Analysis on the formation of the Moli landslide and river blockage risk in Guoye Town, Zhouqu County of Gansu Province
-
摘要: 受降雨的影响,2021年2月26—28日,舟曲县果耶镇磨里滑坡发生蠕动变形,坡体裂缝发育,变形迹象明显,共造成92户402人受灾,直接经济损失约1 446.3万元。文中以舟曲县果耶镇磨里滑坡为研究对象,通过遥感解译、无人机航拍和地质勘察等方法,深入了解磨里滑坡所处的地质环境、土体物理力学性质等,对该滑坡的成因进行了详细分析、对滑坡的稳定进行了理论计算和位移监测分析。在野外调查和钻探分析的基础上,采用Massflow数值模型对舟曲县果耶镇磨里滑坡进行数值模拟与预测,确定物源区范围及厚度以预测滑坡的堆积过程和堵江风险,预测了滑坡堵江的高度、对上下游造成的危害。结果表明:(1)磨里滑坡呈长舌状,有清晰的形态和变形特征,滑体由碎石土和破碎千枚岩组成,平均深度40 m,总体积2 120×104 m3,属特大型深层滑坡。(2)不利的地形条件、岩土体的软化、强烈的构造运动、降雨的入渗和前缘河水冲刷下切形成的临空面是发生滑坡主要因素。(3)该滑坡存在摧毁房屋道路和堵江的风险,建议尽快对受威胁采取避险搬迁措施。本研究可为类似滑坡地质灾害链的成因机制和应急防控等提供参考。Abstract: Due to the heavy rainfall, from February 26th to 28th 2021, the Moli landslide in Guoye Town, Zhouqu County, experienced creeping deformation with the development of slope cracks and obnious signs of deformation. A total of of 92 households with 402 people were affected, causing a direct economic loss of approximately 14.463 million yuan. This study focuses on the Moli landslide in Guoye Town, where the geological environment and physical and mechanical properties of the soil were deeply understood through remote sensing interpretation, aerial photography, and geological investigation. The cause of the landslide formation was analyzed in detail, and the stability of the landslide was calculated theoretically and analyzed for displacement monitoring. Based on field investigation and drilling analysis, the Massflow numerical model was used to simulate and predict the Moli landslide in Guoye Town, Zhouqu County. The range and thickness of the source area were determined to predict the accumulation process of the landslide and the risk of river blocking. The height of the river blocking and the harm caused by the landslide to the upstream and downstream regions were predicted. The results showed that: (1) Moli landslide is a super-large deep landslide with a long tongue shape, clear shape and deformation, and composed of broken phyllite and broken stone soil. The average depth of the slide body is 40m, and the total volume is 21.2 million stere. (2) The main factors of landslide formation are unfavorable topographic conditions, softening of rock and soil, strong tectonic movement, rainfall infiltration, and front river erosion. (3) The landslide has the risk of destroying the landslide houses, roads, and blocking the river. It is suggested that the residents threatened by the Moli landslide should take measures to avoid danger and relocate as soon as possible. This study can provide reference for the formation mechanism and emergency prevention and control of similar landslide geological disaster chains.
-
0. 引 言
随着人类活动的不断加剧和降雨等环境气候的影响,生态及地质环境发生了很大的变化,滑坡堵江成了地质灾害研究的重要课题,2019年舟曲县南峪乡江顶崖滑坡就发生了堵江事故,造成了巨大经济损失。目前,国内对滑坡机制的研究较晚,但最近几十年也取得了一定的成果。胡卸文等[1]研究了唐家山滑坡形成及堵江过程;卢万年[2]推导出高速远程滑坡的速度公式和滑距公式;黄润秋等[3]提出高速滑坡的“滚动摩擦”机制;胡广韬等[4] 在《滑坡动力学》文献中系统地提出、阐述、论证了有关“滑坡动力学”的20余项关键性理论、观点和问题,具有重要的理论意义。
舟曲县果耶镇磨里滑坡是受断层影响的特大型滑坡,该滑坡所处位置的地质构造活动活跃,成因和演化机制复杂。本文以舟曲县果耶镇磨里滑坡为依托,利用钻探、滑坡测斜仪、InSAR监测等工作,认定为老滑坡的局部复活,在降雨、地震等外应力作用或自重作用下极易发生大规模滑坡。为此,通过分析滑坡区的地层岩性、地形地貌等,模拟了滑坡堵江的运动过程,并结合滑坡的演化机制,运用Massflow数值模型原理预测了果耶磨里滑坡堵江趋势以及堵江后对滑坡体和上下游居民造成的生命财产安全的危害,同时为白龙江流域其他堵江事件的应急处置提供了借鉴和参考。
1. 滑坡概况
1.1 滑坡形态特征
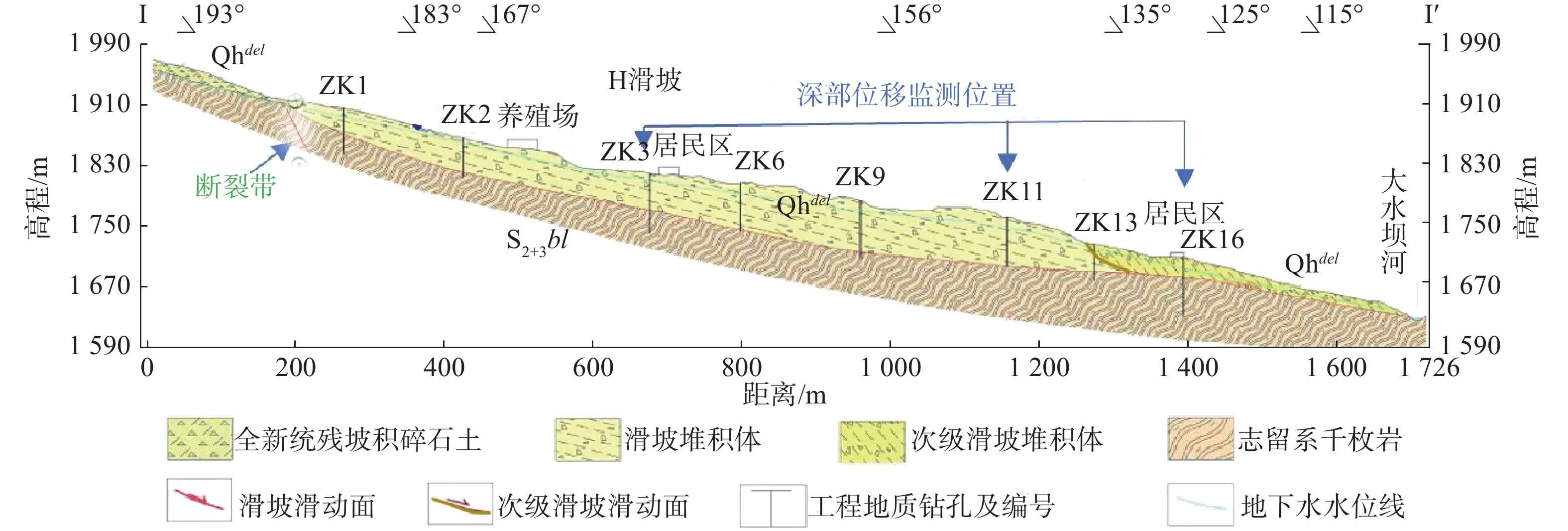
本次磨里复活新滑坡H轮廓整体较清晰,平面形态呈“长舌状”,滑坡平均宽度240~530 m,面积53×104 m2,滑体平均厚度40 m,总体积2120×104 m3,滑体主滑方向170°,沿滑动方向最大长度1 500 m,滑坡体上窄下宽,为特大型堆积层滑坡。滑坡体前缘高程为1663 m,后缘高程为2017 m,相对高差354 m,滑体后部坡度较大,约15°~25°,中下部坡段较缓,约10°~15°,滑体前部受修建房屋道路影响,形成高约2~6 m的台地陡坎,坡度约32°~55°,局部地段近直立(图1)。
1.2 滑坡变形特征
本次磨里新滑坡H于2021年2月26日复活,受降雨和前缘大水坝河周期性水位冲刷的联合作用,滑坡沿着软弱面呈现季节性间歇性蠕动。滑坡主要受黑松坪-三角坪断裂的控制,该断裂带从滑坡体所在后缘经过,且断裂带走向与磨里滑坡滑向约成45°,它们分割地层,控制影响山体走向,使山体表现为断块发育,破坏强烈,形成典型的构造破坏带。受断裂活动的影响,现今活动性明显增强,滑坡体岩土破碎松散,且后缘两侧高陡山体发育崩塌、落石,大量崩落的块石体堆积在相对平缓的滑体上,增加了下滑力。从地面看滑坡后缘高,前缘低,中间形成阶梯状平台,两侧边界“V”字型冲沟发育,冲沟走向与滑体主滑方向基本一致。由于滑坡前缘大水坝河斜坡段,斜坡高差大、坡度陡,受雨水和大水坝河水的冲刷掏蚀的影响,滑坡发生了变形破坏。首先前缘发生次级滑坡,导致上部的房屋墙体开始开裂,局部房屋发生倒塌,其次滑坡东侧变形明显,裂缝逐渐形成,最终贯通至大水坝河左岸,形成长约1.5 km的裂缝,导致房屋受损;滑坡上部西侧变形也较为明显,发生剪切破坏,导致桥梁剪断。滑坡总体变形呈现出前缘变形剧烈,变形迹象明显,房屋道路受损严重,西侧不明显,后部东侧变形较明显的特征。另外,从纵向主剖面Ⅰ—Ⅰ′看出,剖面形态大致呈“折线型”,滑体总体上后部薄,中部较厚,前缘较薄。滑动面岩土体具有明显的分带性,断面可见明显擦痕,滑带土擦痕与水平方向夹角约13°,揉搓较严重,厚度约0.5 m(图2)。
2. 滑坡成因分析
根据本次研究分析认为,滑坡成因分为内因和外因。内因是地形条件和岩土体特性,外因是降雨作用和河水冲刷。
2.1 内因分析
2.1.1 地形条件
磨里滑坡所处的斜坡陡峻,滑坡前缘坡脚与坡顶高差平均达42 m,坡度55°~75°;这种高陡的地形为滑坡的形成提供了良好的临空条件,位于斜坡高处的岩土体由于势能大,在重力作用下,就产生了向坡底移动的趋势,在这个趋势力的作用下,斜坡上部的岩土体具备有一定的下滑动力条件。同时,磨里滑坡地形上极具汇水条件,利于地表水入渗、汇流,影响坡体稳定。
2.1.2 岩土体特性
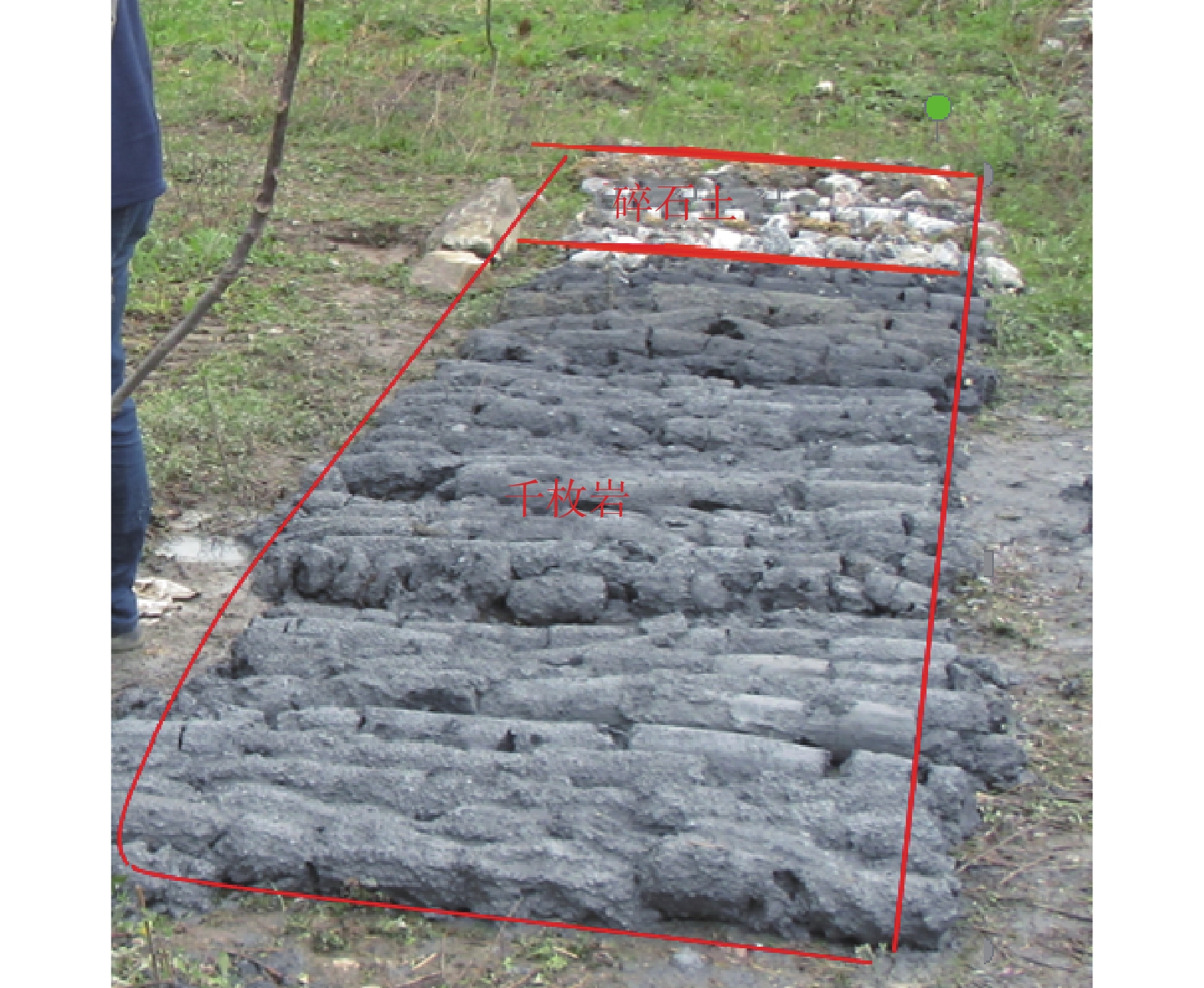
该滑坡发育于磨里老滑坡堆积体,本次滑坡是老滑坡的次级滑坡。老滑坡的原始层为志留系变质岩及泥盆系变质岩和碳酸岩,其中变质岩为千枚岩、板岩等,以软弱夹层的形式存在于斜坡体中,降低了斜坡的稳定性,使该地区易形成滑坡。依据钻孔揭示,滑坡体上层主要为多成因的杂色、青灰色碎石土,下层为千枚岩碎屑,滑床以千枚岩为主(图3)。上层碎石土以块石和碎石为主,架空结构,松散,地表植被稀疏 ,利于地表水的入渗和流通;下层千枚岩碎屑受断裂构造和滑动扰动影响,极其破碎,且该层遇水易软化和泥化,工程性质极差,属于易滑地层;滑床主要为千枚岩,受黑松坪-三角坪断裂影响,本组地层整体较为破碎、产状凌乱、节理发育。上述地层岩性决定了滑坡的发生和发展。
2.2 外因分析
2.2.1 降雨的作用
滑坡区的降雨量在时间和空间上呈不均衡分布,滑坡坡体汇水面积较大,在年内主要集中在4—10月份,其中6—9月降水占全年降水量的61.7%,降雨时间相对集中,并且时有短时暴雨。特别是舟曲“8·17”暴雨接近50年一遇暴雨强度,降雨持续入渗,土体局部饱和,土体的重度增大,岩土体软化,土的抗剪强度降低,增加了滑体的不稳定性,根据滑坡体上雨量计数据,滑坡区2020年降雨量达860.2 mm。降雨与滑坡的发生有关,由于滑坡体的结构松散,坡面裂缝较多,为降雨入渗提供了输送通道[5]。
2.2.2 河水冲刷
根据InSAR解译成果对该滑坡自2010年以来的监测分析,该滑坡一直处于蠕滑变形状态,其前缘一直挤压侵占大水坝河道,但由于大水坝河水的冲刷作用,一直没有堵塞沟道,但河水强烈的冲刷、掏蚀,致使其前缘发生崩塌,从而使上部坡体失去支撑产生滑动变形,并牵引后部土体发生滑动[6-7]。
由此可见,对该滑坡开展滑坡成因与堵江危险性预测分析研究是很有意义的,同时可以减少滑坡带来的危害。
3. 滑坡稳定性分析
3.1 深部位移监测
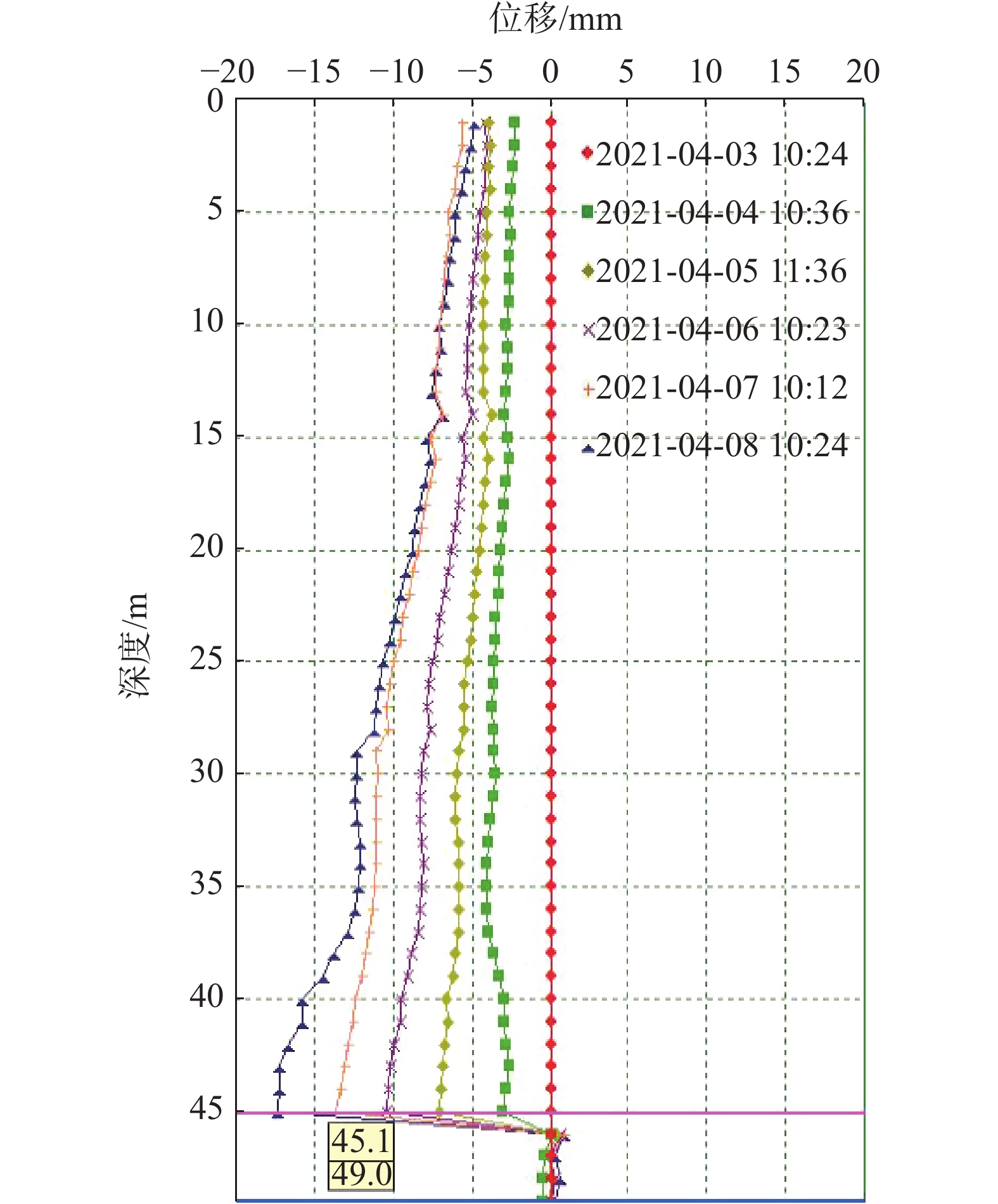
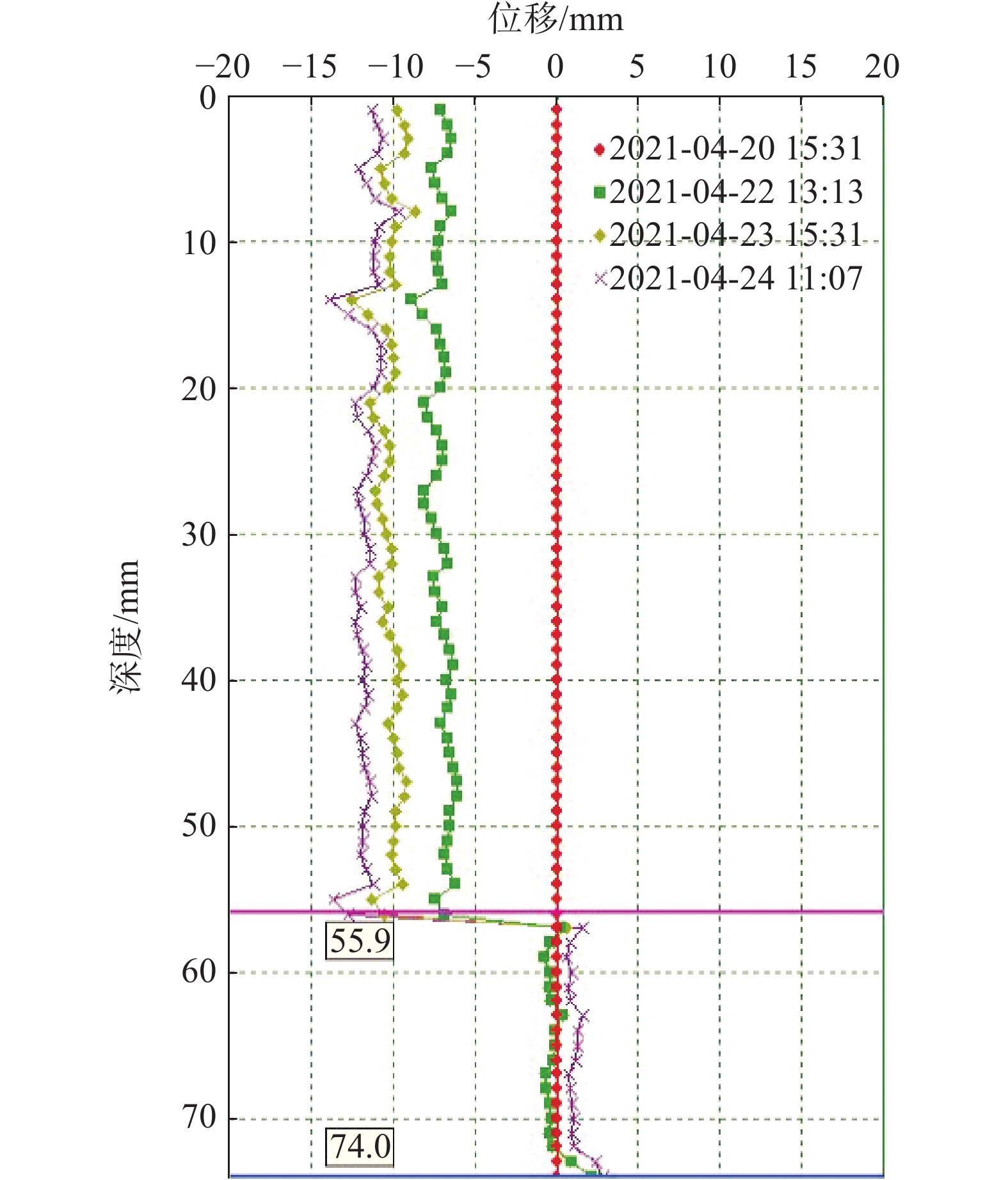
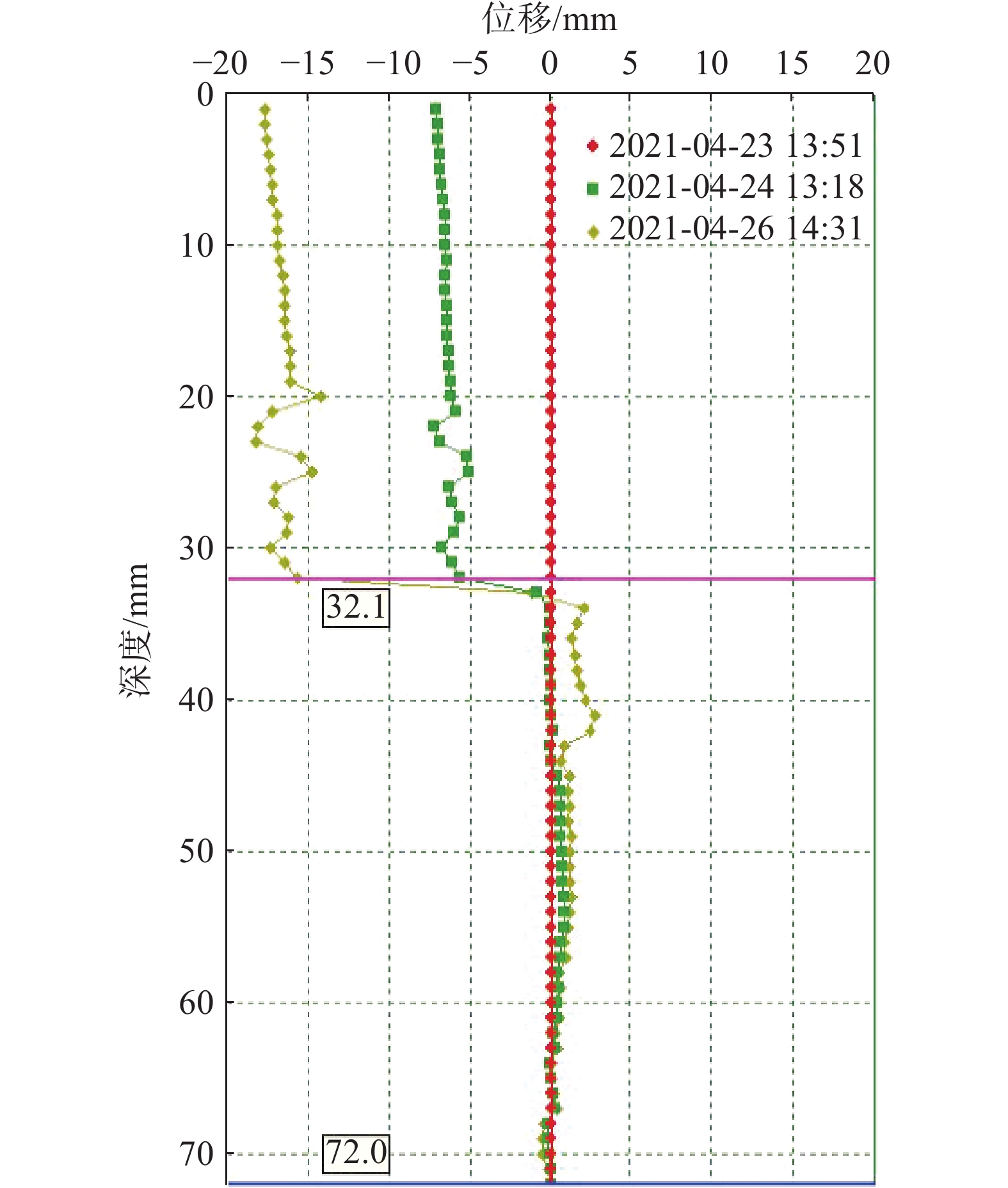
由于该滑坡规模较大,本次滑坡勘查以滑动式测斜仪为主,钻孔成孔之后在主剖面和重要部位的孔内安装了测斜管(图1),采用测斜仪每天对钻孔进行深部测斜,以确定滑动面的位置:滑坡主剖面中部ZK3号孔滑面深度45.1 m,磨里累计位移20 mm(图4)主剖面上部ZK11号孔滑面深度55.9 m,累计位移15 mm(图5),主剖面上部ZK16号孔滑面深度32.1 m,累计位移18 mm(图6)。
3.2 理论计算分析
3.2.1 计算剖面及参数确定
稳定性计算选取滑坡体主滑纵断面Ⅰ-Ⅰ’。计算工况为工况Ⅰ:自重;工况Ⅱ:自重+暴雨;工况Ⅲ:自重+地震。暴雨标准:暴雨强度重现期按50年。地震荷载标准:舟曲县设防烈度为Ⅷ度,地震动峰值加速度取0.2 g。参数选取见表1。
表 1 滑块滑带土取值表Table 1. Property table of the soils at slide block slip zone状态 容重/( kN·m−3) 强度指标 实验标准值 反演值 采用值 天然 18 c/kPa 20.5 19.9 20.2 φ/(°) 16.3 15.9 16.1 饱和 24 c/kPa 18.5 17.9 18.2 φ/(°) 15.3 14.9 15.1 (2)稳定性计算结果
滑坡体土体稳定性计算时,根据其滑面特点近似为折线型滑动面,利用传递系数法验算滑坡体的稳定性。稳定性计算结果见表2。
表 2 滑坡体稳定性成果汇总表Table 2. Summary table of landslide stability results计算工况 稳定系数 稳定状态 工况1:自重 1.070 基本稳定 工况2:自重+暴雨 0.925 不稳定 工况3:自重+地震 0.835 不稳定 滑体的稳定性评价计算结果表明:滑坡体在自然状态下K值为1.07,滑体为基本稳定状态;据勘查,滑带上部滑体内赋存地下水,因此当暴雨工况下,滑体饱水,重度增大,且无地质作用的条件下,K值为0.925,滑体为不稳定状态;当地震力为0.2 g时,K值为0.835,滑体处于不稳定状态[8]。
3.3 地表位移监测
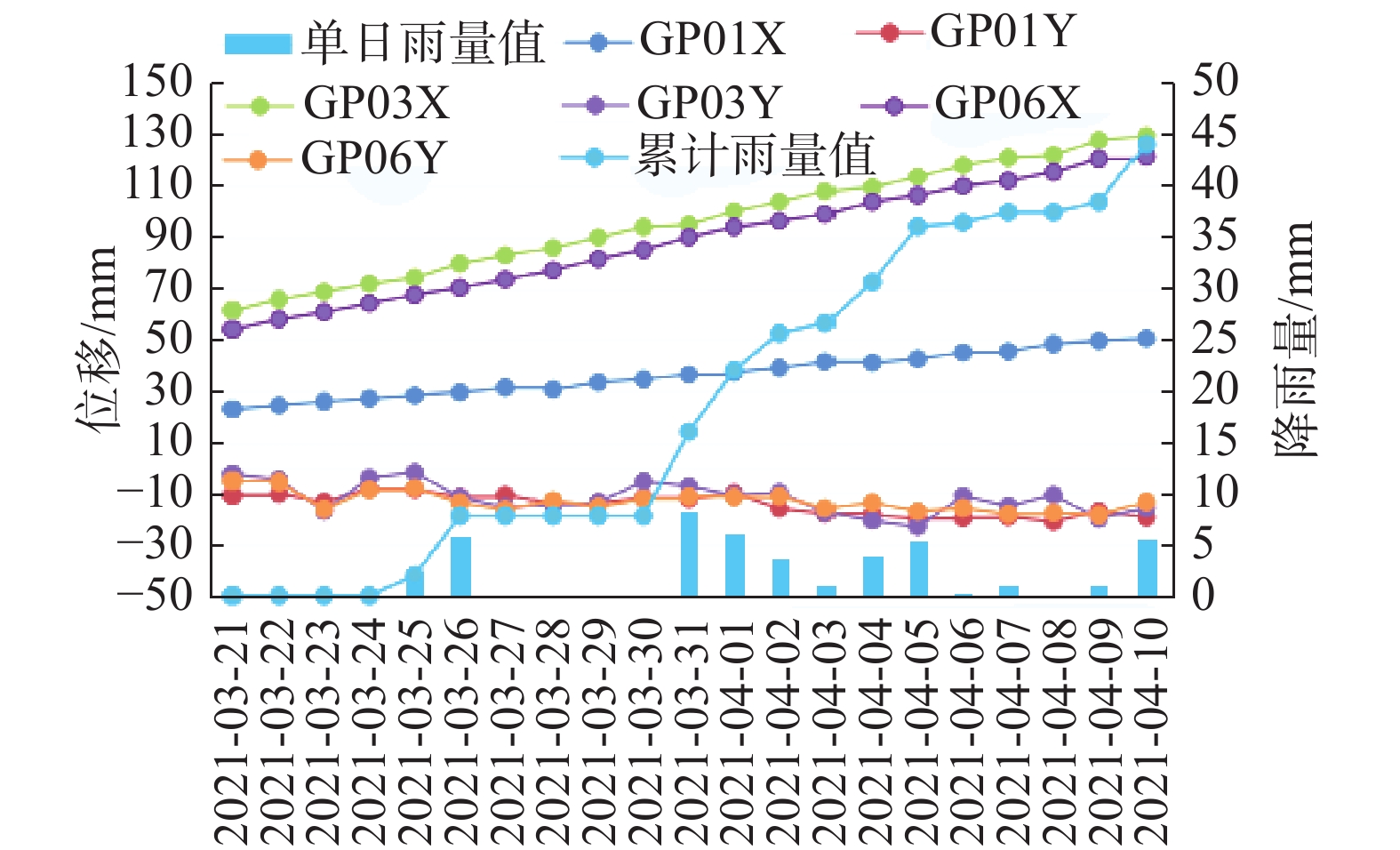
地表位移监测显示,磨里滑坡上部G01位移监测仪自2021年3月5日至4月10日累计水平位移50.4 mm,速率1.40 mm/d;滑坡中部G06位移监测仪自3月9日至4月10日累计水平位移121.3 mm,速率3.79 mm/d;滑坡下部G03位移监测仪自3月5日至4月10日累计水平位移129.2 mm,速率3.59 mm/d。目前滑坡仍处于持续缓慢变形中,见图1(b)、 图7。图7中GP代表雨量值,X表示横坐标,Y表示纵坐标。
从升轨InSAR观测结果来看,磨里滑坡体中后缘自2020年12月后,变形强度明显加快。根据降轨InSAR观测结果,磨里滑坡前缘自2021年1月后存在明显鼓胀隆起的现象(图8)。InSAR观测分析结果与应急监测显示的变形规律一致[9]。
综合分析,理论计算获得的结果与位移监测数据均具有较好的一致性。结果表明:滑坡体前缘松散的堆积体在降雨、地震等外力工况下,极易失稳发生滑动,且下段的滑动速率大于中上部的滑动速率,其最为危险剪出口位于前缘坡脚处。因此,在50年一遇暴雨情况和地震力0.2 g条件下,其失稳过程可细分为两个步骤:首先在地表水的冲刷入渗下,前缘陡坡段首先发生浅层小规模滑坡;其次后部土体受到牵引,此外,滑坡体的后壁及侧壁在降水、地震等条件的引发下有失稳下滑的可能,并对下部中级块体进行加载[10-11]。
4. 滑坡堵江危险性预测分析
4.1 研究方法
本次利用滑坡和洪水演进数值模型开展了滑坡堵江-溃决洪水灾害链的数值模拟与危险性预测。Massflow数值模型基于广义深度积分连续介质力学模型,且满足二阶求解精度,已经被成功应用于金沙江白格滑坡动力过程重建及灾害风险预测分析研究。该模型中滑坡模块的流变模型采用了摩尔库伦理论,需要的参数主要包括黏聚力、内摩擦角和孔隙水压力系数。BASEMENT是一个基于物理侵蚀过程的二维水文动态过程数值模拟模型,常被用于冰湖溃决-洪水(泥石流)地质灾害链。BASEMENT采用二维浅水方程作为本构流方程,并在非结构化双网格计算域内求解水、沙物质状态。考虑了河床、推移质层、悬移质层之间的物质交换。基于流体施加的底部剪切应力与泥沙输移规律来计算物体表面侵蚀;利用三维边坡失稳算法计算侧向坍塌引起的横向破坏。可以实现坝体漫顶侵蚀溃决及下游洪水(泥石流)动态演化过程的二维数值模拟。模型需要的数据包括地形数据、水文数据、土力学参数和边界条件[12-14]。
通过耦合Massflow和BASEMENT开展磨里滑坡堵江-溃决洪水灾害链数值模拟与危险性预测。采用Massflow数值模型对舟曲果耶磨里滑坡进行数值模拟与预测,模型根据实地调查以及高密度电法探测的结果确定物源区范围及厚度以预测滑坡的堆积过程以及堵江风险。共开展了三种不同滑带土含水率下的滑坡堆积预测(表3)。以Massflow输出的滑坡堆积结果作为初始地形,采用BASEMENT数值模型对潜在滑坡坝溃决洪水进行数值模拟与危险性预测。共开展了两种河流流量下溃决洪水危险性预测(表4)。
表 3 滑坡动力过程模拟假设情景与参数Table 3. Simulation scenarios and parameters for landslide dynamic process情景 滑带土含水率/% 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 情景一 6 54.79 35 情景二 18 23.05 24 情景三 30 0.21 15 表 4 溃决洪水演进过程模拟假设情景与参数Table 4. Simulation scenarios and parameters for evaluation of outburst flood情景 河流流量
/(m3·s−1)曼宁
系数抗剪强度
系数床负载
系数模拟时长
/h情景四 20 0.04 0.13 1.5 15 情景五 15 0.04 0.13 1.5 15 4.2 堵江数值模拟与危险性预测分析
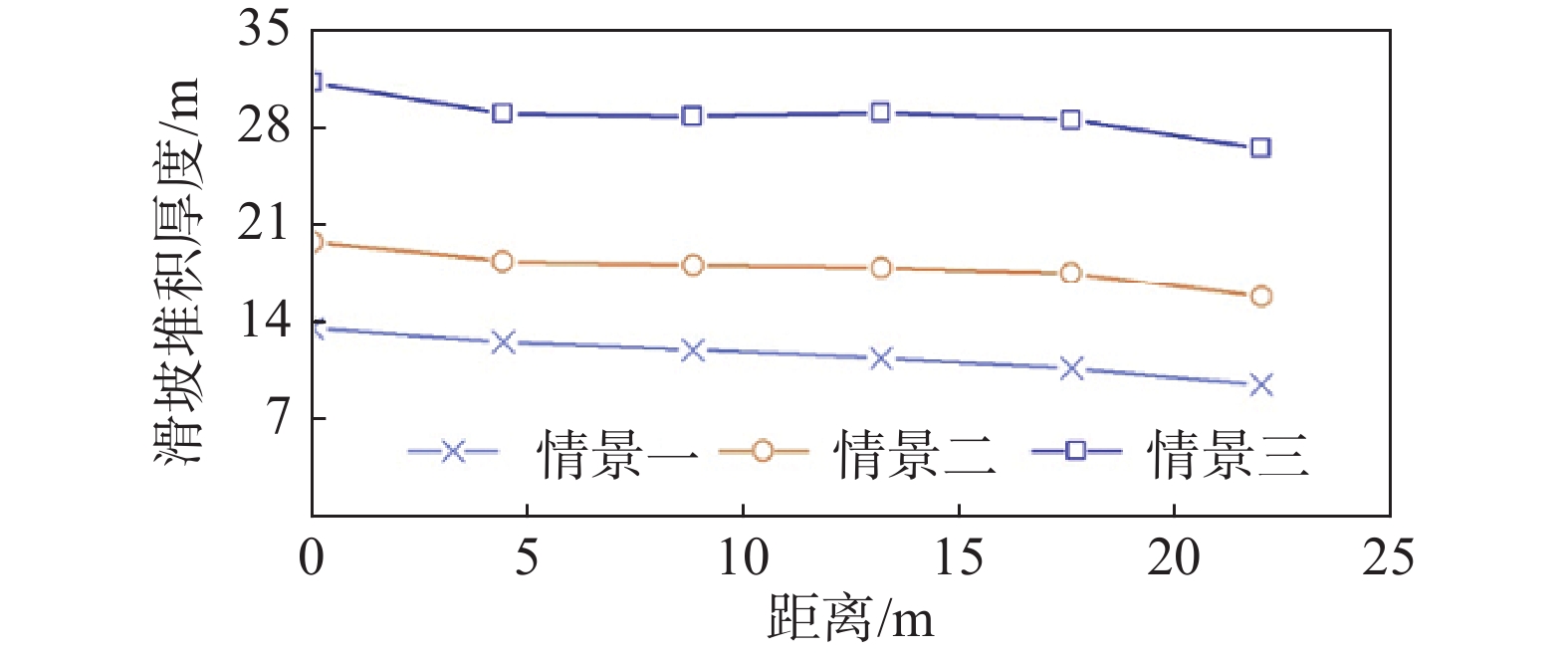
通过假设三种滑带土含水率情景,开展不同滑坡体强度的滑坡堆积模拟预测。情景一的模拟结果显示该强度下滑坡体主要的活动区为下部,滑坡向前滑动距离65 m左右。滑坡体前缘已进入河流中,并堵塞了727 m长的河段。滑坡体前缘的厚度在5~22 m。在滑坡体的中下部,滑坡体向东西两侧滑动扩散,与实地调查的趋势一致(图9所示,红色短线示意了河流剖面提取位置)。
情景二的模拟结果显示该强度下滑坡后部向下滑动,在下方地形变缓处堆积;滑坡的中下部进一步向下滑动且向东西两侧扩散,堆积在前缘及河流中。滑坡向前滑动距离约70 m,滑坡体前缘进入河流中并堵塞了820 m长的河段。滑坡体前缘的厚度在5~30 m(图9)。第三种强度设定的模拟结果显示滑坡整体向下滑动,滑坡向前滑动距离70 m左右。滑坡体前缘已进入河流中,并堵塞了820 m长的河段。滑坡体前缘的厚度在12~40 m(图9)。提取三种情景下河道中滑坡体堆积的截面(图9所示位置)发现,情景一下最厚堆积为13.5 m,可能造成上游415 m范围内受到回水影响,低洼地区被淹没。情景二下最厚堆积为19.8 m,可能造成上游470 m范围内受回水淹没的威胁。情景三下河道中最后堆积达到了31.3 m,若滑坡坝长时间不溃决则可能造成上游630 m范围内低洼地区被淹没(图10所示横坐标0 m处是河岸左侧,20 m处为右侧)。显然,本次堵江成灾是由滑坡前缘产生滑动,中后部受牵引而发生递减的蠕滑变形,形成牵引式滑坡,因此,滑坡经历了由逐级坍滑和到整体下滑的演变,最终致灾规模是整体下滑体积2120×104 m3。
以情景一、情景二和情景三的滑坡堆积结果作为初始地形(图11),对上述3种滑坡体强度的滑坡堆积结果分别开展了下游4.2 km长的溃决洪水演进过程数值模拟,时常都为15 h,设置了两种不同的河流流量对应不同的降雨条件。从情景四的结果来看,首先在滑坡坝上游形成堰塞湖,漫顶后流体在滑坡体前缘低洼处切割出新的流通通道。但3种滑坡堆积结果的漫顶时间不同,情景一30 min后开始漫顶;情景二40 min后开始漫顶,第50 min后到达滑坡坝下游;而情景三中流体在70 min后才流过滑坡堆积体。坝体溃决后,3种滑坡体堆积的下游溃决洪水流深差异较小。然而最终滑坡坝上游堰塞湖深度不同,情景三的堰塞湖深度为9 m,情景二的深度为6 m,情景一深5 m,见图11(a)(b)(c)分别为情景一、情景二、情景三最终时刻的流深分布,(d)(e)(f)分别为情景一、情景二、情景三漫顶时流深分布)[15-21]。
情景五的模拟结果显示情景一40 min后开始漫顶;情景二50 min后开始漫顶,第60 min后流过滑坡堆积体;而情景三中流体在80 min漫顶,第90 min后才到达滑坡体下游。最终滑坡堆坝上游堰塞湖深度也不相同,情景三的堰塞湖深度为9.2 m,情景二的深度为6.6 m,情景一深5.6 m,见图12(a)(b)(c)分别为情景一、情景二、情景三)[22-27]。
5. 结论与建议
通过详细的野外调查、钻探、遥感解译、位移监测、数值模拟等多种方法,分析了位于白龙江流域的舟曲县果耶镇磨里滑坡的成因机理及堵江的危险性,取得如下认识:
(1)舟曲县磨里滑坡平均厚度40 m,总体积2120×104 m3,属特大型深层滑坡。较陡的地形条件、软弱的岩土体组合、断裂带的发育、降雨的入渗和前缘河水冲刷下切形成临空面是磨里滑坡形成的主要因素,其中降雨入渗是磨里滑坡复活的主导因素。
(2)基于3方面的监测数据分析:磨里滑坡坡脚高陡的地形条件使前缘产生滑动,中后部受牵引而发生递减的蠕滑变形,形成牵引式滑坡,该类滑坡形成的地质力学模式可分为滑移—拉裂—剪断三个阶段,水是该滑坡触发的关键因素。
(3)通过对比不同滑带土含水率下的滑坡堆积模拟结果发现,磨里滑坡会不同程度的堵塞河流,形成5~9.2 m深的堰塞湖,且预计在强降雨天气时溃决洪水的峰值流量将达到48.5 m3/s。磨里滑坡存在形成滑坡—堵江—溃决—洪水链式灾害的危险性。
(4)本次为磨里滑坡应急处置提供了参照依据。综合变形监测和堵江数值模拟分析得知:磨里滑坡体上的房屋道路以及上下游村庄都存在安全风险,且滑坡不具备工程治理条件,建议采取避险搬迁措施。
-
表 1 滑块滑带土取值表
Table 1 Property table of the soils at slide block slip zone
状态 容重/( kN·m−3) 强度指标 实验标准值 反演值 采用值 天然 18 c/kPa 20.5 19.9 20.2 φ/(°) 16.3 15.9 16.1 饱和 24 c/kPa 18.5 17.9 18.2 φ/(°) 15.3 14.9 15.1 表 2 滑坡体稳定性成果汇总表
Table 2 Summary table of landslide stability results
计算工况 稳定系数 稳定状态 工况1:自重 1.070 基本稳定 工况2:自重+暴雨 0.925 不稳定 工况3:自重+地震 0.835 不稳定 表 3 滑坡动力过程模拟假设情景与参数
Table 3 Simulation scenarios and parameters for landslide dynamic process
情景 滑带土含水率/% 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 情景一 6 54.79 35 情景二 18 23.05 24 情景三 30 0.21 15 表 4 溃决洪水演进过程模拟假设情景与参数
Table 4 Simulation scenarios and parameters for evaluation of outburst flood
情景 河流流量
/(m3·s−1)曼宁
系数抗剪强度
系数床负载
系数模拟时长
/h情景四 20 0.04 0.13 1.5 15 情景五 15 0.04 0.13 1.5 15 -
[1] 胡卸文,黄润秋,朱海勇,等. 唐家山堰塞湖库区马铃岩滑坡地震复活效应及其稳定性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(6):1270 − 1278. [HU Xiewen,HUANG Runqiu,ZHU Haiyong,et al. Earthquake reactivation effects and stability study of Malingyan landslide in Tangjiashan dammed lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(6):1270 − 1278. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU Xiewen, HUANG Runqiu, ZHU Haiyong, et al. Earthquake reactivation effects and stability study of malingyan landslide in Tangjiashan dammed lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(6): 1270-1278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 卢万年. 用空气动力学分析坡体高速滑坡的滑行问题[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,1991,13(4):77 − 85. [LU Wannian. Airo-dynamic approach to sliding problems of high landslide[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Enivronmental,1991,13(4):77 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract) LU Wannian. Airo-dynamic approach to sliding problems of high landslide[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Enivronmental, 1991, 13(4): 77-85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 黄润秋, 王士天, 张悼元. 斜坡岩体高速滑动的“滚动摩擦”机制[C]//工程地质科学新进展. 成都: 成都科技大学出版社, 1989: 318 − 325 HUANG Runqiu, WANG Shitian, ZHANG Daoyuan. “Rolling friction” mechanism “A” for high-speed sliding of slope rock mass[C]//New Progress in engineering geology. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press, 1989: 318 − 325. (in Chinese)
[4] 胡广韬,赵法锁,李丽,等. 基岩地区高速滑坡的多级冲程与超前溅泥气浪[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,1988,10(1):79 − 87. [HU Guangtao,ZHAO Fasuo,LI Li,et al. Multiple-stroking of high-speed landslides and overstepping gas billows including mud in bed rock areas[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Enivronmental,1988,10(1):79 − 87. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU Guangtao, ZHAO Fasuo, LI Li, et al. Multiple-stroking of high-speed landslides and overstepping gas billows including mud in bed rock areas[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Enivronmental, 1988, 10(1): 79-87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 廖军,邓涛,周越良,等. 降雨作用下第四系堆积体路堤稳定性[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(23):10090 − 10097. [LIAO Jun,DENG Tao,ZHOU Yueliang,et al. Stability of quaternary accumulation embankment under rainfall[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(23):10090 − 10097. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIAO Jun, DENG Tao, ZHOU Yueliang, et al. Stability of quaternary accumulation embankment under rainfall[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(23): 10090-10097. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 云烨,吕孝雷,付希凯,等. 星载InSAR技术在地质灾害监测领域的应用[J]. 雷达学报,2020,9(1):73 − 85. [YUN Ye,LYU Xiaolei,FU Xikai,et al. Application of spaceborne interferometric synthetic aperture radar to geohazard monitoring[J]. Journal of Radars,2020,9(1):73 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract) YUN Ye, LÜ Xiaolei, FU Xikai, et al. Application of spaceborne interferometric synthetic aperture radar to geohazard monitoring[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 73-85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 代聪,李为乐,陆会燕,等. 甘肃省舟曲县城周边活动滑坡InSAR探测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(7):994 − 1002. [DAI Cong,LI Weile,LU Huiyan,et al. Active landslides detection in Zhouqu County,Gansu Province using InSAR technology[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021,46(7):994 − 1002. (in Chinese with English abstract) DAI Cong, LI Weile, LU Huiyan, et al. Active landslides detection in Zhouqu County, Gansu Province using InSAR technology[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(7): 994-1002. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张国帅,王晓亮,夏建新. 入渗条件下颗粒堆积体稳定性试验研究[J]. 泥沙研究,2021,46(5):68 − 73. [ZHANG Guoshuai,WANG Xiaoliang,XIA Jianxin. Experimental study on stability of particle accumulation under infiltration[J]. Journal of Sediment Research,2021,46(5):68 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Guoshuai, WANG Xiaoliang, XIA Jianxin. Experimental study on stability of particle accumulation under infiltration[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2021, 46(5): 68-73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 石固林,徐浪,张璇钰,等. 西山村滑坡时序形变的SBAS-InSAR监测[J]. 测绘科学,2021,46(2):93 − 98. [SHI Gulin,XU Lang,ZHANG Xuanyu,et al. Monitoring time series deformation of Xishancun landslide with SBAS-InSAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2021,46(2):93 − 98. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHI Gulin, XU Lang, ZHANG Xuanyu, et al. Monitoring time series deformation of Xishancun landslide with SBAS-InSAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(2): 93-98. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 朱庆,曾浩炜,丁雨淋,等. 重大滑坡隐患分析方法综述[J]. 测绘学报,2019,48(12):1551 − 1561. [ZHU Qing,ZENG Haowei,DING Yulin,et al. A review of major potential landslide hazards analysis[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2019,48(12):1551 − 1561. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU Qing, ZENG Haowei, DING Yulin, et al. A review of major potential landslide hazards analysis[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2019, 48(12): 1551-1561. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张雨林,石惊涛,涂国祥,等. 粗、巨颗粒富集位置对堆积体降雨入渗的影响[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2021(5):76 − 83. [ZHANG Yulin,SHI Jingtao,TU Guoxiang,et al. Influence of coarse and giant particles enrichment position on rainfall infiltration of accumulation body[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering,2021(5):76 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Yulin, SHI Jingtao, TU Guoxiang, et al. Influence of coarse and giant particles enrichment position on rainfall infiltration of accumulation body[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2021(5): 76-83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 柴贺军,刘汉超,张倬元. 中国滑坡堵江的类型及其特点[J]. 成都理工学院学报,1998,25(3):411 − 416. [CHAI Hejun,LIU Hanchao,ZHANG Zhuoyuan. Study on the categories of landslide damming of rivers and their characteristics[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology,1998,25(3):411 − 416. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHAI Hejun, LIU Hanchao, ZHANG Zhuoyuan. Study on the categories of landslide damming of rivers and their characteristics[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 1998, 25(3): 411-416. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 李娜. 云南省滑坡堵江灾害及其对策[C]// 滑坡文集(9). 北京: 铁道出版社, 1992 LI Na. Landslide Blocking River disaster in Yunnan Province and its countermeasures[C]// Landslide Essays (9). Beijing: Railway Press, 1992. (in Chinese)
[14] 柴贺军,刘汉超,张倬元. 滑坡堵江的基本条件[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,1996,7(1):41 − 46. [CHAI Hejun,LIU Hanchao,ZHANG Zhuoyuan. The main conditions of landslide dam[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Enveronment Preservation,1996,7(1):41 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHAI Hejun, LIU Hanchao, ZHANG Zhuoyuan. The main conditions of landslide dam[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Enveronment Preservation, 1996, 7(1): 41-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 于宝国,边波,李春龙,等. 基于知识图谱的碎石土堆积体滑坡研究热点及发展趋势[J]. 地球科学前沿(汉斯),2021(10):1326 − 1340. [YU Baoguo,BIAN Bo,LI Chunlong,et al. Research hotspot and development trend of gravel soil accumulation landslide based on knowledge graph[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science (Hans),2021(10):1326 − 1340. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU B G, BIAN B, LI C L, et al. Research hotspot and development trend of gravel soil accumulation landslide based on knowledge graph[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science (Hans), 2021(10): 1326-1340. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 李忠生. 国内外地震滑坡灾害研究综述[J]. 灾害学,2003,18(4):64 − 70. [LI Zhongsheng. The state of the art of the research on seismic landslide hazard at home and abroad[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2003,18(4):64 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Zhongsheng. The state of the art of the research on seismic landslide hazard at home and abroad[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2003, 18(4): 64-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 方玉树. 超大型滑坡动力学问题研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1988, 15(6): 20 − 24 FANG Yushu. Study on dynamic problems of super-large landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1988, 15(6): 20 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstrac)
[18] 刘建康,程尊兰,佘涛. 云南鲁甸红石岩堰塞湖溃坝风险及其影响[J]. 山地学报,2016,34(2):208 − 215. [LIU Jiankang,CHENG Zunlan,SHE Tao. Assessment of dam failure and secondary hazards for hongshiyan dammed lake caused by Ludian earthquake in Niulanjiang river[J]. Mountain Research,2016,34(2):208 − 215. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Jiankang, CHENG Zunlan, SHE Tao. Assessment of dam failure and secondary hazards for hongshiyan dammed lake caused by Ludian earthquake in niulanjiang river[J]. Mountain Research, 2016, 34(2): 208-215. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 贺小黑,彭鑫,谭建民,等. 地下水渗流对崩坡积滑坡稳定性和变形的影响—以湖南安化春风滑坡群为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):96 − 103. [HE Xiaohei,PENG Xin,TAN Jianmin,et al. Influence of groundwater seepage on stability and deformation of colluvial deposit landslide:Taking Chunfeng landslide group in Anhua County of Hunan Province as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE Xiaohei, PENG Xin, TAN Jianmin, et al. Influence of groundwater seepage on stability and deformation of colluvial deposit landslide: taking Chunfeng Landslide group in Anhua County of Hunan Province as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 96-103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] TANG Y M,SHU H P,XUE Q A,et al. Field monitoring-based and theoretical analysis of Baota Mountain landslide stability[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2021:1 − 16.
[21] FLAGEOLLET J C,MAQUAIRE O,MARTIN B,et al. Landslides and climatic conditions in the Barcelonnette and Vars Basins (Southern French Alps,France)[J]. Geomorphology,1999,30(1/2):65 − 78.
[22] 杨伟东, 王再旺, 赵涵卓, 等. 基于APSO-SVR-GRU模型的白水河滑坡周期项位移预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):20 − 28. [YANG Weidong, WANG Zaiwang, ZHAO Hanzhuo, et al. Displacement prediction of periodic term of Baishuihe landslide based on APSO-SVR-GRU model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):20 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Weidong, WANG Zaiwang, ZHAO Hanzhuo, et al. Displacement prediction of periodic term of Baishuihe landslide based on APSO-SVR-GRU model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(6): 20-28.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 郭富赟, 周小龙, 火飞飙, 等. 舟曲断裂带滑坡灾害效应与防治对策研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):80 − 89. [GUO Fuyun, ZHOU Xiaolong, HUO Feibiao, et al. Study on the disaster effect and prevention countermeasures of landslide in Zhouqu fault zone[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):80 − 89. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO Fuyun, ZHOU Xiaolong, HUO Feibiao, et al. Study on the disaster effect and prevention countermeasures of landslide in Zhouqu fault zone[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(6): 80-89.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 李彩虹, 李雪, 郭长宝, 等. 青藏高原东部鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性评价[J]. 地质通报,2021,41(8):1473 − 1486. [LI Caihong, LI Xue, GUO Changbao, et al. Seismic landslide hazards assessment along the Xianshuihe fault zone, Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2021,41(8):1473 − 1486. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Caihong, LI Xue, GUO Changbao, et al. Seismic landslide hazards assessment along the Xianshuihe fault zone, Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(8): 1473-1486.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 魏占玺, 谢东武, 毋远召, 等. 基于动态残余强度的不同含水率条件下滑坡稳定性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(2):126 − 136. [WEI Zhanxi, XIE Dongwu, WU Yuanzhao, et al. Research on landslide stability under different water content conditions based on the dynamic residual strength[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(2):126 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract) WEI Zhanxi, XIE Dongwu, WU Yuanzhao, et al. Research on landslide stability under different water content conditions based on the dynamic residual strength[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 126-136.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 田尤, 陈龙, 黄海, 等. 西藏澜沧江流域察雅县城滑坡群成因及现状稳定性[J]. 地质通报,2021,40(12):2034 − 2042. [TIAN You, CHEN Long, HUANG Hai, et al. Origin and stability of landslides in Chaya County, Lancang River Basin, Tibet[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2021,40(12):2034 − 2042. (in Chinese with English abstract) TIAN You, CHEN Long, HUANG Hai, et al. Origin and stability of landslides in Chaya County, Lancang River Basin, Tibet[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(12): 2034-2042.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 韩旭东, 付杰, 李严严, 等. 舟曲江顶崖滑坡的早期判识及风险评估研究[[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):180 − 186. [HAN Xudong, FU Jie, LI Yanyan, et al. A study of the early identification and risk assessment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):180 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN Xudong, FU Jie, LI Yanyan, et al. A study of the early identification and risk assessment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(6): 180-186.(in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 姜鑫,张卫雄,杨校辉,陈昆全,丁保艳. 甘肃舟曲县江顶崖滑坡抗滑桩变形监测与治理效果分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 174-182 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 汪美华,赵慧,倪天翔,余洋,陈红旗. 近30年滑坡研究文献图谱可视化分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(04): 75-85 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:





 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS