Analysis of the rainfall threshold for post-fire debris flow initiation: A case study of the debris flow at Ren’eyong gully in Xiangcheng County, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
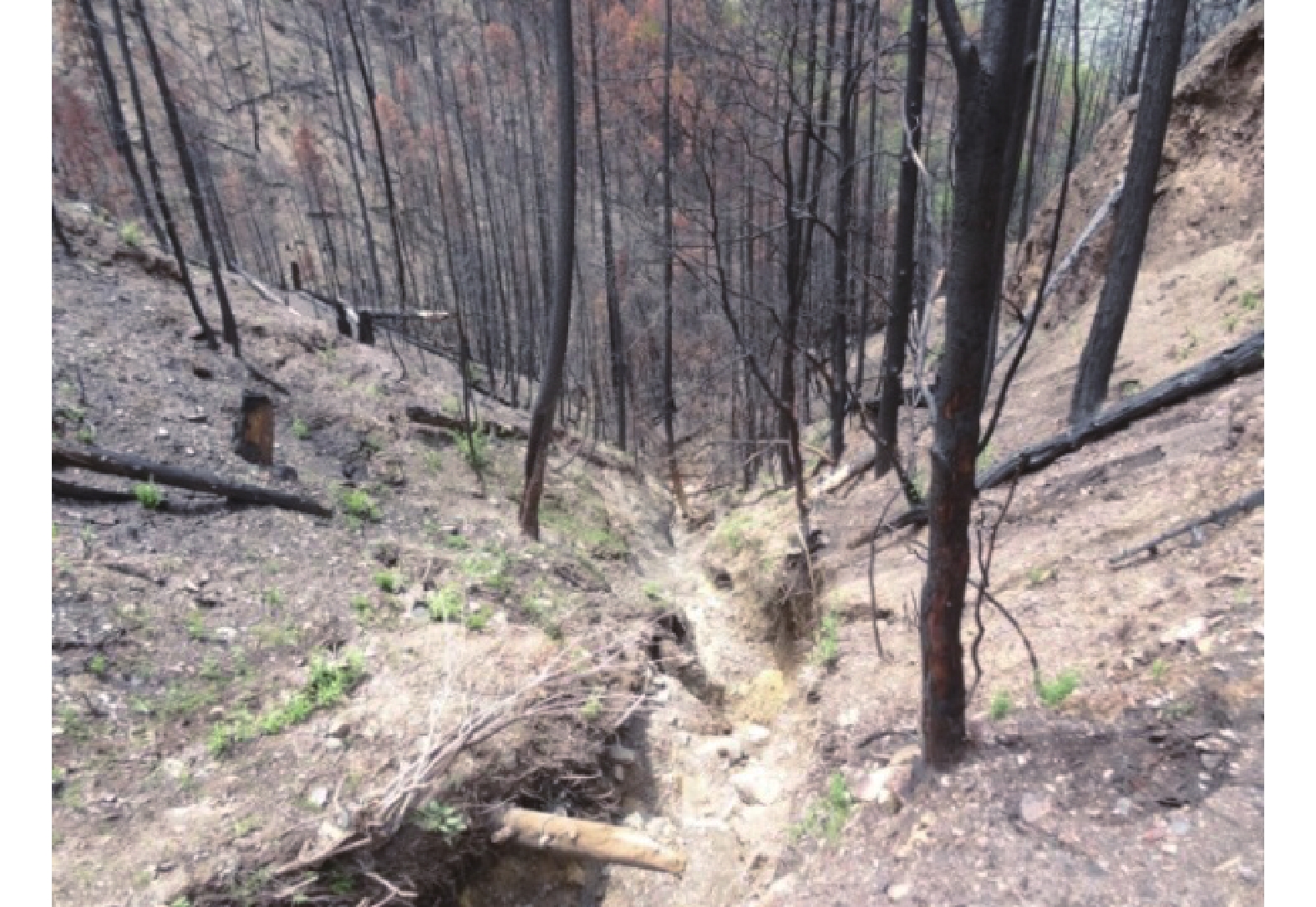
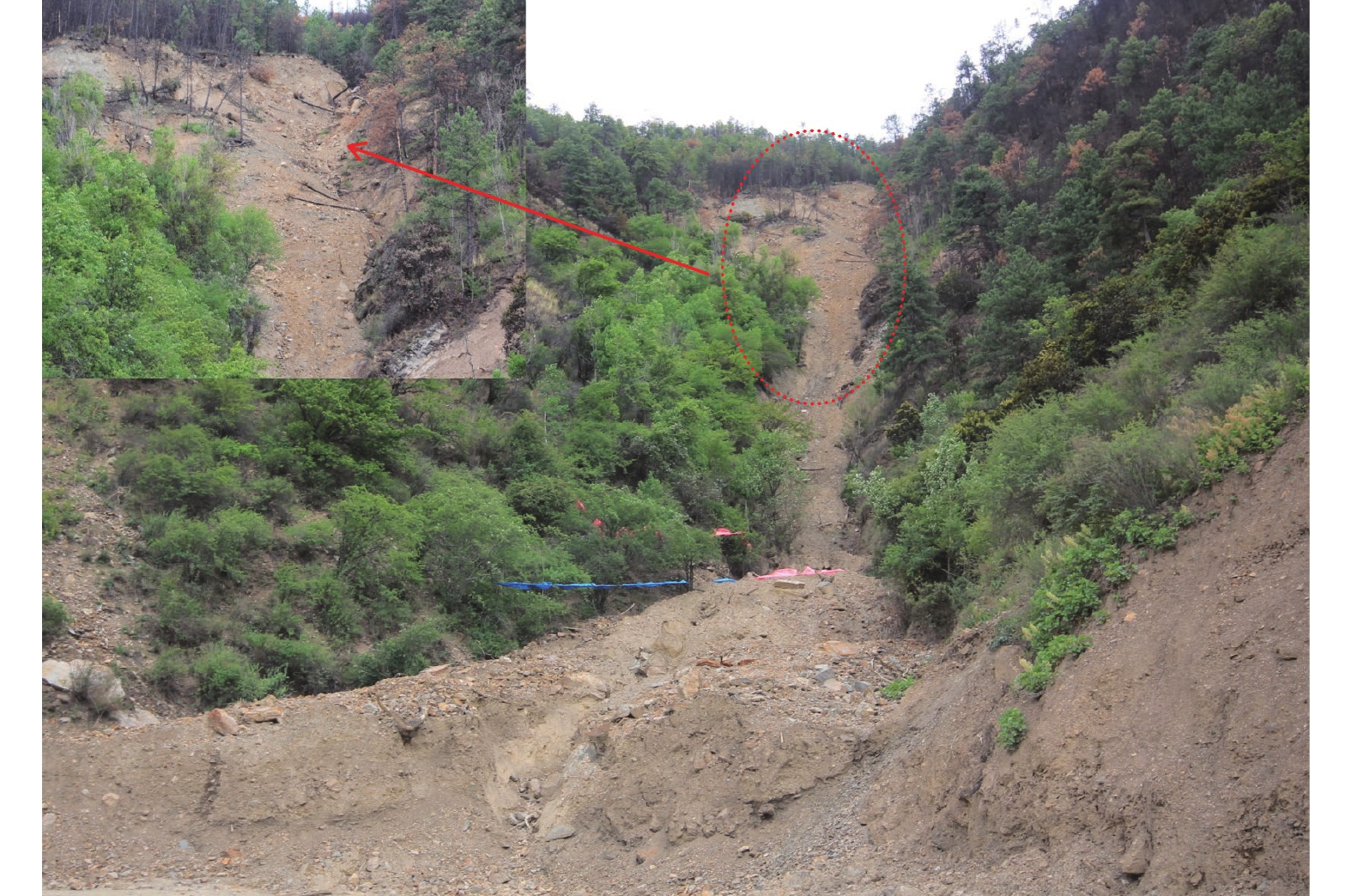
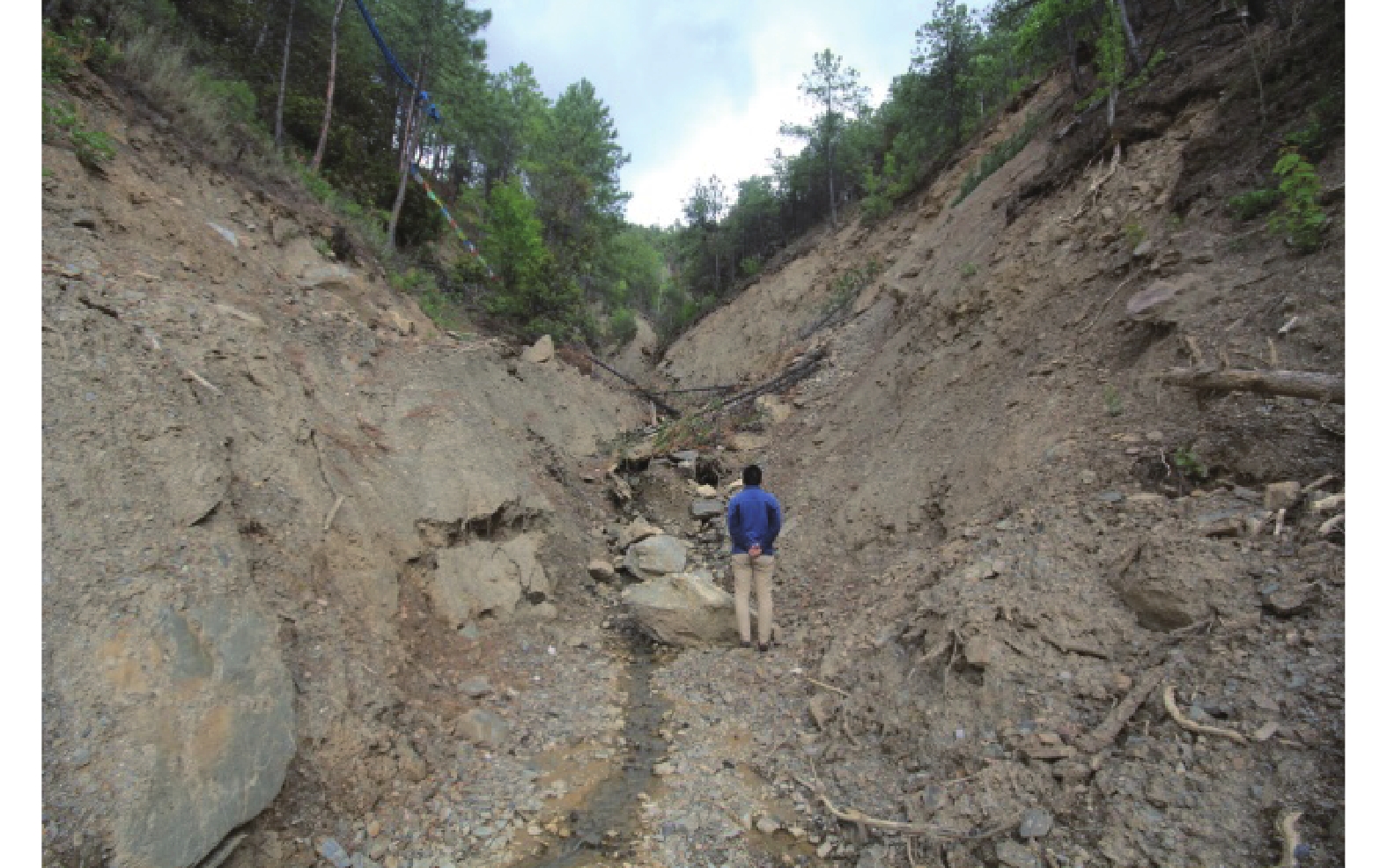
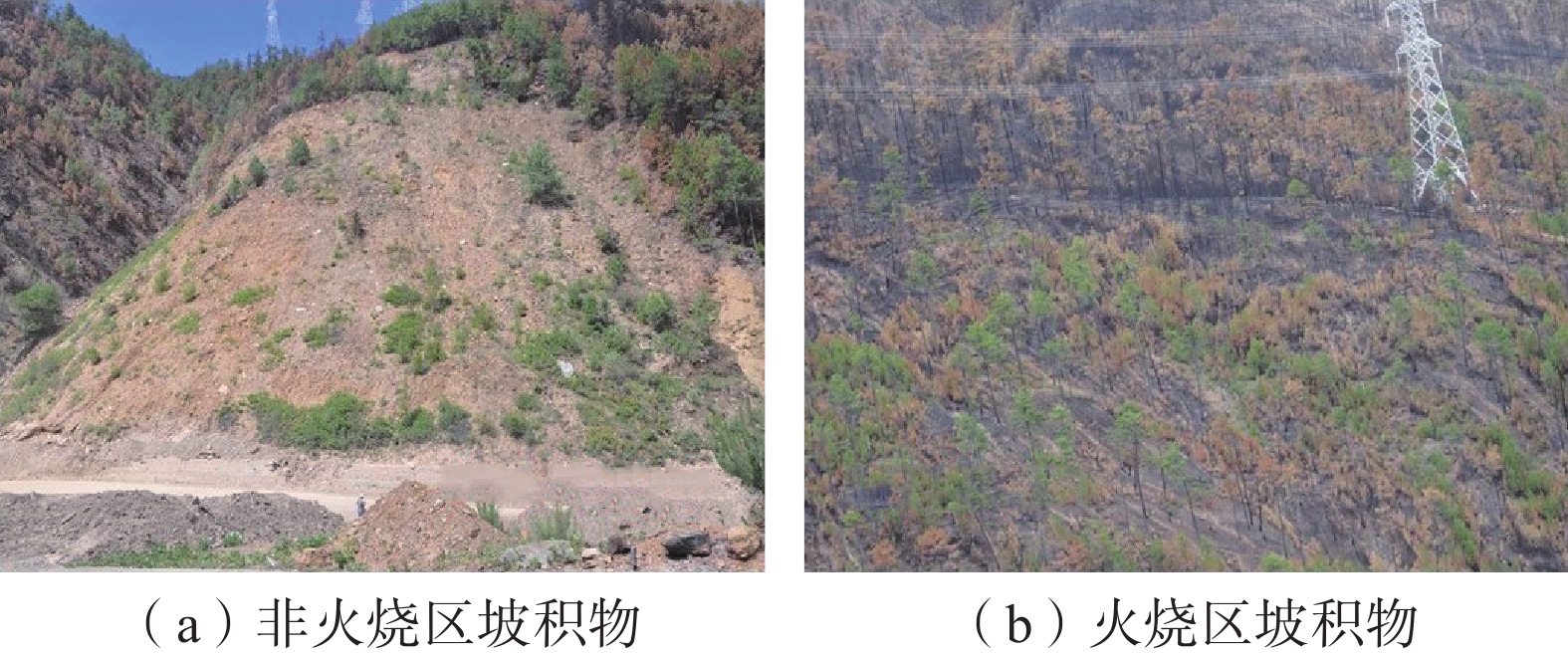
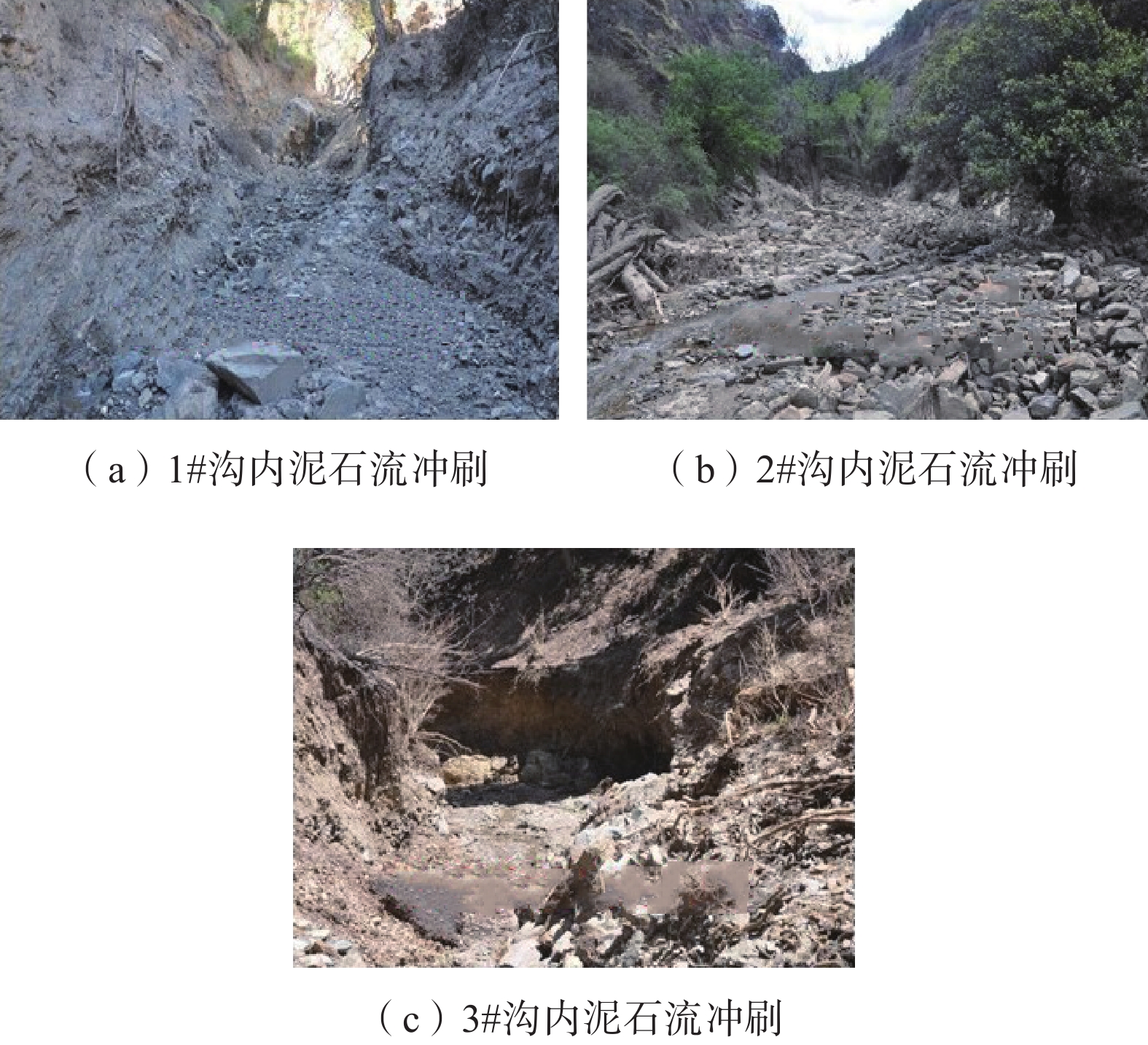
2014年6月1日,中国西南中横断山区仁额拥沟遭受了一次森林大火,火后的短时低雨强降雨在3#支沟内激发了3次泥石流;2015年8月的一次强降雨在仁额拥沟的1#、2#和3#支沟及其他附近的多个更小的流域内均激发了泥石流。为了解火后泥石流的降雨响应特征,文章采用距离修正的方式处理降雨数据,对4次泥石流进行降雨过程分析,查明了流域特征对泥石流启动的作用及其对各支沟泥石流不同降雨阈值的影响。研究发现:(1)泥石流降雨阈值在火后非常低且有随时间推移而增大的趋势;(2)仁额拥沟火后泥石流具有高频率特征,其原因除了在火后天然植被的破坏后降雨对坡面径流和侵蚀效应的放大,流域本身的性质也有极大的贡献;(3)各支沟内泥石流降雨阈值差异的主要原因在于流域面积的差异,泥石流侵蚀受制于径流量大小。
Abstract:In the early summer of 2014, a wildfire ravaged the Ren’eyong valley in the central Mt. Hengduan region of southwestern China. Following the blaze, debris flows were triggered three times in branch No. 3 due to short-term, low intensity rainfall. A year later, in August 2015, a brief period of high-intensity rainfall generated debris flows not only in branch No.3, but also in branch No. 1 and No. 2, as well as several smaller basins in the vicinity. To investigate the rainfall response characteristics of post-wildfire debris flow, the distance correction method was used to process the rainfall data. By analyzing the rainfall patterns of four debris flow events, the reseachers were able to identify the effects of watershed characteristics on the initiation of debris flow and its influence on different rainfall thresholds in each branch. The study found that: 1) Post fire debris flows can occur at a low rainfall threshold, which tends to increase over time. 2) The Ren’eyong valley experience high-frequency post fire debris flows, which can be attributed not only to the amplification of slope runoff and erosion caused by rainfall after the destruction of natural vegetation due to the wildfire, but also to the geological and geomorphic conditions of the area. 3) The rainfall threshold in each branch is primarily dependent on the drainage area, as the magnitude of discharge controls the entrainment.
-
0. 引言
受全球气候变暖影响,极端天气气候事件强度不断增大,百年或数十年一遇超强台风灾害频发[1 − 2]。据资料统计,全球范围内每年由台风造成的经济损失高达260亿美元,台风灾害已成为沿海地区危害最严重的自然灾害之一[3]。
我国东南沿海地区是台风灾害高发区,台风登陆时,风荷载及裹挟的强降雨常在沿海地区触发大量滑坡灾害,造成重大人员伤亡和财产损失。例如:2004年第14号“云娜”台风在浙江省乐清市引发了21处滑坡、泥石流地质灾害,造成42人死亡、288间房屋被摧毁[4];2019年8月,台风“利奇马”以超强姿态登陆浙江,向北席卷期间,对全国11个省份造成影响,并于浙江、福建等地诱发大量地质灾害,共造成
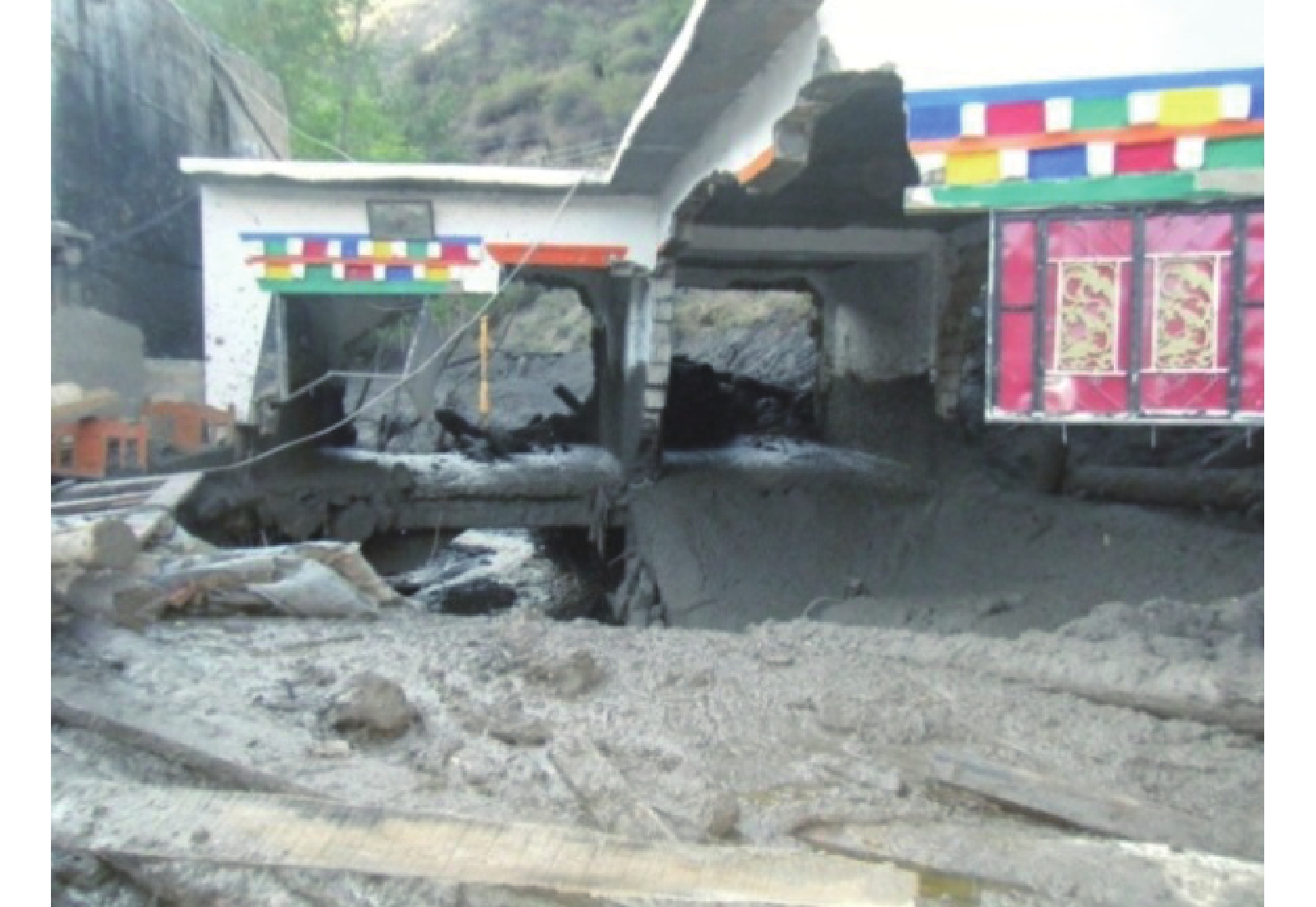
1402 万人受灾,直接经济损失超过500亿元[5]。其中,浙江省永嘉县岩坦镇于8月10日突发山体滑坡,约12×104 m3的滑坡体倾泻而下并形成堰塞湖,摧毁了山早村部分房屋,造成29人死亡、3人失踪[6]。目前,国内外学者已通过数值仿真、物理模型试验以及现场调查等方式探究了台风暴雨型浅层滑坡触发机理[7 − 11]。然而上述研究多将其视作降雨型滑坡开展分析,仅考虑了坡面均匀入渗带来的影响。我国东南沿海地区台风引发的滑坡灾害多为浅层土质滑坡,坡面乔木植被发育、整体覆盖度较高[12 − 15]。乔木植被利用其硕大的迎风面积可将风荷载传递至边坡,同时植被根系通过力学加筋和提供优势渗流通道等方式对边坡稳定性产生影响[16 − 17]。孔维伟等[18]通过风扇等工具模拟风荷载,设计开展模型试验,发现台风期间强风荷载对边坡稳定性有显著影响。Forrer等[19]、Schwarzel等[20]、张家明等[21]开展了染色示踪试验,指出植被根系能通过生物、力学作用加剧土体大孔隙的发育,进而提高土体渗透性能。在此基础上,一些学者[14, 22 − 23]通过数值仿真探究了植被优势渗流和蒸腾等水力作用对边坡稳定性的影响。Zhuang等[15, 24]在现场调查的基础上,基于极限平衡理论和有限元分析,首次探究了台风-降雨-植被综合作用下边坡稳定性分析,指出台风期间发生的浅层土质滑坡是在强风荷载、降雨优势入渗和植被综合作用下触发的。
由此可见,植被对边坡稳定性的影响是复杂且多方面的。台风期间,植被以根系为纽带与边坡土体产生作用,探究植被根系对边坡稳定性的影响对分析台风暴雨型浅层滑坡失稳机理具有重要意义。当前,针对台风期间植被根系力学和水文作用对边坡稳定性影响的试验分析仍十分欠缺。因此,本文选取了典型台风暴雨型浅层滑坡灾害点开挖剖面,统计分析了植被根系空间发育规律,结合室内土工试验明确加筋土物理力学性质和渗透特性变化,并进行现场染色示踪试验,观察林下边坡雨水优势渗流路径构成及发育特征,研究成果将助力于明确台风暴雨型浅层滑坡失稳机理和沿海地区植被覆盖边坡滑坡灾害风险评价。
1. 根系发育特征及根系土物理力学性质
我国东南沿海地区台风暴雨型滑坡灾害多为浅层土质滑坡,坡面植被覆盖度高,集中发生于台风暴雨峰值阶段。现场调查结果表明,研究区台风暴雨型滑坡滑动面多孕育于土-岩基覆界面和土层内部软弱面[14 − 15, 25]。本文于福建省南平市松溪县选取一典型台风暴雨型浅层滑坡灾害点开展试验分析。边坡具有典型的二元结构,即上覆第四系残坡积土,下伏基岩,基岩埋深为2.5~3.0 m,滑坡发生于土-岩界面。该台风暴雨型滑坡灾害发生于路边,失稳后,应急部门迅速清除了滑坡堆积,并对边坡进行了削坡处理,削坡后后缘暴露长度14.6 m。通过对滑坡后缘开挖垂直剖面,统计分析植被根系发育特征,并采样开展室内土工试验,获取了根系对土体物理力学性质的影响。
1.1 植被根系发育特征统计
该边坡植被覆盖类型为马尾松,是研究区台风暴雨型滑坡所在边坡主要乔木植被覆盖类型[12, 15],马尾松高度约20 m,胸径25~30 cm。边坡后缘处共分布有3棵马尾松,自图1左向右分别记作树1、树2和树3。此外,边坡自左向右7~8 m处暴露有残留根系,为滑坡发生后乔木植被残留根系。
对滑坡后缘进行削坡平整后开挖竖向剖面,竖向开挖深度2 m,直至达到根系最大发育深度处。边坡开挖完成后,采用塑料条带对竖向剖面进行网格划分,网格尺寸为20 cm×20 cm,共得到730个网格。采用游标卡尺测量统计每个网格内根系数量和直径,边坡竖向剖面网格划分如图1所示。
根据Leung等[26]和Jotisanjasa等[27],本章节采用单位面积内根系数量(RND)和单位面积内根系截面积(RAD)描述植被根系空间发育特征:
(1) 式中:n——单个网格内根系数量/根;
As——单个网格面积(20×20=400 cm2)。
(2) 式中:di——第i根根系直径/mm;
Ar——单个网格内根系总截面面积/mm2。
1.2 根系土物理力学性质测量
剖面内根系发育特征统计完成后,于植被旁开展环刀采样为后续土工试验做准备(取样位置见图1)。环刀直径50.46 mm、高50 mm,采样深度为地面以下0~2 m,自地面向下以20 cm为间隔分层开挖,并采用取土钻取样,确保采样深度大于根系最大发育深度,即采取试样中包含无根系土和根系土。根系土试样如图2所示。按照《公路土工试验规程》(JTG3430—2020),分别测量土体颗粒比重、干密度、孔隙率、抗剪强度指标和渗透系数。
土粒比重(Gs)采用比重瓶法测量,试样干密度(
(3) 式中:m——试样烘干后质量/g;
V——试样体积/cm3。
测量根系土孔隙率时要考虑根系影响,根系土孔隙率(n)可定义为[27]:
(4) 式中:Vv——孔隙体积/cm3;
Vs——土颗粒体积/cm3;
Vr——根系体积/cm3;
Ws——土颗粒质量/g;
Gs——土颗粒比重;
Wr——根系质量/g;
Gr——根系比重;
无根系土孔隙率定义为:
(5) 考虑到台风暴雨型滑坡失稳时土体多处于饱和状态,因此制备饱和土样开展直剪试验(慢剪),剪切速率为0.01 mm/min,基于摩尔-库伦准则得到土体抗剪强度指标:
(6) 式中:
c——黏聚力/kPa;
对现场环刀法获取的原状试样开展饱和渗透试验,以测量根系土与无根系土渗透特性差异。考虑到研究区残坡积土多为黏性土,因此采用变水头渗透实验测量饱和渗透系数:
(7) 式中:Ks——试样饱和渗透系数/(m·s-1);
a——变水头管截面积/m2;
L——试样高度/m;
A——试样截面积/m2;
t——渗透时间/s;
H1——初始水头/m;
H2——终止水头/m。
1.3 试验结果分析
(1) 根系空间分布特征
植被根系空间分布统计结果见图3。共统计有植被根系1 409根,最大根系发育深度达地面以下2 m,单个网格内最大根系数量为16根(RND=400根/m2),位于地表以下0~0.2 m深度范围,见图3(a)。
从根系竖向分布看,地面以下0.2 m深度内,根系分布较为均匀,整个剖面内均有大量根系发育;地面0.2~0.4 m深度内表现出相似的发育特征,仍可在整个剖面内观察到大量根系;0.4 m深度以下,大量网格为无根区。由此推断,地面以下0.4 m深度内,植被根系由马尾松乔木植被和草本植物提供,草本植物根系在浅表层分布相对均匀,但影响深度较浅。0.4 m深度以下植被根系主要由马尾松提供。
从水平分布来看,边坡内部根系集中于乔木植被附近。地面0.6 m深度以下,仅在乔木植被旁观察到根系存在,最大根系发育深度位于第三棵马尾松处。由于该马尾松紧贴开挖剖面,主根系和侧根系均有暴露在外,因此该处网格揭露了植被根系最大发育深度和发育形式。相比于典型须根系植被,侧向根系相对不发育,是典型的具有主根的深根乔木植被[12, 15],竖向发育深度远大于草本植物,因此对边坡稳定性有重要影响。
植被根系截面积(RAD)空间分布如图3(b)所示。RAD较大处主要集中于3棵马尾松和摧毁植被残留根系附近,并随着埋藏深度的增大呈现降低趋势。浅表层草本植物多具有须根系,发育深度浅且根系直径小,因此根系截面积十分有限。对于乔木植被而言,第三棵马尾松处(树3,边坡剖面最右侧)由于植被主根系暴露于开挖剖面,因此观察到贯穿竖向剖面的高RAD区域。
开挖剖面内不同直径根系数量和截面积RAD随深度变化如图4所示。根据Camire等[28]和宋尊荣等 [29],将根系划分为细根(0~2 mm)、小根(2~5 mm)、中根(5~10 mm)和粗根(>10 mm)。结果表明:植被根系数量和截面积随深度增大均显著降低。地面以下0.2 m深度内根系数量最大,共计437根,0.2~0.4 m深度内根系数量302根,1.0 m深度以下降低至100根以内。尽管开挖剖面内植被根系以细根和小根为主,中根和粗根所占比例于0.4 m深度以下开始上升,这是由于0.4 m深度以下发育根系主要源自于马尾松乔木植被,与图3中根系分布特征较为吻合。不同直径根系截面积随深度变化与根系数量变化规律相似。地表以下0.2 m深度内根系面积最大,约1.0 mm2/cm2,而1.8~2.0 m深度范围根系密度降低至0.04 mm2/cm2。对比分析图4(a)(b),发现尽管边坡内部植被根系以细根和小根为主,但上述两种根系对截面积贡献极为微弱,粗根在不同深度处截面积占比均超过80%,考虑到植被附加黏聚力与根系直径呈幂律关系[30],且草本植物根系发育于地面以下0.4 m深度内,因此认为边坡内部植被根系力学加筋机制主要源自于马尾松乔木植被,且马尾松主要通过大直径粗根加固边坡。
(2) 根系土物理性质
试样物理性质试验结果如图5所示,取样点根系最大发育深度约0.8 m。根据图5a,不同深度处试样土体颗粒比重(Gs)为2.65~2.68 ,表现出较高的一致性,不同深度处试验土样类别均为粉质黏土,边坡内部土质分布较为均匀。试样干密度(
(3) 根系土强度及渗透性
不同深度处试样抗剪强度指标和饱和渗透系数试验结果如图5d—f所示。不同深度处土体内摩擦角为18.5°~23.3°,在深度范围内分布较为一致,随埋深增大、土体密实度提高呈略微增大趋势。然而,土体黏聚力变化显著,于根系最大深度处(地面以下0.8 m)发生突变。加筋区土体黏聚力为7.5~10.6 kN,0.8 m深度以下无根土黏聚力仅4.6~6.0 kN。若将无根土平均黏聚力5.3 kN设为基准,可反推得到表层0.8 m深度内植被根系提供的附加黏聚力为2.2~5.3 kN,该附加黏聚力可显著提高边坡表层土体抗剪强度。抗剪强度试验结果表明:植被根系加筋机制主要通过提供附加黏聚力提高土体抗剪强度和加固边坡,对土体内摩擦角影响相对较小,与国内外学者试验结果相一致[30 − 31]。
试样饱和渗透系数试验结果如图5f所示,不同深度土体饱和渗透系数为2.9×10−6~5.2×10−5 m/s,随深度增大显著降低。其中,地面以下0.8 m深度范围内根系土饱和渗透系数为2.7×10−5~5.2×10−5 m/s,平均渗透系数为3.79×10−5 m/s;0.8 m深度以下无根系土饱和渗透系数为2.9×10−6~5.6×10−6 m/s,平均渗透系数为3.74×10−6 m/s。由此可见,植被根系在提高加筋区土体抗剪强度的同时,还会增大加筋区土体渗透系数,加速台风期间边坡内部雨水入渗。
2. 植被根系优势渗流效应
2.1 染色示踪试验与剖面图像识别
植被根系在提供附加抗剪强度加固边坡的同时还能通过根-土间隙、促进裂隙和结构性孔隙发展等方式提供优势渗流通道加速雨水入渗[32]。根系土渗透试验表明根系的存在导致土体渗透性能大幅提高,因此为进一步明确乔木植被覆盖边坡优势渗流通道发育类型及规律,本文于地形相对平坦处选取一株马尾松植被作为研究对象开展现场染色示踪试验。染色面积1.2 m×1.0 m (图6),主要试验步骤如下:
(1) 沿场地四周边界开挖深度20 cm、宽3 cm凹槽,将木板安置于内,减少染色过程中侧向径流。为保护植被,同时考虑根系发育方向,开挖凹槽位置如图6所示。
(2) 配置4 g/L亚甲基蓝染色示踪剂,按50 mm/h的降雨强度均匀喷洒于试验区,连续喷洒3 h(150 mm降雨量)。溶液喷洒完成后,用树叶和不透明塑料膜遮盖试验区以减少水分蒸发带来的影响。
(3) 静置24 h待染色完成,沿预定位置(图6)开挖竖向剖面,采用毛刷和小刀清理开挖过程中吸附在土体剖面上的松散颗粒,确保剖面整洁;采用高清照相机拍摄染色剖面,用于开展后续图像识别分析。
(4) 采用ImageJ®图像处理软件对染色剖面开展图像识别分析:于ImageJ®软件中调节合适阈值对图像进行灰度化处理,在此基础上采用Java编程语言进行二次开发,利用自动化网格划分技术对染色剖面图像进行竖向等间距自动化分层,并采用Measure和Macro功能实现图像批量处理,计算得到各竖向分层染色面积。该自动化网格划分技术能显著提高图像识别效率和精度。
土体内部雨水入渗由均匀入渗和优势入渗两部分构成,根据Bargues 等[33]和Luo等[34],采用染色面积比(DC)和优势渗流比(Pr-fr)表征土体竖向剖面内染色面积和优势渗流效应:
(8) 式中:DC——染色面积比,为剖面内染色面积与总面积的比值/%;
D——染色面积/m2;
ND——未染色面积/m2。
(9) 式中:Pr-fr——优势渗流比,为优势渗流染色面积与总 染色面积的比值/%;
UniFr——均匀入渗染色深度/m,当土体剖面某一深 度处染色面积达到80%认为发生均匀 入渗,小于80%认为发生优势渗流[33];
W——剖面宽度/m;
TSA——总染色面积/m2。
2.2 染色示踪试验结果分析
染色示踪结果如图7所示,剖面开挖深度为80 cm。为获取剖面染色面积比(DC)随深度变化规律,以2 cm为间隔(共40层)进行自动化网格划分。图像识别结果表明:两处开挖剖面内染色面积比(DC)随深度变化总体呈下降趋势。地面以下0~8 cm染色面积比(DC)超过80%,表明该区域以土体均匀入渗为主;8 cm深度以下,染色面积比(DC)开始迅速降低,此时剖面内渗流以优势入渗为主。
根据式(9),剖面1内总染色面积(TSA)为
2710 cm2,均匀入渗染色面积为724 cm2,优势渗流比Pr-fr为73.3%,优势渗流占比约为坡面均匀入渗3倍。尽管剖面内存在少量裂隙和虫洞,优势渗流染色区域多集中于植被根系附近,特别是大直径粗根。如图7a所示,8 cm深度以下,优势渗流主要发生于剖面左侧起0~40 cm区域内,该区域为植被根系发育区,染色溶液以粗根系为中心向四周呈辐射状扩散渗流,根-土间隙是该剖面内优势渗流的主要来源。剖面2染色示踪结果如图7b所示,染色面积比DC随深度增大不断降低,在65 cm深度处趋近于零。剖面2总染色面积(TSA)为1603 cm2,均匀入渗染色面积为627 cm2,即优势渗流比Pr-fr为60.9%。尽管该剖面内优势渗流占比略低于剖面1,优势渗流所占比重仍高于土体均匀入渗且集中于根系附近。相较于剖面1,剖面2中植被根系数量和截面积相对较小,且缺乏大直径粗根,因此优势渗流通道分布较为零散。为进一步论证植被根系与林下边坡优势渗流特性的关系,于两处开挖剖面内以10 cm为间隔分层采集植被根系信息,分析根系截面积与剖面染色面积关系,结果如图8所示。两处剖面内土体染色面积和根系面积表现出相近的变化规律,随深度增大显著降低且降低幅度相近,表现出正相关性。剖面1中由于大直径粗根的存在,根系最大截面积超过3.5 mm2/cm2,远高于剖面2中根系面积,因此在20 cm深度以下剖面1中染色面积显著高于剖面2染色面积。剖面2中根系面积和染色面积在40 cm深度以下均趋近于零,表明该深度优势渗流效应十分微弱。由此可见,本文染色示踪试验开挖剖面内优势渗流通道主要由马尾松植被根系提供,大直径粗根系由于其大截面面积,产生的优势渗流效应对雨水快速入渗尤为重要,因此在开展边坡稳定性分析、探究台风暴雨型浅层滑坡失稳机制时需重点考虑乔木植被主根系优势渗流效应。
3. 结果综合分析和讨论
我国东南沿海地区台风触发滑坡灾害多发于乔木植被覆盖边坡土岩基覆界面和土层内部软弱界面,时间滞后性弱[14 − 15, 25]。本文试验结果表明,植被可通过力学和水文作用对边坡稳定性产生影响,促进潜在滑面的形成(图9)。
研究区乔木植被为典型的具有主根的深根乔木植被,根系发育深度大,侧向须根相对数量少,可通过大直径根系力学加筋和提供优势渗流通道改变土体物理力学特性,且两种作用机制均与植被根系发育深度密切相关。根系力学加筋机制主要通过根-土作用提供附加黏聚力的方式加固边坡,能显著提高加筋区土体抗剪强度,但同时也导致根系最大发育深度处存在力学性质差异。此外,边坡土体优势渗流所占比重远高于坡面均匀入渗,且土体内部优势渗流通道主要由乔木植被根系提供。根系提供的优势渗流效应能加速台风期间雨水入渗速率,使得浅表层土体在短历时台风期间处于高饱和状态。考虑到加筋区土体渗透性远高于无根土,因此植被根系尖端易形成汇水区。上述力学和水文机制使得植被根系发育深度处形成软弱面。由于研究区台风暴雨型滑坡多发于直线型和凸型边坡[13, 24],相较于凹型边坡,承受风荷载受两侧山体影响较小,台风期间边坡覆盖的植被往往承受更大的风荷载。尽管乔木植被的粗壮根系相比于灌木和草地拥有更大的截面积和更深的发育深度,但其高耸结构和大迎风面积可将风荷载传递至边坡,作为下滑力对边坡稳定性产生不利影响。上述台风暴雨型滑坡特殊的发育特征为明确台风荷载影响提供了依据。考虑到台风期间,乔木植被以根系为纽带与边坡土体作用,将风荷载传递至边坡[15],因此,当下滑力(风荷载、土体自重、植被超载)超过抗滑力时,易于根系最大发育深度附近诱发滑坡灾害,即植被根系最大发育深度处为林下边坡潜在滑面,该类型浅层滑坡可在短时间内发生。
对发生于边坡内部植被根系发育深度以下的区域,潜在滑面埋藏深度大于根系发育深度,根系力学加筋和优势渗流效应影响较小,此时边坡稳定性受控于土-岩基覆界面力学与渗透特性差异。研究区边坡多具有二元结构,上层为第四系松散堆积下伏基岩,完整度较高的基岩可视作不透水或弱透水层。当雨水入渗至土-岩基覆界面时,发生侧向径流,形成瞬态饱和区,显著降低土体抗剪强度。因此,边坡内部土-岩基覆界面同样为台风暴雨型滑坡灾害潜在滑面边坡的风荷载和根系提供的优势渗流效应是边坡快速失稳的关键因素。上述2种边坡失稳模式与现场调查结果基本吻合。
4. 结论
(1) 相较于须根系植被,马尾松大直径粗根系发育,侧向根系相对少,主根系发育深度可达2 m,距地面0.4 m深度以下,植被根系主要由马尾松乔木植被提供,草本植物贡献微弱;相较于细根,剖面内粗根截面积占比超过80%。对边坡稳定性有重要影响。
(2) 土工试验和染色示踪试验结果表明:根系在提供附加黏聚力加固边坡的同时,通过提供优势渗流通道提高土体渗透系数,增大雨水入渗速率,根系土渗透系数可达无根土10倍。此外,土体内部优势渗流效应与根系截面积密切相关,大直径粗根系由于其大截面面积,产生的优势渗流效应对雨水快速入渗尤为重要,雨水会沿根-土界面向四周呈辐射状扩散。边坡内部优势渗流所占比重可达坡面均匀入渗的2~3倍。
(3) 植被对边坡稳定性的影响与其力学和水文机制密切相关。其力学加筋和优势渗流效应促使植被根系最大发育深度处成为潜在滑面,在风荷载和强降雨作用下极易短时间内发生失稳;土-岩基覆界面为林下边坡内部另一潜在滑面,由于埋藏深度较大,受根系力学加筋作用影响微弱,但根系提供的优势渗流效应仍能促使边坡在短历时台风期间失稳。
-
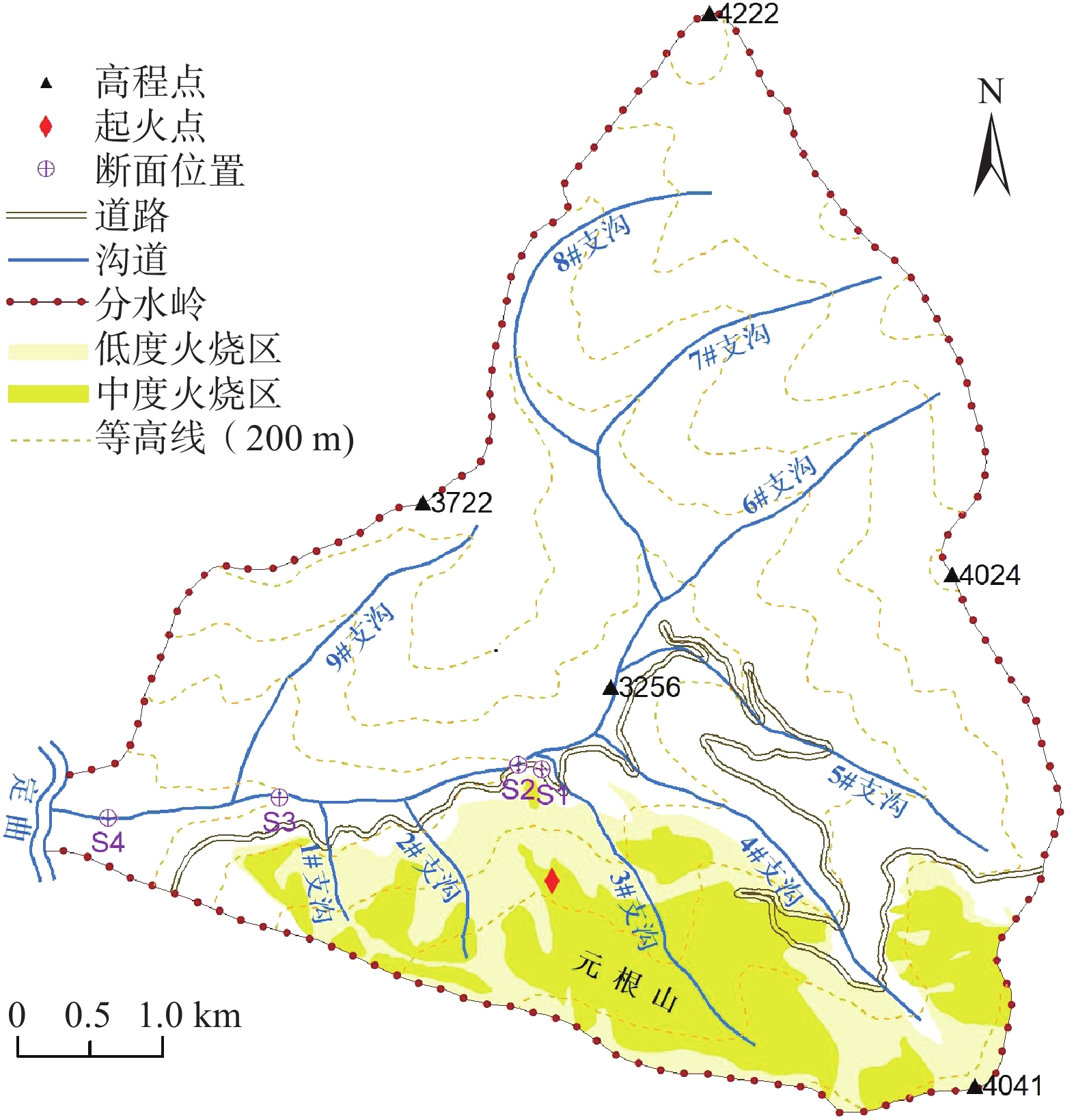
表 1 1#—3#支沟基本信息
Table 1 Geographic information of branches No.1−No.3
编号 流域面积/km2 沟长/m 平均坡度/(°) 1# 0.37 544 27 2# 0.73 755 26 3# 2.30 836 15 表 2 1#—3#支沟火烧强烈程度及面积统计
Table 2 Summary of fire severity classification and affected areas of branches No.1−No.3
编号 火烧面积/km2 轻度火烧/km2 中度火烧/km2 1#支沟 0.31 0.21 0.10 2#支沟 0.64 0.45 0.19 3#支沟 2.11 0.6 1.51 表 3 泥石流基本情况
Table 3 Basic property information of the debris flows
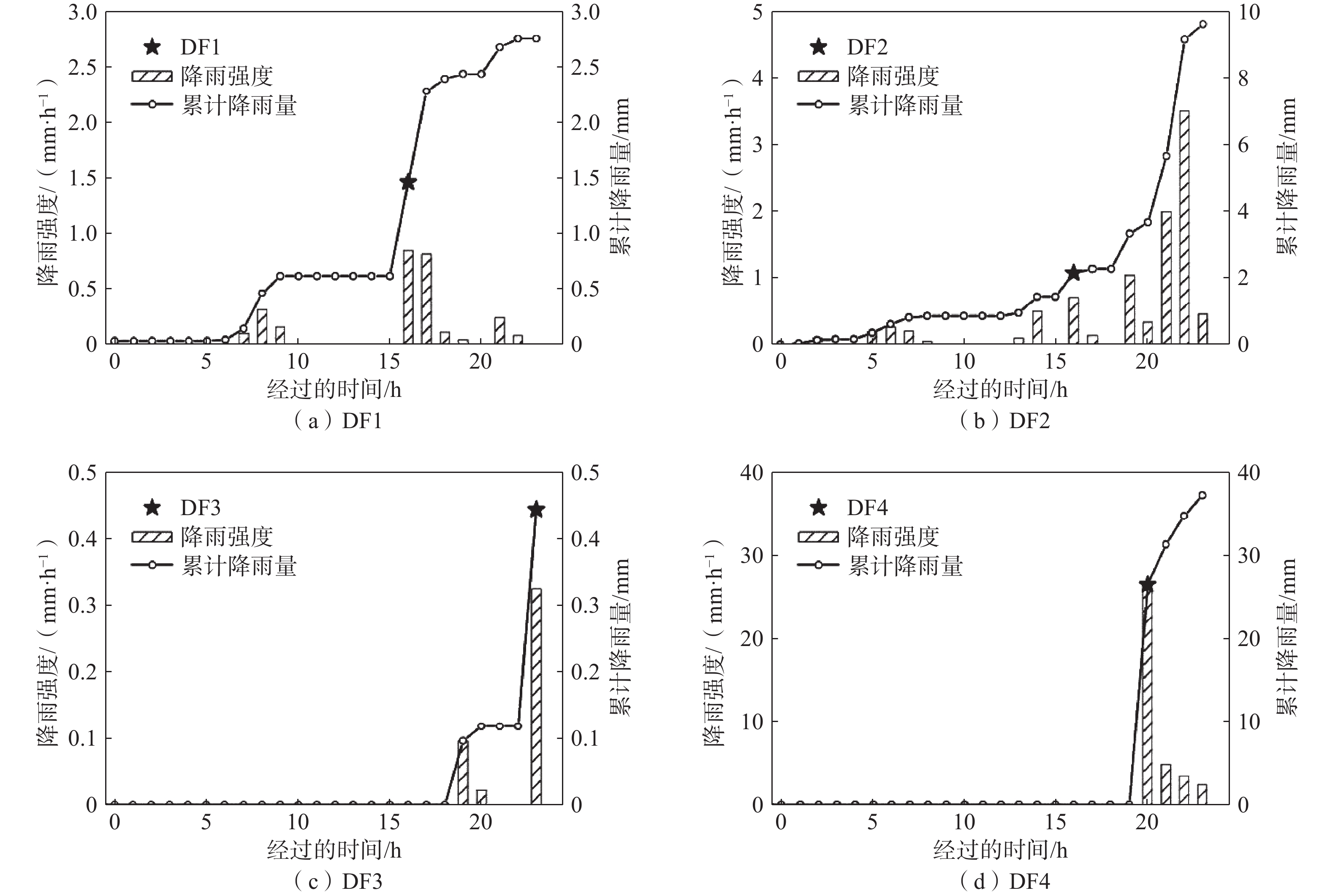
序号 时刻 位置 冲出量
/(104 m3)前期3 d
降雨量/mmDF1 2014年6月8日16:08 3# 0.8 1.11 DF2 2014年6月30日16:00 3# 1.4 14.84 DF3 2014年7月10日23:20 3# 0.5 0.81 DF4 2015年8月24日19:43 1#、2#、3# 2.2 39.97 表 4 3处雨量站基本情况
Table 4 Summary of the basic property information of the three rain gauges
序号 气象站名 海拔/m 距泥石流沟
距离/km精度/mm 1 正斗站 2858 4.10 0.1 0.577 2 热打站 3363 5.56 0.1 0.313 3 阿都站 2783 9.40 0.1 0.110 -
[1] LARSEN I J,MACDONALD L H,BROWN E,et al. Causes of post-fire runoff and erosion:Water repellency,cover,or soil sealing?[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,2009,73(4):1393 − 1407. DOI: 10.2136/sssaj2007.0432
[2] SCOTT,W WOODS,VICTORIA N,et al. The effects of soil texture and ash thickness on the post-fire hydrological response from ash-covered soils[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2010,393(3-4):274 − 286. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.08.025
[3] MACDONALD L H,HUFFMAN E L. Post-fire soil water repellency[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,2004,68(5):1729 − 1734. DOI: 10.2136/sssaj2004.1729
[4] NYMAN P,SHERIDAN G,LANE P N J. Synergistic effects of water repellency and macropore flow on the hydraulic conductivity of a burned forest soil,south-east Australia[J]. Hydrological Processes,2010,24(20):2871 − 2887. DOI: 10.1002/hyp.7701
[5] MOODY J A,EBEL B A,NYMAN P,et al. Relations between soil hydraulic properties and burn severity[J]. International Journal of Wildland Fire,2016,25(3):279. DOI: 10.1071/WF14062
[6] MOODY J A,EBEL B A. Hyper-dry conditions provide new insights into the cause of extreme floods after wildfire[J]. CATENA,2012,93(93):58 − 63.
[7] KEAN J W,STALEY D M,CANNON S H. In situ measurements of post-fire debris flows in southern California:comparisons of the timing and magnitude of 24 debris-flow events with rainfall and soil moisture conditions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,2011,116(F4):F04019.
[8] SMITH H G,SHERIDAN G J,LANE P N J,et al. Paired Eucalyptus forest catchment study of prescribed fire effects on suspended sediment and nutrient exports in south-eastern Australia[J]. International Journal of Wildland Fire,2010,19(5):624. DOI: 10.1071/WF08208
[9] JORDAN P. Post-wildfire debris flows in southern British Columbia,Canada[J]. International Journal of Wildland Fire,2016,25(3):322. DOI: 10.1071/WF14070
[10] CONEDERA M,PETER L,MARXER P,et al. Consequences of forest fires on the hydrogeological response of mountain catchments:a case study of the Riale Buffaga,Ticino,Switzerland[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2003,28(2):117 − 129. DOI: 10.1002/esp.425
[11] 胡卸文,王严,杨瀛. 火后泥石流成灾特点及研究现状[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(6):1562 − 1573. [HU Xiewen,WANG Yan,YANG Ying. Research actuality and evolution mechanism of post-fire debris flow[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(6):1562 − 1573. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018-073 HU Xiewen, WANG Yan, YANG Ying. Research actuality and evolution mechanism of post-fire debris flow[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(6)1562-1573(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018-073
[12] 王严,胡卸文,杨瀛,等. 火烧迹地土壤斥水性和渗透性变化特性[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):40 − 45. [WANG Yan,HU Xiewen,YANG Ying,et al. Research on the change in soil water repellency and permeability in burned areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):40 − 45. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.06.06 WANG Yan, HU Xiewen, YANG Ying, et al. Research on the change in soil water repellency and permeability in burned areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(6)40-45(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.06.06
[13] 任云,胡卸文,王严,等. 四川省九龙县色脚沟火后泥石流成灾机理[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(6):150 − 156. [REN Yun,HU Xiewen,WANG Yan,et al. Disaster mechanism of the Sejiao post-fire debris flow in Jiulong County of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(6):150 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2018.06.22 REN Yun, HU Xiewen, WANG Yan, et al. Disaster mechanism of the Sejiao post-fire debris flow in Jiulong County of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(6)150-156(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2018.06.22
[14] 黄健,胡卸文,金涛,等. 四川西昌 “3•30” 火烧区响水沟火后泥石流成灾机理[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):15 − 22. [HUANG Jian,HU Xiewen,JIN Tao,et al. Mechanism of the post-fire debris flow of the Xiangshui gully in “3•30” fire area of Xichang,Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):15 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG Jian, HU Xiewen, JIN Tao, et al. Mechanism of the post-fire debris flow of the Xiangshui gully in “3·30” fire area of Xichang, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3)15-22(in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 杨相斌,胡卸文,曹希超,等. 四川西昌电池厂沟火后泥石流成灾特征及防治措施分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):1 − 8. [YANG Xiangbin,HU Xiewen,CAO Xichao,et al. Analysis on disaster characteristics and prevention measures of the post-fire debris flow in Dianchichang gully,Xichang of Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202203039 YANG Xiangbin, HU Xiewen, CAO Xichao, et al. Analysis on disaster characteristics and prevention measures of the post-fire debris flow in Dianchichang gully, Xichang of Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4)1-8(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202203039
[16] CHEN J C,HUANG W S,JAN C D,et al. Recent changes in the number of rainfall events related to debris-flow occurrence in the Chenyulan Stream Watershed,Taiwan[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Science,2012,12(5):1539 − 1549. DOI: 10.5194/nhess-12-1539-2012
[17] 刘世康,范宣梅,王文松,等. 降雨模式对震后泥石流起动模式影响的试验研究—以九寨天堂沟为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):278 − 286. [LIU Shikang,FAN Xuanmei,WANG Wensong,et al. Experimental study on the effect of rainfall patterns on the failure mode of debris flows after earthquakes:A case study of Tiantanggou, Jiuzhai[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):278 − 286. (in Chinese with English abstract) [LIU Shikang, FAN Xuanmei, WANG Wensong, et al. Experimental study on the effect of rainfall patterns on the failure mode of debris flows after earthquakes: A case study of Tiantanggou, Jiuzhai[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 278-286. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 谢扬龙,齐信,高鹏,王英豪. 基于多种评价模型在斜坡地质灾害易发性评价中的对比分析——以武汉市为例. 华南地质. 2025(01): 185-196 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴逢涛,杨志全,赵旭光. 基于Stacking集成机器学习模型的川西重大交通干线地质灾害易发性评价. 科学技术与工程. 2025(13): 5340-5350 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 包峻帆,陈婕,杨文涛,杨泽强,侯文青,陈恪,袁野,杨明权,景斐媛,刘淼昕,刘哲,张媛媛,黄灿. 利用可解释机器学习模型判别豫西巩义市康店镇黄土地质灾害易发性. 科学技术与工程. 2025(15): 6200-6219 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 林小慧,何玥,黄炎和,林金石,季翔. “三生空间”视角下基于云模型的崩岗侵蚀危害评价. 山地学报. 2024(03): 411-421 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载:


















 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS