Assessment of rockfall susceptibility along the expressway based on the CF-AHP coupling model: A case study of the Tucheng-Wanglong section of the Rongzun expressway
-
摘要: 蓉遵高速公路(土城—旺隆段)沿线崩塌频繁发生,威胁公路安全甚至人类的生命财产安全。文章通过实地调查蓉遵高速公路(土城-旺隆段)崩塌地质灾害的影响因素,构建了9个影响因子,分别是地形起伏度、高程、归一化植被指数、坡向、地层岩性、距道路距离、距河流距离、坡度及降雨量。采用确定性系数模型(certain factors,CF)、层次分析法(analytic hierarchy process,AHP)及耦合模型(CF-AHP)对研究区进行崩塌地质灾害易发性评价,并分别采用崩塌地质灾害点频率统计和成功率曲线对3种模型的评价精度进行检验。结果表明,CF、AHP和CF-AHP的AUC预测精度分别为0.848,0.835,0.866,且3种评价模型得到的崩塌地质灾害的高、中易发区频率比值占总频率比值均超过70%。 3种模型精确度由大到小分别为CF-AHP、CF、AHP模型,说明CF-AHP模型的滑坡预测优于单一的CF、AHP模型,能精确地评价蓉遵高速公路(土城-旺隆段)崩塌地质灾害易发性,为公路沿线区域崩塌灾害的防灾减灾提供决策依据。
-
关键词:
- 崩塌地质灾害 /
- 高速公路 /
- 易发性评价 /
- CF-AHP耦合模型
Abstract: Frequent geological hazards have occurred along the Rongzun Expressway (Tucheng - Wanglong section, posing a threat to the safety of the highway and even human life and property. This study investigated the causes of rockfall along the expressway and identified nine influencing factors, including terrain fluctuation, elevation, normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), slope direction, lithology, distance from the road, distance from the river, slope, and rainfall. The certainty factor model (CF), analytic hierarchy process (AHP), and coupling model (CF-AHP) were used to evaluate the susceptibility of geological hazard in the study area, and the accuracy of the three models was tested using the distribution of rockfalls at various levels and the success rate curve. The results indicated that the AUC evaluation accuracy of CF, AHP and CF-AHP was 0.848, 0.835 and 0.866, respectively. The frequency ratios of high and moderate prone areas of geohazards obtained by the three evaluation models accounted for more than 70% of the total frequency ratios. The accuracy of the three models in descending order is CF-AHP, CF, AHP models, respectively. This indicates that the CF-AHP model is better than the single CF and AHP models in geohazard prediction and can accurately evaluate the geohazard susceptibility of expressway. It provides a decision-making basis for disaster prevention and mitigation of regional rockfall disaster along the highway. -
0. 引言
崩塌和落石是山区常见的地质灾害现象[1]。高速公路等重要工程建设项目通常沿着崎岖的地形铺设。修建高速公路以削坡为主,在施工阶段已改变边坡的原始应力状态,加剧了地质灾害发生的可能性,威胁公路安全甚至人类生命财产安全。因此,沿高速公路进行边坡治理具有重要的意义,而高速公路的易发区划是边坡整治的首要步骤 [2]。在过去的几十年中,已经建立了许多预测模型来绘制地质灾害敏感性图。主要评价方法包括:经验模型(模糊逻辑[3]、层次分析法[4]等)、统计分析模型(证据权法[5]、信息量法[6]、确定性系数法[7]等)、机器学习模型(人工神经网络[8]、支持向量机[9]、随机森林[10]、逻辑回归算法[11]等)。覃乙根等[12]、刘光辉等[13]、李益敏等[14]将确定性系数模型应用于区域滑坡易发性评价的研究;杨栓成等[15]、李益敏等[16]、李萍等[17]利用层次分析法对区域地质灾害易发性进行了分析研究。综上所述,确定性系数(certain factors,CF)模型和层次分析法(analytic hierarchy process,AHP)因其原理简单、可操作性强、评估效果较理想,已大量应用于地质灾害易发性评价[18 − 19]。 但CF模型忽略了各因子对易发性影响的差异性,而层次分析法则忽略了评价因子内部不同特征值对易发性影响程度,因此,将2种模型相结合进行滑坡易发性评价,能使评价结果精度更高。
贵州省蓉遵(成都—遵义)高速是《贵州省骨架公路网规划(2003—2020)》中“三联”的重要组成路段,为贵州省北上连接成渝经济圈增加一个重要的出口通道,对黔北地区的经济发展具有重大的意义。蓉遵高速公路(土城—旺隆段)共61.851 km,已出现卸荷松动、剥蚀脱落的现象,具有威胁公路安全的隐患。为了解该段公路沿线边坡岩体卸荷、剥落程度及影响因素,沿着该高速公路实地调查,共查出20处崩塌(图1)。公路沿线的危岩崩塌一般位于工程边坡的坡顶或坡面较高位置,分布随机,体积大,与公路面具一定高差。部分孤石底座为强风化砂岩,岩体结构破碎,在雨水对坡面岩体的冲刷作用下,边坡危岩的稳定性难以保障。危岩一旦失稳坠落,将严重威胁着高速公路上行驶的车辆及其人员的生命安全。而关于蓉遵高速公路(土城-旺隆段)的崩塌易发性评价研究甚少,目前仍然缺乏区域性防灾减灾必需的崩塌灾害易发性分区成果地图,特别是针对评价模型的适用性和精度评价方法的对比研究鲜有案例[20 − 21]。
本文综合考虑影响崩塌地质灾害发生的各个致灾因子,以蓉遵高速公路(土城—旺隆段)沿线为研究区,结合对地质环境、崩塌灾害空间分布和特征分析,基于GIS的栅格数据模型,采用CF、AHP、CF-AHP耦合模型的评估方法,开展高速公路沿线的崩塌地质灾害易发性评价,为该高速公路的危险区划提供理论支持,对该高速公路治理具有现实意义。
1. 研究区概况
1.1 工程地质条件
该高速公路位于赤水河左岸河谷阶地以上缓平台地带,处云贵高原向四川盆地过渡地带。按地貌成因和形态特征,研究区属侵蚀型低山地貌,位于中亚热带季风气候区,冬春旱,夏初秋末多雨,但夏伏天期旱,全年日照时数少。研究区降水量丰沛,年际变化较大。多年平均降雨量1290 mm,主要集中在夏、秋季(5—9月),占全年降雨量的68%。据统计,1968年降雨量(约1700 mm)是1963年的近两倍。研究区构造格局受四川盆地影响,其构造形迹展布复杂,断层和褶皱较为发育。区内地层主要有侏罗系(J)和白垩系(K)。侏罗系地层厚度较大,主要为一套红层砂泥岩不等厚互层岩系,其岩性较软、风化程度较高,且发育构造、风化裂隙。而白垩系地层岩性相对较硬,风化程度较低,抗侵蚀和风化能力相对较强。
1.2 地质灾害发育特征
对高速沿线进行危岩体调查,共选出20个危岩。其中规模<100 m3 的崩塌10处,占总数的50%;规模位于100~1000 m3 的崩塌7处,占总数的35%,规模>1000 m3 的崩塌3处,占总数的15%。
通过调查,危岩均分布于白垩系嘉定群组(Kjd)与侏罗系蓬莱镇组(J3p)地层中,岩性主要分为巨厚层砂岩夹薄层泥岩;分布位置均位于边坡坡角大于60°的河谷边坡上,分布高程在310~495 m之间;危岩所在边坡倾向主要发育于NEE向。危岩体沿道路和河流线性分布,主要分布在距离道路200 m,距离河流400 m以内。综上所述,区内地质灾害的分布情况受地形地貌、地层岩性、地质构造的控制作用明显。
2. 研究方法
2.1 数据来源
本文所采用的数据主要包括:蓉遵高速公路(土城-旺隆段)沿线崩塌地质灾害隐患点数据;30 m分辨率数字高程数据(91卫图助手),延伸出高程、坡度、坡向和地形起伏度数据;区域1∶5万地质图,提取地层岩性、水系和地层数据;Landsat 8 遥感影像(地理空间数据云),计算归一化植被指数(NDVI)。
2.2 模型方法
2.2.1 CF模型
CF是一个概率函数,其值在区间[−1,1],值越大,说明发生地质灾害的概率越大。该模型可以计算评价因子等级对地质灾害的贡献度,由于其数据处理简单、易操作且精度较高,被广泛用于地质灾害敏感性评估等[12 − 13]。其表达式为:
$$ {C}{F}=\left\{\begin{split} &\frac{P{P}_{a}-P{P}_{s}}{P{P}_{a}\left(1-P{P}_{s}\right)},P{P}_{a}\geqslant P{P}_{s}\\ &\frac{P{P}_{a}-P{P}_{s}}{P{P}_{s}\left(1-P{P}_{a}\right)},P{P}_{a} < P{P}_{s}\end{split}\right. $$ (1) 式中:
$ {PP}_{a} $ ——评价因子等级a中地质灾害点个数与a面积之比,表示地质灾害在a分类中发生的条件概率;$ {PP}_{s} $ ——整个研究区地质灾害点数量与研究区面积 之比,表示地质灾害发生的先验概率。2.2.2 AHP法
AHP是一种能充分发挥主观判断的层次决策分析方法,其最早是由Saaty提出,广泛使用于各领域 [14]。其原理如下:首先选取评价因子,建立层次结构模型,对选取的评价因子相对重要性进行专家评估打分,打分用Saaty给出的1~9标度法(表1),构造两两判断矩阵,对一致性进行检验,一致性检验指标公式如下[15 − 16]:
表 1 判断矩阵标度及其含义Table 1. Judgment matrix scale and its meaning标度值 含义 1 表示两个因素相比,具有相同重要性 3 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者稍重要 5 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者明显重要 7 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者强烈重要 9 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者极端重要 2,4,6,8 表示上述相邻判断的中间值 倒数 与上述影响情况相反 $$ CI=\frac{{\lambda }_{\max}-n}{n-1},\;\;n > 1 $$ (2) $$ CR=\frac{CI}{RI} $$ (3) 式中:
$ CI $ ——一致性指标;$ CR $ ——随机一致性比率;$ RI $ ——同阶平均随机一致性指标。CR<0.10 时,通过一致性检验,该判断矩阵可用;否则,需要对本层次的各判断矩阵进行调整,直到符合一致性检验标准。各评价因子权重值通过判断矩阵获取,然后归一化各评价因子不同分级状态。最终,通过式(4)计算出易发性指数。
$$ {S} _{i}=\sum {W}_{i}{L}_{i} $$ (4) 式中:
${S} _{i} $ ——层次分析法易发性指数;${W}_{i} $ ——评价因子不同分级权重;${L}_{i} $ ——评价因子不同分级归一化标准值。2.2.3 CF-AHP模型
CF-AHP模型是基于CF值划分评价因子的各分级权重,利用层次分析法科学划分层次并赋予各评价因子权重,将两者相乘叠加,即可得到地质灾害易发性指数LSI,其计算公式为:
$$ LSI=\sum _{i}^{n}{W}_{i}C{F}_{i}\left(i=\mathrm{1,2},\cdots ,n\right) $$ (5) 式中:
$ {W}_{i} $ ——第i 个评价因子的权重;CFi——第i个评价因子各分级的CF值。
3. 评价因子的选取与分级
评价因子的选取对地质灾害易发性评价起着重要作用,应在了解野外实地调查资料、结合研究区孕灾机理的基础上进行选取[12]。综合实地调查该高速公路崩塌地质灾害的影响因素及结合前人的研究[9 − 12],构建了9个影响因子,分别是地形起伏度、高程、归一化植被指数、坡向、地层岩性、距道路距离、距河流距离、坡度及降雨量。基于前人对评价因子分级的方法[9 − 12],本文对9个评价因子的分级情况如下。
3.1 高程
很多研究表明地质灾害与高程分布具有明显的区域规律[9],研究区高程范围为222~790 m,根据ArcGIS里的自然间距法,将研究区地形坡度划分为5类,即222~325 m、>325~407 m、>407~488 m、>488~581 m、>581~790 m,见图2(a)。
3.2 坡度
地形坡度是滑坡发生的主要影响因子之一,不同坡度的坡体,其内部应力分布不同,稳定性不同[9]。在ArcGIS空间分析模块中以DEM为基础获取地形坡度,研究区属侵蚀型低山地貌,将研究区地形坡度划分为6类,即≤10°、>10°~20°、>20°~30°、>30°~40°、>40°~50°、>50°,见图2(b)。
3.3 地形起伏度
地形起伏度能反映在一定范围内地形的宏观特征[10],研究区地形起伏度在152~672 m范围内,并按照自然间断法将其分为5级,分别为152~285 m、286~362 m、363~439 m、440~526 m、527~672 m,见图2(c)。
3.4 坡向
坡向对地质灾害发生的控制作用主要表现在山坡的小气候以及水热比的规律性变化[9 − 10]。坡向按方位分为9类,分别为平面、北、东北、东、东南、西、西南等,见图2(d)。
3.5 地层岩性
地层岩性是产生地质灾害的物质基础,岩石类型和软硬程度决定岩土体的抗风化能力[9],地层岩性按实际地层分为4类,主要包括白垩系嘉定群组一段、二段(Kjd1、Kjd2)与上侏罗统蓬莱镇组一段、二段(J3p1、J3p2),见图2(e)。
3.6 归一化植被指数
归一化植被指数作为一种表征植被特征的指数,植被覆盖度能在一定程度上代表诱发地质灾害发生的外部因素[11]。本文基于Landsat8遥感影像计算得到研究区的NDVI数据,根据ArcGIS里的自然间距法,将研究区NDVI划分为5类,分别为−0.0897~0.0962、0.0963~0.2405、0.2406~0.3432、0.3433~0.4190、0.4191~0.5340,见图2(f)。
3.7 距道路距离
城镇、乡村等道路和居民区工程建设,对地质环境的扰动及破坏较大,易加剧和诱发地质灾害[11]。研究区崩塌主要分布在距离道路200 m以内,以50 m间隔,距道路距离分为6个等级0~50 m、>50~ 100 m、>100~150 m、>150~200 m 、>200 ~250 m、>250 m六个区间,见图2(g)。
3.8 距水系距离
河流水系对斜坡起冲蚀作用、引发滑坡崩塌体内地下水位及孔隙水压力变化,是引起崩塌等地质灾害的主要因素[12]。在提取地表水与滑坡、崩塌地质灾害易发性指标时,将地表水影响范围划分为:0~100 m、>100~200 m、>200~300 m、>300~400 m、>400~500 m 、>500 m六个区间,见图2(h)。
3.9 降雨量
研究区位于中亚热带季风气候区,降雨丰富,且降雨时间集中,地质灾害主要发育在年平均降雨量1000 mm的地区,据此将降雨量划分为3级,分别为:0~800 mm、>800~900mm、>900~1000 mm,见图2(i)。
4. 崩塌地质灾害易发性评价
4.1 基于CF模型
基于ArcGIS软件,对评价因子的栅格图层和崩塌灾害数据进行空间分析,得到23070个独立的属性单元,并进行统计分析。
利用式(1)型计算出各评价因子等级的CF值(表2),并加权叠加即可得到各单元地质灾害易发性指数
${LSI}$ 。其计算公式为[15]:表 2 评价因子分级及CF值Table 2. Classification of evaluation factors and CF values of each grade指标因子 分级 面积/km2 灾害点数/个 点密度/(个·km-2) CF值 高程/m 222~325 7.277 0 0 −1 >325~407 4.458 6 1.345986 0.297557 >407~488 4.587 10 2.179932 0.566281 >488~581 3.609 4 1.10834 0.146942 >581~790 1.451 0 0 −1 坡度/(°) 0~10 2.962 0 0 −1 >10~20 4.497 0 0 −1 >20~30 6.335 3 0.473552 −0.49914 >30~40 4.993 11 2.202996 0.570822 >40 2.595 6 2.312406 0.591128 地形起伏度/m 152~285 1.067 0 0 −1 286~362 6.290 2 0.31796 −0.66371 363~439 6.170 3 0.486192 −0.48577 440~526 5.431 15 2.762126 0.657699 527~672 2.440 0 −1 坡向/(°) 平面 0.002 0 0 −1 北 2.435 3 1.231831 0.23246 东北 6.026 10 1.659613 0.430302 东 5.409 5 0.924385 −0.02231 东南 3.192 1 0.313254 −0.66868 南 1.951 1 0.512505 −0.45794 西南 0.556 0 0 −1 西 0.943 0 0 −1 西北 0.868 0 0 −1 地层 J3p1 0.208 0 0 −1 Kjd1 13.538 11 0.81254 −0.14061 Kjd2 3.333 5 1.500285 0.369801 J3p2 4.086 4 0.978953 0.034193 归一化植被指数 −0.0897~0.0962 1.485 0 0 −1 0.0963~0.2405 2.528 0 0 −1 0.2406~0.3432 3.047 4 1.312982 0.2799 0.3433~0.419 6.817 7 1.026905 0.079293 0.4191~0.534 7.309 9 1.231375 0.232177 距道路距离/m 0~50 2.858 6 2.099076 0.549574 >50~100 2.863 5 1.746481 0.458638 >100~150 2.856 4 1.400707 0.324999 >150~200 2.806 3 1.069061 0.115599 >200~250 2.646 1 0.377929 −0.60028 >250 7.127 1 0.14031 −0.8516 距河流距离/m 0~100 5.868 0 0 −1 >100~200 2.928 3 1.024695 0.077307 >200~300 2.878 8 2.779515 0.659841 >300~400 2.824 8 2.832661 0.666223 400~500 2.713 1 0.36865 −0.61009 >500 3.933 0 −1 降雨量/mm 0~800 5.108 4 1.379483 −0.17168 >800~900 8.063 5 0.620109 −0.34413 >900~1000 7.974 11 0.783162 0.314614 $$ LSI=\sum CF $$ (6) 式中:LSI——崩塌地质灾害易发性指数;
CF——各评价因子各分级的CF值。
4.2 基于AHP模型
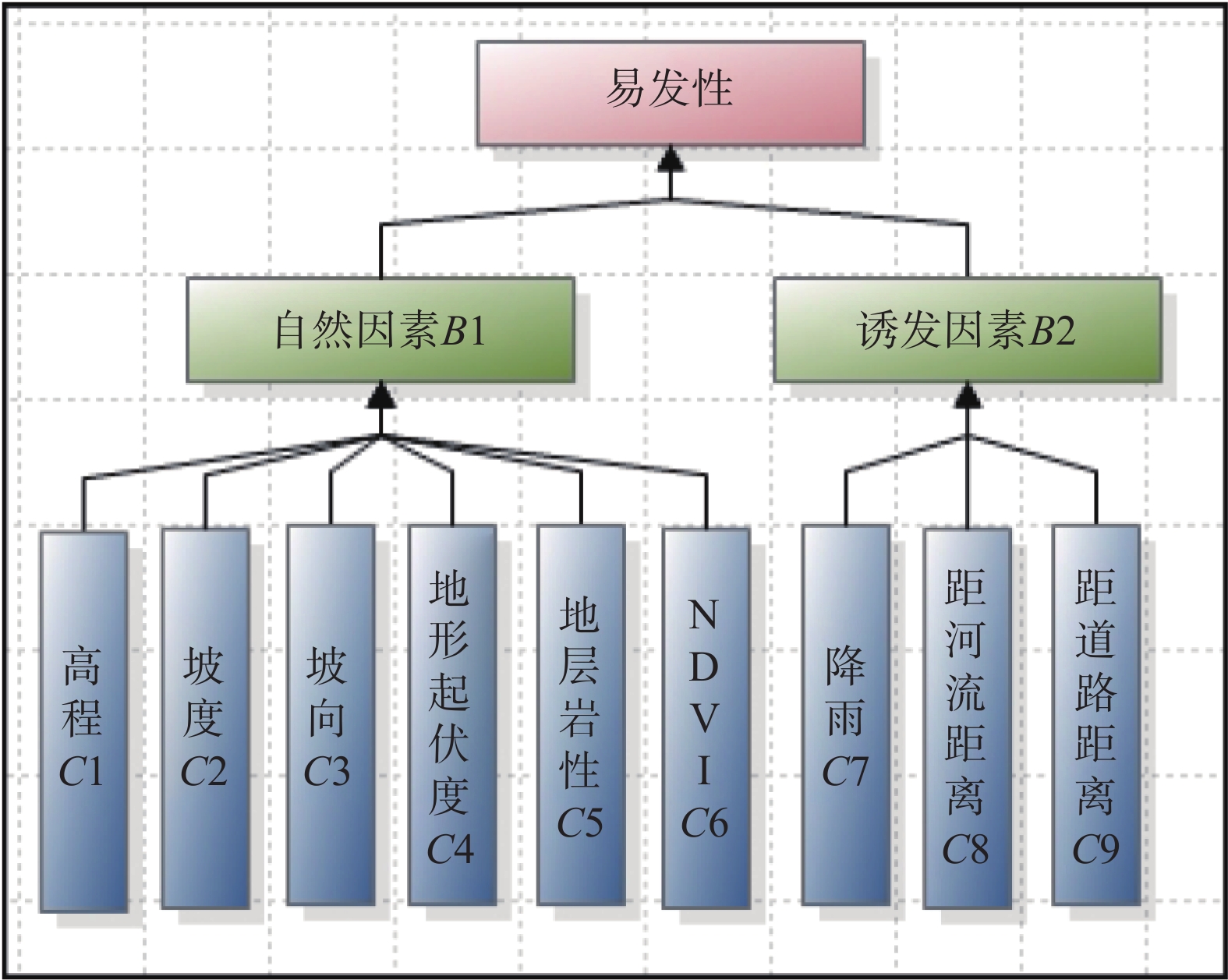
各因子的单位不同,建立模型之前,首先根据表3所计算得到的点密度值,将各因子二级划分值归一化。再将目标层进行层次分级(图3),从准则层开始,分别构建A-B、B-C判断矩阵(表4—6)。经计算,CI=0.144,CR=0.0986<0.1,说明构建判断矩阵是合理的。Matlab计算判断矩阵最大特征根λmax=6.3293,最终得到各个因子的权重(表7)。
表 3 中间层(B)判断矩阵Table 3. Judgment matrix for intermediate layer (B)易发性 诱发因素B2 自然因素B1 权重 诱发因素B2 1 0.3333 0.25 自然因素B1 3 1 0.75 表 4 指标层(B1)判断矩阵Table 4. Judgment matrix for indicator layer (B1)自然因素B1 高程C1 坡度C2 坡向C3 地形起伏度C4 地层岩性C5 归一化植被指数 C6 权重 高程C1 1 0.3333 3 0.3333 0.25 3 0.1017 坡度C2 3 1 5 0.5 0.3333 3 0.1815 坡向C3 0.3333 0.2 1 0.2 0.2 2 0.0543 地形起伏度C4 3 2 5 1 0.5 4 0.247 地层岩性C5 4 3 5 2 1 5 0.3673 NDVI C6 0.3333 0.3333 0.5 0.25 0.2 1 0.0482 表 5 指标层(B2)判断矩阵Table 5. Judgment matrix for indicator layer (B2)诱发因素B2 降雨C7 距河流距离C8 距道路距离C9 权重 降雨量C7 1 3 1 0.4286 距河流距离C8 0.3333 1 0.3333 0.1429 距道路距离C9 1 3 1 0.4286 表 6 各因子的权重Table 6. Influence weight of each factor备选方案 地层岩性C5 地形起伏度C4 坡度C2 降雨量C7 距道路距离C9 高程C1 坡向C3 NDVI C6 距河流距离C8 权重 0.2755 0.1852 0.1361 0.1071 0.1071 0.0763 0.0407 0.0361 0.0357 4.3 基于CF-AHP耦合模型
CF-AHP耦合模型是以CF值赋予各评价因子分级为基础,采用AHP计算各评价因子的相对权重,并按式(7)加权求和,即可地质灾害易发性指数LSI:
$$ \begin{split} LSI&=0.053\;3 C{F}_{1}+0.119\;1 C{F}_{2}+0.099\;6 C{F}_{3}\\ &+0.045 C{F}_{4}+0.148 C{F}_{5}+0.178\;5 C{F}_{6}\\ &+0.196\;1 C{F}_{7}+0.121\;6 C{F}_{8}+0.038\;7 C{F}_{9} \end{split} $$ (7) 4.4 崩塌地质灾害易发性制图
利用ArcGIS栅格计算器计算CF、AHP及CF-AHP模型的崩塌地质灾害易发性指数,并利用ArcGIS自带的自然间断法将其划分为高、中、低、极低易发区(表8、图4)。由表8、图4可知,易发性各分级的面积比中、高易发区面积最小,主要分布于研究区东北、中部及西南路段,该区域切割深、地形坡度较陡,岩性以砂岩夹泥岩为主,由于泥岩相对砂岩来说抗风化能力差,具有失水之后开裂崩解,遇水之后软化等特征,所以造成边坡表面岩体的差异风化,泥岩风化剥落,局部形成了许多的凹岩腔,易发生地质灾害。由表8可知,CF模型和AHP模型的易发性各分级的面积比相近;高易发区,AHP模型面积占比17.15%,CF面积占比14.07%,而CF-AHP模型为13.81%;低易发区,CF-AHP模型面积占比20.92%,CF占比19.43%,AHP占比18.01%。可知CF-AHP模型更符合崩塌易发的实际情况。
表 7 易发性评价结果Table 7. Summary table of geohazard susceptibility for three models易发性等级 CF AHP CF-AHP 栅格数 百分比/% 栅格数 百分比/% 栅格数 百分比/% 极低易发区 4482 19.4278 4156 18.0147 4826 20.9189 低易发区 6934 30.0564 7105 30.7976 8028 34.7984 中易发区 8409 36.4499 7853 34.0399 7029 30.4681 高易发区 3245 14.0659 3956 17.1478 3187 13.8145 表 8 地质灾害易发性评价结果检验Table 8. Verification of geohazards susceptibility assessment results易发性等级 灾害点百分比/% CF AHP CF-AHP 极低易发区 0 0 0 低易发区 0 5 0 中易发区 25 25 15 高易发区 75 70 85 5. 模型精度评价
5.1 易发性分区灾害点统计
通过统计易发性分区下崩塌灾害点占比,可以用来检验评价结果的准确程度 [14], 由表9可知,在CF-AHP模型中,崩塌地质灾害点在高易发区占85%,在中易发区占15%;而CF模型崩塌地质灾害点占高易发区为75%,占中易发区25%; AHP模型崩塌地质灾害点占高易发区70%,占中易发区25%,占低易发区5%。表明采用CF-AHP模型的预测精度优于单一模型CF和AHP。
5.2 ROC曲线分析
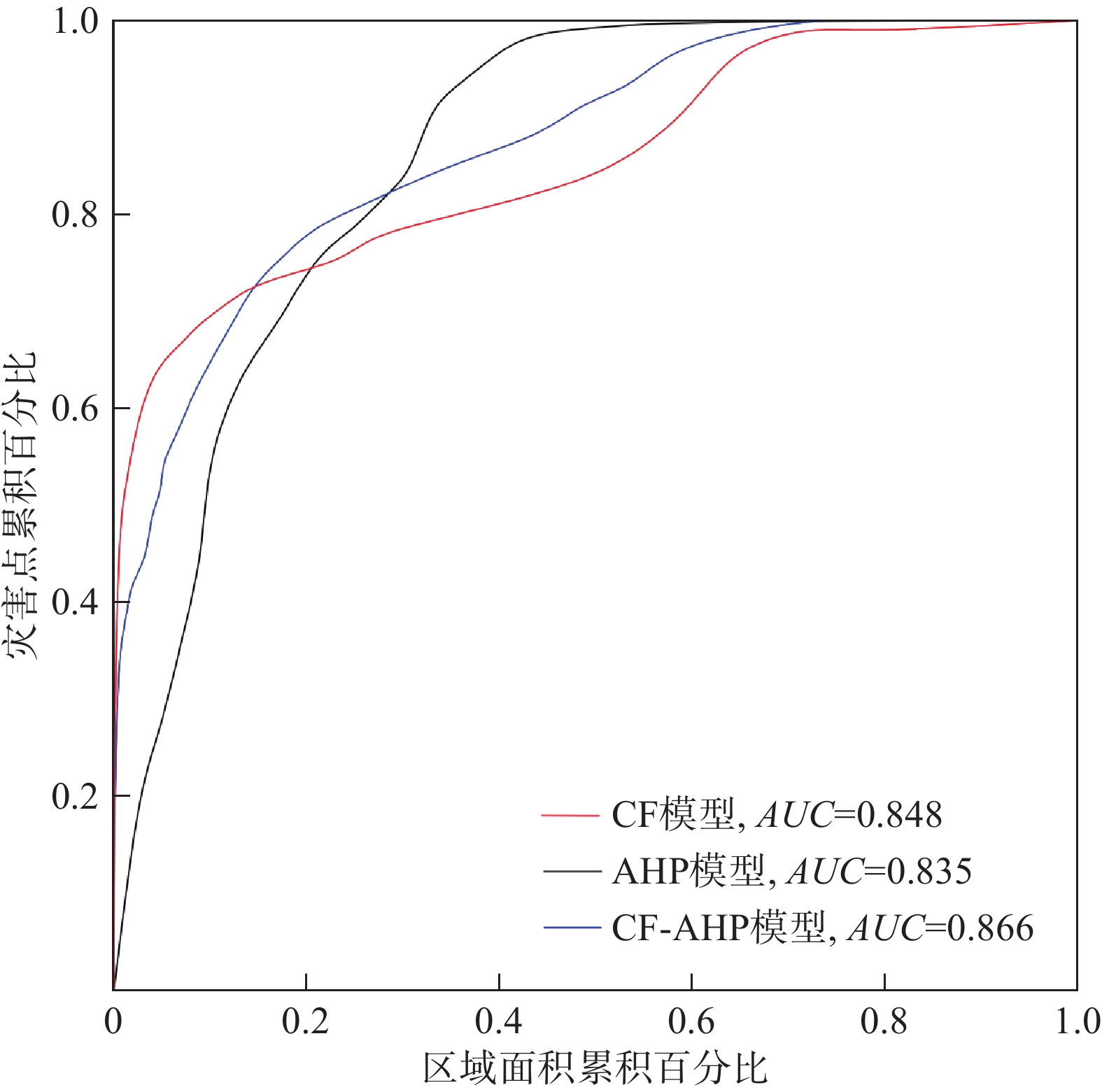
ROC曲线(receiver operation characteristics curve)由于其易懂,常被用于地质灾害易发性评价精度验证。以灾害点百分比为纵坐标,区域面积累积百分比为横坐标,用曲线下面积AUC来衡量模型预测的准确程度,AUC值越大,表明模型预测性能越好[15]。如图5所示,CF模型、AHP模型和CF-AHP模型的AUC值分别为0.848,0.835,0.866。3种模型的AUC值均大于0.8,均能精确地评价该高速公路沿线崩塌易发性,3种模型精确度由大到小分别为CF-AHP、CF、AHP模型,CF-AHP模型成功率要高于分别采用CF、AHP模型的结果。
5.3 不确定分析
对于AHP方法来说,评价体系主要基于专家意见,是一种主观的方法,可能存在很大的缺陷。因此,如果仅从专业知识和一般经验出发,很难估计各因素的实际权重,不能全面分析实际情况。对于CF模型,作为定量分析模型,以数据为主导,比AHP方法更为客观,能很好地解决各评价因子内部不同特征值的易发程度,因此精度高于AHP方法。但是此方法忽略了各因子对易发性影响的差异性,而将CF 模型与层次分析法相结合,通过层次分析法获得各因子权重则很好地解决影响因子的权重的确定和异类数据合并的难题,因此CF-AHP模型的精度与单一的AHP、CF模型相比,具有更高的预测精度。
6. 结论
(1)根据蓉遵高速公路(土城-旺隆段)易发性区划,发现在降雨量≥1000 mm的地区,距河流400 m范围内,距离道路200 m的区域内,归一化植被指数>0.24,海拔407~488 m、坡度>30°的东北坡,以及地层为白垩系嘉定群组(Kjd)的地区崩塌地质灾害发育集中。
(2)蓉遵高速公路(土城-旺隆段)高易发区主要分布于研究区东北、中部及西南路段,面积约为2.92 km2。在该公路进行边坡治理中具有重要的现实意义,需重视高易发区段崩塌地质灾害的发生,为高速公路出行安全提供安全保障。
(3)将CF与AHP方法相结合,利用沿线调查的资料结果,又弥补了层次分析法主观性较强的缺陷。耦合模型CF-AHP的预测精度为0.866,与单一的AHP、CF模型相比,具有更高的预测精度,表明CF-AHP模型对崩塌地质灾害易发性评价比单一模型AHP、CF模型结果可靠,为完善线状工程崩塌等地质灾害评价过程提供了可靠途径。
-
表 1 判断矩阵标度及其含义
Table 1 Judgment matrix scale and its meaning
标度值 含义 1 表示两个因素相比,具有相同重要性 3 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者稍重要 5 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者明显重要 7 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者强烈重要 9 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者极端重要 2,4,6,8 表示上述相邻判断的中间值 倒数 与上述影响情况相反 表 2 评价因子分级及CF值
Table 2 Classification of evaluation factors and CF values of each grade
指标因子 分级 面积/km2 灾害点数/个 点密度/(个·km-2) CF值 高程/m 222~325 7.277 0 0 −1 >325~407 4.458 6 1.345986 0.297557 >407~488 4.587 10 2.179932 0.566281 >488~581 3.609 4 1.10834 0.146942 >581~790 1.451 0 0 −1 坡度/(°) 0~10 2.962 0 0 −1 >10~20 4.497 0 0 −1 >20~30 6.335 3 0.473552 −0.49914 >30~40 4.993 11 2.202996 0.570822 >40 2.595 6 2.312406 0.591128 地形起伏度/m 152~285 1.067 0 0 −1 286~362 6.290 2 0.31796 −0.66371 363~439 6.170 3 0.486192 −0.48577 440~526 5.431 15 2.762126 0.657699 527~672 2.440 0 −1 坡向/(°) 平面 0.002 0 0 −1 北 2.435 3 1.231831 0.23246 东北 6.026 10 1.659613 0.430302 东 5.409 5 0.924385 −0.02231 东南 3.192 1 0.313254 −0.66868 南 1.951 1 0.512505 −0.45794 西南 0.556 0 0 −1 西 0.943 0 0 −1 西北 0.868 0 0 −1 地层 J3p1 0.208 0 0 −1 Kjd1 13.538 11 0.81254 −0.14061 Kjd2 3.333 5 1.500285 0.369801 J3p2 4.086 4 0.978953 0.034193 归一化植被指数 −0.0897~0.0962 1.485 0 0 −1 0.0963~0.2405 2.528 0 0 −1 0.2406~0.3432 3.047 4 1.312982 0.2799 0.3433~0.419 6.817 7 1.026905 0.079293 0.4191~0.534 7.309 9 1.231375 0.232177 距道路距离/m 0~50 2.858 6 2.099076 0.549574 >50~100 2.863 5 1.746481 0.458638 >100~150 2.856 4 1.400707 0.324999 >150~200 2.806 3 1.069061 0.115599 >200~250 2.646 1 0.377929 −0.60028 >250 7.127 1 0.14031 −0.8516 距河流距离/m 0~100 5.868 0 0 −1 >100~200 2.928 3 1.024695 0.077307 >200~300 2.878 8 2.779515 0.659841 >300~400 2.824 8 2.832661 0.666223 400~500 2.713 1 0.36865 −0.61009 >500 3.933 0 −1 降雨量/mm 0~800 5.108 4 1.379483 −0.17168 >800~900 8.063 5 0.620109 −0.34413 >900~1000 7.974 11 0.783162 0.314614 表 3 中间层(B)判断矩阵
Table 3 Judgment matrix for intermediate layer (B)
易发性 诱发因素B2 自然因素B1 权重 诱发因素B2 1 0.3333 0.25 自然因素B1 3 1 0.75 表 4 指标层(B1)判断矩阵
Table 4 Judgment matrix for indicator layer (B1)
自然因素B1 高程C1 坡度C2 坡向C3 地形起伏度C4 地层岩性C5 归一化植被指数 C6 权重 高程C1 1 0.3333 3 0.3333 0.25 3 0.1017 坡度C2 3 1 5 0.5 0.3333 3 0.1815 坡向C3 0.3333 0.2 1 0.2 0.2 2 0.0543 地形起伏度C4 3 2 5 1 0.5 4 0.247 地层岩性C5 4 3 5 2 1 5 0.3673 NDVI C6 0.3333 0.3333 0.5 0.25 0.2 1 0.0482 表 5 指标层(B2)判断矩阵
Table 5 Judgment matrix for indicator layer (B2)
诱发因素B2 降雨C7 距河流距离C8 距道路距离C9 权重 降雨量C7 1 3 1 0.4286 距河流距离C8 0.3333 1 0.3333 0.1429 距道路距离C9 1 3 1 0.4286 表 6 各因子的权重
Table 6 Influence weight of each factor
备选方案 地层岩性C5 地形起伏度C4 坡度C2 降雨量C7 距道路距离C9 高程C1 坡向C3 NDVI C6 距河流距离C8 权重 0.2755 0.1852 0.1361 0.1071 0.1071 0.0763 0.0407 0.0361 0.0357 表 7 易发性评价结果
Table 7 Summary table of geohazard susceptibility for three models
易发性等级 CF AHP CF-AHP 栅格数 百分比/% 栅格数 百分比/% 栅格数 百分比/% 极低易发区 4482 19.4278 4156 18.0147 4826 20.9189 低易发区 6934 30.0564 7105 30.7976 8028 34.7984 中易发区 8409 36.4499 7853 34.0399 7029 30.4681 高易发区 3245 14.0659 3956 17.1478 3187 13.8145 表 8 地质灾害易发性评价结果检验
Table 8 Verification of geohazards susceptibility assessment results
易发性等级 灾害点百分比/% CF AHP CF-AHP 极低易发区 0 0 0 低易发区 0 5 0 中易发区 25 25 15 高易发区 75 70 85 -
[1] 覃乙根,杨根兰,鲁鲲鹏,等. 贵州寨子危岩崩塌风险定量评价研究[J]. 人民长江,2019,50(10):113 − 119. [QIN Yigen,YANG Genlan,LU Kunpeng,et al. Quantitative risk assessment for Zhaizi rockfall in Guizhou Province[J]. Yangtze River,2019,50(10):113 − 119. (in Chinese with English abstract) QIN Yigen, YANG Genlan, LU Kunpeng, et al. Quantitative risk assessment for Zhaizi rockfall in Guizhou Province[J]. Yangtze River, 2019, 50(10): 113-119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 谈树成,刘雪斌,谢亚亚,等. 某拟建高速公路地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 水土保持研究,2019,26(3):373 − 380. [TAN Shucheng,LIU Xuebin,XIE Yaya,et al. Assessment on susceptibility of geohazard for a proposed expressway[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,26(3):373 − 380. (in Chinese with English abstract) TAN Shucheng, LIU Xuebin, XIE Yaya, et al. Assessment on susceptibility of geohazard for a proposed expressway[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(3)373-380(in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 崔志超,王俊豪,崔传峰,等. 基于层次分析法和模糊数学相结合的甘肃东乡八丹沟泥石流易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(1):44 − 50. [CUI Zhichao,WANG Junhao,CUI Chuanfeng,et al. Evaluation of the susceptibility of debris flow in Badan Gully of Dongxiang County of Gansu based on AHP and Fuzzy mathematics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(1):44 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) CUI Zhichao, WANG Junhao, CUI Chuanfeng, et al. Evaluation of the susceptibility of debris flow in Badan Gully of Dongxiang County of Gansu based on AHP and Fuzzy mathematics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(1)44-50(in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 刘宇恒,邓辉,熊倩莹. 基于层次分析法的茂县斜坡地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 长江科学院院报,2017,34(5):31 − 35. [LIU Yuheng,DENG Hui,XIONG Qianying. AHP-based evaluation of slope geo-hazard susceptibility of Maoxian County,Sichuan,China[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2017,34(5):31 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20160155 LIU Yuheng, DENG Hui, XIONG Qianying. AHP-based evaluation of slope geo-hazard susceptibility ofMaoxian County, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2017, 34(5)31-35(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20160155
[5] 尚敏,马锐,张英莹,等. 基于GIS的证据权重法的崩塌敏感性分析研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(5):1211 − 1218. [SHANG Min,MA Rui,ZHANG Yingying,et al. GIS based weights of evidence method for rock fall susceptibility[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(5):1211 − 1218. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHANG Min, MA Rui, ZHANG Yingying, et al. GIS based weights of evidence method for rock fall susceptibility[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(5)1211-1218(in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 谭玉敏,郭栋,白冰心,等. 基于信息量模型的涪陵区地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2015,17(12):1554 − 1562. [TAN Yumin,GUO Dong,BAI Bingxin,et al. Geological hazard risk assessment based on information quantity model in Fuling District,Chongqing City,China[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2015,17(12):1554 − 1562. (in Chinese with English abstract) TAN Yumin, GUO Dong, BAI Bingxin, et al. Geological hazard risk assessment based on information quantity model in Fuling district, Chongqing city, China[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2015, 17(12)1554-1562(in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 覃乙根,杨根兰,江兴元,等. 基于确定性系数模型与逻辑回归模型耦合的地质灾害易发性评价—以贵州省开阳县为例[J]. 科学技术与工程,2020,20(1):96 − 103. [QIN Yigen,YANG Genlan,JIANG Xingyuan,et al. Geohazard susceptibility assessment based on integrated certainty factor model and logistic regression model for Kaiyang,China[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2020,20(1):96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.01.015 QIN Yigen, YANG Genlan, JIANG Xingyuan, et al. Geohazard susceptibility assessment based on integrated certainty factor model and logistic regression model for Kaiyang, China[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(1)96-103(in Chinese with English abstract)) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.01.015
[8] 向喜琼,黄润秋. 基于GIS的人工神经网络模型在地质灾害危险性区划中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2000,11(3):23 − 27. [XIANG Xiqiong,HUANG Runqiu. Application of GIS-based artificial Neural Networks on assessment of geohazards risk[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2000,11(3):23 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract) Xiang Xiqiong, Huang Runqiu. Application of GIS-based artificial Neural Networks on assessment of geohazards risk[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2000, 11(3): 23-27. (in Chinese with English abstract))
[9] 黄发明,殷坤龙,蒋水华,等. 基于聚类分析和支持向量机的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(1):156 − 167. [HUANG Faming,Yin Kunlong,Jiang Shuihua,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on clustering analysis and support vector machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(1):156 − 167. (in Chinese with English abstract) Huang Faming, Yin Kunlong, Jiang Shuihua, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on clustering analysis and support vector machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(1): 156-167. (in Chinese with English abstract))
[10] 吴润泽,胡旭东,梅红波,等. 基于随机森林的滑坡空间易发性评价—以三峡库区湖北段为例[J]. 地球科学,2021(1):321 − 330. [WU Runze,HU Xudong,MEI Hongbo,et al. Spatial susceptibility assessment of landslides based on random forest:A case study from Hubei section in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Earth Science,2021(1):321 − 330. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Runze, HU Xudong, MEI Hongbo, et al. Spatial susceptibility assessment of landslides based on random forest: a case study from Hubei section in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Earth Science, 2021(1): 321-330. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 胡涛,樊鑫,王硕,等. 基于逻辑回归模型和3S技术的思南县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2020(2):113 − 121. [HU Tao,FAN Xin,WANG Shuo,et al. Landslide susceptibility evaluation of Sinan County using logistics regression model and 3S technology[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2020(2):113 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU Tao, FAN Xin, WANG Shuo, et al. Landslide susceptibility evaluation of Sinan County using logistics regression model and 3S technology[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2020(2): 113-121. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 覃乙根,杨根兰,谢金,等. 贵州省开阳县斜坡地质灾害孕灾因子敏感性分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(4):190 − 198. [QIN Yigen,YANG Genlan,XIE Jin,et al. Sensitivity analysis of disaster-pregnant environmental factors for slope geological hazards in Kaiyang County,Guizhou Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(4):190 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract) Qin Yigen, Yang Genlan, Xie Jin, et al. Sensitivity analysis of disaster-pregnant environmental factors for slope geological hazards in Kaiyang County, Guizhou Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(4): 190-198. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘光辉,刘汉湖,姚昆,等. 基于证据权法与确定系数法的滑坡危险区划对比分析—以虹口乡为例[J]. 物探化探计算技术,2016,38(6):848 − 853. [LIU Guanghui,LIU Hanhu,YAO Kun,et al. Based on the weights of evidence method and certainty factor method of landslide danger division comparative analysis:A case study in Hongkou,China[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2016,38(6):848 − 853. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2016.06.21 LIU Guanghui, LIU Hanhu, YAO Kun, et al. Based on the weights of evidence method and certainty factor method of landslide danger division comparative analysis: -a case study in Hongkou, chine[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 38(6)848-853(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2016.06.21
[14] 李益敏,李驭豪,赵志芳. 基于确定性系数模型的泸水市泥石流易发性评价[J]. 水土保持研究,2019,26(4):336 − 342. [LI Yimin,LI Yuhao,ZHAO Zhifang. Assessment on susceptibility of debris flow in Lushui based on the certain factor model[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,26(4):336 − 342. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Yimin, LI Yuhao, ZHAO Zhifang. Assessment on susceptibility of debris flow in Lushui based on the certain factor model[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(4)336-342(in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 杨栓成,王运生. 基于GIS的涪江上游南坝-水晶流域滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(6):15 − 22. [YANG Shuancheng,WANG Yunsheng. GIS-based landslide risk assessment along the Nanba-Shuijing reaches in the Fujiang River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(6):15 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Shuancheng, WANG Yunsheng. GIS-based landslide risk assessment along the Nanba-Shuijing reaches in the Fujiang River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(6): 15-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 李益敏,袁静,蒋德明,等. 基于GIS的高山峡谷区滑坡灾害危险性评价—以泸水市为例[J]. 水土保持研究,2021,28(3):355 − 363. [LI Yimin,YUAN Jing,JIANG Deming,et al. GIS-based risk assessment of landslide disaster in high mountain valley:Taking Lushui City as an example[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,28(3):355 − 363. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Yimin, YUAN Jing, JIANG Deming, et al. GIS-based risk assessment of landslide disaster in high mountain valley—taking Lushui city as an example[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 28(3): 355-363. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李萍,叶辉,谈树成. 基于层次分析法的永德县地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 水土保持研究,2021,28(5):394 − 399. [LI Ping,YE Hui,TAN Shucheng. Evaluation of geological hazards in Yongde County based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,28(5):394 − 399. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Ping, YE Hui, TAN Shucheng. Evaluation of geological hazards in Yongde County based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 28(5): 394-399. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 刘建强,许强,郑光,等. 贵州省鸡场滑坡地下水化学特征反映的水-岩(土)作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):132 − 140. [LIU Jianqiang,XU Qiang,ZHENG Guang,et al. Water-rock/soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202103009 LIU Jianqiang, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Water-rock/soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 132-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202103009
[19] 黄煜,谢婉丽,刘琦琦,等. 基于GIS与MaxEnt模型的滑坡易发性评价—以铜川市中部城区为例[J]. 西北地质,2023,56(1):266 − 275. [HUANG Yu,XIE Wanli,LIU Qiqi,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on GIS and MaxEnt model:Example from central districts in Tongchuan city[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023,56(1):266 − 275. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12401/j.nwg.2022001 HUANG Yu, XIE Wanli, LIU Qiqi, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on GIS and MaxEnt model: example from central districts in Tongchuan city[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(1): 266-275. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12401/j.nwg.2022001
[20] 唐军峰,唐雪梅,周基,等. 滑坡堆积体变形失稳机制—以贵州剑河县东岭信滑坡为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(2):503 − 516. [TANG Junfeng,TANG Xuemei,ZHOU Ji,et al. Deformation and instability mechanism of landslide accumulation:A case study of Donglingxin landslide accumulation in Jianhe County,Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(2):503 − 516. (in Chinese with English abstract) TANG Junfeng, TANG Xuemei, ZHOU Ji, et al. Deformation and instability mechanism of landslide accumulation: a case study of donglingxin landslide accumulation in Jianhe County, Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2022, 52(2): 503-516. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 赵无忌,殷志强,马吉福,等. 黄河上游贵德盆地席芨滩巨型滑坡发育特征及地貌演化[J]. 地质论评,2016,62(3):709 − 721. [ZHAO Wuji,YIN Zhiqiang,MA Jifu,et al. Multi-stage development characteristics and geomorphic evolution process of the Xijitan super large landslide in the Guide basin,upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. Geological Review,2016,62(3):709 − 721. (in Chinese with English abstract) Zhao Wuji, Yin Zhiqiang, Ma Jifu, et al. Multi-stage development characteristics and geomorphic evolution process of the xijitan super large landslide in the guide basin, upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(3): 709-721. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 曹苏傲,郭振,陈佳乐. 基于改进信息量模型的地质灾害易发性评价——以西藏察隅县G219国道沿线为例. 地质通报. 2025(01): 185-200 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张桂香. 基于AHP法及综合指数法的城市地下空间利用地质环境条件适宜性评价——以深圳西部重点片区为例. 城市勘测. 2025(01): 197-201 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 何娜,朱习松,吴福,刘昶,吴秋菊,黄希明,蒋力,肖吉贵,文海涛,何添杰,常鸣. 基于全连接神经网络的广西北流市崩塌滑坡风险评价. 水土保持通报. 2025(01): 127-136 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 吴玉婷. 天长市区域地质灾害易发性评价. 地下水. 2025(01): 182-184 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 朱习松,常鸣,周贤熙,赵伯驹,刘洋. 基于全连接神经网络的弥勒市域滑坡风险测度与分级评价. 防灾减灾学报. 2025(01): 8-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 谢扬龙,齐信,高鹏,王英豪. 基于多种评价模型在斜坡地质灾害易发性评价中的对比分析——以武汉市为例. 华南地质. 2025(01): 185-196 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张必昌,陈毅. 山西省普通国省公路地质灾害分布特征研究. 山西交通科技. 2024(03): 35-38+46 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 何子军,刘惠军. 基于信息量-随机森林模型的滑坡易发性评价——以云南省双江县滑坡为例. 甘肃水利水电技术. 2024(09): 55-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 梁峰,江攀和. 基于IVM-CF耦合模型的贵定县滑坡地质灾害易发性评价. 水利水电技术(中英文). 2024(S2): 669-677 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 梁峰,江攀和,唐广,刘双. 基于AHP及信息量模型的凤冈县地质灾害易发性评价. 贵州地质. 2024(04): 446-455 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:

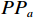
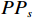
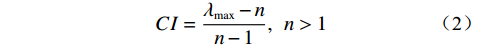
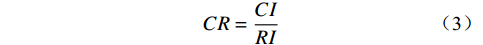
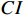
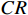
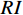
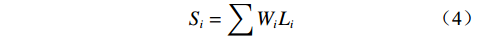
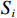
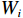
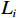
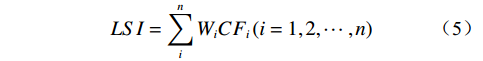
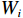

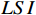
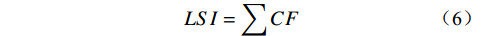
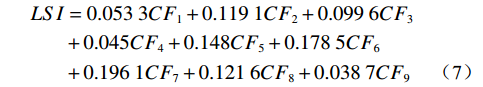

 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS