Development characteristics and causal analysis of karst collapses in Chengnan community, Yingde City, Guangdong Province
-
摘要: 以广东省英德市英城街道城南社区地面塌陷为研究对象,在系统收集研究区及周边区域地质环境条件、历史灾情、水位监测等资料的基础上,通过地面调查、物探、钻探等技术手段,查明研究区岩溶塌陷发育特征,分析岩溶塌陷的主要成因。结果表明:(1)研究区内塌陷坑单体规模以小型为主,少量为中、大型;共连续发生31处岩溶塌陷,影响面积0.6 km2,岩溶塌陷地质灾害规模为特大型。塌陷坑平面形态以圆形、椭圆形为主,剖面形态以圆柱状为主。(2)研究区岩溶塌陷主要受地质构造、覆盖土层、水文地质、大气降雨及人类活动等因素影响,综合分析认为,地质构造、覆盖土层与水文地质条件为主导因素,大气降雨和人类活动为诱发因素。(3)综合以上分析,可将研究区岩溶塌陷总结为“傍河型隐伏岩溶区地面塌陷模式”,在对河道附近岩溶塌陷成因研究中,可首先考虑河道水位涨落及人类抽水、排水的影响因素,再结合实际情况考虑其他影响因素,此规律可为后期针对河道附近岩溶塌陷的研究提供参考。Abstract: This research endeavors to investigate the development characteristics, spatial-temporal distribution, and cause of karst collapses in Chengnan community, Yingcheng Street, Yingde City, Guangdong Province. Various technological means such as ground investigation, geophysical exploration, and drilling were employed to examine the collapses discovered in the study area, along with systematic data collection on environmental geologic conditions, historical disasters, and water-level monitoring in the study area and its surrounding areas. The results show that: (1) The karst collapses in the study area constitute an extremely large geological disaster, affecting an area of 0.6 km2, with 31 consecutive eruptions. Most of the surface collapse pits in the study area are small-scale, while a few are medium and large-scale. The planar shape of the collapse pits is primarily circular and elliptical, while the cross-section shape is mainly cylindrical. (2) The occurrence of karst collapses in the study area is influenced by geological structure, covering-layer of soil, atmospheric rainfall, hydrogeological characteristics, and human activities. Among these factors, geological structure, covering-layer of soil, and hydrogeological characteristics are considered as primary factors, whereas atmospheric rainfall and human activities act as inducing factors after a comprehensive assessment. (3) To conclude, the karst collapses erupted in the study area can be categorized as “the mode of collapse near rivers in subsurface karst areas”. During the causal analysis, priority should be given to considering water level fluctuations, pumping, and drainage. Subsequently, other influencing factors should be taken into account based on specific conditions, providing valuable insights for future research on karst collapses erupted near rivers.
-
Keywords:
- karst collapse /
- development characteristics /
- distribution pattern /
- causal analysis
-
0. 引言
2011年以来,我国逐步建立了地质灾害调查评价、监测预警、综合防治、应急救援四大体系,针对地质灾害隐患点的防治管控措施日趋成熟,“点控”体系日趋完善。截至2022年,我国已完成2041个县地质灾害风险普查和1522个县1∶5万地质灾害风险调查,针对可能发生地质灾害的风险区的管控措施和“面控”体系的探索成为目前我国地质灾害防治的重要任务和研究方向。
当前我国地质灾害防治形势仍面临新挑战新要求:一是我国地质条件复杂,构造活动频繁,极端天气和强震频发,地质灾害隐患点多面广,造成群死群伤、重大经济损失或社会影响的地质灾害事件仍年年发生[1]。地质灾害具有隐蔽性、突发性等特点,许多潜在隐患还未全面查清。以四川省为例,近年来先后发生了2017年茂县“6•24”滑坡[2 − 3]、2018年金沙江白格滑坡[4 − 6]、2019年甘洛县“8•14”滑坡[7]、2020年丹巴县阿娘寨滑坡[8 − 9]和汉源县中海村滑坡[10]等突发地质灾害,造成重大伤亡和经济损失。二是随着经济社会高质量发展,在地质灾害多发的广大山区,重大工程建设和快速推进的城镇化,正在面对地质环境尤其是地质灾害的严峻考验,出现了许多高风险甚至是不设防的城市和村镇[11],人民群众生命财产安全和美好生活的需求对地质灾害防治提出更高要求。三是各地区的地质灾害风险普查成果存在风险识别精准度不够、风险区划科学性不足、点面双控机制不完善等问题[12],急需制定相关法律法规,规范地质灾害风险管理程序,将减灾防灾和应急救灾过程按管理程序有效进行[13]。
地质灾害风险评价研究,是近年来兴起的一个越来越受到重视的新领域[14],广泛迅速发展起来[15 − 18]。如何构建有效的地质灾害风险区管控模式,将地质灾害风险“点控”和“面控”有机结合,提高地质灾害风险综合防控能力,是目前西南地区地质灾害防灾减灾急需突破的难题[12, 19 − 20]。本文在总结四川省喜德县已有防灾减灾工作成效的基础上,通过在喜德县开展地质灾害风险“点面双控”试点探索与实践,构建了风险调查评价与动态调整、监测预警与响应处置、风险常态管理与防御、科普宣传与培训演练、制度建设五个板块的点面双控体系,成果可为其他地区提供科学参考。
1. 地质环境概况
喜德县地处四川省西南部,凉山彝族自治州的中北部,总辖区面积2206 km2(图1)。是低纬度高海拔地区,属亚热带季风和高原气候,多年平均降雨量1006.1 mm,最高达1231.4 mm,多雨但时空分布不均。具有“夏短、秋长、冬春(天数)相近,气候温凉,四季不分明”的气候特点。
喜德县地貌以中、深切割剥蚀侵蚀构造中山地貌为主,沿河流分布带状剥蚀侵蚀构造低中山地貌。位于川滇SN构造带北段,主要地质构造线方向近SN向,在县城以西地区南北向断裂和褶皱发育,县城以东地区断裂稀少,褶皱平缓。境内基岩地层按成因分为沉积地层、火山地层、变质地层,主体基岩地层为沉积地层,分布最广。
河流主要有安宁河水系的孙水河、热水河、东河、西河,以及大渡河水系的尼波河。其中,孙水河、热水河水系沟谷较发育,支沟较多,是泥石流灾害主要分布区域,常发生泥石流,并造成严重损失,特别是孙水河沿岸,对成昆铁路,泸普公路,桥梁及沟口附近居住的群众威胁较大。
2. 地质灾害发育特征与防灾减灾成效
2.1 地质灾害发育特征
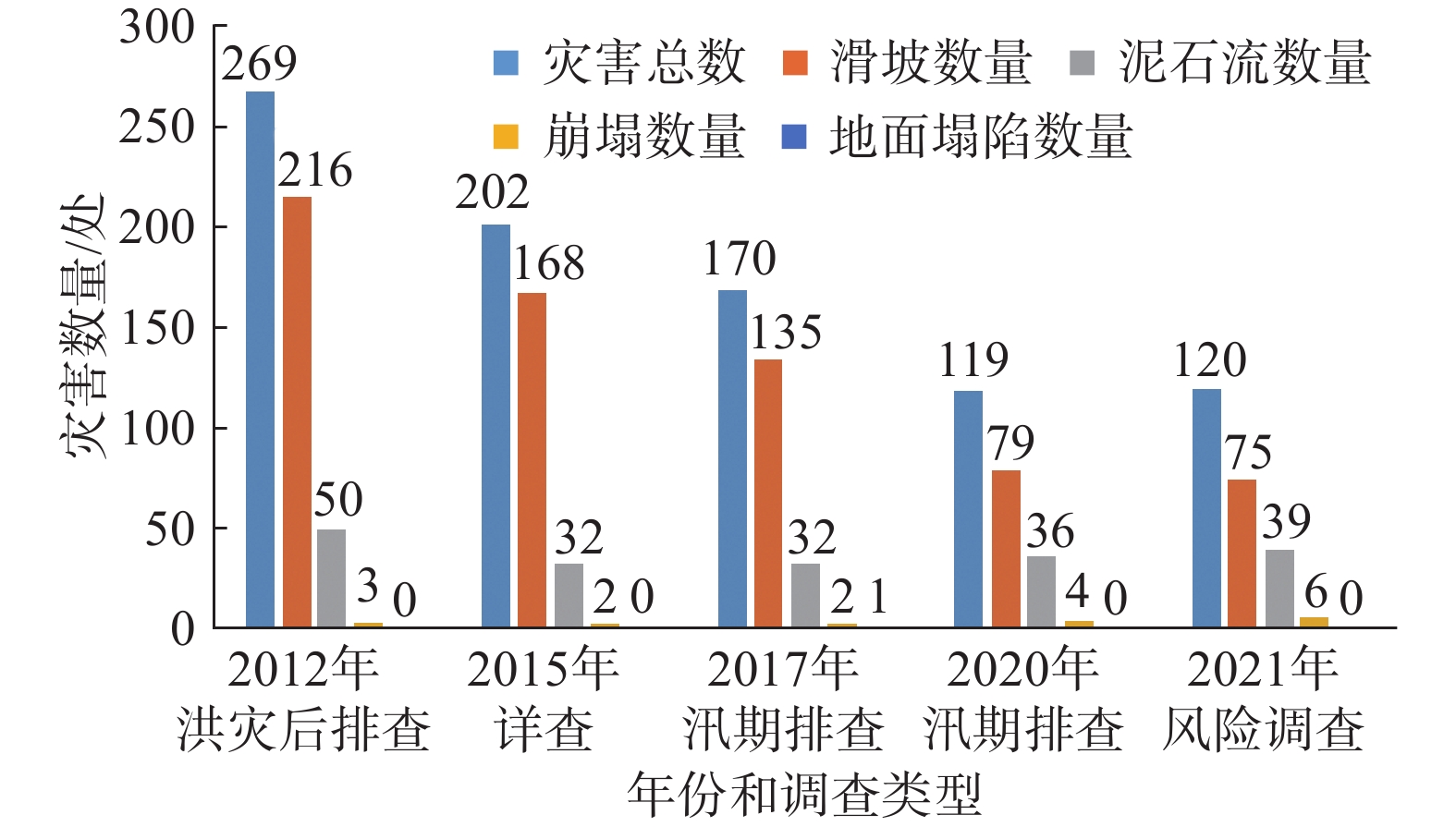
喜德县发育地质灾害点120处(截至2021年底),如图2所示,以滑坡和泥石流为主:滑坡灾害75处,以小型浅层红层滑坡为主,占地质灾害总量的62.5%;泥石流39处,占比32.5%;崩塌6处,占比5%。地质灾害发生月份主要集中于7—8月,发生灾害数量分别占总数的19.77%、64.37%。降雨、人类工程活动(采矿、切坡等)是喜德县地质灾害的主要诱发因素。
2.2 调查评价与监测预警
喜德县自2012年以来,开展了多次针对全县的地质灾害调查、排查(图2),通过工程治理和搬迁避让,地质灾害总数逐年减少,2021年地质灾害总数较2012年减少149处。2021年,喜德县开展了1∶5万县域的地质灾害风险调查与评价,系统查明了风险隐患底数,现有4处极高风险区,总面积7.89 km2,发育有7处地质灾害点;38处高风险区,总面积44.49 km2,发育42处地质灾害点;中风险区总面积344.5 km2,发育71处地质灾害点;低风险区总面积1720 km2。
自2018年以来,经过近5年的持续建设,喜德县共计完成82个地质灾害隐患点和72个极高—高风险区(含1∶5万县域风险评价极高—高风险区42处和1∶1万重点乡镇风险评价极高—高风险区30处)的自动化监测建设,构成了“点控”和“面控”相结合的实时监测预警网络。
3. 点面双控体系的探索与实践
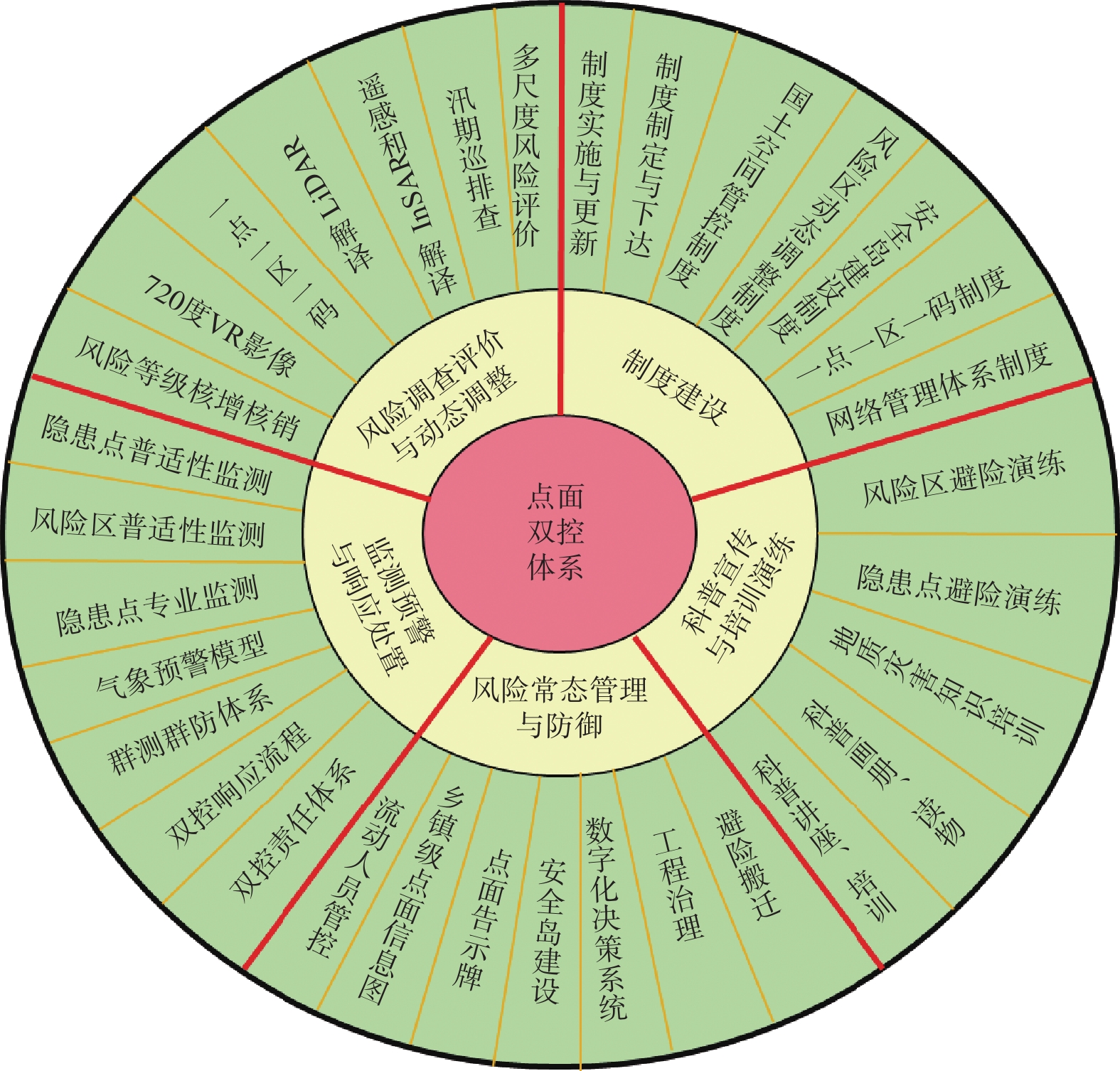
通过在喜德县开展地质灾害风险“点面双控”试点探索,在我国建立的地质灾害调查评价、监测预警、综合防治、应急救援四大体系的基础上,提出调查评价与动态调整、监测预警与响应处置、常态管理与防御、科普宣传与培训演练、制度建设五个板块的点面双控体系(图3)。
3.1 风险调查评价与动态调整
3.1.1 “点面双控”的针对性和时效性
喜德县完成县域1∶5万地质灾害风险调查与评价后,如图4(a)所示,查明了风险区分布情况,为“点面双控”工作奠定了基础,但此次风险普查的比例尺和精准度有限,风险区面积偏大。2022年,喜德县开展了1∶1万斜坡地质灾害隐患风险详查,将全县域划分斜坡单元和沟谷单元开展精细化调查评价,如图4(b)所示,调查精准度和结果科学性有了大幅提升,精细查明风险区的范围和分布,掌握了“面控”靶区。
在调查评价与动态调整板块中,风险评价的结果以县域1∶5万地质灾害风险普查成果为准,开展了1∶1万斜坡地质灾害隐患风险详查的,以斜坡地质灾害隐患风险详查结果为准。同时,“点控”和“面控”是一个长期的、动态更新的过程,利用好各区县每年汛期排查成果,针对县域、隐患点和风险区,采用空天地一体化的新技术新方法,相互验证和多期次对比,实时掌握隐患点和风险区的变形情况,更新隐患点和风险区的数据库,提高“点控”和“面控”的针对性和时效性。
3.1.2 “点面双控”的可操作性
在风险调查评价后,每一个风险区的范围、风险等级、承灾体、变形特征等信息均纳入四川省级数据库,进行统一管理和更新,如图4(c)所示,将传统的“统一编号”等信息转化为二维码图像,建立了“地质灾害专属身份证二维码”。扫描二维码后,可实现一键报灾、电话上报等功能,增强了“点控”和“面控”的可操作性。同时,采用720VR影像技术以3D形式直观形象展示每个隐患点和风险区的全貌和发育特征,如图4(d)所示,增强“点控”和“面控”的可读性。
地质灾害风险区(斜坡)的动态调整,包括风险区的核实认定、动态核增与动态核销、更新信息库等工作,动态调整流程如图4(e)所示。风险区的动态核增主要针对由于地震、暴雨、人类工程活动等原因造成的地质环境破坏和地表变形的情况。风险区的动态核销主要针对通过避险搬迁、排危除险、工程治理等措施消除了风险隐患和威胁的情况。
3.2 监测预警与响应处置
3.2.1 “点面双控”的监测覆盖面和预警准确度
喜德县已对82处地质灾害隐患点和72个极高—高风险区开展了普适型监测,提高了风险隐患监测覆盖面。沟谷型风险区域以雨量和泥位监测为主,斜坡型风险区域以雨量、倾角和GNSS监测为主。“点控”和“面控”监测预警网络已基本建成,并在人防+技防的防灾过程中发挥了科技支撑作用,如洛哈镇沿米市河高风险区的雨量计监测到(图5):2022年6月11—17日,每日均有不同程度的小雨;18日,该区域日降雨量达49.2 mm,发布预警信息后防灾责任人和监测员及时响应;19日风险区局部区域发生滑塌,未造成人员伤亡。
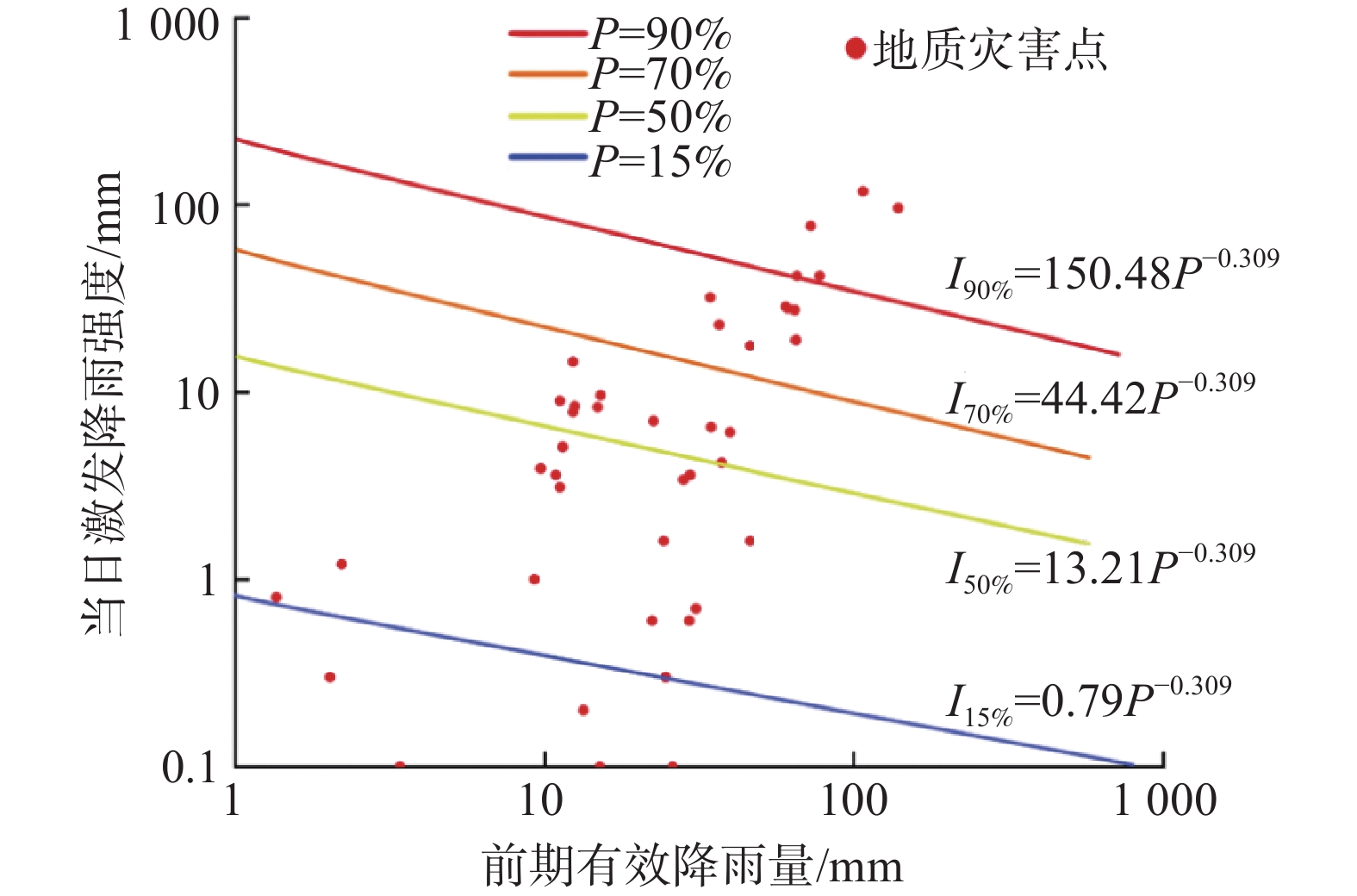
降雨是诱发红层滑坡的主要因素,构建县级精细化降雨预警模型,可提升“点控”和“面控”预警准确度。选取94个滑坡灾害作为样本,统计滑坡灾害发生前7 d降水量,建立降雨强度-前期有效降雨量(I-P)阈值模型和降雨强度-降雨历时(I-D)阈值模型。对比发现I-D降雨阈值模型具有更高的预测精度(图6),最终建立了喜德县降雨型地质灾害预警模型(表1)。
表 1 喜德县降雨型地质灾害预警模型Table 1. Rainfall-type geological hazard early warning model for Xide County降雨阈值模型
(0.1≤D≤120 h)当日降雨量/
mm累计降雨量/
mm对应预警等级
及形式I15%>0.87D−0.277 8.64 25 注意级 I50%>3.05D−0.277 26.5 49 警示级 I70%>4.18D−0.277 41.52 73 警戒级 I90%>8.225 D−0.279 81.22 145 警报级 3.2.2 责任体系的完善
当前,地质灾害隐患点的监测员体系已较完善,但地质灾害风险区的监测员体系还处于起步阶段,相关制度、响应流程、职责等还有待完善。以“面控”响应流程为例(图7)从常态、红—橙—黄—蓝四级气象预警、气象短临预警、突发险情六种工况,明确了“点控”和“面控”在预警响应时各级主管部门和相关责任人的响应流程,进一步完善了“点控”和“面控”的责任体系,明确了分工提高了响应效率。
3.3 风险常态管理与防御
“点面双控”的常态管理与防御板块包括流动人员管控、信息牌建设、安全岛建设、地质灾害“点面双控”数字化管控与决策支持系统等(图8)。① 流动人员管控,采用红外探测声光文字预警装置,安装于受崩塌滑坡灾害威胁的流动性大、承灾体多的路段,如图8(a)所示,人员车辆经过时,会以语音播报、显示屏宣传、闪灯警示、视频监控的形式自动发出提醒,尤其是在夜间,山区路段昏暗,人员车辆疲惫,可起到更好的提醒效果。② 信息牌建设采用乡镇级地质灾害隐患点和风险区信息图、地质灾害隐患点和风险区告示牌的形式,如图8(b)、(d)所示,向防灾管理人员、责任人和受威胁群众展示本乡镇的每一个隐患点和风险区的风险等级、威胁对象、撤离路线、避险安置点等信息,提高基层应急响应处置能力和管理水平。③ 安全岛建设按照就近设立、交通便利、不受地质灾害威胁的原则,每个隐患点和风险区在相对平坦区域设置至少1处安全岛,为受威胁群众应对突发事件提供临时生活应急空间和必要物资,如图8(c)所示。④ 地质灾害“点面双控”数字化管控与决策支持系统,如图8(e)所示,集成多期遥感数据、三调数据成果、房屋土地数据、地质灾害风险评价数据、斜坡精细化数据等信息,实现对县域每一处地质灾害隐患点、风险区(斜坡)的房屋住户信息的快速统计、自动分配安全岛、智能选取救援路线等功能,推动了地质灾害“点面双控”向数字化智能化方向发展。
3.4 科普宣传与培训演练
通过科普讲座、科普系列著作、科普画册、科普公众号等多样化的形式,同时充分利用“全国防灾减灾日”“国际减灾日”等时间节点,面向全社会开展防灾减灾知识的科普宣传,提高社会大众尤其是受地质灾害威胁群众的地质灾害认知水平和防灾避灾能力,达到全民参与点面双控和全民防灾减灾的效果。
针对各级行政管理人员、技术支撑人员、应急救援人员、群测群防员(隐患点监测员和风险区监测员)等,在各县及乡镇每年开展不少于1次的地质灾害防治知识培训。同时,每年针对重要地质灾害隐患点和极高—高风险区的受威胁群众开展至少1次防灾应急演练,达到提升全社会地质灾害避险撤离和自救互救能力的效果。
3.5 “点面双控”的制度建设
制度建设是“点面双控”体系的最终环节,完善的制度建设可以让“点面双控”体系真正的落到实处和高效运行。因此,在制定四川省“隐患点+风险区”双控相关制度过程中应着重解决地质灾害防范网格管理体系建设的选聘要求和职责分工、二维码建设的宣传和操作培训、山区城镇安全岛建设的要求和建设标准、风险区(斜坡)动态调整的程序流程和职责划分、特殊岩土体发育地区的特色管控措施等方面的难点,达到显著提升全社会风险管控能力的目标。
4. 结论及建议
通过在四川省喜德县探索开展地质灾害“点面双控”,构建了风险调查评价与动态调整、监测预警与响应处置、风险常态管理与防御、科普宣传与培训演练、制度建设五个板块的点面双控体系。
(1)喜德县经过近5年的持续建设,建成了“点控”和“面控”监测预警网络,提高了风险隐患监测覆盖面;通过构建县级精细化降雨预警模型,提升“点面双控”预警准确度。梳理的不同工况下隐患点和风险区的响应流程,完善了“点面双控”责任体系,提高了响应效率。
(2)采用红外探测声光文字预警装置、乡镇级地质灾害隐患点和风险区信息图、风险区告示牌、安全岛建设、研发地质灾害“点面双控”数字化管控与决策支持系统等方法,探索了流动人员管控、信息牌建设、安全岛建设,提高“点面双控”常态防御能力与管理水平,推动防御和管理向数字化和智能化转变。
(3)“点面双控”是长期、动态的过程,调查评价与动态调整时,应结合县域1∶5万地质灾害风险普查成果和1∶1万斜坡地质灾害隐患风险详查成果,采用空天地一体化的新技术新方法,提高“点控”和“面控”的针对性和时效性。
(4)应推动地质灾害“点面双控”持续向数字化、智能化方向发展,在探索与实践过程中,仍有不少亟待解决的问题,包括:尽快出台相关制度法规,明确风险防控责任和奖惩办法;继续推进地质灾害气象风险预警预报网络建设和综合信息平台建设,探索地质灾害多参数(雨量、位移、泥位等)综合预警预报等。
-
表 1 研究区主要地层岩性表
Table 1 Lithology table of main strata in the study area
地质时代 地层单元及代号 岩性概述 第四系 冲积层(Qal) 岩性主要为淤泥质土、粉质黏土、粉砂及卵石,零星分布于研究区东北部的北江沿岸、
浈阳湖周边及东部的污水厂附近坡积层(Qdl) 岩性主要为粉质黏土,局部含风化角砾,层厚0.1~17.3 m,平均层厚5.19 m,主要分布于研究区东北部、中部及南部 残积层(Qel) 岩性主要为粉质黏土,含较多测水组泥质岩类风化残留物及泥岩碎块,局部夹黑色有机质,
层厚1.3~28.5 m,平均层厚8.97 m,在研究区内大部分区域均有分布石炭系 石磴子组(C1s) 岩性以灰岩为主,次为炭质灰岩,发育网状方解石细脉,岩质脆硬,局部可见溶蚀现象 表 2 断裂特征统计表
Table 2 Statistical table of fracture characteristics
断裂名称 断裂特征 F1-1 NE向展布,走向约20°~40°为推测隐伏断裂,推测断裂层顶深度12.50~31.40 m,断裂宽度约50~100 m,区内延伸长度约1.0 km F1-2 NE向展布,走向约25°~35°,为推测隐伏断裂,推测断裂层顶深度6.20~25.60 m,断裂宽度约50~100 m,区内延伸长度约1.1 km F1-3 NE向展布,走向约5°~25°,为推测隐伏断裂,推测断裂层顶深度14.50~16.80 m,断裂宽度约20~30 m,研究区内延伸长度约0.3 km 表 3 研究区塌陷坑基本特征表
Table 3 Basic characteristics of karst collapse sinkholes in the study area
编号 直径或(长轴×短轴)/m 平面形态 发生日期 TK1 24.5×19.3 椭圆形 2020-11-28 TK2 9 圆形 2020-11-28 TK3 7 圆形 2020-11-28 TK4 5.8×3 椭圆形 2020-11-28 TK5 14×13.6 椭圆形 2020-11-28 TK6 4 近似圆形 2020-11-28 TK7 3 近似圆形 2020-11-28 TK8 10 近似圆形 2020-11-28 TK9 3.2 近似圆形 2020-12-01 TK10 5 近似圆形 2020-11-28 TK11 5.5×4.6 近似椭圆形 2020-11-28 TK12 6 近似圆形 2020-12-02 TK13 6 圆形 2020-12-03 TK14 5 圆形 2020-12-09 TK15 3.3×2.5 椭圆形 2020-12-01 TK16 9×5 椭圆形 2020-12-14 TK17 7 圆形 2020-12-16 TK18 15 圆形 2020-11-28 TK19 1 近似圆形 2020-11-28 TK20 2 圆形 2020-12-16 TK21 6×4.5 椭圆形 2020-11-28 TK22 3 圆形 2020-12-28 TK23 4.5 圆形 2020-11-30 TK24 2 圆形 2020-12-30 TK25 7 圆形 2020-12-29 TK26 6×4.2 椭圆形 2021-01-11 TK27 5 圆形 2021-02-11 TK28 4×3 椭圆形 2020-11-28 TK29 5×4 椭圆形 2021-03-06 TK30 5×4 椭圆形 2021-03-07 TK31 1.5 圆形 2021-03-16 -
[1] 赵建军. 广东省英德市地质灾害发育特征及形成条件研究[J]. 地下水,2018,40(3):108 − 109. [ZHAO Jianjun. Research on geological disaster development characteristics and formation conditions in Yingde City,Guangdong Province[J]. Ground Water,2018,40(3):108 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO Jianjun . Research on geological disaster development characteristics and formation conditions in Yingde City, Guangdong Province[J]. Ground Water,2018 ,40 (3 ):108 −109 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 周心经,郭宇,郑小战,等. 广州市白云区夏茅村岩溶地面塌陷特征及致灾因素和风险分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):63 − 71. [ZHOU Xinjing,GUO Yu,ZHENG Xiaozhan,et al. karst collapse characteristics,disaster factors and risk analysis in Xiamao Village,Baiyun District,Guangzhou City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):63 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU Xinjing, GUO Yu, ZHENG Xiaozhan, et al . karst collapse characteristics, disaster factors and risk analysis in Xiamao Village, Baiyun District, Guangzhou City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (6 ):63 −71 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 王恒,赵魁,赵建军,等. 广东省英德市英城街道城南地面塌陷地质灾害应急勘查报告[R]. 广州:广东省化工地质勘查院,2021. [WANG Heng,ZHAO Kui,ZHAO Jianjun,et al. Emergency exploration report of ground collapse geological disaster in the south of Yingcheng sub district,Yingde City,Guangdong Province[R] Guangzhou:Guangdong Institute of Chemical Geology,2021. (in Chinese) WANG Heng, ZHAO Kui, ZHAO Jianjun, et al. Emergency exploration report of ground collapse geological disaster in the south of Yingcheng sub district, Yingde City, Guangdong Province[R] Guangzhou: Guangdong Institute of Chemical Geology, 2021. (in Chinese)
[4] 韩庆定,罗锡宜,易守勇,等. 广东佛山市高明区三洲盆地岩溶塌陷发育特征与时空分布规律[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):131 − 139. [HAN Qingding,LUO Xiyi,YI Shouyong,et al. Characteristics and spatial-temporal distribution law of karst collapse in Sanzhou Basin in Gaoming District of Foshan City,Guangdong Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):131 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN Qingding, LUO Xiyi, YI Shouyong, et al . Characteristics and spatial-temporal distribution law of karst collapse in Sanzhou Basin in Gaoming District of Foshan City, Guangdong Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (3 ):131 −139 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 于贺艳. 武广客运专线英德段岩溶塌陷模式及致塌因素的研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2006. [YU Heyan. Study on the karst collapse mode and the factors of collapse in Ying de df special railway line for passenger transport from Wu han to Guang zhou[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2006. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU Heyan. Study on the karst collapse mode and the factors of collapse in Ying de df special railway line for passenger transport from Wu han to Guang zhou[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 卢丽,邹胜章,赵一,等. 桂林会仙湿地狮子岩地下河系统水循环对降水的响应[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):63 − 72. [LU Li, ZOU Shengzhang, ZHAO Yi, et al. Response of water cycle to precipitation in Shizhiyan underground river system in Huixian wetland of Guilin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):63 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract) LU Li, ZOU Shengzhang, ZHAO Yi, et al . Response of water cycle to precipitation in Shizhiyan underground river system in Huixian wetland of Guilin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022 ,49 (5 ):63 −72 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[7] 吴远斌,罗伟权,殷仁朝,等. 重庆市龙泉村——庆丰山村岩溶塌陷分布规律与成因机制[J]. 中国岩溶,2021,40(6):932 − 942. [WU Yuanbin,LUO Weiquan,YIN Renchao,et al. Distribution law and genetic mechanism of karst collapse in Longquan Village-Qingfengshan Village,Chongqing[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2021,40(6):932 − 942. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Yuanbin, LUO Weiquan, YIN Renchao, et al . Distribution law and genetic mechanism of karst collapse in Longquan Village-Qingfengshan Village, Chongqing[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2021 ,40 (6 ):932 −942 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 中国地质灾害防治工程行业协会. 岩溶地面塌陷防治工程勘查规范(试行):T/CAGHP 076—2020[S]. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社,2020. [China Geological Disaster Prevention and Control Engineering Industry Association. Code for geological investigation of karst collapse prevention:China University of Geoscience Press,T/CAGHP 076—2020[S]. 2020. (in Chinese) China Geological Disaster Prevention and Control Engineering Industry Association. Code for geological investigation of karst collapse prevention: China University of Geoscience Press, T/CAGHP 076—2020[S]. 2020. (in Chinese)
[9] 韩庆定,罗锡宜. 广东佛山市高明区李家村岩溶塌陷群成因机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):56 − 64. [HAN Qingding,LUO Xiyi. Analysis on the formation mechanism and development process of karst collapses in Lijia Village,Gaoming District of Foshan City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):56 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN Qingding, LUO Xiyi . Analysis on the formation mechanism and development process of karst collapses in Lijia Village, Gaoming District of Foshan City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (4 ):56 −64 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] 康晓波,王宇,张华,等. 云南高原岩溶塌陷发育特征及成因机制[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(5):50 − 58. [KANG Xiaobo, WANG Yu, ZHANG Hua, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of karst collapse in Yunnan Plateau[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(5):50 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract) KANG Xiaobo, WANG Yu, ZHANG Hua, et al . Characteristics and formation mechanism of karst collapse in Yunnan Plateau[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (5 ):50 −58 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 卢薇,易顺民. 广州市大坦沙岛岩溶塌陷成因分析及防治对策[J]. 安全与环境工程,2021,28(4):121 − 130. [LU Wei,YI Shunmin. Formation analysis and prevention and remediation measures of karst collapse in datansha island,Guangzhou[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2021,28(4):121 − 130. (in Chinese with English abstract) LU Wei, YI Shunmin . Formation analysis and prevention and remediation measures of karst collapse in datansha island, Guangzhou[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2021 ,28 (4 ):121 −130 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 李华明,张永辉,胡志平,等. 峨汉高速庙子坪隧道岩溶发育特征及工程效应分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):92 − 98. [LI Huaming,ZHANG Yonghui,HU Zhiping,et al. Analysis of karst development characteristics and influence of Miaoziping tunnel in E-Han expressway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):92 − 98. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Huaming, ZHANG Yonghui, HU Zhiping, et al . Analysis of karst development characteristics and influence of Miaoziping tunnel in E-Han expressway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (1 ):92 −98 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 郑小战,郭宇,戴建玲,等. 广州市典型岩溶塌陷区岩溶发育及影响因素[J]. 热带地理,2014,34(6):794 − 803. [ZHENG Xiaozhan,GUO Yu,DAI Jianling,et al. karst development and influencing factors in typical karst collapse districts of Guangzhou[J]. Tropical Geography,2014,34(6):794 − 803. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG Xiaozhan, GUO Yu, DAI Jianling, et al . karst development and influencing factors in typical karst collapse districts of Guangzhou[J]. Tropical Geography,2014 ,34 (6 ):794 −803 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 蔡建斯,龚鹏,任宏剑. 深圳市某片区岩溶塌陷致塌成因分析及预防措施[J]. 中国矿业,2022,31(2):173 − 179. [CAI Jiansi,GONG Peng,REN Hongjian. Cause analysis and preventive measures of karst collapse in a certain area of Shenzhen City[J]. China Mining Magazine,2022,31(2):173 − 179. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2022.02.027 CAI Jiansi, GONG Peng, REN Hongjian . Cause analysis and preventive measures of karst collapse in a certain area of Shenzhen City[J]. China Mining Magazine,2022 ,31 (2 ):173 −179 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2022.02.027 -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 彭双庆,刘朋飞,陈刚,王丽萍,张伟,罗文文,景熙亮. 信息量法与随机森林耦合模型和临界月平均降雨阈值的区域滑坡危险性评价与区划——以重庆市涪陵区为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2025(01): 131-145 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:







 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS