Open-pit mine soft rock slope internal row tracking pressure side control engineering:A case study at the south side of the first mining area of Hesigewula south open-pit coal mine
-
摘要:
软岩露天煤矿实现安全高效开采的重点是边坡稳定。为解决露天矿顺倾软岩边坡稳定性治理难题,在分析边坡稳定性主控因素的基础上,提出了露天矿顺倾软岩边坡内排追踪压帮治理工程。以贺斯格乌拉南露天煤矿首采区南帮为工程背景,兼顾采场与内排土场边坡稳定性,采用极限平衡法和数值模拟相结合的手段,设计了采场边坡的空间形态,提出了采场与内排土场边坡协同治理方案,可最大限度地安全回收边坡压覆煤炭资源。研究结果表明:弱层暴露长度是露天矿顺倾软岩边坡稳定性的主控因素,控制采场与内排土场间的追踪距离是改善边坡稳定性的有效途径;随着追踪距离的增加,边坡破坏模式从以圆弧为侧界面、弱层为底界面的切层-顺层-剪出滑动逐渐过渡为以圆弧为侧界面、弱层为底界面的切层-顺层滑动,边坡稳定性逐渐下降;内排土场及其与采场构成的复合边坡稳定性随破坏底板弱层回填岩石范围的增大呈指数函数规律提高;贺斯格乌拉南露天煤矿首采区南帮浅部边坡留设40 m运输平盘、15 m保安平盘,底帮深部边坡角29°,追踪距离控制在50 m之内时可满足安全要求;内排土场基底弱层完全破坏并回填岩石倾向长度60 m时可满足安全要求。研究成果为软岩露天煤矿边坡稳定性治理提供了新思路。
Abstract:Slope stability control is crucial for safe and efficient coal mining in open-pit mines with soft rock. To address the challenge of stabilizing dip soft rock slope rock slopes, the treatment engineering of inner row tracking pressure side of dip soft rock slope in open-pit mine is proposed based on the analysis of the main controlling factors of slope stability. This study takes the south side of the first mining area of Hesigewula south open-pit coal mine as the engineering background and proposes a synergistic treatment scheme for the slope stability of the stope and inner dump, utilizing the combination of limit equilibrium method and numerical simulation to design the spatial form of the stope slope. This treatment scheme maximizes the safe recovery of the coal resources covered by the slope. The research results indicate that the length of exposed weak layer is the primary controlling factor of the stability in inclined soft rock slopes in open-pit mines. Controlling the tracking distance between the stope and the inner dump is an effective way to improve slope stability. With an increase in tracking distance, the slope damage mode transitions from the cut-layer-sublayer-shear-out sliding with an arc as the side interface and the weak layer as the bottom interface to cut-layer-sublayer sliding with an arc as the side interface and weak layer as the bottom interface, leading to a gradual decrease in slope stability. Moreover, the stability of the inner dump and its composite slope with the stope increases exponentially with an increase in the backfill rock range of the weak layer of the failure floor. The study sets the shallow slope of the south slope of the first mining area of Hesigewula coal mine to be 40 m transportation flat and 15 m security flat, and the deep slope angle of the bottom slope is 29°. When the tracking distance is controlled within 50 m, it can meet the safety requirements. When the weak layer of the inner dump base is destroyed, and the inclined length of the backfill rock is 60 m, it can also meet the safety requirements. The study provides new insights into slope stability control in soft rock open-pit coal mines.
-
Keywords:
- open-pit coal mine /
- downdip soft rock /
- inner row tracking /
- pressure governance /
- spatial form /
- slope stability
-
0. 引 言
近年来,中国建设开发了数十座软岩露天煤矿,在开采过程中采场及排土场均发生过一定规模的滑坡,对于采场底帮顺倾软岩边坡与顺倾软基底内排土场边坡滑坡灾害尤为严重。滑坡灾害直接影响剥采排工程的发展,造成人员伤害和设备损毁及地貌景观破坏,严重制约着露天矿的安全高效生产[1-2],边坡稳定性治理问题已成为边坡工程领域亟待解决的难题之一。
目前国内外学者们应用不同理论对其展开大量有意义的研究,成果丰硕。王东等[3]综合运用极限平衡法及数值模拟法,分析了不同压帮高度下边坡稳定性变化规律,提出了逆倾软岩边坡变形的治理措施;刘子春等[4]以扎尼河露天矿为背景,通过分析扩帮、内排压角等治理措施的基础上,提出了一种条带式开采技术的边坡治理方案;陈毓等[5]采用ANSYS对黑山露天矿内排土场边坡稳定性和破坏机理进行了分析,揭示了内排土场滑坡模式为“坐落滑移式”滑动,运用削坡治理技术来保证内排土场稳定性;唐文亮等[6]系统分析了露天矿内排土场滑坡影响因素,提出了预留煤柱的滑坡治理方法;李伟[7]揭示了阴湾排土场边坡变形破坏机理并结合数值模拟法和极限平衡法,分析了内排不同压脚方案下边坡稳定性,提出了阴湾排土场滑坡治理措施;王刚等[8]基于有限元数值模拟法和极限平衡法,分析了边坡破坏机理并对边坡进行了稳定性计算,提出了削坡减载的治理措施。软岩露天煤矿采场边坡稳定性治理最经济有效的方式是内排追踪压帮,内排土场稳定是前提,但现有方法均是单一针对采场或排土场边坡稳定性分析和治理,未能同时兼顾采场与内排土场边坡的稳定性,对工程实际的指导性不强。
本文以贺斯格乌拉南露天煤矿首采区南帮为工程背景,在兼顾采场与内排土场边坡稳定性的基础上,提出了露天煤矿顺倾软岩边坡内排追踪压帮治理工程,为深入研究顺倾软岩露天煤矿边坡稳定性治理方法提供新的参考。
1. 边坡工程地质条件分析
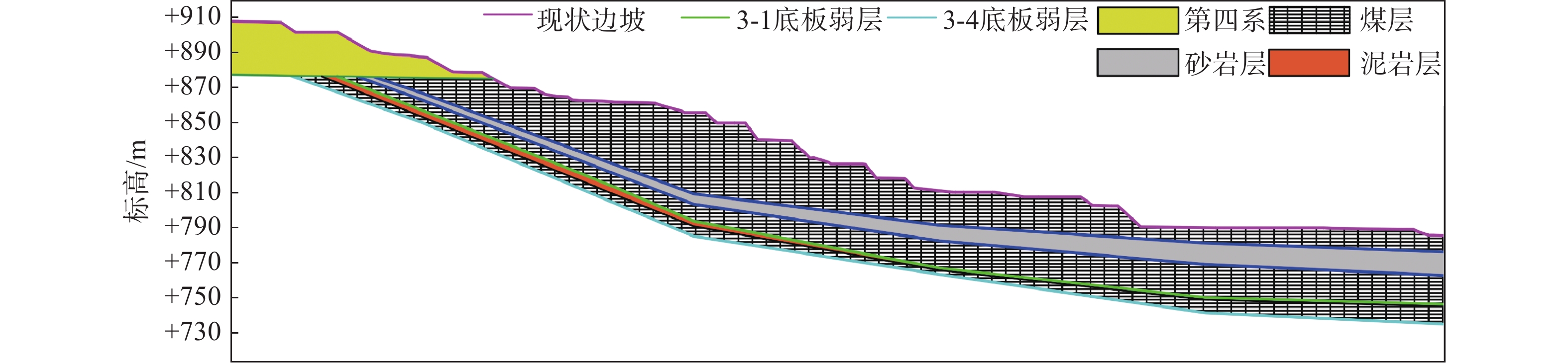
贺斯格乌拉南露天煤矿设计生产能力为15 Mt/a,首采区南帮地层自上而下主要发育第四系、2煤组、2煤组与3煤组间夹石、3煤组、3煤组底板和盆地基底火山岩,含煤岩系主要以泥岩为主,全区可采的有2-1、3-1煤层,第四系以粉砂质黏土为主,局部夹黄-浅灰色细砂及含砾粗砂层,岩性较差,首采区土层赋存较薄,且其地层中多赋存软弱夹层,主要以3-1、3-4煤底板弱层主,属于典型的顺倾软岩边坡,岩土体物理力学指标如表1所示,典型工程地质剖面如图1所示。
表 1 岩土体物理力学指标Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of rock mass岩体名称 内摩擦角/(°) 黏聚力/kPa 容重/(kN·m−3) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 砂岩 26.00 65 19.6 35 0.42 粉质黏土 14.06 22 19.8 46 0.38 煤 29.00 85 12.1 40 0.35 泥岩 20.00 40 19.4 75 0.36 排弃物 14.49 20 19.0 60 0.40 弱层 6.00 0 19.1 20 0.42 回填岩石 20.00 40 19.0 − − 2. 采场底帮浅层边坡二维稳定性分析
影响顺倾软岩露天煤矿采场边坡稳定性的主控因素是弱层及其暴露长度,采用追踪压帮方式治理该类边坡稳定性时,可忽略软弱夹层为底界面的切层-顺层组合滑动模式[9-10],仅考虑剪胀破坏模式。由于贺斯格乌拉南露天矿边坡体内赋存软弱夹层,主要以3-1、3-4煤底板弱层为主,顺倾角度大,岩质松软,对于此类边坡,浅部可通过平盘参数进行重新设计,深部必须利用三维效应,实现稳定性控制。可采用刚体极限平衡法中的剩余推力法对浅层边坡进行稳定性计算[11-12]。该方法的优点是可以用来计算求解给定任意边坡潜在滑面的稳定系数,并且可以考虑在复杂外力作用下的不同抗剪参数滑动岩体对边坡稳定性的影响。稳定系数求解公式为:
$$ {P_i} = \frac{{{W_i}\sin {\alpha _i}({W_i}\sin {\alpha _i}\tan {\varphi _i}) + {C_i}{L_i}}}{{{F_{\rm{s}}}}} + {\phi _i}{p_{i - 1}} $$ (1) $$ {\phi _i} = \frac{{\cos ({\alpha _{i - 1}} - {\alpha _i})\tan {\varphi _i}\sin ({\alpha _{i - 1}} - {\alpha _i})}}{{{F_{\rm{s}}}}} $$ (2) 式中:
${P_i}$ ——第$i$ 条块的剩余推力/kN;$ {W_i} $ ——第$i$ 条块的重量/(N·m−3);$\alpha_i$ ——第$i$ 条块的滑面倾角/(°);${\varphi _i}$ ——第$i$ 条块的推力传递系数;${C_i}$ ——第$i$ 条块的滑面黏聚力/kPa;${L_i}$ ——第$i$ 条块的底面长度/m;${\phi _i}$ ——第$i$ 条块的滑面摩擦角/(°);${F_{\rm{s}}}$ ——稳定性系数。依据《煤炭工业露天矿设计规范》(GB 50197―2015)[13]综合考虑贺斯格乌拉南露天煤矿首采区南帮边坡服务年限、地质条件与力学参数的可靠性、潜在滑坡危害程度等,确定安全储备系数为1.2。
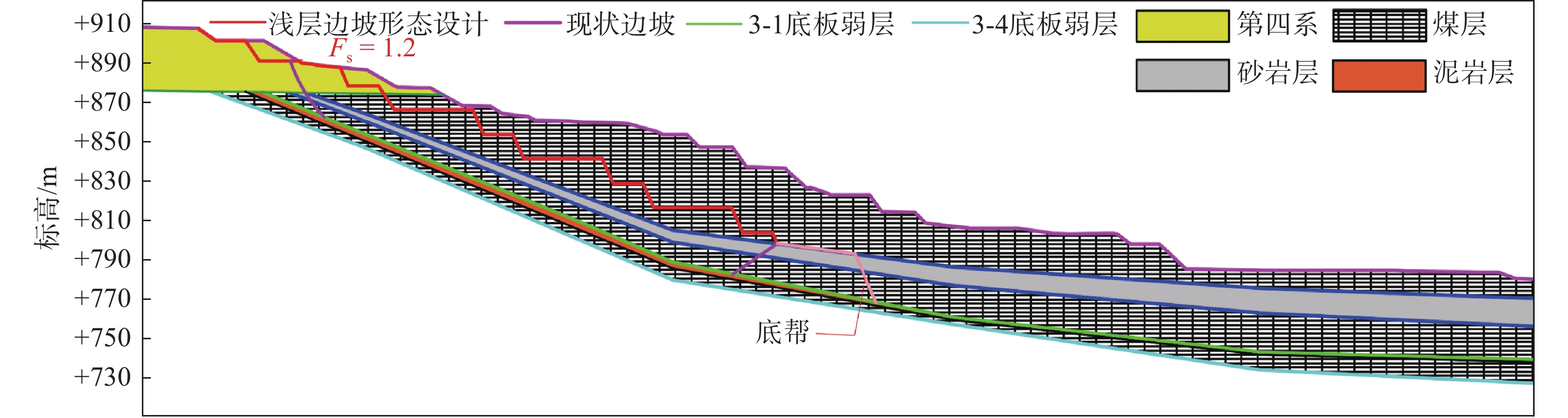
由于南帮压覆大量煤层,在保证安全前提下,为实现最大限度回采压覆的煤炭资源,需要对边坡形态重新设计。本文选取典型剖面为研究对象,浅层边坡形态按照40 m运输平盘、15 m保安平盘进行设计,深部利用横采内排三维支挡效应回采采场底帮深部压覆煤炭资源。通过上述情况对浅层边坡进行了分析,边坡稳定性计算结果如图2所示。
分析图2可知,浅部边坡形态可按照40 m运输平盘、15 m保安平盘进行设计,由于弱层上部存在煤岩支挡,边坡潜在滑坡模式为以圆弧为侧界面、3-1煤底板弱层为底界面、沿边坡坡脚处剪出,此时,浅层边坡能满足安全储备系数1.2的要求。
3. 采场底帮深部边坡稳定性三维效应分析
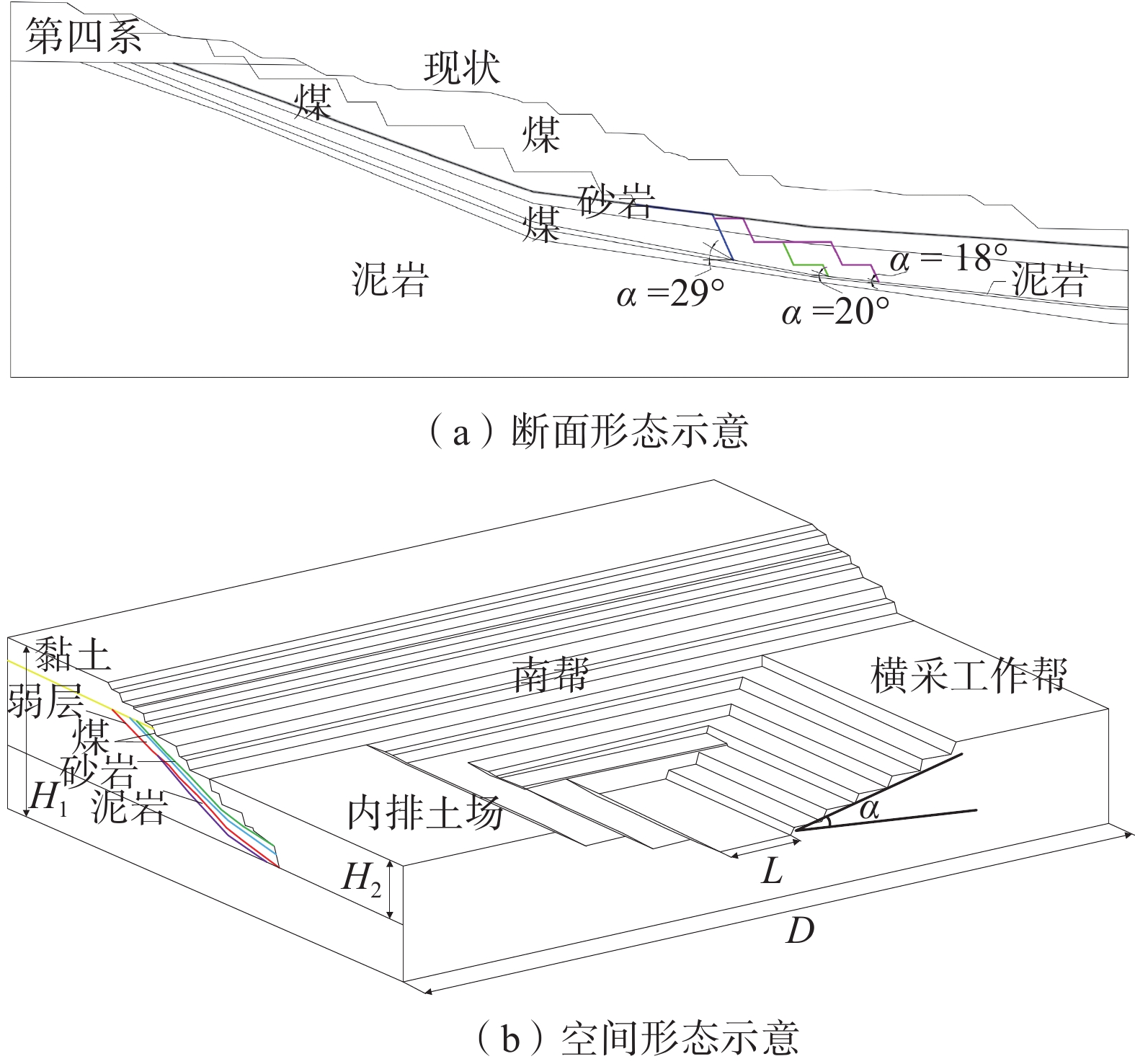
基于浅层边坡二维稳定性分析结果可知,实现深部稳定性控制,必须借助横采工作帮与内排土场的双重支挡作用进行压煤回采,因此提出了利用横采内排三维支挡效应回采采场深部压覆煤炭资源[14]。本文借助FLAC3D数值模拟软件,分析不同降深角度和不同追踪距离条件下的边坡三维稳定性,以期获得最优的边坡空间形态参数。
(1) 模型的建立
考虑到FLAC3D建模较为复杂,采用CAD与Rhino相结合的方法,首先在CAD中对剖面进行整理,然后在Rhino软件中进行模型成体与网格划分的处理,并用Griddle将网格导出,生成精细的六面体网格模型[15 − 17],最后导入采用于FLAC3D进行数值模拟计算。为尽可能凸显边坡稳定性的三维效应,以南帮断面形态设计边坡为数值模拟对象,共计建立15种工况模型,模型如图3,追踪距离分别为50,100,200,300,400 m。为避免边界效应,在模型的底部和两侧分别施加水平和垂直位移约束,加载方式为重力加载[18]。
(2) 计算结果分析
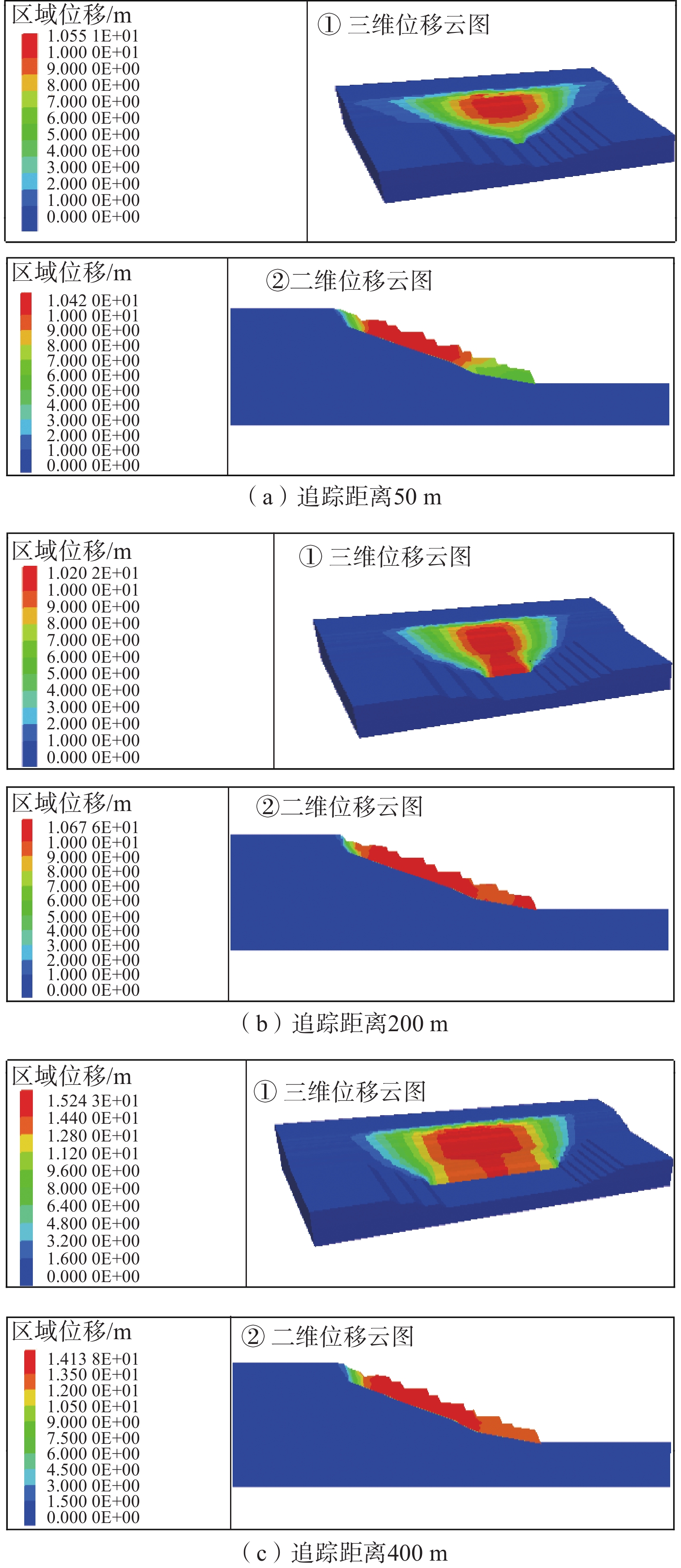
由于计算结果过多,本文仅列举降深角度α=29°,追踪距离50,200,400 m工况下边坡位移云图(切割位置为沿模型走向中间处),如图4所示。南帮边坡三维稳定性计算结果如图5所示。
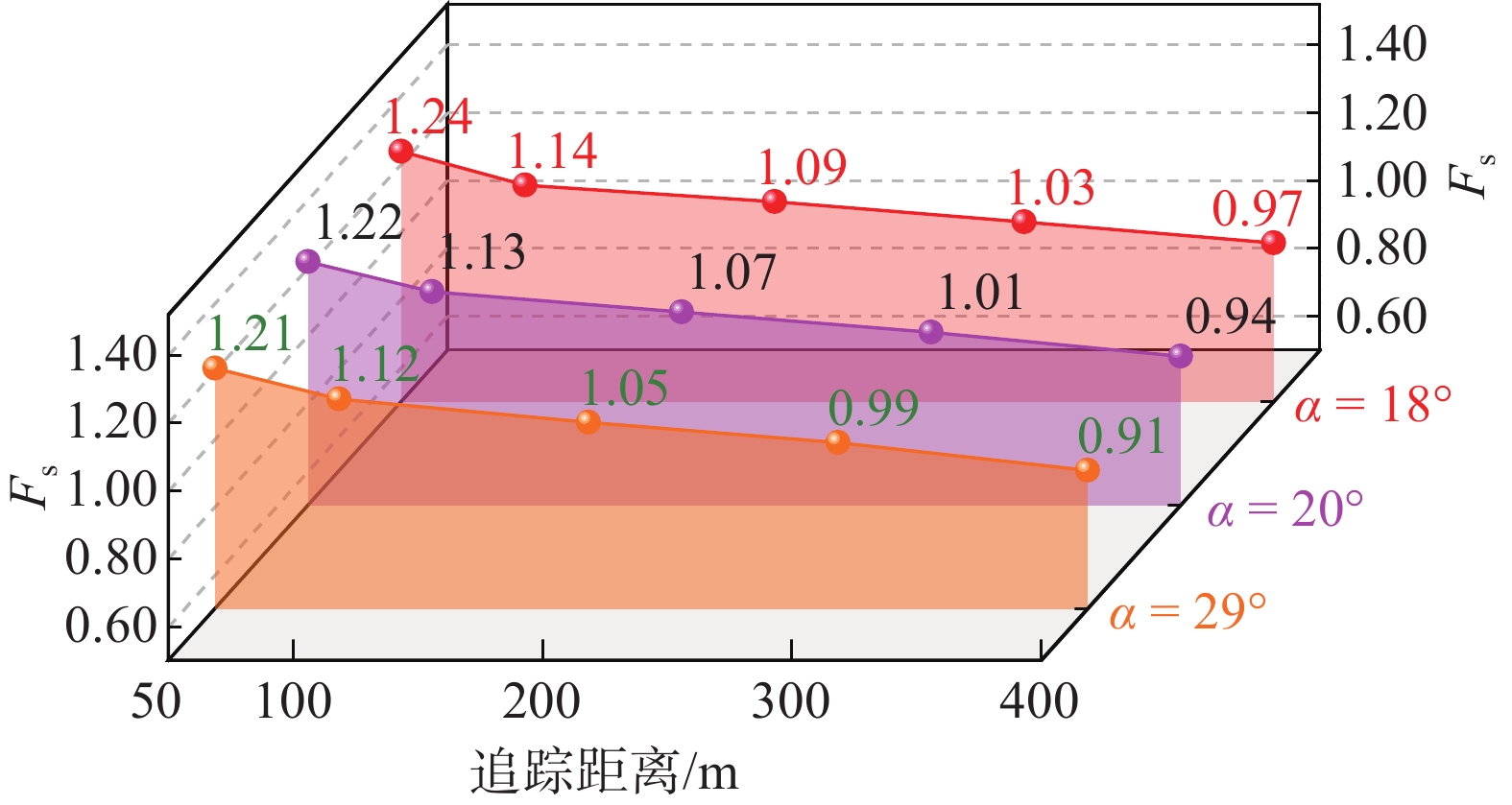
分析图4、图5可知,追踪距离50 m时,三维支挡效应显著,边坡深部位移明显小于上部,发生以圆弧为侧界面、3-1煤底板弱层为底界面的切层-顺层-剪出滑动,稳定系数大于1.2。当追踪距离大于50 m时,通过对比分析不同深部边坡角(α)条件下的数值模拟结果可知,深部边坡角对边坡稳定性系数影响较小,随着追踪距离的增加,边坡的破坏模式过渡为以圆弧为侧界面、3-1煤底板弱层为底界面的切层-顺层滑动,并且此时边坡的稳定性不满足安全储备系数1.2要求。因此,内排土场追踪距离需控制在50 m以内,深部边坡角设计为29°。
4. 内排土场压帮边坡稳定性分析与治理
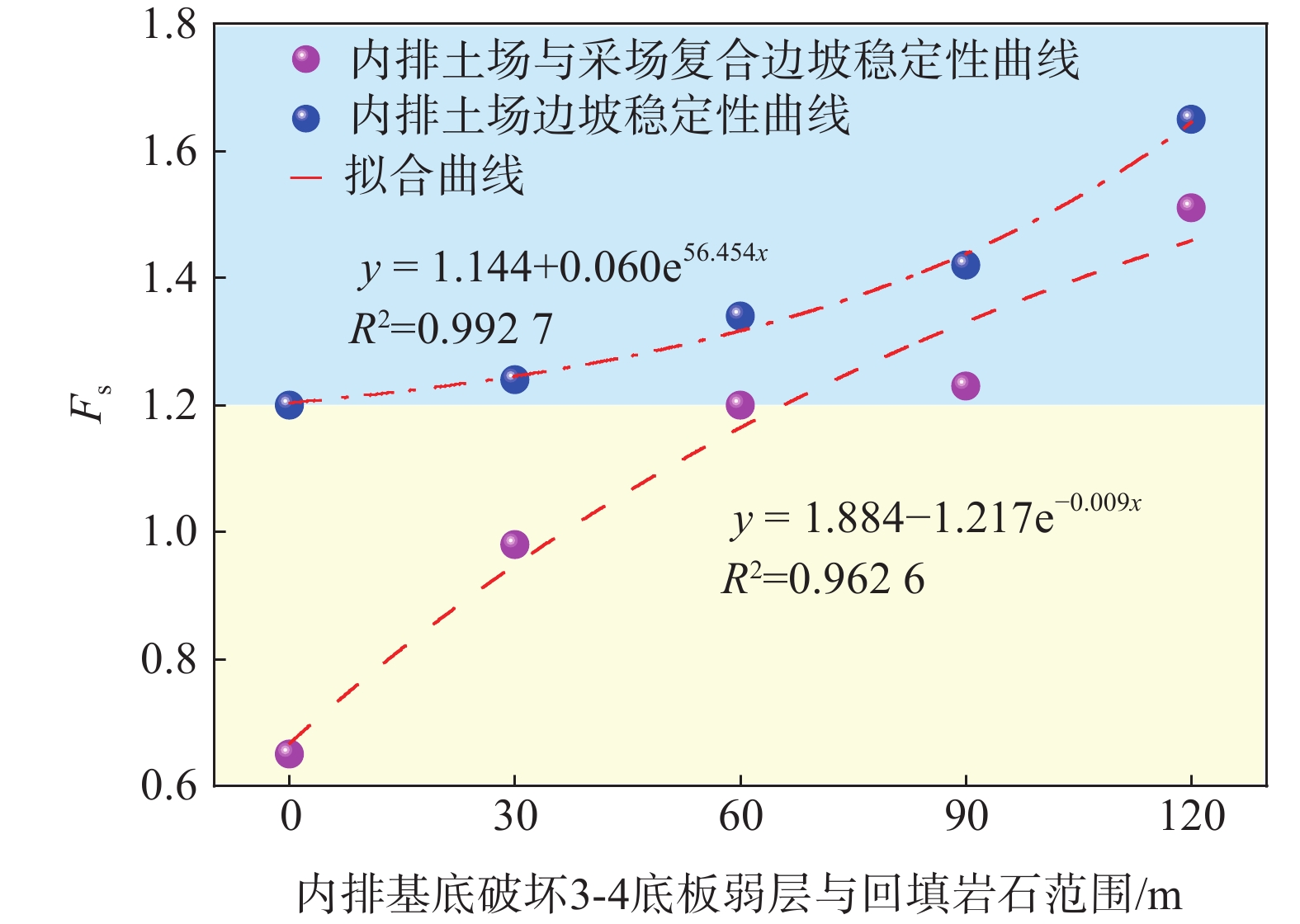
露天矿内排土场边坡稳定的主控因素是软弱基底,软弱基底分为自身软弱岩土层和受外界条影响转变为软弱岩土层2种类型。排土场下沉是软弱基底内排土场失稳的特征,主要现象是含有纵向强烈挤压区,基底上部岩层隆起,地面出现滑坡等[19 − 21]。在保证采场南帮安全的前提下降深至3-1煤底板,须借助横采工作帮与内排土场的双重支挡作用,内排土场稳定是前提[22]。由于内排土场基底为3-1、3-4煤底板弱层,顺倾角度较大,按照内排土场设计参数,其稳定性无法满足安全储备系数的要求[23]。从提供基底强度角度出发,采用破坏弱层回填岩石的方式提高内排土场边坡稳定性。按照排土台阶高度24 m、平盘宽度60 m、坡面角33°对不同内排压帮标高边坡稳定性进行试算,确定内排最小压帮标高为+844水平,因此本文分析了内排基于+844水平的压帮高度下内排土场基底不同的处理方式时的边坡稳定性计算结果如图6—7所示,边坡稳定性与破坏弱层回填岩石范围关系曲线如图8所示。
分析图6—图8可知,当内排基于+844的压帮高度,内排基底3-1底板弱层完全破坏并回填岩石,破坏3-4底板弱层并回填岩石倾向长度达60 m时,内排土场及其与采场南帮复合边坡稳定性均可满足安全系数1.2要求。边坡稳定性随破坏底板弱层回填岩石范围的增大呈正指数函数规律提高,随着回填岩石范围长度的不断增加,边坡稳定性系数不断提高。采用破坏弱层回填岩石的基底处理方法,既保证了边坡的稳定又规避了过渡处理基底的生产成本。
5. 结 论
(1) 弱层暴露长度是露天矿顺倾软岩边坡稳定性的主控因素,据此提出了露天矿顺倾软岩边坡内排追踪压帮治理工程,可最大限度的安全回收边坡压覆煤炭资源。
(2) 控制采场与内排土场间的追踪距离是改善边坡稳定性的有效途径。随着追踪距离的增加,边坡破坏模式从以圆弧为侧界面、弱层为底界面的切层-顺层-剪出滑动逐渐过渡为以圆弧为侧界面、弱层为底界面的切层-顺层滑动。
(3) 内排土场及其与采场构成的复合边坡稳定性随破坏底板弱层回填岩石范围的增大呈指数函数规律提高,随着回填岩石范围长度的不断增加,边坡稳定性系数不断提高。
(4) 贺斯格乌拉南露天煤矿首采区南帮浅部边坡留设40 m运输平盘、15 m保安平盘,底帮深部边坡角29°,追踪距离控制在50 m之内时可满足安全要求;内排基底弱层完全破坏并回填岩石倾向长度60 m时可满足安全需求。
-
表 1 岩土体物理力学指标
Table 1 Physical and mechanical parameters of rock mass
岩体名称 内摩擦角/(°) 黏聚力/kPa 容重/(kN·m−3) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 砂岩 26.00 65 19.6 35 0.42 粉质黏土 14.06 22 19.8 46 0.38 煤 29.00 85 12.1 40 0.35 泥岩 20.00 40 19.4 75 0.36 排弃物 14.49 20 19.0 60 0.40 弱层 6.00 0 19.1 20 0.42 回填岩石 20.00 40 19.0 − − -
[1] 徐晓惠. 露天煤矿顺倾层状软岩边坡三维稳定性及其控制研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2015 XU Xiaohui. Study on three-dimensional stability and its control of dip bedded soft rock slope in surface coal mine[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 马婧佳,王勇,黄浩轩,等. 宝日希勒露天煤矿南帮边坡靠帮开采方案[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(11):240 − 244. [MA Jingjia,WANG Yong,HUANG Haoxuan,et al. Mining plan for south slope of Baorixile open-pit coal mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2021,52(11):240 − 244. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA Jingjia, WANG Yong, HUANG Haoxuan, et al. Mining plan for south slope of Baorixile Open-pit Coal Mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(11): 240-244. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 王东,姜聚宇,韩新平,等. 三道岭露天煤矿逆倾软岩边坡变形破坏治理方案研究[J]. 安全与环境学报,2019,19(5):1587 − 1594. [WANG Dong,JIANG Juyu,HAN Xinping,et al. Treating scheme of the inclined soft rock slope in the Sandaoling open-pit coal mine with its deformation and damage[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2019,19(5):1587 − 1594. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Dong, JIANG Juyu, HAN Xinping, et al. Treating scheme of the inclined soft rock slope in the Sandaoling open-pit coal mine with its deformation and damage[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2019, 19(5): 1587-1594. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 刘子春, 韩猛. 扎尼河露天矿边坡治理措施与效果[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2017, 45(增刊1): 174 − 176 LIU Zichun, HAN Meng. Initial effect and measures of slope treatment in Zhanihe open-pit mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2017, 45(Sup 1): 174 − 176. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 陈毓,周西华. 黑山露天矿内排土场边坡稳定分析及治理措施[J]. 煤矿安全,2019,50(12):231 − 233. [CHEN Yu,ZHOU Xihua. Analysis and treatment of slope stability of inner dump in Heishan open-pit mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2019,50(12):231 − 233. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Yu, ZHOU Xihua. Analysis and treatment of slope stability of inner dump in Heishan open-pit mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50(12): 231-233. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 唐文亮,彭洪阁,马力,等. 露天矿内排土场滑坡成因及治理措施研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2016,35(8):166 − 168. [TANG Wenliang,PENG Hongge,MA Li,et al. Study on cause and control measures of internal waste dump landslide in open-pit[J]. Coal Technology,2016,35(8):166 − 168. (in Chinese with English abstract) TANG Wenliang, PENG Hongge, MA Li, et al. Study on cause and control measures of internal waste dump landslide in open-pit[J]. Coal Technology, 2016, 35(8): 166-168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李伟. 露天煤矿排土场边坡稳定性分析与治理技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2014,42(10):37 − 40. [LI Wei. Treatment technology and stability analysis of dump slope in open mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2014,42(10):37 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Wei. Treatment technology and stability analysis of dump slope in open mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2014, 42(10): 37-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 王刚,侯成恒,缪海宾. 露天煤矿软岩顺倾边坡变形破坏机理及治理措施研究[J]. 露天采矿技术,2018,33(4):47 − 50. [WANG Gang,HOU Chengheng,MIAO Haibin. Research on deformation failure mechanism and control measures of soft rock consequent slope in open-pit mine[J]. Opencast Mining Technology,2018,33(4):47 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Gang, HOU Chengheng, MIAO Haibin. Research on deformation failure mechanism and control measures of soft rock consequent slope in Open-pit Mine[J]. Opencast Mining Technology, 2018, 33(4): 47-50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 刘小平. 蒙东地区露天矿边坡稳定性影响因子与敏感度分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2014,42(3):74 − 77. [LIU Xiaoping. Analysis on influencing factors and their sensitivity for slope stability in opencast coal mine of eastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2014,42(3):74 − 77. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2014.03.017 Liu Xiaoping. Analysis on influencing factors and their sensitivity for slope stability in opencast coal mine of eastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2014, 42(3): 74-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2014.03.017
[10] 常剑,侯成恒,赵旭. 多弱层边坡破坏机理分析及形态优化[J]. 现代矿业,2022,38(5):81 − 84. [CHANG Jian,HOU Chengheng,ZHAO Xu. Failure mechanism analysis and shape optimization of multi weak layer slope[J]. Modern Mining,2022,38(5):81 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHANG Jian, HOU Chengheng, ZHAO Xu. Failure mechanism analysis and shape optimization of multi weak layer slope[J]. Modern Mining, 2022, 38(5): 81-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 宋子岭,王向磊,杨添,等. 端帮压帮的陡边坡开采技术分析[J]. 金属矿山,2017(3):40 − 44. [SONG Ziling,WANG Xianglei,YANG Tian,et al. Analysis on the mining technology of steep slope under the burying slope of the end slope[J]. Metal Mine,2017(3):40 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract) SONG Ziling, WANG Xianglei, YANG Tian, et al. Analysis on the mining technology of steep slope under the burying slope of the end slope[J]. Metal Mine, 2017(3): 40-44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 崔中良,张东方,姚艳领. 极限平衡法在边坡稳定性分析中的应用[J]. 中国锰业,2016,34(5):135 − 137. [CUI Zhongliang,ZHANG Dongfang,YAO Yanling. The application of the limit equilibrium method in slope stability analysis[J]. China ’s Manganese Industry,2016,34(5):135 − 137. (in Chinese with English abstract) CUI Zhongliang, ZHANG Dongfang, YAO Yanling. The application of the limit equilibrium method in slope stability analysis[J]. China’s Manganese Industry, 2016, 34(5): 135-137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 煤炭工业露天矿设计规范: GB 50197—2015[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2015 Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Code for design of open pit mine of coal industry: GB 50197—2015[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
[14] 王东,赵明明,贾宏君. 露天矿顺倾软岩边坡稳定性三维效应及其应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(4):53 − 58. [WANG Dong,ZHAO Mingming,JIA Hongjun. Three dimensional effects of dip bedded soft rock slope stability in surface mines[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(4):53 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Dong, ZHAO Mingming, JIA Hongjun. Three dimensional effects of dip bedded soft rock slope stability in surface mines[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2017, 28(4): 53-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 刘帅. 白音华一号露天煤矿首采区东南帮边坡稳定性研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2017. LIU Shuai. Stability of South-eastn slope in 1st mining area of Baiyinhua No. 1 Open-pit Coal Mine [D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 杨世豪. 基于物元理论的昔格达地层边坡稳定性评价模型研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院水利部成都山地灾害与环境研究所), 2020 YANG Shihao. Study on evaluation model of xiegeda slope stability based on matter element theory[D]. Chengdu: Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 汪锦文. 皖江上游石灰岩残积红黏土工程特性及对边坡稳定性影响[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2020 WANG Jinwen. Engineering characteristics of limestone residual red clay in upper reaches of Wanjiang River and its influence on slope stability[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science & Technology, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 黄润秋,许强. 显式拉格朗日差分分析在岩石边坡工程中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,1995,14(4):346 − 354. [HUANG Runqiu,XU Qiang. Application of explicit Lagrangian finite-difference method in rock slope engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,1995,14(4):346 − 354. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG Runqiu, XU Qiang. Application of explicit Lagrangian finite-difference method in rock slope engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1995, 14(4): 346-354. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 李维国. 依兰露天煤矿内排土场边坡稳定分析[J]. 科技信息,2011(23):800. [LI Weiguo. Slope stability analysis of internal dump in Yilan open-pit coal mine[J]. Science & Technology Information,2011(23):800. (in Chinese) LI Weiguo. Slope stability analysis of internal dump in Yilan open-pit coal mine[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2011(23): 800. (in Chinese)
[20] 杨丽萍. 准格尔黑岱沟露天煤矿内排土场边坡稳定性分析[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2007 YANG Liping. Analysis the slope stability inner spoil dump of Zhunge’er Heidaigou open-pit coal mine[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 王东旭,孙艳辉. 白音华三号露天矿外排土场与非工作帮复合边坡稳定性分析[J]. 露天采矿技术,2009,24(5):10 − 13. [WANG Dongxu,SUN Yanhui. Stability analysis of outer dump and non-working wall composite slope in the third ore of Baiyinhua surface mine[J]. Opencast Mining Technology,2009,24(5):10 − 13. (in Chinese) WANG Dongxu, SUN Yanhui. Stability analysis of outer dump and non-working wall composite slope in the third ore of Baiyinhua surface mine[J]. Opencast Mining Technology, 2009, 24(5): 10-13. (in Chinese)
[22] 李芳玮,王东,尹立. 露天矿含断层与顺倾弱层群边坡形态分段优化研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2022,54(1):148 − 153. [LI Fangwei,WANG Dong,YIN Li. Subsection optimization of soft rock slope with faults and dipping weak strata group in open-pit mine[J]. Coal Engineering,2022,54(1):148 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Fangwei, WANG Dong, YIN Li. Subsection optimization of soft rock slope with faults and dipping weak strata group in open-pit mine[J]. Coal Engineering, 2022, 54(1): 148-153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 李志国,徐涛,刘永杰,等. 露天矿边坡稳定性的层次分析-模糊综合评价耦合分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(1):116 − 123. [LI Zhiguo,XU Tao,LIU Yongjie,et al. Open-pit mine slopes stability analysis based on analytic hierarchy process-fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(1):116 − 123. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Zhiguo, XU Tao, LIU Yongjie, et al. Open-pit mine slopes stability analysis based on analytic hierarchy process-fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2024, 35(1): 116-123.(in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 管少杰,吕进国,王康,张砚力. 露天矿下伏采空区距坡脚水平距离对边坡稳定性的影响. 工矿自动化. 2025(02): 113-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王林康,郑子涵,章广成,曾鑫,丁柄栋,崩兴涛. 顺层陡倾岩质边坡倾倒模式试验. 地质科技通报. 2025(02): 340-354 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王胆,马明红,蒋香莲,陈奇,林令鑫,李昊阳,李泽辰. 先锋露天矿北帮顺倾软岩边坡变形机理. 露天采矿技术. 2025(02): 13-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 周志伟,田羽,张周爱. 横采内排追踪压帮技术下边坡稳定控制开采参数确定. 露天采矿技术. 2025(02): 41-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:

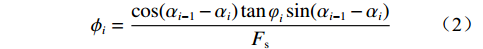
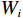
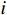
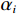
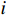
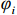
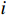

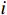
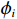
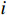
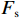


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS