年均降雨量
隶属度地表变形速率
隶属度稳定 0 0.86 1 0 基本稳定 0.16 0.14 0 0.83 欠稳定 0.84 0 0 0.17 不稳定 0 0 0 0 表 6 北帮边坡定性指标隶属度
Table 6 Membership degrees of qualitative indexes for the northern slope
稳定性 岩性隶属度 结构类型
隶属度弱层隶属度 地面变形
隶属度地下水影响
隶属度稳定 0 0.80 0.20 0 0.05 基本稳定 0.20 0.20 0.70 0 0.10 欠稳定 0.50 0 0.10 0.20 0.30 不稳定 0.30 0 0 0.80 0.55 表 7 岩层物理力学参数表
Table 7 Physico-mechanical parameters of strata
岩层 重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 排弃物料 17.70 10.0 20.0 第四系地层 17.90 17.0 11.7 弱层 17.90 8.0 5.7 新近系和古近系地层 17.90 14.0 13.0 泥岩层 20.20 33.7 15.4 砂岩层 24.40 40.0 28.0 泥砂岩互层 23.45 35.0 24.6 煤层 12.70 24.5 21.0 表 8 边坡稳定性状态划分
Table 8 Classification of slope stability states
边坡安全系数 F<1.00 1.00≤F<1.05 1.05≤F<1.20 F≥1.20 边坡稳定状态 不稳定 欠稳定 基本稳定 稳定 -
[1] 李浩荡,佘长超,周永利,等. 我国露天煤矿开采技术综述及展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(10):24 − 35. [LI Haodang,SHE Changchao,ZHOU Yongli,et al. Summary and prospect of open-pit coal mining technology in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019,47(10):24 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Haodang, SHE Changchao, ZHOU Yongli, et al . Summary and prospect of open-pit coal mining technology in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2019 ,47 (10 ):24 −35 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] WEI Zuoan,YIN Guangzhi,WAN Ling,et al. Case history of controlling a landslide at Panluo open-pit mine in China[J]. Environmental Geology,2008,54(4):699 − 709. DOI: 10.1007/s00254-007-0839-y
[3] 谭文辉,乔兰,王鹏. 高陡边坡岩体力学环境的模糊综合评判研究[J]. 金属矿山,2002(12):20 − 22. [TAN Wenhui,QIAO Lan,WANG Peng. Study on the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of the mechanical environment of rockmass in high-steep slopes[J]. Metal Mine,2002(12):20 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2002.12.007 TAN Wenhui, QIAO Lan, WANG Peng . Study on the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of the mechanical environment of rockmass in high-steep slopes[J]. Metal Mine,2002 (12 ):20 −22 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2002.12.007[4] 张永杰,邓俊强,李侑军,等. 考虑隶属函数特性的边坡模糊可靠性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(7):1350 − 1358. [ZHANG Yongjie,DENG Junqiang,LI Youjun,et al. Fuzzy reliability analysis of slopes considering characteristics of membership function[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018,40(7):1350 − 1358. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Yongjie, DENG Junqiang, LI Youjun, et al . Fuzzy reliability analysis of slopes considering characteristics of membership function[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018 ,40 (7 ):1350 −1358 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 蒋中明. 模糊分析理论及其岩土工程中的应用研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(24):4263. [JIANG Zhongming. Study on fuzzy analysis theory and its application in geotechnical engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004,23(24):4263. (in Chinese with English abstract)] JIANG Zhongming . Study on fuzzy analysis theory and its application in geotechnical engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004 ,23 (24 ):4263 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 杨正荣,喜文飞,史正涛,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的白鹤滩水电站库岸潜在滑坡变形分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(5):83 − 92. [YANG Zhengrong,XI Wenfei,SHI Zhengtao,et al. Deformation analysis in the bank slopes in the reservoir area of Baihetan Hydropower Station based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(5):83 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Zhengrong, XI Wenfei, SHI Zhengtao, et al. Deformation analysis in the bank slopes in the reservoir area of Baihetan Hydropower Station based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(5): 83 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 廖小平, 徐风光, 蔡旭东, 等. 香丽高速公路边坡地质灾害发育特征与易发性区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):121 − 129. [LIAO Xiaoping, XU Fengguang, CAI Xudong,etal. Development characteristics and susceptibality zoning of slope geological hazards in Xiangli expressway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):121 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIAO Xiaoping, XU Fengguang, CAI Xudong, etal . Development characteristics and susceptibality zoning of slope geological hazards in Xiangli expressway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (5 ):121 −129 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 刘春. 运用AHP-FUZZY法判定岩质边坡稳定性[J]. 华侨大学学报(自然科学版),2006,27(4):388 − 391. [LIU Chun. Slope stability analysis by AHP-FUZZY method[J]. Journal of Huaqiao University (Natural Science),2006,27(4):388 − 391. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Chun . Slope stability analysis by AHP-FUZZY method[J]. Journal of Huaqiao University (Natural Science),2006 ,27 (4 ):388 −391 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 胡田飞,朱本珍. 基于熵权法和层次分析法的复杂边坡稳定性模糊综合评价方法[J]. 铁道建筑,2013,53(12):69 − 73. [HU Tianfei,ZHU Benzhen. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method of complex slope stability based on entropy weight method and analytic hierarchy process[J]. Railway Engineering,2013,53(12):69 − 73. (in Chinese)] HU Tianfei, ZHU Benzhen . Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method of complex slope stability based on entropy weight method and analytic hierarchy process[J]. Railway Engineering,2013 ,53 (12 ):69 −73 . (in Chinese)[10] 张紫杉,王述红,王斐笠. 基于空间块体表征的岩质边坡稳定性综合评价[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2018,39(6):896 − 901. [ZHANG Zishan,WANG Shuhong,WANG Feili. Comprehensive assessment of rock slope stability based on spatial block identification[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2018,39(6):896 − 901. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Zishan, WANG Shuhong, WANG Feili . Comprehensive assessment of rock slope stability based on spatial block identification[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2018 ,39 (6 ):896 −901 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 张勇慧,李红旭,盛谦,等. 基于模糊综合评判的公路岩质边坡稳定性分级研究[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(10):3151 − 3156. [ZHANG Yonghui,LI Hongxu,SHENG Qian,et al. Study of stability gradation of highway rock slopes based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(10):3151 − 3156. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Yonghui, LI Hongxu, SHENG Qian, et al . Study of stability gradation of highway rock slopes based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010 ,31 (10 ):3151 −3156 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 煤炭工业露天矿边坡工程设计标准:GB51289—2018[S]. 北京:中国计划出版社:2018. [Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for design of slope engineering of open pit mine of coal industry:GB51289—2018[S]. Beijing:China Planning Press:2018. (in Chinese)] Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for design of slope engineering of open pit mine of coal industry: GB51289—2018[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press: 2018. (in Chinese)
[13] 孙书伟,朱本珍,马惠民. 一种基于模糊理论的区域性高边坡稳定性评价方法[J]. 铁道学报,2010,32(3):77 − 83. [SUN Shuwei,ZHU Benzhen,MA Huimin. Method based on fuzzy theory for evaluation of regional high slopes stability[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society,2010,32(3):77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.03.014 SUN Shuwei, ZHU Benzhen, MA Huimin . Method based on fuzzy theory for evaluation of regional high slopes stability[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society,2010 ,32 (3 ):77 −83 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.03.014[14] CHEN Wei,LI Wenping,CHAI Huichan,et al. GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and certainty factor (CF) models for the Baozhong region of Baoji City,China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(1):63. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-015-4795-7
[15] 张卜平, 朱兴华, 成玉祥,等. 黄土潜蚀机理及其致灾效应研究综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):41 − 52. [ZHANG Buping, ZHU Xinghua, CHENG Yuxiang, etal. A review on loess subsurface-erosion mechanism and it’s hazard effects[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):41 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Buping, ZHU Xinghua, CHENG Yuxiang, etal . A review on loess subsurface-erosion mechanism and it’s hazard effects[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (6 ):41 −52 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 谢全敏,夏元友. 岩体边坡治理决策的模糊层次分析方法研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2003,22(7):1117 − 1120. [XIE Quanmin,XIA Yuanyou. Fuzzy hierarchy analysis on decision making of rockmass slope treatment based on entropy weight[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2003,22(7):1117 − 1120. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XIE Quanmin, XIA Yuanyou . Fuzzy hierarchy analysis on decision making of rockmass slope treatment based on entropy weight[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2003 ,22 (7 ):1117 −1120 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] 徐卫亚,蒋中明,石安池. 基于模糊集理论的边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2003,25(4):409 − 413. [XU Weiya,JIANG Zhongming,SHI Anchi. Slope stability analysis using fuzzy sets theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2003,25(4):409 − 413. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XU Weiya, JIANG Zhongming, SHI Anchi . Slope stability analysis using fuzzy sets theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2003 ,25 (4 ):409 −413 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 牛昴懿,杨春风. 锚固路堑高边坡稳定性非线性模糊评判[J]. 公路交通技术,2015,31(2):13 − 19. [NIU Maoyi,YANG Chunfeng. Nonlinear fuzzy evaluation for stability of high cut slopes after anchorage[J]. Technology of Highway and Transport,2015,31(2):13 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)] NIU Maoyi, YANG Chunfeng . Nonlinear fuzzy evaluation for stability of high cut slopes after anchorage[J]. Technology of Highway and Transport,2015 ,31 (2 ):13 −19 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] SUN Wenbin,XUE Yanchao. An improved fuzzy comprehensive evaluation system and application for risk assessment of floor water inrush in deep mining[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering,2019,37(3):1135 − 1145. DOI: 10.1007/s10706-018-0673-x
[20] 徐勇超,李苗苗. 扎哈淖尔露天矿北帮边坡稳定性研究[J]. 露天采矿技术,2020,35(2):14 − 18. [XU Yongchao,LI Miaomiao. Study on stability of north slope of Zhahanao'er open-pit mine[J]. Opencast Mining Technology,2020,35(2):14 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XU Yongchao, LI Miaomiao . Study on stability of north slope of Zhahanao'er open-pit mine[J]. Opencast Mining Technology,2020 ,35 (2 ):14 −18 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[21] 靳鹏,申力,韩晓极,等. 辽宁抚顺西露天矿地质灾害时空分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):68 − 76. [JIN Peng,SHEN Li,HAN Xiaoji,et al. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of geological disasters in the open-pit mining area of western Fushun,Liaoning Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):68 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract)] JIN Peng, SHEN Li, HAN Xiaoji, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of geological disasters in the open-pit mining area of western Fushun,Liaoning Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3): 68 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 付玉宁. 边坡形态与岩层产状对反倾向边坡稳定性影响的数值分析[D]. 西安:长安大学,2015. [FU Yuning. Numerical analysis of the influence of slope shape and rock occurrence on the stability of anti-dip slope[D]. Xi’an:Changan University,2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)] FU Yuning. Numerical analysis of the influence of slope shape and rock occurrence on the stability of anti-dip slope[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 梁乃森,钱程,穆文平,等. 大牛地气田区地下水水质模糊综合评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):52 − 59. [LIANG Naisen,QIAN Cheng,MU Wenping,et al. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of groundwater quality of the Daniudi gas field area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):52 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIANG Naisen, QIAN Cheng, MU Wenping, et al . Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of groundwater quality of the Daniudi gas field area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020 ,47 (3 ):52 −59 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[24] 朱小飞,王永君,李大军. 模糊评价中最大隶属度原则有效性检验[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息,2016,39(5):135 − 137. [ZHU Xiaofei,WANG Yongjun,LI Dajun. The effectiveness test of the maximum membership principle in fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology,2016,39(5):135 − 137. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2016.05.039 ZHU Xiaofei, WANG Yongjun, LI Dajun . The effectiveness test of the maximum membership principle in fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology,2016 ,39 (5 ):135 −137 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2016.05.039[25] 陈亮,邬长福,陈祖云,等. 基于AHP-模糊综合评价法的非煤露天矿山安全标准化复评体系研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发,2016,36(4):99 − 103. [CHEN Liang,WU Changfu,CHEN Zuyun,et al. Study on the reevaluation system of non-coal open-pit mine safety standardization by AHP-fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. Mining Research and Development,2016,36(4):99 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHEN Liang, WU Changfu, CHEN Zuyun, et al . Study on the reevaluation system of non-coal open-pit mine safety standardization by AHP-fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. Mining Research and Development,2016 ,36 (4 ):99 −103 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[26] ZHANG Fei,YANG Tianhong,LI Lianchong,et al. Cooperative monitoring and numerical investigation on the stability of the south slope of the Fushun west open-pit mine[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2019,78(4):2409 − 2429. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-018-1248-z
[27] LI Yuchao,CHEN Jianping,ZHOU Fujun,et al. Stability evaluation of rock slope based on discrete fracture network and discrete element model:A case study for the right bank of Yigong Zangbu Bridge[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2022,17(4):1423 − 1441. DOI: 10.1007/s11440-021-01369-5
[28] 杨建成,邓琴. 基于局部强度折减法的多级边坡潜在滑动面分析[J]. 公路,2016,61(12):19 − 23. [YANG Jiancheng,DENG Qin. Analysis of multi-stage slope potential sliding surface based on local strength reduction method[J]. Highway,2016,61(12):19 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Jiancheng, DENG Qin . Analysis of multi-stage slope potential sliding surface based on local strength reduction method[J]. Highway,2016 ,61 (12 ):19 −23 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[29] 侯世伟,马士贺,李宏男,等. 基于局部强度阶梯折减法的边坡渐进破坏研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2020,40(1):72 − 78. [HOU Shiwei,MA Shihe,LI Hongnan,et al. Research on progressive slope failure based on stepwise reduction method of local strength[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2020,40(1):72 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HOU Shiwei, MA Shihe, LI Hongnan, et al . Research on progressive slope failure based on stepwise reduction method of local strength[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2020 ,40 (1 ):72 −78 . (in Chinese with English abstract)




 下载:
下载:
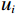
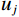
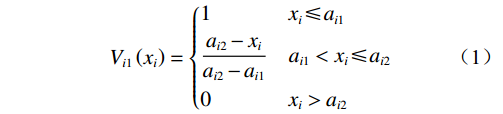
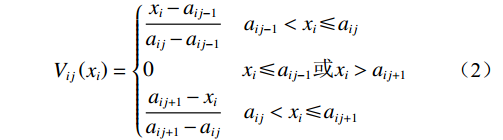
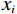
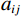




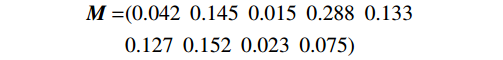
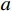
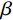
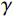
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS