Analysis and application of safety risks for gas pipelines in karst sinkhole-prone areas based on the D/I-MICMAC-VS integrated method
-
摘要: 为降低岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道的风险水平,基于人、物、环境、管理4类事故诱因,选用DEMATEL/ISM法厘清系统因素间的层次结构和因果关系,结合MICMAC法分析风险因素的依赖度和驱动力,并基于Visual Studio平台开发了“岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道风险分析软件”,形成了一种D/I-MICMAC-VS集成风险分析方法并开展实例研究。结果表明:(1)岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道风险因素分布于6个层级,通过对表层直接因素的严格管理可以在短期内降低风险事故发生的可能性;中层间接因素在系统中起承上启下作用;只有重视深层根本因素,才能够从根本上对燃气管道事故进行控制。(2)自发集群是燃气管道事故风险管控的关键抓手,通过优先干预可对事故防治起到显著作用;独立集群通过自身的变化发展直接影响系统的风险水平;联动集群对事故的演化发展起到传递推动作用。只有厘清诱发依赖集群变化的深层根本因素才能实现有效风险管控。
-
关键词:
- DEMATEL/ISM法 /
- MICMAC法 /
- Visual Studio /
- 岩溶塌陷;隐患区 /
- 燃气管道 /
- 风险分析
Abstract: To mitigate the risk of gas pipelines in karst sinkhole-prone areas, this study employs the DEMATEL/ISM method to elucidate the hierarchical structure and causal relationships among various factors in the system, considering four categories of accident causes: human, material, environment and management. Additionally, the MICMAC method is utilized to analyze the dependence and driving force of risk factors. Utilizing the Visual Studio platform, the software for risk analysis of gas pipelines in karst sinkhole-prone areas is developed. This research introduces the D/I-MICMAC-VS integrated risk analysis method and provides an example analysis. The results demonstrate that: (1) The risk factors for gas pipelines in karst sinkhole-prone areas are distributed across six levels. The possibility of risk accidents can be reduced in the short term by rigorously managing surface-level direct factors, while middle-level indirect factors play an intermediary role in the system. Effective control of gas pipeline accidents can only be achieved by addressing deep-rooted factors fundamentally. (2) The spontaneous cluster serves as a key element for risk management and control of gas pipeline accidents, and prioritized intervention significantly aids in accident prevention. The independent cluster directly influences the system’s risk level through its own changes and development. The linkage cluster plays a pivotal role in transmitting and promoting the evolution and development of accidents. Effective risk management and control can be achieved by discerning the deep root factors that inducing changes in the dependency cluster.-
Keywords:
- DEMATEL/ISM method /
- MICMAC method /
- Visual Studio /
- karst sinkhole; prone area /
- gas pipeline /
- risk analysis
-
0. 引言
随着“碳达峰”“碳中和”目标的进一步提出,天然气由于其清洁、高效、稳定、灵活、经济等优点逐渐成为国民经济社会发展的主体能源。由于埋地管道与岩土直接接触,因而不可避免地受到岩土活动的影响[1]。我国西南一带岩溶面积占地区面积的三分之一以上,地震、滑坡等地质灾害频发[2 − 3],降水强度较大,极易引发岩溶塌陷导致埋地管道变形、悬空甚至断裂,不仅会给人类的生命财产造成极大的损失,而且也对燃气普及产生巨大的负面作用,严重影响中国能源系统的清洁低碳转型进程。因此,有必要系统地研究造成岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道事故的本质风险因素,为社会防灾减灾提供理论依据。
近年来,针对燃气管道安全风险分析的研究主要是以事故树法、贝叶斯网络、模糊综合评价法为主。Li等[4]基于贝叶斯网络从“人-机械-环境-管理”四个维度开展了城市埋地燃气管道事故的风险因素分析。黄健陵等[5]基于模糊事故树方法从“人-机-料-法-环”五个维度开展了施工现场地下燃气管线泄漏事故的风险因素分析。骆正山等[6]提出了基于事故树分析与动态贝叶斯网络模型的城市燃气管道泄漏事故风险诊断方法,并结合某燃气管道泄漏爆炸事件开展风险因素的实例分析。目前,针对燃气管道风险因素的研究主要是将其当作孤立的事物,而未考虑因素间的耦合作用,且忽略了不同层级风险因素间的异质性影响效应。因此,有必要立足多级递阶和系统安全角度对燃气管道的风险分析进行全面研究。
自周德群等[7]提出决策实验室分析法(decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory,DEMATEL)和解释结构模型(interpretative structural modeling method,ISM)存在一定共性,可形成集成方法后,许多学者将其应用于风险因素分析中,如王军武等[8]以DEMATEL-ISM法构建了装配式建筑工程吊装事故的风险因素辨识模型,明确了风险因素间的内在关联和层次结构。总之,DEMATEL/ISM法能够将具有耦合关系的风险因素系统解构为直观的多级递阶模型。但与此同时,由于DEMATEL/ISM法不能体现同一层级因素对下一层级因素的作用异质性,因此可以结合交叉影响矩阵相乘法(cross-impact matrix multiplication applied to classification,MICMAC)实现多级递阶结构由源到链的更深层次研究。MICMAC法基于风险因素的关系矩阵,确定各因素的依赖度和驱动力,并通过归纳分类把握风险因素在系统中所起的实质性作用[9]。
基于此,本文提出一种岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道D/I-MICMAC-VS集成风险分析方法。该方法在Visual Studio环境下开发“岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道风险分析软件”,兼顾因果连锁和轨迹交叉理论搭建事故复合致因模型,基于DEMATEL/ISM法确定系统因素间的层次结构和因果关系,分析引发事故的表层直接原因、中层间接原因和深层根本原因,并结合MICMAC法确定各因素的依赖度和驱动力,将系统中所有因素划分为独立集群、依赖集群、联动集群和自发集群。通过MICMAC法的实质性作用分析弥补DEMATEL/ISM法不能体现同一层级因素对下一层级因素作用异质性的缺陷,借助计算机数值动态分析实现风险研究的智能化、高效化,从而助力决策者厘清复杂系统结构、掌握关键风险因素,为从根本上遏制岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道事故提供科学合理依据。
1. D/I-MICMAC-VS集成风险分析方法
1.1 岩溶塌陷的形成原因
岩溶塌陷是在具备岩溶洞隙、一定厚度松散盖层以及地下水活动等基本形成条件的基础上,在多种自然因素以及人为因素的耦合作用下产生的一种土体塌陷现象,具体形成原因汇总于表1。
表 1 岩溶塌陷形成原因Table 1. Formation causes of karst collapse类型 具体形成原因 自然因素 地下水活动 地下水活动对岩溶塌陷的诱发作用主要表现在溶蚀、渗透潜蚀、真空吸蚀、地下水位波动的散解、
地下水的水击等方面大气降水及地表水渗透潜蚀 大气降水与地表水借由土体缝隙逐层下渗或通过落水洞、漏斗等以渗漏直接注入的方式向岩溶水
补给,对沿层土体进行潜蚀、淘空地震作用 地震载荷诱发土层错动,导致岩溶土洞顶板破裂坍塌;岩溶洞隙上覆浅埋的松散饱水细粒砂层在地
震作用下引发“土壤液化”现象,导致土体强度降低、土拱结构破坏重力作用 在土拱结构支撑下小尺寸土洞通常趋于稳态,但在外部因素驱动下土洞逐渐向上发育扩展,土洞顶
板在岩溶覆盖层重力作用下持续受力,最终达到强度极限并失稳坍塌人类活动
作用地下工程导致地下水失衡 工程施工极易引起地下水位波动诱发地质失衡,对岩溶土体稳定性造成直接影响 酸碱液化学潜蚀 工业废液通过土层缝隙流入地下后与可溶性物质发生化学反应,加剧岩溶土体的溶蚀作用 占压荷载产生附加压力 城镇化发展带动地表占压载荷的施加将加剧地下土拱结构失稳,诱发岩溶土洞顶板坍塌 1.2 风险因素的遴选
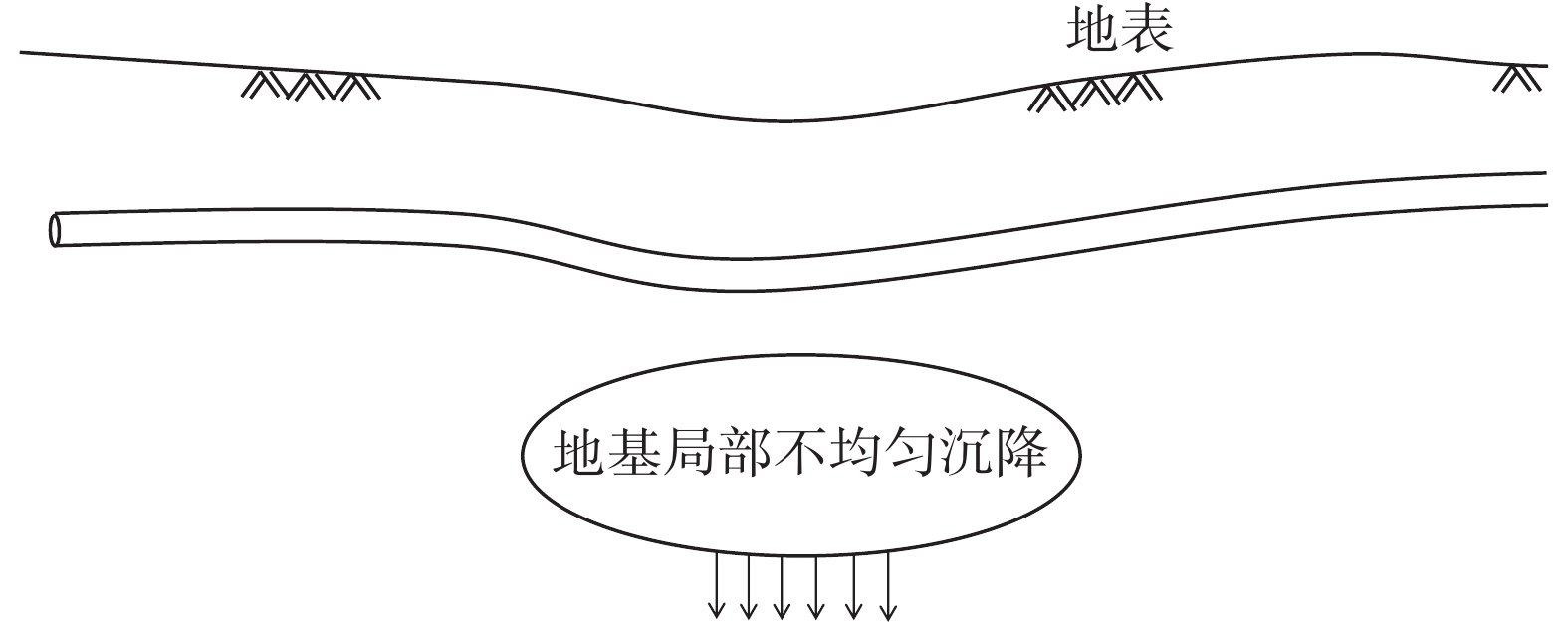
为了保证燃气管道的稳定性并减小外界因素造成的影响,埋地燃气管通常敷设于地下1~3 m,在岩溶发育过程中,埋地管道与管周土体构成了一种特殊受力结构,土体对管道既是一种形变驱动力,同时也是一种运动约束介质。岩溶发育过程中埋地管道的变形特征如图1所示。
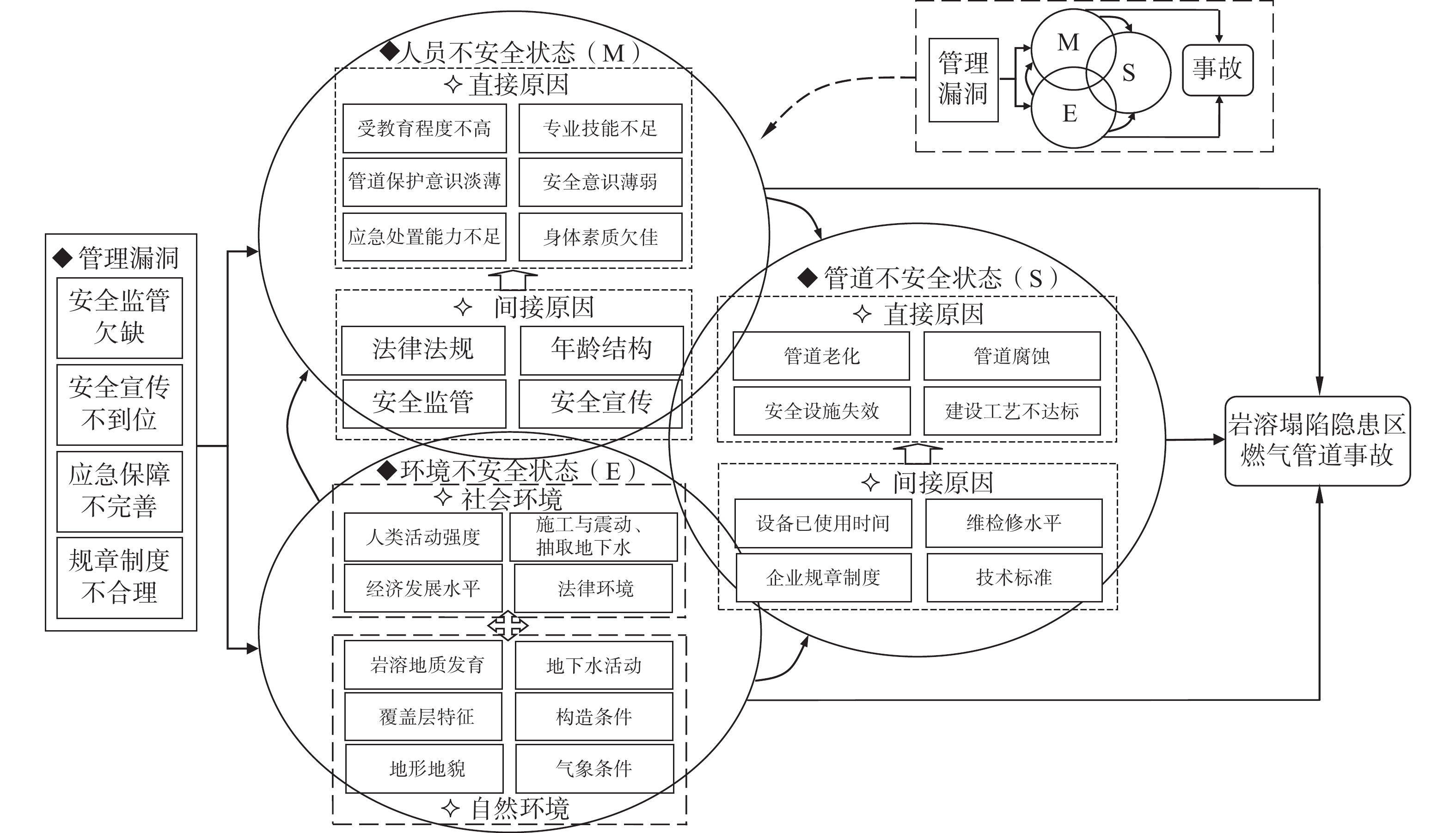
根据国家安全生产监督管理部门网站及相关学术文献,收集了近30例岩溶塌陷隐患区管道失效事故案例,并将其作为统计资料源。通过计量分析可得,虽然岩溶塌陷隐患区管道失效事故的诱因复杂多变,但均可以归纳为“人员不安全状态-管道不安全状态-环境不安全状态-管理漏洞”四个维度。考虑到因果连锁理论从纵向角度分析了风险因素间的动态因果关系,轨迹交叉理论从横向角度分析了不同风险因素间交互作用而最终导致事故发生的演化路径。故兼顾双重视角建立岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道轨迹交叉-因果连锁事故复合致因模型,具体如图2所示。
基于此,结合岩溶塌陷的形成原因及其对管道的损伤特征,并采用频度统计法将频度不低于3的指标纳入岩溶塌陷隐患区管道风险因素体系,最终选定24个风险因素并逐一编号,具体汇总于表2。
表 2 风险因素指标体系Table 2. Risk factor indicator system维度 具体风险因素 人员不安全状态 受教育程度不高(e1)、专业技能不足(e2)、管道保护意识淡薄(e3)、安全意识薄弱(e4)、应急处置能力不足(e5) 管道不安全状态 管道老化(e6)、管道腐蚀(e7)、安全设施失效(e8)、建设工艺不达标(e9) 环境不安全状态 人类活动强度(e10)、施工与震动(e11)、抽取地下水(e12)、经济发展水平(e13)、法律法规(e14)、岩溶地质发育(e15)、
地下水活动(e16)、覆盖层特征(e17)、构造条件(e18)、地形地貌(e19)、气象条件(e20)管理漏洞 安全监管欠缺(e21)、安全宣传不到位(e22)、应急保障不完善(e23)、规章制度不合理(e24) 1.3 基于DEMATEL/ISM法的层次结构分析
DEMATEL/ISM法的具体算法[10 − 12]步骤如下:
(1)构建直接影响矩阵。针对燃气管道行业专家和工作人员开展访谈调研,根据反馈结果得出直接影响矩阵U。
(2)计算综合影响矩阵。对直接影响矩阵进行规范化处理得到矩阵M,具体方法如式(1)所示。
$$ {\boldsymbol{M}} = \frac{1}{{\mathop {\max }\limits_{1 \leqslant i \leqslant n} \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^n {{u_{ij}}} }}{\boldsymbol{U}} $$ (1) 式中
$ {u_{ij}} $ ——系统因素ei对ej的直接影响程度;$ \mathop {\max }\limits_{1 \leqslant i \leqslant n} \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^n {{u_{ij}}} $ ——矩阵行因素之和的最大值,经过规 范化处理后矩阵M内各因素均满 足0<mij<1。为了综合评估各个因素对整体风险系统的影响效应,考虑到多元因素间的直接作用和间接传导路径,将规范化处理后的矩阵M进一步转化为综合影响矩阵V,具体方法如(2)所示。
$${\boldsymbol{ V}} = {{\boldsymbol{M}}^1} + {{\boldsymbol{M}}^2} + \cdots + {{\boldsymbol{M}}^n} = \displaystyle\sum_{i = 1}^n {{{\boldsymbol{M}}^i}} $$ (2) 由于
$ 0 < {m_{ij}} < 1 $ ,当$ n \to \infty $ 时,$ {{\boldsymbol{M}}^{n - 1}} \to 0 $ ,即可采用式(3)近似计算出综合影响矩阵V。$$ {\boldsymbol{V}} = {\boldsymbol{M}}{({\boldsymbol{I}} -{\boldsymbol{ M}})^{ - 1}} $$ (3) 式中:I——单位矩阵。
(3)确定中心度和原因度。风险因素ei的影响度pi和被影响度qi,中心度si(表征风险因素在系统中占据的重要程度[13])和原因度ti(原因度小于0表示该因素对其他因素不存在显著影响,属于结果因素;反之则属于原因因素)的计算公式分别为:
$$ {p_i} = \sum\limits_{j = 1}^n {{v_{ij}}} $$ (4) $$ {q_i} = \sum\limits_{j = 1}^n {{v_{ji}}} $$ (5) $$ {s_i} = {p_i} + {q_i} $$ (6) $$ {t_i} = {p_i} - {q_i} $$ (7) 式中:
$ {v}_{ij}、{v}_{ji} $ ——矩阵V的i行j列或i列j行对应的因 素,i = 1, 2, ···, n,j = 1, 2, ···, n。(4)构建可达矩阵。考虑到I作为单位矩阵可以表征因素对自身的影响,因此结合单位矩阵I将综合影响矩阵V进一步转化为整体关系矩阵H,具体方法如式(8)所示。
$$ {\boldsymbol{H}} = {\boldsymbol{V}} + {\boldsymbol{I}} = {\left[ {{h_{ij}}} \right]_{n \times n}} $$ (8) 式中:hij——矩阵H的i行j列对应的因素,i = 1, 2, ···, n, j = 1, 2, ···, n。
为了去除影响程度较小的耦合关系,简化研究系统的层次结构,通过给定阈值β变换整体关系矩阵H,从而构建可达矩阵G,具体遵循如下准则:当整体关系矩阵因素hij≥β时,对应可达矩阵因素gij为1;当整体关系矩阵因素hij<β时,对应可达矩阵因素gij为0。阈值β的取值将对系统因素间的因果关系和层次结构分析产生关键影响[14]。
(5)建立多级递阶结构模型。首先基于式(9)和式(10)确定可达矩阵G的可达集合Xi和前因集合Yi,然后验证等式“Xi=Xi∩Yi”是否成立,若成立则表明风险因素ei为底层因素,并且从可达矩阵G中移除第i行和第i列的所有元素。重复以上步骤,直至厘清所有风险因素的层级,并依据因素划分的前后顺序,最终建立起多级递阶结构模型。
$$ {{\boldsymbol{X}}_i} = \{ e{}_i{\text{|}}{e_i} \in {\boldsymbol{E}},{h_{ij}} \ne 0\} $$ (9) $$ {{\boldsymbol{Y}}_i} = \{ e{}_i{\text{|}}e{}_i \in {\boldsymbol{E}},{h_{ji}} \ne 0\} $$ (10) 式中:E——所有风险因素的集合;
ei——序号为i的某一具体风险因素,i = 1, 2, ···, n。
1.4 基于MICMAC法的实质性作用分析
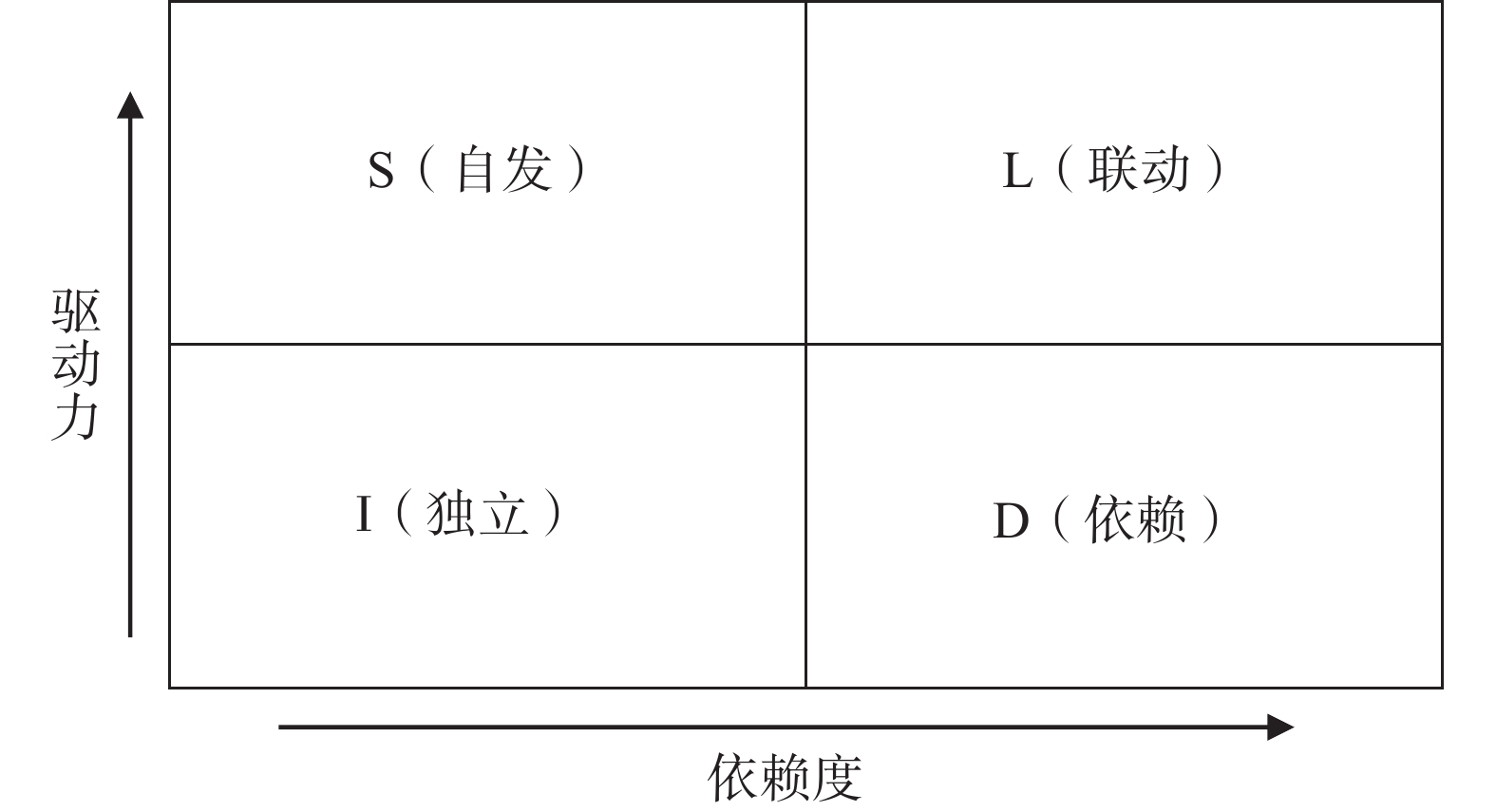
由于在DEMATEL/ISM法中,同一层级因素对下一层级因素的差异化作用效果无法得以体现。为弥补这一缺陷,本文提出采用MICMAC法对构建的多级递阶结构模型进行更深层次的总结分析,以明确风险演化控制的关键点。MICMAC法的核心思想为依据关键风险因素间的直接和间接影响,并结合依赖度和驱动力数值将所有因素归纳划分为独立、依赖、联动和自发4类集群,从而识别关键因素并把握其在系统中的实质性作用[15]。
MICMAC法的分析结果可借助Cartesian坐标系进行展示,通常以横坐标表征依赖度,纵坐标表征驱动力。其中,依赖度等于对该因素造成影响的多元因素数目,驱动力等于受到该因素影响的多元因素数目[16]。基于Cartesian坐标系的MICMAC分析结果如图3所示。
在所划分的四个集群中,自发集群包含的风险因素驱动力较强但依赖度较弱,因此这类因素在系统中的地位通常最为关键,管理层在对其进行处理时应格外谨慎。联动集群包含的风险因素驱动力和依赖度均较强,作为不稳定因素,与其相关的任何行为变动都会对其他因素造成影响,并反过来对自身产生反射作用。独立集群包含的风险因素驱动力和依赖度均较弱,其通常直接对顶层目标造成影响。依赖集群包含的风险因素驱动力较弱但依赖度较强,一般属于最终风险因素。
1.5 岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道风险分析软件编制
基于DEMATEL/ISM和MICMAC方法,结合Visual Studio平台开发“岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道风险分析软件”,从而实现风险因素分析的智能化、高效化,提高岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道安全风险的分析效率。软件旨在实现以下功能:
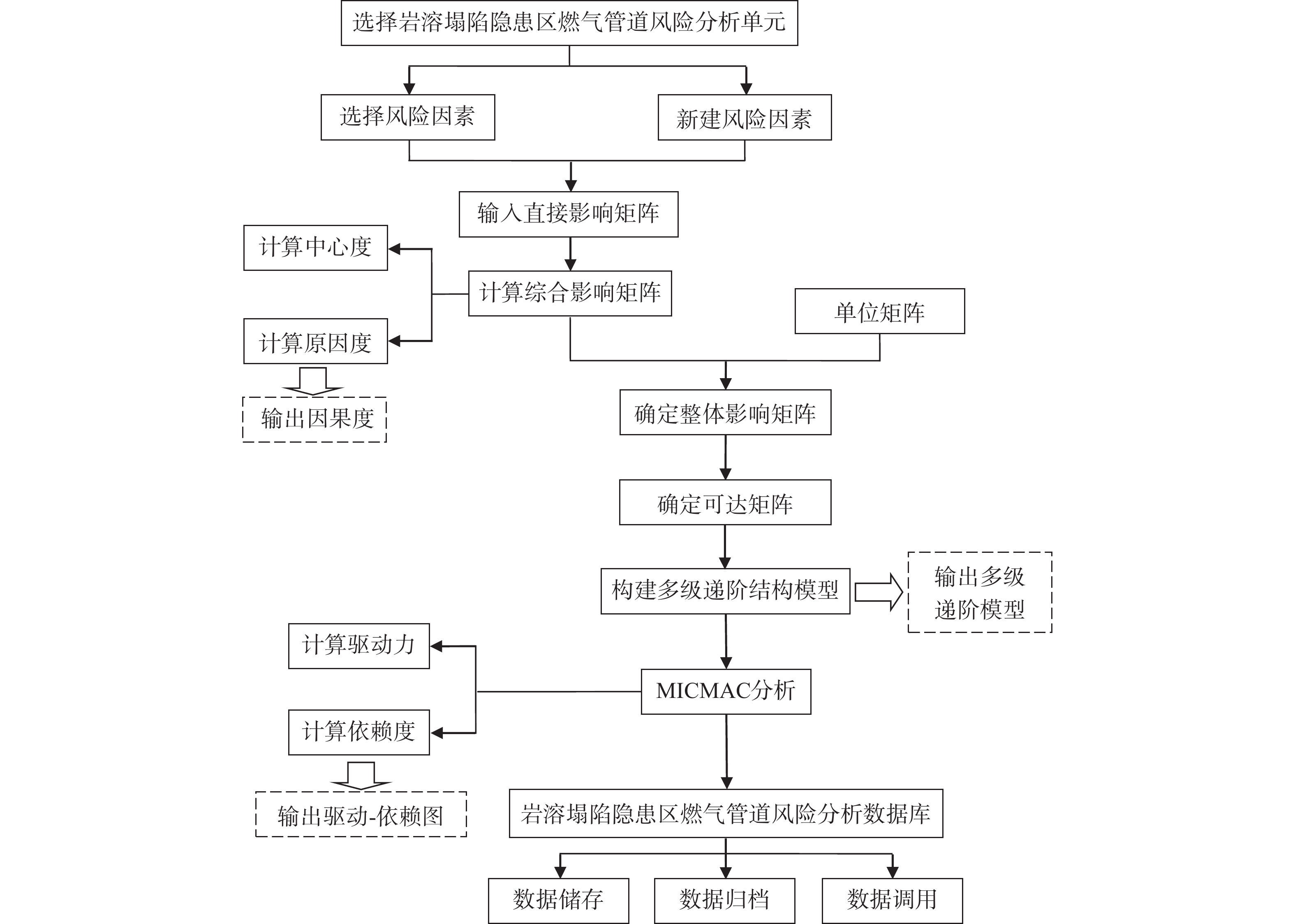
(1)基于DEMATEL/ISM方法分析风险因素的层次结构。基于前文构建的风险因素指标体系,选择开展风险分析的子系统单元(人员子系统、管道子系统、环境子系统、管理子系统),在输入结合专家经验的直接影响矩阵后,软件首先计算得出综合影响矩阵并输出中心度和原因度,接着计算得出可达矩阵且建立起多级递阶结构模型,并以可视化图表形式输出,便于用户对岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道多元风险因素间的因果关系和层次结构进行直观的了解和把握。
(2)基于MICMAC方法分析风险因素的实质作用。为了弥补DEMATEL/ISM方法无法体现同一层级因素对下一层级因素影响差异的缺陷,结合MICMAC方法计算不同风险因素的依赖度和驱动力,并以可视化图表形式输出,从而对多级递阶结构模型进行更深层次分析。基于实质性作用分析结果开展风险因素的归纳分类,便于用户直观地了解和把握关键驱动因素和主要依赖因素。与此同时,借助Microsoft Access数据库以实现不同子系统风险分析数据的储存及归档,在研究后期便可通过数据调用功能,针对岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道整体的风险演化特征进行总结分析,从而明确风险管控的关键抓手和着力点。
软件总体编制思路如图4所示。
2. 案例分析
贵州某岩溶区段位于纳雍—开阳东西向构造带与织金北东向构造带的交汇处,在内、外营力的共同雕塑下区段内形成了千姿百态的喀斯特地貌景观。近年来,在矿山无序开采、地下洞穴发育、持续强降雨及地震活动等多重因素影响下,每年发生明显地面塌陷40余次,并愈发呈现出增强趋势。选择该区段内一埋地燃气管道项目作为研究案例,其基础数据的获取主要基于燃气管道风险管理专家的意见,并结合了该管段的岩溶勘探和实地调研数据。基于DEMATEL/ISM和MICMAC方法,结合“岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道风险分析软件”实证分析该研究案例中风险因素的层次结构及实质性作用。
2.1 多级递阶结构模型确定
针对管道风险因素间的相互关系和影响程度进行研判,通过“0~4”的差异化赋值划分5个等级[17],参考岩溶勘探、实地调研和专家意见数据构建直接影响矩阵U,具体如表3所示。
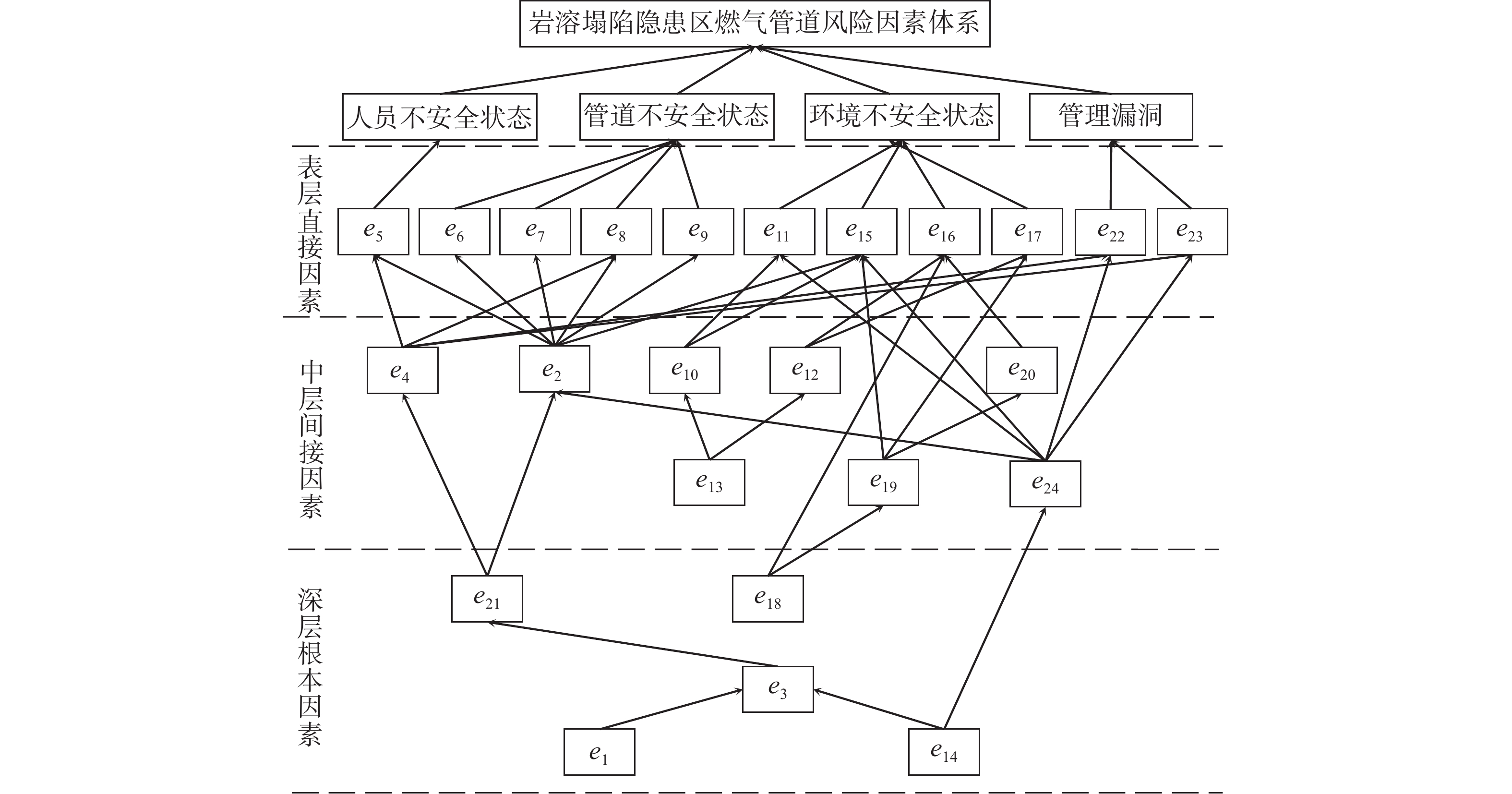
表 3 风险因素的直接影响矩阵Table 3. Direct impact matrix of risk factorse1 e2 e3 e4 e5 e6 e7 e8 e9 e10 e11 e12 e13 e14 e15 e16 e17 e18 e19 e20 e21 e22 e23 e24 e1 0 4 4 4 4 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 3 3 e2 2 0 2 2 4 4 4 4 4 0 0 0 0 2 4 2 2 3 3 3 3 2 3 2 e3 0 0 0 4 0 2 2 2 0 3 3 3 0 2 2 0 0 0 2 0 4 4 4 3 e4 0 2 4 0 3 0 0 3 3 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 3 e5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 4 0 e6 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 e7 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 e8 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 e9 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 e10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 3 2 3 3 0 0 3 2 0 0 0 0 e11 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 2 0 3 2 0 3 3 2 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 e12 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 e13 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 4 4 0 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 e14 2 4 4 4 4 2 2 3 4 0 4 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 4 e15 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 3 4 0 0 0 0 0 e16 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 0 3 3 2 2 0 0 0 0 e17 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 e18 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 e19 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 3 3 0 4 4 4 2 0 4 0 0 0 0 e20 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 3 4 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 e21 0 4 0 4 4 4 4 4 4 3 4 6 0 2 3 0 0 3 0 0 0 4 4 4 e22 0 2 4 4 3 2 2 2 3 2 3 3 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 3 2 e23 0 3 2 2 4 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 3 0 0 0 0 3 2 2 0 3 e24 0 4 2 3 3 3 3 3 4 2 4 4 0 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 0 将基础数据输入“岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道风险分析软件”,通过咨询行业专家和决策者取阈值为0.025,构建风险因素多级递阶结构模型如图5所示。
由构建的多级递阶结构模型可以看出:
(1)岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道的多元风险因素分布于6个层级,各层级因素之间具有明显的影响和传递关系,所有因素从直接和间接两个维度通过差异化作用路径和效应对安全风险水平产生影响。
(2)各层级风险因素的作用机理呈现异质性特征,造成岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道安全风险增大的表层直接因素位于多级递阶结构模型的最高层,对管道事故的演化造成直接影响。表层直接因素既包括了人员的不安全状态(应急处置能力不足)和管理漏洞(安全宣传不到位、应急保障不完善),也涵盖了管道的不安全状态(管道老化、管道腐蚀、安全设施失效、建设工艺不达标)和环境的不安全状态(施工与震动、岩溶地质发育、地下水活动、覆盖层特征),是降低岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道事故可能性的首要目标。
(3)中层间接因素在风险系统中起传递作用,将深层根本因素的影响传递给表层直接因素。例如,深层根本因素安全监管欠缺(e21)直接影响中层间接因素专业技能不足(e2)和安全意识薄弱(e4),而中层间接因素专业技能不足(e2)和安全意识薄弱(e4)直接影响表层直接因素应急处置能力不足(e5)、管道腐蚀(e7)、安全设施失效(e8)、建设工艺不达标(e9)、安全宣传不到位(e23)、应急保障不完善(e24)等;深层根本因素构造条件(e18)直接影响中层间接因素地形地貌(e19),中层间接因素地形地貌(e19)一方面直接影响表层直接因素岩溶地质发育(e15)和覆盖层特征(e17),另一方面经由气象条件(e20)间接影响表层直接因素地下水活动(e16)。
(4)深层根本因素位于多级递阶结构的最底层,不受其他因素的作用,并从根源上影响安全事故的发生。对于岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道事故,其深层根本因素为构造条件(e18)、安全监管欠缺(e21)、管道保护意识淡薄(e3)、法律法规(e14)和受教育程度不高(e1)[18]。
2.2 风险因素实质作用确定
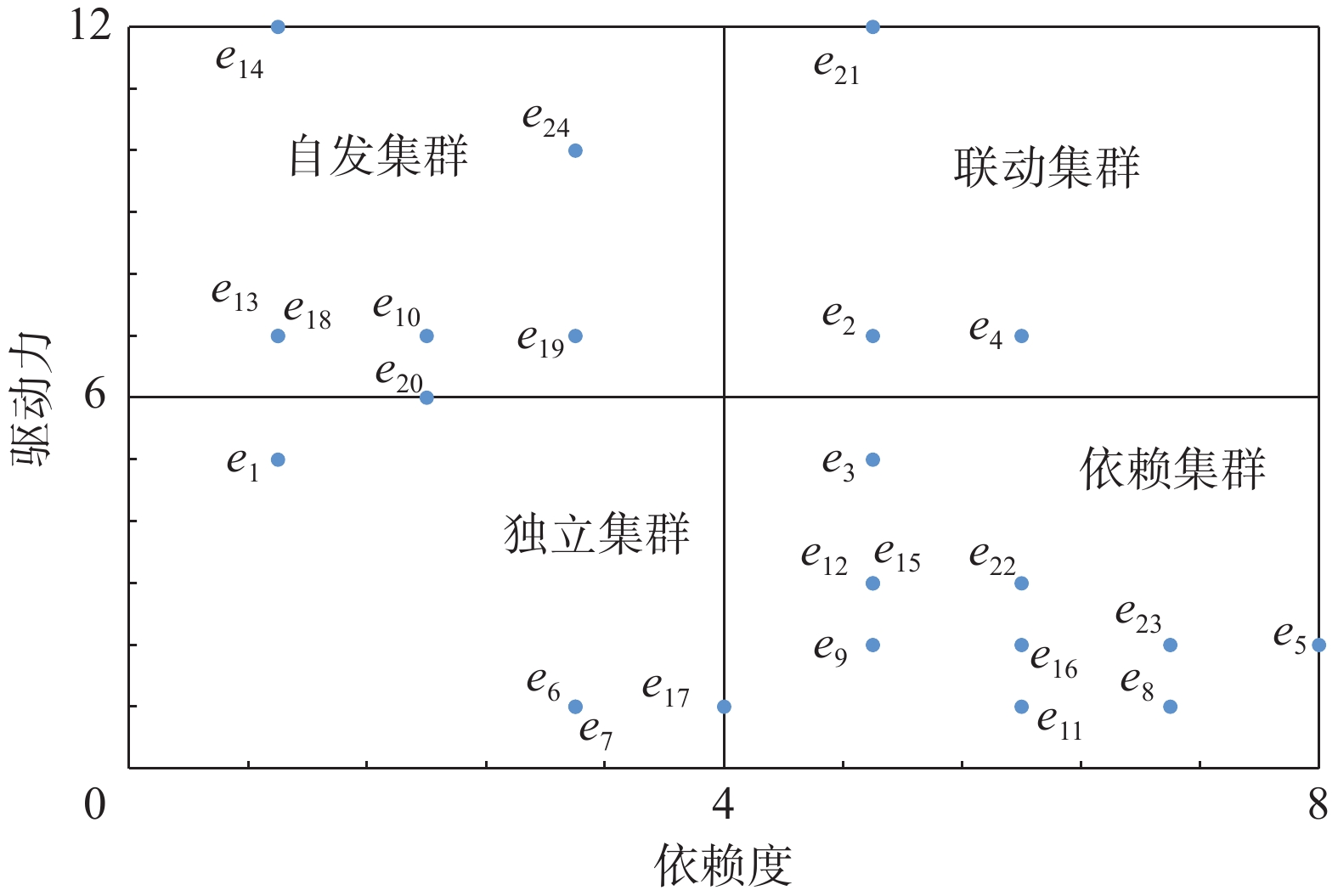
一般而言,依赖度较高的风险因素受到其他因素的影响较大,即需要通过解决多个且位于不同层次的其他因素才能实现该因素的有效规避;而驱动力较高则意味着该类风险因素一旦被有效控制,其余因素可能会由于连锁反应而被同步制约[19 − 20]。根据MICMAC法的基本思想,结合所开发软件进一步构建岩溶塌陷隐患区埋地燃气管道风险因素的依赖度-驱动力图,具体如图6所示。
通过对风险因素依赖度-驱动力图进行分析,可见:
(1)岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道风险因素的自发集群主要包括人类活动强度(e10)、经济发展水平(e13)、法律法规(e14)、构造条件(e18)、地形地貌(e19)、气象条件(e20)以及规章制度不合理(e24),上述因素对其他因素驱动效应显著,是岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道事故风险管控的关键抓手。
(2)独立集群主要包括受教育程度不高(e1)、管道老化(e6)、管道腐蚀(e7)以及覆盖层特征(e17),上述因素在安全事故演化的整个时间跨度内对其他因素呈现低依赖度、低驱动力,通过自身的变化发展直接影响系统整体的风险水平,对独立集群的风险管控应当因地制宜采取针对性措施。
(3)联动集群主要包括专业技能不足(e2)、安全意识薄弱(e4)以及安全监管欠缺(e21),上述因素对其他因素呈现高驱动力、高依赖度,在显著受到自发集群(法律法规、规章制度不合理等)影响的同时对依赖集群(应急处置能力不足、安全设施失效、施工与震动、岩溶地质发育等)也产生较大影响,因此对安全事故的演化发展起到传递推动作用。
(4)依赖集群主要包括管道保护意识淡薄(e3)、应急处置能力不足(e5)、安全设施失效(e8)、建设工艺不达标(e9)、施工与震动(e11)、抽取地下水(e12)、岩溶地质发育(e15)、地下水活动(e16)、安全宣传不到位(e22)、应急保障不完善(e23),上述因素对其他因素依赖效应显著,直接干预难度较大。
3. 结论
(1)将DEMATEL/ISM方法、MICMAC方法和Visual Studio平台相结合对岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道的安全风险进行分析,能够厘清多元耦合效应下系统因素间的层次结构和因果关系,弥补DEMATEL/ISM法不能体现同一层级因素对下一层级因素作用异质性的缺陷,并通过计算机智能测算提高风险分析效率,有助于从根本上遏制灾害隐患区管道安全事故的发生。
(2)岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道的风险因素分布于6个递阶层级,通过差异化的作用路径和效应对整体风险水平产生影响。通过对表层直接因素的严格管理,可以在短期内降低事故发生的可能性;中层间接因素在系统中起承上启下作用,将深层根本因素的影响传递给表层直接因素;只有重视深层根本因素,才能够实现风险的根本性控制。结合分析结果可得,降低安全风险水平的关键在于加强岩溶地质勘探评估、建立长效安全监管机制、完善燃气行业法律法规、营造灾害隐患区良好社会环境。
(3)人类活动强度、法律法规、构造条件等构成的自发集群驱动效应显著,通过优先干预可对事故防治起到显著作用;受教育程度不高、管道老化等构成的独立集群驱动效应和依赖效应均较弱,通过自身的变化发展直接影响整体系统,对其应做到“一事一案”因地制宜采取风险管控措施;专业技能不足、安全监管欠缺等构成的联动集群驱动效应和依赖效应均较强,对安全事故演化发展起到传递推动作用;安全设施失效、岩溶地质发育、应急保障不完善等构成的依赖集群依赖效应显著,只有厘清诱发依赖集群变化的深层根本因素才能实现有效风险管控。
-
表 1 岩溶塌陷形成原因
Table 1 Formation causes of karst collapse
类型 具体形成原因 自然因素 地下水活动 地下水活动对岩溶塌陷的诱发作用主要表现在溶蚀、渗透潜蚀、真空吸蚀、地下水位波动的散解、
地下水的水击等方面大气降水及地表水渗透潜蚀 大气降水与地表水借由土体缝隙逐层下渗或通过落水洞、漏斗等以渗漏直接注入的方式向岩溶水
补给,对沿层土体进行潜蚀、淘空地震作用 地震载荷诱发土层错动,导致岩溶土洞顶板破裂坍塌;岩溶洞隙上覆浅埋的松散饱水细粒砂层在地
震作用下引发“土壤液化”现象,导致土体强度降低、土拱结构破坏重力作用 在土拱结构支撑下小尺寸土洞通常趋于稳态,但在外部因素驱动下土洞逐渐向上发育扩展,土洞顶
板在岩溶覆盖层重力作用下持续受力,最终达到强度极限并失稳坍塌人类活动
作用地下工程导致地下水失衡 工程施工极易引起地下水位波动诱发地质失衡,对岩溶土体稳定性造成直接影响 酸碱液化学潜蚀 工业废液通过土层缝隙流入地下后与可溶性物质发生化学反应,加剧岩溶土体的溶蚀作用 占压荷载产生附加压力 城镇化发展带动地表占压载荷的施加将加剧地下土拱结构失稳,诱发岩溶土洞顶板坍塌 表 2 风险因素指标体系
Table 2 Risk factor indicator system
维度 具体风险因素 人员不安全状态 受教育程度不高(e1)、专业技能不足(e2)、管道保护意识淡薄(e3)、安全意识薄弱(e4)、应急处置能力不足(e5) 管道不安全状态 管道老化(e6)、管道腐蚀(e7)、安全设施失效(e8)、建设工艺不达标(e9) 环境不安全状态 人类活动强度(e10)、施工与震动(e11)、抽取地下水(e12)、经济发展水平(e13)、法律法规(e14)、岩溶地质发育(e15)、
地下水活动(e16)、覆盖层特征(e17)、构造条件(e18)、地形地貌(e19)、气象条件(e20)管理漏洞 安全监管欠缺(e21)、安全宣传不到位(e22)、应急保障不完善(e23)、规章制度不合理(e24) 表 3 风险因素的直接影响矩阵
Table 3 Direct impact matrix of risk factors
e1 e2 e3 e4 e5 e6 e7 e8 e9 e10 e11 e12 e13 e14 e15 e16 e17 e18 e19 e20 e21 e22 e23 e24 e1 0 4 4 4 4 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 3 3 e2 2 0 2 2 4 4 4 4 4 0 0 0 0 2 4 2 2 3 3 3 3 2 3 2 e3 0 0 0 4 0 2 2 2 0 3 3 3 0 2 2 0 0 0 2 0 4 4 4 3 e4 0 2 4 0 3 0 0 3 3 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 3 e5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 4 0 e6 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 e7 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 e8 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 e9 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 e10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 3 2 3 3 0 0 3 2 0 0 0 0 e11 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 2 0 3 2 0 3 3 2 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 e12 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 e13 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 4 4 4 0 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 e14 2 4 4 4 4 2 2 3 4 0 4 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 4 e15 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 3 4 0 0 0 0 0 e16 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 0 3 3 2 2 0 0 0 0 e17 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 e18 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 e19 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 3 3 0 4 4 4 2 0 4 0 0 0 0 e20 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 3 4 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 e21 0 4 0 4 4 4 4 4 4 3 4 6 0 2 3 0 0 3 0 0 0 4 4 4 e22 0 2 4 4 3 2 2 2 3 2 3 3 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 3 2 e23 0 3 2 2 4 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 3 0 0 0 0 3 2 2 0 3 e24 0 4 2 3 3 3 3 3 4 2 4 4 0 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 0 -
[1] LI Qiaochu,HE Sha. Research on effect factors of mechanical response of cross-fault buried gas pipeline based on fluid–structure interaction[J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology,2021,143(6):061402. DOI: 10.1115/1.4051366
[2] 李滨,殷跃平,高杨,等. 西南岩溶山区大型崩滑灾害研究的关键问题[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):5 − 13. [LI Bin,YIN Yueping,GAO Yang,et al. Critical issues in rock avalanches in the karst mountain areas of southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):5 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202003060 LI Bin, YIN Yueping, GAO Yang, et al . Critical issues in rock avalanches in the karst mountain areas of southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020 ,47 (4 ):5 −13 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202003060[3] 李华明,蔡乐军,陈南南,等. 基于室内试验的四川峨眉——汉源高速廖山隧道碳酸盐岩溶蚀特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):73 − 84. [LI Huaming,CAI Lejun,CHEN Nannan,et al. Experimental analysis on dissolution characteristics of carbonate rocks in Liaoshan tunnel of Emei-Hanyuan expressway in Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):73 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.04-10 LI Huaming, CAI Lejun, CHEN Nannan, et al . Experimental analysis on dissolution characteristics of carbonate rocks in Liaoshan tunnel of Emei-Hanyuan expressway in Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (4 ):73 −84 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.04-10[4] LI Feng,WANG Wenhe,DUBLJEVIC S,et al. Analysis on accident-causing factors of urban buried gas pipeline network by combining DEMATEL,ISM and BN methods[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries,2019,61:49 − 57. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2019.06.001
[5] 黄健陵,田苾. 基于模糊事故树的施工现场地下管线泄漏风险分析[J]. 安全与环境学报,2017,17(6):2072 − 2078. [HUANG Jianling,TIAN Bi. Risk analysis over the underground pipeline leakage in a construction site based on the fuzzy fault tree[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2017,17(6):2072 − 2078. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2017.06.007 HUANG Jianling, TIAN Bi . Risk analysis over the underground pipeline leakage in a construction site based on the fuzzy fault tree[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2017 ,17 (6 ):2072 −2078 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2017.06.007[6] 骆正山,巫忱忱. 基于FTA-DBN的燃气管道泄漏风险研究[J]. 消防科学与技术,2020,39(3):401 − 404. [LUO Zhengshan,WU Chenchen. Research on risk of gas pipeline leakage based on FTA-DBN[J]. Fire Science and Technology,2020,39(3):401 − 404. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2020.03.031 LUO Zhengshan, WU Chenchen . Research on risk of gas pipeline leakage based on FTA-DBN[J]. Fire Science and Technology,2020 ,39 (3 ):401 −404 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2020.03.031[7] 周德群,章玲. 集成DEMATEL/ISM的复杂系统层次划分研究[J]. 管理科学学报,2008,11(2):20 − 26. [ZHOU Dequn,ZHANG Ling. Establishing hierarchy structure in complex systems based on the integration of DEMATEL and ISM[J]. Journal of Management Sciences in China,2008,11(2):20 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9807.2008.02.003 ZHOU Dequn, ZHANG Ling . Establishing hierarchy structure in complex systems based on the integration of DEMATEL and ISM[J]. Journal of Management Sciences in China,2008 ,11 (2 ):20 −26 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9807.2008.02.003[8] 王军武,陆超. 关联性视角下装配式建筑工程吊装事故致因机理分析[J]. 安全与环境学报,2021,21(3):1158 − 1164. [WANG Junwu,LU Chao. On the cause-result consequence of the hoisting accidents in the prefabricated construction projects from the perspective of relevance[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2021,21(3):1158 − 1164. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2019.1662 WANG Junwu, LU Chao . On the cause-result consequence of the hoisting accidents in the prefabricated construction projects from the perspective of relevance[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2021 ,21 (3 ):1158 −1164 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2019.1662[9] MELEWAR T C,GORANE S J,KANT R. Modelling the SCM enablers:an integrated ISM-fuzzy MICMAC approach[J]. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics,2013,25(2):263 − 286.
[10] PUENTE J,FERNANDEZ I,GOMEZ A,et al. Integrating sustainability in the quality assessment of EHEA institutions:a hybrid FDEMATEL-ANP-FIS model[J]. Sustainability,2020,12(5):1707. DOI: 10.3390/su12051707
[11] LI Yongbo,SANKARANARAYANAN B,THRESH KUMAR D,et al. Risks assessment in thermalpower plants using ISM methodology[J]. Annals of Operations Research,2019,279(1/2):89 − 113.
[12] CHAUHAN,SINGH,JHARKHARIA. An interpretive structural modeling (ISM) and decision-making trail and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) method approach for the analysis of barriers of waste recycling in India[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association,2018,68(2):100 − 110.
[13] 张勇,王祥宇. 基于DEMATEL-ISM-BN的施工人员不安全行为致因研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2020,16(11):110 − 116. [ZHANG Yong,WANG Xiangyu. Study on causes of unsafe behaviors of construction workers based on DEMAREL-ISM-BN[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2020,16(11):110 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Yong, WANG Xiangyu . Study on causes of unsafe behaviors of construction workers based on DEMAREL-ISM-BN[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2020 ,16 (11 ):110 −116 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 冯雨翔. 盐穴地下储气库风险评估研究[D]. 成都:西南石油大学,2019. [FENG Yuxiang. Study on risk assessment of underground gas storage in salt cavern[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Petroleum University,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) FENG Yuxiang. Study on risk assessment of underground gas storage in salt cavern[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] JIANG Xiaoyan, LU Kun, XIA Bo, et al. Identifying significant risks and analyzing risk relationship for construction PPP projects in China using integrated FISM-MICMAC approach[J]. Sustainability,2019,11(19):5206.
[16] HOGEWEG P,HESPER B. Two predators and one prey in a patchy environment:an application of MICMAC modelling[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology,1981,93(2):411 − 432. DOI: 10.1016/0022-5193(81)90113-2
[17] LIANG Yi,WANG Haichao,ZHAO Xinyue. Analysis of factors affecting economic operation of electric vehicle charging station based on DEMATEL-ISM[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering,2022,163:107818.
[18] 李乔楚,陈军华. 基于WSR的岩溶区域管道破坏特征与风险管控措施[J]. 焊管,2022,45(2):32 − 38. [LI Qiaochu,CHEN Junhua. Failure characteristics and risk control measures of pipeline in karst area based on WSR[J]. Welded Pipe and Tube,2022,45(2):32 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.19291/j.cnki.1001-3938.2022.02.005 LI Qiaochu, CHEN Junhua . Failure characteristics and risk control measures of pipeline in karst area based on WSR[J]. Welded Pipe and Tube,2022 ,45 (2 ):32 −38 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.19291/j.cnki.1001-3938.2022.02.005[19] 缪秀梅,陈烨天,米传民. 基于ISM和在线评论的汤山温泉顾客满意度研究[J]. 中国管理科学,2019,27(7):186 − 194. [MIAO Xiumei,CHEN Yetian,MI Chuanmin. Study on consumer satisfaction of Tangshan hot springs based on ISM and online reviews[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science,2019,27(7):186 − 194. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2019.07.018 MIAO Xiumei, CHEN Yetian, MI Chuanmin . Study on consumer satisfaction of Tangshan hot springs based on ISM and online reviews[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science,2019 ,27 (7 ):186 −194 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2019.07.018[20] 李明柱,王文东,张智超. 基于ISM与MICMAC的建筑施工风险因素研究[J]. 安全与环境学报,2022,22(1):22 − 28. [LI Mingzhu,WANG Wendong,ZHANG Zhichao. Study on construction risk factors based on ISM and MICMAC[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2022,22(1):22 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2021.0578 LI Mingzhu, WANG Wendong, ZHANG Zhichao . Study on construction risk factors based on ISM and MICMAC[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2022 ,22 (1 ):22 −28 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2021.0578 -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李乔楚. 系统性视角下的燃气管道灾害多因素耦合理论研究. 焊管. 2025(03): 35-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:
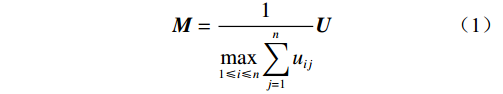
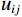
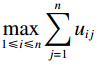
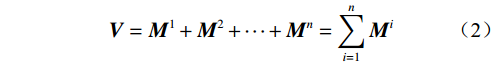
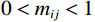
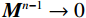
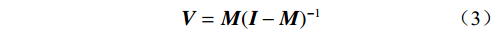
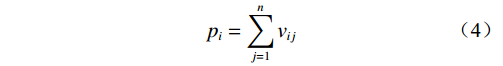
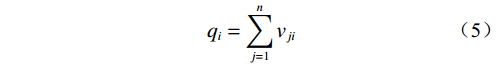
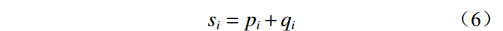
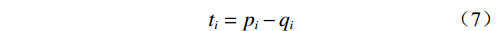
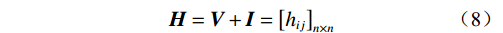

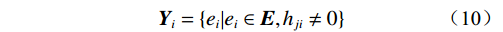
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS