Study on the method for determining the position of landslide slip surface based on “D” type inclinometer curve
-
摘要:
在实际的深孔位移监测中,测斜曲线的突变特征是滑动面辨识的关键依据,前人通过大量的研究总结将滑动面迹象显著的测斜曲线类型分为了“B”型、“D”型、“r”型等几种。其中,对于“D”型测斜曲线通常是将曲线的鼓包凸起点作为滑动面的位置,但这种方法容易受到测点布置间隔和横纵坐标观测尺度的影响,存在滑面位置定义不清晰、数值不确定的问题。为了能够有效地克服这些缺点,提升测斜曲线滑动面辨识的准确度,基于“D”型测斜曲线变化特征,将滑坡抽象为由“滑动体”“滑动区间”以及“不动体”三者组成的概化模型,根据三者抗弯刚度的差异建立外界荷载作用下的杆件力学模型,深入分析滑坡运动过程中不同深度处土体的变形特点。研究表明,由于“D”型曲线滑动面并未完全贯通,使得土体沿深度方向变形连续无突变,力学模型中杆件正负弯矩的分界点是变形曲线水平位移最大处,能够真实地反映滑坡变形特点以及滑动面的位置。将土体累计位移转化为相对位移,则“D”型深孔测斜曲线变为了“S”型相对位移-深度曲线,且“S”型曲线的拐点与滑动面的位置相近;通过提取监测期内不同深度处土体的平均相对位移,运用三次样条插值法计算“S”型区段内拐点的深度值,能够更加精准地确定滑动面位置,更好地提升深孔位移监测的可靠度和准确度,具有较大的实用价值。
Abstract:In borehole monitoring for deep displacement, the abrupt characteristics of inclinometer curves are the key basis for identifying the sliding surface. Previous studies have summarized several types of inclinometer curve patterns that exhibit significant sliding surface signals, including “B” “D”and “r” types. For “D” type inclinometer curves, the convex point of the curve is typically used as the position of the sliding surface. However, this method is susceptible to the influence of observation points spacing and coordinate observation scales, which can result in an unclear definition of the sliding surface position and uncertain numerical values. To overcome these drawbacks and improve the accuracy of sliding surface identification in inclinometer curves, a generalized model of landslides composed of “sliding body” “sliding interval” and “immovable body” was developed based on the variation characteristics of the “D” type inclinometer curve. A mechanical strut model subjected to external loads was established based on the different flexural rigidity of the three members, and the deformation characteristics of soil at different depths during landslide movement were analyzed in depth. The study found that the sliding surface of “D” curve does not entirely penetrate, leading to continuous soil deformation along the depth direction without abrupt change. The demarcation point of the positive and negative bending moments in the mechanical model is a location where the horizontal displacement of deformation curve is the largest, which can reflect the real deformation characteristics of the landslide and the position of the sliding surface. By converted the accumulated soil displacement into relative displacement, the “D” type inclinometer curve is transformed into “S” type relative displacement-depth curve, and the inflection point of the “S” type curve is close to the position of the sliding surface. By extracting the average relative displacement of soil at different depths during the monitoring period and calculating the depth value of the inflection point in the “S” type segment by using the cubic spline interpolation method, the position of the sliding surface can be determined more accurately, which can greatly improve the reliability and accuracy of deep displacement monitoring and has significant practical value.
-
0. 引 言
滑坡变形监测作为分析滑坡地质结构、变形动态特征的重要依据,是滑坡整治工程信息化设计及灾害预测、预报的可靠技术保障。尤其在国家广泛倡导的“空-天-地-孔”多方位一体地质灾害监测与防治的大背景下,相比于其他监测方式,滑坡深孔位移监测有着其独特优势,不仅可以准确得到滑坡滑动面的位置,还可以获取滑坡在不同时间、不同深度的位移变形特征,有利于准确把握深层、多层和性质复杂的滑坡性状,是滑坡动态监测不可或缺的关键一环[1 − 3]。
由于土体变形贯穿于整个滑坡运动过程,位移作为深孔位移监测中的最主要参数,其变化特征是滑坡变形及运动特征的直观反映[4 − 5]。因此,准确辨识滑坡深孔位移曲线形态特征,是确定滑坡滑动面位置及分析坡体稳定性的重要依据。
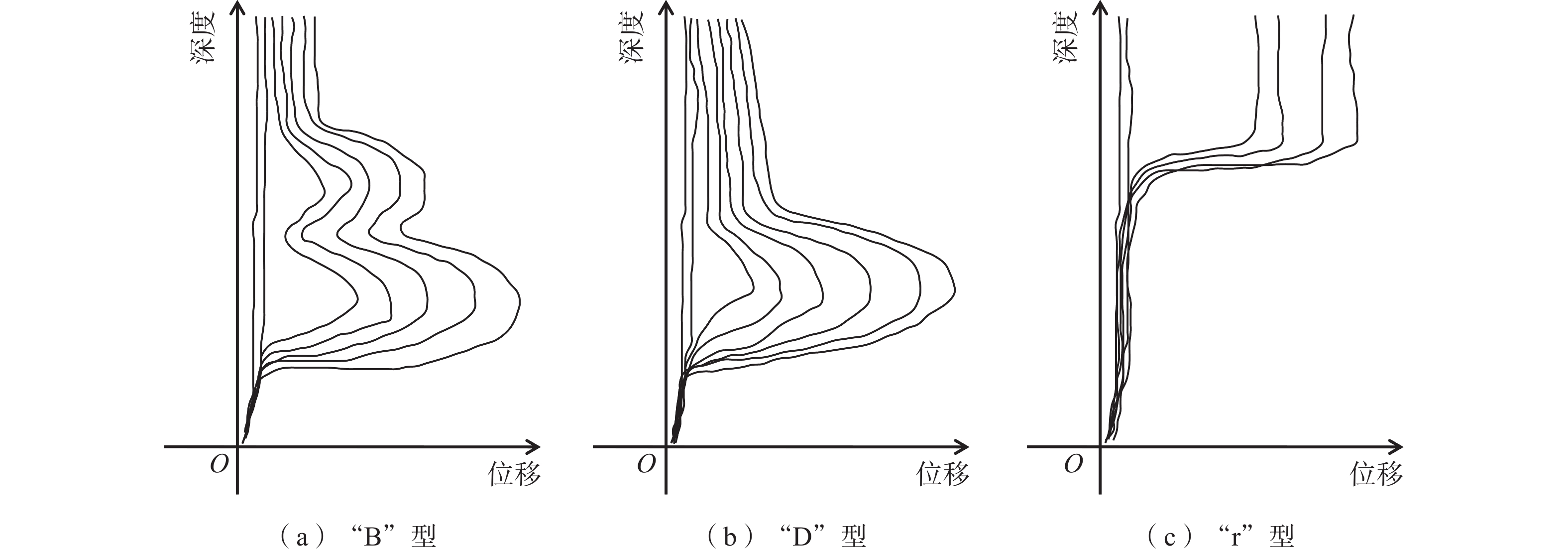
此外,基于深孔位移曲线形态特征,建立科学可靠的分析方法有助于勘探人员快速获取滑坡运动信息、准确确定滑动面的位置。而目前,运用深孔位移曲线形态特征准确辨识滑动面位置的研究尚浅,大部分学者的研究集中在位移曲线形态的表层分析,缺乏相应的理论分析和数据层面的深入挖掘。国内研究学者综合分析了整体复活深层滑坡、覆盖层浅表滑坡及地震滑坡深部位移监测成果,将深孔测斜曲线分为“V”型、“B”型、“D”型、“r”型、钟摆型及复合型等几种,不同曲线类型代表着不同的滑坡变形特征。其中,能够表明滑坡滑动面迹象显著的深孔测斜曲线特征主要为“B”型、“D”型及“r”型3种[6 − 7]。
此外,边坡内部位移作为了解滑坡动态的重要数据[5],大多数学者通常将测斜曲线的位移突变点作为滑动面位置的辨识依据。对于“D”型测斜曲线,一般以鼓包凸起点所在深度作为滑动面的位置,而这种判别方法容易受测点布置间隔、横纵坐标观测尺度的影响,存在滑动面位置定义不清晰、数值不确定的问题。另外,各种数学处理手段和数据挖掘方法在深孔位移监测数据上的运用,主要集中在滑坡监测预警方向,而将其运用在滑坡勘察和治理设计中解决底层问题的研究尚不多[8 − 10];准确确定滑动面位置作为关键的底层问题之一,如何充分利用深孔位移监测数据进一步提升滑动面辨识的准确度是一个重要的研究内容[11 − 13]。
为了能够有效地克服这些缺点,解决“D”型测斜曲线中存在的问题,提升深孔位移监测数据的利用程度。本研究基于“D”型曲线的变形特征,结合其上下部土体的运动特点,考虑不同位置处土体相对位移的变化规律,建立相应的概化模型和力学模型,分析土体相对位移曲线拐点与滑动面位置之间的关系,通过提取监测期内不同位置处土体的相对位移平均值,运用三次样条插值法计算曲线拐点对应的深度值,从而确定滑动面的具体位置。
通过实际案例运用分析表明,该方法能够显著提升“D”型深孔测斜曲线在滑动面位置辨识上的准确度,具有更加科学合理的数学依据,可为各类深孔测斜曲线的深入挖掘提供参考,并为滑坡防治工程设计提供重要信息。
1. 滑坡位移监测的主要曲线类型
1.1 深部位移曲线的种类
张位华等[13]结合工程实践研究发现,对研究滑坡变形有意义的曲线主要有以下几种:
(1)累计位移-深度曲线,即累计位移随深度的变化;
(2)相对位移-深度曲线,即相对位移随深度的变化;
(3)位移-时间曲线,即位移过程曲线,可分为累计位移或相对位移过程曲线;
(4)位移矢量-深度曲线,即同一时刻不同深度的位移矢量变化;
(5)位移矢量-时间曲线,即同一测点在不同时刻的位移矢量变化。
常用的深孔测斜曲线即为累计位移-深度曲线,基于深孔测斜曲线通过改变自变量和因变量并辅以位移方向,则可以分别得到(2)(3)(4)(5)不同的曲线类型,每种曲线类型有着不同的物理意义,有助于辨识滑坡的目前性状及其发展阶段。
1.2 深孔测斜曲线的特征类型
部分研究学者采用有限元数值模拟与深部位移曲线类型分析相结合的方法,结合靳晓光等[14]的深部位移变形曲线形态分类方法,对各类典型滑坡变形机制进行了较为深入的研究分析[15 − 17]。本文通过总结归纳前人的研究成果,得到不同位移曲线形态所对应的坡体破坏类型、曲线变形特征、滑坡变形破坏情况以及滑动面发展程度等重要信息(表1)。
表 1 深孔测斜曲线典型类型Table 1. Typical types of deep-hole inclinometer curve曲线类型 坡体破坏类型 曲线特征 滑坡变形破坏情况 滑动面发展程度 钟摆型 倾倒变形 累计位移在整个深度范围内于初测值附近摆动,
摆动幅度一般小于10 mm滑坡岩土体的深部位移很小,
边坡处于稳定状态未贯通 “V”型 顺层溃屈 上部位移较大而底部位移很小,曲线总体呈线性特征 滑坡内部没有形成明显的滑动面,
处于蠕动变形阶段未贯通 “r”型 切层滑移、顺层滑移、崩塌 累计位移在一个较浅的位置产生较为明显的突变,
而其下部的位置则相对较小滑坡岩土体在浅部形成明显的滑动面 贯通 “D”型 切层滑移、顺层溃屈 累计位移在某一个较深的位置产生突变,
而其上部产生近似整体的移动滑坡深部产生了一个明显的滑动面 接近贯通 “B”型 顺层滑移 累计位移在多个位置产生较为明显的突变,
曲线呈现类似“阶梯”或“波浪”状滑坡岩土体内部形成了多个滑动面 接近贯通 其中,“B”型、“D”型和“r”型表明滑坡变形已经显示出明显的滑动面迹象,根据不同的曲线类型选择累计位移或相对位移变化特征能够为准确确定滑坡滑动面具体位置提供关键信息[14](图1)。
曲线“B”型变形特征指滑坡有两个或两个以上明显的滑动面,但各滑块(体)的运动速率不一致,滑坡以其中一个滑面处的相对运动为主,滑坡处于蠕变-滑移阶段。
曲线“D”型变形特征指滑坡只有一个明显的滑动面,且滑动面位置较深,滑面以上滑体呈整体运动。
曲线“r”型变形特征指滑坡只有一个明显的滑动面,且滑动面一般位于浅表部,上部和下部之间的土体位移相差较大。
2. 滑坡体概化模型分析
2.1 概化模型构建
对比图1(b)(c)可以发现,具有“r”型变形特征的滑坡其滑带厚度较薄常位于浅表部,土体位移在滑带附近产生突变将土体明显分为上下两部分,上部土体为整体平移近似刚体运动,下部土体变形微弱水平位移小,表明滑动面已经发展成型。而具有“D”型变形特征的滑坡其滑带厚度一般较厚且位于地下较深处,滑带内的土体随着滑动面的发展抗剪强度逐渐降低,但未达到剪切破坏的状态处在缓慢滑移的阶段;上部土体运动受坡体结构面类型、岩土性质以及外界阻滞作用(如坡体堆载产生的反向偏压、支档结构的作用力等)影响显著,使得上部土体位移量明显小于滑带内的土体;而下部土体抗剪强度高、性质稳定,土体变形小。表明滑动面仍处在不断发展变形的阶段。
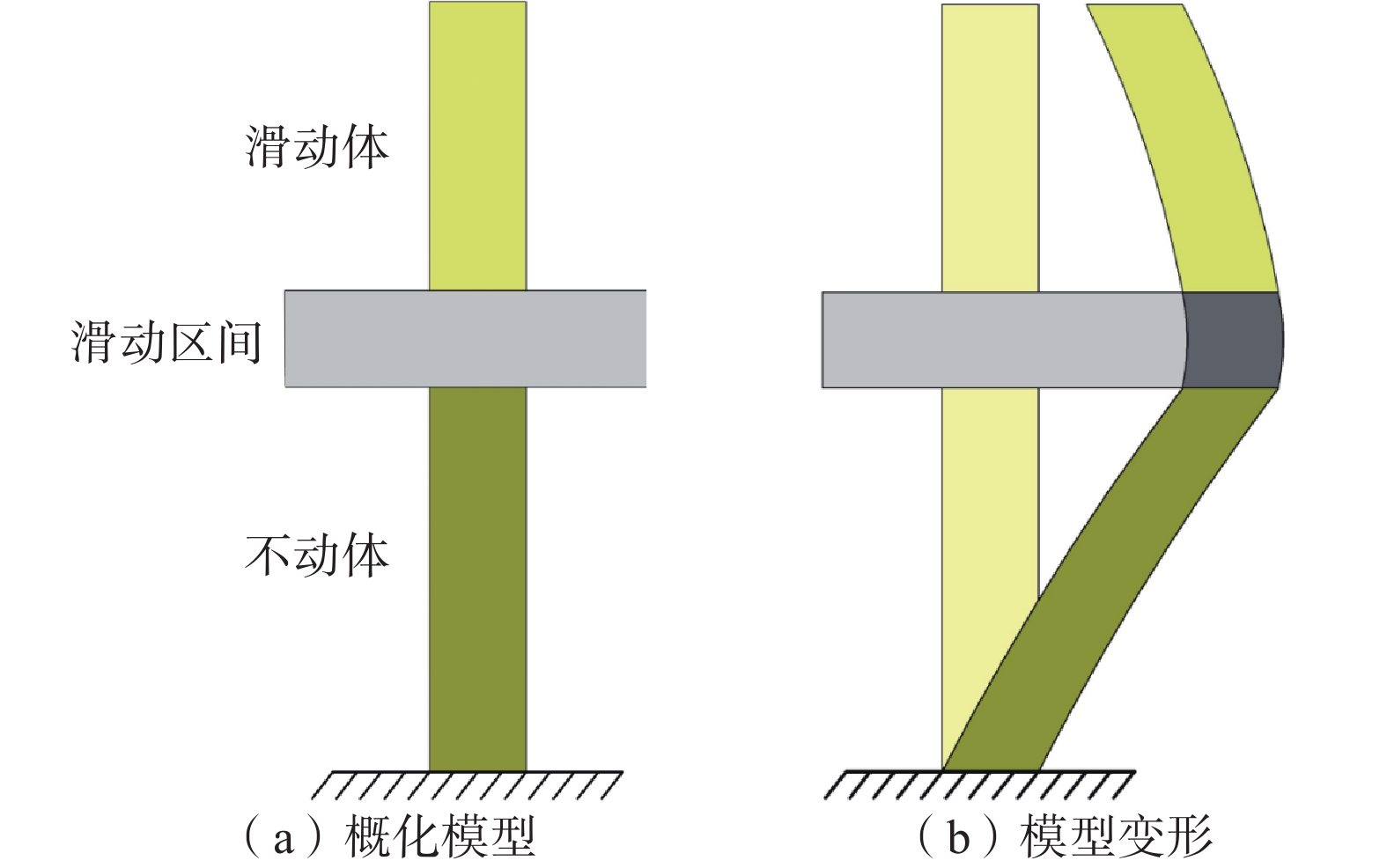
基于“D”型曲线滑坡体变形特征,建立概化模型有利于更加简明深入地分析土体变形特点与滑动面位置之间的关系。
在滑坡的运动变形过程中,上部滑坡体近似弯曲变形,呈整体偏移的特点;中间的滑动带是具有一定厚度的软弱带,且滑带附近土质软弱,滑动面的存在使得滑带上下部的土体产生明显的位移差;下部滑床性质稳定,土体变形相对较小,且土体深度越大位移量越趋近于0,近似底端固定的变形体。因此,为了便于说明并体现滑坡各组成部分的运动特点,将滑坡体、滑动带及滑床分别称为滑动体、滑动区间和不动体[2],见图2(a)。
当坡体产生滑动时,滑动体和不动体变形较小,滑动区间内的土体随着滑动面的发展不断向前偏移,由于滑动面并未发展成型完全贯通,土体位移沿深度方向的变化是连续无突变的,整体呈两端小中间凸的变形特征,见图2(b)。
2.2 概化模型分析
由图2可知,随着滑动面的不断发展,滑坡体的各个组成部分协调变形,且各个组成部分的土体力学性质差异显著。
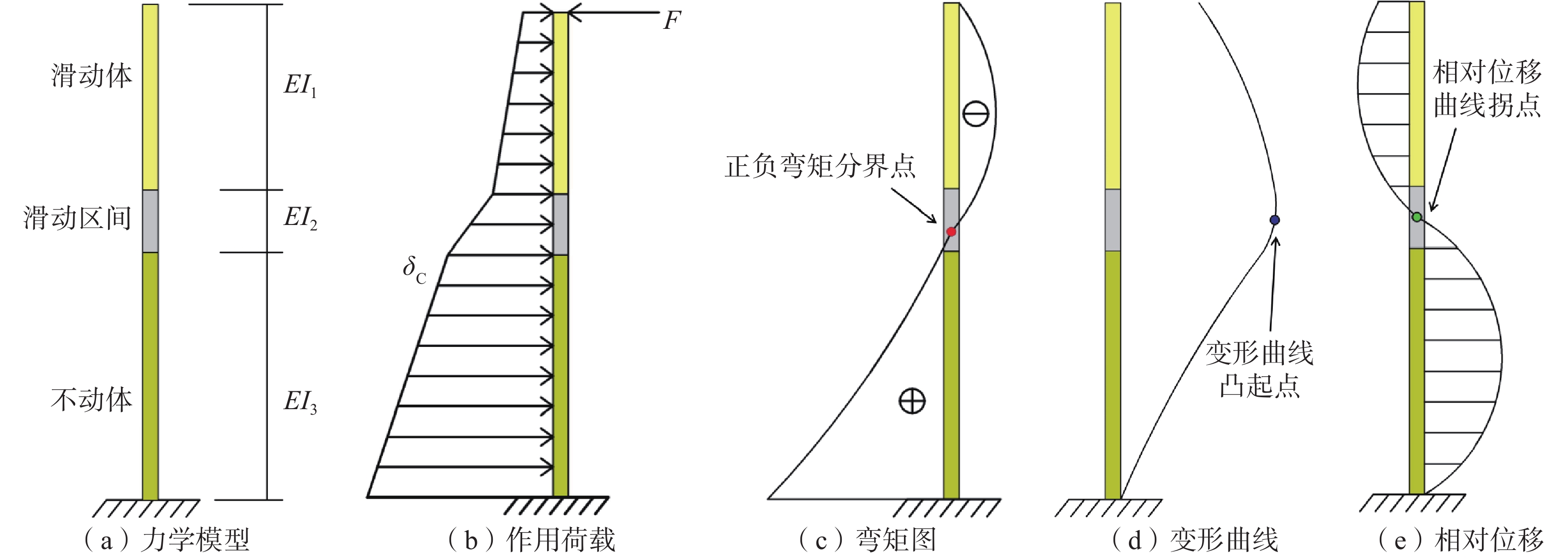
(1)上部土体受到的外界阻滞作用各有差异,如坡体堆载产生的反向偏压作用在土体上沿深度方向近似水平线性荷载、支档结构对上部土体产生被动土压力,土层锚杆对上部土体产生径向锚固力等。由于具有“D”型曲线特征的滑坡,其滑动面的位置通常在土层深处,而上部土体受到的外界阻滞作用主要分布在近地表处且分布区间较短。因此,基于概化模型考虑上部土体的阻滞作用,可将其简化为自由端作用一集中力(F)的悬臂杆件力学模型,见图3(a)(b),杆件变形以弯曲变形为主。
(2)悬臂杆件的抗弯刚度(EI)与各个组成部分相对应,假设滑动体、滑动区间、不动体的抗弯刚度分别为EI1、EI2、EI3,其中,滑带土性质软弱抗剪强度低,则其抗弯刚度(EI2)在三者中最小。在实际的滑坡中,不同深度区间内的土体性质差异明显,假设滑动体、滑动区间、不动体三者各自区间内的土体性质一致,则土体自重应力(δc)沿深度方向的不同区间按直线规律分布,作用在杆件上的土体自重应力等效为与土体重度相关的水平线荷载,模型受力简图如图3(b)所示。
(3)由图3(b)(c)(d)可以发现,在顶部集中力和水平线荷载的共同作用下,杆件上部产生负弯矩下部产生正弯矩,不同位置处的杆件区间沿不同方向产生弯曲变形。其中,正负弯矩分界点处弯矩值为0,结合杆件变形特点和弯矩分布图可以知道,正负弯矩分界点下部杆件左侧受拉,上部杆件右侧受拉,杆件整体向右偏移,杆件变形在正负弯矩分界点处达到最大值,即变形曲线的凸起点与正负弯矩分界点相重合,该位置处的水平位移最大。
(4)由图3(d)(e)可知,杆件变形曲线凸起点下部的土体自下而上位移逐渐增加,凸起点上部土体自下而上位移逐渐减小。将任一位置处的杆件变形量减去与其相邻的下部位置处的杆件变形量,则沿杆件长度方向可以得到近似“S”型的相对位移曲线。如此计算,在与杆件变形曲线凸起点相对应的位置附近将会存在相对位移正负值相反且值为0的临界点(即相对位移曲线拐点)。当杆件上相邻两个计算点之间的间隔越小,则相对位移曲线拐点的理论位置与变形曲线凸起点的位置就越接近。
(5)对于“D”型滑坡体,滑带附近土质最为软弱、抵抗变形能力差,使得该区间内土体位移量明显大于滑动体和不动体[1, 15 − 20];由图3可知,荷载作用下不同区间内的位移差异是造成累计位移-深度曲线呈鼓包状凸起的根本原因,而滑动面作为滑带内的最薄弱位置,该位置处的土体内摩擦角和黏聚力小于其余任一位置处的土体,其位置与正负弯矩分界点相对应,是滑坡体内部水平位移最大处,即变形曲线凸起点位置与滑动面位置重合。因此,准确辨识“D”型曲线滑动面深度的关键在于精准确定变形曲线凸起点的位置;而当变形曲线凸起点的位置不能直接计算或清楚界定时,可以通过计算相对位移曲线拐点的位置间接获取变形曲线凸起点的计算值。
2.3 滑面位置辨识的关键特征
在实际的深孔测斜曲线分析中,对于“D”型测斜曲线,通常是将深孔测斜曲线水平位移最大值所在的深度作为滑动面的位置;然而在实际的勘察监测中,测斜仪上测点的布置间隔是固定的一般为0.5m,意味着测点和滑动面两者的位置并不一定重合,彼此之间存在一定的差距。表明实际深孔测斜曲线中鼓包凸起点的位置并非滑动面的准确位置,其误差范围大致在0.5 m以内。因此,基于深孔位移监测数据若能将滑动面的位置进一步精确化,则可以显著降低误差范围,提升滑动面位置辨识的准确性,并为实际的滑坡勘测和治理提供更为可靠的依据。
由上可知,对于现场采集的“D”型深孔测斜曲线,受测点间隔的影响,滑动面的位置与深孔测斜曲线中的位移最大点并不对应,且基于深孔测斜曲线并不能直接确定滑动面的具体位置。而由前面概化模型的分析可知,通过求解不同深度处相邻土体之间的相对位移,将深孔测斜曲线(即累计位移-深度曲线)转变为相对位移-深度曲线,可以得到形状近似“S”型的相对位移曲线,而相对位移曲线中“S”型段的曲线拐点能够贴近真实变形曲线凸起点的位置。因此,基于相对位移曲线计算出其拐点处的深度值,则能够更加准确地获取滑动面的具体位置。
3. 实际运用分析
3.1 钻孔概况
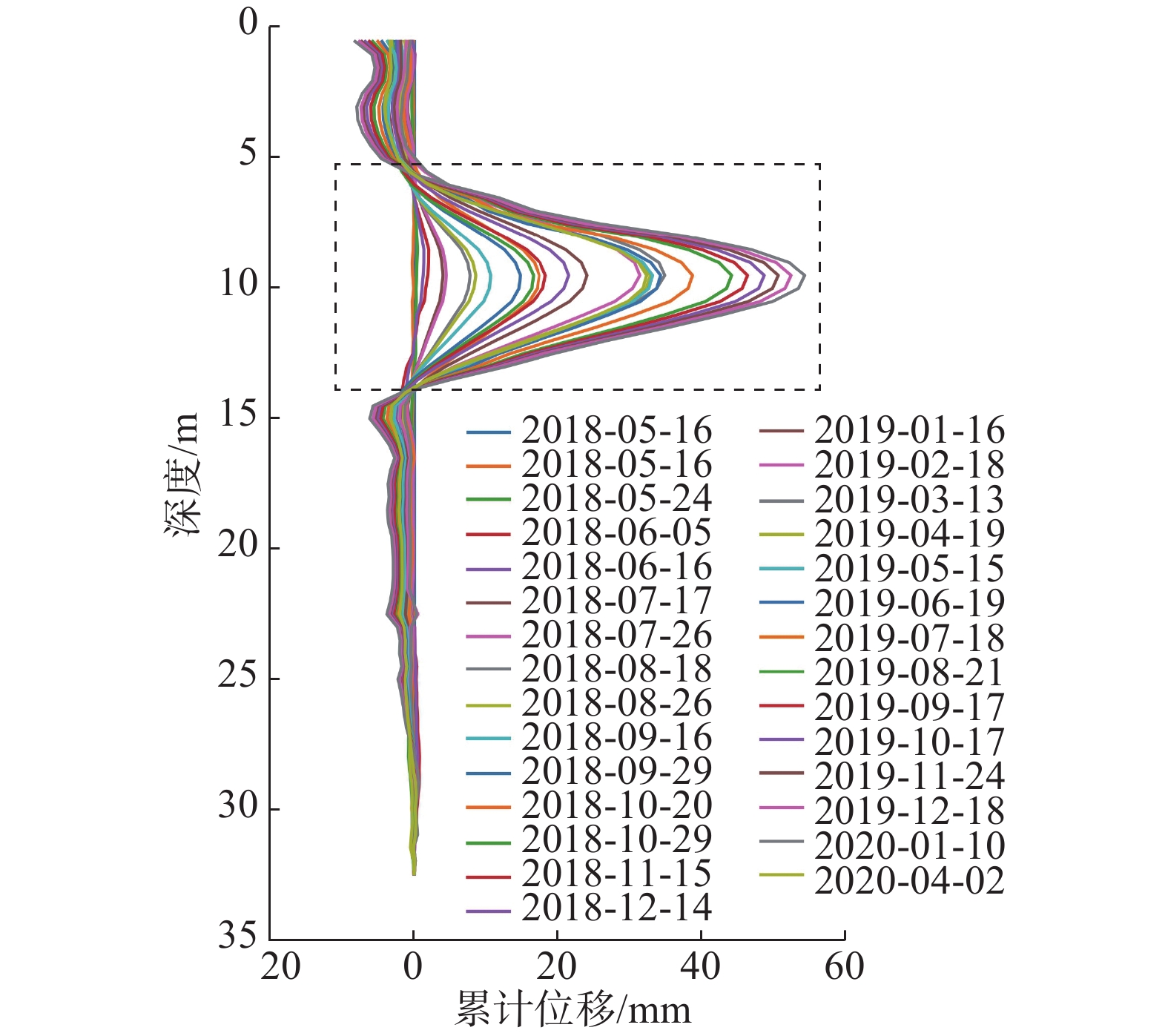
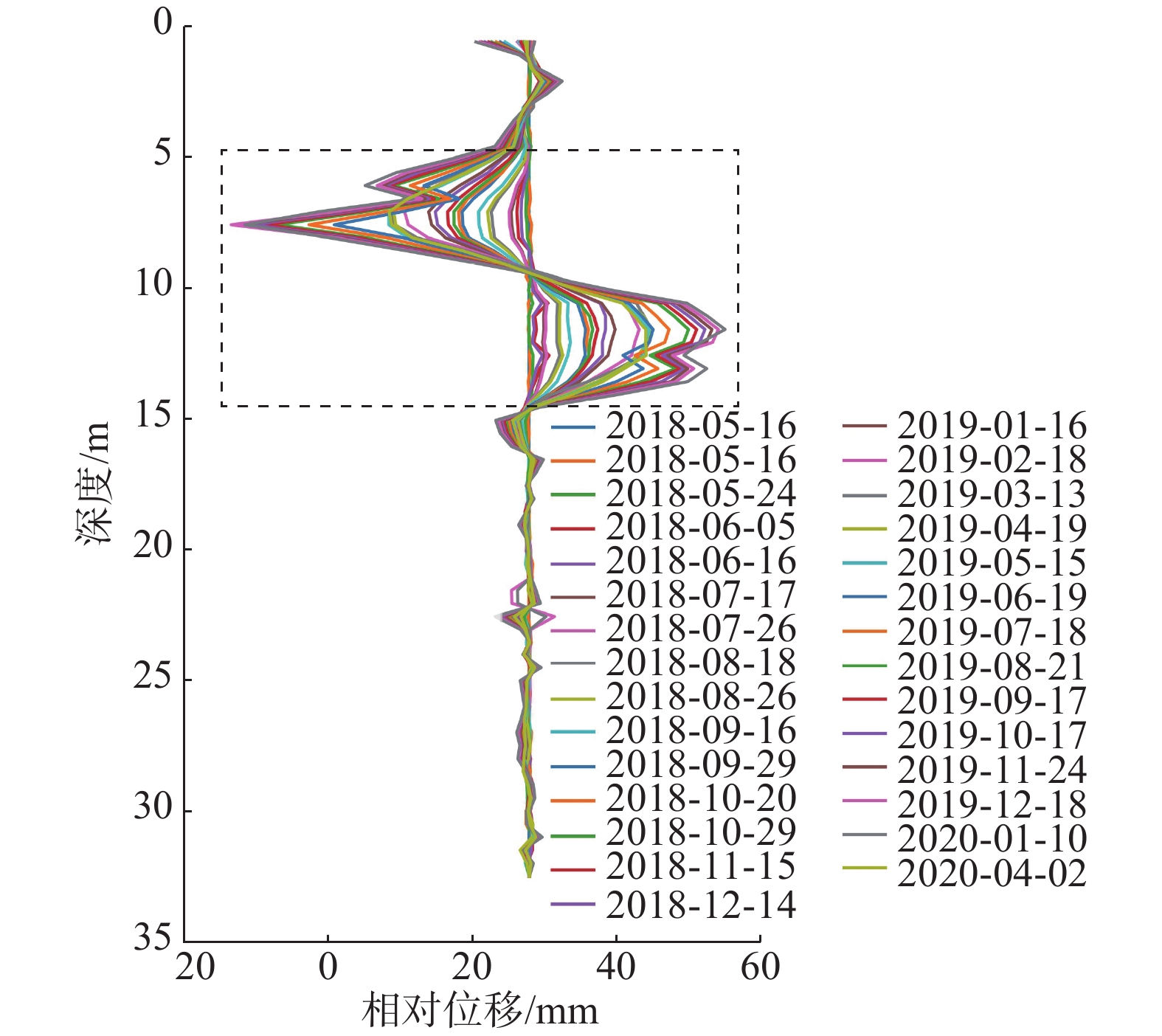
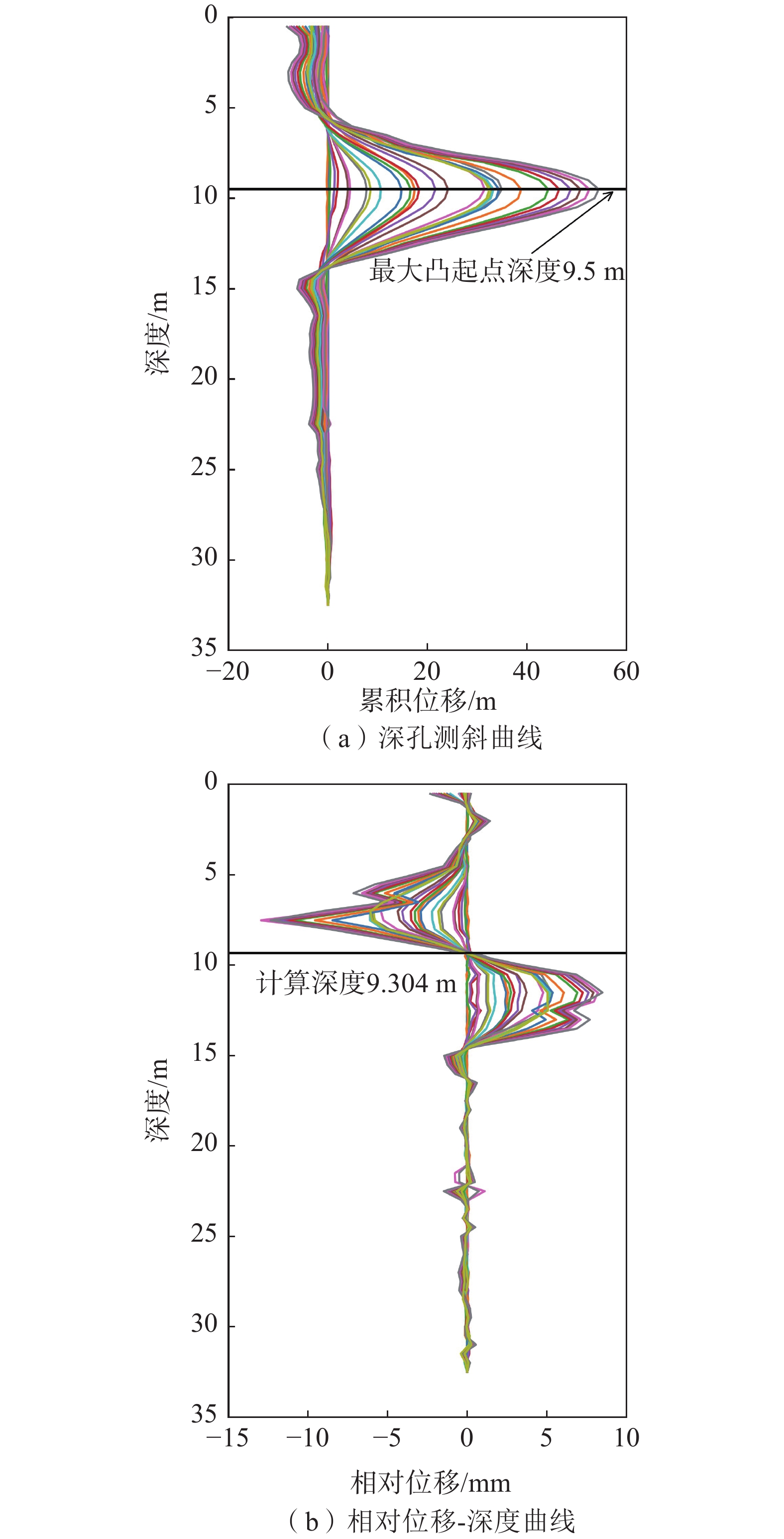
基于上述理论分析,选取中国云南省某铁路滑坡工点的实际监测数据进行分析验证,钻孔全深为32.5 m,数据采集深度为0.5~32.5 m,测点布置间隔为0.5 m,数据采集时间为2018年5月16日—2020年4月2日,深孔测斜曲线如图4所示,两端小中间凸具有典型的“D”型曲线特征。
其中,0.5~5.5 m处的上部土体累计位移呈现沿相反方向增长的特点,由前面概化模型分析可知,造成这一变形特点的原因是由于该钻孔上部土体所受到的外界阻滞作用大,且外界阻滞作用力产生的土体变形占主导,使得上部土体累计位移沿反方向逐渐增长。下部15~32.5 m处测量管产生了一定幅度的旋转,使得采集的位移落在测量方向上的负区间,从而出现底部位移负增长的情况。此外,由现场地勘报告发现,该钻孔靠近坡体的抗滑桩支档结构,进一步证明了外界阻滞作用对曲线形态的影响以及概化模型假设的合理性。
3.2 相对位移曲线分析
3.2.1 钻孔相对位移
分别计算监测期内不同深度处的土体相对位移,即监测期内任一测点深度处的土体相对位移等于该深度处的累计位移减去与其相邻的下部测点的累计位移,结果如图5所示。由该图5可以发现,监测期内相对位移曲线簇近似呈“S”型分布,相对位移沿深度方向明显分为正负两部分。由前面概化模型的分析可知,确定相对位移曲线拐点的具体深度是准确辨识滑动面位置的关键,则提取相对位移-深度曲线正负区间分界点处的有效信息是重要的研究内容。
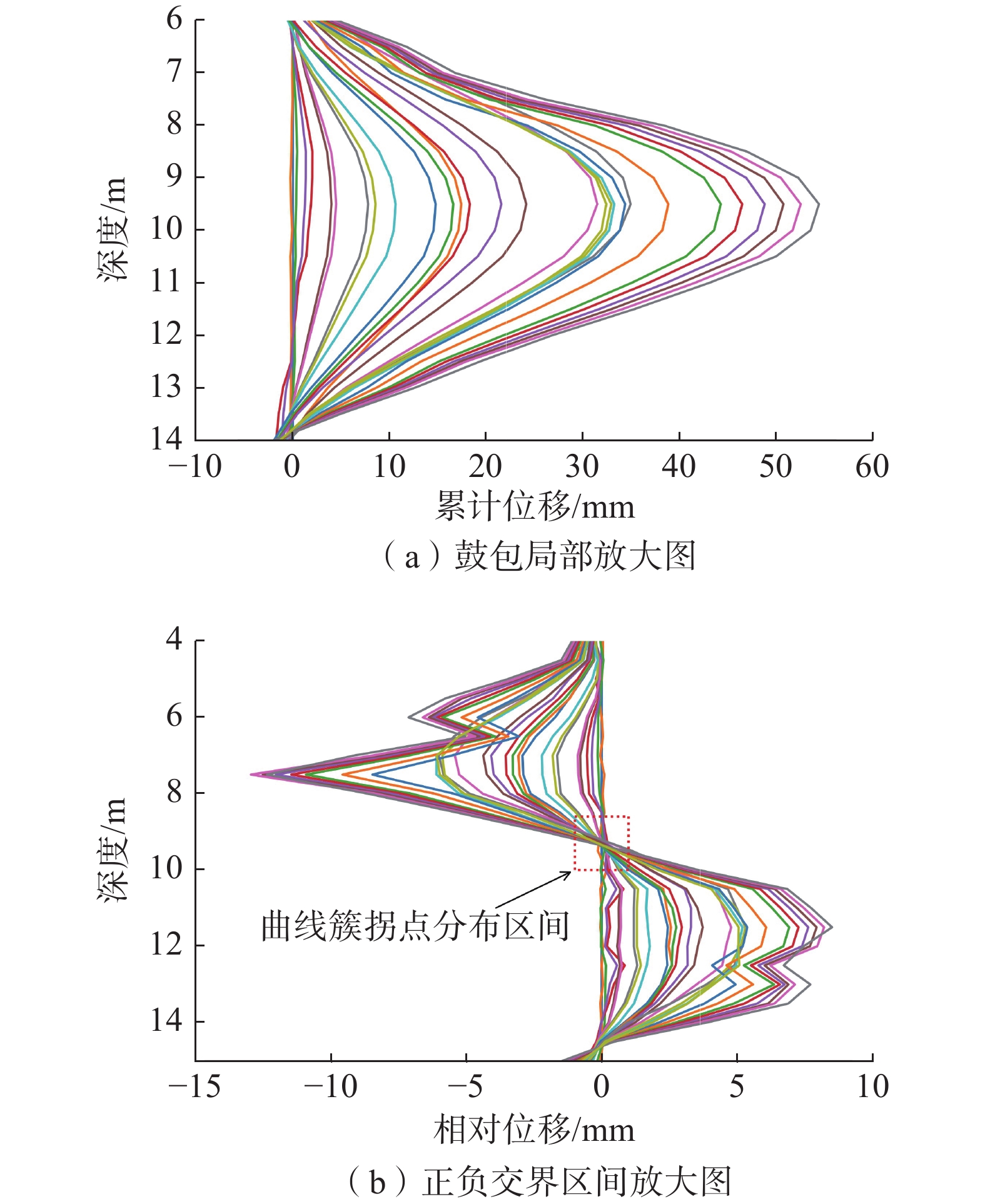
分别放大深孔测斜曲线鼓包凸起区间内的曲线,以及相对位移-深度曲线正负值交界区间内的曲线(见图4—5红色虚线方框区域),如图6所示。
从图6可以发现,初期滑动面发展变形较弱,滑带附近土体位移量增长缓慢,相对位移曲线近似呈一直线;中期滑动面变形增大,滑带附近土体位移量显著增大,相对位移曲线的曲率逐渐增大,愈加趋近“S”型分布;后期滑动面变形速度减缓,滑带附近土体位移量缓慢增长,曲线密集分布,而此时土体累计位移量已经达到较高水平,见图6(a),相对位移曲线具有了明显的“S”型特征。监测期内,不同日期的相对位移曲线相互交错形成一个拐点分布区间,见图6(b)中的红色方框,这一分布区间是准确提取拐点位置的重要依据。
3.2.2 钻孔相对位移坐标转换
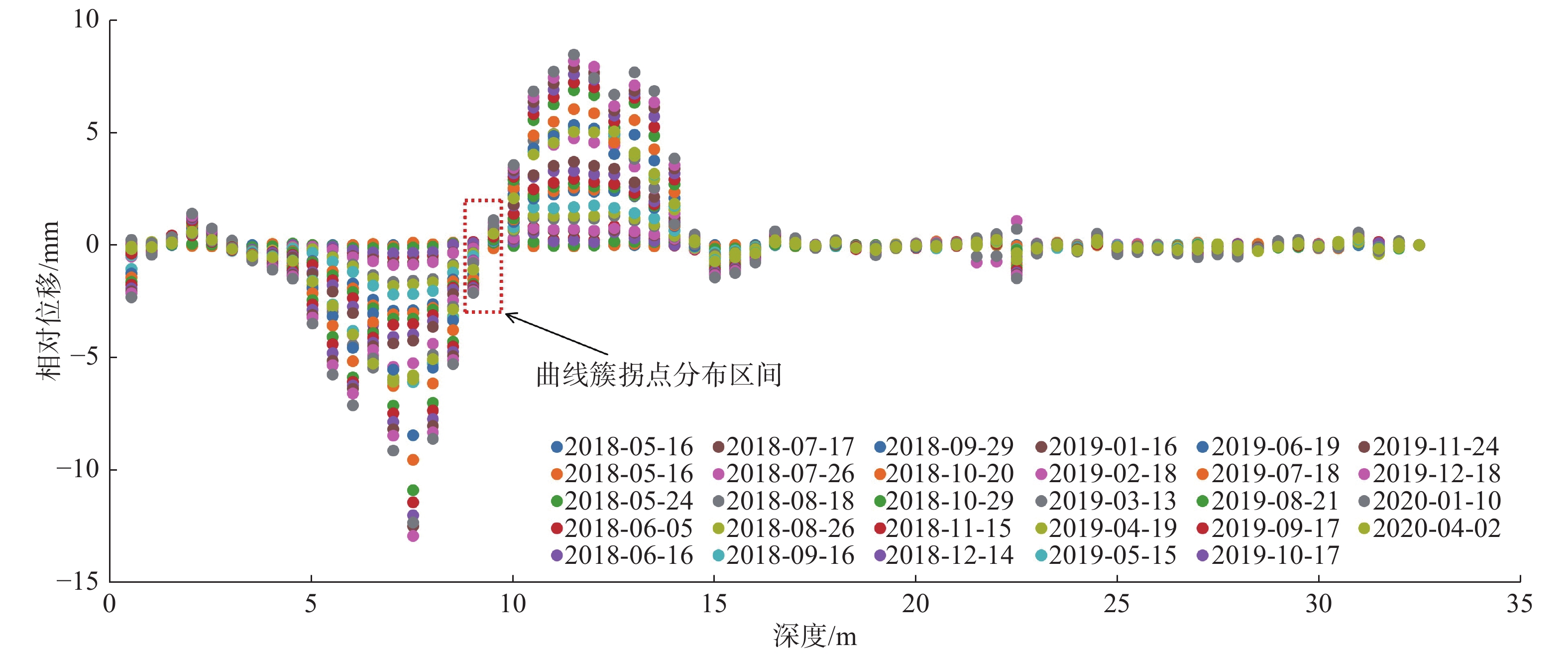
为了进一步放大拐点分布区间的数据特征,提取相对位移曲线中的有效信息。将相对位移-深度曲线横纵坐标转置,以土体深度值为横坐标、相对位移为纵坐标,绘制钻孔相对位移-深度散点图,结果如图7所示。
由图7可以发现,相较于图5的曲线图,采用散点图能够更加清晰直观地展现监测期内不同位置处土体相对位移的变化情况,有利于快速辨识相对位移-深度曲线中“S”型段的正负区间交界区域。通过对比分析可以知道,图6(b)中曲线簇的拐点分布区间为9.0~9.5 m(图7红色方框),即滑动面的位置位于该区间内。
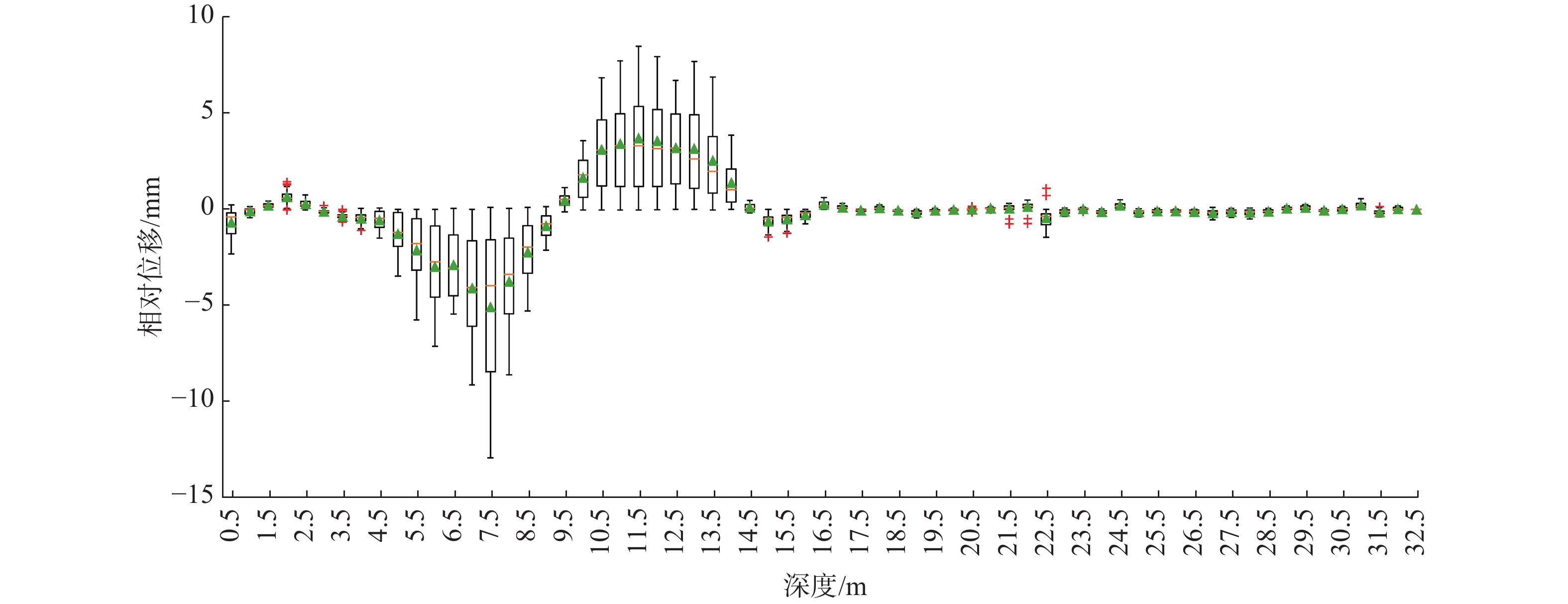
3.2.3 钻孔相对位移箱型图数据分析
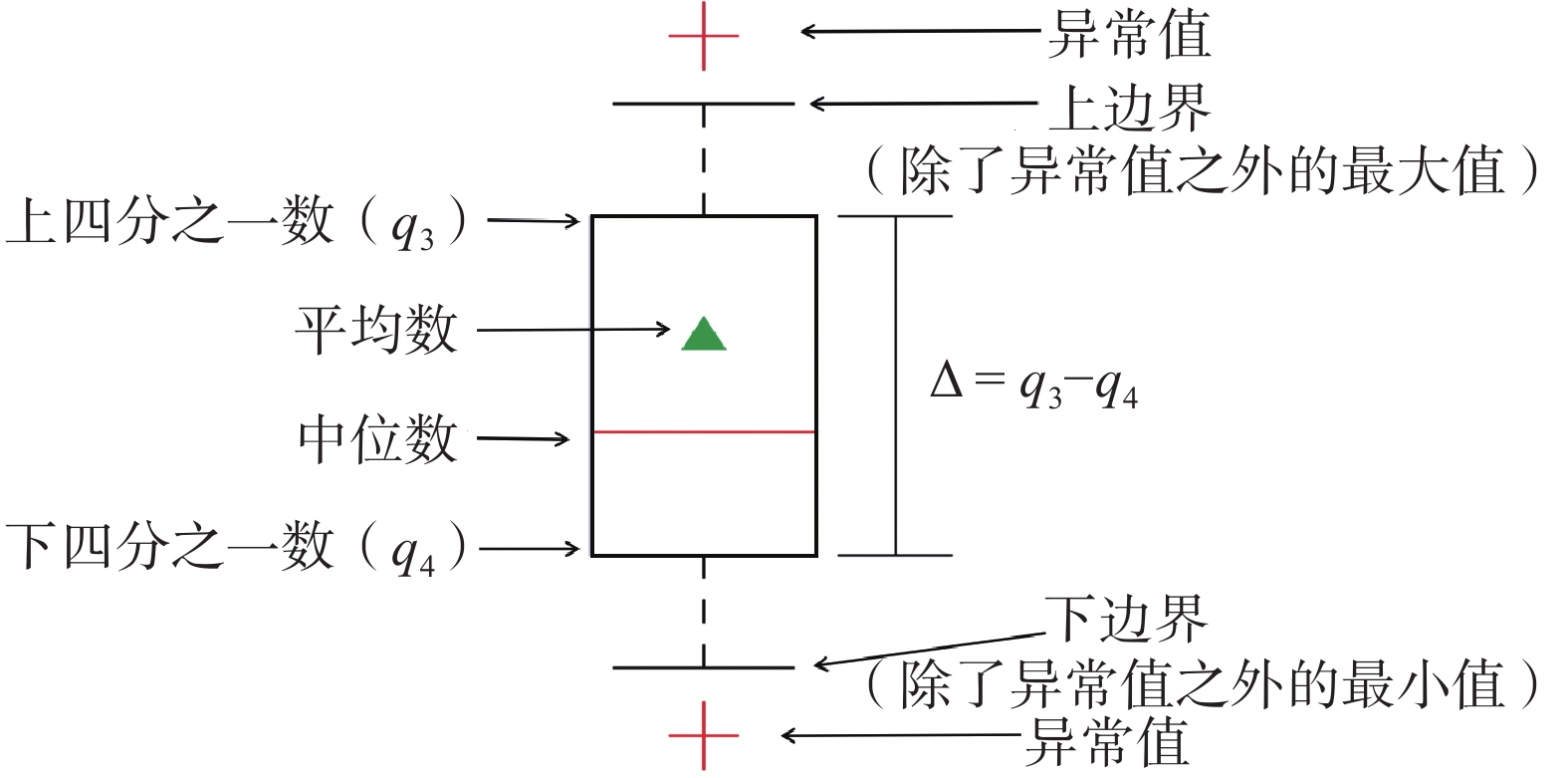
箱形图作为显示一组数据分散情况资料的统计图,可以清晰地反映原始数据分布的特征,还可以进行多组数据分布特征的比较,能够提供有关数据位置和分散情况的关键信息,而且不受异常值的影响,能够准确稳定地描绘出数据的离散分布情况。箱型图图例如图8所示。
为了进一步确定曲线拐点位置,深入挖掘不同深度处土体位移信息。基于相对位移-深度散点图,研究采用箱型图分析深孔位移监测数据的分布特征,重点提取相对位移与滑动面位置之间的关键信息(图9)。
由图9可以发现:
(1)相对位移数据异常值较少,主要分布在滑动体端部和下部,且对应分布区间的相对位移小,表明该钻孔处滑坡体的相对位移沿深度方向形态分布稳定,数据可靠度高。
(2)箱型图在左右两端小、“S”型区段内大,且箱型图在凹凸点处达到最大,表明上下部土体的相对位移数据分布集中,且数值偏小趋近于0;而“S”型区段内的数据分布较为平滑,进一步表明滑带土的位移量会随着滑动面的发展变形出现协同增长的特征。
此外,箱型图中的中位数和平均数作为反映监测期内任一深度处土体变形量的重要数据指标,选取适合的数据指标将监测期内的多条相对位移-深度曲线转变成一条单一的相对位移-深度曲线,能够显著地降低数据分析量,并能直观地展现监测期内土体的变形情况,且可以更加清晰准确地确定相对位移曲线簇的拐点位置。而中位数和平均数两个不同的数据指标有着其各自的适用性:
(3)箱型图中的中位数能较好地反映监测期内不同深度处土体的相对位移值,但是滑动面的变形发展是一个非稳态过程,会随着时间和外界环境的变化而改变,使得监测期内不同时期下的相对位移值有着显著的差异。当初期滑动面发展缓慢且持续时间较长时,相对位移集中分布且数值较小,则计算所得的中位数明显偏小。由于箱型图的中位数容易受土体变形快慢的影响,故并不适合作为任一深度处土体变形情况的代表值。
(4)相较于中位数,箱型图的平均数能够反映监测期内任一深度处土体的平均变形量,且监测期内数据采集的频率越高、时间越长,则箱型图中平均数的代表性就越高,并能有效克服滑坡动态变形过程中由于不同时期土体变形增长速率不一致导致监测期内位移增长量分布离散的问题,弥补了中位数存在的不足,能够充分反映监测期内不同深度处土体的位移变形情况。因此,可将箱型图的平均数作为监测期内不同深度处土体位移量的代表值。
3.3 滑动面位置精准确定
3.3.1 数据降维
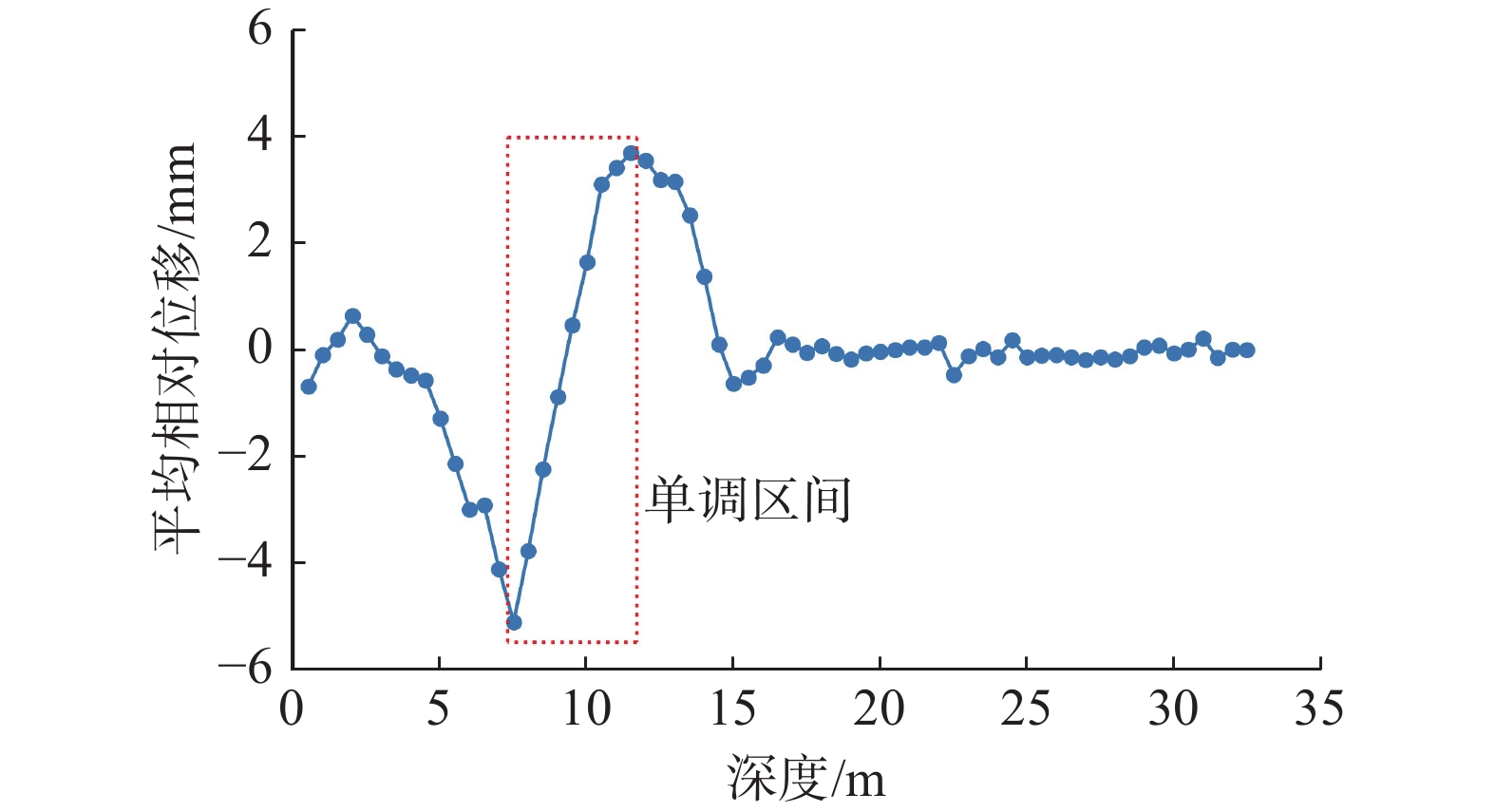
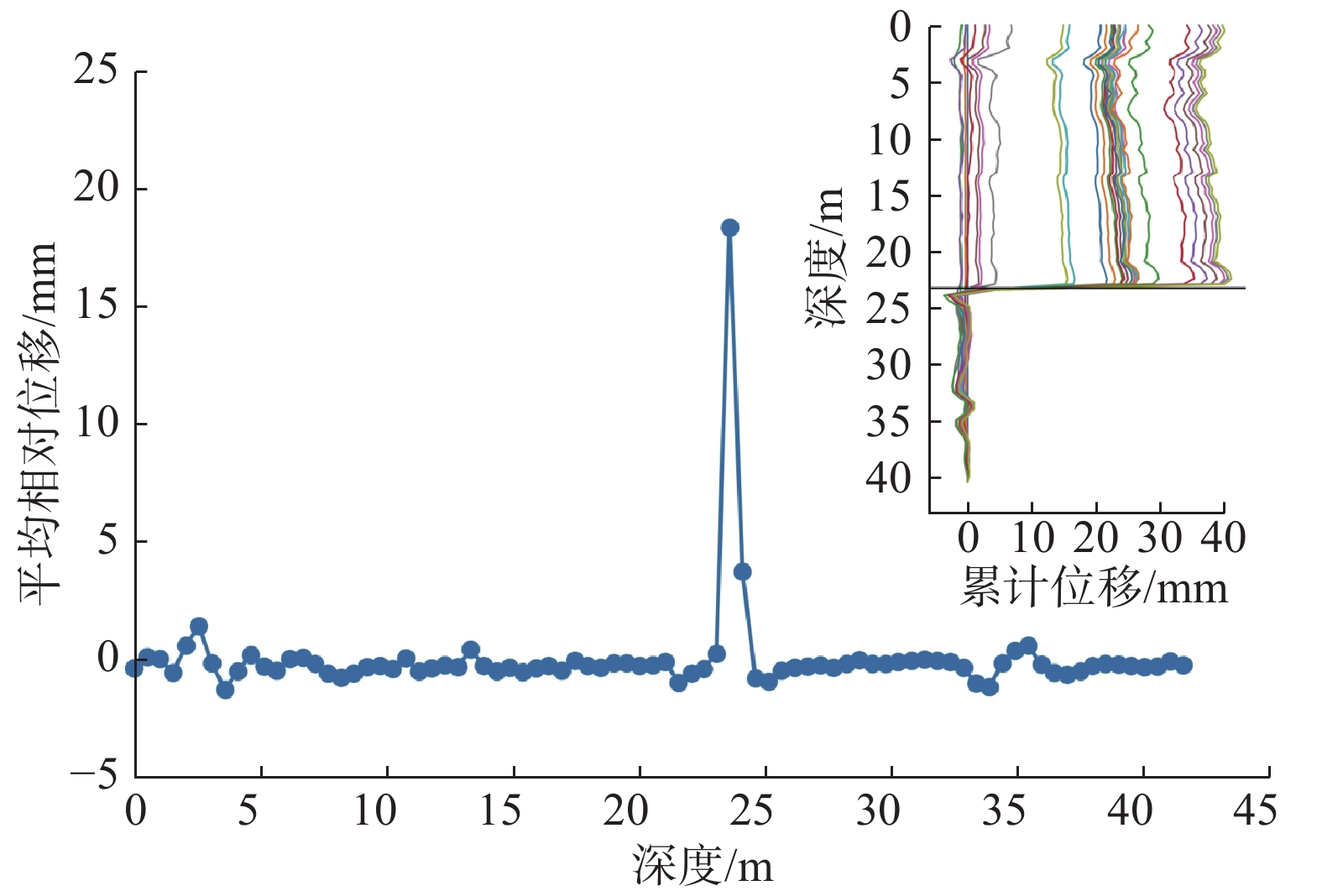
由于相对位移-深度曲线本质上属于由土体相对位移、土体深度和监测时间组成的三维数据;通过上述分析可知,可以选取监测期内不同深度处土体相对位移的平均值作为该深度处的相对位移量,则相对位移-深度曲线变为由土体平均相对位移和土体深度组成的二维数据(图10)。
由图10可以发现,经过数据降维所需分析的数据量大大减少,且平均相对位移-深度点线图仍然以近似“S”型的曲线形态分布。此时,目标拐点落在“S”型区段内的单调区间,即以凹凸点为左右边界所组成的数据区间(图10红色虚线方框区域)。
3.3.2 曲线拐点位置计算
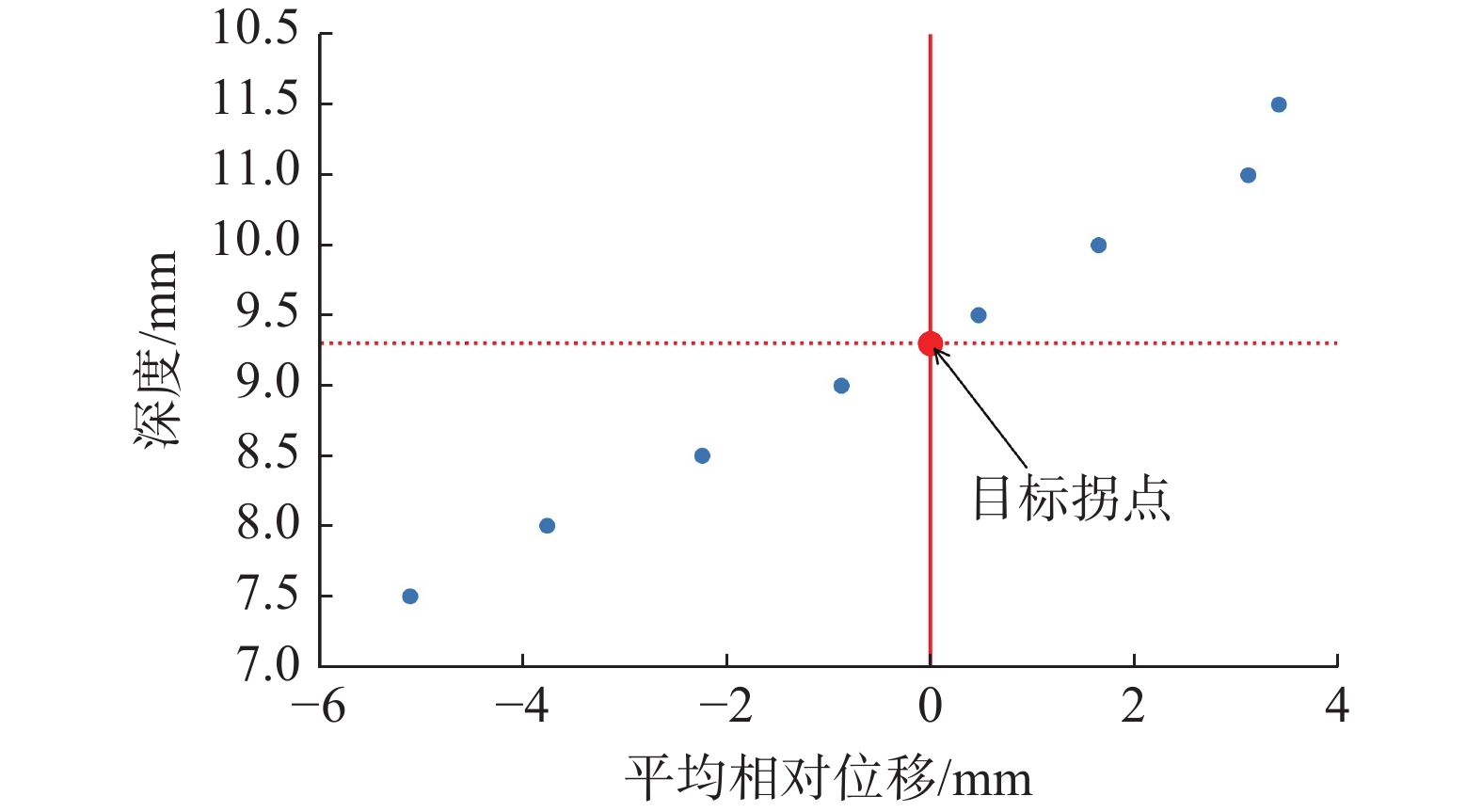
提取图10单调区间内的数据,以平均相对位移为横坐标、土体深度为纵坐标(图11),则拐点位置的计算转化为求解平均相对位移为0时(图11红色实线)对应的深度值(图11红色虚线)。
由图11可以发现,所需计算的数据为离散数据点,则“拟合法”和“插值法”是较为理想的计算方法,而不同的计算方法有着其各自的适用性。
(1)“拟合法”对于多数据点的计算通常采用高阶多项式拟合,然而这种方法的精度取决于幂次的选择,幂次过低则拟合曲线不能穿越所有数据点且拟合误差大,幂次过高则拟合曲线容易出现龙格现象[21]。但高阶多项式幂次选择是一个复杂多变的问题,并不适合广泛运用于目标拐点位置的计算。
(2)为了能够穿越区间内的所有数据点,并且保持曲线连续光滑的特性,选择采用“三次样条插值法”。陈辉[22]基于深孔测斜曲线采用了不同类型的插值法进行计算分析对比,结果表明三次样条插值法的稳定性、贴合度以及精度都是最高的。该方法的本质是在相邻的数据节点间构成一段三次多项式,再把每一段三次多项式按顺序拼接成光滑的曲线,具有更好的收敛性,能够有效克服牛顿插值法、拉格朗日插值法存在的尖点问题以及多项式阶数过高时存在的龙格现象,且无需求解过多的导数信息、计算更加简便,适合用于目标拐点位置的计算[22 − 25]。
因此,选择三次样条插值法更加符合实际运算,其数学计算模型如下:
假设一系列互不相等的数据节点[xi, yi](
(1) 式中:
3.3.3 滑面位置计算结果分析
通过Python编程求取三次样条插值函数,代入单调区间内的所有数据点(图10)进行计算,可以得到x=0所在区间内的三次样条插值函数为:
(2) 将x=0代入式(2)中,可以得到x=0时对应的s值为
9.30377 ,即曲线拐点的深度约为9.304 m。因此,通过计算可以知道滑动面位于地下9.304 m处。将常规的深孔测斜曲线滑面位置辨识方法与本研究提出的计算方法相比较,可以发现:(1)常规的滑动面位置辨识方法是基于钻孔累计位移-深度曲线,通过寻找曲线最大凸起点对应的深度从而确定滑动面的位置,则采用该方法可以得到该钻孔内的滑动面位于地下9.5 m处,见图12(a)黑色水平线[26 − 32]。
(2)本文提出的计算方法是在累计位移-深度曲线的基础上,通过构建概化模型提取滑动面位置与上下部土体之间的变形关系,建立基于相对位移-深度曲线的滑动面位置计算方法,使滑动面的位置可计算化,具有更加科学的数学依据和理论依据,且通过计算可以得到相对位移曲线簇的拐点位于地下9.304 m处,见图12(b)黑色水平线,即滑动面的计算深度为9.304 m。
此外,由现场钻探报告可知,该钻孔附近的坡体自上至下土体在9.0 m左右存在滞水现象,且钻孔开挖至9.25 m处发现明显的滑动擦痕,故可推测滑动面的真实位置应为地下9.25 m,则常规方法所得的滑面位置误差约为0.250 m,本文计算所得的滑面位置误差约为0.054 m。结果表明,该计算方法能够进一步提升滑面位置辨识的准确度,减小常规辨识方法的误差[33 − 44]。
4. 讨论
4.1 适用性分析
通过对实际案例的运用分析可以发现,滑动面的实际深度与深孔测斜曲线鼓包凸起点的位置相近,且与相对位移-深度曲线拐点位置的计算深度基本重合,表明研究提出的方法具有更高的可靠度,可以更加准确地获取滑动面的位置信息。其适用性主要体现在以下几个方面:
(1)具有更加科学可靠的理论依据。研究基于滑坡体概化模型结合“D”型曲线滑坡体变形特征,考虑不同位置处的土体变形规律,建立了相应的力学分析模型,并从杆件受力变形机理上深入分析了“D”型曲线变形特征的根本原因。
(2)充分挖掘“D”型深孔测斜曲线的关键特征,具有广泛的适用性。研究表明,滑动面作为滑坡体中的最薄弱界面,荷载作用下该处土体变形量最大,其位置与变形曲线凸起点的位置相对应。将“D”型深孔测斜曲线转变为相对位移-深度曲线,则形状近似“S”型;其中,“S”型区段内的拐点位置与变形曲线凸起点相近,可作为反映滑动面具体位置的关键参量。
(3)具有合理的数学依据,有着更高的可靠度。本方法通过提取监测期内不同深度处的土体相对位移平均值,将深孔位移监测数据由三维降至二维,大大降低了数据分析的复杂程度。由于拐点位置处的相对位移为0,进一步地,基于降维后的数据,针对“S”型区段内的单调区间采用“三次样条插值法”计算平均相对位移为0时的深度值,可以得到滑动面位置的计算深度,使得滑动面位置的确定可计算化。
基于以上特点,研究提出的计算方法能够有效克服深孔测斜曲线传统辨识方法中存在的滑动面定义不清晰、数值不确定的问题,避免了因观测尺度选取不当导致曲线特征误判以及人为主观判别导致滑面辨识误差较大的情况。
4.2 方法优化分析
研究提出的方法虽然较好地解决了“D型”曲线在滑动面位置辨识中存在的各种问题,但方法本身也存在着一定的局限性,制约了滑动面计算深度的精度,仍然需要更加深入的研究分析,从而进一步优化计算方法。
(1)“S”型单调区间内数据点的数量直接影响滑动面计算深度的精度。当区间内数据点过多时,数据间隔的数量会随之增加,意味着区间内的土体厚度大大增加。由于不同位置处的土体性质存在较大差异,使得区间内数据点的分布状态差异明显,运用“三次样条插值法”得到的滑动面计算深度与真实深度之间的误差会有所增加。
因此,当单调区间内数据点较多时,可以在涵括拐点位置的前提下,考虑适当减小单调区间的范围以降低运算的数据量,从而提升滑动面计算深度的准确性。
(2)研究提出的计算方法是基于“D”型深孔测斜曲线,不一定适用于其它类型的测斜曲线,但能够为其滑动面位置的确定提供参考。不同滑坡的运动变形过程虽然差异显著,但同样存在一定的共性。该方法以相对位移曲线的拐点位置作为滑动面辨识的关键依据,将这种方法用在与“D”型曲线具有相似变形特征的“r”型曲线上(图13),则会出现滑带区间内多数据点突出的情况,可以将相对位移最大值点对应的深度作为滑动面的参考位置。但同样地,受测点布置间隔的影响,该深度也并不一定为滑动面的准确位置,仍需从土体位移变形规律的角度继续挖掘滑带和滑动面之间的关系,提取滑动面辨识的关键依据,进而建立相应的数学计算方法,解决滑动面位置辨识模糊的问题。
5. 结 论
(1)具有“D”型曲线特征滑坡的相对位移-深度曲线形状近似“S”型,且“S”型区段内的拐点位置可作为滑动面辨识的关键依据。
(2)不同深度处土体的平均相对位移可以充分反映监测期内土体的变形情况,提取不同深度处土体的平均相对位移,可以保持相对位移曲线-深度曲线的“S”型特征,且能够降低数据维度,大大减少数据的分析量。
(3)基于降维后的平均相对位移-深度曲线,提取“S”型区段内的单调区间数据,运用“三次样条插值法”计算平均相对位移值为0的土体深度,可以更加准确获取滑动面的具体位置。
-
表 1 深孔测斜曲线典型类型
Table 1 Typical types of deep-hole inclinometer curve
曲线类型 坡体破坏类型 曲线特征 滑坡变形破坏情况 滑动面发展程度 钟摆型 倾倒变形 累计位移在整个深度范围内于初测值附近摆动,
摆动幅度一般小于10 mm滑坡岩土体的深部位移很小,
边坡处于稳定状态未贯通 “V”型 顺层溃屈 上部位移较大而底部位移很小,曲线总体呈线性特征 滑坡内部没有形成明显的滑动面,
处于蠕动变形阶段未贯通 “r”型 切层滑移、顺层滑移、崩塌 累计位移在一个较浅的位置产生较为明显的突变,
而其下部的位置则相对较小滑坡岩土体在浅部形成明显的滑动面 贯通 “D”型 切层滑移、顺层溃屈 累计位移在某一个较深的位置产生突变,
而其上部产生近似整体的移动滑坡深部产生了一个明显的滑动面 接近贯通 “B”型 顺层滑移 累计位移在多个位置产生较为明显的突变,
曲线呈现类似“阶梯”或“波浪”状滑坡岩土体内部形成了多个滑动面 接近贯通 -
[1] 徐邦栋. 滑坡分析与防治[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2001 XU Bangdong. Landslide analysis and prevention[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 2001. (in Chinese)
[2] 陈开圣,彭小平. 测斜仪在滑坡变形监测中的应用[J]. 岩土工程技术,2006,20(1):39 − 41. [CHEN Kaisheng,PENG Xiaoping. Applications of inclinometer in monitoring deformations of landslide[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2006,20(1):39 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Kaisheng, PENG Xiaoping. Applications of inclinometer in monitoring deformations of landslide[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2006, 20(1): 39-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] ZHAO Xin,LI Guo,ZHAO Zhifang,et al. Identifying the spatiotemporal characteristics of individual red bed landslides:A case study in western Yunnan,China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2022,19(6):1748 − 1766. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-022-7339-0
[4] JIN Xiaoguang, HONG Wei, ZHU Ling, et al. Study on time-space motivation and operation mechanic of landslide: A case of Zhenzilin landslide in Sichuan-Tibet highway[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 243/244/245/246/247/248/249: 2811-2818.
[5] HAI Dongjiang. Study on statistical characteristics of deep displacement of monitoring data for soil slope[J]. Environmental and Earth Sciences Research Journal,2015,2(4):11 − 16.
[6] 靳晓光,王兰生,李晓红. 滑坡滑动面位置的确定及超前预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2001,12(1):10 − 12. [JIN Xiaoguang,WANG Lansheng,LI Xiaohong. Determination and advanced forcasting on slide plane position for landslide[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2001,12(1):10 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIN Xiaoguang, WANG Lansheng, LI Xiaohong. Determination and advanced forcasting on slide plane position for landslide[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2001, 12(1): 10-12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] FEARNHEAD N,MANISCALCO K,STANDING J R,et al. Deep excavations:Monitoring mechanisms of ground displacement[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers - Geotechnical Engineering,2014,167(2):117 − 129. DOI: 10.1680/geng.13.00047
[8] 陈贺, 汤华, 葛修润, 等. 基于深部位移的蠕滑型滑坡预警指标及预警预报研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(增刊1): 3015 − 3024 CHEN He, TANG Hua, GE Xiurun, et al. Research on early warning of creep landslide by early-warning indictors based on deep displacements[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(Sup 1): 3015 − 3024. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 李聪,朱杰兵,汪斌,等. 滑坡不同变形阶段演化规律与变形速率预警判据研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(7):1407 − 1414. [LI Cong,ZHU Jiebing,WANG Bin,et al. Critical deformation velocity of landslides in different deformation phases[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(7):1407 − 1414. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Cong, ZHU Jiebing, WANG Bin, et al. Critical deformation velocity of landslides in different deformation phases[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(7): 1407-1414. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 许强,曾裕平,钱江澎,等. 一种改进的切线角及对应的滑坡预警判据[J]. 地质通报,2009,28(4):501 − 505. [XU Qiang,ZENG Yuping,QIAN Jiangpeng,et al. Study on a improved tangential angle and the corresponding landslide pre-warning criteria[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2009,28(4):501 − 505. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Qiang, ZENG Yuping, QIAN Jiangpeng, et al. Study on a improved tangential angle and the corresponding landslide pre-warning criteria[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(4): 501-505. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 吴香根,夏阳,邢志会. 深孔位移监测技术在滑坡勘察中的应用[J]. 路基工程,2010(5):195 − 198. [WU Xianggen,XIA Yang,XING Zhihui. Application of deep hole displacement monitoring technique in landslide survey[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2010(5):195 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Xianggen, XIA Yang, XING Zhihui. Application of deep hole displacement monitoring technique in landslide survey[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2010(5): 195-198. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 陈云生,刘光彬,张一铭,等. 阳鹿高速公路K52新滑坡变形特征与成因机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):83 − 91. [CHEN Yunsheng, LIU Guangbin, ZHANG Yiming, et al. Deformation characteristics and genetic mechanism of a new landslide at K52 of Luyang freeway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):83 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Yunsheng, LIU Guangbin, ZHANG Yiming, et al. Deformation characteristics and genetic mechanism of a new landslide at K52 of Luyang freeway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(1): 83-91.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 张位华,刘勇,彭小平. 钻孔测斜成果曲线在贵州省晴隆滑坡稳定性判识中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2009,20(1):108 − 112. [ZHANG Weihua,LIU Yong,PENG Xiaoping. Application of borehole deep displacement measuring production curve in stability discrimination of Qinglong landslide[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2009,20(1):108 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Weihua, LIU Yong, PENG Xiaoping. Application of borehole deep displacement measuring production curve in stability discrimination of Qinglong landslide[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2009, 20(1): 108-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 靳晓光,李晓红,王兰生,等. 滑坡深部位移曲线特征及稳定性判识[J]. 山地学报,2000,18(5):440 − 444. [JIN Xiaoguang,LI Xiaohong,WANG Lansheng,et al. Characteristics of landslide deep displacement curve and stability discriminant[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2000,18(5):440 − 444. (in Chinese with English abstract) Jin Xiaoguang, Li Xiaohong, Wang Lansheng, et al. Characteristics of landslide deep displacement curve and stability discriminant[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2000, 18(5): /span>440-444spanstyle=color: rgb(51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 胡瑞林,王珊珊. 滑坡滑面(带)的辩识[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(1):35 − 40. [HU Ruilin,WANG Shanshan. Main features and identification method of sliding-surfaces in soil and rock slopes[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(1):35 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU Ruilin, WANG Shanshan. Main features and identification method of sliding-surfaces in soil and rock slopes[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(1): 35-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 潘惠芳. 基于深部位移曲线形态的边坡变形特征分析[J]. 福建建筑,2019(5):54 − 61. [PAN Huifang. Analysis of slope deformation characteristics based on deep displacement curves[J]. Fujian Architecture & Construction,2019(5):54 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract) PAN Huifang. Analysis of slope deformation characteristics based on deep displacement curves[J]. Fujian Architecture & Construction, 2019(5): 54-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 朱泽奇,胡琪堂,龚擎玉,等. 基于深部位移曲线特征的公路边坡稳定性评价方法研究[J]. 公路,2019,64(1):13 − 19. [ZHU Zeqi,HU Qitang,GONG Qingyu,et al. Evaluation method of highway slope stability based on deep displacement curve characteristics[J]. Highway,2019,64(1):13 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU Zeqi, HU Qitang, GONG Qingyu, et al. Evaluation method of highway slope stability based on deep displacement curve characteristics[J]. Highway, 2019, 64(1): 13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 中国铁道科学研究院集团有限公司, 红层地区典型地质灾害失稳机理与新型防治方法技术研究[R]. 2019 China Academy of Railway Sciences, Study on instability mechanism and new prevention methods and technologies of typical geological disasters in red bed area[R]. 2019. (in Chinese))
[19] 孙志彬,杨小礼. 基于深部位移的边坡滑动特征分析[J]. 长沙理工大学学报(自然科学版),2010,7(2):43 − 47. [SUN Zhibin,YANG Xiaoli. Sliding characteristics analysis of land slide based on the deep displacement[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science & Technology (Natural Science),2010,7(2):43 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract) SUN Zhibin, YANG Xiaoli. Sliding characteristics analysis of land slide based on the deep displacement[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science & Technology (Natural Science), 2010, 7(2): 43-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 靳晓光. 山区公路建设中的岩土工程监测与信息化控制[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2000 JIN Xiaoguang. Geotechnical engineering monitoring and information controlling in intermontane highway construction[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2000. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 朱琪. 高次插值的龙格现象的测试[J]. 湖南科技学院学报,2005,26(11):206 − 208. [ZHU Qi. The runger phenomenal test of the high order interpolation[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Engineering,2005,26(11):206 − 208. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU Qi. The Runger phenomenal test of the high order interpolation[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Engineering, 2005, 26(11): 206-208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 陈辉. 插值法在测斜数据处理中的应用[J]. 福建建设科技,2020(2):19 − 20. [CHEN Hui. Application of interpolation method in inclinometer data processing[J]. Fujian Construction Science & Technology,2020(2):19 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Hui. Application of interpolation method in inclinometer data processing[J]. Fujian Construction Science & Technology, 2020(2): 19-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 李守定,李晓,吴疆,等. 大型基岩顺层滑坡滑带形成演化过程与模式[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(12):2473 − 2480. [LI Shouding,LI Xiao,WU Jiang,et al. Evolution process and pattern of sliding zone in large consequent bedding rock landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(12):2473 − 2480. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Shouding, LI Xiao, WU Jiang, et al. Evolution process and pattern of sliding zone in large consequent bedding rock landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(12): 2473-2480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 许强. 滑坡的变形破坏行为与内在机理[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(2):145 − 151. [XU Qiang. Theoretical studies on prediction of landslides using slope deformation process data[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(2):145 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Qiang. Theoretical studies on prediction of landslides using slope deformation process data[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(2): 145-151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 叶咸,高瑜,李果,等. 滑坡深部位移监测孔合位移计算与分析[J]. 公路,2020,65(10):5 − 10. [YE Xian,GAO Yu,LI Guo,et al. Calculation and analysis of combined displacement of deep displacement monitoring holes in landslide[J]. Highway,2020,65(10):5 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) YE Xian, GAO Yu, LI Guo, et al. Calculation and analysis of combined displacement of deep displacement monitoring holes in landslide[J]. Highway, 2020, 65(10): 5-10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 陈贺, 李亚军, 房锐, 等. 滑坡深部位移监测新技术及预警预报研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(增刊2): 4063 − 4070 CHEN He, LI Yajun, FANG Rui, et al. A novel technique for monitoring deep displacement and early-warning of landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(Sup 2): 4063 − 4070. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 董秀军,许强,唐川,等. 滑坡位移-时间曲线特征的物理模拟试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2015,23(3):401 − 407. [DONG Xiujun,XU Qiang,TANG Chuan,et al. Characteristics of landslide displacement-time curve by physical simulation experiment[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2015,23(3):401 − 407. (in Chinese with English abstract) DONG Xiujun, XU Qiang, TANG Chuan, et al. Characteristics of landslide displacement-time curve by physical simulation experiment[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(3): 401-407. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 熊超,孙红月. 基于多因素-多尺度分析的阶跃型滑坡位移预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2023,53(4):1175 − 1184. [XIONG Chao, SUN Hongyue. Step-like landslide displacement prediction based on multi-factor and multi-scale analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2023,53(4):1175 − 1184. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIONG Chao, SUN Hongyue. Step-like landslide displacement prediction based on multi-factor and multi-scale analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1175-1184.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 顾春生,杨磊,闵望,等. 江苏常州地面沉降监测与发展趋势分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(2):82 − 91. [GU Chunsheng, YANG Lei, MIN Wang, et al. Monitoring and analyzing the development trend of land subsidence in Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(2):82 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract) GU Chunsheng, YANG Lei, MIN Wang, et al. Monitoring and analyzing the development trend of land subsidence in Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(2): 82-91.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 赵振宇. 基于数值计算的测斜仪监测误差分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):157 − 161. [ZHAO Zhenyu. Error analysis of an inclinometer based on numerical analysis[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):157 − 161. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO Zhenyu. Error analysis of an inclinometer based on numerical analysis[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(3): 157-161.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 杨志华,吴瑞安,郭长宝,等. 川西巴塘断裂带地质灾害效应与典型滑坡发育特征[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(2):355 − 368. [YANG Zhihua, WU Ruian, GUO Changbao, et al. Geo-hazard effects and typical landslide characteristics of the Batang fault zone in the western Sichuan[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(2):355 − 368. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Zhihua, WU Ruian, GUO Changbao, et al. Geo-hazard effects and typical landslide characteristics of the Batang fault zone in the western Sichuan[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(2): 355-368.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] HERRERA G,FERNÁNDEZ-MERODO J A,MULAS J,et al. A landslide forecasting model using ground based SAR data:The Portalet case study[J]. Engineering Geology,2009,105(3/4):220 − 230.
[33] N D ROSE,O HUNGR. Forecasting potential rock slope failure in open pit minesusing the inverse-velocity method[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2007,44:308 − 320. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.07.014
[34] 朱赛楠,魏英娟,王平,等. 大型单斜层状基岩滑坡变形特征与失稳机制研究—以重庆石柱县龙井滑坡为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(4):739 − 750. [ZHU Sainan,WEI Yingjuan,WANG Ping,et al. Research on deformation characteristics and instability mechanisms of large monoclinal layered bedrock landslides:A case study of the Longjing landslide in Shizhu County,Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(4):739 − 750. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU Sainan, WEI Yingjuan, WANG Ping, et al. Research on deformation characteristics and instability mechanisms of large monoclinal layered bedrock landslides: a case study of the Longjing landslide in Shizhu County, Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(4): 739-750. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 黄秋香, 汪家林, 邓建辉. 基于多点位移计监测成果的坡体变形特征分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(增刊1): 2667 − 2673 HUANG Qiuxiang, WANG Jialin, DENG Jianhui. Slope deformation character analysis based on monitoring results of multiple multi-point borehole extensometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(Sup 1): 2667 − 2673. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] CROSTA G B,AGLIARDI F. How to obtain alert velocity thresholds for large rockslides[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,Parts A/B/C,2002,27(36):1557 − 1565. DOI: 10.1016/S1474-7065(02)00177-8
[37] 焦龙进,李磊,姜德民. 滑坡勘查中滑动面判定方法分析[J]. 建筑技术开发,2019,46(11):134 − 135. [JIAO Longjin,LI Lei,JIANG Demin. Simple analysis of sliding surface determination method in landslide exploration[J]. Building Technology Development,2019,46(11):134 − 135. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIAO Longjin, LI Lei, JIANG Demin. Simple analysis of sliding surface determination method in landslide exploration[J]. Building Technology Development, 2019, 46(11): 134-135. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] VAN ASCH T W J,VAN BEEK L P H,BOGAARD T A. Problems in predicting the mobility of slow-moving landslides[J]. Engineering Geology,2007,91(1):46 − 55. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2006.12.012
[39] HE Chuncan,HU Xinli,TANNANT D D,et al. Response of a landslide to reservoir impoundment in model tests[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,247:84 − 93. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.10.021
[40] SONG Jian,FAN Qingqing,FENG Tugen,et al. A multi-block sliding approach to calculate the permanent seismic displacement of slopes[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,255:48 − 58. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.04.012
[41] STEAD D,WOLTER A. A critical review of rock slope failure mechanisms:the importance of structural geology[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2015,74:1 − 23. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsg.2015.02.002
[42] HUNGR O,LEROUEIL S,PICARELLI L. The Varnes classification of landslide types,an update[J]. Landslides,2014,11(2):167 − 194. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-013-0436-y
[43] ZHANG Shilin,ZHU Zhaohui,QI Shunchao,et al. Deformation process and mechanism analyses for a planar sliding in the Mayanpo massive bedding rock slope at the Xiangjiaba Hydropower Station[J]. Landslides,2018,15(10):2061 − 2073. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-018-1041-x
[44] ZHAN Liangtong,GUO Xiaogang,SUN Qianqian,et al. The 2015 Shenzhen catastrophic landslide in a construction waste dump:analyses of undrained strength and slope stability[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2021,16(4):1247 − 1263. DOI: 10.1007/s11440-020-01083-8
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 冉鲁光,周小燕,李双平,张斌,刘祖强,王华为,李建川. 大坝边坡测斜孔变形自动化监测及变形模式识别研究. 水电能源科学. 2025(03): 147-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:

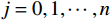
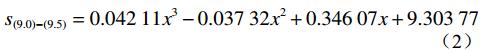
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS