Analysis of the formation process of the covered karst ground collapse induced by groundwater changes based on the coupled LBM-DEM numerical simulation at micro scale
-
摘要:
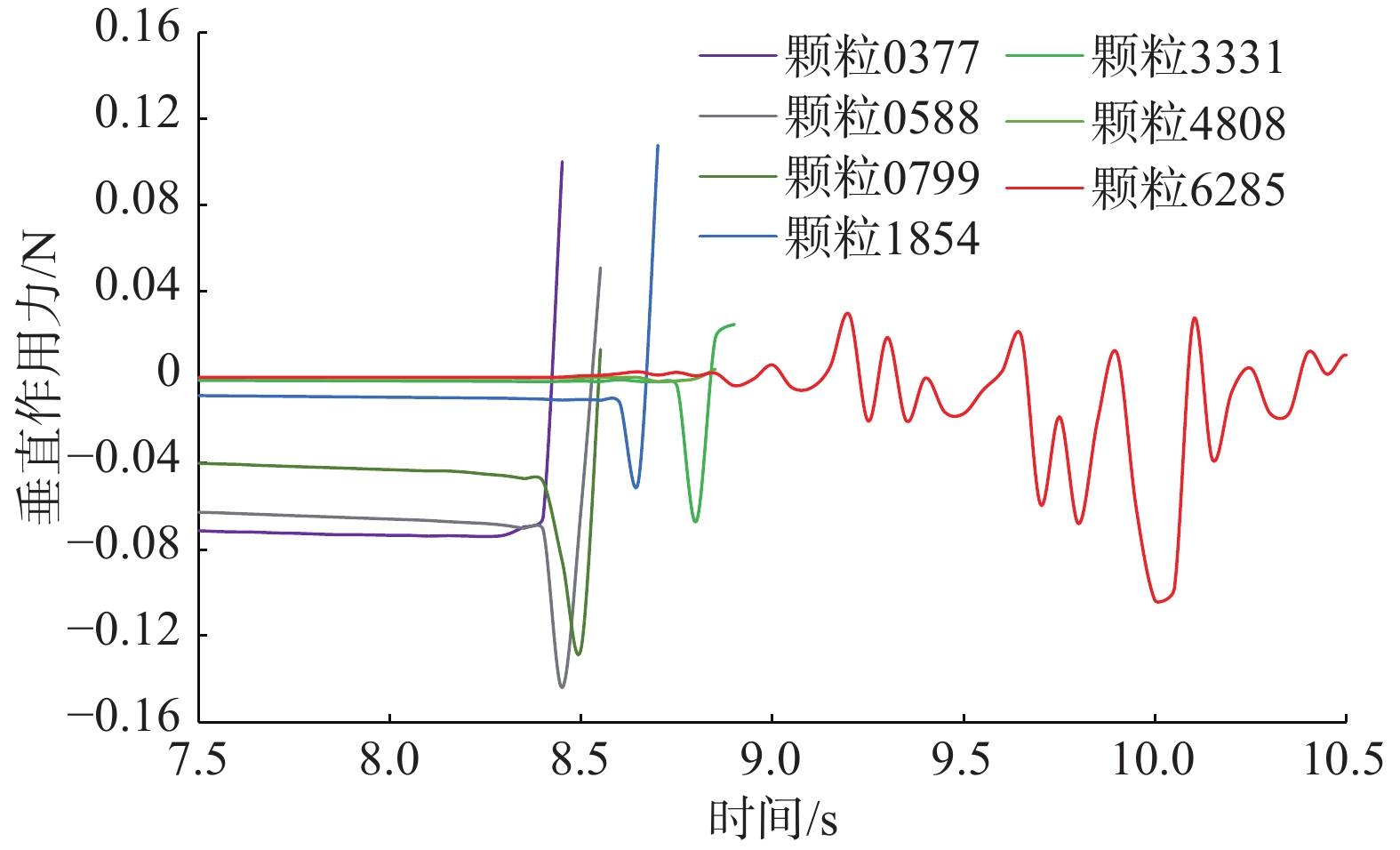
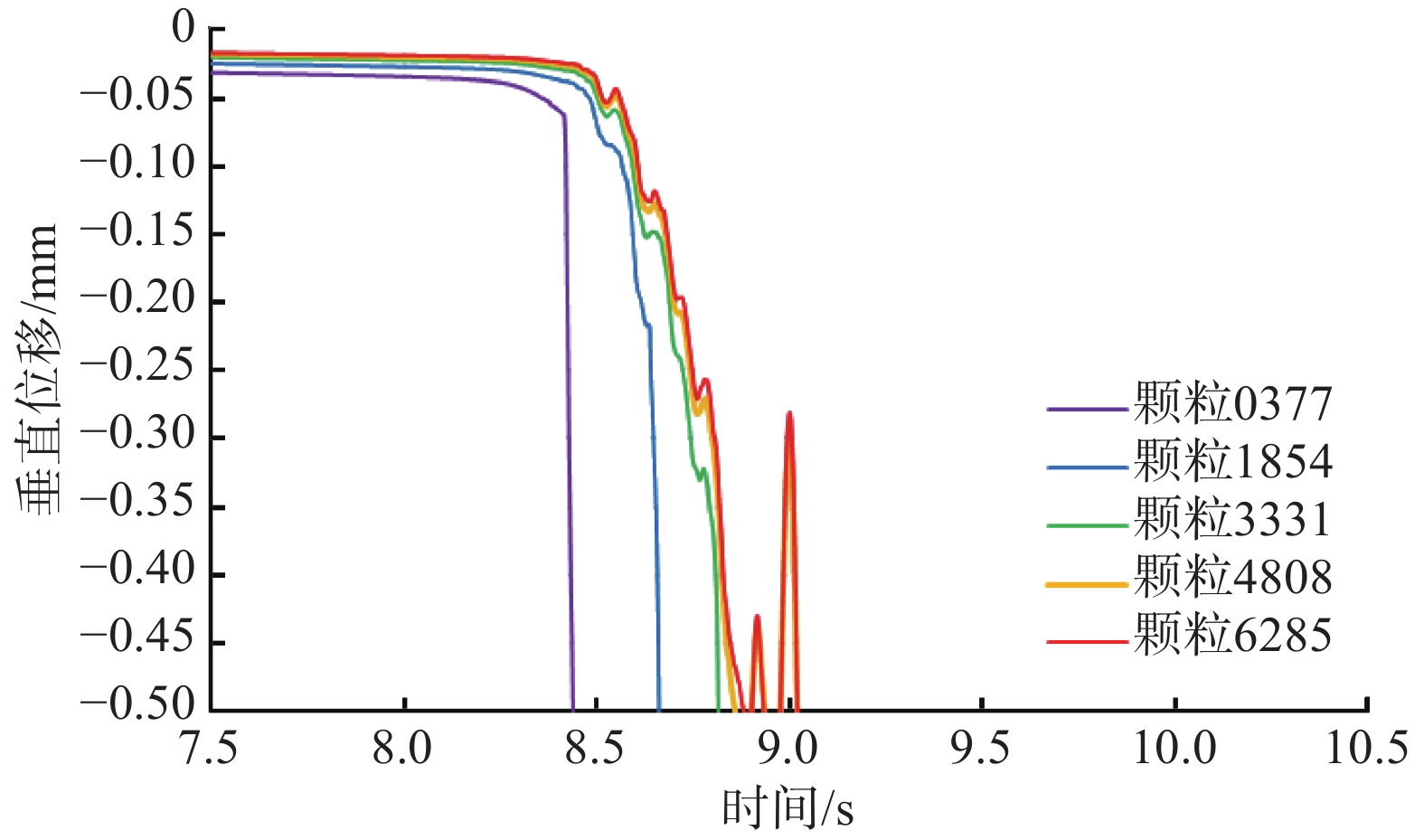
文章以水力驱动的覆盖型岩溶地面塌陷为背景,基于离散元方法和格子Boltzmann方法,采用Bouzidi插值反弹边界格式和动量交换法,建立一种可以从细观角度模拟覆盖型岩溶塌陷的二维格子Boltzmann方法—离散元方法流固耦合模型。在此基础上对承压水下降引起的覆盖型岩溶塌陷数值模拟开展了探索性研究。模拟结果表明:承压水位下降工况中地下水主要对隔水层岩溶开口处的颗粒产生影响,对土洞周围土体产生向下的作用力;土体颗粒的剥落容易造成土颗粒原位置和上方位置处水压的陡降,从而造成较强的水力坡降,使得地下水对内部颗粒作用力陡增,容易引起上方颗粒在地下水作用力和重力作用下失稳,导致从土体颗粒失稳至土层塌陷逐渐加速。研究成果对进一步从细观尺度进行水力驱动的覆盖型岩溶地面塌陷的发育过程与特征研究具有理论及实际意义。
-
关键词:
- 覆盖型岩溶;地面塌陷 /
- 地下水 /
- 数值模拟 /
- LBM-DEM方法 /
- 细观尺度
Abstract:To investigate the hydraulic characteristics and soil behaviors during the formation of covered karst ground collapse induced by the groundwater changes, a 2D fluid-solid coupling model was developed based on discrete element method and lattice Boltzmann method. This model utilizes the linearly interpolated bounce-back scheme of Bouzidi and the momentum exchange method, allowing for the simulation of the formation of covered karst ground collapse from a microscopic perspective. Using the fluid-solid coupling model, an exploratory study was conducted to simulate the formation of covered karst ground collapse induced by a decrease in the hydraulic head of confined aquifers. Simulation results indicate that when the water level of a confined aquifer declines, the groundwater flow mainly affects the particles located above a cave opening and produces a downward force on the surrounding soil. When soil particles spall, the hydraulic heads at the positions of the spalled soil particles drop sharply. This results in a significant increase in the hydraulic gradient, causing the groundwater force on internal particles to sharply increase as well. As a result, the upper particles lose stability due to the combined force of groundwater dragging and gravitational force, which can lead to a gradual acceleration process of collapse. The research results provide valuable insights into the understanding of covered karst ground collapse formation induced by the groundwater changes.
-
Keywords:
- covered karst ground collapse /
- groundwater /
- numerical simulation /
- LBM-DEM method /
- micro scale
-
0. 引言
被誉为“世界屋脊”的青藏高原东南缘和横断山系中段是闻名的“三江并流”带,区内峡谷陡峭,物源丰富,降水集中,自然环境极易受到内外动力和人类活动的影响,在耦合下泥石流灾害也相对明显[1]。“三江并流”带建筑多依河傍山而建,空间上呈现出坡脚集中修筑的特点,在以上环境背景下,一旦暴发泥石流灾害,将对区内经济和居民生命安全造成巨大的威胁和损失[2]。在泥石流频率上,高、中、低频泥石流灾害在云南省均有发育,其中高频泥石流频率为1~5 a,中频泥石流频率为5~20 a,低频泥石流频率为20~100 a[3]。云南省哈达沟是一条典型的中频泥石流沟,据调查统计,其在1966年、1976年、2001年及2010年均暴发过较大规模的泥石流灾害,其中2010年7月28日暴发的泥石流灾害规模最大,沟道冲出物堵塞腊普河口长达一个小时,并威胁到香维高速公路的安全,造成的直接经济损失和潜在经济损失巨大。此次暴发后,之后的几年其活动相对减弱,未发生明显的大规模泥石流灾害。中频泥石流存在暴发周期长、潜伏期长、易忽视的特点,在工程防治中不利于长期监测和精确定位[4-5]。其潜在的危险性大,为保障区内环境、人文、经济安全,有必要对其进行研究。
由于泥石流暴发周期长(短则几年,长则几十年),监测工作困难。在许多重点泥石流研究区设有监测站(东川、波密等)并配备监测仪器设备,但大多数泥石流沟依然依凭人力监测,准确度不高,所以在频率的确定上依然存在一定的困难。目前国内外研究针对泥石流暴发频率判识方法主要有:基于粗大块石粒径、岩性、岩体坚固系数特性的判识方法;基于水文计算判识的方法等[3]。为更加准确地对泥石流进行分类定性,中频泥石流这一概念初次在国内提出。但针对中频泥石流的相关文献相对较少,其常被模糊式地判定为低频泥石流[6]。目前国内外在中频泥石流的研究都稍显不足,因此,对其特征和危险定性并没有详细的研究分析和取证。但在结合前人提出的关于单沟泥石流的危险性评价模型的基础上,在特定参数条件下也能完成中频泥石流的危险定性。此外,中频泥石流与高频泥石流共有的类似特征也是界定的一个难点。没有文献参考和评价示范做支撑,中频泥石流的危险度定性模糊(高度危险度—极度危险度),由于其处于低频与高频之间,在人们的主观认知下,其危险性习惯性地被认为是中度危险或接近高度危险。危险定性在泥石流灾害的防治中是一个极其重要的指标,不能妄下定论。
本文针对中频泥石流研究上的不足,以哈达沟中频泥石流为研究对象,分析中频泥石流发育特征、运动特征以及其发生堵溃的危害性。在野外调查、理论分析、模型计算的基础上,比较堵塞隐患点的断面过流最大流量与中频泥石流流量(以分析暴发频率10%为主),分析隐患点(以沟口公路涵洞为主要研究对象)是否满足过流条件,得出哈达沟再次发生堵溃淤埋道路和桥梁的危险性。基于权重采用层次分析法计算哈达沟中频泥石流危险度,综合分析中频泥石流灾害的危险性,绘制危险分区并对其提出相关防治建议。
1. 研究区概况
哈达沟为金沙江右岸腊普河右岸二级支流,流经云南省维西县启别村。哈达沟区域地形属于侵蚀剥蚀高中山峡谷区,研究区位置如图1所示。哈达沟流域后缘位于沟源山脊处,高程约3304 m,前缘为启别村与腊普河交界处,约1976 m,相对高差1460 m,流域面积8.79 km2,主沟道长5.02 km,平均纵坡比降约246.5‰,坡度30°~65°,地貌分割明显,沟谷上部切割强烈,两岸岸坡地形陡峭,沟谷呈典型深“V”字形[7]。哈达沟流域共发育有4条支沟,为泥石流形成提供了充足水源条件和物源条件。其中:清水区位于2610~3304 m段,形成区位于2170~2610 m段,流通区位于2050~2170 m段,堆积区位于2050 m至沟口段,特征分布如图2所示。
2. 哈达沟泥石流形成条件与特征
2.1 泥石流形成条件
2.1.1 物源条件
根据野外调查,哈达沟流域内共发育15处典型滑坡物源,其中2处典型崩滑物源如图3所示。这些物源主要为切坡构成的崩滑体物源和滑坡堆积物源,疏松固体物源总量为9.65×104 m3,能参加泥石流运动的动储备约为3.05×104 m3。
由于流域周边人类工程活动导致边坡土壤侵蚀和风化,形成边坡侵蚀物源。不稳定斜坡上表层物源在雨水冲刷作用下进入沟道,成为沟床堆积物源,沿着整段沟道,堆积物源从上至下均有分布,支沟内也有分布,哈达沟沟道堆积物源如图4所示。
据调查,该泥石流沟域内两岸上部岸坡陡峻,岸坡坡度为40°~60°,两岸岸坡植被繁茂,高大树木发育,植被覆盖率在60%以上,土体厚度在1~5 m,平均厚度2.5 m,通过遥感解译,估算沟道周边侵蚀面积。物源数据统计见表1。通过现场勘察分析,泥石流再次发生时,崩塌堆积物源和沟床堆积物源将会是参加哈达沟泥石流运动的主要物源。崩塌堆积物源是按照实地勘察现场测量估算的物源总量,再按照25%的冲刷计算可参与泥石流活动的动储量;沟道物源动储量是对沟道的特征段进行现场测量和观察长度、宽度、厚度、颗粒分布、淤埋情况,估算而出;坡面侵蚀物源是根据地形坡度、植被覆盖率等划分强度、中度及轻度侵蚀区,估算出物源和动储量物源。
表 1 哈达沟泥石流物源汇总统计表Table 1. Summary of source of debris flow in Hada gully物源类型 坡面侵蚀物源/104 m3 崩塌堆积物源/104 m3 沟床堆积物源/104 m3 合计/104 m3 总量 动储量 总量 动储量 总量 动储量 总量 动储量 数值 306.7 4.73 9.65 3.05 12.5 3.68 328.85 11.46 2.1.2 水源条件
哈达沟泥石流的水源主要来源于大气降水。泥石流均发生于雨季(图5),勘查区降雨较丰沛,且雨量集中,此外,沟域内地下水匮乏,不构成引发泥石流的主要水源,沟域内没有水库、湖泊等集中的地表水体,因此判定暴雨形成的地表径流是引发泥石流的主要水源,暴雨是泥石流的主要激发因素。
2.1.3 气象条件
根据维西县气象局(1955—2014年)60年气象资料显示,维西县年平均降雨量947.7 mm,最大日降雨量93.4 mm,年最大降雨量1266.9 mm。根据资料分析,1986年、1989年、1992年、1994年、1995年、2000年、2001年、2002年、2010年降雨量偏多且集中,致使腊普河流域以及周边流域的地质灾害强度增大,频率增高。维西县月平均降雨量如图5所示[7]。
不同频率下多年平均24 h降雨强度如表2所示。
表 2 不同频率H24值表Table 2. List of parameters and results of 24-hour rainstorm intensity of different precipitation frequencies in Hada gully设计暴雨的频率P 倍比
系数KpH24p
/mm备注 100年一遇最大日暴雨量(P=1%) 2.11 116.05 云南省水文
手册查定50年一遇最大日暴雨量(P=2%) 1.92 105.6 30年一遇最大日暴雨量(P=3.33%) 1.79 98.45 20年一遇最大日暴雨量(P=5%) 1.67 91.85 10年一遇最大日暴雨量(P=10%) 1.47 80.85 采用《云南省水文手册》法计算10 a、20 a、30 a、50 a、100 a一遇设计暴雨量[8-9]。计算公式如下:
(1) 式中:
1.1——换算系数。
查《云南省水文手册》附图19,相关计算结果见表2。
2.1.4 人类工程活动影响
根据现场调查,勘查区内的人类工程活动主要为居民耕地、土地恢复整理、房屋修建、道路修建及砍伐树木等;其中对该泥石流影响较大的为砍伐树木,是3#支沟的物源成因之一,为主沟泥石流的形成提供了一定物源量。其次为居民耕地及土地恢复,土地恢复势必对部分林地进行改造,对部分灌木丛进行梯田整理,从而减少了林地的比例,加剧水土流失,在暴雨的作用下,加速并扩大了哈达沟中频泥石流灾害;居民房屋修建及道路修建主要集中在沟口处,位于泥石流的堆积区,对泥石流形成影响较小。
综上所述,沟域内人类工程活动较强烈,对泥石流灾害的形成扩大和发育影响较大。
2.2 运动参数特征
哈达沟泥石流属中频泥石流(5~20 a),最近几年都未发生过泥石流,因此泥石流流体密度采用配方法和查表法综合确定[10],依照《泥石流灾害防治工程勘查规范》(DZ/T0220—2006)附录H填写泥石流调查表并按附录G进行易发程度评分[11],按表G.2查表确定哈达沟泥石流重度和泥沙修正系数,其结果如表3所示[12]。
表 3 哈达沟泥石流流体重度查表法结果统计表Table 3. List of parameters and results of basic characteristics of the Hada gully debris flow易发程度
数量化评分易发程度
评价重度
/(t·m−3)平均重度
/(t·m−3)1+φ
(γh=2.65)97 易发 1.669 1.611 1.701 本次设计结合上述两种方法,泥石流容重最终取值1.62 t/m3,属于黏性泥石流。
根据实际情况采用水文研究所法计算清水洪峰流量,计算公式为[13]:
(3) (4) 式中:QB——最大清水流量/(m3·s−1);
k——径流系数,0.35;
i——平均1 h降雨强度/(mm·h−1);
F——流域面积/km2;
t——流域汇流时间/h;
L——沿主河从出口断面至分水岭最长距离/km;
m——汇流参数,m=0.5θ0.36,θ=L/I1/3F1/4;
J——沿流程L的平均比降(计算时以小数计);
Qm——各暴雨频率下的清水流量计算统计如表4 所示。
表 4 不同频率下清水洪峰流量计算成果表Table 4. List of parameters and results of peak flow discharge calculation at different precipitation frequencies in Hada gully设计暴雨
频率/%流域汇流
时间/h平均1 h降雨强度
/(mm·h−1)最大清水流量
/(m3·s−1)1 2.74 42.97 35.95 2 2.42 39.15 31.75 3.33 2.21 36.34 28.81 5 1.99 34.13 26.36 10 1.66 30.11 22.22 泥石流流速采用《泥石流灾害防治工程勘查规范》(DZ/T 0220-2006)[11]中东川泥石流改进公式进行计算:
(5) 式中:Vc——泥石流流速/(m·s−1);
Hc——平均泥深/m;
Ic——泥位纵坡率,以沟道纵坡率代替;
K——黏性泥石流流速系数,查规范[11]中表I.3黏性泥石流参数K值表。
通过现场调查选取沟域中12处特征点进行计算,其中7处堵塞隐患点位置如图6所示,泥石流流速计算取值统计表如表5所示。泥石流其他估算模型如表6所示[14],计算模型均根据实际情况选择。
表 5 哈达沟泥石流流速计算表Table 5. List of flow velocity results at different site location of the Hada gully debris flow序号 平均泥深
/m泥位纵坡降
/‰流速系数 泥石流流速
/(m·s−1)1(形成区上部) 2.000 461 10 7.857 2(形成区中部) 2.000 416 10 6.633 3(形成区下部) 2.000 387 10 6.538 4(堵塞隐患点7) 2.000 361 10 6.447 5(堵塞隐患点6) 1.800 339 10 6.404 6(堵塞隐患点5) 1.800 332 10 6.340 7(堵塞隐患点4) 1.600 313 10 5.371 8(堵塞隐患点3) 1.600 311 10 5.364 9(堵塞隐患点2) 1.500 306 10 4.901 10(堵塞隐患点1
公路涵洞)1.500 296 10 4.869 11 1.500 285 10 4.832 12(全流域沟口处) 1.200 274 10 4.794 表 6 哈达沟泥石流其他动态参数模型Table 6. List of dynamic parameter model of the Hada gully debris flow估算模型 计算的主要参数 设计暴雨频率/% 参数特征值 全沟域不同
频率下泥石流
流量/(m3·s−1)Qc= QB(1+φ)Dc
雨洪修正法[15]QB由表4所得,
φ=(γc−1)/(γh−γc)=0.633;
Dc取1.5,γc取1.62;γh取2.6。1.00 88.06 2.00 77.77 3.33 70.57 5.00 64.57 10.00 54.43 全沟域不同
频率下一次
泥石流总量/m3Q=0.264TQC《泥石流灾害防治工程勘查规范》
(DT/T0220-2006)附录I提供的计算公式[11]T=1800 s 1.00 17906.06 2.00 15818.86 3.33 14478.68 5.00 13132.24 10.00 11072.03 注:表中Qc是泥石流流量。 2.3 泥石流类型特征
按《泥石流防治工程勘查规范》(DZ/T 0220—2006)[7, 11]判断,泥石流基本特征汇总如表7所示。
表 7 泥石流基本特征汇总表Table 7. Summary of basic characteristics of debris flow特征项目 基本特征 分类 泥石流发生的地形条件 泥石流的发生、运动和堆积过程,在发育完整的沟谷内进行,可划分为形成水源区、流通区及堆积区 沟谷型泥石流 物质组成 主要为碎石土 泥石型 泥石流流体性质 堆积物松散,断面无明显的分选性;流体呈稀浆状,ρc=1.62 t/m3,固体物质ρH=2.6 t/m3。 黏性泥石流 固体物质提供方式 上部形成水源区主要为沟道堆积物源,中部流通区主要为崩滑堆积物源及沟道堆积物源 滑坡、崩塌 水体供给 雨量充沛,暴雨激发 暴雨泥石流 暴发频率 现场调查,资料统计,历年不同危害程度发生 中频泥石流 灾害严重程度 哈达村50户222人及启别村64户310人的生命财产安全,以及居民耕地多余0.52km2。并且威胁省道S303线香维公路的安全,总计威胁资产约5000万元,直接经济损失可达1000万元,潜在经济损失巨大。 大型 发展阶段 根据物源、坡度、不良地质现象、主河变形情况判定 发展期 成因 自然因素为主,人类活动影响较小 自然泥石流 规模 根据泥石流一次堆积总量 中型 综合分类 暴雨激发、沟谷泥石型、中型、中频发展期黏性泥石流 3. 哈达沟泥石流堵溃及其危险性评价
3.1 堵溃危险性分析
3.1.1 沟道调查与分析
哈达沟泥石流流域目前存在沟口处香维线公路涵洞过流堵塞历史,因泥石流沟道下游冲淤严重,使河床抬升,严重威胁到沟道两旁的居民人身财产安全,如图7所示为损毁居民房屋泥痕。因为沟口桥涵堵塞,泥石流翻过路面直接冲进腊普河(图8)。据资料显示,2010年泥石流暴发漫过沟口桥面,直接流入腊普河,造成长达1 h的堵塞。
3.1.2 沟域堵溃和堵河危险分析
据现场调查,香维线过沟处为公路桥涵,涵洞尺寸宽约2.3 m,高1.5 m,断面面积为3.45 m2,如图8(a)所示为哈达沟沟口处盖板桥涵特征。该处流速为4.794 m/s,过流量为16.5 m3/s,小于10 a一遇泥石流流量(表6),如表8所示(雨洪修正法计算),因而该处涵洞不能满足要求。若再次发生大规模泥石流,泥石流大概率堵塞沟道中隐患点,淤埋沟道桥面或路面(图7),尤其威胁到沟口处香维线公路,泥石流将冲上沟道两岸,给下游居民人身财产安全造成危害。
表 8 下游涵洞泥石流流量计算成果Table 8. List of parameters and results of sediment flush-out calculation of the Hada gully debris flow in downstream culverts位置 设计暴雨频率
/%最大清水流量
/(m3·s−1)泥石流流量
/(m3·s−1)沟口涵洞 1 36.71 89.91 2 32.43 79.43 3.33 29.42 72.07 5 26.92 65.94 10 22.70 55.59 据相关资料显示,2010年暴发泥石流再次证明该涵洞不能满足过流要求,泥石流堵塞沟道,导致泥石流直接越过路面,损毁下游沟道两岸居民房屋。哈达沟与主河腊普河夹角呈直角(图9),泥石流直接冲进主河河道,堵塞腊普河1 h,冲刷深度在0.3~0.8 m,如图6(b)所示为腊普河主河。
根据往期资料和参数计算结果,哈达沟泥石流一次固体物质冲出量与主河挟沙能力相差不大(1000 m3的主河水流挟沙能力约0.3 m3),作为中频泥石流条件下计算所得一次冲出泥石流总量(表6),堵塞主河道可能性较小,危险性较2010年7月28有所下降。
3.2 哈达沟中频泥石流危险性分析
针对中频泥石流的危险性分析采用基于权重的分析方法,依据钟政等[4]、侯兰功等[16]提出的方法对哈达沟中频泥石流不同暴雨频率下进行危险性评价。相关计算公式如下[4]:
(6) 式中:H——危险性;
Gi——评价因子权重;
Dj——危险系数,取值0~1;
p——降雨强度级别,哈达沟中频泥石流降雨强度级别为2。
本文采用刘希林[17]、杨志全等[18]提出的分级标准(表9)。
表 9 泥石流危险度分级标准Table 9. Classification standards of hazard level of debris flow危险等级 轻度危险 中度危险 高度危险 极度危险 判别标准 0~0.35 0.35~0.6 0.6~0.85 0.85~1 选取泥石流评价因子并进行权重计算[19-20]。本文结合野外调查和哈达沟实际情况,筛选出以下8个评价因子进行危险度评价:泥石流规模y1、松散物源量y2、24 h最大降雨y3(鉴于本文哈达沟为中频泥石流,取频率10%设计暴雨强度值)、泥石流发生频率y4(本文主要讨论中频泥石流,因此主要分析频率10%下泥石流危险性)、沟谷流域面积y5、主沟长度y6、流域相对高差y7、不稳定沟床比降y8 [19, 21-22]。
哈达沟流域雨季降雨主要为7、8月份﹐雨量大且集中﹐发生泥石流的危险性高。因此本文选取24 h降雨量作为评价指标。各评价因子危险度分级和计算结果如表10所示。权重计算采用层次分析法(AHP),计算结果如表11所示。
表 10 泥石流危险因子等级划分Table 10. Classification of hazard factors of debris flow评价因子 数值 等级 危险系数 0 0.4 0.7 1 泥石流规模y1/104 m3 2.48 ≤1 (1,10) [10,100) ≥100 0.4 松散物源量y2/104 m3 328.85 ≤10 (10,100) [100,200) ≥200 1 24 h最大降雨量y3/mm 80.85 ≤25 (25,50) [50,100) ≥100 0.7 泥石流发生频率y4/% 10 10 5 2 1 0 沟谷流域面积y5/km2 8.79 ≤0.5 (0.5,10) [10,35) ≥35 0.4 主沟长度y6/km 5.02 ≤1 (1,5) [5,10) ≥10 0.7 流域相对高差y7/km 1.46 ≤1 (1,1.5) [1.5,2) ≥2 0.4 不稳定沟床比降y8 0.461 ≤0.1 (0.1,0.3) [0.3,0.6) ≥0.6 0.7 表 11 矩阵权重计算结果Table 11. Summary of matrix weight calculation results of the Hada Gully debris flowy1 y2 y3 y4 y5 y6 y7 y8 权重 y1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 0.3698 y2 1/2 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 0.1849 y3 1/3 1/2 1 2 3 4 5 7 0.1233 y4 1/4 1/3 1/2 1 2 3 4 6 0.0925 y5 1/5 1/4 1/3 1/2 1 2 3 5 0.0740 y6 1/6 1/5 1/4 1/3 1/2 1 2 4 0.0616 y7 1/7 1/6 1/5 1/4 1/3 1/4 1 3 0.0528 y8 1/9 1/8 1/7 1/6 1/5 1/2 1/3 1 0.0411 将表10、11计算结果带入公式(6)中,计算结果为H10%=0.736频泥石流危险度为高度危险,与2010年7月28日当地发生的大规模泥石流灾害危险度评测结果相比有所下降。
根据哈达沟泥石流的形成特征、泥石流灾害区域分布、影响范围和经验公式计算,依据《泥石流灾害防治工程勘查规范》(DT/T0220—2006)中“泥石流活动危险区划分”标准[11],将哈达沟中频泥石流划分为极危险区、危险区和影响区三个区,各区域特征评述如表12所示。哈达沟危险分区如图9所示,其中离沟口最近位置的堵塞隐患点为香维线公路经过沟道所修涵洞(堵塞隐患点1)。
表 12 哈达沟泥石流危险分区评述Table 12. Description of hazard zones for Hada gully debris flow危险等级 区域范围 极危险区 哈达沟中下游段至沟口腊普河河边区域,主要为历史最高泥位线以下地区,面积约0.85 km2 危险区 河沟两岸崩塌、滑坡后缘裂隙以上50~100 m的范围,面积约0.19 km2 影响区 高于危险区与危险区相邻的地区,它不会直接与泥石流遭遇,但却有可能间接受到泥石流危害的
牵连而发生某些级别的灾害的地区,面积约0.27 km2综上所述,由于云南西北地区最近几年频发地震等极端灾害,人类工程活动活跃,为泥石流的形成提供了条件。根据现场调查访问,近几年云南6—9月雨水的增加,目前哈达沟泥石流正处于活跃期,沟域内每年均有小规模泥石流或者水石流发生,根据这几年哈达沟泥石流发生频率从时间和空间上推测,哈达沟中频泥石流转化为高频的可能性较高。高频泥石流暴发周期短、规模相对较小,易于监测和防范[3],哈达沟泥石流的危险性将减少,但依然属于高度危险,对其重视程度不可减少,沟道的清淤和疏通工作仍需定时进行。
4. 结论与建议
4.1 结论
本文通过现场调查、参数计算、泥石流堵溃和堵河分析以及泥石流危险性评价,针对哈达沟中频泥石流的特征和危险性取得以下结论和认识:
(1)研究区物源动储量11.46×104 m2,其中崩塌堆积物源和沟床堆积物源为参加泥石流运动的主要物源;水源条件满足暴发大型泥石流条件,区域泥石流发生主要是集中、大量降雨诱导;沟域内人类工程活动较强烈,对泥石流灾害的形成和发育影响较大。
(2)在哈达沟流域中下游有7处堵塞隐患点,本次主要研究沟口处香维线公路与哈达沟交汇处涵洞堵溃危险性。若发生较大规模(中频泥石流或低频泥石流)泥石流活动,则会堵塞沟道中各隐患点,尤其是沟口涵洞,泥石流漫过香维线公路路面,影响周边居民的生命财产安全以及公路交通安全。针对中频泥石流情况下(一次冲出泥石流总量11042.03 m3,泥石流峰值流量54.43 m3/s)堵塞腊普河的可能性较2010年7月28日有所下降,但依然有堵河的可能性,危险性不易忽视。
(3)基于权重和层次分析法计算得出,哈达沟中频泥石流危险度为高度危险,较2010年7月28日泥石流危险度有下降。对研究区进行危险分区,其中极危险区约0.85 km2,危险区约0.19 km2,影响区约0.27 km2。
(4)根据最近地质灾害发生实例综合分析,哈达沟流域泥石流频率从中频泥石流转换为高频泥石流的可能性高,危险性将减少。但哈达沟中频泥石流成灾可能性大(尤其是在每年7—8月),需同低频泥石流一样重视,做出相应的防治措施减少或遏制其危害。
4.2 建议
(1)哈达沟中频泥石流虽为中等发生频率,但其危险性已然与低频泥石流相仿,且运动周期低于低频泥石流(哈达沟泥石流频率还有上升的趋势),应当及时针对中频泥石流实施相应的防护治理措施。从表面上看,相较于低频泥石流防治所需的大量投入人力与物力,对于中频泥石流的防治,收益和成效是较高的。
(2)对于减少中频泥石流灾害的危险性,找出隐患点加以整改,在降雨集中的月份进行沟道清淤,防止物源堆积减少泥石流的启始能量。若中频泥石流向高频泥石流发展,泥石流危险性也会相对减少,要做好相应的监测和防范工作。
(3)泥石流是一种在空间和时间上不断变化的地质灾害,突发性强,破坏性大,想要详细分析出其中的规律和特征依然困难,还有许多待挖掘。定义泥石流暴发频率的准确度还需要提升(许多小型泥石流容易忽视且不易监测),同时未来还需要研讨出针对特定频率下泥石流的定性定量方法,以便我们能快速地对特定的泥石流进行危险评价并迅速采取措施和治理工作。
致谢:对于本次研究工作,感谢四川省煤田地质工程勘察设计研究院、维西县自然资源局、塔城镇启别村所提供的资料和在调查中给予的工作帮助。
-
表 1 计算模型参数
Table 1 Summary of simulation model parameters
参数名称 值 固体(DEM) 密度/(kg·m−3) 2700 杨氏模量/Pa 100×106 泊松比 0.3 内摩擦角/(°) 20 法向黏聚力/(N·m−1) 150 切向黏聚力/(N·m−1) 150 时间步长/s 2.5×10−5 重力加速度/(m·s−2) 9.8 流体(LBM) 密度/(kg·m−3) 1000 运动黏滞系数/(m2·s−1) 1.01×10−6 时间步长/s 0.0001 空间步长/m 0.0001 -
[1] ZALASIEWICZ J,WILLIAMS M,STEFFEN W,et al. The new world of the anthropocene[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2010,44(7):2228 − 2231.
[2] PRICE S J,FORD J R,COOPER A H,et al. Humans as major geological and geomorphological agents in the Anthropocene:The significance of artificial ground in Great Britain[J]. Philosophical Transactions Series A,Mathematical,Physical,and Engineering Sciences,2011,369(1938):1056 − 1084.
[3] 李前银. 再论岩溶塌陷的形成机制[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2009,20(3):52 − 55. [LI Qianyin. Further study on formation mechanism of karst collaps[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2009,20(3):52 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2009.03.018 LI Qianyin. Further study on formation mechanism of karst collaps[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2009, 20(3): 52-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2009.03.018
[4] 余政兴,金福喜,段选亮. 河床透-阻型岩溶塌陷形成机理[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(2):57 − 66. [YU Zhengxing,JIN Fuxi,DUAN Xuanliang. Formation mechanism of karst collapse with unconfined aquifer-aquitaed system in riverbed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(2):57 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.02.08 YU Zhengxing, JIN Fuxi, DUAN Xuanliang. Formation mechanism of karst collapse with unconfined aquifer-aquitaed system in riverbed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(2)57-66(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.02.08
[5] 车增光,刘洪,喻永祥. 苏州市金庭镇蒋东岩溶塌陷地质条件及形成机理研究[J]. 华东地质,2021,42(1):85 − 92. [CHE Zengguang,LIU Hong,YU Yongxiang. Study on geological conditions and formation mechanism of karst collapse in Jiangdong Village,Jinting Town,Suzhou City[J]. East China Geology,2021,42(1):85 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract) Che Zengguang, LIU Hong, YU Yongxiang. Study on geological conditions and formation mechanism of karst collapse in Jiangdong Village, Jinting Town, Suzhou City[J]. East China Geology, 2021, 42(1): 85-92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 缪世贤,黄敬军,武鑫,等. 徐州岩溶地质调查及其发育特征分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):172 − 177. [MIAO Shixian,HUANG Jingjun,WU Xin,et al. Karst geological survey and analysis of its development characteristics in Xuzhou[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):172 − 177. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2017.02.26 MIAO Shixian, HUANG Jingjun, WU Xin, et al. Karst geological survey and analysis of its development characteristics in Xuzhou[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(2)172-177(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2017.02.26
[7] 万志清,秦四清,李志刚,等. 土洞形成的机理及起始条件[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2003,22(8):1377 − 1382. [WAN Zhiqing,QIN Siqing,LI Zhigang,et al. Formation mechanism and initial condition of soil cavity[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2003,22(8):1377 − 1382. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.08.028 WAN Zhiqing, QIN Siqing, LI Zhigang, et al. Formation mechanism and initial condition of soil cavity[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(8): 1377-1382. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.08.028
[8] 王滨,贺可强. 岩溶塌陷临界土洞的极限平衡高度公式[J]. 岩土力学,2006,27(3):458 − 462. [WANG Bin,HE Keqiang. Study on limit equilibrium height expression of critical soil cave of karst collapse[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2006,27(3):458 − 462. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.03.024 WANG Bin, HE Keqiang. Study on limit equilibrium height expression of critical soil cave of karst collapse[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(3): 458-462. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.03.024
[9] 陶小虎,赵坚,WANG Xiaoming,等. 地下水位变化对透-阻型岩溶塌陷影响的分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2017,36(6):777 − 785. [TAO Xiaohu,ZHAO Jian,WANG Xiaoming,et al. Analysis of seepage effect on the formation of sinkhole in unconfined aquifer-aquitard system caused by groundwater changes[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2017,36(6):777 − 785. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11932/karst2017y50 TAO Xiaohu, ZHAO Jian, WANG Xiaoming, et al. Analysis of seepage effect on the formation of sinkhole in unconfined aquifer-aquitard system caused by groundwater changes[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(6): 777-785. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11932/karst2017y50
[10] 孙金辉. 覆盖型岩溶塌陷临界参数模型试验与数值模拟研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2011: 7 − 35 SUN Jinhui. Study on critical parameterin cover karst collapseby model experimentand numerical simulation[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011: 7 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] LEI Mingtang, GAO Yongli, JIANG Xiaozhen, et al. Experimental study of physical models for sinkhole collapses in Wuhan, China[C]//Sinkholes and the Engineering and Environmental Impacts of Karst. San Antonio, Texas, USA. Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2005: 91-102.
[12] MAHMOUD A. Application of digital image cross correlation to study sinkhole collapse[J]. ISRN Soil Science,2013:1 − 6.
[13] Y F,ZHOU. The mechanism of soil failures along cracks subjected to water infiltration[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2014,55:330 − 341. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2013.09.009
[14] ALI S M. Modelling the effect of void migration underneath landfill liner system [D]. University of Nottingham, 2003.
[15] 金晓文,陈植华,曾斌,等. 岩溶塌陷机理定量研究的初步思考[J]. 中国岩溶,2013,32(4):437 − 446. [JIN Xiaowen,CHEN Zhihua,ZENG Bin,et al. Preliminary thinking of quantitative research on the mechanism of karst collapse[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2013,32(4):437 − 446. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIN Xiaowen, CHEN Zhihua, ZENG Bin, et al. Preliminary thinking of quantitative research on the mechanism of karst collapse[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2013, 32(4): 437-446. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] CUNDALL P A. A computer model for simulating progressive large scale movements in blocky rock systems[M]. In Proc Int Symp Rock Fracture. Nancy; ISRM. 1971: 2 − 8.
[17] 周健, 贾敏才. 土工细观模型试验与数值模拟[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008 ZHOU Jian, JIA Mincai. Meso-model test and numerical simulation of geotechnical engineering[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008. (in Chinese)
[18] 陈松贵. 宾汉姆流体的LBM-DEM方法及自密实混凝土复杂流动研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2014: 44 − 50 CHEN Songgui. Development of LBM-DEM for Bingham suspensions with application to self-compacting concrete[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2014: 44 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] QIAN Y H,D'HUMIÈRES D,LALLEMAND P. Lattice BGK models for navier-stokes equation[J]. Europhysics Letters (EPL),1992,17(6):479 − 484. DOI: 10.1209/0295-5075/17/6/001
[20] BOUZIDI M,FIRDAOUSS M,LALLEMAND P. Momentum transfer of a Boltzmann-lattice fluid with boundaries[J]. Physics of Fluids,2001,13(11):3452 − 3459. DOI: 10.1063/1.1399290
[21] MEI Renwei, YU Dazhi, SHYY W, et al. Force evaluation in the lattice Boltzmann method involving curved geometry[J]. Physical Review E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2002, 65(4 Pt 1): 041203.
[22] CUI Xilin. Numerical simulation of internal fluidisation and cavity evolution due to a leaking pipe using the coupled Dem-lbm technique[D]. Birmingham, West Midlands, UK: University of Birmingham, 2013.
[23] 陈玉璞, 王惠民. 流体动力学[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2013. CHEN Yupu, WANG Huimin. Fluid dynamics[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2013. (in Chinese)
[24] LOMINÉ F,SCHOLTÈS L,SIBILLE L,et al. Modeling of fluid-solid interaction in granular media with coupled lattice Boltzmann/discrete element methods:Application to piping erosion[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics,2013,37(6):577 − 596. DOI: 10.1002/nag.1109
[25] LHL A,GN B,ZB A,et al. Hydro-mechanical modeling of sinkhole occurrence processes in covered karst terrains during a flood[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,260:105249. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105249
[26] HENTZ S. Modélisation d’une structure en béton armé soumise à un choc par la méthode des eléments discrets [D]. Grenoble: Université Grenoble 1 - Joseph Fourier, 2003.
[27] MIKIO,SAKAI. Study on a large-scale discrete element model for fine particles in a fluidized bed[J]. Advanced Powder Technology,2012,23(5):673 − 681. DOI: 10.1016/j.apt.2011.08.006
[28] 汤志刚,蔡承刚,王艳红,等. 基于光纤传感的石膏矿地面塌陷监测预警系统[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(5):93 − 101. [TANG Zhigang,CAI Chenggang,WANG Yanhong,et al. Monitoring and warning system for ground subsidence of gypsum mine based on fiber sensing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(5):93 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202108034 TANG Zhigang, CAI Chenggang, WANG Yanhong, et al. Monitoring and warning system for ground subsidence of gypsum mine based on fiber sensing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(5)93-101(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202108034
[29] 何军,刘磊,黎清华,等. 隐伏岩溶区地下空间探测技术方法研究—以武汉市为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):47 − 56. [HE Jun,LIU Lei,LI Qinghua,et al. Techniques for detecting underground space in hidden karst region:Taking Wuhan as an example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):47 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE Jun, LIU Lei, LI Qinghua, et al. Techniques for detecting underground space in hidden karst region: taking Wuhan as an example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(6): 47-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 查甫生,刘从民,苏晶文,等. 铜陵市朝山地区岩溶塌陷形成条件与地面稳定性评价分析[J]. 地质论评,2020,66(1):246 − 254. [ZHA Fusheng,LIU Congmin,SU Jingwen,et al. Formation conditions of karst collapse and evaluation of ground stability in Chaoshan area of Tongling City[J]. Geological Review,2020,66(1):246 − 254. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16509/j.georeview.2020.01.018 ZHA Fusheng, LIU Congmin, SU Jingwen, et al. Formation conditions of karst collapse and evaluation of ground stability in Chaoshan area of Tongling City[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(1): 246-254. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16509/j.georeview.2020.01.018
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 石化波,王刚,曾怀恩. 一种ICEEMDAN-CNN-SVR滑坡位移组合预测模型. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 37-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李龙灿,吴鑫,刘永红,海英,张满,张龙梅,黄成佳. 松散堆积体斜坡变形-滑移过程的声发射特征参数演化规律. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 151-159 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:


















 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS