Application of multiple InSAR techniques and SAR data from multi-sources to landslide deformation monitoring: A case study of the Zhixincun landslide in Jilin Province
-
摘要:
为实现对吉林省治新村滑坡的有效监测,文章选取2017年27景Sentinel-1A数据,基于小基线雷达干涉测量技术(SBAS-InSAR)对治新村滑坡进行形变监测,分析了其时序演化态势。选用2016、2017年2景ALOS-2数据,采用差分雷达干涉测量技术(D-InSAR)监测了该滑坡形变体的特征。SBAS-InSAR对滑坡形变时序演化态势进行监测,而D-InSAR则主要对滑坡具体的形变体进行形变监测,且L波段的ALOS-2数据穿透性强于C波段的Sentinel-1A数据,可以获得更完整的干涉信息,两者监测结果可交叉验证,提高结果的可靠性。SBAS-InSAR监测结果表明:治新村滑坡汇水区滑坡后缘在监测期间发生了沉降,并且在2017年7月5—29日期间滑坡后缘地表沉降达12.47 mm,监测期间平均沉降速率为2.88 mm/a;位于山谷的受威胁居民区发生了抬升,至2017年12月8日平均累计抬升达19.59 mm,监测期间平均抬升速率19.99 mm/a。D-InSAR结果显示:治新村滑坡汇水区斜坡存在5处主要变形体,面积最大变形体17973 m2,位于西侧斜坡,最不稳定变形体位于斜坡东侧,监测期间平均累计形变量最大达49.9 mm。两种监测方法都表明,滑坡灾害威胁主要来自植被覆盖较差的西侧斜坡,雨季是治新村滑坡灾害防治的重点时期。
-
关键词:
- 滑坡 /
- 治新村 /
- SBAS-InSAR /
- D-InSAR /
- ALOS-2 /
- Sentinel-1A
Abstract:In order to realize effective monitoring of Zhixincun landslide, this paper selected 27 sentinel-1A data in 2017, and conducted deformation monitoring of Zhixincun landslide based on small baseline radar interferometry technology (SBAS-InSAR), and analyzed its temporal evolution situation. Using ALOS-2 data from 2016 and 2017, differential radar interferometry (D-InSAR) was used to monitor the characteristics of the landslide variant. SBAS-InSAR monitors the temporal evolution situation of landslide deformation, while D-InSAR mainly monitors the deformation of specific landslide shape and variation. Moreover, the penetration of L-band ALOS-2 data is stronger than that of C-band sentinel-1A data, which can obtain more complete interference information. The monitoring results of both can be cross-verified. Improve the reliability of the results. The SBAS-InSAR monitoring results showed that the slope end of the landslide catchment area in Zhixincun had subsidence during the monitoring period, and the surface subsidence at the landslide end reached 12.47mm from July 5 to July 29, with an average subsidence rate of 2.88mm/a during the monitoring period. Uplift occurred in the threatened residential areas in the valley, with an average cumulative uplift of 19.59mm on December 8 and an average uplift rate of 19.99mm/a during the monitoring period. The D-InSAR results showed that there were five major deformations on the slope of Zhixincun landslide catchment area. The largest deformations with an area of 17 973m2 were located on the west side of the slope, and the most unstable deformations were located on the east side of the slope. The average cumulative shape variable reached 49.9mm during the monitoring period. Both monitoring methods showed that the threat of landslide disaster mainly came from the west slope with poor vegetation cover, and the rainy season was the key period of landslide disaster prevention and control in Zhixincun.
-
Keywords:
- landslide /
- Zhixincun /
- SBAS-InSAR /
- D-InSAR /
- ALOS-2 /
- Sentinel-1A
-
0. 引言
新世纪以来,人类活动对环境和气候的影响逐渐增大,生态环境及各种地质条件也随之发生了较大的改变。中国构造运动频繁,地形结构复杂,地质灾害频发,滑坡、崩塌等地质灾害呈现出分布广、高易发等特点。地质灾害严重威胁群众的生命财产安全,并限制区域经济发展[1-2]。滑坡是斜坡岩石体以及大面积冰雪覆盖体沿着贯通的剪切面所发生的体位滑动现象,由于气候、天气、地形、交通、通讯等因素的影响,很难做到早期预警和提前防范[3]。由于环境限制,传统测量手段如水准测量、GPS测量难以大范围开展地质灾害监测[4];光学遥感技术易受气候条件影响,并且难以实现对缓慢变形地质灾害隐患的识别[5-6]。
合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术(interferometricsynthetic aperture radar,InSAR)作为一种新型地表形变监测技术,具有空间分辨高、时间分辨率高、精度高以及大范围空间连续覆盖等优势,已成为地质灾害监测的重要手段之一,被众多学者用于地震[7]、滑坡灾害应急排查[8]、滑坡发育监测[9]、地面沉降[10]等的形变监测研究。法国学者Fruneau等[11]于1996年首次将InSAR技术应用于滑坡监测领域,采用差分雷达干涉技术(differential interferometric synthetic aperture radar,D-InSAR)技术处理ERS-1数据获取了6景差分干涉图,监测结果清晰的呈现了滑坡的形变特征,且与实测结果一致。由于不同时期获取的SAR影像间的相干性较差或失相干,以及大气效应的影响制约了D-InSAR技术在滑坡形变监测领域的应用,而差分干涉测量短基线集时序分析技术(small baseline subset InSAR, SBAS-InSAR ) [12-13]可实现对目标区域的连续时空监测,意大利学者Ferretti等[14]提出的永久散射体差分干涉测量技术(persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar,PS-InSAR)以及Berardino等[15]SBAS-InSAR,能够获取地面较高精度的地形数据以及地表时序形变数据,较大程度提升了SAR数据干涉测量的精度。姚佳明等[16]利用SBAS-InSAR技术对煤层开采诱发的地表形变模式进行了研究,证实了SBAS-InSAR技术监测地表形变的准确性;赵富萌等[17]采用SBAS-InSAR技术识别了Karakorum公路沿线滑坡点;Zhang等[18]利用了传统经验模型与SBAS-InSAR监测相结合的方式成功实现了甘肃省中部黄河黑泰河潜在滑坡的分析评价。InSAR技术已被广泛应用于滑坡地质灾害监测,但单一SAR数据监测的局限性限制了对滑坡形变的监测效果。C波段的Sentinel-1A影像时间基线小,影像数据多,适合应用时序InSAR技术监测滑坡时序形变特征,但在植被覆盖区因相干性过低而获得的监测点稀少;L波段的ALOS-2数据时间基线长,影像数量少,适合利用D-InSAR技术进行滑坡形变特征监测。采用少量长波段ALOS-2影像和大量短波段Sentinel-1A影像结合进行滑坡形变监测,能够在具有一定植被覆盖度的山区探测到较为明显的滑坡地表形变[19-20]。
治新村滑坡是吉林市内非常典型的土质滑坡,在2017年7月强降雨过程中发生了滑动,滑坡体滑到村民住宅墙根处,造成住宅后墙变形,雨水进入民房内,但未造成人员伤亡。以往对该滑坡的监测,只是传统的人工地面调查,基于InSAR技术对治新村滑坡进行形变监测的研究却鲜有报道。本文选取2017年1月6日—2017年12月8日的27景Sentinel-1A数据,使用SBAS-InSAR技术对治新村滑坡及周边区域进行了地表形变监测,并进行形变特征及趋势分析。考虑到滑坡所在区域植被覆盖情况及东北地区季节性积雪对SAR影像相干性的影响,选取2景穿透性更强的L波段ALOS-2数据监测滑坡体变形特征,综合运用SBAS-InSAR和D-InSAR技术,以及C波段的Sentinel-1A数据和L波段ALOS-2数据,以期验证监测结果的可靠性。研究结果对治新村滑坡灾害防治具有重要的指导意义,并可为后期类似滑坡地质灾害监测和研究提供参考依据。
1. 研究区概况及数据
1.1 治新村滑坡
治新村滑坡位于吉林省吉林市船营区大绥河镇治新村12社(图1)。滑坡前缘高程306.8 m,后缘高程322.8 m,长约327 m,宽约48 m,滑坡面积达15696 m2。平面形态为不规则扇形,滑动面剖面形态为凹形,产状:151°∠33°。土质滑体,平均厚1.2 m。地层岩性为残坡积物砂砾质土,滑床岩性为范家屯组板岩、粉砂岩。滑坡陡坎、后壁发育状况一般,尚可辩认。侧边界不发育,前缘、剪出口发育一般,尚可辩认。拉张裂缝、剪切裂缝较发育,裂缝宽度一般在0.4 m,长1~5 m不等,规模较小,贯通性较差,见有树木歪斜现象。滑坡体在雨水的浸润作用下,沿基覆界面滑动形成滑坡,为自然滑坡。目前,该滑坡现处于蠕变阶段,不稳定。
1.2 SAR影像和DEM数据
文中用于SBAS-InSAR的C波段数据为欧空局于2014年发射的Sentinel-1A卫星影像,该卫星轨道高度693 km,重访周期12 d,覆盖范围达到42500 km2,方位向分辨率为13.98 m,斜距向分辨率为 2.33 m,雷达波长为 5.6 cm,具有条带模式(strip map,SM)、宽幅干涉模式(interferometric wide,IW)、极宽模式(extra-wide swath,EW)和波模式(wave mode)4种成像模式;用于D-InSAR处理的L波段数据采用日本陆地观测卫星ALOS PALSAR-2影像,L波段的ALOS PALSAR-2数据具有较强的穿透力,可以很好地监测地壳运动,获取较准确的数据。
本文选用了C波段(2017-01-06—2017-12-08)27景降轨影像(表1),成像模式为IW模式,极化方式为VV;L波段(2016-07-26—2017-08-22)2景影像(表2),成像模式为ScanSAR扫描模式,极化方式为HH。DEM数据可用于去除地形相位以及高程误差相位计算,是SAR数据处理的辅助数据,选用NASA和NIMA联合发布的分辨率为90 m的SRTM3数据。
表 1 Sentinel-1A数据集Table 1. Sentinel-1A data set序号 成像日期 时间基线/d 空间基线/m 01 2017-01-06 60 43.8 02 2017-01-18 48 19.9 03 2017-01-30 36 75.9 04 2017-02-11 24 170.1 05 2017-02-23 12 109.8 06 2017-03-07 0 0 07 2017-03-19 12 −15.5 08 2017-03-31 24 32.9 09 2017-04-12 36 57.4 10 2017-04-24 48 128.3 11 2017-05-06 60 92.7 12 2017-05-18 72 47.9 13 2017-05-30 84 −70.3 14 2017-06-11 96 104.5 15 2017-06-23 108 95.2 16 2017-07-05 120 25.1 17 2017-07-29 144 43.2 18 2017-08-10 156 71.3 19 2017-08-22 168 27.8 20 2017-09-03 180 62.6 21 2017-09-15 192 107.1 22 2017-09-27 204 62.3 23 2017-10-09 216 70.1 24 2017-10-21 228 122.2 25 2017-11-02 240 145.3 26 2017-11-26 264 56.1 27 2017-12-08 276 61.5 表 2 ALOS-2影像信息Table 2. ALOS-2 image information序号 成像日期 时间基线/d 空间基线/m 01 2016-07-26 392 −225.5 02 2017-08-22 2. 研究方法
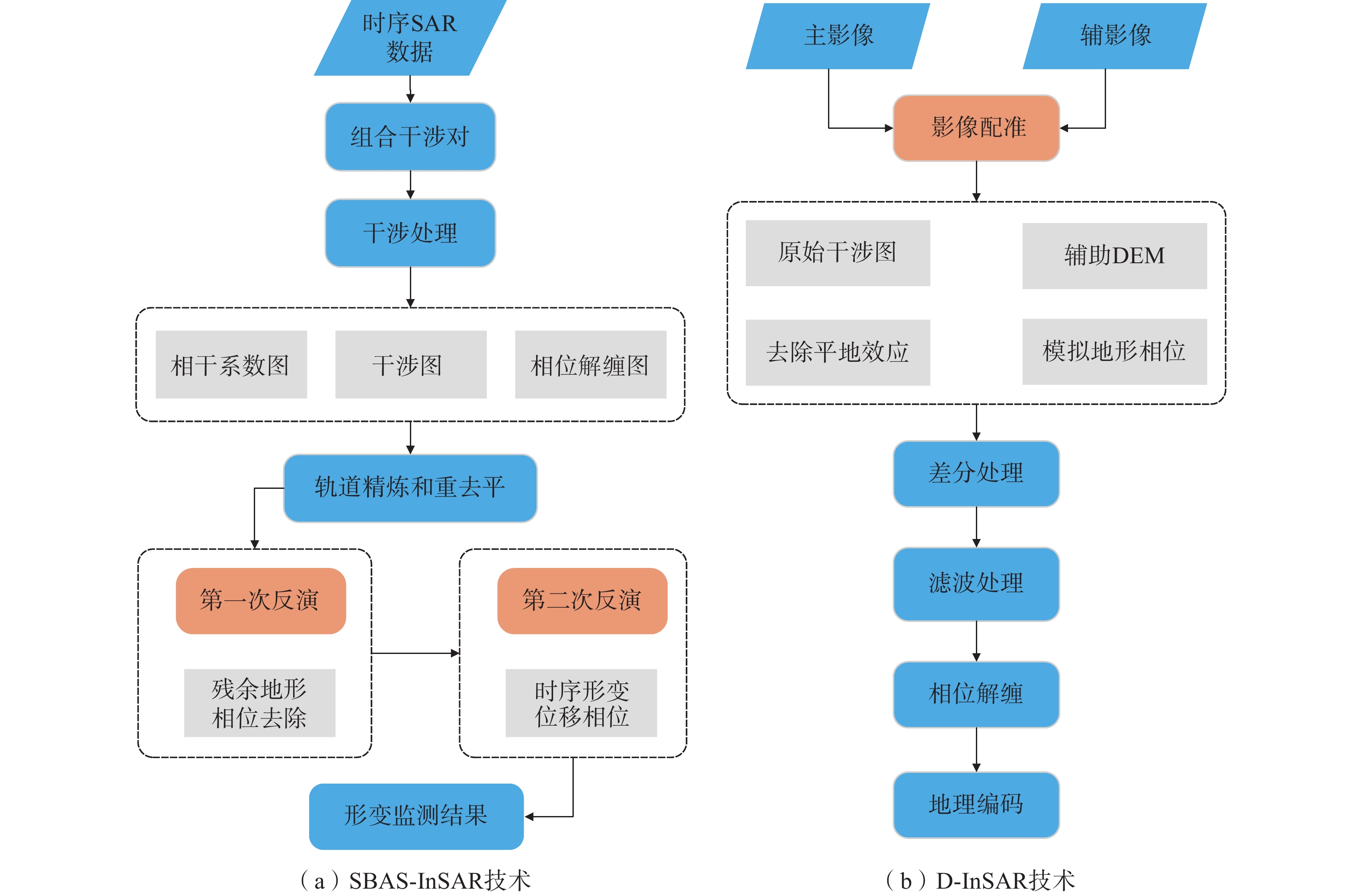
数据处理使用ENVI SARscape平台。采用SBAS-InSAR、D-InSAR方法分别对C波段和L波段SAR数据进行处理,SBAS-InSAR对配准好的多幅SAR影像通过设定的时间基线和空间基线阈值选取合适的干涉对组合,并基于相干目标进行相位解缠和参数解算获取长时间序列的形变信息,相较于D-InSAR,SBAS-InSAR可以分析更大时间序列数据,更好地克服了时空失相干的影响,并减小了大气延迟误差、地形误差、高程误差和其余噪声误差。SBAS-InSAR、D-InSAR数据处理流程如图2所示。
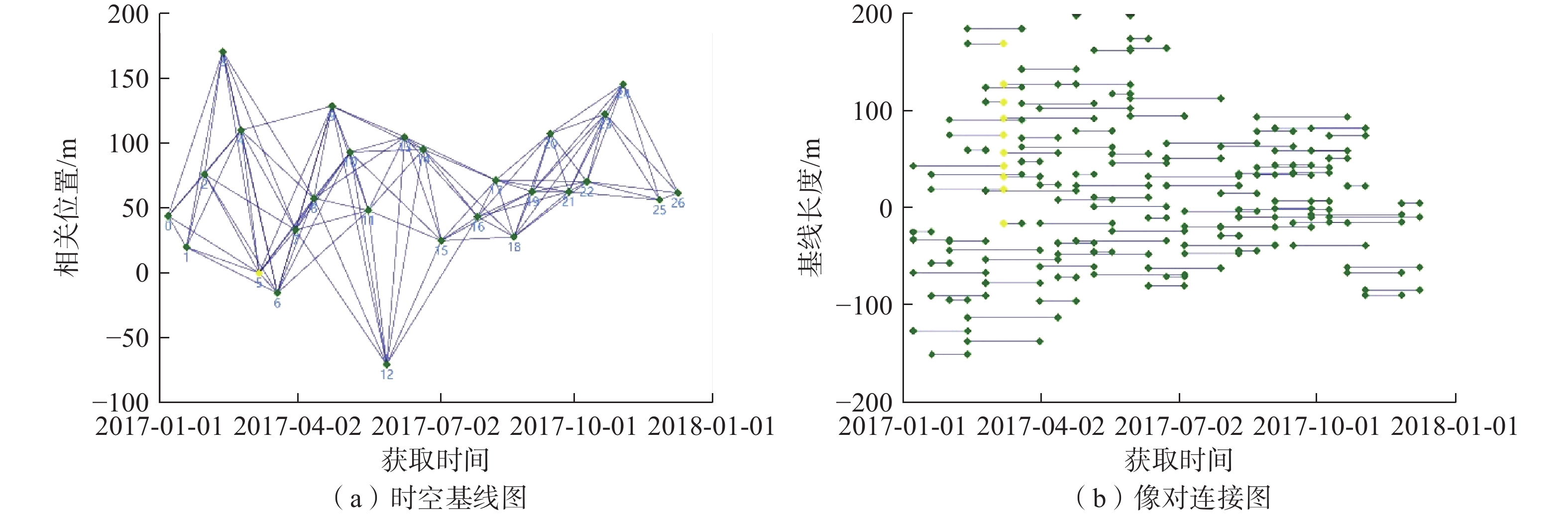
SBAS-InSAR是一种基于分布式目标的时间序列分析技术,将时空基线较短的影像两两配对成干涉像对,应用奇异值分解的方法求解单点的形变相位方程,解算高程误差及形变速率,通过残余相位对大气相位和非线性形变进行反演后获得该时间段内的形变时间序列。本文通过设置时间基线、空间基阈值控制Sentinel-1A数据集生成干涉像对的数量,时间基线长度为 60 d,空间基线阈值为理论空间基线值的45%,C波段27景SAR影像共获取干涉像对98对,其中主影像日期为 2017 年3 月31日,干涉像对以及基线连接情况如图3 所示。然后基于干涉像对进行SLC影像配准,生成干涉图,经过Goldstein滤波处理提高干涉条纹的清晰度。选取近30个控制点进行轨道精炼和重去平处理,选择automatic refinement方法消除可能的斜坡相位。历经2次SBAS反演,精确估计且去除地形残余相位、大气效应相位,最后结合DEM数据进行地理编码后获取各期累计形变图和平均形变速率图。
D-InSAR技术是对2景SAR影像进行差分干涉,同时需要外部的DEM数据模拟地形相位,进而去除掉地形相位的影响,仅保留形变相位。首先估算2景ALOS-2影像基线情况,包括像对的时间基线、空间基线、多普勒频移、相位代表的高程变化值等,作为InSAR形变监测的前提,然后基于DEM数据对主辅影像配准和干涉处理,获取干涉相位图,本文选取2016年7月26日影像为主影像,2017年8月22日影像为辅影像。采用Goldstein滤波提高干涉条纹的清晰度,减少由于时空基线引起的失相干的噪声,使用最小费用流(minimum cost flow,MCF)进行相位解缠,解决相位模糊度的问题。在相对稳定区域选择GCP进行轨道精炼与重去平处理,采用automatic refinement方法消除可能的斜坡相位。最后将经过绝对校准和解缠的相位结合,并将合成相位通过地理编码转换到制图坐标系统。
3. 结果与分析
3.1 SBAS-InSAR监测结果
由于治新村滑坡低矮植被覆盖和冬季积雪影响,对于C波段的Sentinel-1A数据,干涉测量时失相干较严重,获取的监测点主要位于滑坡后缘和滑坡前缘居民区(图4)。SBAS-InSAR监测结果显示,滑坡后缘斜坡在2017年发生沉降,而山谷村落地表发生抬升。滑坡后缘斜坡LOS向平均沉降速率为2.88 mm/a,山谷村落LOS向平均抬升速率为19.99 mm/a。
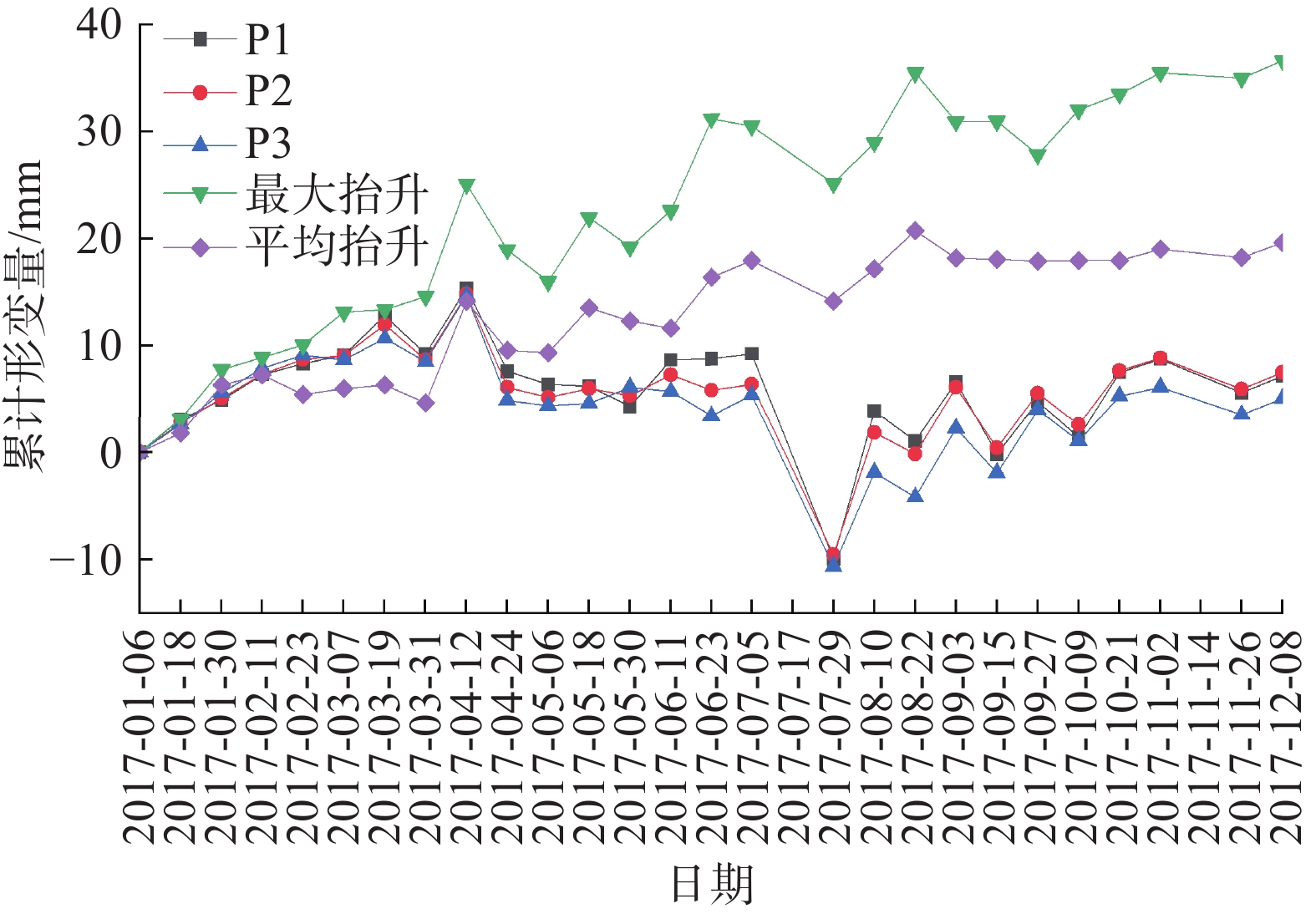
为进一步获取滑坡后缘斜坡及山谷居民区地表形变特征,对滑坡后缘监测点P1、P2、P3(图4)进行累计形变量时序分析,同时综合分析居民区最大抬升点和平均抬升累计形变特征,分析滑坡对居民区的影响。图5说明了滑坡后缘3个监测点(P1、P2、P3)沿雷达视线方向(LOS向)的累计形变特征。滑坡后缘在2017年1月6日—4月12日期间处于缓慢抬升阶段,至4月12日累计抬升达10.95 mm;4月12日—7月5日发生剧烈沉降后处于稳定状态;7月5日—7月29日期间滑坡后缘地表沉降达12.47 mm,此后地表抬升8.21 mm后处于相对稳定的起伏变化,最终累计地表累计抬升4.81 mm。同时,图4展示了受滑坡威胁的山谷村落监测点平均累计形变量变化图,山谷村落地表在1月6日—4月24日期间同滑坡后缘形变趋势相似,但在4月24日之后便持续抬升,至12月8日平均累计抬升达19.59 mm,最大抬升点累计抬升达36.62 mm。
2017年7月13日8时—14日8时,吉林市遭受罕见暴雨天气影响;7月19日8时—21日8时,吉林地区再次出现大范围暴雨、大暴雨天气,结合图4可以看出,治新村滑坡后缘在1月6日—7月5日期间地表处于相对稳定状态,而在7月5日—8月10日出现剧烈的沉降抬升变化,7月5日—7月29日期间的高强度降雨导致了此次滑坡灾害的发生,具体表现为滑坡后缘先沉降后抬升。因此,雨季是治新村滑坡监测与防治的重点时期。
3.2 D-InSAR监测结果
D-InSAR监测结果表明,监测期间在治新村滑坡斜坡上存在5处主要变形体(图6、表3)。1号变形体位于治新村滑坡汇水区西南侧斜坡顶端,变形体面积达5318 m2,监测期间最大沉降量为58.6 mm,最小沉降量为29.4 mm,平均沉降量达43.2 mm;2号变形体位于滑坡汇水区西侧斜坡中上部,变形体面积达17973 m2,监测期间最大沉降量为50.6 mm,最小沉降量为24.2 mm,平均沉降量达36.4 mm;3号变形体位于滑坡汇水区东侧斜坡顶端,变形体面积为4636 m2,监测期间最大沉降量为68.7 mm,最小沉降量为29.8 mm,平均沉降量达43.5 mm;4号变形体位于滑坡汇水区东侧斜坡顶端,与3号变形体北侧相接,变形体面积3043 m2,监测期间最大沉降量为71.8 mm,最小沉降量为31.3 mm,平均沉降量达49.9 mm;5号变形体位于滑坡汇水区西侧斜坡北部顶端,较接近居民区,变形体面积达11281 m2,监测期间最大沉降量为47.6 mm,最小沉降量为20.1 mm,平均沉降量达38.3 mm。
表 3 斜坡变形体Table 3. Deformation of slope编号 面积/m² 最大沉降量/mm 最小沉降量/mm 平均沉降量/mm 1 5318 58.6 29.4 43.2 2 17973 50.6 24.2 36.4 3 4636 68.7 29.8 43.5 4 3043 71.8 31.3 49.9 5 11281 47.6 20.1 38.3 汇水区两侧斜坡变形体分布及变形体沉降量显示,西侧斜坡大面积处于不稳定状态,并向斜坡下端逐步延伸;东侧斜坡虽然顶端变形体形变量较大,但是变形体面积较小,整个东侧斜坡大部分区域由于植被覆盖程度较好,处于相对稳定状态。因此,治新村滑坡威胁主要来源于汇水区植被覆盖程度较差的西侧斜坡。
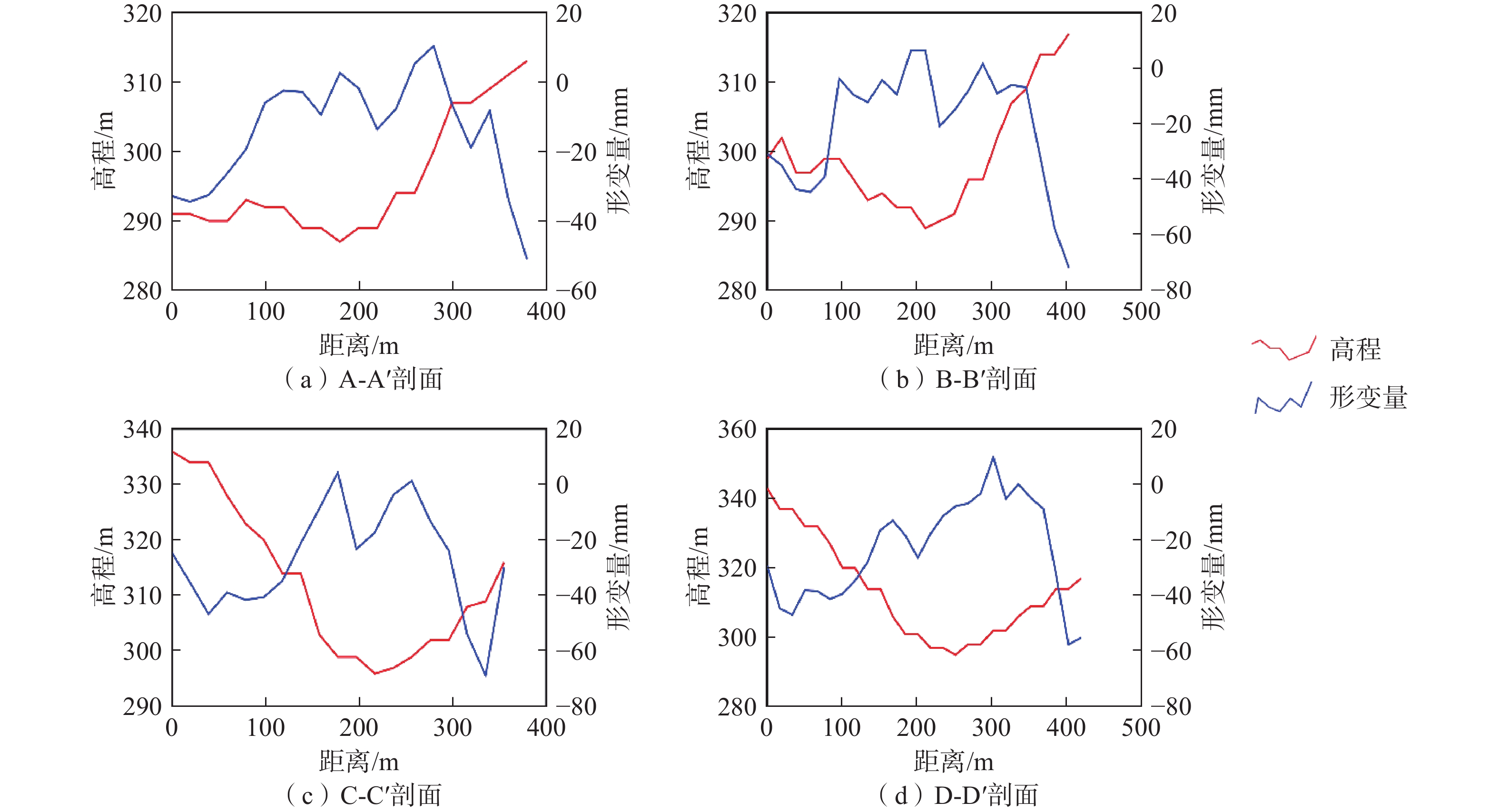
根据斜坡两侧变形体特征及斜坡地形特征,针对剖线AA′、BB′、CC′、DD′作形变量及高程变化剖面分析,对比二者变化特征(图7)。从图7可以看出,区域形变累计量与斜坡高程存在明显负相关,即斜坡高处相对沉降量较大,而随着斜坡高程降低,沉降量亦逐渐减小,局部居民区由于滑坡物质累积,地表呈现抬升现象。
4. 结论
(1)SBAS-InSAR技术可以监测滑坡形变演化特征,D-InSAR技术可以监测滑坡形变体特征,二者结合进行监测可以更全面地反映滑坡时空演化态势。受研究区低矮植被和冬季积雪的影响,通过C波段Sentinel-1A影像获取的滑坡体监测点较少,使用L波段ALOS-2数据则可以很好的解决影像失相干的问题。
(2)滑坡后缘在监测期间发生了明显形变,该区域在7月份强降雨过程中发生了先沉降后抬升的形变,期间沉降量达12.47 mm,监测期间平均沉降速率为2.88 mm/a。同时,山谷居民区地表也在降雨后处于持续抬升阶段,至12月8日平均累计抬升达19.59 mm,最大抬升点累计抬升达36.62 mm,监测期间平均抬升速率19.99 mm/a。因此,雨季是治新村滑坡灾害防治的重点时期。
(3)基西侧斜坡大面积处于不稳定状态,有向斜坡下端逐步延伸的趋势,最大变形体面积17973 m2,平均沉降量36.4 mm;东侧斜坡变形体面积小于西侧,但变形体形变量较大,平均沉降量49.9 mm。结合实际调查,东侧斜坡大部分区域由于植被覆盖程度较好,处于相对稳定状态。因此,治新村滑坡灾害的主要威胁来源于汇水区植被覆盖程度较差的西侧斜坡,且形变同地形相关明显,斜坡顶端沉降量几乎是最大的,随着斜坡高度降低,沉降量亦逐渐降低,但山谷居民区由于滑坡物质累积则呈现地表抬升。
-
表 1 Sentinel-1A数据集
Table 1 Sentinel-1A data set
序号 成像日期 时间基线/d 空间基线/m 01 2017-01-06 60 43.8 02 2017-01-18 48 19.9 03 2017-01-30 36 75.9 04 2017-02-11 24 170.1 05 2017-02-23 12 109.8 06 2017-03-07 0 0 07 2017-03-19 12 −15.5 08 2017-03-31 24 32.9 09 2017-04-12 36 57.4 10 2017-04-24 48 128.3 11 2017-05-06 60 92.7 12 2017-05-18 72 47.9 13 2017-05-30 84 −70.3 14 2017-06-11 96 104.5 15 2017-06-23 108 95.2 16 2017-07-05 120 25.1 17 2017-07-29 144 43.2 18 2017-08-10 156 71.3 19 2017-08-22 168 27.8 20 2017-09-03 180 62.6 21 2017-09-15 192 107.1 22 2017-09-27 204 62.3 23 2017-10-09 216 70.1 24 2017-10-21 228 122.2 25 2017-11-02 240 145.3 26 2017-11-26 264 56.1 27 2017-12-08 276 61.5 表 2 ALOS-2影像信息
Table 2 ALOS-2 image information
序号 成像日期 时间基线/d 空间基线/m 01 2016-07-26 392 −225.5 02 2017-08-22 表 3 斜坡变形体
Table 3 Deformation of slope
编号 面积/m² 最大沉降量/mm 最小沉降量/mm 平均沉降量/mm 1 5318 58.6 29.4 43.2 2 17973 50.6 24.2 36.4 3 4636 68.7 29.8 43.5 4 3043 71.8 31.3 49.9 5 11281 47.6 20.1 38.3 -
[1] 殷跃平,王文沛. 高位远程滑坡动力侵蚀犁切计算模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(8):1513 − 1521. [YIN Yueping,WANG Wenpei. Study on calculation model of dynamic erosion plowing of high-level remote landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(8):1513 − 1521. (in Chinese with English abstract) Yin Yueping, Wang Wenpei. Study on calculation model of dynamic erosion plowing of high-level remote landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(8): 1513-1521. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 黄海峰,林海玉,吕奕铭,等. 基于小型无人机遥感的单体地质灾害应急调查方法与实践[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(2):447 − 454. [HUANG Haifeng,LIN Haiyu,LYU Yiming,et al. Micro unmanned aerial vehicle based remote sensing method and application for emergency survey of individual geohazard[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(2):447 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG Haifeng, LIN Haiyu, LYU Yiming, et al. Micro unmanned aerial vehicle based remote sensing method and application for emergency survey of individual geohazard[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(2): 447-454. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 朱庆,曾浩炜,丁雨淋,等. 重大滑坡隐患分析方法综述[J]. 测绘学报,2019,48(12):1551 − 1561. [ZHU Qing,ZENG Haowei,DING Yulin,et al. A review of major potential landslide hazards analysis[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2019,48(12):1551 − 1561. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU Qing, ZENG Haowei, DING Yulin, et al. A review of major potential landslide hazards analysis[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2019, 48(12): 1551-1561. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张勤,黄观文,杨成生. 地质灾害监测预警中的精密空间对地观测技术[J]. 测绘学报,2017,46(10):1300 − 1307. [ZHANG Qin,HUANG Guanwen,YANG Chengsheng. Precision space observation technique for geological hazard monitoring and early warning[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2017,46(10):1300 − 1307. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170453 ZHANG Qin, HUANG Guanwen, YANG Chengsheng. Precision space observation technique for geological hazard monitoring and early warning[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1300-1307. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170453
[5] 刘文,王猛,朱赛楠,等. 基于光学遥感技术的高山极高山区高位地质灾害链式特征分析—以金沙江上游典型堵江滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):29 − 39. [LIU Wen,WANG Meng,ZHU Sainan,et al. An analysis on chain characteristics of highstand geological disasters in high mountains and extremely high mountains based on optical remote sensing technology:A case study of representative large landslides in upper reach of Jinsha River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):29 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Wen, WANG Meng, ZHU Sainan, et al. An analysis on chain characteristics of highstand geological disasters in high mountains and extremely high mountains based on optical remote sensing technology: a case study of representative large landslides in upper reach of Jinsha River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(5): 29-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] XIE Mingli,ZHAO Weihua,JU Nengpan,et al. Landslide evolution assessment based on InSAR and real-time monitoring of a large reactivated landslide,Wenchuan,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,277:105781. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105781
[7] 王洵,周云,孙蒙,等. 青海玉树Mw6.9级地震震源破裂过程[J]. 地质通报,2014,33(4):517 − 523. [WANG Xun,ZHOU Yun,SUN Meng,et al. Rupture process of the 2010 Mw6.9 Yushu earthquake in Qinghai Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2014,33(4):517 − 523. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Xun, ZHOU Yun, SUN Meng, et al. Rupture process of the 2010 Mw6.9 Yushu earthquake in Qinghai Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(4): 517-523. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘星洪,姚鑫,周振凯,等. 滑坡灾害InSAR应急排查技术方法研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2018,24(2):229 − 237. [LIU Xinghong,YAO Xin,ZHOU Zhenkai,et al. Study of the technique for landslide rapid recognition by InSAR[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2018,24(2):229 − 237. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Xinghong, YAO Xin, ZHOU Zhenkai, et al. Study of the technique for landslide rapid recognition by insar[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 24(2): 229-237. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 张佳佳,田尤,陈龙,等. 澜沧江昌都段滑坡发育特征及形成机制[J]. 地质通报,2021,40(12):2024 − 2033. [ZHANG Jiajia,TIAN You,CHEN Long,et al. Development and formation mechanism of landslides along Changdu section of Lancang River[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2021,40(12):2024 − 2033. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Jiajia, TIAN You, CHEN Long, et al. Development and formation mechanism of landslides along Changdu section of Lancang River[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(12): 2024-2033. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 许军强,马涛,卢意恺,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的豫北平原地面沉降监测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2019,49(4):1182 − 1191. [XU Junqiang,MA Tao,LU Yikai,et al. Land subsidence monitoring in North Henan plain based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2019,49(4):1182 − 1191. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Junqiang, MA Tao, LU Yikai, et al. Land subsidence monitoring in North Henan plain based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1182-1191. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] FRUNEAU B,ACHACHE J,DELACOURT C. Observation and modelling of the Saint-Étienne-de-Tinée landslide using SAR interferometry[J]. Tectonophysics,1996,265(3/4):181 − 190.
[12] MADSEN S N,ZEBKER H A,MARTIN J. Topographic mapping using radar interferometry:processing techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,1993,31(1):246 − 256. DOI: 10.1109/36.210464
[13] 邓云凯,禹卫东,张衡,等. 未来星载SAR技术发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报,2020,9(1):1 − 33. [DENG Yunkai,YU Weidong,ZHANG Heng,et al. Forthcoming spaceborne SAR development[J]. Journal of Radars,2020,9(1):1 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract) DENG Yunkai, YU Weidong, ZHANG Heng, et al. Forthcoming spaceborne SAR development[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 1-33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] FERRETTI A, PRATI C, ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[C]//IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. January 2001, IEEE, 2002: 8 − 20.
[15] BERARDINO P,FORNARO G,LANARI R,et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2002,40(11):2375 − 2383. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792
[16] 姚佳明,姚鑫,陈剑,等. 基于InSAR技术的缓倾煤层开采诱发顺层岩体地表变形模式研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):135 − 146. [YAO Jiaming,YAO Xin,CHEN Jian,et al. A study of deformation mode and formation mechanism of a bedding landslide induced by mining of gently inclined coal seam based on InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):135 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201903072 YAO Jiaming, YAO Xin, CHEN Jian, et al. A study of deformation mode and formation mechanism of a bedding landslide induced by mining of gently inclined coal seam based on InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(3): 135-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201903072
[17] 赵富萌,张毅,孟兴民,等. 基于小基线集雷达干涉测量的中巴公路盖孜河谷地质灾害早期识别[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):142 − 152. [ZHAO Fumeng,ZHANG Yi,MENG Xingmin,et al. Early identification of geological hazards in the Gaizi valley near the Karakoran highway based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):142 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO Fumeng, ZHANG Yi, MENG Xingmin, et al. Early identification of geological hazards in the Gaizi valley near the Karakoran Highway based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(1): 142-152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] ZHANG Y,MENG X M,DIJKSTRA T A,et al. Forecasting the magnitude of potential landslides based on InSAR techniques[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2020,241:111738. DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111738
[19] 季灵运,王庆良,崔笃信,等. 利用SBAS-DInSAR技术提取腾冲火山区形变时间序列[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2011,31(4):149 − 153. [JI Lingyun,WANG Qingliang,CUI Duxin,et al. Time series of deformation in Tengchong volcanic area extracted by SBAS-DInSAR[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2011,31(4):149 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2011.04.034 JI Lingyun, WANG Qingliang, CUI Duxin, et al. Time series of deformation in Tengchong volcanic area extracted by sbas-dinsar[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2011, 31(4): 149-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2011.04.034
[20] 葛伟丽,李元杰,张春明,等. 基于InSAR技术的内蒙古巴彦淖尔市地面沉降演化特征及成因分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(4):198 − 206. [GE Weili,LI Yuanjie,ZHANG Chunming,et al. An attribution analysis of land subsidence features in the city of Bayannur in Inner Mongolia based on InSAR[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(4):198 − 206. (in Chinese with English abstract) GE Weili, LI Yuanjie, ZHANG Chunming, et al. An attribution analysis of land subsidence features in the city of Bayannur in Inner Mongolia based on InSAR[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(4): 198-206. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王林峰,蒋辉,唐宁,黄晓明,谭国金. 无人机贴近摄影技术在高陡边坡的三维重建与结构面识别中的应用. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2025(01): 92-100 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 谢梅生,刘文军,易明华. 丘陵山区地质灾害隐患综合遥感识别方法研究. 江西测绘. 2025(01): 22-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 赵琳,徐晓臣,奚歌,许健,谢津平. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的水库边坡形变监测应用分析. 水利规划与设计. 2024(10): 79-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张克利,姚爱敏,张建全,闫宇蕾,秦宏楠. GB-InSAR滑坡应急监测的快速建模与三维匹配试验及应用. 水文地质工程地质. 2024(06): 190-197 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吴迪,梁泰铭,吴静,吴建建,易杨,娄万鹏. 基于MEMS传感器的滑坡监测算法设计与试验. 地质科技通报. 2024(06): 39-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS