Vulnerability assessment of landslide hazards based on hazard intensity at slope level: A case study in Xiangxiang County of Hunan
-
摘要:
以斜坡为单元,基于潜在灾害强度的区域性易损性评价是地质灾害防治亟待解决的重要问题之一。以湖南省湘乡市为研究区,在采用加权信息量方法进行易发性区划的基础上,逐个提取斜坡单元最高易发值点的高程、坡高、坡度、坡向、月平均降雨量为特征参数,分别代入BP神经网络、PSO-BP神经网络、随机森林及支持向量机模型。通过训练与精度测试对比,构建基于PSO优化BP神经网络算法的滑坡体积预测模型,建立以灾害体积为灾害强度指标,以建筑密度、人口密度、财产密度等为脆弱性指标的易损性综合评价模型。针对研究区开展基于潜在灾害强度的区域性易损性评价,完成高易损区(面积占比1.5%)、中易损区(面积占比28.5%)和低易损区(面积占比70%)的区划,实现了区域性易损性评价过程中致灾体灾害强度与承灾体脆弱性的有机结合,增强了评价的客观性和科学性。
-
关键词:
- 滑坡易损性评价 /
- 滑坡体积 /
- PSO-BP神经网络 /
- 斜坡单元
Abstract:Taking a slope as a unit, the regional vulnerability assessment based on potential disaster intensity is one of the important problems to be solved urgently. In this paper, the city of Xiangxiang in Hunan is selected as the research area. On the basis of susceptibility regionalization with the weighted information value method, the elevation, slope height, slope, slope direction and monthly average rainfall of the highest prone points of slope units are extract one by one as the characteristic parameters, which are put into the BP neural network, PSO-BP neural network, random forest and support vector machine model, respectively. A landslide volume prediction model based on BP neural network algorithm optimized by PSO is constructed through training and precision test comparison. A comprehensive vulnerability evaluation model is established with disaster volume as disaster intensity index and building density, population density and property density as vulnerability indexes. Regional vulnerability evaluation based on potential disaster intensity is carried out for the study area. The divisions of high-vulnerable areas (1.5% of the total area), medium-vulnerable areas (28.5% of the total area) and low-vulnerable areas (70% of the total area) are completed, which realize the organic combination of the disaster intensity of the disaster-causing body and the vulnerability of the disaster-bearing body in the process of regional vulnerability evaluation, and enhance the objectivity and scientific nature of the evaluation.
-
0. 引言
易损性评价是地质灾害风险评价与风险管控的基础工作之一,包括致灾体灾害强度评价和承灾体脆弱性评价两个方面[1]。一般而言,易损性评价多偏向于人口密度、财产密度以及建筑密度等承灾体脆弱性指标,灾害强度评价则相对弱化[2 − 3]。随着地质灾害风险评价和防控工作要求的不断提升,如何开展基于灾害强度分析的易损性评价成为亟待解决的问题之一。
滑坡是地质灾害中常见的一种灾害,在滑坡灾害强度分析方面,基于经验分析或数理统计手段,在分析灾害信息得到致灾因子与灾害规模相关性的基础上对灾害强度进行评价,如:Guzzetti等[4]在分析滑坡面积与体积之间相关性的基础上,将拟合得到的滑坡体积作为强度等级;Glade等[5]采用经验方法将滑坡体积、滑动距离和滑移速率作为强度评价指标;彭令等[6]采用统计学方法,以获得的滑距、滑速、体积和滑动面深度等参数的平均值评价灾害强度。有学者基于翔实的岩土工程参数,采用物理力学模型通过计算获得灾害体积,从而评价灾害强度,如Kaynia等[7]通过泥石流速度和流体密度建立冲击力公式,以冲击力代替灾害强度;薛强等[8]采用GeoStudio软件计算不同含水率条件下灾害体体积并作为灾害强度的评价依据。上述评价方法所采用的基础数据多源自针对特定斜坡单元的专项坡勘察,数据则以岩土物理力学指标、滑动面强度、滑动面深度等详尽数据为主。而区域性地质灾害评价受评价尺度和基础数据影响,常以区域地质、遥感影像、地形地貌等为评价指标,且评价对象也多以栅格为主[9 − 10],获取的灾害信息多不能满足以上滑坡灾害强度预测方法,制约了以斜坡为单元,基于潜在灾害强度的区域性易损性评价开展。
以湖南省湘乡市为研究区,基于“以人找坡,以房定坡”的原则划分斜坡单元,在采用加权信息量模型进行易发性区划的基础上,逐坡提取斜坡单元易发值最高点的高程、坡高、坡度、坡向、月平均降雨量等评价指标,通过不同模型训练与精度测试对比,建立以粒子群优化算法(partical swarm algorithm,PSO)优化BP神经网络(back propagation neural network,BP)模型,预测潜在灾害体体积为灾害强度指标,以人口密度、建筑密度、财产密度等为脆弱性评价指标的易损性综合评价模型,实现了针对研究区以斜坡为单元,基于潜在灾害强度的区域性易损性评价。
1. 评价模型
1.1 灾害强度预测模型
1.1.1 BP神经网络模型
BP神经网络模型[11 − 12]是一种按照传播误差进行逆向修正权值训练的多层前馈神经网络模型。以神经元为基本单元,数据从输入层正向传播至隐含层处理再传播至输出层,通过损失函数计算出传播误差进行反向传播,采用梯度下降法修正各连接权值并反复训练直至满足误差要求。神经元的输入和输出关系可表示为式(1)。
$$ {y_i} = {f_1}\left( {\sum_{i = 1}^I {{w_{ij}}{x_i} - {a_j}} } \right) $$ (1) 式中:
$ {y}_{j} $ ——隐含层j神经元;$ {x}_{i} $ ——输入层i神经元;$ {f}_{1} $ ——激活函数;$ {w}_{ij} $ ——输入层i与隐含层j两层连接权值;$ {a}_{j} $ ——两层间阈值。1.1.2 PSO-BP神经网络模型
粒子群优化算法(PSO)[13 − 14]是目前比较常用的一种参数优化计算技术。PSO-BP神经网络模型利用PSO代替BP神经网络当中的逆向传播算法进行模型训练,运用初始权重和阈值建立粒子间合作与信息共享关系找到最优的组合方案,并获得目标误差,可得到优化后的层间连接权重和阈值进行神经网络模型的训练,较好地解决了BP神经网络存在的收敛速度慢、易陷入局部极小值等问题。
1.1.3 随机森林(RF)模型
随机森林(random forest,RF)[15]是一个包含多个决策树的分类器,在进行分类预测时利用各样本集构建对应决策树,每个决策树可选出最优分类结果,再采取投票方式预测最终结果。由于各决策树对数据及特征的选取随机化,可以极大程度的减少模型的过拟合。
1.1.4 支持向量机(SVM)模型
支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)[16]基于结构化风险最小化原理,通过核函数将输入向量从低维空间映射到高维空间,从而在高维空间中寻找最优超平面。其映射关系如式(2)。
$$ f(x) = \left[ {{\boldsymbol{\omega}} \cdot \varphi(x)} \right] + b $$ (2) 式中:
$ {\boldsymbol{\omega}} $ ——高维空间超平面的特征向量;$ \varphi $ ——低维空间到高维空间变换的映射函数;$ b $ ——阈值。1.2 易损性综合评价模型
易损性由承灾体脆弱性和致灾体灾害强度构成,以斜坡单元为评价对象的易损性计算公式一般表达为式(3)[1, 17],参照“地质灾害风险定性综合评估方法”[18 − 19]进行易损性计算(表1)。
表 1 斜坡单元易损性综合评价Table 1. Comprehensive evaluation of the vulnerability of slope units易损性等级 脆弱性等级 低脆弱性 中脆弱性 高脆弱性 灾害强度
等级弱灾害强度 低 中 中 中灾害强度 低 中 高 强灾害强度 中 高 高 $$ {V}_{i}=f\left({I}_{i},{S}_{i}\right) $$ (3) 式中:
$ {V}_{i} $ ——第$ i $ 个斜坡单元易损性值;$ {I}_{i} $ ——第$ i $ 个斜坡单元灾害强度;$ {S}_{i} $ ——第$ i $ 个斜坡单元脆弱性值。斜坡单元脆弱性
$ {S}_{i} $ 采用综合指数模型计算[20 − 21],如式(4):$$ {S_i} = \sum_{k = 1}^n {{p_{ik}} \cdot {w_k}} $$ (4) 式中:
$ i $ ——评价单元;$ {S}_{i} $ ——第$ i $ 个评价单元脆弱性值;$ k $ ——脆弱性评价指标;$ {p}_{ik} $ ——第$ i $ 个评价单元第$ k $ 个脆弱性评价指标归一化值;$ {w}_{k} $ ——第$ k $ 个脆弱性评价指标权重。斜坡单元灾害强度
$ {I}_{i} $ 以潜在滑坡体积作为评价指标。斜坡潜在滑坡体积则根据已发灾滑坡数据,通过精度比选确定的数理模型预测获得。每个斜坡单元的
$ {S}_{i} $ 及$ {I}_{i} $ 确定后,按照自然断点法将其划分为3个区间,从高到低依次定义为高(强)、中、低(弱),代入表1后确定出每个斜坡单元的易损性等级。2. 研究区概况
湖南省湘乡市总面积1 967.4 km2,地处湘中丘陵向湘江河谷平原的过渡带,西、南部地势较高,东部及东北部较宽缓低平,海拔37.2~807 m。境内出露元古代至新生代地层和多期次的岩浆岩,主要地层为:新元古界板溪群、南华系及震旦系;下古生界寒武系;上古生界泥盆系、石炭系、二叠系;中生界三叠系、白垩系;新生界古近系、新近系和第四系。区域构造可分为东西向构造、北东向构造、弧形构造和北西向构造,以北东向构造为主。境内水系主要由涟水、沩水和靳水组成,受亚热带季风湿润气候影响,四季分明,雨量充沛,年平均降雨量1387.4 mm,降雨主要集中在春夏两季,占年总降雨量的69%。湘乡市地质灾害点超过300处,主要为滑坡灾害,共计163处,以小型滑坡灾害为主,占研究区滑坡总数的97.8%;滑体厚度一般2~6 m,主要为浅层滑坡灾害(占97.2%);滑坡运动形式以牵引式滑坡为主(占75.8%)。研究区滑坡最大体积为160000 m³,最小体积约为1000 m3。受灾害威胁人口约2500人,潜在经济损失接近18亿元,为地质灾害影响较大的县区之一,基础数据来源如表2所示。
表 2 研究区基础数据Table 2. Basic data of the study area名称 类型 精度 遥感影像 栅格 0.5 m DEM 栅格 1∶10 000 工程地质图、土地利用类型图 矢量 1∶50 000 断层图、路网图 矢量 1∶50 000 行政区划图 矢量 1∶10 000 降雨数据 数据表 − 历史灾害点 数据表 − GDP 数据表 湘乡市 人口、建筑面积、道路、财产 数据表 斜坡单元 斜坡单元面积 数据表 斜坡单元 3. 灾害强度
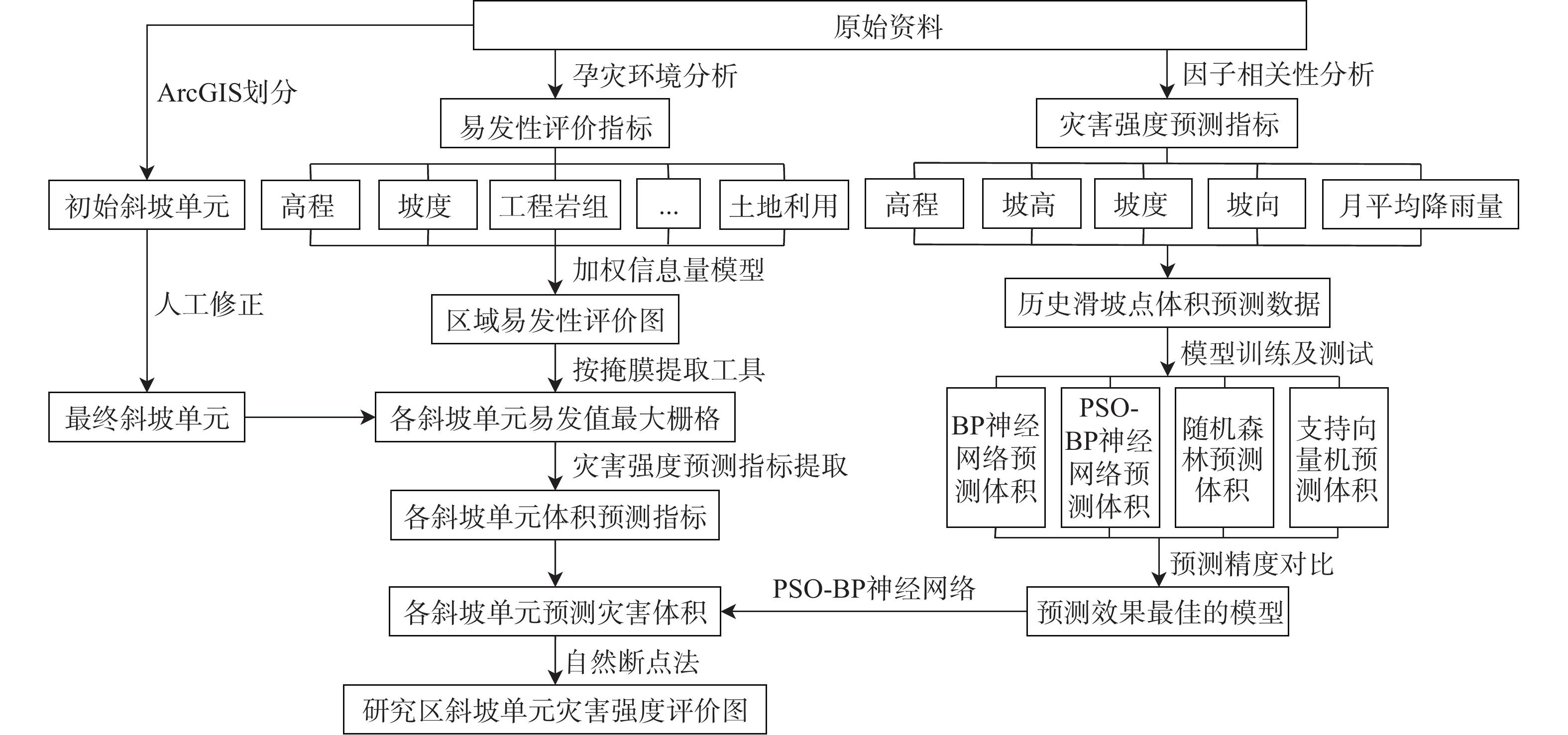
斜坡单元灾害强度
$ {I}_{i} $ 以潜在滑坡体积作为评价指标,具体计算过程见图1。①在提取高程、坡度、工程地质岩组、土地利用、距断层距离等主要致灾因子信息的基础上,以10 m×10 m栅格单元为评价对象进行易发性区划;②以分水岭、山脊线等为边界,结合滑坡灾害发育特征,基于“以人找坡,以房定坡”的原则划分斜坡单元[22];③以斜坡单元内易发性值最高栅格点(即最易发生地质灾害点)作为体积评估特征点,提取该点高程、坡高、坡度、坡向、月平均降雨量;④在采用BP神经网络、PSO-BP神经网络、随机森林及支持向量机模型进行预测精度对比的基础上,选取斜坡潜在灾害体最佳预测体积并将之作为灾害强度指标。3.1 易发性评价指标提取
地质灾害诱因主要分为孕灾环境因子和诱发因子[23 − 24]。孕灾因子选取:高程、坡度、坡向、工程地质岩组、距断层距离;诱发因子选取:距道路距离、土地利用情况、月平均降雨量,共8个评价指标。高程、坡度和坡向信息由比例尺1∶10000的DEM提取;距断层距离和距道路距离数据由比例尺1∶50000的断层图及路网图采用多环缓冲区功能划分获取;工程地质岩组及土地利用类型数据由比例尺1∶50000的工程地质图和土地利用类型图中提取;月平均降雨量数据由研究区气象站2010—2019年降雨数据,根据站点位置利用反距离插值法得到。
3.2 研究区易发性评价
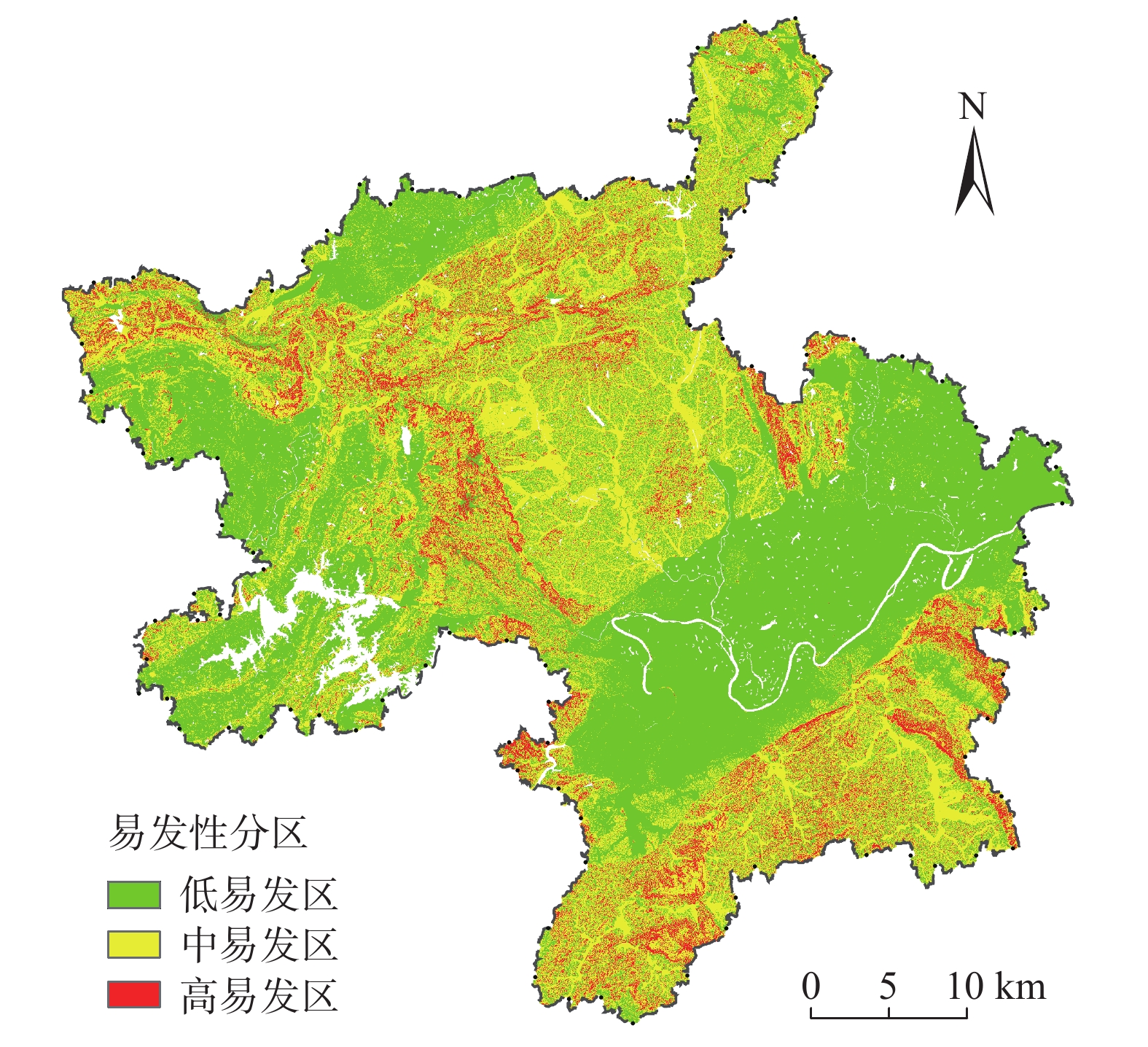
将研究区划分为19632859个栅格单元,并基于自然断点法划分二级指标区间(表3),生成各指标因子栅格图,采用距离函数结合层次分析法与熵权法进行主客观组合赋权,在各一级指标组合权重赋权的基础上得到对应各二级指标区间加权信息量值;基于加权信息量模型,利用ArcGIS软件重分类工具及栅格计算器进行因子图层叠加,并将计算得到的总信息量值利用自然断点法划分为高、中、低易发3个区间,进而得到研究区易发性评价图(图2),统计各易发性等级分区情况如表4所示。
表 3 易发性评价指标分区结果Table 3. Partition results of the susceptibility evaluation indicators评价指标 二级指标区间 高程/m 32~101;101~171;171~267;267~409;>409 坡度/(°) 0~6;6~17;17~28;28~40;>40 坡向 平面;北;东北;东;东南;南;西南;西;西北 工程地质岩组 硅质岩、硅质板岩;浅变质砂岩夹板岩;板岩;砂岩、砂砾岩;碳酸盐岩与碎屑岩互层;碳酸盐岩;岩浆岩;土体;红色碎屑岩;砂岩、页岩;硅质岩、硅质页岩 距断层距离/m <100;100~200;200~300;300~400;>400 距道路距离/m <100;100~200;200~300;300~400;>400 土地利用情况 耕地;林地;草地;水域;城乡、工矿居民用地;未利用土地类型 月平均降雨量/mm <100;100~150;150~200;>200 表 4 湘乡市地质灾害易发性分区结果Table 4. Results of geological hazard susceptibility zoning in the city of Xiangxiang易发性分区 面积比例/% 灾害点数量/个 灾害点比例/% 灾积比 高易发 8.2 216 71.3 1.430 中易发 39.3 75 24.8 0.100 低易发 52.5 12 3.9 0.012 根据易发性评价结果,研究区高易发区灾积比1.43,远超过低易发区灾积比0.012。此外,高易发区面积占研究区总面积的8.2%,但灾害点数量占了研究区所有发灾数量的71.3%。以上说明评价结果较合理。
3.3 灾害强度预测指标选取
研究区内共划分斜坡单元4 734个,结合前人研究基础[25]及研究区地质环境条件和历史灾害特征,采用SPSS软件基于Pearson相关系数法对研究区历史滑坡灾害数据及各滑坡体积进行分析[26 − 27]。当Pearson相关系数r绝对值小于0.1时,两因子无相关性;大于0.1且小于0.3时,两因子呈现弱相关性;但大于0.3时表示两因子存在中或强相关性。基于此,选出因子间相关性较小而与滑坡体积相关性较大(即对斜坡灾害体积影响较大)的指标参数进行斜坡单元灾害体积预测。根据因子相关性分析结果(表5),其中工程地质岩组、距断层距离、距道路距离、土地利用情况4个因子均存在与其他因子相关性较大的情况,且该4个因子与滑坡体积相关性较小,因此对其进行剔除,最终选取对灾害体积影响较大的斜坡高程、坡高、坡度、坡向、月平均降雨量5个指标作为灾害强度预测指标进行体积预测。
表 5 指标因子相关性分析Table 5. Correlation of the controlling factors指标因子 高程 坡高 坡度 坡向 工程地质岩组 距断层距离 距道路距离 土地利用情况 月平均降雨量 滑坡体积 高程 1 0.057 −0.055 −0.036 −0.169 −0.358 0.328 0.103 0.013 0.239 坡高 1 0.042 −0.028 −0.310 −0.260 −0.199 0.168 0.034 0.333 坡度 1 −0.027 −0.428 −0.104 0.245 0.051 −0.133 −0.205 坡向 1 0.003 0.007 −0.066 −0.493 −0.123 0.196 工程地质岩组 1 0.070 0.208 −0.024 0.043 0.003 距断层距离 1 −0.211 −0.102 0.207 −0.026 距道路距离 1 0.284 0.022 0.060 土地利用情况 1 −0.047 −0.102 月平均降雨量 1 −0.313 滑坡体积 1 3.4 灾害强度预测模型比选
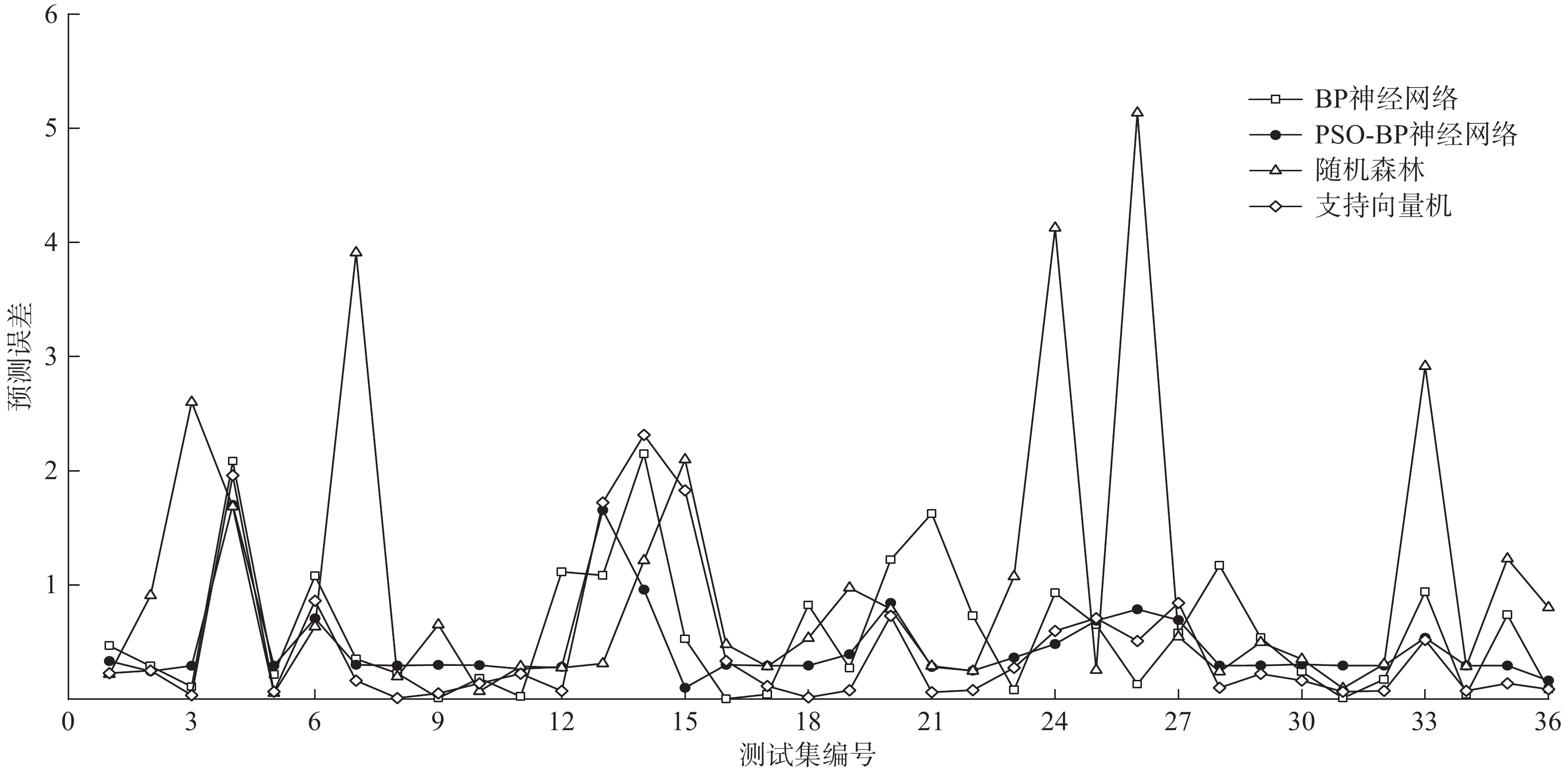
随机抽取区内127个(占比80%)滑坡历史灾害点作为训练集样本,余下36个(占比20%)灾害点作为测试集样本。将提取的灾害点高程、坡高、坡度、坡向、月平均降雨量以及滑坡体积等数据分别代入BP神经网络、PSO-BP神经网络、随机森林及支持向量机模型训练与测试。在统计各模型测试集样本预测值与真实值之间的差值,得到各样本预测误差大小的基础上,绘制各模型预测误差统计曲线如图3所示,各模型测试集预测精度(预测正确样本量/总样本量)结果如表6所示。由图3及表6可知,BP神经网络、PSO-BP神经网络、随机森林、支持向量机模型预测精度分别为58.33%、80.56%、50.00%、69.44%,以PSO-BP神经网络模型预测精度最高且整体误差最小,较BP神经网络、随机森林和支持向量机模型分别提升了22.23%、30.56%和11.12%。因此,选取PSO-BP神经网络模型作为灾害强度预测计算模型。
表 6 各模型预测结果精度对比Table 6. Comparison of prediction accuracy of each model测试集结果 预测正确样本量/个 预测错误样本量/个 预测精度/% BP神经网络 21 15 58.33 PSO-BP神经网络 29 7 80.56 随机森林 18 18 50.00 支持向量机 25 11 69.44 3.5 灾害强度评价
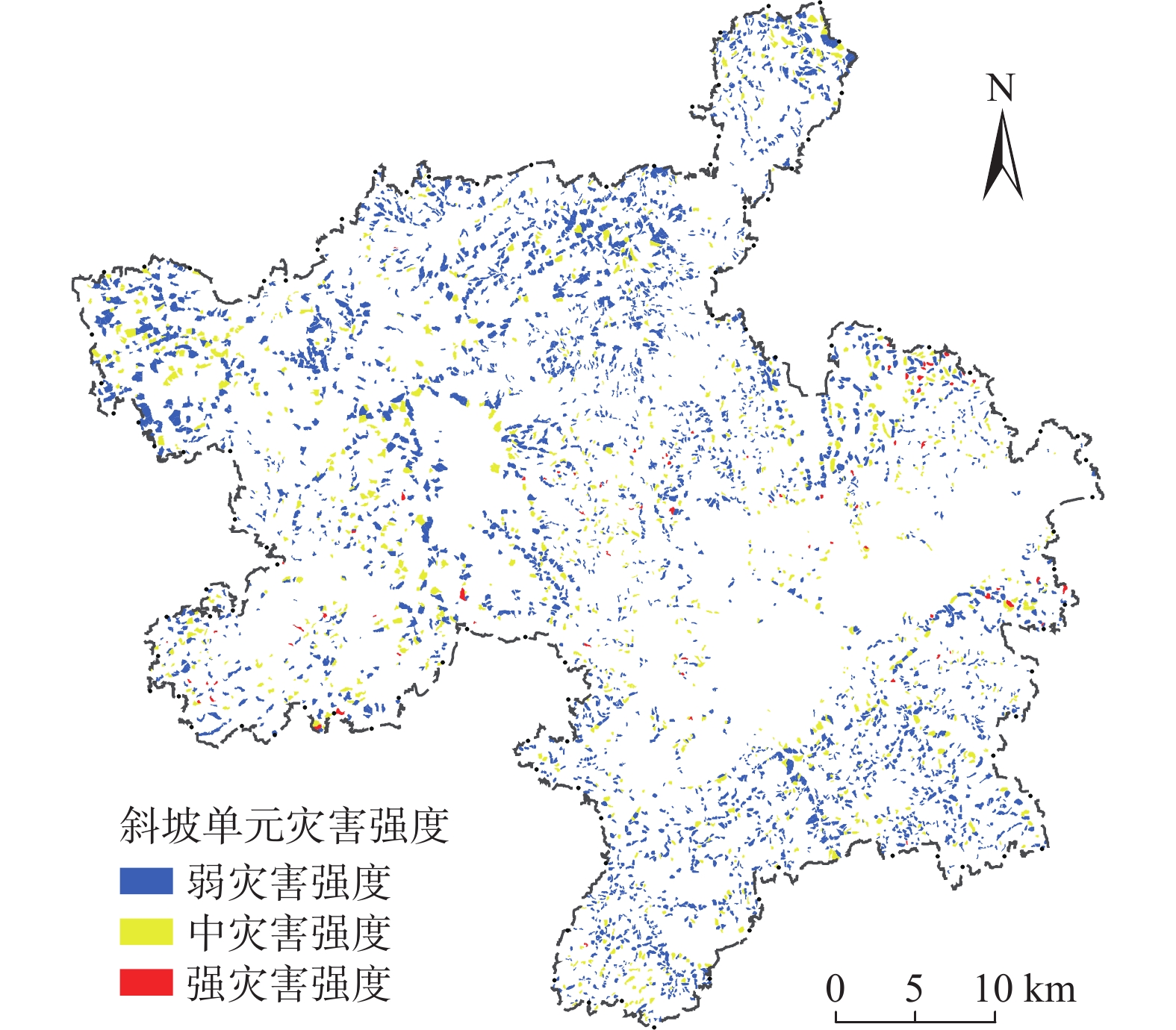
以易发性评价结果为基础,选取一个斜坡单元利用ArcGIS软件按掩膜提取工具提取其范围内的所有栅格,查找属性表中信息量值最大的栅格点作为该单元体积预测的特征点,通过叠加高程、坡度、坡向和月平均降雨量因子图层,识别特征点对应指标数据,并计算该点高程值与该斜坡单元坡脚最低高程值之差得到坡高指标。根据以上步骤逐一提取出所有斜坡单元的指标数据,采用训练好的PSO-BP神经网络模型预测研究区斜坡单元灾害体积。利用自然断点法将斜坡单元灾害体积划分为强、中、弱灾害强度3个等级(表7),评价得到研究区斜坡单元灾害强度分布情况如图4所示。
表 7 斜坡单元灾害强度等级分区结果Table 7. Results of disaster intensity classification of slope units预测体积分区/m³ 灾害强度等级 <15 000 弱灾害强度 15 000~45 000 中灾害强度 >45 000 强灾害强度 根据研究区斜坡单元灾害强度预测结果统计,弱灾害强度等级共有3 592个斜坡单元,占总数的75.9%;中灾害强度等级共有1 067个斜坡单元,占总数22.5%;强灾害强度等级共有75个斜坡单元,占总数1.6%,整体以弱、中灾害强度等级为主,与历史灾害体积特征相符合,说明该模型能较好地预测斜坡潜在灾害体体积。
4. 易损性评价
4.1 脆弱性评价
在分析研究区历史灾害点和承灾体分布特征的基础上[28 − 29],从物质、社会和经济3个方面选取建筑密度、道路密度、人口密度、财产密度和GDP密度5个指标构建承灾体脆弱性评价指标体系。根据各斜坡单元野外调查数据计算与其面积之比得到各密度指标值,各斜坡单元GDP数据由湘乡市总GDP按式(5)及式(6)计算得出。
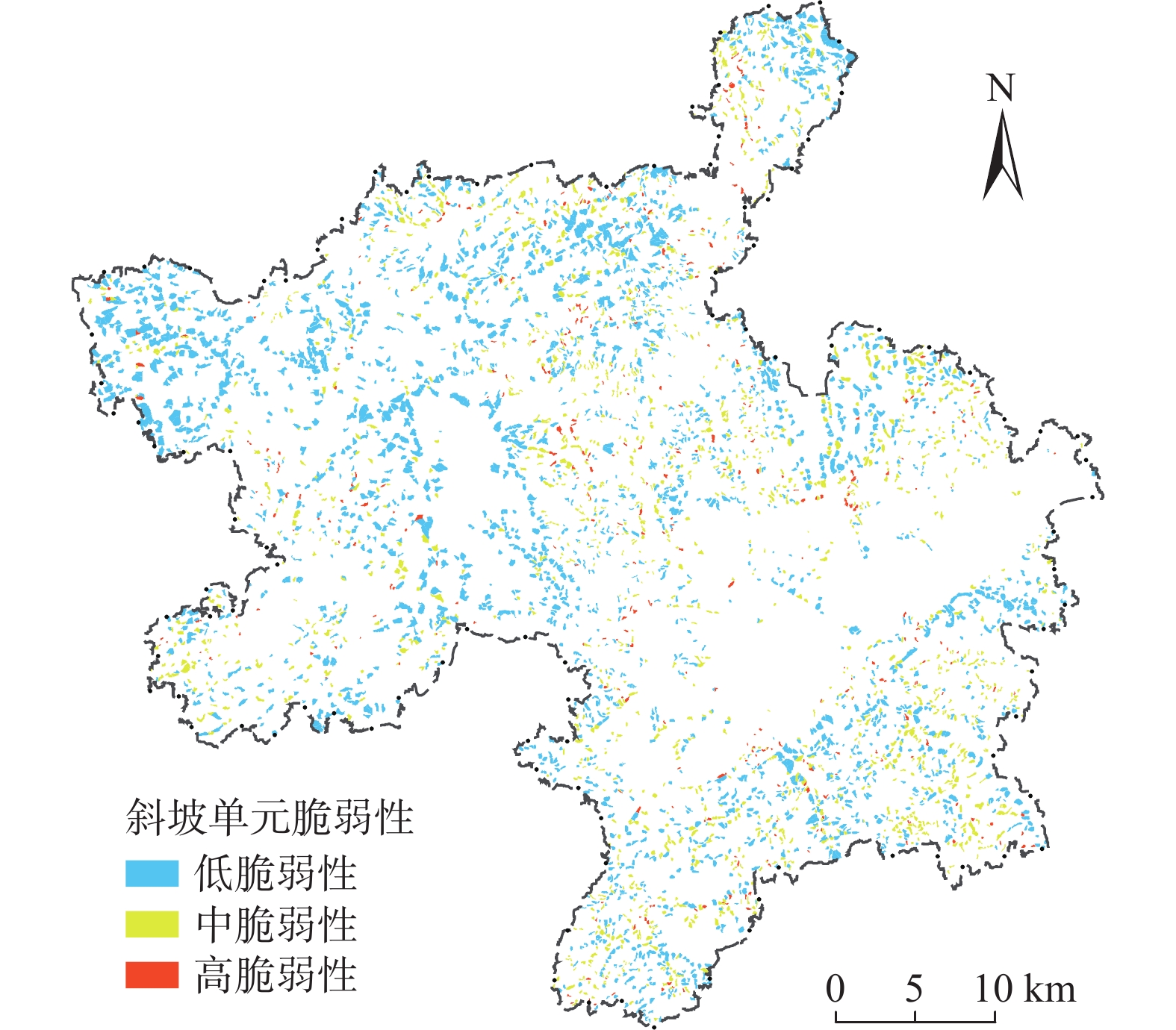
$$ \begin{split} \text{斜坡单元}{\rm{GDP}}&=\text{(乡镇总}{\rm{GDP}}/\text{乡镇总人口)}\\ &\times\text{各斜坡单元总人口} \end{split} $$ (5) $$ \begin{split} \text{乡镇总}{\rm{GDP}}&=\text{湘乡市总}{\rm{GDP}}\\ &\times\text{各乡镇面积所占总面积百分比} \end{split} $$ (6) 将建筑密度、道路密度、人口密度、财产密度、GDP密度等5个脆弱性评价指标数据进行归一化处理,运用距离函数结合层次分析法和熵权法计算出各脆弱性评价指标的组合权重值,计算结果见表8。按照式(4)综合指数模型将所有归一化指标数据与对应评价指标组合权重值相乘再叠加,得到研究区各斜坡单元的脆弱性值。按自然断点法将斜坡单元总脆弱性值划分为低、中、高脆弱性3个等级(表9),得到研究区斜坡单元脆弱性评价结果如图5所示。
表 8 脆弱性评价指标组合权重结果Table 8. Combined weight results of vulnerability assessment indicators评价因子 权重值 人口密度 0.3072 建筑密度 0.2160 道路密度 0.2141 GDP密度 0.1607 财产密度 0.1026 表 9 斜坡单元脆弱性等级分区结果Table 9. Results of vulnerability classification of slope units脆弱性值分区 脆弱性等级 <0.0845 低脆弱性 0.0845 ~ 0.1750 中脆弱性 >0.1750 高脆弱性 4.2 易损性综合评价
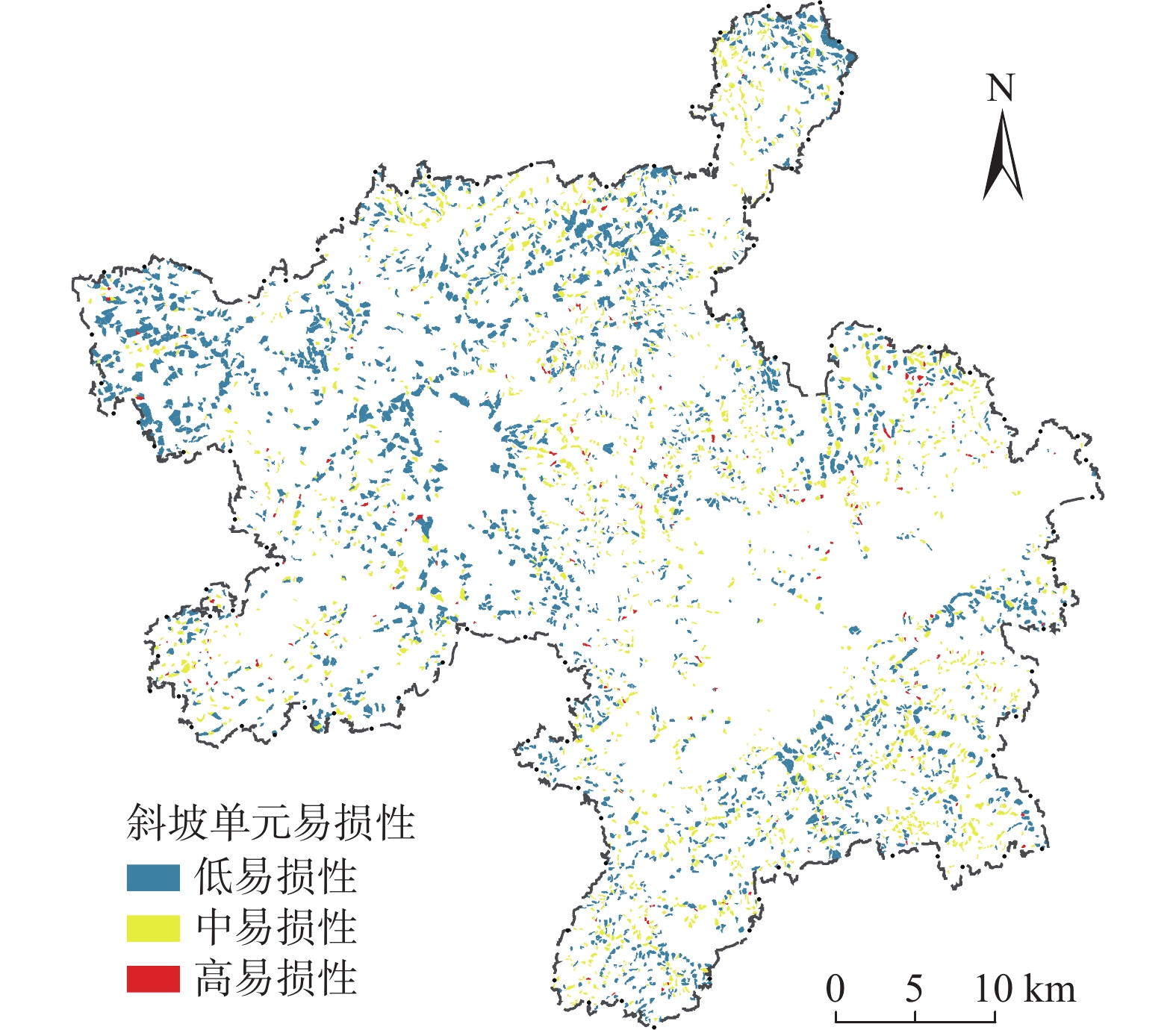
将斜坡单元灾害强度预测值与承灾体脆弱性值按照表7及表9分级评价结果分别代入表1,并对每个斜坡单元逐个进行易损性评价(图6、表10)。
表 10 斜坡单元易损性统计结果Table 10. Statistical results of slope unit vulnerability易损性分区 斜坡单元数量/个 斜坡单元数量占比/% 高易损区 124 2.6 中易损区 2 023 42.7 低易损区 2 587 54.7 由评价结果可知,研究区以中、低易损性为主。高易损性斜坡单元124个,总面积为3.46 km²,主要分布在湘乡市中部和东部地区,占总斜坡单元面积的1.5%;中易损性斜坡单元2 023个,总面积为64.5 km²,占总斜坡单元面积的28.5%;低易损性斜坡单元2 587个,总面积为158.2 km²,占总斜坡单元面积的70%。
5. 总结
(1)在采用加权信息量模型评价研究区易发性的基础上,将提取的各斜坡单元易发值最高点高程、坡高、坡度、坡向、月平均降雨量分别代入BP神经网络、PSO-BP神经网络、随机森林及支持向量机模型,并通过训练与精度测试建立了以PSO优化BP神经网络模型的滑坡体积预测模型,预测精度达到80.56%。
(2)构建了以灾害体积为灾害强度指标,以建筑密度、道路密度等为脆弱性指标的易损性评价指标体系,参照“地质灾害风险定性综合评估方法”对研究区进行了以斜坡为单元,基于潜在灾害强度的区域性易损性评价,实现了致灾体评价和承灾体评价的有机结合,提高了评价全面性。
(3)湘乡市以中、低易损性为主,高易损区占1.5%,主要分布在中部及东部地区,中易损区和低易损区分别占比28.5%与70%,评价结果可为湘乡市灾害防治提供参考。
-
表 1 斜坡单元易损性综合评价
Table 1 Comprehensive evaluation of the vulnerability of slope units
易损性等级 脆弱性等级 低脆弱性 中脆弱性 高脆弱性 灾害强度
等级弱灾害强度 低 中 中 中灾害强度 低 中 高 强灾害强度 中 高 高 表 2 研究区基础数据
Table 2 Basic data of the study area
名称 类型 精度 遥感影像 栅格 0.5 m DEM 栅格 1∶10 000 工程地质图、土地利用类型图 矢量 1∶50 000 断层图、路网图 矢量 1∶50 000 行政区划图 矢量 1∶10 000 降雨数据 数据表 − 历史灾害点 数据表 − GDP 数据表 湘乡市 人口、建筑面积、道路、财产 数据表 斜坡单元 斜坡单元面积 数据表 斜坡单元 表 3 易发性评价指标分区结果
Table 3 Partition results of the susceptibility evaluation indicators
评价指标 二级指标区间 高程/m 32~101;101~171;171~267;267~409;>409 坡度/(°) 0~6;6~17;17~28;28~40;>40 坡向 平面;北;东北;东;东南;南;西南;西;西北 工程地质岩组 硅质岩、硅质板岩;浅变质砂岩夹板岩;板岩;砂岩、砂砾岩;碳酸盐岩与碎屑岩互层;碳酸盐岩;岩浆岩;土体;红色碎屑岩;砂岩、页岩;硅质岩、硅质页岩 距断层距离/m <100;100~200;200~300;300~400;>400 距道路距离/m <100;100~200;200~300;300~400;>400 土地利用情况 耕地;林地;草地;水域;城乡、工矿居民用地;未利用土地类型 月平均降雨量/mm <100;100~150;150~200;>200 表 4 湘乡市地质灾害易发性分区结果
Table 4 Results of geological hazard susceptibility zoning in the city of Xiangxiang
易发性分区 面积比例/% 灾害点数量/个 灾害点比例/% 灾积比 高易发 8.2 216 71.3 1.430 中易发 39.3 75 24.8 0.100 低易发 52.5 12 3.9 0.012 表 5 指标因子相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation of the controlling factors
指标因子 高程 坡高 坡度 坡向 工程地质岩组 距断层距离 距道路距离 土地利用情况 月平均降雨量 滑坡体积 高程 1 0.057 −0.055 −0.036 −0.169 −0.358 0.328 0.103 0.013 0.239 坡高 1 0.042 −0.028 −0.310 −0.260 −0.199 0.168 0.034 0.333 坡度 1 −0.027 −0.428 −0.104 0.245 0.051 −0.133 −0.205 坡向 1 0.003 0.007 −0.066 −0.493 −0.123 0.196 工程地质岩组 1 0.070 0.208 −0.024 0.043 0.003 距断层距离 1 −0.211 −0.102 0.207 −0.026 距道路距离 1 0.284 0.022 0.060 土地利用情况 1 −0.047 −0.102 月平均降雨量 1 −0.313 滑坡体积 1 表 6 各模型预测结果精度对比
Table 6 Comparison of prediction accuracy of each model
测试集结果 预测正确样本量/个 预测错误样本量/个 预测精度/% BP神经网络 21 15 58.33 PSO-BP神经网络 29 7 80.56 随机森林 18 18 50.00 支持向量机 25 11 69.44 表 7 斜坡单元灾害强度等级分区结果
Table 7 Results of disaster intensity classification of slope units
预测体积分区/m³ 灾害强度等级 <15 000 弱灾害强度 15 000~45 000 中灾害强度 >45 000 强灾害强度 表 8 脆弱性评价指标组合权重结果
Table 8 Combined weight results of vulnerability assessment indicators
评价因子 权重值 人口密度 0.3072 建筑密度 0.2160 道路密度 0.2141 GDP密度 0.1607 财产密度 0.1026 表 9 斜坡单元脆弱性等级分区结果
Table 9 Results of vulnerability classification of slope units
脆弱性值分区 脆弱性等级 <0.0845 低脆弱性 0.0845 ~ 0.1750 中脆弱性 >0.1750 高脆弱性 表 10 斜坡单元易损性统计结果
Table 10 Statistical results of slope unit vulnerability
易损性分区 斜坡单元数量/个 斜坡单元数量占比/% 高易损区 124 2.6 中易损区 2 023 42.7 低易损区 2 587 54.7 -
[1] UZIELLI M,NADIM F,LACASSE S,et al. A conceptual framework for quantitative estimation of physical vulnerability to landslides[J]. Engineering Geology,2008,102(3/4):251 − 256.
[2] 许强,张一凡,陈伟. 西南山区城镇地质灾害易损性评价方法—以四川省丹巴县城为例[J]. 地质通报,2010,29(5):729 − 738. [XU Qiang,ZHANG Yifan,CHEN Wei. Vulnerability assessment of geo-hazards in southwest mountainous area:Danba County,Sichuan,China as an example[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2010,29(5):729 − 738. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.05.013 XU Qiang, ZHANG Yifan, CHEN Wei. Vulnerability assessment of geo-hazards in southwest mountainous area: Danba County, Sichuan, China as an example[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(5): 729-738. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.05.013
[3] REYES-HARDY M P,AGUILERA BARRAZA F,SEPÚLVEDA BIRKE J P,et al. GIS-based volcanic hazards,vulnerability and risks assessment of the Guallatiri Volcano,Arica y Parinacota Region,Chile[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences,2021,109:103262. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsames.2021.103262
[4] GUZZETTI F,ARDIZZONE F,CARDINALI M,et al. Landslide volumes and landslide mobilization rates in Umbria,central Italy[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2009,279(3/4):222 − 229.
[5] GLADE T, ANDERSON M, CROZIER M J. Landslide hazard and risk [M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2005: 41-74.
[6] 彭令,牛瑞卿,赵艳南,等. 区域滑坡灾害风险评估—以长江三峡库区秭归县为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2013,43(3):891 − 901. [PENG Ling,NIU Ruiqing,ZHAO Yannan,et al. Risk assessment of a regional landslide:A case of Zigui County territory in Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2013,43(3):891 − 901. (in Chinese with English abstract) PENG Ling, NIU Ruiqing, ZHAO Yannan, et al. Risk assessment of a regional landslide: A case of Zigui County territory in Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2013, 43(3): 891-901. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] KAYNIA A M,PAPATHOMA-KÖHLE M,NEUHÄUSER B,et al. Probabilistic assessment of vulnerability to landslide:application to the village of Lichtenstein,Baden-Württemberg,Germany[J]. Engineering Geology,2008,101(1/2):33 − 48.
[8] 薛强,张茂省,高波,等. 陕西省绥德县城区地质灾害风险评估[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(3):711 − 719. [XUE Qiang,ZHANG Maosheng,GAO Bo,et al. Risk assessment of geological hazards in Suide City,Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(3):711 − 719. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017-205 XUE Qiang, ZHANG Maosheng, GAO Bo, et al. Risk assessment of geological hazards in Suide city, Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(3): 711-719. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017-205
[9] 张以晨,秦胜伍,翟健健,等. 基于信息量的长白山地区泥石流易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(2):150 − 158. [ZHANG Yichen,QIN Shengwu,ZHAI Jianjian,et al. Susceptibility assessment of debris flow based on GIS and weight information for the Changbai Mountain area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(2):150 − 158. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2018.02.23 ZHANG Yichen, QIN Shengwu, ZHAI Jianjian, et al. Susceptibility assessment of debris flow based on GIS and weight information for the Changbai Mountain area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(2): 150-158. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2018.02.23
[10] 田春山,刘希林,汪佳. 基于CF和Logistic回归模型的广东省地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(6):154 − 161. [TIAN Chunshan,LIU Xilin,WANG Jia. Geohazard susceptibility assessment based on CF model and Logistic Regression models in Guangdong[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(6):154 − 161. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2016.06.24 TIAN Chunshan, LIU Xilin, WANG Jia. Geohazard susceptibility assessment based on CF model and Logistic Regression models in Guangdong[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(6): 154-161. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2016.06.24
[11] 陈飞, 蔡超, 李小双, 等. 基于信息量与神经网络模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(增刊1): 2859 − 2870 CHEN Fei, CAI Chao, LI Xiaoshuang, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on information volume and neural network model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(Sup 1): 2859 − 2870. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 李骅锦,许强,何雨森,等. 甘肃黑方台滑坡滑距参数的BP神经网络模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):141 − 146. [LI Huajin,XU Qiang,HE Yusen,et al. BP neural network model for analyzing the impact factors of the travel distance of the Heifangtai landslide in Gansu[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):141 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2016.04.23 LI Huajin, XU Qiang, HE Yusen, et al. BP neural network model for analyzing the impact factors of the travel distance of the Heifangtai landslide in Gansu[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(4): 141-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2016.04.23
[13] 王念秦,朱文博,郭有金. 基于PSO-SVM模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 长江科学院院报,2021,38(4):56 − 62. [WANG Nianqin,ZHU Wenbo,GUO Youjin. Assessment of landslide susceptibility based on PSO-SVM model[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2021,38(4):56 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200074 WANG Nianqin, ZHU Wenbo, GUO Youjin. Assessment of landslide susceptibility based on PSO-SVM model[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2021, 38(4): 56-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200074
[14] 吴迪. 基于PSO-SVM的凤县公路边坡地质灾害空间预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(6):112 − 120. [WU Di. Spatial prediction of highway slope geo-hazards in Feng County based on PSO-SVM[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(6):112 − 120. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Di. Spatial prediction of highway slope geo-hazards in Feng County based on PSO-SVM[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(6): 112-120. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 何书,鲜木斯艳·阿布迪克依木,胡萌,等. 基于自组织特征映射网络-随机森林模型的滑坡易发性评价—以江西大余县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):132 − 140. [HE Shu,ABUDIKEYIMU XMSY,HU Meng,et al. Evaluation on landslide susceptibility based on self-organizing feature map network and random forest model:A case study of Dayu County of Jiangxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE Shu, ABUDIKEYIMU XMSY, HU Meng, et al. Evaluation on landslide susceptibility based on self-organizing feature map network and random forest model: A case study of Dayu County of Jiangxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(1): 132-140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 夏辉,殷坤龙,梁鑫,等. 基于SVM-ANN模型的滑坡易发性评价—以三峡库区巫山县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):13 − 19. [XIA Hui,YIN Kunlong,LIANG Xin,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on SVM-ANN Models:A case stualy for Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):13 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2018.05.03 XIA Hui, YIN Kunlong, LIANG Xin, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on SVM-ANN Models: a case stualy for Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(5): 13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2018.05.03
[17] LI Zhihong,NADIM F,HUANG Hongwei,et al. Quantitative vulnerability estimation for scenario-based landslide hazards[J]. Landslides,2010,7(2):125 − 134. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-009-0190-3
[18] 李春燕,孟晖,张若琳,等. 中国县域单元地质灾害风险评估[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):160 − 166. [LI Chunyan,MENG Hui,ZHANG Ruolin,et al. Risk assessment of geo-hazard of China in County unit[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):160 − 166. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2017.02.24 LI Chunyan, MENG Hui, ZHANG Ruolin, et al. Risk assessment of geo-hazard of China in County unit[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(2): 160-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2017.02.24
[19] 李春燕,孟晖,张若琳,等. 基于承灾体易损性的县域单元地质灾害风险评估[J]. 地质通报,2021,40(9):1547 − 1559. [LI Chunyan,MENG Hui,ZHANG Ruolin,et al. Geological hazard risk assessment based on vulnerability of disaster-bearing body at County unite scale[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2021,40(9):1547 − 1559. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.09.014 LI Chunyan, MENG Hui, ZHANG Ruolin, et al. Geological hazard risk assessment based on vulnerability of disaster-bearing body at County unite scale[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(9): 1547-1559. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.09.014
[20] 陈东景,李培英,刘乐军,等. 我国沿海城市海底地质灾害易损性评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2010,20(11):11 − 17. [CHEN Dongjing,LI Peiying,LIU Lejun,et al. Evaluation on submarine geological hazard vulnerability of coastal cities in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2010,20(11):11 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2010.11.002 CHEN Dongjing, LI Peiying, LIU Lejun, et al. Evaluation on submarine geological hazard vulnerability of coastal cities in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2010, 20(11): 11-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2010.11.002
[21] 罗路广,裴向军,谷虎,等. 基于GIS的“8 • 8”九寨沟地震景区地质灾害风险评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2020,29(3):193 − 202. [LUO Luguang,PEI Xiangjun,GU Hu,et al. Risk assessment of geohazards induced by “8·8” earthquake based on GIS in Jiuzhaigou scenic area[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2020,29(3):193 − 202. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13577/j.jnd.2020.0321 LUO Luguang, PEI Xiangjun, GU Hu, et al. Risk assessment of geohazards induced by “8.8” earthquake based on GIS in Jiuzhaigou scenic area[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2020, 29(3): 193-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13577/j.jnd.2020.0321
[22] 邹凤钗,冷洋洋,陶小郎,等. 基于斜坡单元的滑坡风险识别—以贵州万山浅层土质斜坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):114 − 122. [ZOU Fengchai,LENG Yangyang,TAO Xiaolang,et al. Landslide hazard identification based on slope unit:A case study of shallow soil slope in Wanshan,Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):114 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZOU Fengchai, LENG Yangyang, TAO Xiaolang, et al. Landslide hazard identification based on slope unit: a case study of shallow soil slope in Wanshan, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3): 114-122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 杜国梁,杨志华,袁颖,等. 基于逻辑回归-信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang,YANG Zhihua,YUAN Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 102-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 张俊,殷坤龙,王佳佳,等. 三峡库区万州区滑坡灾害易发性评价研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(2):284 − 296. [ZHANG Jun,YIN Kunlong,WANG Jiajia,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou District of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(2):284 − 296. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.0318 ZHANG Jun, YIN Kunlong, WANG Jiajia, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou district of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(2): 284-296. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.0318
[25] 张群,许强,吴礼舟,等. 南江滑坡群体积的BP神经网络模型与预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(1):134 − 139. [ZHANG Qun,XU Qiang,WU Lizhou,et al. BP neural network model for forecasting volume of landslide group in Nanjiang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(1):134 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2015.01.23 ZHANG Qun, XU Qiang, WU Lizhou, et al. BP neural network model for forecasting volume of landslide group in Nanjiang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(1): 134-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2015.01.23
[26] 屠水云,张钟远,付弘流,等. 基于CF与CF-LR模型的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):96 − 104. [TU Shuiyun,ZHANG Zhongyuan,FU Hongliu,et al. Geological hazard susceptibility evaluation based on CF and CF-LR model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):96 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract) TU Shuiyun, ZHANG Zhongyuan, FU Hongliu, et al. Geological hazard susceptibility evaluation based on CF and CF-LR model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 96-104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 闫举生,谭建民. 基于不同因子分级法的滑坡易发性评价—以湖北远安县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):52 − 60. [YAN Jusheng,TAN Jianmin. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on different factor classification methods:A case study in Yuan’an County of Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):52 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.01.06 YAN Jusheng, TAN Jianmin. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on different factor classification methods—a case study in Yuan'an County of Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(1): 52-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.01.06
[28] 唐波,刘希林,尚志海. 城市灾害易损性及其评价指标[J]. 灾害学,2012,27(4):6 − 11. [TANG Bo,LIU Xilin,SHANG Zhihai. Vulnerability of urban disasters and its evaluation index[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2012,27(4):6 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2012.04.002 TANG Bo, LIU Xilin, SHANG Zhihai. Vulnerability of urban disasters and its evaluation index[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2012, 27(4): 6-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2012.04.002
[29] 刘希林,莫多闻. 泥石流易损度评价[J]. 地理研究,2002,21(5):569 − 577. [LIU Xilin,MO Duowen. Site-specific debris flow vulnerability assessment[J]. Geographical Research,2002,21(5):569 − 577. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2002.05.005 LIU Xilin, MO Duowen. Site-specific debris flow vulnerability assessment[J]. Geographical Research, 2002, 21(5): 569-577. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2002.05.005














 下载:
下载:
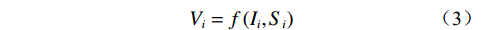
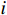
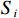
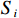
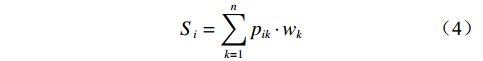
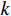
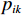
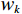
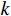
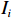
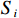
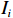
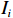

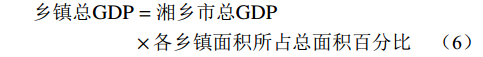
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS