Exploration of hidden structure and prediction of gas anomaly area based on gas control projects
-
摘要:
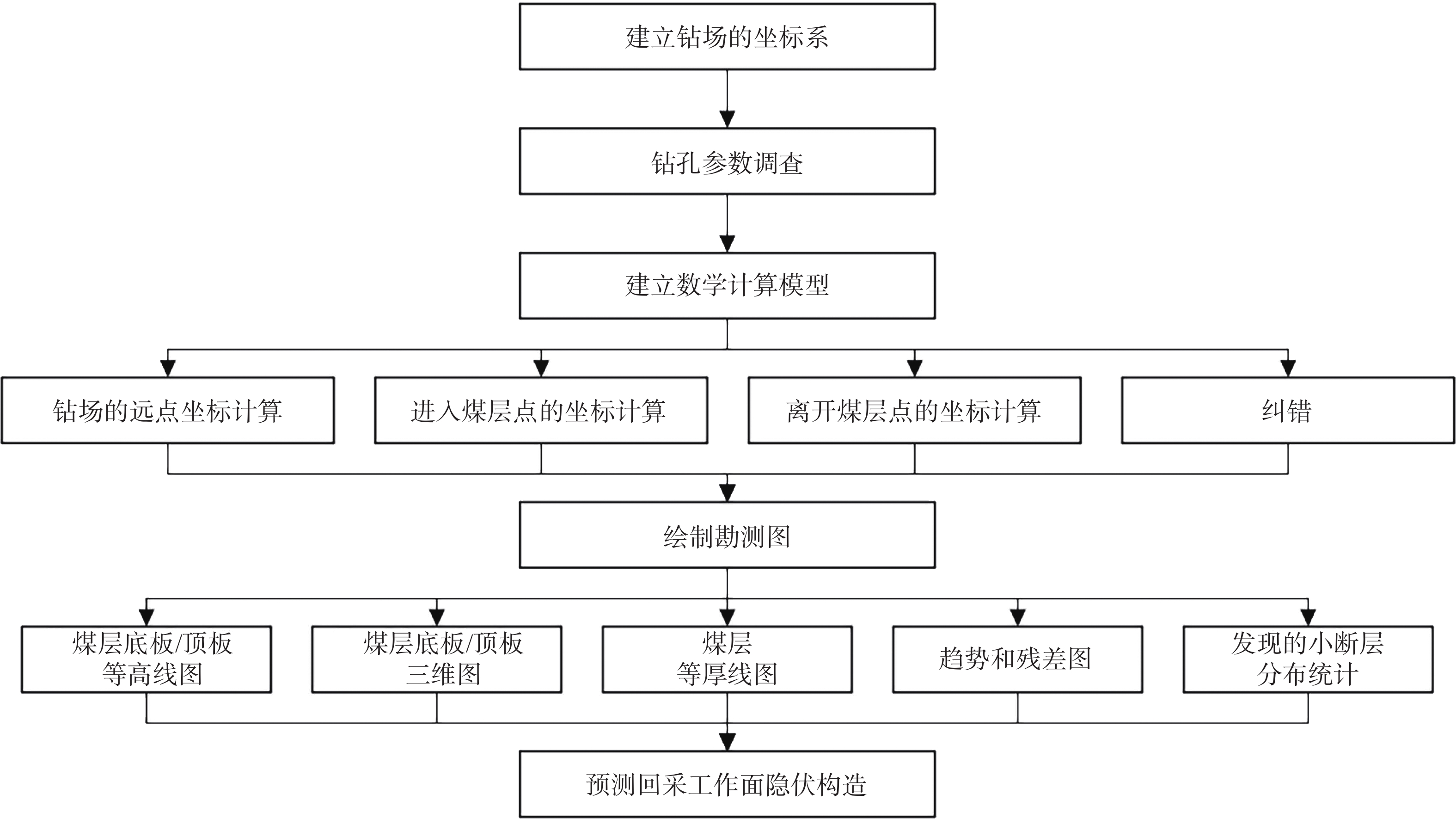
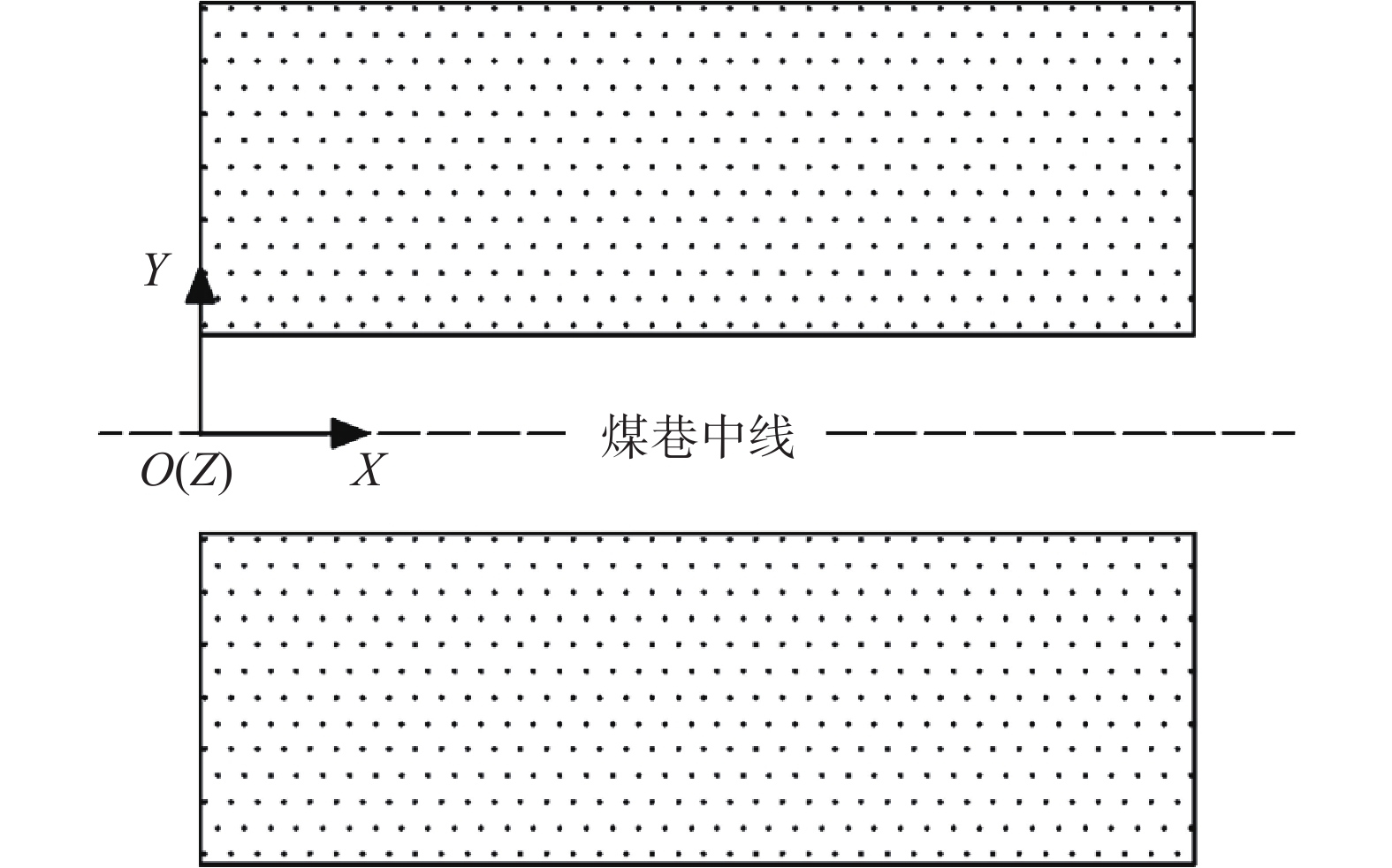
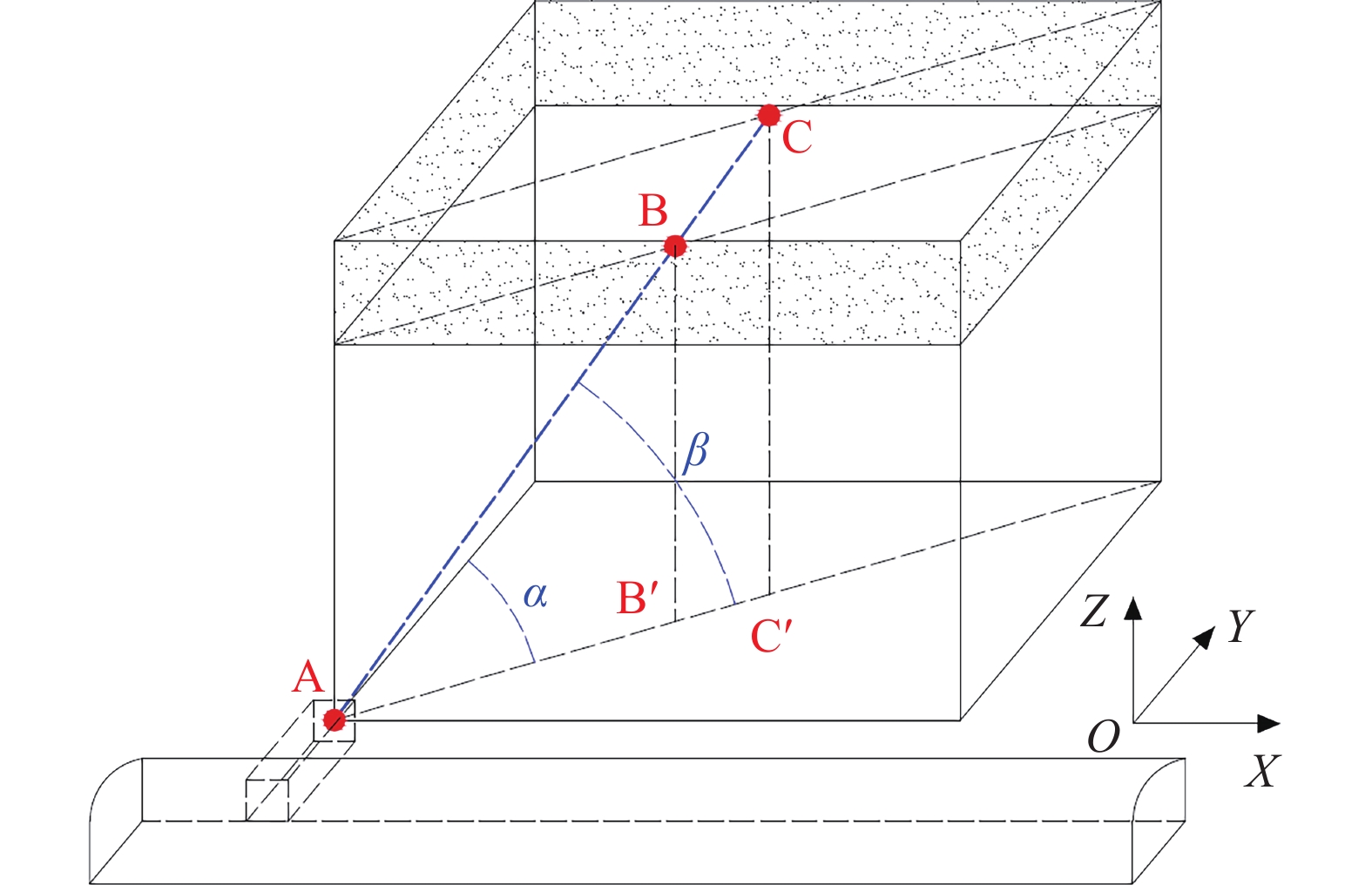
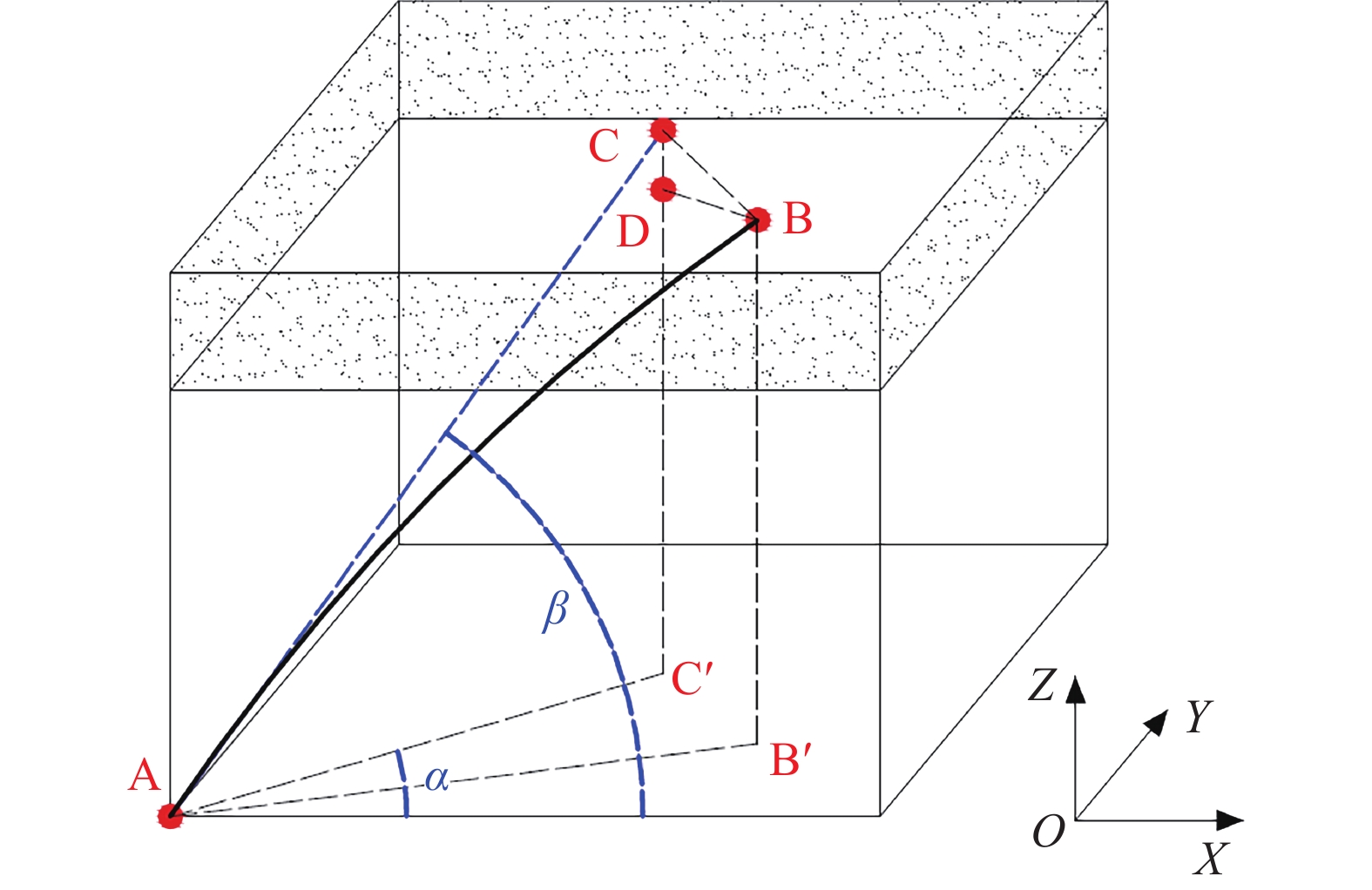
隐伏构造勘查与瓦斯异常区域预测研究是瓦斯灾害防治工程的基础。根据中国煤矿生产法律规章,开采具有瓦斯灾害危险的煤层前,必须实施瓦斯抽放工程。通常,地质异常区域即是瓦斯灾害危险区,构造应力场和采动应力场的叠加会扰动煤体并加压瓦斯。为精准定位地质异常区,评价其瓦斯致灾潜能,提出了一种基于瓦斯抽采工程进行瓦斯异常区域勘测的研究方法。该方法利用抽采钻孔参数和施工记录,采集钻孔数据并计算煤层顶底板控制点坐标,进而利用二维投影图件及三维应力场模型对隐伏地质构造(如小的断层、褶曲、局部煤厚异常变化等)进行勘查和预测;通过分析小型地质构造周围的附加应力场,并对瓦斯致灾潜能进行动态预测。应用该方法,可以对地质异常区进行精细调查,揭示采煤工作面瓦斯地质演化的一般规律。其研究结果为高瓦斯或突出煤层瓦斯灾害防治措施优化设计及有效实施提供科学依据。
Abstract:The investigation of hidden structures and the prediction of gas abnormal area form the foundation of gas disaster prevention engineering. In accordance with the laws and regulations governing coal mining in our country, a gas pumping project must be implemented prior to mining coal seams with a gas hazard. Typically, geologic anomaly area represent gas hazard zones, where the combination of tectonic stress field and mining-induced stress field can disturb coal bodies and pressurize gas. To accurately locate geologic anomaly areas and evaluate their gas disaster potential, a gas geologic anomaly survey method has been proposed based on gas extraction projects. This method uses drilling parameters and records to calculate the coordinates of the control points of the coal seam roof and bottom, and then utilizes two-dimensional projection diagrams and three-dimensional stress field models to survey and forecast small, hidden geological structures (such as small faults, folds, and locally abnormal coal thicknesses). By analyzing the additional stress field surrounding small geological structures, gas disaster potential can be dynamically predicted. The application of this method enables the detailed investigation of geological anomalies and reveals the general pattern of gas geological evolution at coal mining worksites. The research results provide a scientific basis for the optimal design and effective implementation of disaster prevention and control measures for coal seams with high gas content or at risk of gas outbursts.
-
0. 引言
随着社会经济的快速发展,公路、铁路等交通设施建设工作不断向地质环境条件复杂的山区推进,这些线路不可避免地要通过一些自然斜坡和开挖、切坡形成的人工边坡,由边坡失稳造成的人民的生命和财产损失日益严重[1 − 3]。公路、铁路边坡长期处于车辆高强度振动环境之中,不可避免的受到频率、振幅随着时间作周期性或非周期性的振动荷载作用。在振动荷载的长期循环作用下,斜坡岩土体中的原生结构面可能扩大并产生新的破裂面,导致斜坡岩土体性能弱化,形成潜在滑动面或者贯通的结构面,影响边坡的稳定性[4 − 7]。国内外对斜坡岩土体动力响应研究很多,主要以爆破冲击荷载和地震荷载作用下边坡动态响应和稳定性分析为主[8 − 13],常用的研究方法有拟静力法、Newmark法、模型试验法、数值分析法和能量分析法等 [14 − 15]。交通循环荷载具有小振幅、多循环的特点,动力响应十分复杂,目前国内外对交通循环荷载作用下土动力特性以及路基和隧道的动力响应研究较多,而对边坡动力响应研究相对较少[16 − 19]。因此,研究斜坡岩土体在交通荷载作用下的动态响应规律,合理地评价交通荷载对斜坡岩土体的影响,具有十分重要的理论意义和工程应用价值。
本文在前人研究的基础上,将交通荷载简化为半正弦波振动荷载,采用有限差分数值模拟软件,对不同条件交通循载作用下黄土边坡的动力响应规律进行分析。
1. 交通荷载模型
车辆荷载受发动机周期性振动、汽车变速引起的振动、路面不平整引起的车辆振动以及车辆轴重等因素影响,动力特性十分复杂,具有随机性、瞬时性、长期反复性等特点。受路面状况和车辆行驶速度的影响,车轮在路面某点处的作用时间为0.01~0.1 s,具有瞬时性;但是,在道路的寿命期限内,交通荷载作用又是一种循环往复的过程,具有长期反复性;并且受车辆因素影响,交通荷载作用充满了随机性。交通荷载的模拟方式可以分为恒载作用、移动恒载作用和振动移动荷载作用[20]。根据问题研究的侧重面不同,可采用经验简化模拟来满足研究需要。受汽车本身振动特性和道路结构的影响,轮胎在路面行驶时受力并不均匀,时大时小,呈现出一种波动的状态,当汽车轮迹通过路面上某点时,这个过程可以用加载和卸载的组合形式来表示[21 − 22]。交通荷载的变化用多个半正弦波的形式来表达,如图1所示。
图中每个波形代表一次荷载作用,t0表示荷载的间隔,当车辆距离监测点较远时,监测点所受应力趋近于零,当车辆逐渐驶向监测点时,应力逐渐增大,当车辆到达监测点时,应力到达峰值,此后随着车辆远去,应力逐渐变小并趋近于零,这个过程中监测点所受到的应力大小变化表现出了一个半正弦波形式,监测点所受荷载可用式(1)进行表示[21 − 22]:
(1) 式中:p——静荷载;
q(t)——动荷载,可由如下公式确定:
(2) 式中:qmax——车辆附加动荷载,幅值一般小于0.3p;
T——荷载周期/s,T=12 L/v;
v——车辆速度/(m·s−1);
L——轮胎接触面的半径/m,一般取0.15 m。
若取qmax=0.2p,则交通荷载可简化为如下表达式:
(3) 2. 数值模型
2.1 边坡算例
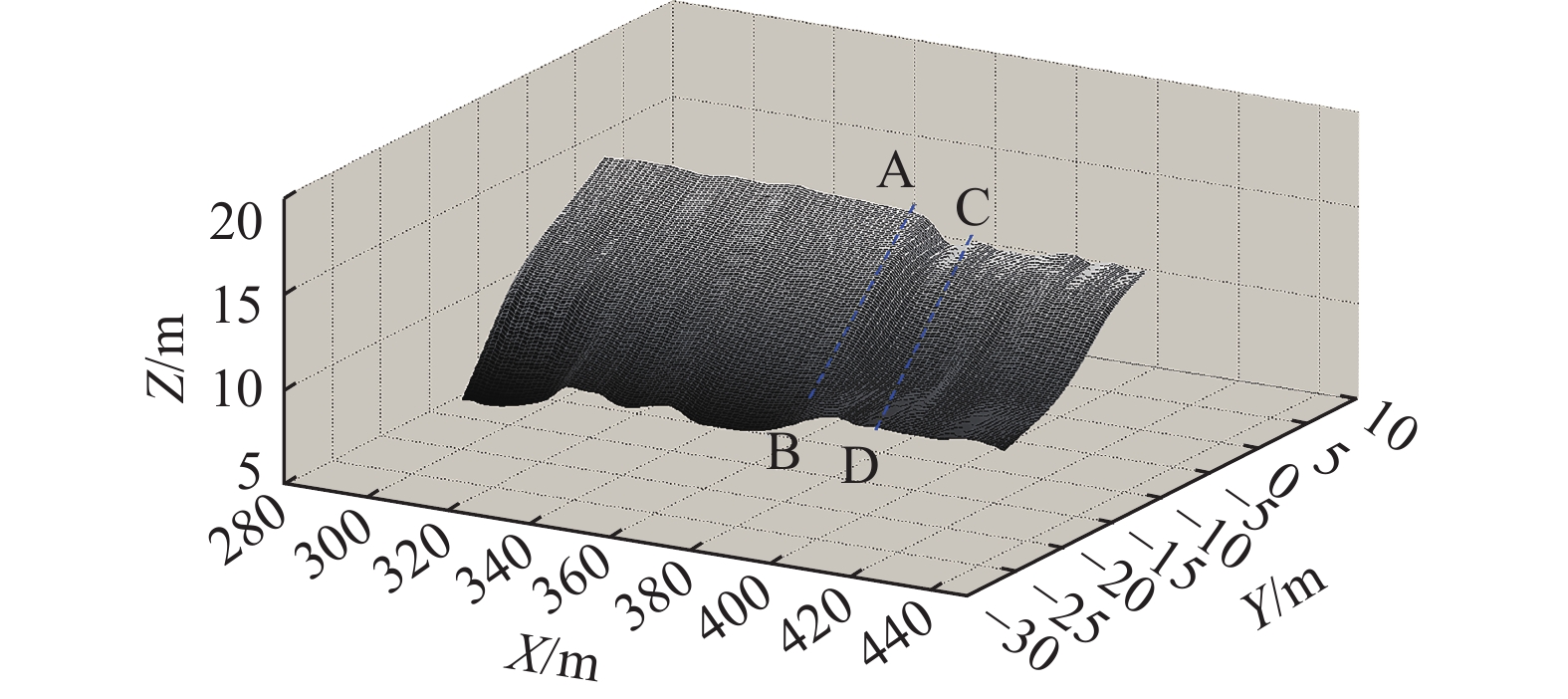
黄土是在第四纪干旱、半干旱条件下形成的陆相疏松堆积物,是一种极其复杂的复合体,在我国广泛分布。在自然状态下,黄土具有较高的强度、较低的压缩性和较强的结构性,其颗粒主要由粉粒组成,具有多孔性,颗粒之间的胶结物质耐水性较差,在受到一定压力或与水作用后,其结构会迅速破坏并发生显著沉降,这些特性决定了黄土边坡研究的复杂性。本文以简单的黄土边坡概化模型为例,建立数值计算模型,模拟普通道路在坡肩时,不同车辆荷载作用下边坡的动力响应。边坡模型坡高20m,坡角45°,模型左侧边界高10 m,右侧边界高30 m,底部边界长35 m,道路位于距坡面2 m的坡肩,厚0.3 m,宽4 m(图2)。其中,在坡体表面从坡肩到坡脚每隔4 m设置S1、S2、S3、S4、S5、S6 6个监测点,在道路中心点下方0,2,4,6,8,10,12 m处设置I1、I2、I3、I4、I5、I6、I7七个监测点,对斜坡体内部和表面的加速度、速度和位移进行监测。
2.2 模型参数及网格尺寸
综合考虑前人研究成果和参数反演分析确定边坡岩土体的物理力学参数[23 − 25],岩土体的物理力学参数如表1 所示。
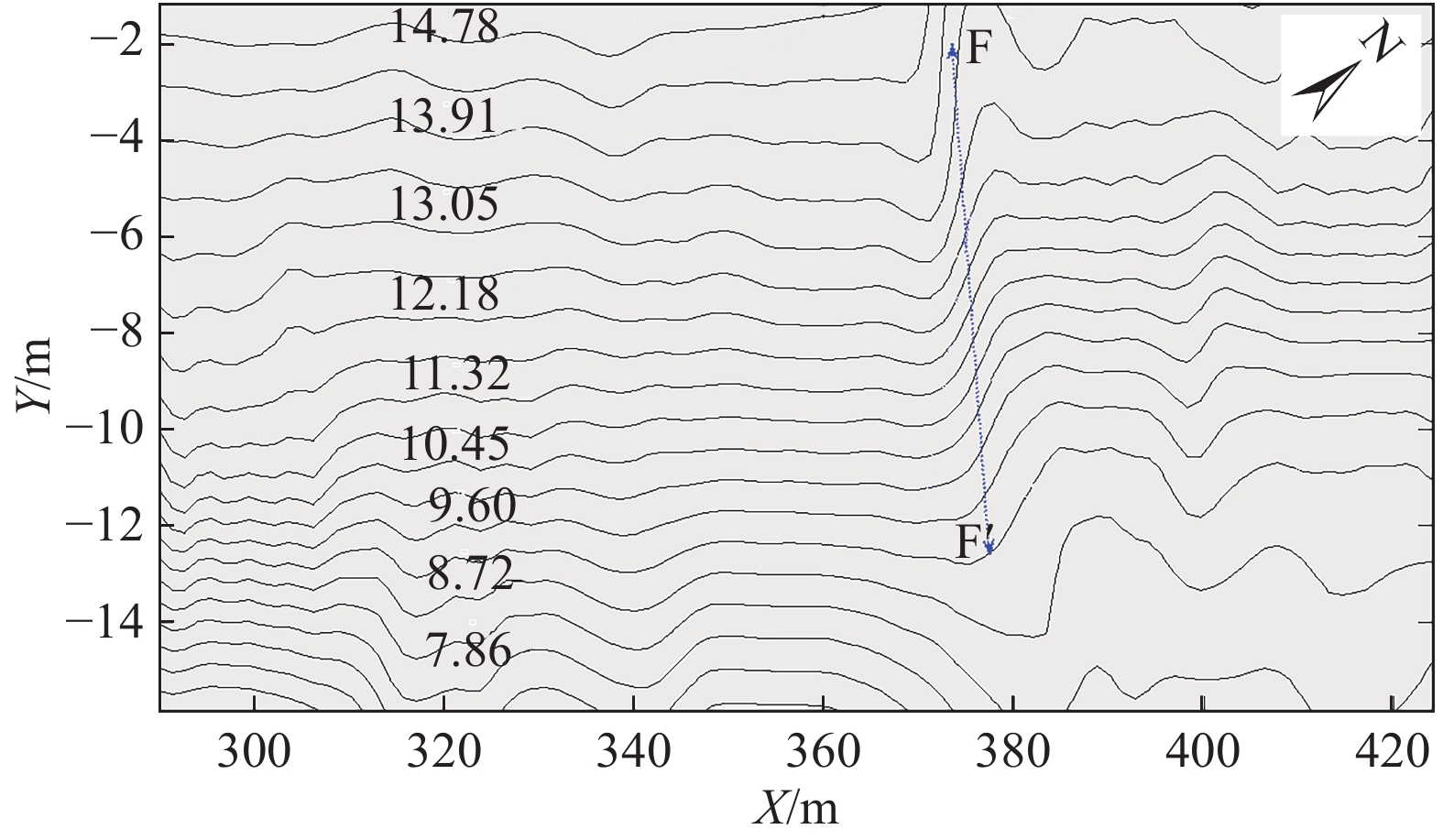
表 1 斜坡体物理力学参数表Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of the slope岩土体 天然密度
/(kg·m−3)黏聚力
/kPa内摩擦角
/(°)体积模量
/MPa剪切模量
/MPa道路 2500 − − 600 360 斜坡体 1850 15 18 16.67 7.69 车辆荷载作为一种随机荷载,过往车辆重量不一,速度不一,车辆时间间隔不一。考虑到边坡上方道路为普通公路,本文交通荷载中轴载取20,40,60,80,100 kN 5种工况,速度则取20,40,60,80 km/h 4种工况。为了简化,本文考虑车辆连续作用下边坡的动力响应,车辆荷载的间隔t0取0。
为了能精确模拟振动波在斜坡体中的传播过程及斜坡的动力响应机制,数值模型网格单元的尺寸必须小于振动波最高频率时波长的1/10~1/8,最高频率所对应的波长λ可用以下公式计算[26]:
(4) (5) 式中:fmax——输入波的最高频率/s,
Cs——S波在介质中的传播速度/(km·h-1);
1850 kg/m3;G——剪切模量,取7.69 MPa。
T=12 L/v,轮胎接触面的半径L=0.15 m,速度20,40,60,80 km/h对应的周期分别:0.324,0.162,0.108,0.081 s,其中80 km/h的周期最小为0.081 s,根据式(4)(5)可以推导出模型允许输入的网格最大尺寸为0.52~0.65 m,综合考虑计算速度与模拟精度,本文采用0.5 m的网格间距。
2.3 本构模型及边界条件
黄土力学行为复杂,在外力的作用下,不仅产生弹性变形,还会产生不可恢复的塑性变形。因此,本文的黄土边坡模型采用弹塑性本构关系,屈服准则采用Mohr-Coulomb强度准则。道路由于结构材料均匀、产生变形较小,则采用弹性本构关系。在模拟过程中,首先约束两侧边界水平方向的位移和底部边界竖直方向的位移,使得模型在自重条件下达到平衡状态。在动力分析过程时,去掉模型道路顶部的静力约束条件,边坡模型四周设置为自由场边界,假设汽车在道路中央行驶,轮胎间距为2 m,轮胎宽度0.2 m,在道路中央两侧1 m处,施加宽度为0.2 m的交通荷载,交通荷载连续施加100个周期。阻尼则采用局部阻尼来再现能量损失。
3. 数值模拟结果及分析
3.1 边坡动力响应分析
(1)潜在滑动面分析
坡体内部受应力作用会产生不同程度的塑性变形,斜坡体(潜在)滑动面可根据剪应变增量的变化来判断,斜坡的变形破坏多沿剪应变增量发生较大变化的部位发生,剪应变增量不发生变化或者较小的部位,一般不会有潜在滑动面的产生。由斜坡体剪应变增量云图可知(图3),在天然状态下,坡体内部产生局部塑性变形,潜在滑动带呈圆弧状从坡脚逐渐向坡顶方向发展,尚未延伸到坡顶,圆弧状应变带在坡脚处剪切应变增量最大。加载轴载100 kN、速度为60 km/h车辆循环荷载后,剪应变增量带向上延伸。施加荷载与未施加荷载的应力应变对比表明:边坡受汽车循环荷载的影响,有发展为滑移面的可能,边坡的失稳最先从坡脚处的剪切破坏开始。
(2)竖直方向的加速度、速度、位移变化规律
本文对轴载100 kN、速度为60 km/h车辆通过道路中央时道路以下0,2,4,6,8,10,12 m不同深度竖向最大加速度、速度和位移随时间的变化规律进行分析(图4)。从图4可以看出,竖向最大加速度、速度时程曲线变化规律类似,在车辆循环荷载作用下,随着深度的增加,变形逐渐减小。监测到不同深度处竖向位移最大值分别为7.16,6.30,5.58,4.91,4.45,4.18,3.96 mm,其随深度的增减逐渐减小。结果表明:轴载100 kN、速度为60 km/h车辆循环荷载作用下,道路下方边坡内部竖向最大加速度、速度和位移沿深度方向衰减,衰减速度逐渐减缓并趋于稳定,车辆循环荷载引起的振动影响深度约为10 m左右,10 m以下车辆循环荷载对土体的扰动较小,最大动应力发生在作用荷载的下部。
3.2 不同车辆荷载对边坡动力响应的影响
本文分析了车辆速度为60 km/h,轴载为20,40,60,80,100 kN 5种工况下斜坡的动力响应规律。通过分析不同轴载作用下边坡表面和内部各监测点的竖向最大加速度、速度和位移的变化规律(图5),结果表明:各轴载作用下,从边坡坡肩到坡脚(从S1到S6)或道路下方随深度的增加(从I1到I7),边坡上监测点远离荷载源,监测点动力响应减弱,竖向最大加速度、速度和位移都表现为逐渐减小的趋势,并且离震源越近的点动力响应越敏感,最大加速度、最大速度的衰减的幅度越大,随着与震源距离的增加衰减幅度逐渐减小。随着车辆轴载的增大,边坡表面和内部的各个监测点的竖向最大加速度、最大速度和最大位移都呈逐渐增大的趋势,其增大的幅度也呈现出离震源越近,增大幅度越大。
3.3 车辆速度对边坡动力响应的影响
本文分析在100 kN轴载下,行车速度为20,40,60,80 km/h 4种工况条件下斜坡的动力响应规律。通过对边坡表面和内部各监测点的不同行车速度下竖向最大加速度、速度和位移进行监测(图6),结果表明:各行车速度下,边坡表面和内部各监测点的竖向最大加速度、速度和位移变化规律基本相同,都随着与动荷载距离的增加呈逐渐减小的趋势。随行车速度的增加,坡体内部监测点的竖向最大加速度和速度都而逐渐增大,但这种情况只发生在了距坡表10 m范围内,超过10 m后不同车速下的竖向最大速度、加速度都趋向于稳定,位移则随着行车速度的增加而逐渐减小,这主要是因为速度减小,汽车与斜坡体作用时间增加,道路下方坡体的沉降量增加。随行车速度的增加,边坡表面监测点的竖向最大加速度和速度的规律出现波动,但整体还是呈现为逐渐增大,坡表位移与坡体内部监测点位移规律一致,随着行车速度的增加而逐渐减小。
4. 结论
(1)在天然状态下,斜坡体内部会产生局部的塑性变形,剪应变增量带从坡脚呈圆弧状向坡中延伸,施加轴载100 kN、速度为60 km/h交通荷载后,剪应变增量带向坡顶延伸发展,边坡受汽车循环荷载的影响,有发展为滑移面的可能,并且最先从坡脚处的剪切破坏开始。
(2)在轴载100 kN、速度为60 km/h交通荷载作用下,边坡道路下方竖向最大加速度、速度和位移会随着深度的增加而不断衰减。车辆振动荷载对边坡的影响范围大约10 m左右,最大动应力产生在荷载的下部。
(3)在车辆速度为60 km/h不同轴载情况下,随着距荷载源距离的不断增大,竖向最大加速度、速度及位移逐渐减小,并且振动衰减幅度也随着距离的增大而逐渐减小。随着车辆轴载的逐渐增大,边坡斜坡表面和内部监测点的竖向最大速度、加速度和位移呈现逐渐增大的规律。
(4)在100 kN轴载不同速度情况下,随着距荷载源距离的不断增大,竖向最大加速度、速度和位移呈逐渐减小趋势。随着车速增加,坡体内部和表面竖向最大加速度和速度都逐渐增大,最大位移则随着车速的增大而逐渐减小。
(5)值得注意的是,本文以黄土边坡概化模型为例,分析了交通荷载作用下黄土边坡动力响应的普适性规律。但是,考虑到黄土的水敏性和动荷载的振动促渗作用的影响,在后续研究中将进一步结合实际黄土边坡监测数据,并考虑降雨影响,深入剖析交通荷载作用下黄土边坡的动力响应特征与规律。
-
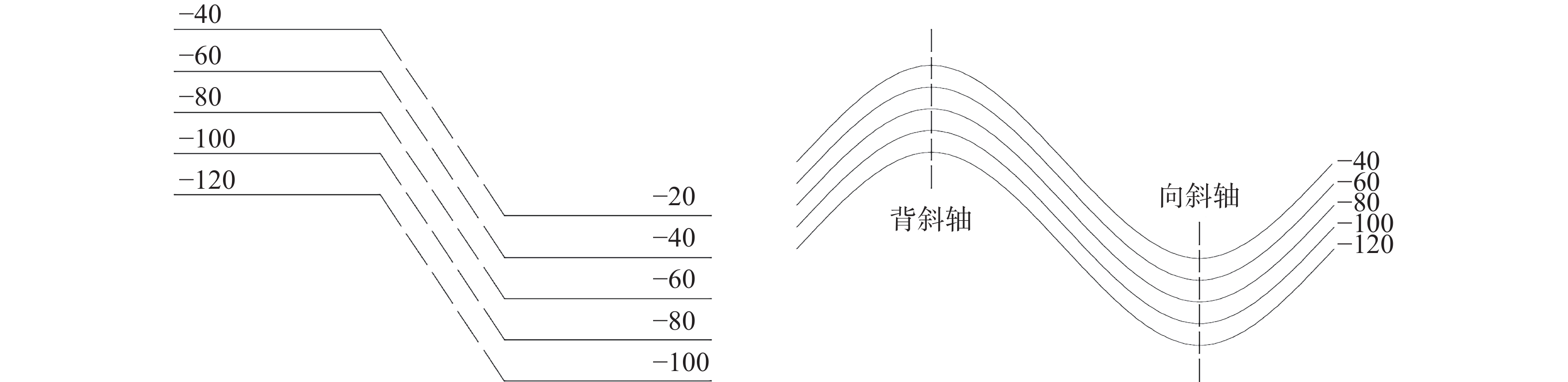
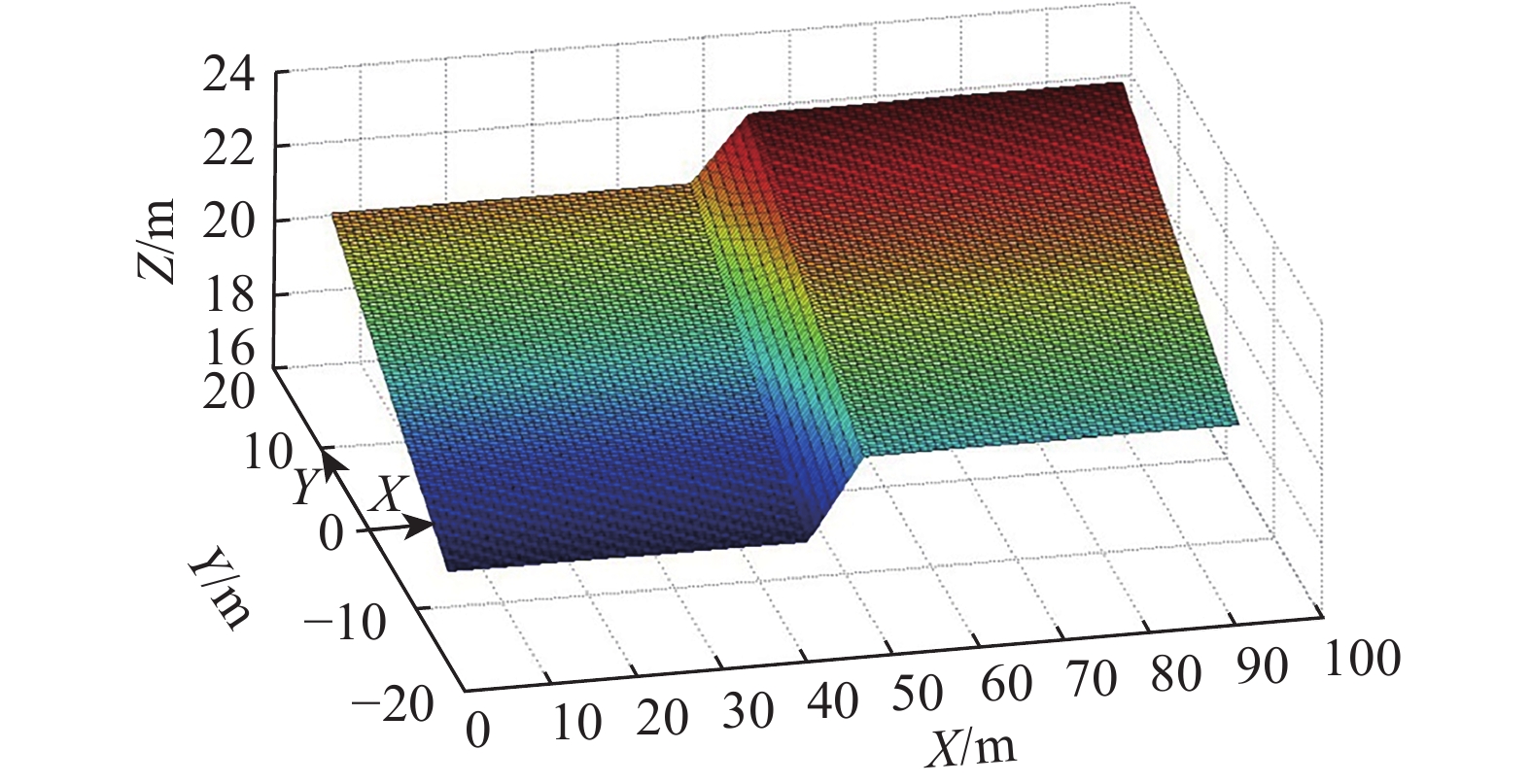
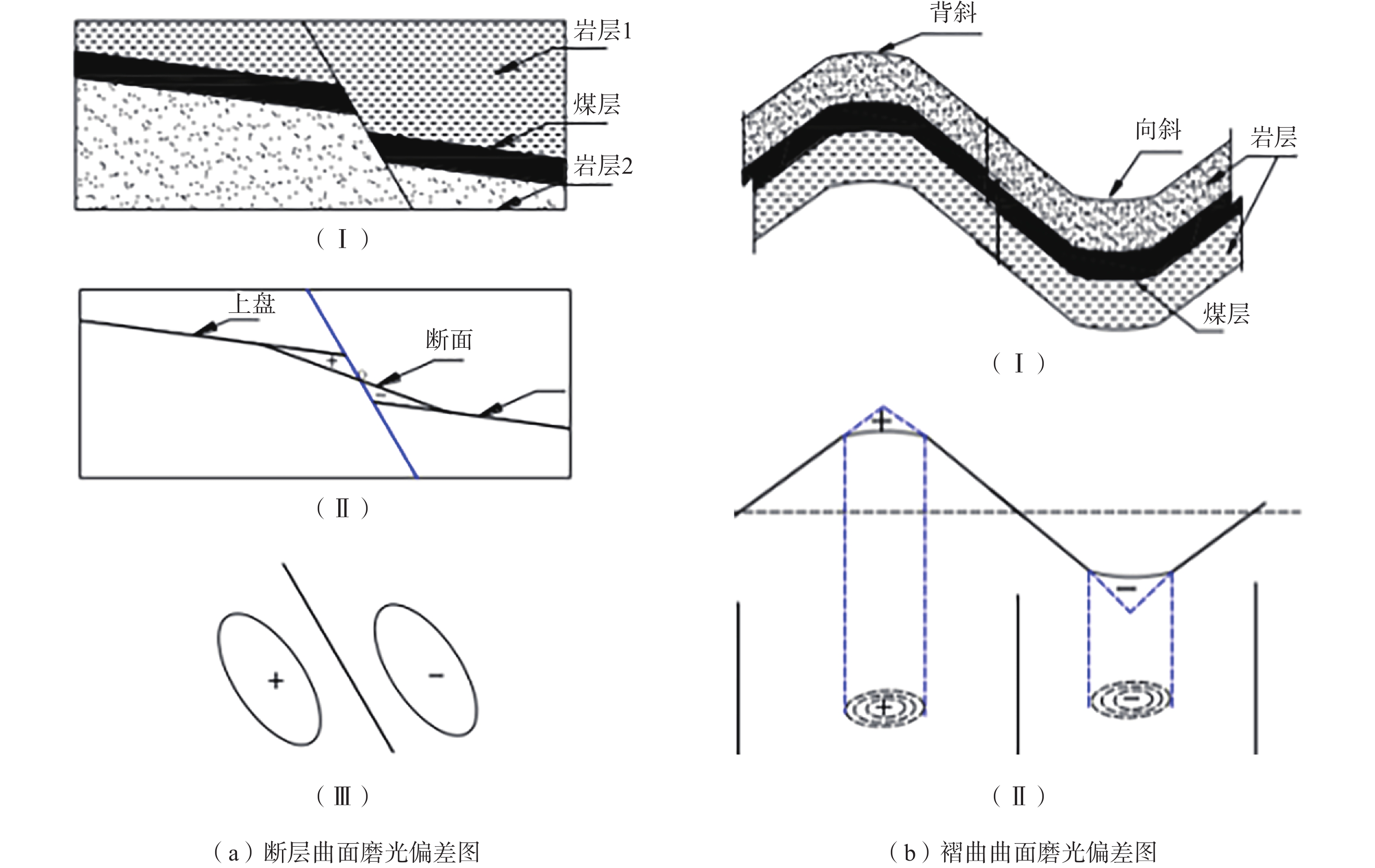
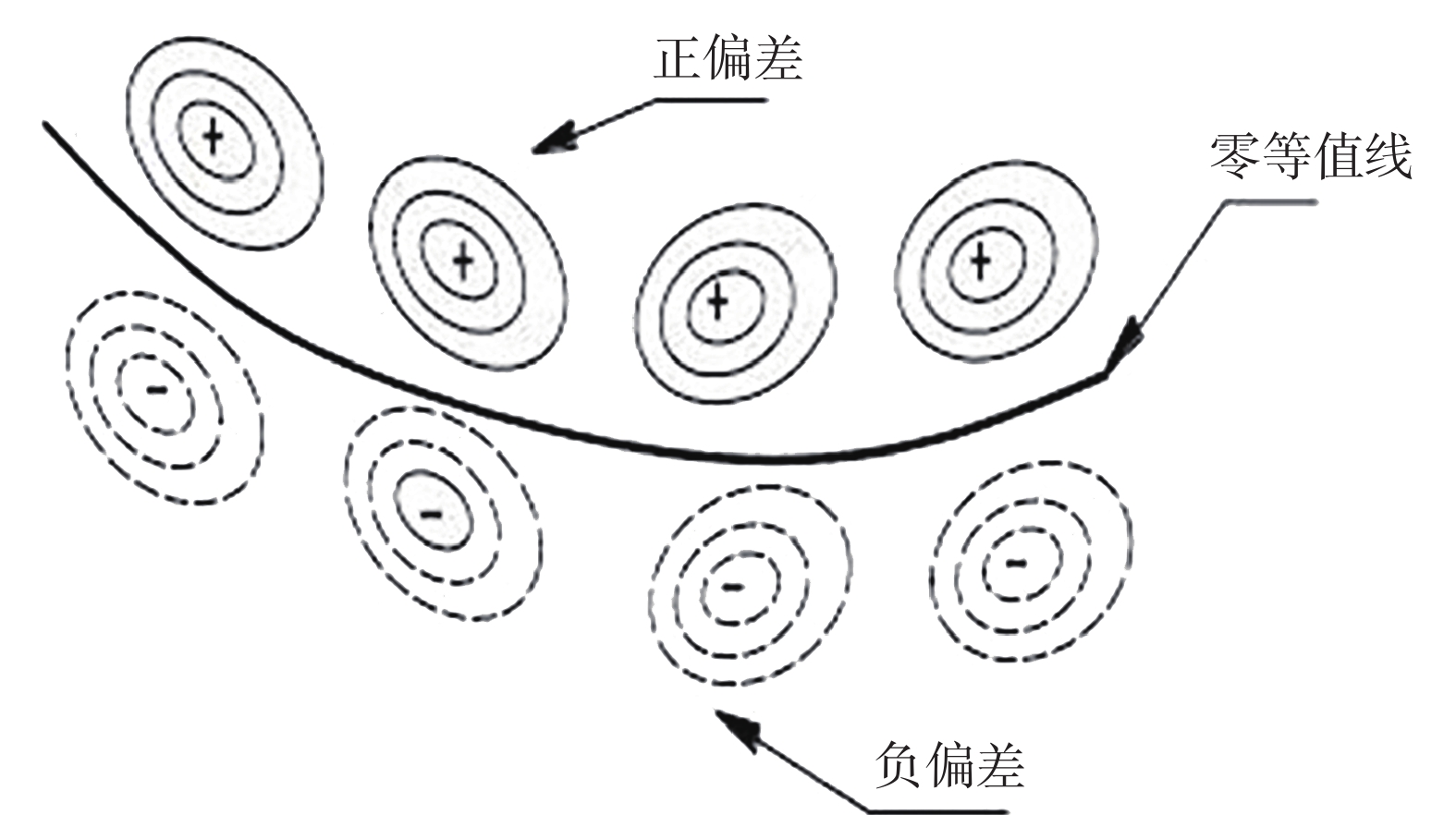
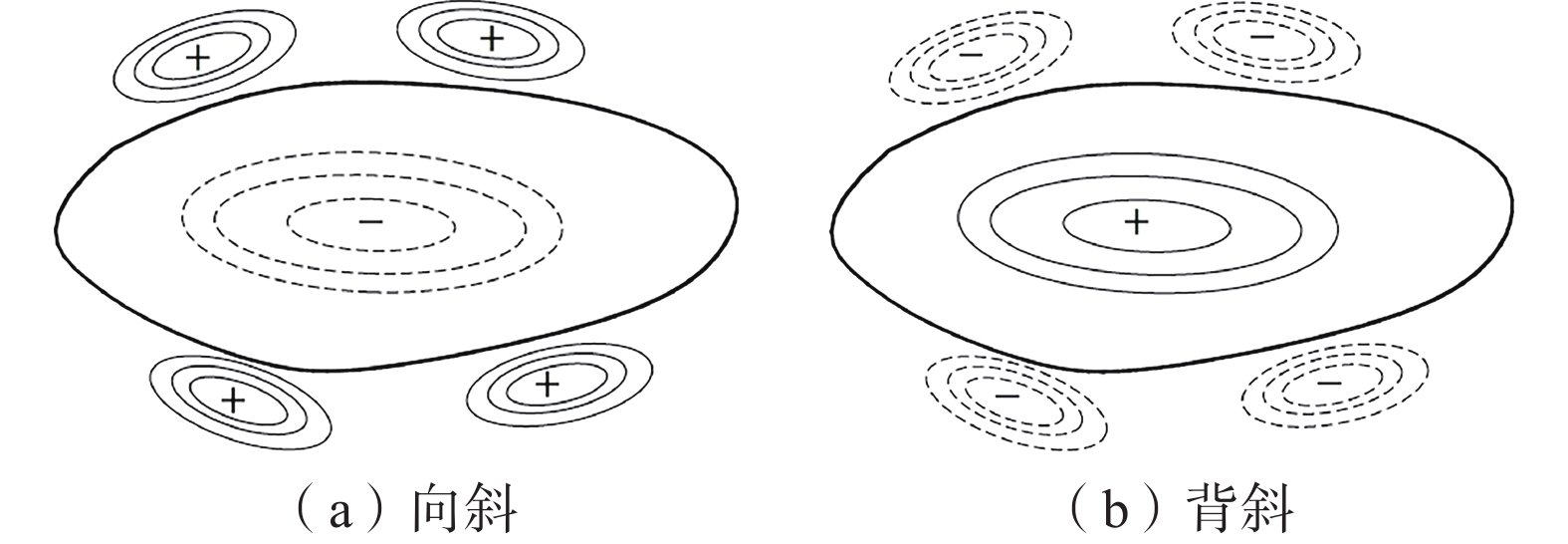
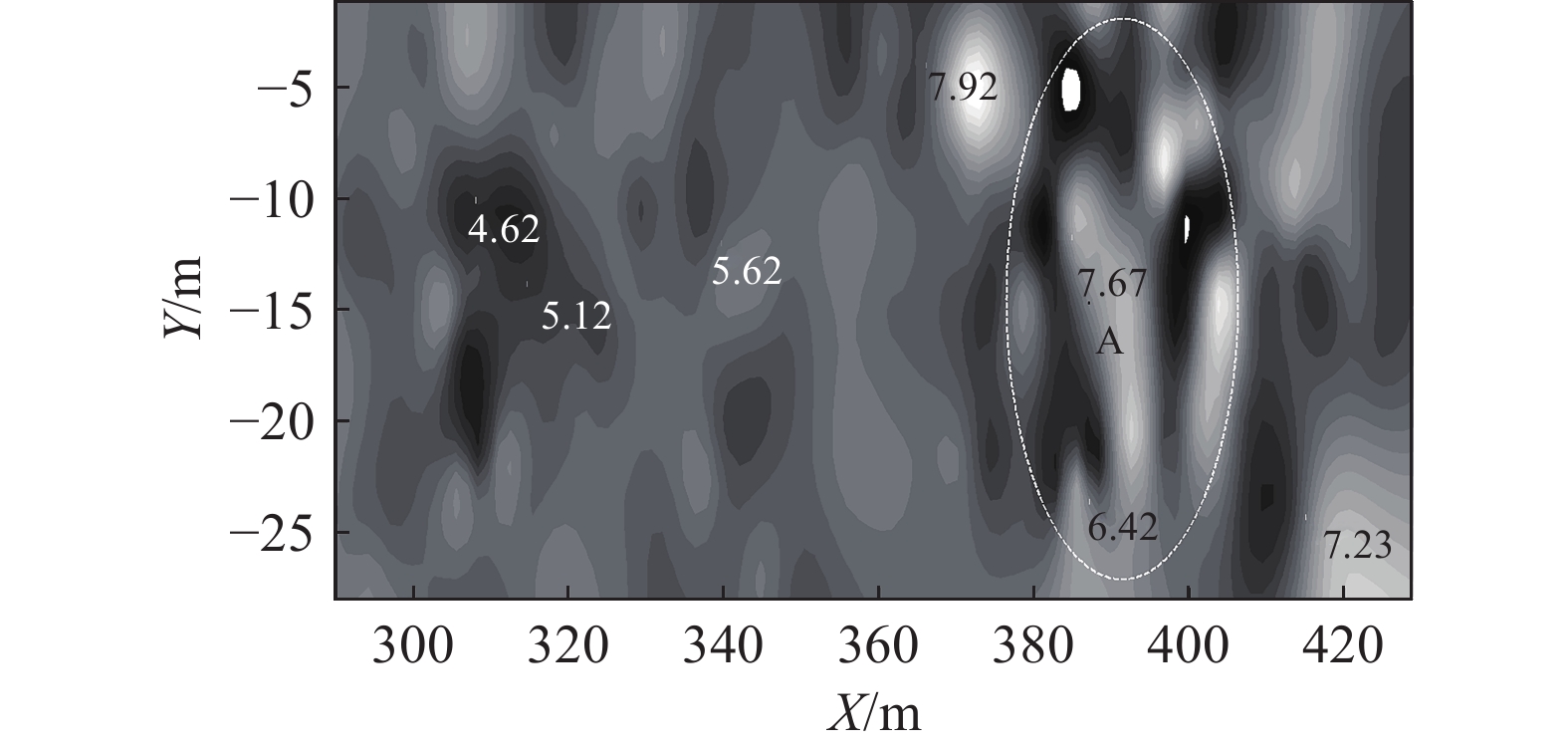
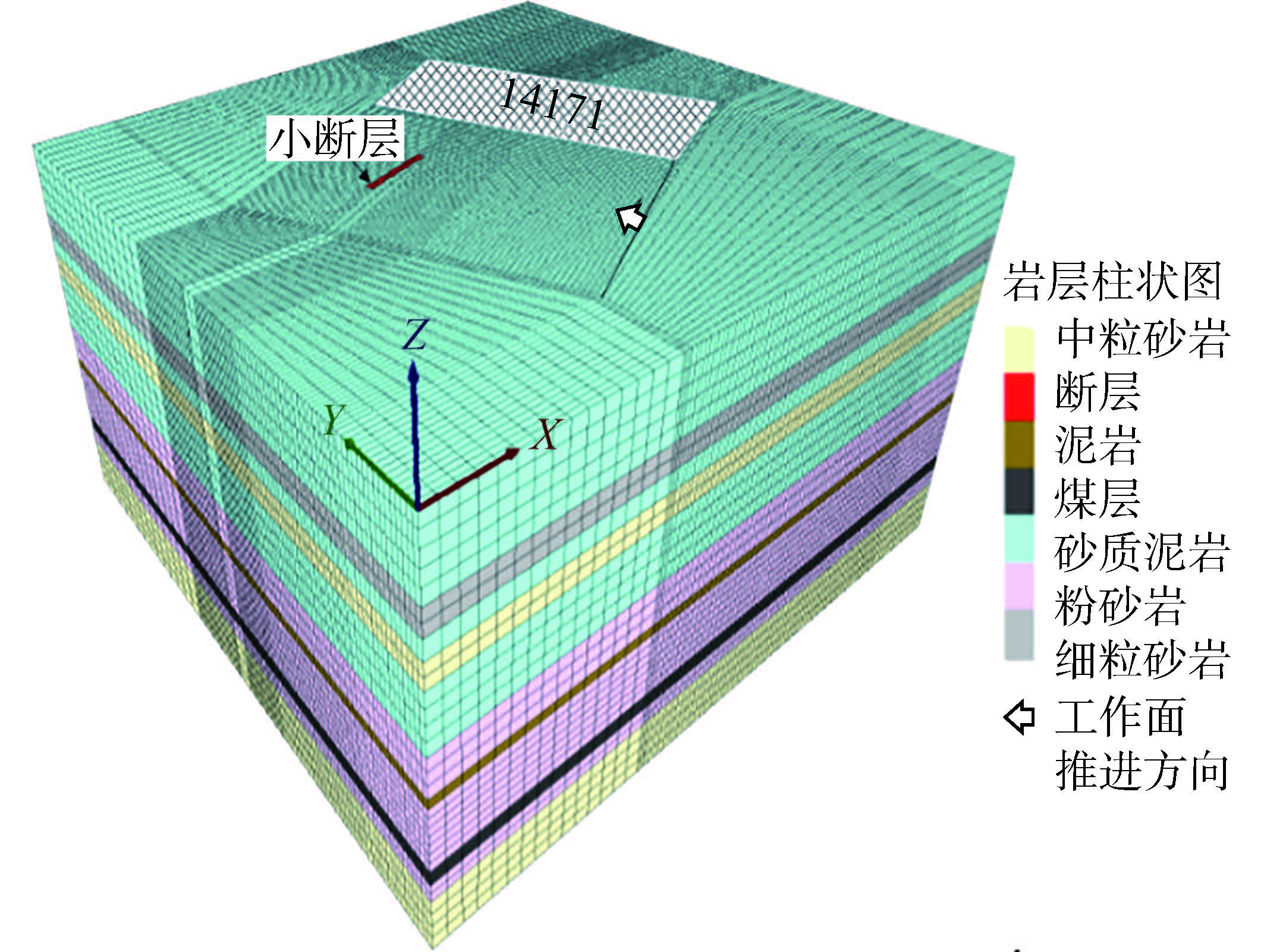
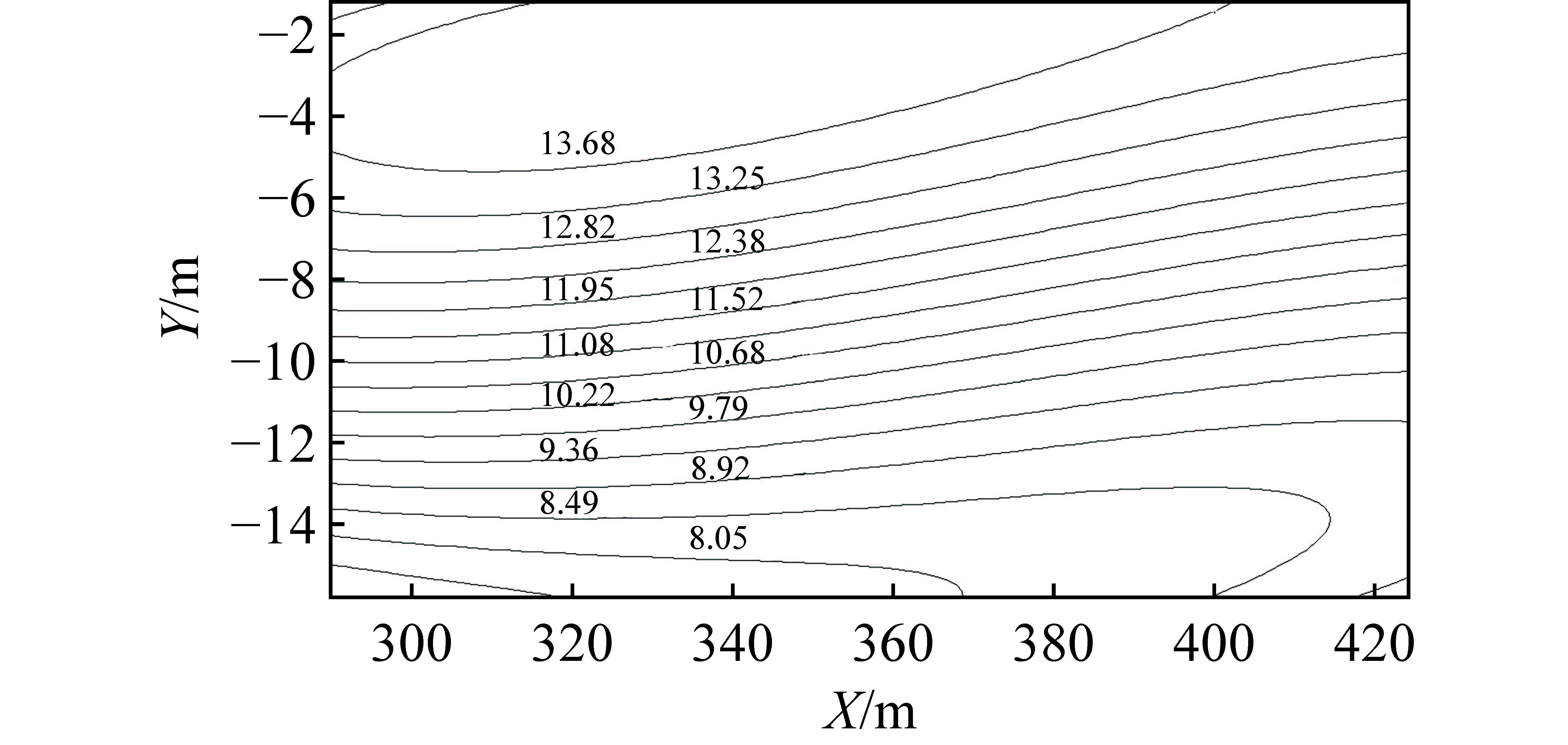
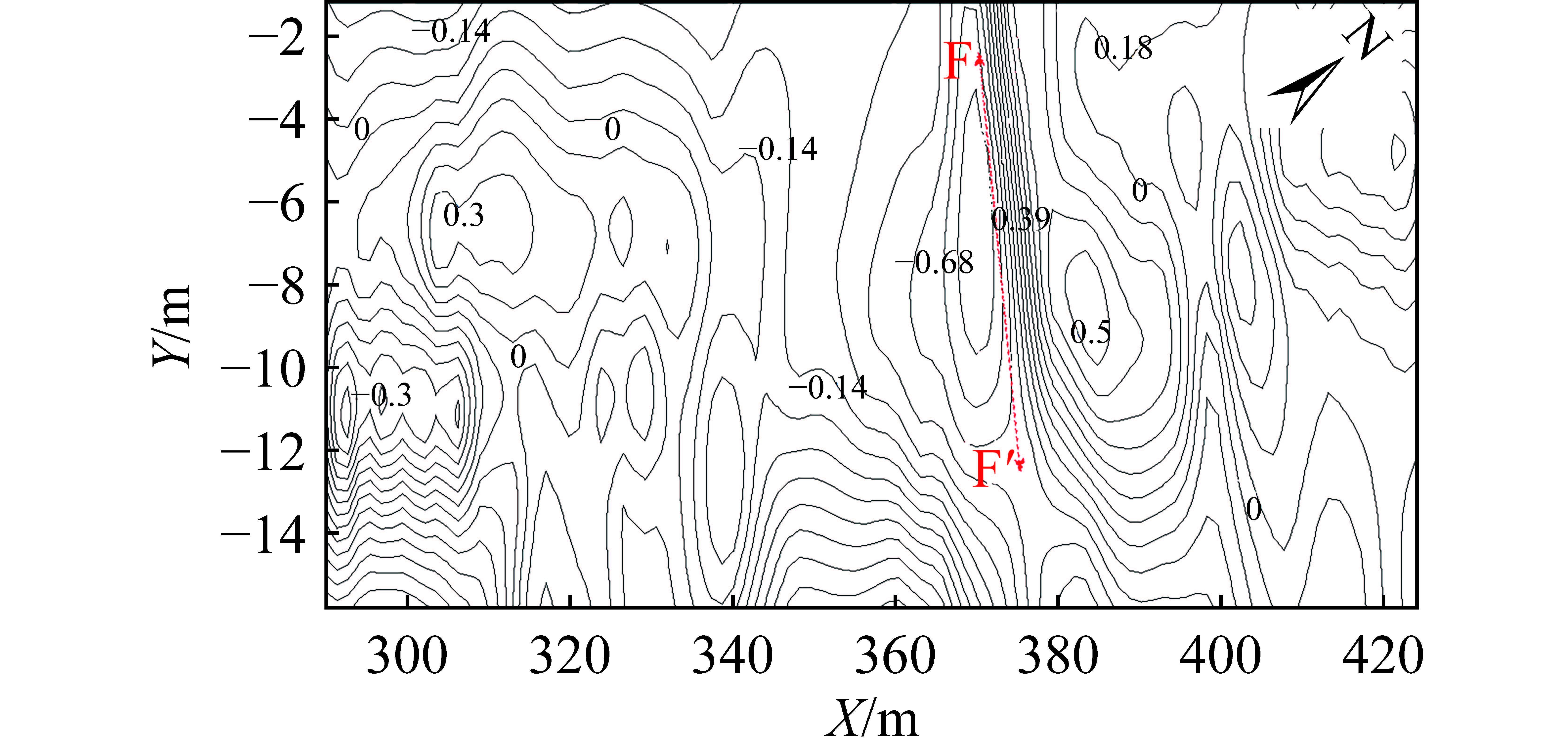
表 1 不同构造类型趋势面分析表
Table 1 Analysis table of trending surfaces for different tectonic types
构造
类型构造模型 煤层顶板/底板
等值线示意图趋势面残差示意图 断层 走向
断层


倾向
断层


褶曲 


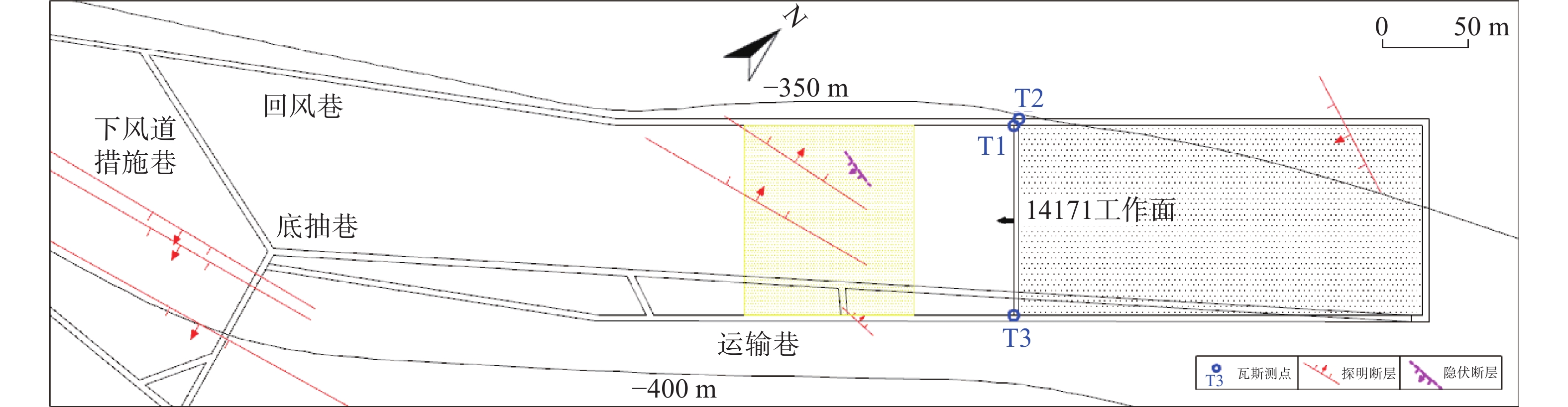
表 2 不同构造类型叠加应力场数值模拟
Table 2 Numerical simulation of superimposed stress fields of different tectonic types
构造
类型0°夹角断层 45°夹角断层 90°夹角断层 构造模型 


开采前 


20 m迎头 


6 m迎头 


-
[1] 李忠华,梁影,包思远,等. 断层冲击地压的影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):126 − 131. [LI Zhonghua,LIANG Ying,BAO Siyuan,et al. Analysis on influence factors of the fault rock burst[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):126 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Zhonghua, LIANG Ying, BAO Siyuan, et al. Analysis on influence factors of the fault rock burst[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(3)126-131 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] PETER HATHERLY. Overview on the application of geophysics in coal mining[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2013,114:74 − 84. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2013.02.006
[3] 贾天让,王蔚,张子敏,等. 现代构造应力场下断层走向对瓦斯突出的影响[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2013,30(6):930 − 934. [JIA Tianrang,WANG Wei,ZHANG Zhimin,et al. Influence of fault strike on gas outburst under modern tectonic stress field[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2013,30(6):930 − 934. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIA Tianrang, WEI Wei, ZHANG Zhimin, et al. Influence of fault strike on gas outburst under modern tectonic stress field[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2013, 30(6): 930-934. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] LI Shucai,LI Shuchen,ZHANG Qingsong,et al. Predicting geological hazards during tunnel construction[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2010,2(3):232 − 242. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1235.2010.00232
[5] 魏国营,王保军,闫江伟,等. 平顶山八矿突出煤层瓦斯地质控制特征[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(3):555 − 561. [WEI Guoying,WANG Baojun,YAN Jiangwei,et al. Gas geological control characteristics of outbursts coal seam in Pingdingshan No. 8 Mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(3):555 − 561. (in Chinese with English abstract) WEI Guoying, WANG Baojun, YAN Jiangwei, et al. Gas geological control characteristics of outbursts coal seam in Pingdingshan No. 8 Mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(3): 555-561. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 崔洪庆,姚念岗. 不渗透断层与瓦斯灾害防治[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(9):1486 − 1489. [CUI Hongqing,YAO Niangang. Impermeable faults and prevention of gas hazards[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2010,35(9):1486 − 1489. (in Chinese) Cui Hongqing, Yao Niangang. Impermeable faults and prevention of gas hazards[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2010, 35(9): 1486-1489. (in Chinese)
[7] ZHU Baolong. Quantitative evaluation of coal-mining geological condition[J]. Procedia Engineering,2011,26:630 − 639. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.2216
[8] 杨陆武,彭立世,曹运兴. 应用瓦斯地质单元法预测煤与瓦斯突出[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,1997,8(3):21 − 26. [YANG Luwu,PENG Lishi,CAO Yunxing. Application of gas geological division in controlling coal and gas outburst[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,1997,8(3):21 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Luwu, PENG Lishi, CAO Yunxing. Application of gas geological division in controlling coal and gas outburst[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1997, 8(3): 21-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 冉恒谦,张金昌,谢文卫,等. 地质钻探技术与应用研究[J]. 地质学报,2011,85(11):1806 − 1822. [RAN Hengqian,ZHANG Jinchang,XIE Wenwei,et al. Applications study of geo-drilling technology[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2011,85(11):1806 − 1822. (in Chinese) RAN Hengqian, ZHANG Jinchang, XIE Wenwei, et al. Applications study of geo-drilling technology[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(11): 1806-1822. (in Chinese)
[10] YAO Ningping,ZHANG Jie,JIN Xing,et al. Status and development of directional drilling technology in coal mine[J]. Procedia Engineering,2014,73:289 − 298. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeng.2014.06.201
[11] LI Shucai, LIU Bin, XU Xianji, et al. An overview of ahead geological prospecting in tunneling[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology Incorporating Trenchless Technology Research, 2017, 63: 69 − 93.
[12] 汪佩,吕闫生,张金陵. 基于地质构造分区的瓦斯地质单元区划方法[J]. 煤炭技术,2021,40(2):89 − 92. [WANG Pei,LYU Yansheng,ZHANG Jinling. Gas geological unit dividing method based on geological structure zoning[J]. Coal Technology,2021,40(2):89 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Pei, LYU Runsheng, ZHANG Jinling. Gas geological unit dividing method based on geological structure zoning[J]. Coal Technology, 2021, 40(2): 89-92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] CAI Yidong,LIU Dameng,YAO Yanbin et al. Geological controls on prediction of coalbed methane of No. 3 coal seam in southern Qinshui Basin,North China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2011,88(2/3):101 − 112.
[14] PAUL S, CHATTERJEE R. Determination of sub-surface stress direction from coal permeability and underground cleat orientation mapping for coal bed methane exploration, Jharia Coalfield, India[C]//International Conference on Unconventional Sources of Fossil Fuels and Carbon Management (ICUSFFCM 2011), 2011, 87(2): 87 − 96.
[15] KANG H,ZHANG X,SI L,et al. In-situ stress measurements and stress distribution characteristics in underground coal mines in China[J]. Engineering Geology,2010,116(3 − 4):333 − 345. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.09.015
[16] YANG Wei,LIN Baiquan,ZHAI Cheng. A new technology for coal and gas control based on the in situ stress distribution and the roadway layout[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2012,22(2):145 − 149. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2011.08.002
[17] 伍小刚,李天斌,张中,等. 传统瞬变电磁法的改进及其在隧道超前地质预报中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):163 − 170. [WU Xiaogang,LI Tianbin,ZHANG Zhong,et al. Improvement of the traditional transient electromagnetic method and its application to advanced geological forecast of tunnel[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):163 − 170. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Xiaogang, LI Tianbin, ZHANG Zhong, et al. Improvement of the traditional transient electromagnetic method and its application to advanced geological forecast of tunnel[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(1): 163-170. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] SUN Xueyang, XIA Yucheng. Research on development character of middle and small size fault structure in DongPang Mine field on fractal theory[C]//2010 International Conference on Computing, Control and Industrial Engineering. June 5 − 6, 2010, Wuhan, China. IEEE, 2010: 170 − 174.
[19] NIU Yan, ZHAO Jun, LI Zhiyuan, et al. Optimization of geological and mineral exploration by integrating remote sensing technology and borehole database[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2022: P717749.
[20] DENG Zhaopeng, CAO Maoyong, GENG Yushui, et al. Generating a cylindrical panorama from a forward-looking borehole video for borehole condition analysis[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(16): 3437.
[21] VAN DYKEM, KLEMETTI T, WICKLINE J. Geologic data collection and assessment techniques in coal mining for ground control[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2020,30(1):131 − 139. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2019.12.003
[22] ZHANG Lei,PAN Jienan,ZHANG Xiaomin. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of mining geological condition in the No. 9 coal seam,Linhuan coal mine,Huaibei Coalfield,China[J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences,2012,12:9 − 16. DOI: 10.1016/j.proenv.2012.01.240
[23] 武强,陈红,刘守强. 基于环套原理的ANN型矿井小构造预测方法与应用—以淄博岭子煤矿为例[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(3):449 − 453. [WU Qiang,CHEN Hong,LIU Shouqiang. Methodology and application on size-limited structure predictions with ANN based on loop overlapping theory:A case study of Lingzi coal mine in Zibo[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2010,35(3):449 − 453. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Qiang, CHEN Hong, LIU Shouqiang. Methodology and application on size-limited structure predictions with ANN based on loop overlapping theory: a case study of Lingzi Coal Mine in Zibo[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2010, 35(3): 449-453. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 孙米银. 基于钻孔成像的煤层地质趋势面分析技术[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(8):113 − 117. [SUN Miyin. Coal seam geological trend surface analysis technology based on borehole imaging[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2021,52(8):113 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract) Sun Miyin. Coal seam geological trend surface analysis technology based on borehole imaging[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(8): 113-117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 贾晓亮,崔洪庆,张子敏. 断层端部地应力影响因素数值分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2010,38(4):47 − 51. [JIA Xiaoliang,CUI Hongqing,ZHANG Zimin. Numerical simulation of geostatic stress influening factor at the end of fault[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2010,38(4):47 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIA Xiaoliang, CUI Hongqing, ZHANG Zimin. Numerical simulation of geostatic stress influening factor at the end of fault[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2010, 38(4)47-51 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 刘少伟,焦建康. 九里山井田断层构造区应力分析及区域划分[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2014,10(2):44 − 50. [LIU Shaowei,JIAO Jiankang. Stress analysis and division of fault tectonic region in Jiulishan coal field[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2014,10(2):44 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Shaowei, JIAO Jiankang. Stress analysis and division of fault tectonic region in Jiulishan coal field[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2014, 10(2): 44-50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 李胜,罗明坤,范超军,等. 采煤工作面煤与瓦斯突出危险性智能判识技术[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2016,26(10):76 − 81. [LI Sheng,LUO Mingkun,FAN Chaojun,et al. Research on coal and gas outburst risk intelligent recognition in mining face[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2016,26(10):76 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Sheng, LUO Mingkun, FAN Chaojun, et al. Research on coal and gas outburst risk intelligent recognition in mining face[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(10)76-81(in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 关金锋. 采煤工作面小构造探测及动态分析方法研究[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2016. GUAN Jinfeng. Study on detection and dynamic analysis method of small structure in coal mining face[D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] HATHERLY P,LEUNG R,SCHEDING S,et al. Drill monitoring results reveal geological conditions in blasthole drilling[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2015,78:144 − 154. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.05.006
[30] YANG Wei,LIN Baiquan,XU Jiangtao. Gas outburst affected by original rock stress direction[J]. Natural Hazards,2014,72(2):1063 − 1074. DOI: 10.1007/s11069-014-1049-z
[31] 刘杰,王恩元,赵恩来,等. 深部工作面采动应力场分布变化规律实测研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2014,31(1):60 − 65. [LIU Jie,WANG Enyuan,ZHAO Enlai,et al. Distribution and variation of mining-induced stress field in deep workface[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering,2014,31(1):60 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Jie, WANG Enyuan, ZHAO Enlai, et al. Distribution and variation of mining-induced stress field in deep workface[J]. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering, 2014, 31(1): 60-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 勾攀峰,韦四江,张盛. 不同水平应力对巷道稳定性的模拟研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2010,27(2):143 − 148. [GOU Panfeng,WEI Sijiang,ZHANG Sheng. Numerical simulation of effect of horizontal stresses at different levels on stability of roadways[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2010,27(2):143 − 148. (in Chinese with English abstract) GOU Panfeng, WEI Sijiang, ZHANG Sheng. Numerical simulation of effect of horizontal stresses at different levels on stability of roadways[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2010, 27(2): 143-148. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] BABAEI KHORZOUGHI M,HALL R. Processing of measurement while drilling data for rock mass characterization[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2016,26(6):989 − 994. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2016.09.005
[34] 张纪星,师修昌. 浅埋采空区大采高条件下覆岩破坏规律[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):92 − 97. [ZHANG Jixing,SHI Xiuchang. Failure of overburden rock under large mining height in shallow buried goaf area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):92 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Jixing, SHI Xiuchang. Failure of overburden rock under large mining height in shallow buried goaf area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(5)92-97 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 蒋金泉,武泉林,曲华. 硬厚覆岩正断层附近采动应力演化特征[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2014,31(6):881 − 887. [JIANG Jinquan,WU Quanlin,QU Hua. Evolutionary characteristics of mining stress near the hard-thick overburden normal faults[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2014,31(6):881 − 887. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIANG Jinquan, WU Quanlin, QU Hua. Evolutionary characteristics of mining stress near the hard-thick overburden normal faults[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2014, 31(6): 881-887. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 孙嘉琪,古远,陈欣欣,祁明静,丁琛. 基于时序InSAR的广州典型沉降区特征及成因分析. 地质装备. 2024(05): 43-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 万鹏,韩贤权,谭勇,秦朋. 基于云计算的引调水工程星载TD-InSAR地表形变监测. 长江科学院院报. 2024(10): 206-214 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 纪振付,罗奕,张国沅,李建颖. 汕头市谷饶地区地面沉降特征及成因分析. 云南地质. 2024(04): 598-603 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:






 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS