Analysis of stability and kinematics of the dangerous rock mass in Zhangjiagou, Baoxing, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
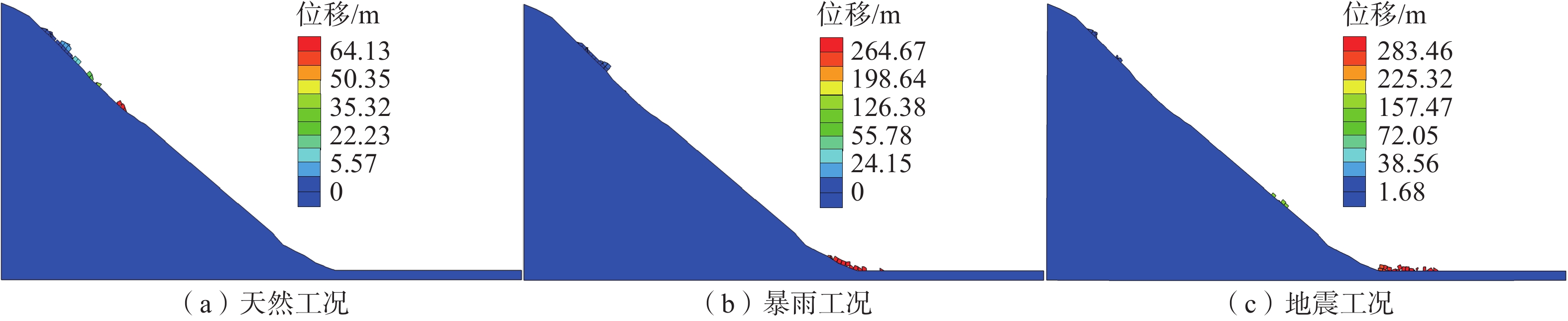
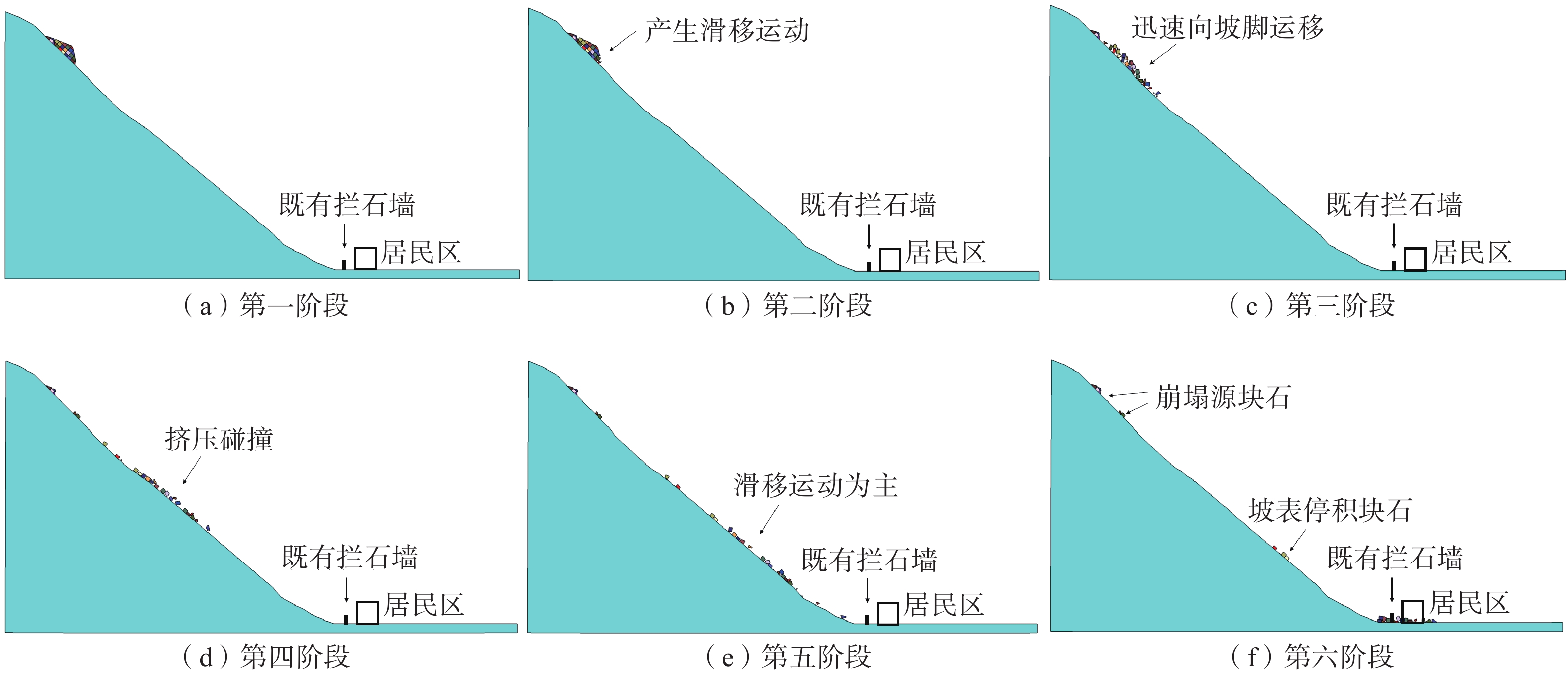
张家沟危岩体在2022年“6•1”芦山地震后被发现,稳定性差,严重威胁下方居民生命财产安全。基于稳定性计算及离散元数值分析方法对危岩体进行评价,选取稳定性最差的地震工况进行运动学分析,在上述研究基础上结合解析解与数值解成果设计相应防护措施。主要结论有:(1)张家沟危岩体结构破碎,顺坡向控制性结构面发育,破坏模式为滑移式;(2)稳定性计算与数值模拟结果皆表明张家沟危岩体在天然、暴雨、地震工况下均会失稳,其中地震工况下运动距离最长;(3)地震工况下危岩体的破坏模式为震裂—滑移式,运动过程中块石以滑移为主,跳高较小,同时坡面形态显著影响着落石运动特征;(4)落石间相互碰撞挤压会改变其运动特征及冲击动能大小,在一定程度上可增加致灾范围。成果可为类似灾害防治提供参考。
Abstract:After the “6 • 1” Lushan earthquake, unstable rock mass was discovered in Zhangjiagou, posing a severe threat to the safety of the residents and their property below. The dangerous rock mass was evaluated using stability calculation and the discrete element numerical analysis method, and the seismic condition with the highest threat level was selected for kinematic analysis. Based on this research, a combination of analytical solution and numerical solution was used to design corresponding protective measures. The main conclusions are as follows : (1) The structure of the unstable rock mass in Zhangjiagou is broken, and a controlling structural plane is developed along the slope. (2) The stability calculations and numerical simulations show that the Zhangjiagou unstable rock mass will become unstable under natural, rainstorm and seismic conditions, with the longest movement distance occurring during an earthquake. (3) The failure mode of the dangerous rock mass under seismic conditions is a shatter-slip type, where the rock mainly slips during movement, and the jump height is small. Additionally, the slope shape significantly affects the characteristics of rockfall movement. (4) The collision and extrusion between rockfalls can change their motion characteristics and impact kinetic energy, potentially increasing the scope of the disaster. The research results can provide a reference for similar disaster prevention and control efforts.
-
0. 引言
西南山地存在众多的不同成因的堆积体斜坡,坡体上常聚居村落、交通和水利水电等基础设施。在多种因素的作用下,堆积体斜坡常易形成大规模的滑坡,威胁人民生命财产安全。这类滑坡地处高山峡谷地貌,地质环境条件复杂多变,诱发滑坡变形的因素众多,其中地震和强降雨是主要的诱发因素,特别是两因素常相互作用防治难度大[1-2]。
炉霍县旦都乡马居滑坡位于鲜水河断裂带附近,受近年来地震活动[3]和降雨影响,从2015年开始明显变形,且逐年加剧,现已演化为一大型滑坡。滑坡的破坏模式和滑坡机理在区域内具有典型性,本次拟对此滑坡的变形破坏机理进行研究,以期理清这类滑坡变形发展的过程和各因素相互作用的影响,进一步优化防治方案,评价方案的有效性和安全性,为地质灾害防治和风险管控提供依据。
1. 研究区地质环境条件
炉霍县地处青藏高原东南边缘,高山峡谷地貌区,海拔高度3300~3600 m,区域内河流为鲜水河支流。平均年降雨量700 ~920 mm。近10年降雨量较平稳。区域内地质构造复杂,新近构造活动强烈(图1)。历史上遭受多次地震的影响,1973年炉霍县鲜水河断裂带发生7.6级地震,2014年11月22日鲜水河断裂带的康定地区发生6.3级地震及多次余震。研究区基本地震动峰值加速度为0.3 g,反应谱特征周期为0.4 s[4]。
![]() 图 1 研究区地震断裂及历史地震分布图[4]Figure 1. Distribution map of seismic faults and historical earthquakes in the study area
图 1 研究区地震断裂及历史地震分布图[4]Figure 1. Distribution map of seismic faults and historical earthquakes in the study area研究区地层主要为三叠系上统雅江组上段(
2. 滑坡基本特征
2.1 滑坡基本概况
滑坡整体呈圈椅状,滑坡后缘以寺庙(马居庙)外侧围墙前拉张裂缝为界,前缘以俄觉龙日沟沟床为界,左侧和右侧以水沟为界,滑坡面积4.6×104 m2,厚10~13 m,体积60×104 m3,属中型土质滑坡。滑坡主滑方向为100°,整体坡度约30°,呈前陡后缓的趋势,前缘坡度约35°~40°,后缘坡度约20°~25°。
2.2 变形特征
根据滑坡的变形破坏特征将该滑坡划分为2个变形区,其中Ⅰ区为寺庙及下方坡体,Ⅱ区为寺庙外北侧区域。变形Ⅰ区主要变形特征有:前缘沟床侵蚀垮塌下错台坎,横向拉张裂缝,后缘拉裂缝、寺庙房屋裂缝等。变形Ⅱ区主要变形特征有:后缘拉裂缝、地面开裂、电杆歪斜、前缘多级下错陡坎群等。
调查表明,该滑坡区在2015年以前未出现可见变形,受2014年11月康定地震及余震影响,该区震感明显,2015年雨季时滑坡前缘陆续变形,以后每年雨季滑坡体变形呈现出了逐年加剧的趋势,滑坡体后缘也陆续出现了变形,2020年发生了一次短历时强降雨,雨强约为50年一遇降雨,诱发了俄觉龙日沟泥石流,对坡脚冲刷淘蚀,滑坡前缘出现了大规模的滑坡变形,并进一步牵引后缘变形加剧。
2.3 坡体结构特征
滑体主要由第四系全新统滑坡堆积层组成。厚度为10~13 m,主要成份为含黏碎石土,所充填黏性土褐黄色,稍湿,无摇振反应,干强度较高,切面较光滑,碎石成分主要为变质砂质、板岩,常见钙质胶结,粒径一般2~10 cm,含量大于50%。滑带位于滑体或基覆界面,含水量较大,地下水活动痕迹明显。滑床为三叠系上统雅江组上段含粉砂炭质绢云板岩(T3y3)和变质长石石英砂岩互层(表1)。滑坡区工程地质平面图见图2,滑坡体结构特征见图3。
表 1 滑坡区主要岩土参数表Table 1. Geotechnical parameters of landslide area岩土体 体积模量/MPa 剪变模量
/MPa天然状态 饱和状态 重度/(t·m−3) 内聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 重度/(t·m−3) 内聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 滑坡体 15.60 5.18 2.01 24.3 30.8 2.05 22.9 27.8 强风化 15.20 7.80 22 40 35 - - - 中风化基岩 20.00 12.00 27 1900 42.8 - - - 3. 滑坡变形破坏机理分析
马居滑坡是位于地震区的一堆积体滑坡,勘查表明,该滑坡坡度较陡,滑坡体结构为含黏碎石土层。下覆基岩为含粉砂炭质绢云板岩具有较好的隔水性,基覆界面地下水活动较强。受2014年地震作用滑坡体结构完整性和稳定性变差,随后受降雨和坡脚下切作用坡体变形持续加大,滑坡体处于不稳定—欠稳定状态。
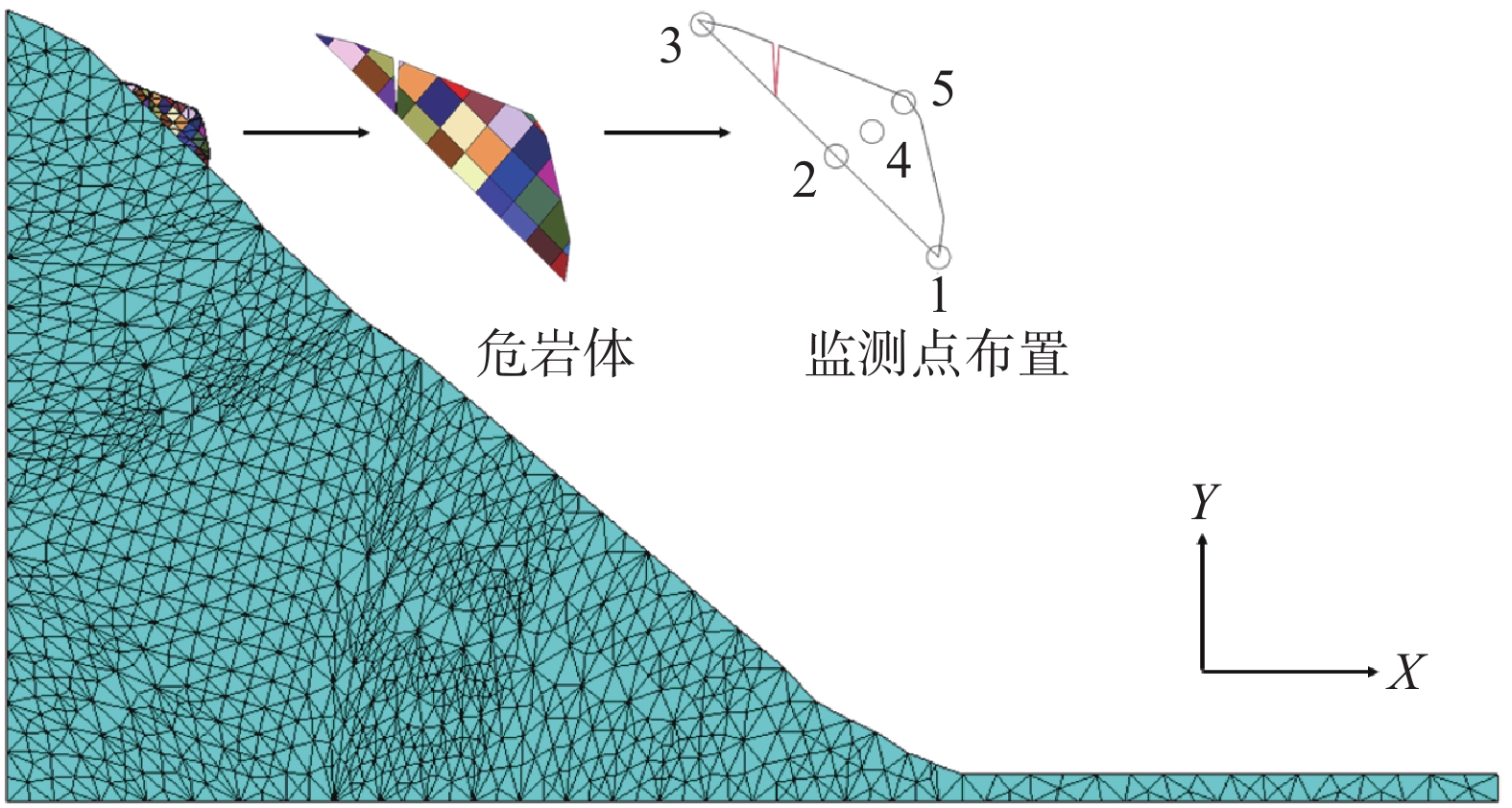
该滑坡变形过程及所受影响因素明确,但总体来说,该滑坡地质环境条件复杂多变,诱发因素和作用方式多变,通过对滑坡变形特征及变形历史分析,基本理清了近期滑坡变形的时空关系,为更好地查清该滑坡变形破坏机理,更好地指导滑坡防治方案的制定,这里对滑坡三个重要的影响因素进行数值分析。选取的分析剖面为滑坡主滑方向的2-2′剖面,模型水平方向左右采用位移约束,模型的底部采用竖向位移约束。共划分14070个结点,6811个单元。参数见表1。
3.1 地震作用下坡体变形机理分析
对马居滑坡变形历史调查表明,2014年发生在鲜水河断裂带上的康定地震,对该滑坡稳定性影响大,为了进一步查明地震对该滑坡具体影响程度,这里选取该地区多遇地震加速度及特征周期人工合成地震波进行时程分析[5]。人工合成的地震波见图4。
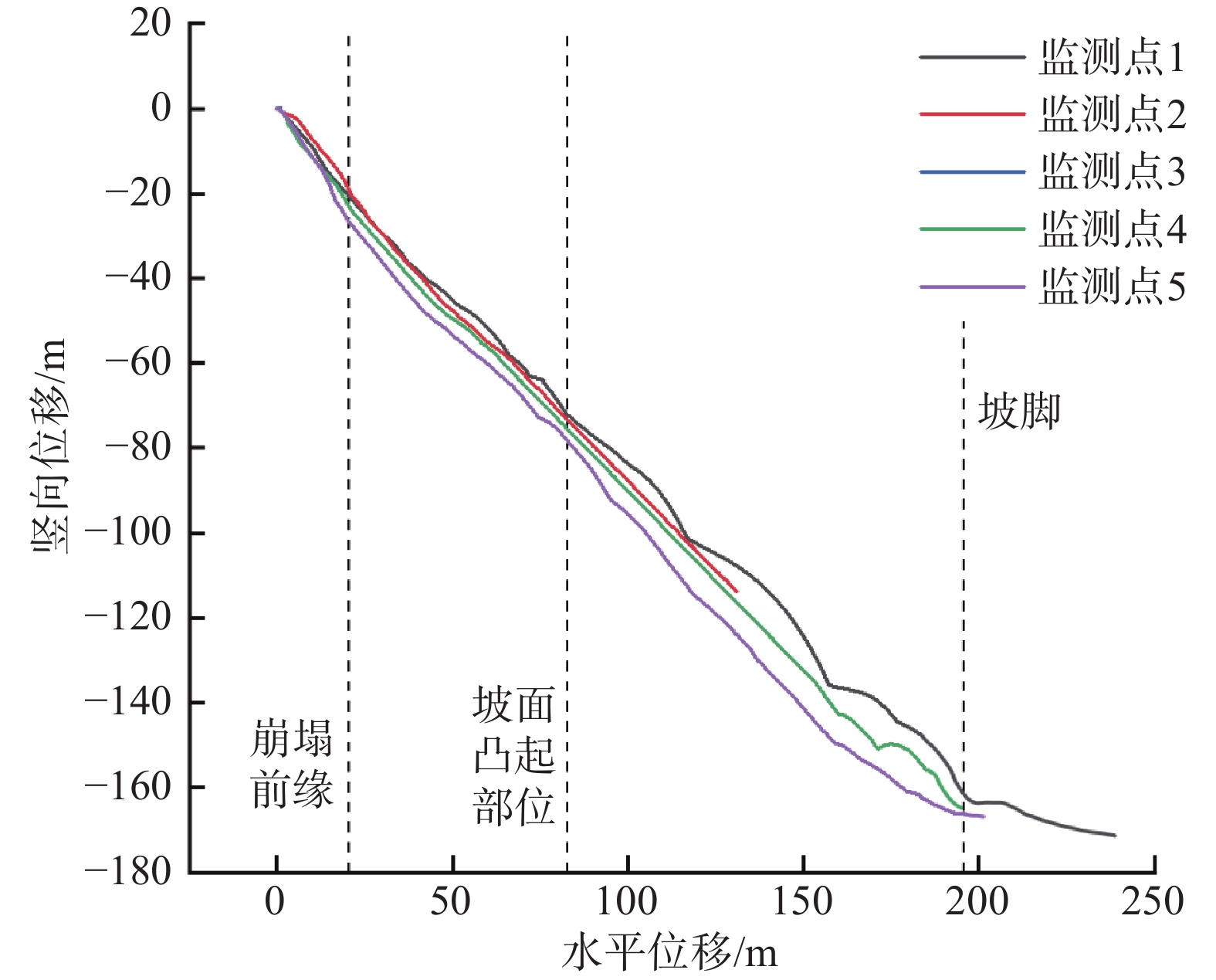
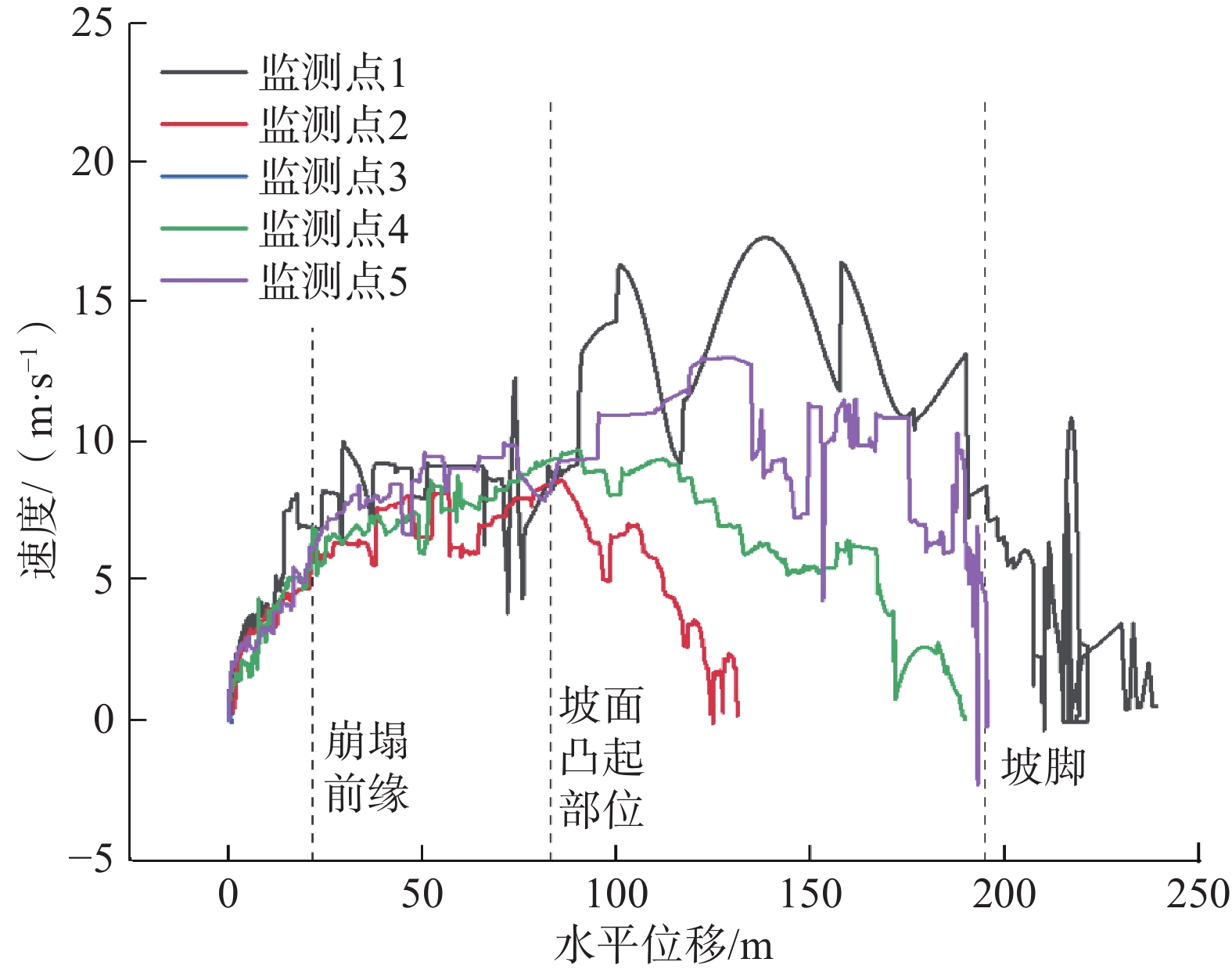
时程分析获得了斜坡在地震作用下坡体的塑性区分布图及最大剪应变增量云图[6](图5、图6)。
模拟结果表明地震作用对斜坡稳定性影响大,斜坡体内塑性区基本上成片相连,特别是斜坡顶部出现了大面积的塑性区,该区域也是地表裂缝发现最多的区域,剪应变云图表明在基覆界面处剪应变增量最大,且出现了两个较大的区域,特别是沟道向上约10~30 m的位置,勘查表明该区裂缝发育密集。在地震荷载作用下,坡体稳定性下降,斜坡土体结构遭到破坏,地震后不久,在坡体缓坡平台前缘部分相继出现开裂,该点随即纳入监控。
3.2 坡脚沟道下切诱发坡体变形破坏分析
2020年7月该区域暴发了短历时强降雨,俄觉龙日沟暴发了50年一遇泥石流,坡脚沟道淘蚀严重,滑坡体前缘变形加剧。为了查明沟道下切对滑坡稳定性影响,以本次勘查沟道内的基覆界面作为最大冲刷深度进行数值分析,采用参数折减法进行稳定系数计算。获得下切后稳定系数为1.00,最大剪应变区域延伸至沟道底部,表明沟道下切后牵引作用明显,直接导致坡体变形加剧(图7)。
3.3 不同降雨频率条件下稳定性分析
该滑坡不但受到短历时强降雨冲刷坡脚的影响,变形历史表明,长历时降雨也对滑坡的稳定性影响较大。研究表明[7-19],滑坡体采用Mein-Larson降雨入渗模型能较好地模拟出降雨对坡体含水率影响,可计算出不同时刻坡体湿润锋深度,降雨结束后,再采用渗透模型计算各时刻地下水的分布特征,对于特征时间结点采用强度折减法计算出各时刻滑坡稳定系数,以此评价降雨全历时滑坡的稳定性变化。滑坡体的饱和渗透系数为0.42 m/h,100年一遇降雨强度为0.034 m/h,50年一遇降雨强度为0.031 m/h,20年一遇降雨强度为0.026 m/h,10年一遇降雨强度为0.023 m/h,常年降雨强度为0.015 m/h,滑坡体的饱和渗透系数大于小时降雨强度,则垂直湿润锋深度
(1) 式中:M——饱和含水率与初始含水率的差值(本次取0.1);
p——降雨强度m/h;
t——降雨历时/h。
本次降雨历时综合近年来该地区长历时强降雨并综合类似文献[6]后综合确定计算时长为10 d。强降雨入渗坡体后采用地下水渗透模型进行模拟分析,地表及沟道表明设置为透水边界,其余设置为不透水边界条件。
分析结果可以看出强降雨的雨强越大对滑坡的稳定性影响越大,强降雨在降雨过程中坡体浅表饱和,湿润锋下移,但是滑坡稳定下降不明显,随着湿润锋向坡体转移过中滑坡体的稳定性有较大幅度的下降,随后随着地下水沿着隔水界面活动时,滑坡稳定性长期处于不稳定状态,待滑坡体内的地下水基本被疏干后滑坡体整体稳定性逐渐恢复到初始状态。说明滑坡风险管控中不但要关注降雨时刻会诱发滑坡灾害,在降雨过后较长时间(可能5 d左右)内照样会出现滑坡灾害(图8)。
本次对于降雨入渗研究表明厚层堆积体滑坡的稳定性较降雨条件下浅表层滑坡稳定性的变化在降雨阶段有所不同,主要体现在浅表层无限边坡和岩质边坡[20]的稳定性在降雨期间下降很快[6],而厚层堆积体滑坡的整体稳定性虽有向下的趋势,但是整体稳定性下降不大(图9)。
3.4 滑坡变形破坏机理小结
文中对马居滑培的机理分析遵循该滑坡变形历史过程进行模拟,力求获得该滑坡地震、坡脚下切、强降雨入渗等因素的影响。分析结果表明:马居滑坡先是地震作用对坡体损伤作用明显,促使坡体裂隙发育,位于基覆界面的滑面基本形成,滑坡体整体处于欠稳定状态,后期随着降雨入渗的影响,滑坡体处于缓慢变形,2020年的短历时强降雨诱发泥石流冲刷下切坡脚,诱发前缘大规模滑坡,牵引作用使得滑面进一步贯通,变形加剧,坡体整体稳定性进一步下降。模拟结果很好地拟合了滑坡变形破坏过程,进一步揭示了滑坡变形破坏机理,这为工程防治和风险管控打下了基础。
4. 滑坡防治方案分析
4.1 防治方案
马居滑坡坡体上常住人口多,周边斜坡失稳后将直接威胁寺庙安全,其后果严重,属大型地质灾害。该滑坡地质环境条件复杂,滑坡诱发因素多,地震、降雨等叠加后易形成特大型灾害。
滑坡体及周边地形坡度大,从寺庙至沟道斜坡基本上不具备设置抗滑支挡的工程施工条件,但该段斜坡稳定性最差,在天然状态下其稳定系数介于1.03~1.05,沟道下切后坡体的稳定性将下降到1.0附近,若继续冲刷将整体失稳。寺庙建在缓坡平台上,寺庙前缘有一较缓坡平台,可作为抗滑桩施工场地,若在此设置抗滑桩将直接针寺庙建筑物进行保护。
所以,在综合考虑滑坡变形破坏机理和施工条件的基础上,确定了本滑坡治理方案:在滑坡体中部(寺庙前缘)抗滑支挡,坡脚沟道固床防止下切。
4.2 坡脚防护
坡脚沟道下切持续牵引坡体整体变形,坡脚沟道的防护措施是必要的。坡脚防护有两种方案,一种是沟道固床,保持现有状态,沟道不继续下切,前缘坡体在自然条件下逐步稳定。另外一种方案就是回淤压脚,提高滑坡前缘稳定性。后一种方案属于主动防治方案,这里选取回淤高度2 m、4 m、6 m、8 m、10 m进行回淤压脚效果分析,分析采用参数折减法。
分析结果表明,不同回淤高度的压脚提升滑坡稳定性差距较大,回淤高度8 m以内对滑坡前缘稳定性基本上无明显改善,只有当回淤高度超过8 m时才有较大幅度的提高。通过对滑坡前缘非稳定状态下的最大剪应变云图分析,滑坡前缘最不利滑面的剪出口距沟底的高度大于8 m,若回淤高度小于8 m,对稳定性的贡献基本上很小,所以稳定系数一直处于徘徊于1.03附近,若要大幅度提高滑坡整体稳定性,回淤压脚的高度至少要大于10 m,考虑到该滑坡体坡脚沟道纵坡较陡、沟道较长,必须采用多道高坝才能达到治理的效果(图10)。
4.3 极端条件下防治方案安全性评价
滑坡区地处中国最活跃的地震断裂带上,发生地震可能性大,对在地震工况及强降雨条件下防治方案的安全性进行评价是必要的[21-22]。本次考虑到在极端条件下,如地震和长历时强降雨来袭后,滑坡前缘失稳,或者在坡脚淘蚀作用长期作用下滑坡前缘坡体累进破坏导致前缘整体失稳,使抗滑桩前缘失去支挡,在这种条件下对上部抗滑桩方案的安全性进行评价。滑坡区基本地震动峰值加速度为0.3 g,多遇地震动峰值加速度为0.1 g,罕遇地震0.57g[4](通过数值分析获得了各工况条件下滑坡稳定性分区云图图11-图15)。
数值分析表明前缘失去支挡后,抗滑桩方案对上部保护对象能有效的保护,稳定性差的部分就是上部滑体及后缘陡坡部分,天然工况及三种地震工况下稳定系数依次降低,分别为1.4,1.3,1.2,1.0。数值分析结果说明在极端情况发生后,上部滑坡不会随着前缘失去支挡后随即破坏且还具有一定安全余度,但是该斜坡坡度陡,易在余震和强降雨作用下再次发生变形破坏,故在极端情况发生后,抗滑桩方案能够为斜坡上的居民赢得撤离时间,提高抗风险的能力。
5. 结论
通过对马居堆积体滑坡变形破坏机理及防治方案研究,得到如下结论:
(1)马居滑坡受地震作用和降雨作用双重影响下,地震作用下坡体结构损伤严重,滑坡体稳定性下降,后期降雨作用下滑坡变形进一步加剧,滑坡目前处于欠稳定和不稳定状态。
(2)对降雨入渗坡体的研究表明,短历时降雨对滑坡的稳定性影响较小,长历时降雨在土体的湿润锋到达一定深度后滑坡的稳定性才有较大幅度的下降,若降雨历时较短,对滑坡的稳定性影响有限,这相对于无限斜坡整体稳定性要好。
(3)短历时强降雨能形成较强的地表径流,形成洪水或泥石流冲刷和淘蚀滑坡坡脚,对滑坡的稳定性的影响较大,易形成牵引式滑坡,进而堵塞沟道形成泥石流的堵溃点。
(4)推荐采用抗滑桩加固床防治方案,固床回淤高度应综合考虑滑坡剪出口位置,抗滑支档方案在极端情况下有一定抗风险能力。
-
表 1 岩体力学基本参数取值(天然)
Table 1 Fundamental mechanical parameters of rock mass (natural)
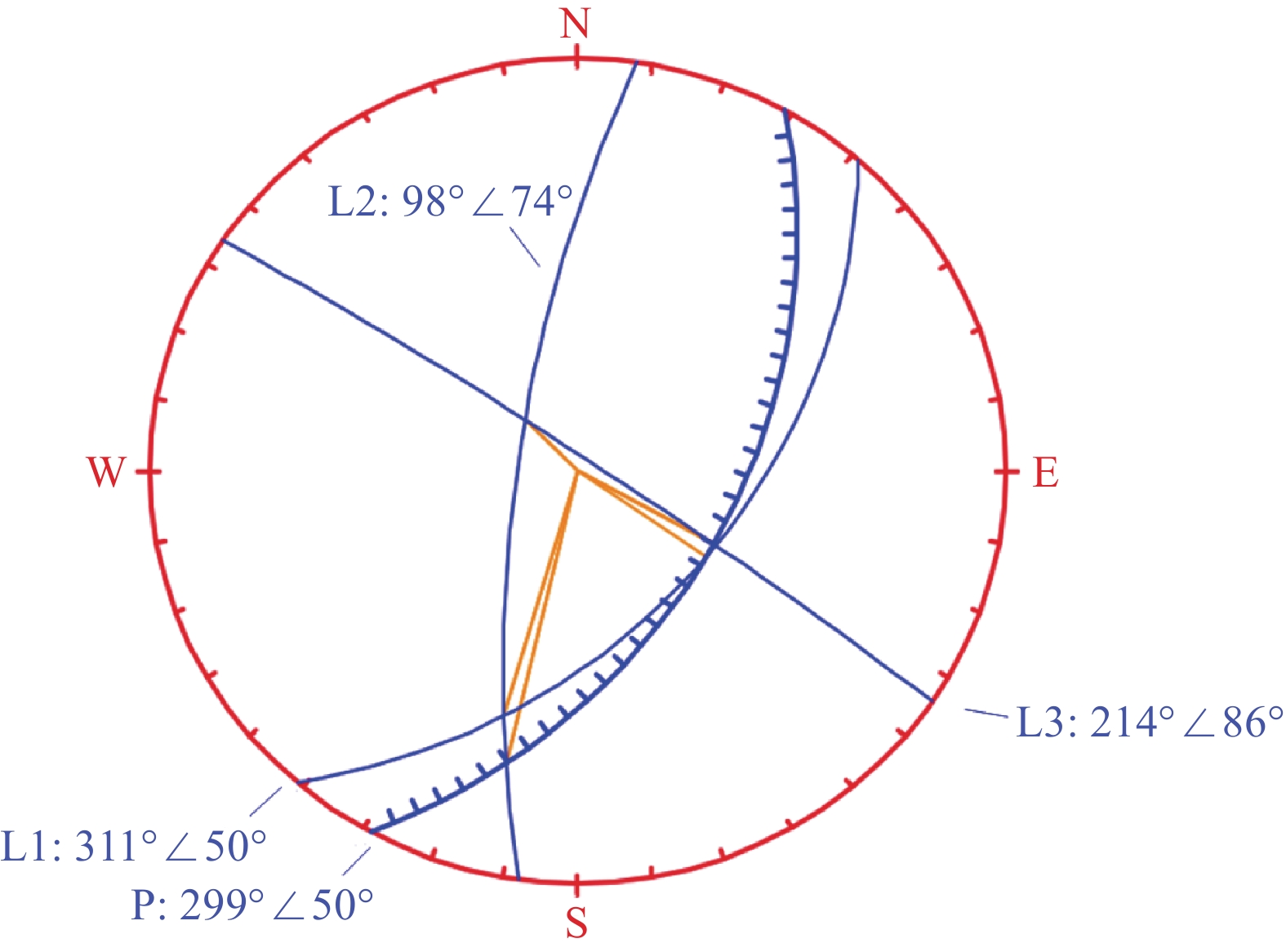
岩性 密度/(kg·m−3) 节理刚度/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 黏聚力/MPa 花岗岩 2750 47.5 11.2 基岩 2960 58.2 15.7 L1 2.2 30.5 0.8 L2 2.2 24.9 0.6 L3 2.2 25.3 0.7 表 2 稳定性计算参数选取
Table 2 Selection of calculation parameters for stability analysis
计算
工况重度/
(kN·m−3)后缘陡倾裂隙
深度/m裂隙或滑面充水
高度/m滑面长度/
m裂隙水压力/
(kN·m−1)软弱结构面
倾角/ (°)地震水平
系数结构面综合
黏聚力/MPa结构面综合
内摩擦角/(°)天然 26.95 6.68 1.96 25.32 19.2 45 0 0.65 31 暴雨 27.45 6.68 2.25 25.32 25.3 45 0 0.61 27 地震 26.95 6.68 1.96 25.32 19.2 45 0.16 0.65 31 表 3 稳定性计算结果
Table 3 Stability analysis calculation results
计算工况 破坏模式 稳定性系数 稳定状态 天然 滑移式 1.18 欠稳定 暴雨 滑移式 1.00 欠稳定 地震 滑移式 0.93 欠稳定 -
[1] 张倬元, 王士天, 王兰生. 工程地质分析原理[M]. 4版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016: 1 − 5 ZHANG Zhuoyuan, WANG Shitian, WANG Lansheng. Principles of engineering geological analysis[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016: 1 − 5. (in Chinese)
[2] ASHWOOD W,HUNGR O. Estimating total resisting force in flexible barrier impacted by a granular avalanche using physical and numerical modeling[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2016,53(10):1700 − 1717. DOI: 10.1139/cgj-2015-0481
[3] FAN X M,SCARINGI G,KORUP O,et al. Earthquake-induced chains of geologic hazards:patterns,mechanisms,and impacts[J]. Reviews of Geophysics,2019,57(2):421 − 503. DOI: 10.1029/2018RG000626
[4] 梅雪峰. 落石冲击荷载作用下的桩板拦石墙-缓冲层组合结构动力响应[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2022. MEI Xuefeng. Dynamic response of pile-sheet retaining wall with cushion layer under rockfall impact[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 尹迪,董培育,曹建玲,等. 川滇地区地震危险性数值分析[J]. 地球物理学报,2022,65(5):1612 − 1627. [YIN Di,DONG Peiyu,CAO Jianling,et al. Numerical analysis of the seismic hazard in Sichuan-Yunnan region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2022,65(5):1612 − 1627. (in Chinese with English abstract) YIN Di, DONG Peiyu, CAO Jianling, et al. Numerical analysis of the seismic hazard in Sichuan-Yunnan region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(5): 1612-1627. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] MAERZ N H. New risk-consequence rockfall hazard rating system for Missouri highways using digital image analysis[J]. Environmental and Engineering Geoscience,2005,11(3):229 − 249. DOI: 10.2113/11.3.229
[7] P BUDETTA, C DE LUCA ,M NAPPI. Quantitative rockfall risk assessment for an important road by means of the rockfall risk management (RO.MA.) method[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2016,75(4):1377–1397.
[8] 杨志法,尚彦军,刘英. 关于岩土工程类比法的研究[J]. 工程地质学报,1997,5(4):299 − 305. [YANG Zhifa,SHANG Yanjun,LIU Ying. Study on the analogism in geotechnical engineering[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,1997,5(4):299 − 305. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Zhifa, SHANG Yanjun, LIU Ying. Study on the analogism in geotechnical engineering[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 1997, 5(4): 299-305. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王玉锁,杨国柱. 隧道洞口段危岩落石风险评估[J]. 现代隧道技术,2010,47(6):33 − 39. [WANG Yusuo,YANG Guozhu. Rockfall risk assessment for a tunnel portal section[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2010,47(6):33 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Yusuo, YANG Guozhu. Rockfall risk assessment for a tunnel portal section[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2010, 47(6): 33-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 王新民,康虔,秦健春,等. 层次分析法-可拓学模型在岩质边坡稳定性安全评价中的应用[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2013,44(6):2455 − 2462. [WANG Xinmin,KANG Qian,QIN Jianchun,et al. Application of AHP-extenics model to safety evaluation of rock slope stability[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2013,44(6):2455 − 2462. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Xinmin, KANG Qian, QIN Jianchun, et al. Application of AHP-extenics model to safety evaluation of rock slope stability[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(6): 2455-2462. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 刘贺军,吴玉涛,李晓乐,等. 河北阜平县石滩地村危岩体变形破坏模式及稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(4):50 − 57. [LIU Hejun,WU Yutao,LI Xiaole,et al. Deformation failure mode and stability analysis of dangerous rock mass in Shitandi Village,Fuping County of Hebei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(4):50 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Hejun, WU Yutao, LI Xiaole, et al. Deformation failure mode and stability analysis of dangerous rock mass in Shitandi Village, Fuping County of Hebei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(4): 50-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 邬爱清. 基于关键块体理论的岩体稳定性分析方法及其在三峡工程中的应用[J]. 长江科学院院报,2019,36(2):1 − 7. [WU Aiqing. Series methods of analyzing rock mass stability based on key block theory and their applications to Three Gorges project[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2019,36(2):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Aiqing. Series methods of analyzing rock mass stability based on key block theory and their applications to Three Gorges project[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2019, 36(2): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 陈宙翔,叶咸,张文波,等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影的强震区公路高位危岩崩塌形成机制及稳定性评价[J]. 地震工程学报,2019,41(1):257 − 267. [CHEN Zhouxiang,YE Xian,ZHANG Wenbo,et al. Formation mechanism analysis and stability evaluation of dangerous rock collapses based on the oblique photography by unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2019,41(1):257 − 267. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Zhouxiang, YE Xian, ZHANG Wenbo, et al. Formation mechanism analysis and stability evaluation of dangerous rock collapses based on the oblique photography by unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2019, 41(1): 257-267. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 马显东, 周剑, 张路青, 等. 强震区公路沿线崩塌危岩体特征提取及失稳分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(增刊1): 2901 − 2914 MA Xiandong, ZHOU Jian, ZHANG Luqing, et al. Feature extraction and instability analysis of dangerous rock mass along highway in meizoseismal areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(Sup 1): 2901 − 2914. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 刘宝臣,王良玉,曾榕,等. 桂林翻山危岩稳定性评价的离散元分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2022,22(6):2409 − 2418. [LIU Baochen,WANG Liangyu,ZENG Rong,et al. Discrete element analysis of stability evaluation of Guilin Fanshan dangerous rock[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2022,22(6):2409 − 2418. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.06.034 LIU Baochen, WANG Liangyu, ZENG Rong, et al. Discrete element analysis of stability evaluation of Guilin Fanshan dangerous rock[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(6): 2409-2418. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.06.034
[16] 刘国阳,孟海怡,宁宝宽,等. 基于三维非连续变形分析的巨石崩塌运动研究[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(1):246 − 256. [LIU Guoyang,MENG Haiyi,NING Baokuan,et al. Study on collapse and movement of a boulder based on 3D discontinuous deformation analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(1):246 − 256. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Guoyang, MENG Haiyi, NING Baokuan, et al. Study on collapse and movement of a boulder based on 3D discontinuous deformation analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(1): 246-256. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 王朋,贾洪彪,马淑芝,等. 梳妆台危岩体稳定性评价及落石运动特征研究[J]. 安全与环境工程,2022,29(4):139 − 146. [WANG Peng,JIA Hongbiao,MA Shuzhi,et al. Stability evaluation of dangerous rock mass in dressing table and study on characteristics of rockfall movement[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2022,29(4):139 − 146. (in Chinese) WANG Peng, JIA Hongbiao, MA Shuzhi, et al. Stability evaluation of dangerous rock mass in dressing table and study on characteristics of rockfall movement[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(4): 139-146. (in Chinese)
[18] 张青宇,唐世明,沈军辉. 四川麻柳沟地震崩塌落石运动特征分析[J]. 人民长江,2015,46(13):39 − 41. [ZHANG Qingyu,TANG Shiming,SHEN Junhui. Analysis of movement characteristics of collapse rockfall in Maliugou earthquake[J]. Yangtze River,2015,46(13):39 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Qingyu, TANG Shiming, SHEN Junhui. Analysis of movement characteristics of collapse rockfall in Maliugou earthquake[J]. Yangtze River, 2015, 46(13): 39-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王栋,王剑锋,李天斌,等. 西南山区某铁路隧道口高位落石三维运动特征分析[J]. 地质力学学报,2021,27(1):96 − 104. [WANG Dong,WANG Jianfeng,LI Tianbin,et al. Analysis of three-dimensional movement characteristics of rockfall:A case study at a railway tunnel entrance in the southwestern mountainous area,China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2021,27(1):96 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Dong, WANG Jianfeng, LI Tianbin, et al. Analysis of three-dimensional movement characteristics of rockfall: a case study at a railway tunnel entrance in the southwestern mountainous area, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2021, 27(1): 96-104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 李源亮,郭阿龙. 高风险落石运动分析及边坡防护综合设计[J]. 长江科学院院报,2022,39(9):65 − 70. [LI Yuanliang,GUO Along. Analysis of highly risky rockfall movement and comprehensive design of slope protection[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2022,39(9):65 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Yuanliang, GUO Along. Analysis of highly risky rockfall movement and comprehensive design of slope protection[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2022, 39(9): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 柳万里,晏鄂川,魏鹏飞,等. 落石运动特征试验及影响因素敏感性分析[J]. 山地学报,2021,39(1):47 − 58. [LIU Wanli,YAN Echuan,WEI Pengfei,et al. Experimental study on rockfall and sensitivity analysis of influencing factors[J]. Mountain Research,2021,39(1):47 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Wanli, YAN Echuan, WEI Pengfei, et al. Experimental study on rockfall and sensitivity analysis of influencing factors[J]. Mountain Research, 2021, 39(1): 47-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 黎尤,何坤,胡卸文,等. 震裂山体崩塌形成特征及运动学三维模拟—以汶川县三官庙村崩塌为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(2):542 − 552. [LI You,HE Kun,HU Xiewen,et al. Formation characteristics and kinematics 3-D simulation of rockfall evolved from shattered mountain:Case study of Sanguanmiao village rockfall in Wenchuan County[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(2):542 − 552. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI You, HE Kun, HU Xiewen, et al. Formation characteristics and kinematics 3-d simulation of rockfall evolved from shattered mountain—case study of Sanguanmiao village rockfall in Wenchuan County[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(2): 542-552. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 蔡国军,陈锡锐,尹保国,等. 岩体力学参数对反倾边坡稳定性影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 人民珠江,2020,41(9):25 − 31. [CAI Guojun,CHEN Xirui,YIN Baoguo,et al. Numerical simulation study on influence of rock mass mechanical parameters on stability of anti-dip slope[J]. Pearl River,2020,41(9):25 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) CAI Guojun, CHEN Xirui, YIN Baoguo, et al. Numerical simulation study on influence of rock mass mechanical parameters on stability of anti-dip slope[J]. Pearl River, 2020, 41(9): 25-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] ASTERIOU P,SAROGLOU H,TSIAMBAOS G. Geotechnical and kinematic parameters affecting the coefficients of restitution for rock fall analysis[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2012,54:103 − 113. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.05.029
[25] 蔡国军,陈锡锐,孙文鹏,等. 强震作用下斜坡表面放大效应的三维离散元模拟[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):104 − 112. [CAI Guojun,CHEN Xirui,SUN Wenpeng,et al. Three-dimensional discrete element simulation of the amplification effect of the slope surface under the action of strong earthquakes[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):104 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract) CAI Guojun, CHEN Xirui, SUN Wenpeng, et al. Three-dimensional discrete element simulation of the amplification effect of the slope surface under the action of strong earthquakes[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 104-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 唐建辉. 隧道洞口坡面落石运动特性及冲击明洞作用机理研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2022. TANG Jianhui. Study on movement characteristics of rockfall on the slope of tunnel portal and the mechanism of impacting open cut tunnel[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 宋德光, 吴瑞安, 马德芹, 等. 四川泸定昔格达组滑坡灾害运动过程模拟分析[J]. 地质通报,2023,42(12):2185 − 2197. [SONG Deguang, WU Ruian, MA Deqin, et al. Simulation analysis of landslide disaster movement process in Xigeda Formation, Luding County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2023,42(12):2185 − 2197. (in Chinese with English abstract) SONG Deguang, WU Ruian, MA Deqin, et al. Simulation analysis of landslide disaster movement process in Xigeda Formation, Luding County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(12): 2185-2197.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 庞鑫, 袁明, 卢渊, 等. 基于无人机LiDAR仿地飞行技术的高陡边坡危岩体快速识别方法[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(6):21 − 30. [PANG Xin, YUAN Ming, LU Yuan, et al. Rapid identification method for the dangerous rock mass of a high-steep slope based on UAV LiDAR and ground imitation flight[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(6):21 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) PANG Xin, YUAN Ming, LU Yuan, et al. Rapid identification method for the dangerous rock mass of a high-steep slope based on UAV LiDAR and ground imitation flight[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 21-30.(in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李龙灿,吴鑫,刘永红,海英,张满,张龙梅,黄成佳. 松散堆积体斜坡变形-滑移过程的声发射特征参数演化规律. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 151-159 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:























 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS