Integrated assessment of soil cutting slope stability using fuzzy mathematics and numerical simulation
-
摘要: 影响黄土区人工边坡稳定性的因素具有复杂性与不确定性,难以通过单一方法作出客观准确的评价。为了研究山西太原古交市营立村采石场人工土质边坡稳定性,基于坡体工程地质条件采用模糊数学构建了模糊综合评价模型,进而结合相互关系矩阵评价其稳定性,最后通过FLAC3D 软件模拟分析了降雨条件下该土质边坡稳定性变化规律。结果表明:模糊数学理论评价营立村采石场人工土质边坡天然条件下稳定性系数为1.429(>1.15),处于稳定状态;FLAC3D 模拟显示天然状态下边坡稳定系数为1.426,日降雨量增加引起了浅层土体稳定性短暂上升后下降,降雨量150 mm/d时边坡稳定系数趋近于1,已处于极限稳定状态,可能诱发滑坡地质灾害。联合运用两种方法相互佐证能够提高评价准确性,使结果更符合边坡实际情况。Abstract: The complexity and uncertainty of the factors affecting the stability of artificial slope in loess regions pose challenges for achieving objective and accurate assessments through a single method. To investigate the stability of the artificial soil slope at Yingli Village Quarry in Gujiao City, a fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model was constructed based on the engineering geological conditions of the slope using fuzzy mathematics. Subsequently, its stability was evaluated by integrating an interrelationship matrix. Furthermore, the stability change law of the soil slope under rainfall conditions was simulated and analysed by FLAC3D software. The results show that the fuzzy mathematical theory evaluates that the artificial soil slope of Yingli Village Quarry is in a stable state under natural conditions, with Fs =1.429>1.15. The simulation results of FLAC3D show that the stability coefficient of the slope in the natural state is Fs=1.426. Increasing daily rainfall briefly evaluates the stability of shallow soil layers, followed by a decline. When rainfall reaches 150 mm/d, the slope's stability coefficient approaches 1, indicating it has reached the limit of stability. This condition may trigger landslide disaster. The combined utilization of both methods enhances the accuracy of the assessment, aligning the results more closely with the actual slope conditions.
-
Keywords:
- soil slope /
- FLAC3D simulation /
- extreme rainfall /
- stability
-
0. 引言
滑坡是威胁山西地区人民生命和财产安全的主要地质灾害之一,广布的黄土层为滑坡灾害的发生提供了物质基础,尤其是汾河流域多为非自重的湿陷性黄土,具有显著的结构疏松与压缩性高的性质[1 − 2],而土质边坡以易发生、危害强、难预测等特点危害性更为突出[3 − 4]。滑坡现象多为内部因素和外部因素共同作用触发,内部因素包括坡体本身的性质弱化以及较差的地质构造环境等,降雨、工程开挖等外部因素是诱发土质边坡失稳的直接原因[5 − 6]。
众多学者围绕土质边坡稳定性问题开展了一系列卓有成效的研究,尤其是20世纪70年代后,有限元法借助计算机开始被广泛应用于边坡稳定分析。然而,在实际应用中,有限元法仍存在一些局限性,如较难确定边坡的初始应力状态以及把握边坡临近破坏时的弹塑性本构关系等。极限平衡法逐渐形成了垂直条分法和滑移线法两个独立的分支[7 − 8]。我国学者在滑动机理及监测方面也取得了一系列研究成果,彭建兵等[9]研究了黄土高原滑坡灾害形成的动力学机制问题,认为区域构造应力、边坡构造应力及易灾特性是黄土滑坡的“三大元凶”;董震等[1]聚焦山西省黄土地质灾害问题,认为黄土地质灾害的发生受其特有的物质成分和工程性质控制,并具有地域性分布的特点;支泽民等[10]研究发现,边坡稳定性影响因子相互作用会促进滑坡发育;蔡欣育等[11]开展了不同降雨类型对边坡稳定性的影响研究,重点分析了不同降雨类型条件下边坡孔隙水压力的分布特征;侯天顺等[12]也进行了人工降雨作用下的滑坡试验,模拟长期连续降雨边坡稳定系数的变化规律;马蓓青等[13]探讨了降雨条件下边坡裂缝发育规律及其对稳定性的影响;苗青等[14]通过LASSO算法建立了能够预测滑坡危险区域的模型。
然而,在工程扰动下土质边坡稳定性愈加复杂,很难用一种模式概括其滑动机理与影响因素。调查表明,多数土质边坡的滑坡与降雨有直接或间接的关系。在近年极端天气频发的背景下,探讨工程场地客观地质条件下极端降雨对土质边坡稳定性的影响是十分必要的。本文在山西太原古交市马兰镇营立村拟建水泥厂地质调研基础上,基于模糊数学理论获取该土质边坡稳定的主要影响因素,确定权值并计算稳定系数,结合FLAC3D软件模拟得到不同降雨强度下边坡稳定系数变化特征,进而得到现有条件下维持该边坡稳定所能承受的极端降雨条件,从而综合判断边坡的稳定状态。
1. 工程地质条件
1.1 地形与岩性特征
研究区位于山西省太原市西部山区的古交市马兰镇营立村水泥厂,属于地形起伏较大的山间河谷地貌单元区,拟建场地地形起伏较大,各钻孔孔口标高介于1182.43~1194.64 m,相对高差为12.21 m。区内地层发育不完全,据勘察及钻孔揭露的地层情况,勘察深度范围内地层主要由全新统粉土、圆砾与中奥陶统石灰岩组成(图1)。粉土(Qh)呈褐黄色,稍密,稍湿,土质较松散;场地局部出露,可见零星煤屑、云母、氧化铁及植物根系,摇振反应中等,无光泽反应,干强度和韧性低。圆砾(
$ \rm{Qh}_{ }^{\rm{\mathit{al}+\mathit{pl}}} $ )为杂色,中密,稍湿,母岩成分主要为灰岩和砂岩,呈椭圆状,磨圆度较好,一般粒径为3~10 cm,最大粒径为18 cm,以粉土、中砂充填其中,含大量漂石,中奥陶统马家沟组石灰岩(O2m)为灰白色,强风化-中风化,岩体节理裂隙较发育,岩芯较完整,呈短柱状或柱状,一般在10.0~30.0 cm,敲击声较清脆,不易击碎,为较硬岩。1.2 水文地质与气候
场地内水文地质条件简单,在勘察深度内未发现稳定地下水位。研究区属于典型的季风气候,当地历年降雨资料显示年平均降雨量为426.1 mm,降雨主要集中在7—8月,其降雨量约在60~90 mm,但近年极端天气明显增多[14],多次出现了日降水量超过100 mm的大暴雨,极端天气频现给区域内土质边坡稳定性带来了挑战,也增加了研究的复杂性和难度。
2. 边坡稳定性模糊数学分析
2.1 边坡稳定性评判模型
边坡稳定性受到内因和外因的双重影响。在现场调研基础上,采用层次分析法确定了影响该水泥厂边坡稳定性的因素及其分级标准(表1),确定了地层岩性、地貌特征、风化作用、降雨及人类活动[15]等 5 项影响因素,构建了边坡稳定性的模糊综合评价模型
表 1 稳定性影响因素与量化取值表Table 1. Stability influencing factors and quantified values评价指标 滑坡稳定性级别及其分级标准 因素 因子 稳定(1) 基本稳定(2) 欠稳定(3) 不稳定(4) 降雨U1 降雨量/
(mm·d−1)25~<50 50~<100 100~250 >250 人类活动U2 工程活动 弱 一般 较强 强 地貌特征U3 坡面形态 平直形 凸状 凹状 阶状 坡度(θ)/(°) 0~<10 10~<30 30~<50 50~90 坡高(h)/m 0~<25 25~<35 35~<45 45~55 地层岩性U4 岩土性质 坚石 软石 硬土 普通土 风化作用U5 风化程度 微风化 中风化 强风化 全风化 根据构建的边坡稳定性模糊综合评价模型[16],建立评价对象的关联因素集,表示为:
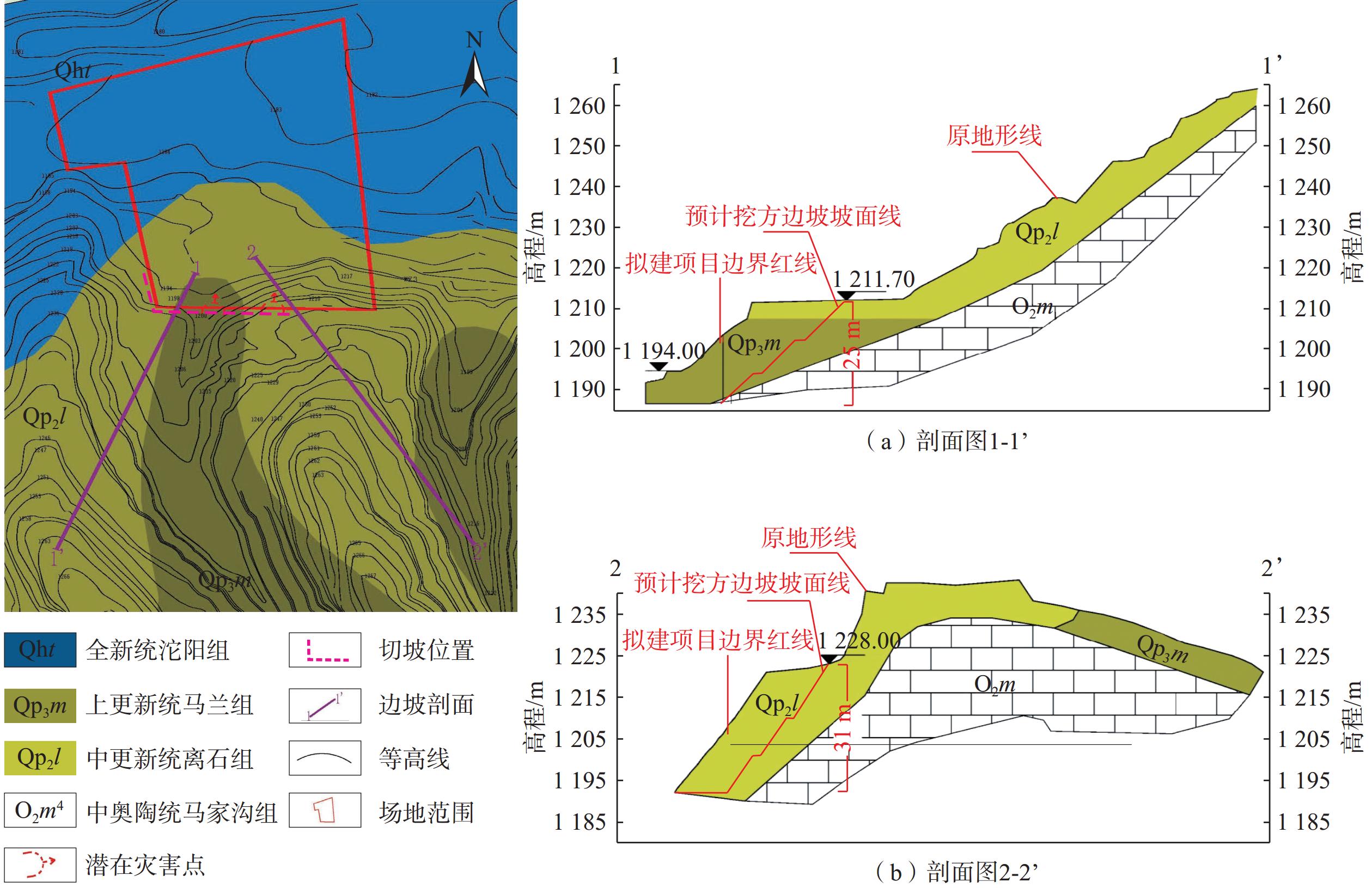
$$ {\boldsymbol{U}}=\{u_{1},u_{2},u_{3},u_{4},u_{5}\} $$ (1) 根据边坡实际情况,结合半定量取值法,确定不同因素权重集,表示为:
$$ {\boldsymbol{Q}}=\{q_{1},q_{2},q_{3},q_{4},q_{5}\} $$ (2) 通过评价对象可能出现的结果建立备择集,表示为:
$$ {\boldsymbol{W}}=\{w_{1},w_{2},w_{3},w_{4},w_{5}\} $$ (3) 根据单个影响因素,联立式(2)与(3),确定各离散值对备择集的隶属程度,得出评判矩阵,表示为:
$$ {\boldsymbol{R }}= \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {R_{{w_1}}^{{q_1}}}&{R_{{w_2}}^{{q_1}}}&{R_{{w_3}}^{{q_1}}}&{R_{{w_4}}^{{q_1}}}&{R_{{w_5}}^{{q_1}}} \\ {R_{{w_1}}^{{q_2}}}&{R_{{w_2}}^{{q_2}}}&{R_{{w_3}}^{{q_2}}}&{R_{{w_4}}^{{q_2}}}&{R_{{w_5}}^{{q_2}}} \\ {R_{{w_1}}^{{q_3}}}&{R_{{w_2}}^{{q_3}}}&{R_{{w_3}}^{{q_3}}}&{R_{{w_4}}^{{q_3}}}&{R_{{w_5}}^{{q_3}}} \\ {R_{{w_1}}^{{q_4}}}&{R_{{w_2}}^{{q_4}}}&{R_{{w_3}}^{{q_4}}}&{R_{{w_4}}^{{q_4}}}&{R_{{w_5}}^{{q_4}}} \\ {R_{{w_1}}^{{q_5}}}&{R_{{w_2}}^{{q_5}}}&{R_{{w_3}}^{{q_5}}}&{R_{{w_4}}^{{q_5}}}&{R_{{w_5}}^{{q_5}}} \end{array}} \right] $$ (4) 根据式(2)与(4),依据权重集与影响因素评判关系矩阵的乘积可以有效地表达所有因素对判定对象的综合影响指数,表示为:
$$ B = Q \cdot R = \left\{ {{Z_{{w_1}}},{Z_{{w_2}}}, \cdots ,{Z_{w_5}}} \right\} $$ (5) 2.2 边坡稳定影响因素关系矩阵
基于地质资料及调查结果,对各影响因素在不同稳定系数下的影响程度进行评价。基于所构建边坡稳定性评价模型的降雨量、人类活动、地貌特征、地层岩性与风化程度等5项因素建立关系矩阵,矩阵主对角线上数据表示各影响因素在不同稳定系数下的影响程度。矩阵中各行表示该因素对其它因素在不同稳定系数下的影响程度,设该因素为A。矩阵中各列表示其它因素对其在相同稳定系数下的影响程度,设其为B。不同因素对不同稳定系数的影响具有差异性,因而选用编码方式加以区分。按影响程度由弱到强分别赋值为0,1,2,3,4。其中,Aa为关系矩阵中不同稳定系数的稳定性影响程度,该值越大表示影响越大;Bb为关系矩阵中相同稳定系数的稳定性重要程度,该值越大表示越重要。
基于以上原则建立了关系矩阵,计算公式如下:
$$ {A_a} = \frac{{A + B}}{{\sqrt 2 }} $$ (6) $$ {B_b} = \frac{{A - B}}{{\sqrt 2 }} $$ (7) $$ {H}_{i}=\frac{{A}_{a}+{B}_{b}}{{\displaystyle \sum \left({A}_{a}+{B}_{b}\right)}}\times 100\% $$ (8) 式中:Aa——稳定性影响程度;
Bb——稳定性重要程度;
Hi——影响因素的权重(表2)。
表 2 营立村水泥厂切坡稳定性影响因素赋值表Table 2. Impact factors of artificial slope cutting stability in Yingli Village quarryP A A+B A-B Hi/% Aa Bb P1 3 2 1 1 11 23 −1 26 16.26 −0.707 3 P2 2 2 1 10 19 1 22 13.44 0.707 2 1 P3 1 1 7 15 −1 17 10.06 −0.707 2 2 1 P4 3 10 17 3 19 12.02 2.120 1 1 1 1 P5 6 14 −2 16 9.90 −1.410 B 12 9 8 7 8 88 根据地质调查结果及相关地质资料与规范,由式(6)—(8)计算,最终确定各影响因素的权重,降雨为26%、人类活动为22%、地貌特征为17%、地层岩性为19%、风化程度为16%。确定权重集为:
$$ {\boldsymbol{Q}}=\{0.26,0.22,0.17,0.19,0.16\} $$ 一般土质边坡的稳定系数区间为[1.20, 2.00],区间为0.25均匀分布,建立备择集表示如下:
$$ {\boldsymbol{W}}=\{1.00,1.25,1.50,1.75,2.00\} $$ 由此,计算得出综合评价结果为:
$$ {\boldsymbol{B}}={\boldsymbol{Q}}\cdot {\boldsymbol{R}}=(2.58,1.93,1.65,1.41,1.54) $$ 最后,对综合评价结果加权平均求得边坡稳定系数,计算结果如下:
$$ F_{\mathrm{S}}=\frac{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j=1}^5b_jw_j}{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j=1}^5b_j}=\frac{13.02}{9.11}=1.429 $$ 式中:Fs——边坡稳定系数。
综上可知,基于模糊数学求得Fs =1.429>1.15,根据《滑坡防治工程勘察规范》(GBT 32864—2016) [17]第13. 3. 4 条滑坡稳定状态划分标准,该土质边坡天然条件下处于稳定状态。
3. 边坡稳定性FLAC3D分析
3.1 模型构建与物理力学参数获取
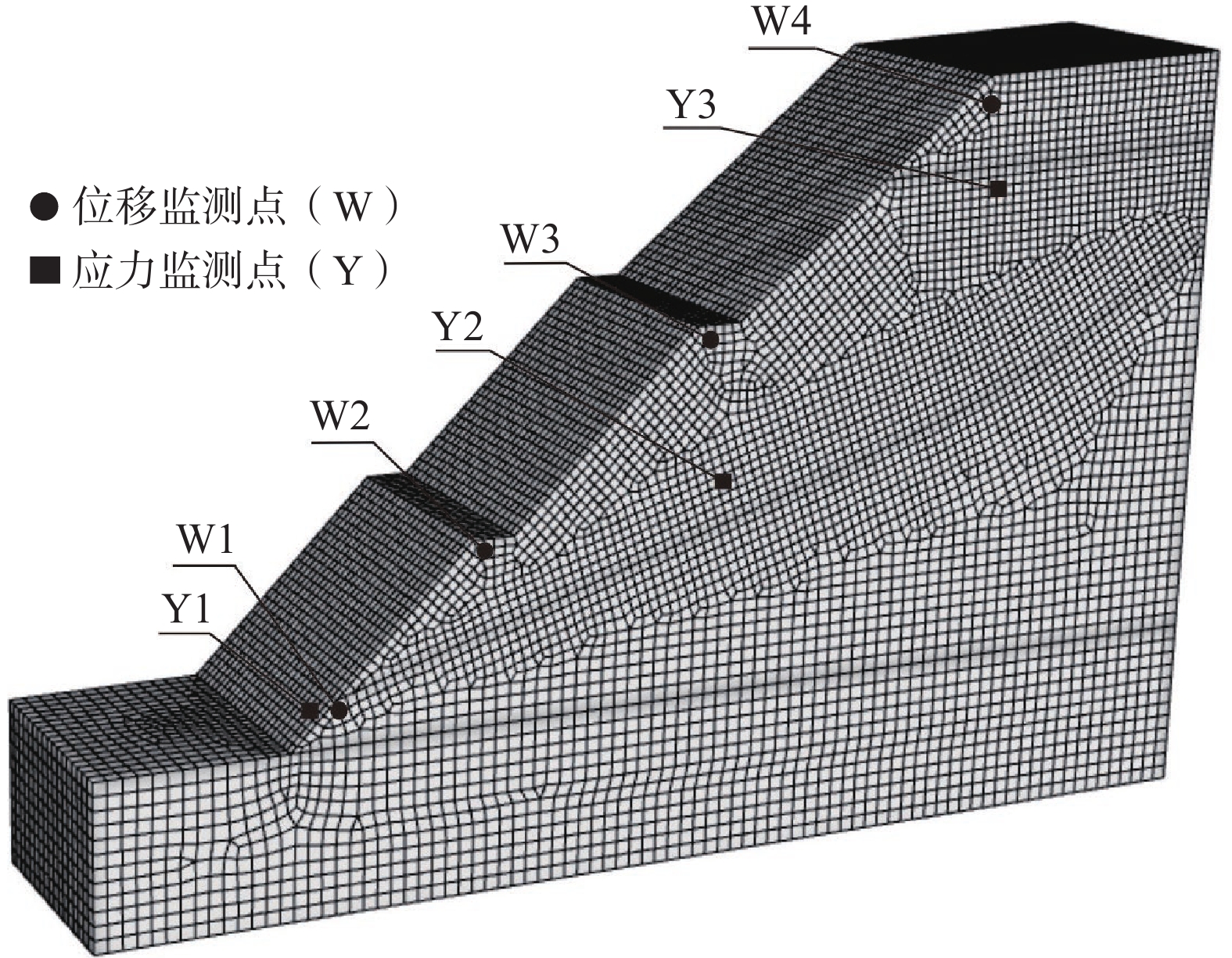
基于模糊数学分析已知降雨是营立村水泥厂土质边坡稳定性的主要影响因素,为进一步量化分析该土质边坡稳定性,使用FLAC3D 软件模拟不同降雨条件下该边坡的稳定性演变特征[18]。模型主要依据边坡的坡高、坡角等几何尺寸建立,由于边坡开挖为阶梯状,z轴分别为8.5 m、13.5 m、25.3 m,x轴长度为42 m,y轴长度为40 m。模型初始边界条件为:流体边界设置边坡表层为渗透面,坡脚和边坡底部为渗漏面;位移边界固定边坡底面,约束模型两侧的y轴位移。此外,为便于分析坡体在不同降雨条件下各层岩土体弹性模量、容量、剪应力、摩擦角等物理力学参数的变化情况[19],本次模拟在所建模型每级台阶坡脚处在对应台阶内部提取位移监测点与应力监测点(图2)。
岩土体物理力学参数基于地质调查结果及土工试验确定(表3),所建边坡模型采用Mohr-Coulomb准则和强度折减法求取稳定系数[20]。潜在滑动面主要计算原理如下:
表 3 边坡岩土体物理参数指标Table 3. Physical parameter indicators of slope rock and soil类型 容重
/(kg·m−3)泊松比 黏聚力
/MPa内摩擦角
/(°)抗剪强度
/MPa饱和粉土 1960 0.3 0.02 18 0.35 粉土 1820 0.25 0.04 25 0.51 砂岩 2550 0.25 8.2 35 8.91 石灰岩 2800 0.18 11.4 38 12.18 $$ {F_{\mathrm{S}}} = \frac{c}{{c'}} = \frac{{\tan \varphi }}{{\tan \varphi '}} $$ (9) $$ \alpha = \frac{1}{2}\arccos \left(\frac{{\left({\delta _1} - {\delta _3}\right)\tan {{\varphi '}}}}{2{c'} + \left({\delta _1} + {\delta _3}\right)\tan \varphi '}\right) $$ (10) 式中:c、c′——边坡土体初始状态和临界状态下的黏 聚力/kPa;
φ、φ′——边坡土体初始状态和临界状态下的内摩 擦角/(°);
α——最危险滑动面与最小主应力夹角/(°);
δ1、δ3——土体单元的第1和第3主应力/kPa。
3.2 天然状态下边坡稳定模拟分析
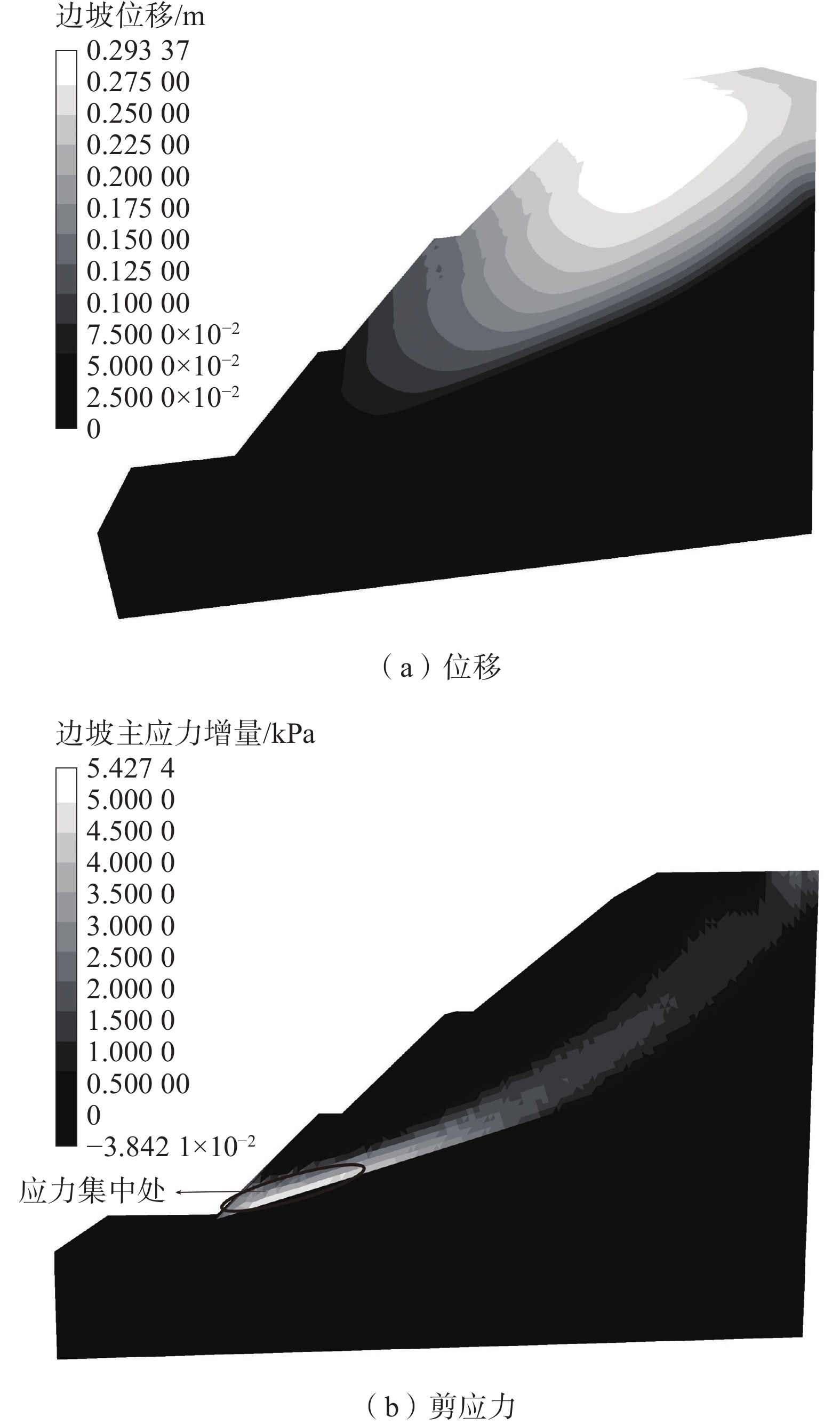
基于表3的岩土体力学参数采用FLAC3D数值模拟得到营立村水泥厂土质边坡在天然状态下边坡位移和剪应力空间分布图(图3)。图3(a)表明,天然状态下边坡的位移集中在边坡顶部区域,最大位移为29.3 cm,自坡顶向坡脚位移量具有减小趋势,直至边坡中下部无位移量。图3(b)表明,边坡内部应力变化最为显著,坡体在自重及岩性影响下剪应力集中分布于石灰岩及其上覆第四系沉积层界面附近,剪切力增量向边坡底部集中,最大剪切力累积在坡脚位置,说明在没有断裂的情况下马家沟组灰岩与其上覆第四系沉积层界面存在明显的渗透系数差,是最主要的结构面。模拟分析结果显示,此状态下边坡Fs=1.426,与模糊数学分析法得出的Fs=1.429几乎一致,综合判定该边坡天然状态下处于稳定状态。
3.3 降雨状态下边坡稳定性变化
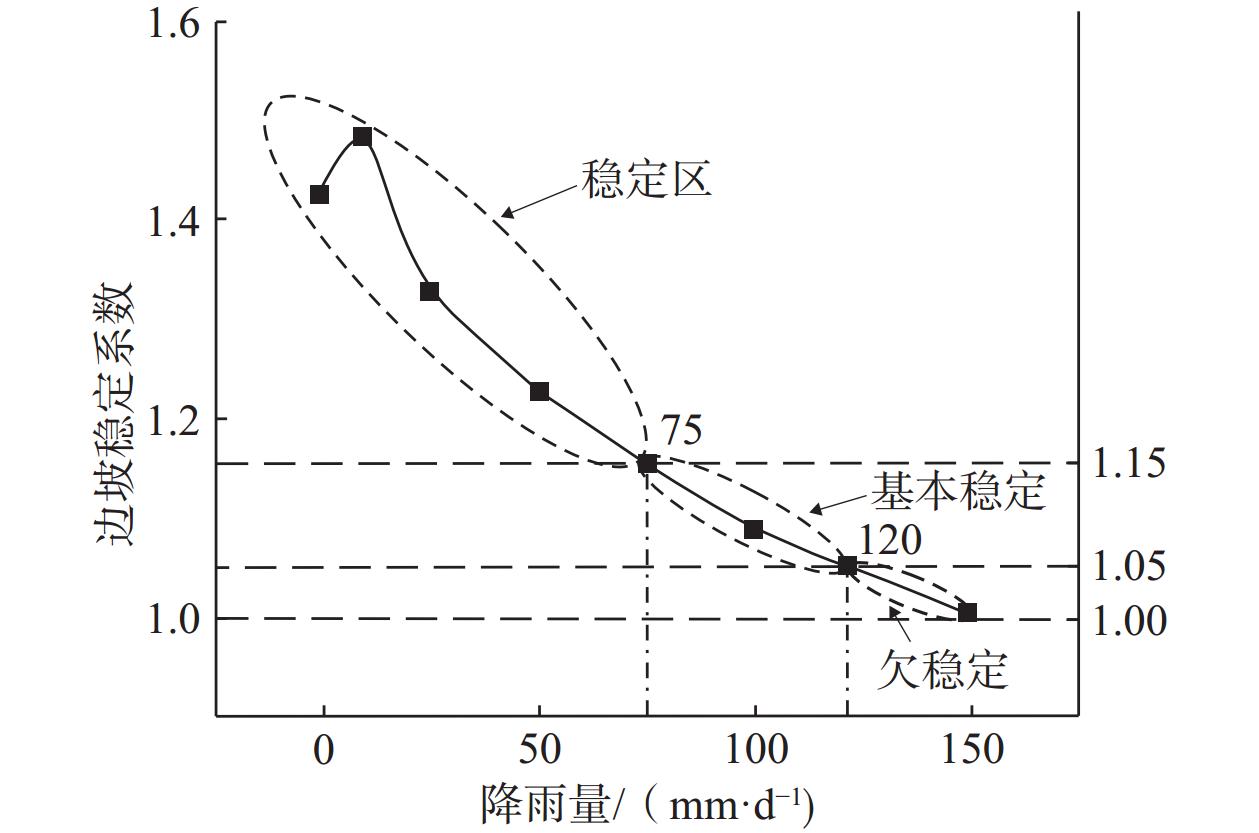
降雨会引起土体黏聚力和内摩擦角改变,进而影响边坡稳定性[21 − 23]。为了简化研究,将均匀雨型日降雨量设为基础分析条件。FLAC3D 模拟不同降雨强度条件下该边坡的稳定性,结果显示,随着日降水量增加稳定系数小幅升高后下降,整体呈现单峰型曲线形态(图4)。由图4可知,较小的降雨强度对边坡渗流场影响有限,基本无法引起地下水位变化,而雨水渗透引起边坡粉土的黏聚力增大超过了内摩擦角减小的效应,因此边坡稳定性出现了小幅升高。随着日降雨量继续增加,土体黏聚力与内摩擦角均为下降趋势,导致稳定系数快速下降,当降雨量增长至75 mm/d时Fs=1.15,边坡处于稳定状态;当降雨量增长至120 mm/d时Fs=1.05,边坡处于基本稳定状态;当降雨量增长至150 mm/d时,稳定系数为1.004,此时边坡已处于极限平衡的欠稳定状态,存在发生滑坡的潜在风险。
3.4 极端降雨条件下边坡稳定状态分析
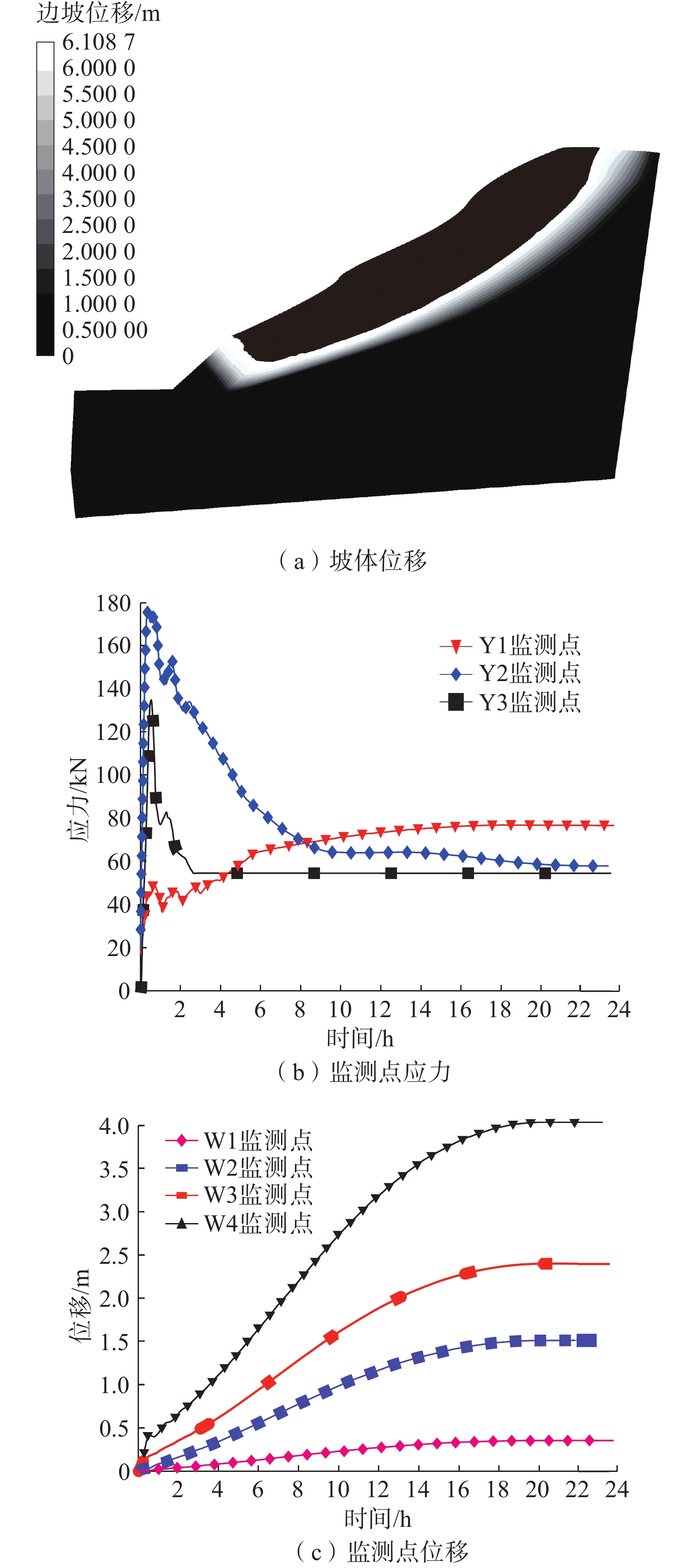
150 mm/d的极端降雨引起了潜在滑动带由坡体表面逐渐向坡体深部转移,直至滑动带沟通了岩土界面,计算模型中出现了一条明显的塑性剪切带,见图5(a)。降雨约为0.5 h时,雨水快速入渗引起土体自重增大,变形区域主要集中在表土层,局部具有轻微向外隆起的趋势,Y2、Y3监测点应力随之上升,分别为178.2 kN、132.4 kN;降雨约为3 h时,因入渗土体中水不能及时排出,孔隙水压力抵消一部分土体压力,内部的应力则呈现减小的趋势,Y2、Y3监测点应力分别为123.5 kN、53.5 kN;此后,Y3监测点应力基本不变,Y2监测点经历快速下降(3~9 h)后进入缓慢下降阶段,约至20 h时,Y2监测点应力稳定为59.8 kN。处于坡脚岩土界面附近的Y1监测点应力随降雨历时整体呈上升趋势,变化趋势大致呈三个阶段,6 h内为应力较快上升阶段,6~16 h为应力缓慢上升阶段,16 h后应力增长达到最大限度,最大应力增量约为78 kN,见图5(b)。随降雨历时增加,边坡顶面浅表层首先产生了拉裂缝,裂缝产生的位移量由顶部表层向内部减小,即相同降雨历时条件下,监测点位移量W4>W3>W2>W1。降雨约18 h时,各监测点位移量达到最大值,见图5(c),边坡已基本处于极限平衡状态。
4. 结论
综上可知,降雨对土质边坡稳定性有着显著的影响,雨水入渗导致土体自重增大、强度减小,使边坡内部发生局部剪切作用。随着降雨强度增大,边坡岩土层剪切面贯通形成完整的滑动面,最终导致土质边坡失稳。
(1) 基于地质资料及野外调研基础上,构建了边坡稳定性模糊综合评价模型,结合关系矩阵确定降雨为营立村水泥厂边坡稳定性最主要的影响因素(26%),并求得Fs =1.429>1.15,表明该土质边坡天然条件下处于稳定状态。
(2) 使用FLAC3D 模拟分析结果显示天然状态下边坡Fs=1.426;当降雨量75~120 mm/d时,Fs由1.15降至1.05;降雨量120~150 mm/d时,Fs由1.05降至1.004,此时边坡已处于极限平衡的欠稳定状态,存在发生滑坡的潜在风险。
(3) 模糊数学与FLAC3D 评价营立村水泥厂土质边坡天然状态下稳定性结果几乎一致,联合运用两种方法相互佐证能够提高评价准确性,使结果更符合边坡实际情况。
-
表 1 稳定性影响因素与量化取值表
Table 1 Stability influencing factors and quantified values
评价指标 滑坡稳定性级别及其分级标准 因素 因子 稳定(1) 基本稳定(2) 欠稳定(3) 不稳定(4) 降雨U1 降雨量/
(mm·d−1)25~<50 50~<100 100~250 >250 人类活动U2 工程活动 弱 一般 较强 强 地貌特征U3 坡面形态 平直形 凸状 凹状 阶状 坡度(θ)/(°) 0~<10 10~<30 30~<50 50~90 坡高(h)/m 0~<25 25~<35 35~<45 45~55 地层岩性U4 岩土性质 坚石 软石 硬土 普通土 风化作用U5 风化程度 微风化 中风化 强风化 全风化 表 2 营立村水泥厂切坡稳定性影响因素赋值表
Table 2 Impact factors of artificial slope cutting stability in Yingli Village quarry
P A A+B A-B Hi/% Aa Bb P1 3 2 1 1 11 23 −1 26 16.26 −0.707 3 P2 2 2 1 10 19 1 22 13.44 0.707 2 1 P3 1 1 7 15 −1 17 10.06 −0.707 2 2 1 P4 3 10 17 3 19 12.02 2.120 1 1 1 1 P5 6 14 −2 16 9.90 −1.410 B 12 9 8 7 8 88 表 3 边坡岩土体物理参数指标
Table 3 Physical parameter indicators of slope rock and soil
类型 容重
/(kg·m−3)泊松比 黏聚力
/MPa内摩擦角
/(°)抗剪强度
/MPa饱和粉土 1960 0.3 0.02 18 0.35 粉土 1820 0.25 0.04 25 0.51 砂岩 2550 0.25 8.2 35 8.91 石灰岩 2800 0.18 11.4 38 12.18 -
[1] 董震,巨玉文. 山西黄土地质灾害的特性及治理研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2015,15(7):138 − 141. [DONG Zhen,JU Yuwen. Characteristics of geological disasters in Shanxi loess and governance[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2015,15(7):138 − 141. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.07.025 DONG Zhen, JU Yuwen . Characteristics of geological disasters in Shanxi loess and governance[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2015 ,15 (7 ):138 −141 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.07.025[2] 万飞鹏, 杨为民, 邱占林, 等. 甘肃岷县纳古呢沟滑坡-泥石流灾害链成灾机制及其演化[J]. 中国地质,2023,50(3):911 − 925. [WAN Feipeng, YANG Weimin, QIU Zhanlin, et al. Disaster mechanism and evolution of Nagune Gully landslide-debris flow disaster chain in Minxian County, Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China,2023,50(3):911 − 925. (in Chinese with English abstract) WAN Feipeng, YANG Weimin, QIU Zhanlin, et al . Disaster mechanism and evolution of Nagune Gully landslide-debris flow disaster chain in Minxian County, Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China,2023 ,50 (3 ):911 −925 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 宋胜武,冯学敏,向柏宇,等. 西南水电高陡岩石边坡工程关键技术研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011,30(1):1 − 22. [SONG Shengwu,FENG Xuemin,XIANG Baiyu,et al. Research on key technologies for high and steep rock slopes of hydropower engineering in southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2011,30(1):1 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) SONG Shengwu, FENG Xuemin, XIANG Baiyu, et al . Research on key technologies for high and steep rock slopes of hydropower engineering in southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2011 ,30 (1 ):1 −22 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[4] 王继成,俞建霖,龚晓南,等. 大降雨条件下气压力对边坡稳定的影响研究[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(11):3157 − 3162. [WANG Jicheng,YU Jianlin,GONG Xiaonan,et al. Research on effect of closed air pressure on slope stability under intense rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(11):3157 − 3162. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2014.11.011 WANG Jicheng, YU Jianlin, GONG Xiaonan, et al . Research on effect of closed air pressure on slope stability under intense rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014 ,35 (11 ):3157 −3162 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2014.11.011[5] 刘传正, 崔原, 陈春利, 等. 辽宁抚顺西露天矿南帮滑坡成因[J]. 地质通报,2022,41(5):713 − 726. [LIU Chuanzheng, CUI Yuan, CHEN Chunli, et al. Research on the south side landslide at west open-pit coal mine in Fushun City, Liaoning Province of China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2022,41(5):713 − 726. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Chuanzheng, CUI Yuan, CHEN Chunli, et al
. Research on the south side landslide at west open-pit coal mine in Fushun City, Liaoning Province of China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022 ,41 (5 ):713 −726 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 张江伟,李小军,迟明杰,等. 滑坡灾害的成因机制及其特征分析[J]. 自然灾害学报,2015,24(6):42 − 49. [ZHANG Jiangwei,LI Xiaojun,CHI Mingjie,et al. Analysis of formation mechanism and characteristics of landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2015,24(6):42 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13577/j.jnd.2015.0605 ZHANG Jiangwei, LI Xiaojun, CHI Mingjie, et al . Analysis of formation mechanism and characteristics of landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2015 ,24 (6 ):42 −49 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13577/j.jnd.2015.0605[7] 罗忠行,雷宏权. 基于FLAC3D的米贝复式滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):52 − 62. [LUO Zhongxing,LEI Hongquan. Study on Mibei Landslide analysis based on FLAC3D[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):52 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) LUO Zhongxing, LEI Hongquan . Study on Mibei Landslide analysis based on FLAC3D[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020 ,31 (4 ):52 −62 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 王洋, 魏玉峰, 贺琮栖, 等. 反倾岩质边坡多级破坏边界折断深度计算模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(3):630 − 639. [WANG Yang, WEI Yufeng, HE Congxi, et al. A calculation model of boundary breaking depth for multilevel failure of anti-dip rock slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023,42(3):630 − 639. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Yang, WEI Yufeng, HE Congxi, et al . A calculation model of boundary breaking depth for multilevel failure of anti-dip rock slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023 ,42 (3 ):630 −639 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 彭建兵,王启耀,庄建琦,等. 黄土高原滑坡灾害形成动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(5):714 − 730. [PENG Jianbing,WANG Qiyao,ZHUANG Jianqi,et al. Dynamic formation mechanism of landslide disaster on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(5):714 − 730. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.05.059 PENG Jianbing, WANG Qiyao, ZHUANG Jianqi, et al . Dynamic formation mechanism of landslide disaster on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020 ,26 (5 ):714 −730 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.05.059[10] 支泽民,陈琼,张强,等. 地理探测器在判别滑坡稳定性影响因素中的应用——以西藏江达县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):19 − 26. [ZHI Zemin,CHEN Qiong,ZHANG Qiang,et al. Application of geographic detector in identifying influencing factors of landslide stability:A case study of the Jiangda County,Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):19 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.02.03 ZHI Zemin, CHEN Qiong, ZHANG Qiang, et al . Application of geographic detector in identifying influencing factors of landslide stability: A case study of the Jiangda County, Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (2 ):19 −26 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.02.03[11] 蔡欣育,任旭华,张继勋,等. 不同降雨类型对边坡稳定性影响的研究[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版),2020,42(2):34 − 39. [CAI Xinyu,REN Xuhua,ZHANG Jixun,et al. Study on the influence of different rainfall types on slope stability[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences),2020,42(2):34 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) CAI Xinyu, REN Xuhua, ZHANG Jixun, et al . Study on the influence of different rainfall types on slope stability[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences),2020 ,42 (2 ):34 −39 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] HOU Tianshun,DUAN Xiang,LIU Haoyu. Study on stability of exit slope of Chenjiapo tunnel under condition of long-term rainfall[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2021,80(17):1 − 14.
[13] 马蓓青,杜玉鹏,王怀星,等. 持续降雨条件下黄土边坡稳定性试验研究[J]. 水土保持学报,2021,35(5):50 − 56. [MA Beiqing,DU Yupeng,WANG Huaixing,et al. Experimental study on stability of loess slope stability under continuous rainfall[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,35(5):50 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2021.05.008 MA Beiqing, DU Yupeng, WANG Huaixing, et al . Experimental study on stability of loess slope stability under continuous rainfall[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2021 ,35 (5 ):50 −56 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2021.05.008[14] 苗青,白自斌,王洪霞,等. 山西秋季一次极端暴雨过程的异常特征分析[J]. 干旱气象,2021,39(6):984 − 994. [MIAO Qing,BAI Zibin,WANG Hongxia,et al. Abnormal characteristics of an extreme rainstorm process in autumn in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology,2021,39(6):984 − 994. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2021)-06-0984 MIAO Qing, BAI Zibin, WANG Hongxia, et al . Abnormal characteristics of an extreme rainstorm process in autumn in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology,2021 ,39 (6 ):984 −994 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2021)-06-0984[15] 邹凤钗,冷洋洋,陶小郎,等. 基于斜坡单元的滑坡风险识别——以贵州万山浅层土质斜坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):114 − 122. [ZOU Fengchai,LENG Yangyang,TAO Xiaolang,et al. Landslide hazard identification based on slope unit:A case study of shallow soil slope in Wanshan,Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):114 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZOU Fengchai, LENG Yangyang, TAO Xiaolang, et al . Landslide hazard identification based on slope unit: A case study of shallow soil slope in Wanshan, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (3 ):114 −122 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 王艳霞. 模糊数学在边坡稳定分析中的应用[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(9):3000 − 3004. [WANG Yanxia. Application of fuzzy mathematics to slope stability analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(9):3000 − 3004. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.09.053 WANG Yanxia . Application of fuzzy mathematics to slope stability analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010 ,31 (9 ):3000 −3004 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.09.053[17] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会. 滑坡防治工程勘查规范:GB/T 32864—2016[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2017. [General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China,Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Code for geological investigation of landslide prevention:GB/T 32864—2016[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China,2017. (in Chinese) General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Code for geological investigation of landslide prevention: GB/T 32864—2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. (in Chinese)
[18] 徐文刚,余旭荣,年廷凯,等. 基于FLAC3D的三维边坡稳定性强度折减法计算效率改进算法及其应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(5):1347 − 1355. [XU Wengang,YU Xurong,NIAN Tingkai,et al. Optimization and application of FLAC3D strength-reduction computation in three-dimension slope stability analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(5):1347 − 1355. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Wengang, YU Xurong, NIAN Tingkai, et al . Optimization and application of FLAC3D strength-reduction computation in three-dimension slope stability analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021 ,51 (5 ):1347 −1355 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] 吴朋宇, 张志红, 戴福初, 等. 顺层岩质边坡溃屈变形机制及失稳判定方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(2):517 − 525. [WU Pengyu, ZHANG Zhihong, DAI Fuchu, et al. Buckling deformation mechanism and instability judgment method of bedding rock slope[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(2):517 − 525. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Pengyu, ZHANG Zhihong, DAI Fuchu, et al . Buckling deformation mechanism and instability judgment method of bedding rock slope[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022 ,52 (2 ):517 −525 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[20] LI Tianzheng,GONG Wenping,YANG Xiaoli. Stability analysis of a non-circular tunnel face in soils characterized by modified Mohr-Coulomb yield criterion[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2021,109:103785. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103785
[21] MEDINA V,HÜRLIMANN M,GUO Zizheng,et al. Fast physically-based model for rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility assessment at regional scale[J]. CATENA,2021,201:105213. DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105213
[22] 陈林万,张晓超,裴向军,等. 降雨诱发直线型黄土填方边坡失稳模型试验[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):151 − 160. [CHEN Linwan,ZHANG Xiaochao,PEI Xiangjun,et al. Model test of the linear loess fill slope instability induced by rainfall[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):151 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202010041 CHEN Linwan, ZHANG Xiaochao, PEI Xiangjun, et al . Model test of the linear loess fill slope instability induced by rainfall[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (6 ):151 −160 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202010041[23] 王如宾,夏瑞,徐卫亚,等. 滑坡堆积体降雨入渗过程物理模拟试验研究[J]. 工程科学与技术,2019,51(4):47 − 54. [WANG Rubin,XIA Rui,XU Weiya,et al. Study on physical simulation of rainfall infiltration process of landslide accumulation body[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2019,51(4):47 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Rubin, XIA Rui, XU Weiya, et al . Study on physical simulation of rainfall infiltration process of landslide accumulation body[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2019 ,51 (4 ):47 −54 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(3)




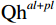
 下载:
下载:
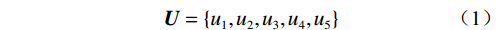
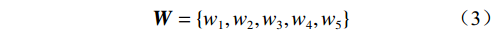
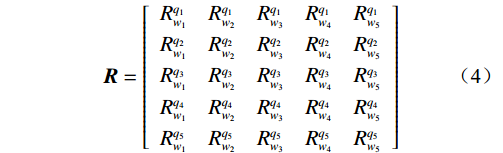
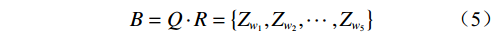
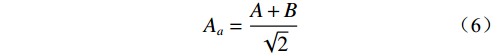
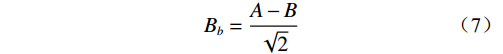
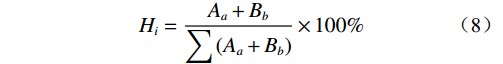
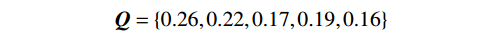
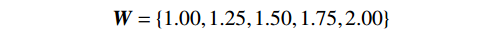
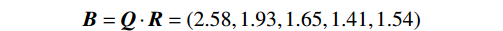
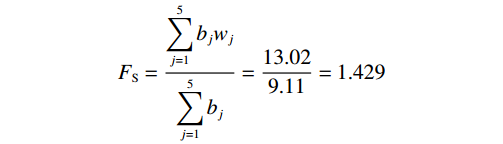
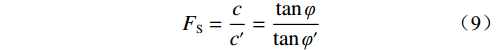
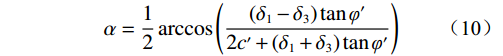
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS