Deformation characteristics and reactivation mechanism of Hongyanzi landslide in Pubugou reservoir area of the Dadu River
-
摘要: 库水涨落常诱发库岸滑坡变形破坏。为了研究库岸滑坡的变形特征及变形机理,以大渡河瀑布沟水电站红岩子滑坡为对象,通过详细的地表宏观变形调查和对监测数据的深入分析,结合GeoStudio数值模拟,深入研究了该滑坡的变形特征、渗流场、稳定性及库水对滑坡的作用机理。结果表明:红岩子滑坡地表宏观变形显著,累计位移曲线呈“阶跃”式特征,库水下降是滑坡变形的主要诱发因素;库水位由850 m高水位集中下降至830 m以下时,位移阶跃启动,“阶跃”段的累计变形量占全年总变形量的90%以上,当库水位下降速率大于0.5 m/d时,滑坡加速变形;滑坡变形模式为蠕滑-拉裂,库水升降导致滑体内部渗透力的变化,对滑坡稳定性影响很大,引发滑坡“阶跃”变形。Abstract: Reservoir water fluctuation can often trigger deformation and failure of reservoir bank landslides. This study focuses on the Hongyanzi landslide in the Pubugou hydropower Station of the Dadu River to investigate the deformation characteristics and deformation mechanisms of the reservoir bank landslides. Through detailed surface macro deformation surveys, monitoring data analysis, and GeoStudio numerical simulation, the deformation characteristics, seepage field, stability and the influence of reservoir water on landslide were studied in depth. The research revealed significant macro deformation of the Hongyanzi landslide surface, with a cumulative displacement curve exhibiting a “step-like” characteristic. The primary inducing factor of landslide deformation was found to be the decrease in the reservoir water level. When the reservoir water level dropped from 850 m to below 830 m, the displacement step was triggered, and the cumulative deformation of the “step” segment accounted for over 90% of the total annual deformation. Accelerated deformation of the landslide occurred when the rate of the reservoir water level decline was greater than 0.5 m/d. The landslide deformation mode was identified as creep slip-tensile cracking, with the rise and fall of the reservoir water level significantly impacting the internal permeability of the sliding body and causing a large impact on the landslide’s stability, leading to the “step-like” deformation of the landslide.
-
0. 引言
库岸滑坡是水利工程运行过程中诱发的一种地质灾害,常对当地居民生命财产安全造成重大威胁[1]。多年来,库水波动诱发滑坡的案例屡见不鲜[2-3]。1963年,瓦依昂水库蓄水3a后诱发右岸2亿多立方米的巨型滑坡,涌浪造成下游2000余人死亡[4-5];2003年7月13日,三峡水库初次蓄水即诱发千将坪滑坡的复活变形,造成长江支流堵江,24人死亡;青杠坪滑坡为溪洛渡库区于2014年复活的巨型古滑坡,灾害摧毁了147间房屋,直接经济损失达500万元,滑坡目前仍在变形中[6]。因此,研究库岸滑坡变形发展规律,揭示其变形破坏机制,具有重要意义。
近年来,国内外学者针对库岸滑坡变形特征、变形机制及稳定性做了大量研究,取得了一些进展。郑颖人等[7]提出了库水位下降时渗透力及地下水浸润线的计算方法。时卫民等[8]认为库水位下降时,影响库岸边坡稳定的因素有渗透系数、给水度、库水下降速度、含水层厚度和下降高度等。Zangerl等[9]、Paronuzzi等[10]认为滑坡渗透性、滑面形状及库水升降速度等因素都会对库岸古滑坡的稳定性造成影响。李松林等[11]对三峡库区不同滑面形态涉水老滑坡的变形特征、变形破坏模式及数量进行总结。朱赛楠等[12]研究了三峡库区巫山轿顶峰 2 号滑坡变形特征与失稳机理。黄达等[13]、代贞伟等[14]研究了三峡库区藕塘滑坡变形特点及复活机制。尚敏等[15]定量分析了白家包滑坡变形与库水位、降雨的相关性。邓茂林等[16-17]基于监测数据分析了库水与降雨作用下白家包、木鱼包滑坡的变形特征及机制。汤明高等[18]分析了石榴树包滑坡地下水位对库水位及降雨的响应规律,并建立了地下水位浸润线模型。裴小龙等[19]分析了雅砻江楞古水电站夏日滑坡发育特征及稳定性。卢书强等[20]研究了树坪滑坡的变形失稳机制。综上所述,目前的研究多为对库岸滑坡阶跃变形特征的定性研究,并基于变形监测数据与数值模拟分析库水位与降雨等因素对库岸滑坡的影响,很少对库岸滑坡阶跃变形特征展开精细化的定量研究及探讨阶跃变形特征的机理。
红岩子滑坡为瀑布沟水库2009年蓄水以来复活的一处大型古滑坡,自然资源部四川雅安地质灾害野外科学观测研究站正在运行的重要监测预警点,多年的监测数据表明,红岩子滑坡每年都会发生相当量的变形。韩冰[21]、祝斌[22]基于红岩子滑坡的地表、深部位移监测数据,分析了红岩子滑坡变形的影响因素、稳定性及变形预测,对该滑坡的变形特征及变形机制研究较少。本文基于野外调查工作及多年的位移监测数据,并结合数值模拟的方法,研究红岩子滑坡的变形特征,并揭示其变形机理,为红岩子滑坡的监测预警工作提供支持,为库岸滑坡的研究提供借鉴。
1. 滑坡区工程地质概况
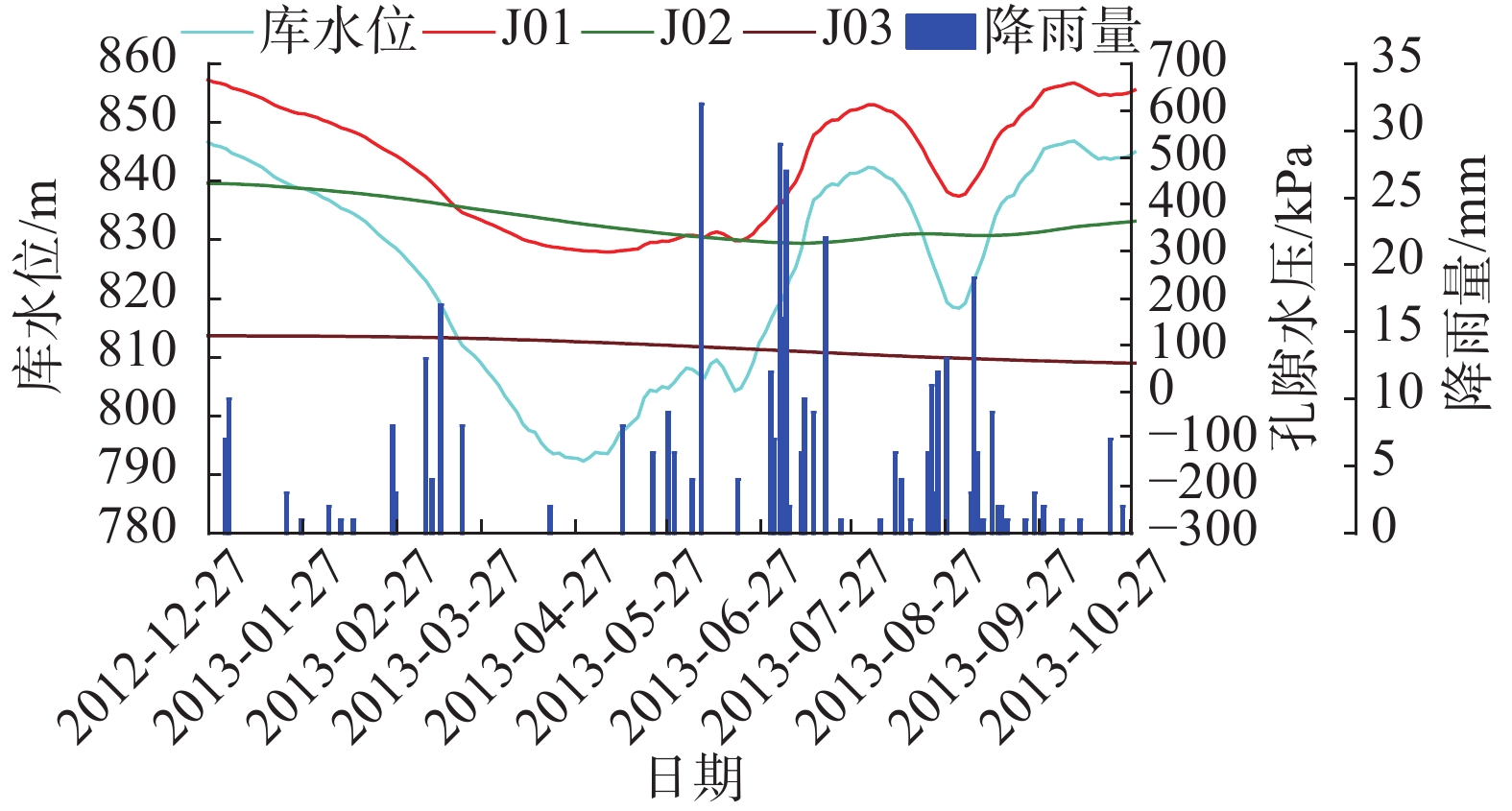
红岩子滑坡位于汉源县桂贤镇红岩子村,大渡河瀑布沟水库南岸,距瀑布沟大坝23 km。该区域年平均降雨743 mm, 6—9月份降雨量占全年的70%以上。滑坡处于库水消落带上,滑坡的变形受库水位变化的影响,自2009年11月起,瀑布沟水库每年库水位基本是先下降至790 m再回升至850 m。
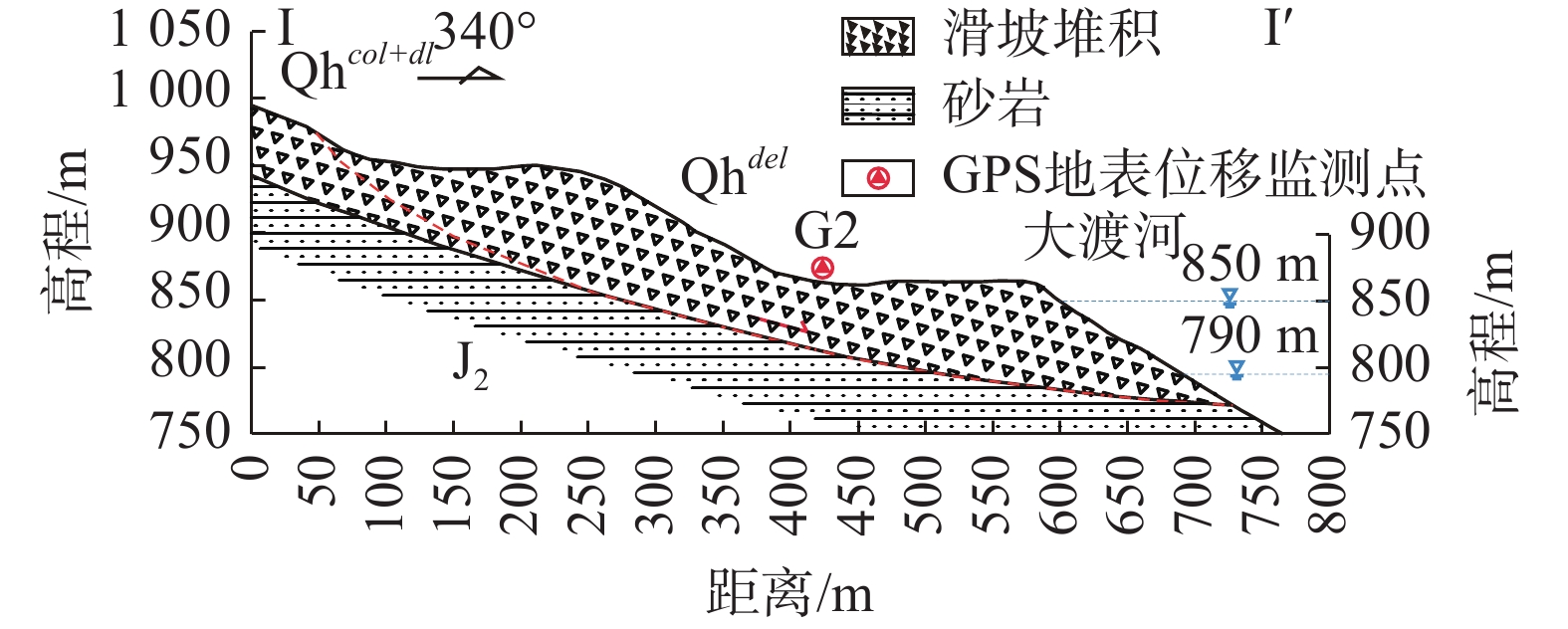
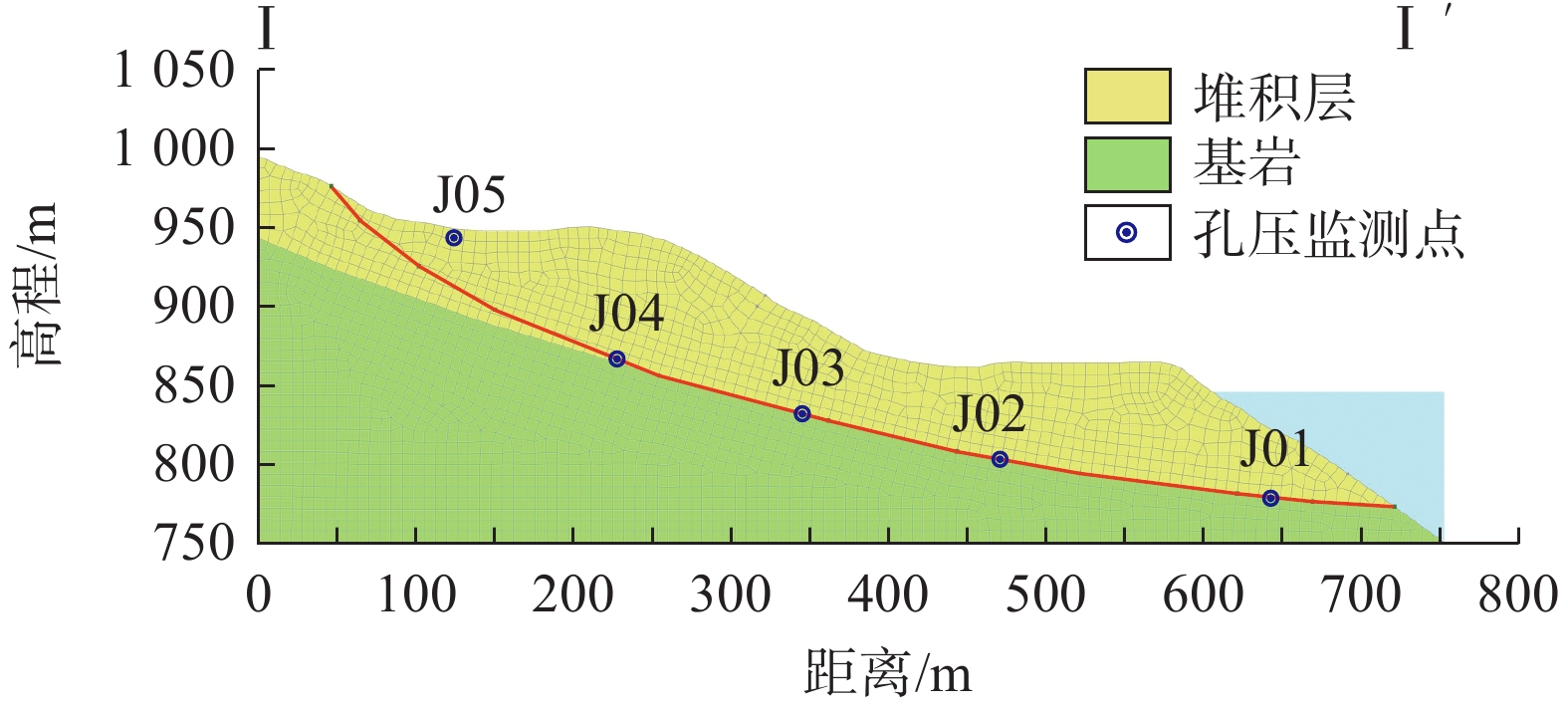
红岩子滑坡地形南高北低,陡缓相间。红岩子滑坡后缘高程1050 m,前缘剪出口高程770 m,高程860~1050 m间地形呈台阶状,分布有多个平台,地形坡度0°~40°,前缘860 m以下地形较陡,坡度40°~50°。滑坡右以小冲沟及环湖路上下错动段界,左以环湖路内侧破坏处与垮塌纵向裂缝线为界,后缘高程1050 m山坡为界,前缘直抵大渡河。滑体纵长约600 m,横宽580 m,分布面积约34×104 m2,厚30~70 m,总体积约750×104 m3,属于大型滑坡(图1)。
红岩子滑坡滑体物质由第四系碎块(卵)石土夹碎裂岩体及孤石组成,结构中密—密实,碎块、孤石含量60%~80%,呈棱角状,粒径一般1~100 cm不等,最大者可达15 m,主要成分为灰岩,卵石层岩性成分复杂,磨圆度、具分选性较好,粒径 2~20 cm。滑床为侏罗系中统红色泥质粉砂岩,该地层产状近水平,岩体表层风化强烈,结构破碎。滑坡工程地质剖面图见图2。
2. 滑坡变形特征
通过研究滑坡变形特征,总结其地表变形规律,再结合地形地貌、地层岩性、地质构造、气象水文等条件,是进一步分析出滑坡变形机制的基础[23-25]。
2.1 地表宏观变形特征
自瀑布沟水电站2010年运行以来,红岩子滑坡每年都会发生变形,到目前为止,滑坡地表已出现许多明显变形迹象,据2022年6月的地面调查,红岩子滑坡目前的地表变形如下。
滑坡中部形成裂缝群,其中最大裂缝长60 m,宽90 cm,深1.1 m,延伸方向330°(图1中C2);滑坡中后部山路旁形成数条裂缝,其类型包括拉张、剪切,截断道路,其中最大者长17.5 m,张开度50~80 cm,走向295°~310°(图1中C3);滑坡后部山路右边界处道路拓宽部位下沉形成长21 m、下错20 cm、走向236°的裂缝(图1中C4);滑坡后缘发育许多拉张裂缝,长度、宽度均较大(图1中C5)。
滑坡体前缘、后缘及中部发生多处局部滑塌,其中,前缘一处崩塌,估计体积500~1000 m3(图1中C1);后缘两处较大局部滑坡,估计体积500~1000 m3,此外还有多处小规模滑坡,估计体积在50~100 m3不等(图1中C5);滑坡中后部左边界山路以下区域由于变形形成局部塌陷,塌陷深度达8 m(图1中C6)。
滑坡体前缘岩体破碎,节理极为发育,受库水涨落的影响,滑坡前缘库水消落带岩土体均有一定的蚀变破坏,主要表现在对土体的掏蚀和对灰岩的溶解,导致前缘岩土体局部垮塌。
2.2 监测布置及监测结果
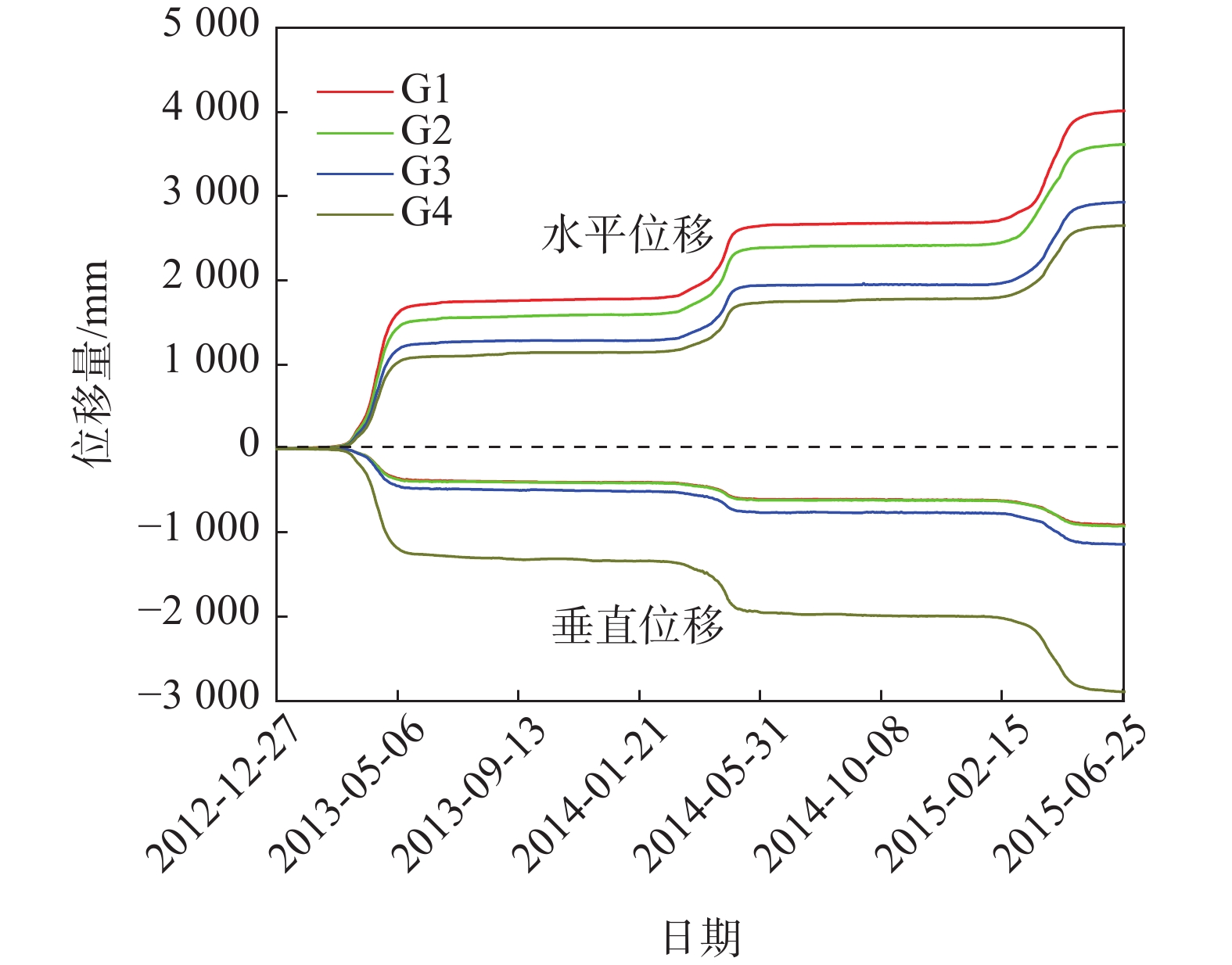
为了监测滑坡变形特征和及研究变形规律,在滑体上建立了监测系统:在滑体中部、中后部及右侧共布设4台GPS地表位移监测站(G1、G2、G3、G4)(图1),自2012年11月开始对滑坡开展长期监测。
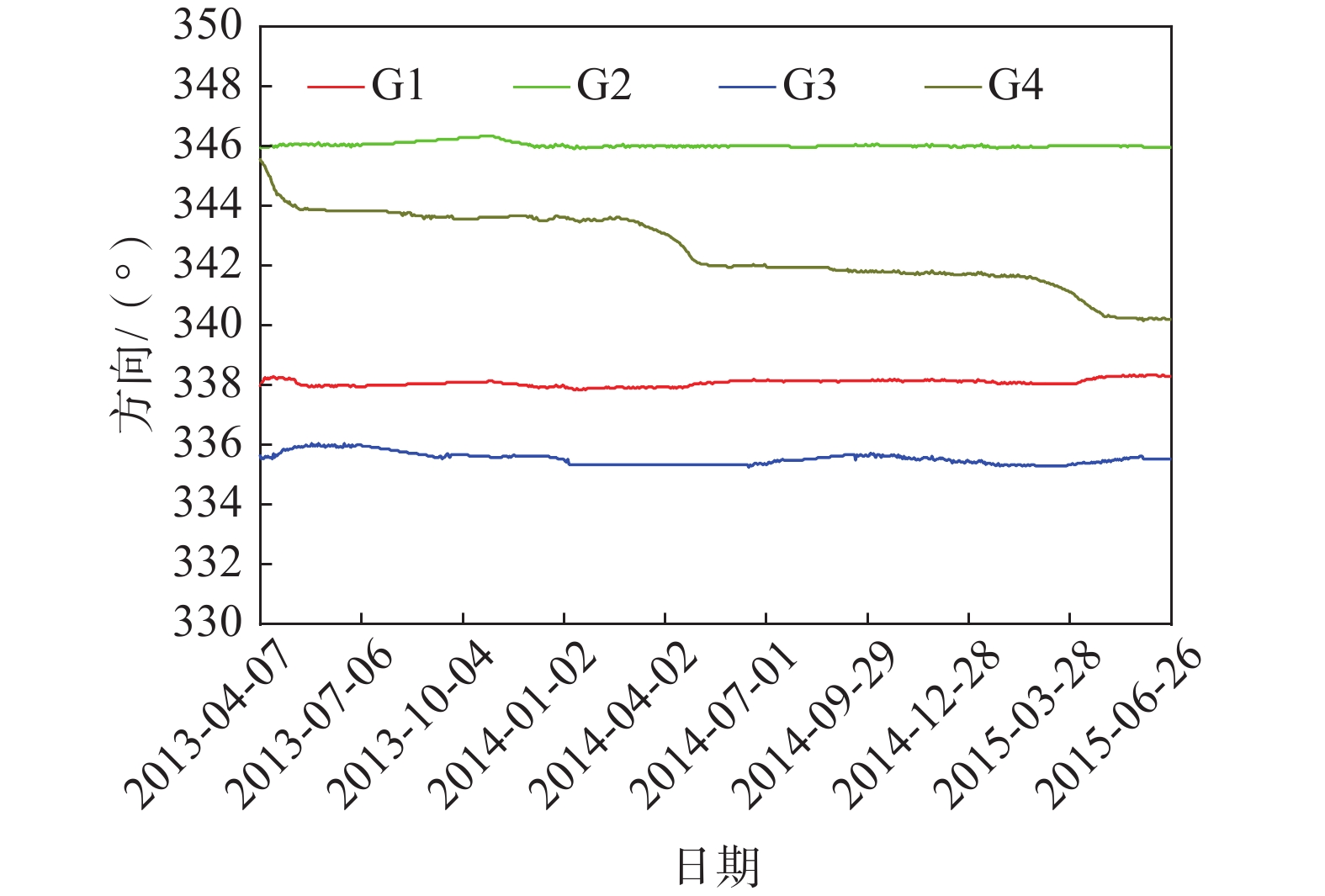
红岩子滑坡2013—2015年的水平与垂直位移曲线见图3,其中,最大水平位移点为G1,最大垂直位移点为G4;累计垂直位移监测点G4远大于其他三点,并超过水平位移,主要原因是该监测点位于滑坡中后部的陡坎上,受地形影响较大。四个地表位移监测点运动的主方位角在335°~347°,其中G1—G3位移方向基本保持稳定,G4位移方向在每年滑坡集中变形期向西有1°左右的偏移,主要受滑坡的微观形态和整体变形控制(图4)。
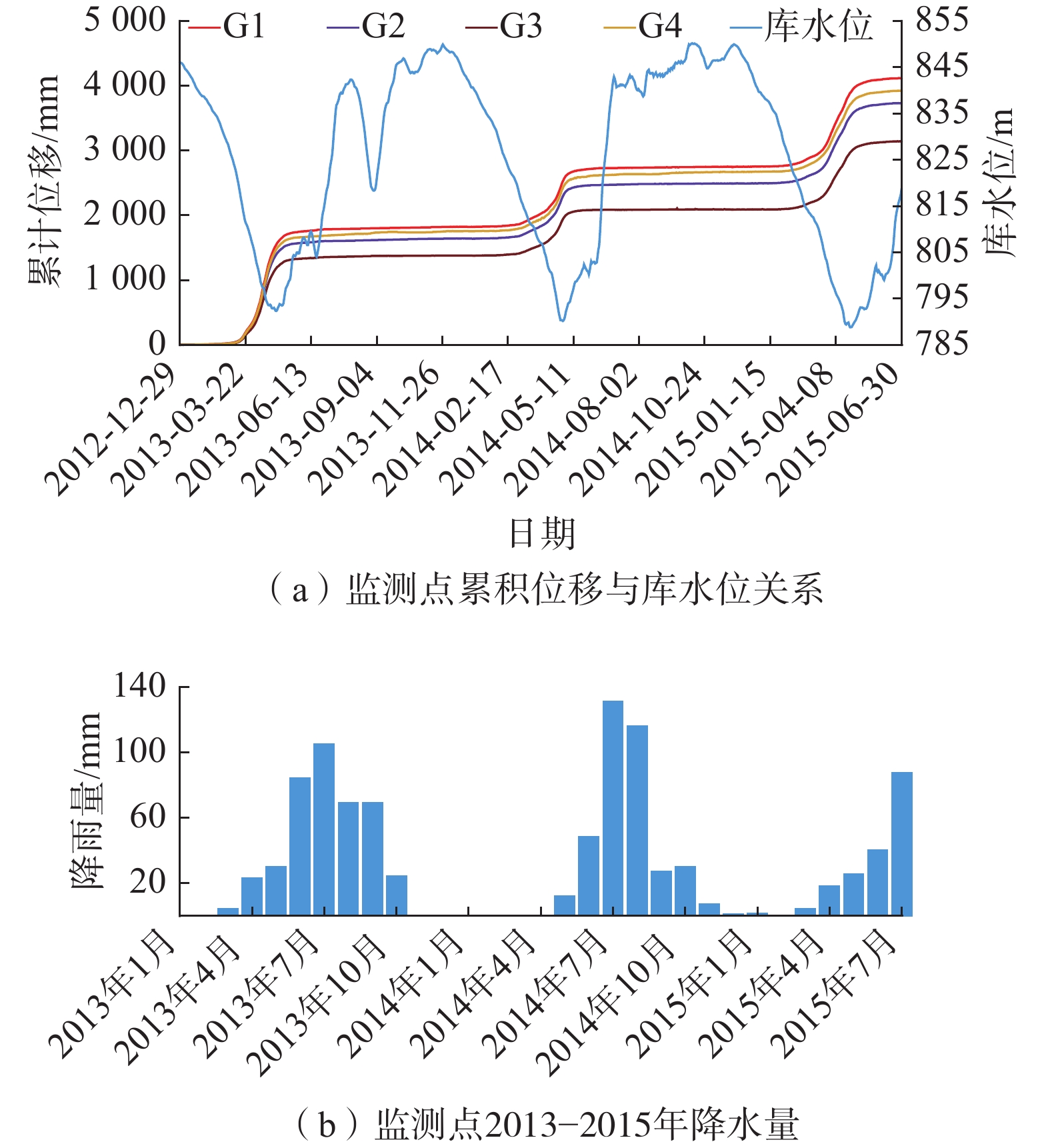
通过图5和监测数据可知,红岩子滑坡在变形曲线上呈现明显的“阶跃”特征,“阶跃”段对应每年库水位下降中后期至上升初期,一般在每年3—5月份,这段时间内滑坡的变形量占滑坡全年累计变形量的90%以上,2013—2015年期间内最大位移量分别为G1的1706 mm、834 mm、1111 mm,其中2013年出现较大位移,主要是水库运行初期坡体内部应力调整所致。在库水位上升期,滑坡变形明显趋缓,在库水位快速上升期至第二年库水位下降前期,滑坡变形很小,总变形量不超过130 mm,平均速率不超过0.5 mm/d。红岩子滑坡区域降雨集中在6—8月份,此时滑坡变形很小;而在滑坡“阶跃”段,降雨量小,如2013—2015年3—5月,总降雨量分别为57 mm、11.8 mm、47.6 mm。分析认为,红岩子滑坡变形主要与库水下降有关,降雨对滑坡整体变形影响很小。
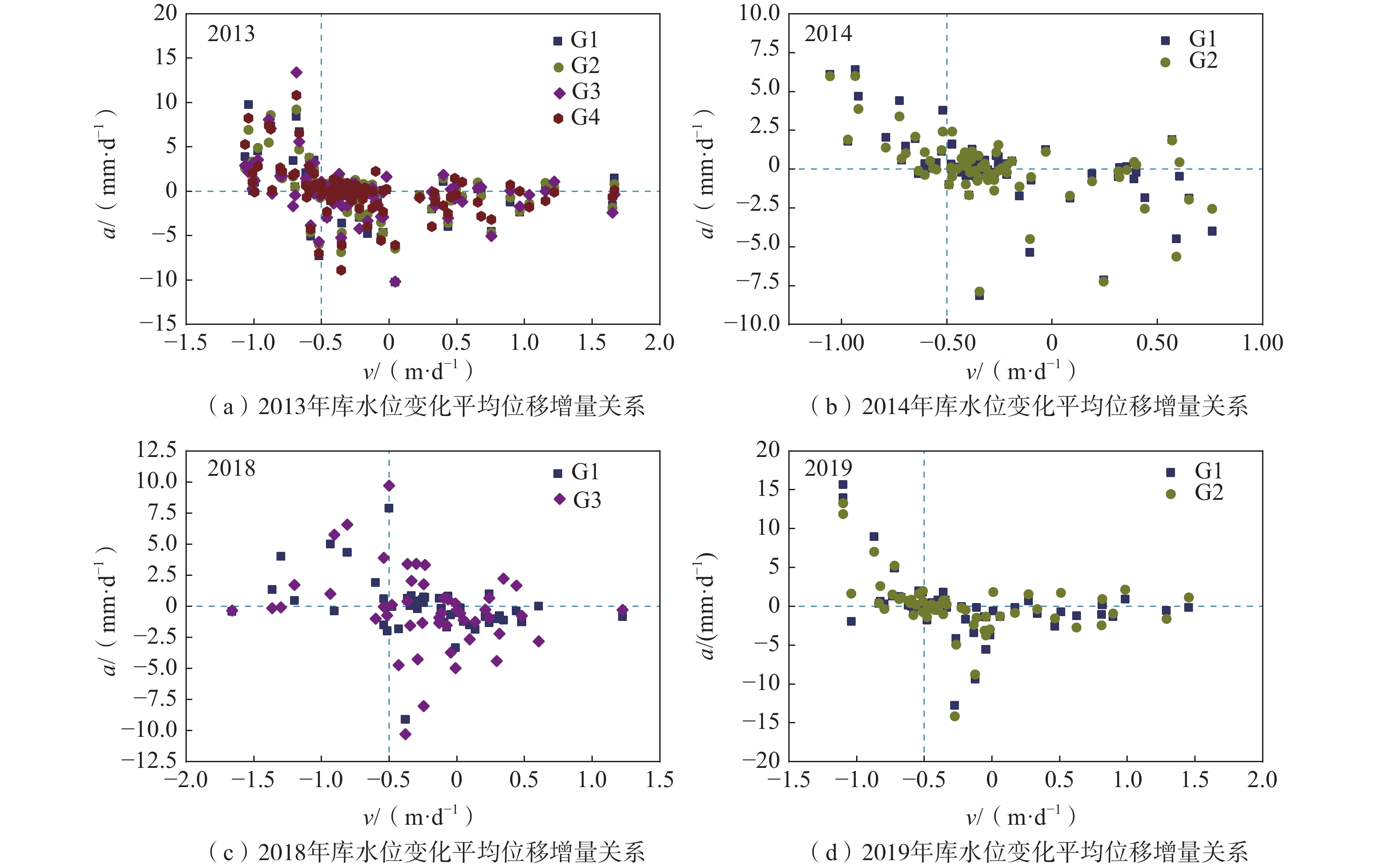
图6显示了2013、2014、2018及2019年红岩子滑坡各监测点地表位移速率与库水位升降速率,可以看出滑坡各年变形速率波动较大,在2013、2014、2019年3—5月及2018年1—3月,各监测点变形速率均处于波峰,在此期间滑坡变形最为剧烈,即对应累计位移曲线“阶跃”阶段。如2013年4月12日,滑坡达单日最大变形速率62 mm/d。为了精细化研究库水位变化诱发“阶跃”型变形特征,可将滑坡变形曲线分为缓慢变形、加速变形、减速变形及匀速变形4个阶段。
(1)缓慢变形阶段(图6中①):在2013、2014、2019年份1—3月、6—12月,2018年5—12月,滑坡变形速率接近0,最大日变形速率不超过5 mm/d。此时库水一般处于上升期、高水位期及850~830 m的下降期。
(2)加速变形阶段(图6中②):滑坡变形开始明显加速均出现在库水位集中下降一定高度之后,2013、2014、2018和2019年滑坡开始明显加速变形时库水位已经分别下降至827 m、819 m、819 m和820 m。表1列举了2013、2014、2018和2019年滑坡变形加速阶段的库水位平均下降速率,显然,滑坡加速变形阶段均对应着较大的库水位下降速率。反之,在2013年6月15日—6月19日、8月11日—8月28日,2014年2月4日—2月11日,库水位平均下降速率分别达0.96 m/d、1.1 m/d、0.6 m/d,但滑坡却未出现明显加速变形,说明在高库水位时期,或者在库水集中上升后的小幅库水下降时,即使库水位降速较大,滑坡也不会出现加速变形现象。因此,滑坡开始明显加速变形须满足2个条件:①库水位由高库水位850 m集中下降至一定高度之后,一般在830 m以下;②库水下降速率较大。
表 1 滑坡变形加速阶段库水下降速率均值Table 1. Summary table of mean decline rate of reservoir water during landslide deformation acceleration phase年份 日期 库水下降速率/(m·d−1) 2013 3月1日—3月22日 0.76 3月27日—4月12日 0.72 4月15日—4月17日 0.87 2014 3月2日—3月9日 0.59 4月4日—4月10日 0.67 4月15日—4月25日 0.91 2018 1月23日—2月10日 0.85 3月27日—3月31日 0.56 2019 2月22日—3月2日 0.72 3月22日—4月2日 0.89 4月26日—4月29日 0.70 (3)减速变形阶段(图6中③):此阶段出现在加速变形阶段之后,当库水位无法维持较高的下降速率时,滑坡即由加速变形转入减速变形或匀速变形,可见滑坡变形速率对库水降速反应灵敏。
(4)匀速变形阶段(图6中④):在2014年3月10日—3月24日、2019年3月3日—3月21日,G1和G2变形速率均在5 mm/d上下波动,此阶段库水下降速率在滑坡加减速变形的库水降速阈值上下波动,波动幅度较大,波动频率较快。
为了进一步研究库水下降速率与滑坡变形速率间的关系,确定滑坡加速变形的库水降速阈值,同时为了降低数据波动对结果的影响,利用图8中的库水位及GPS位移数据,取2日平均库水变化值(v)及2日平均位移增量(a),表达式如下:
$$ v=\frac{{V}_{n+1}+{V}_{n+2}}{2} $$ $$ a=\frac{{A}_{n+3}+{A}_{n+2}}{2}-\frac{{A}_{n+1}+{A}_{n}}{2} $$ 其中:v——2日平均库水位变化值/(m·d−1);
Vn——第n天库水位下降值/(m·d−1);
a——2日平均位移增量/(mm·d−1);
An——第n天日位移,
$ n=1,3,5,\cdots$ 。二者的关系如图7所示,由图可知,a的分布在v=0.5 m/d处呈现明显的分水岭,当v<−0.5 m/d时,a基本上大于0,此时滑坡将加速变形;当v>−0.5 m/d时,a大部分小于0,另外小部分大于但接近0,可视为正常波动,这表示滑坡将减速或者以较稳定的速率变形。
综合以上分析,滑坡变形的“阶跃”发生在库水位由850 m高水位集中下降至830 m以下之后, 库水位下降速率0.5 m/d是决定滑坡加速变形的阈值,持续的0.5 m/d的库水位下降速率是诱发滑坡发生“阶跃”的驱动因素。
3. 数值模拟
3.1 数值模型的建立
为了进一步研究红岩子滑坡的变形机制,本节基于非饱和渗流理论及非饱和土强度理论,采用GeoStudio分析库水波动及降雨作用下滑坡渗流场与稳定性的变化特征。
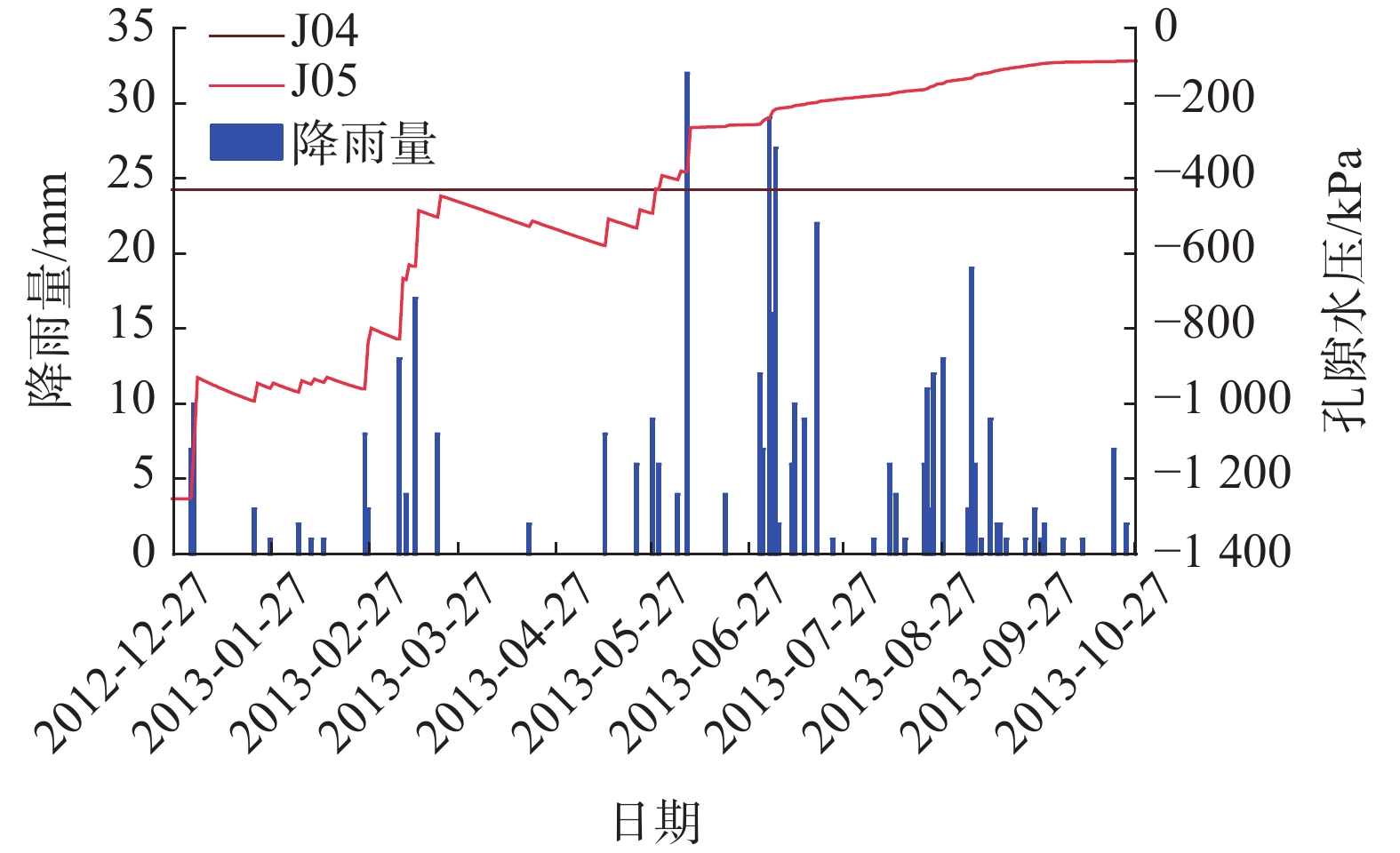
选取滑坡的Ⅰ—Ⅰ’剖面建立二维数值模型,可见图8,模型共有2100个单元, 2218个节点,并在滑坡模型上设置J01—J05等5个监测点。滑坡的水文与力学参数来自前人成果[22]与现场抽水试验,具体取值见表2。
表 2 滑坡物理力学参数Table 2. Physical and mechanical parameters of the landslide岩性 重度
/(kN·m−3)黏聚力
/kPa内摩擦角
/(°)渗透系数
/(m·d−1)堆积层 20 20 15 0.450 基岩 26 3200 44 0.001 3.2 分析工况及荷载
滑坡渗流及稳定性分析所采用的计算工况及荷载组合如表3所示,由于红岩子滑坡2013年出现了最大位移,计算所采用的降雨及库水位均为2013年的真实数据。
表 3 滑坡计算参数Table 3. Landslide calculation parameters编号 模拟工况 荷载组合 I 降雨 自重+2013年真实降雨 II 降雨+库水 自重+2013年真实降雨+2013年库水位 3.3 滑坡渗流特征分析
(1)降雨条件下滑坡渗流特征
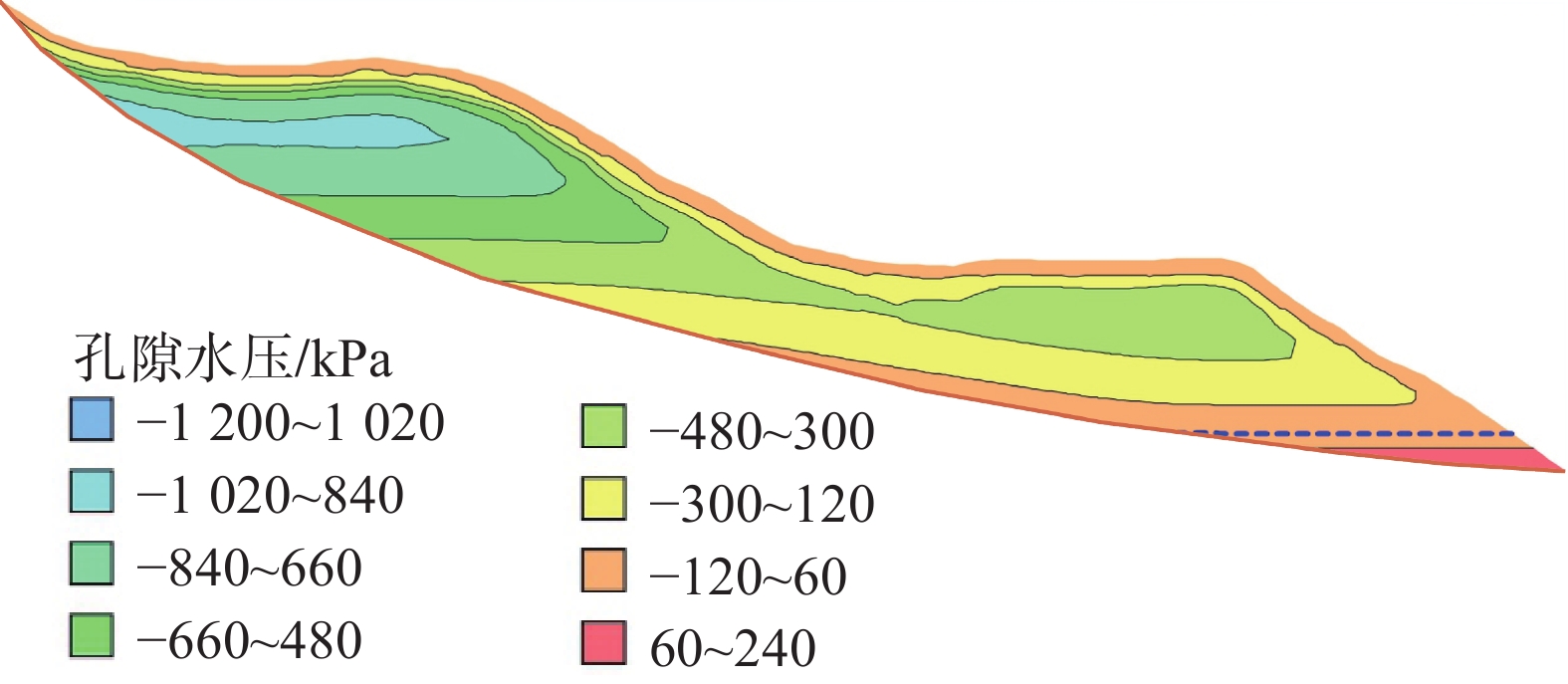
2013年9月2日真实降雨条件下红岩子滑坡渗流场计算结果表明,降雨主要影响滑坡表层的孔隙压力,难以入渗至滑坡深部而对滑体内部渗流产生影响(图9)。滑坡表层孔隙水压力在降雨时显著上升,在雨后又有所回落,而滑坡深部的孔隙水压力则受降雨影响十分有限,基本变化不大(图10)。
(2)降雨+库水条件下滑坡渗流特征
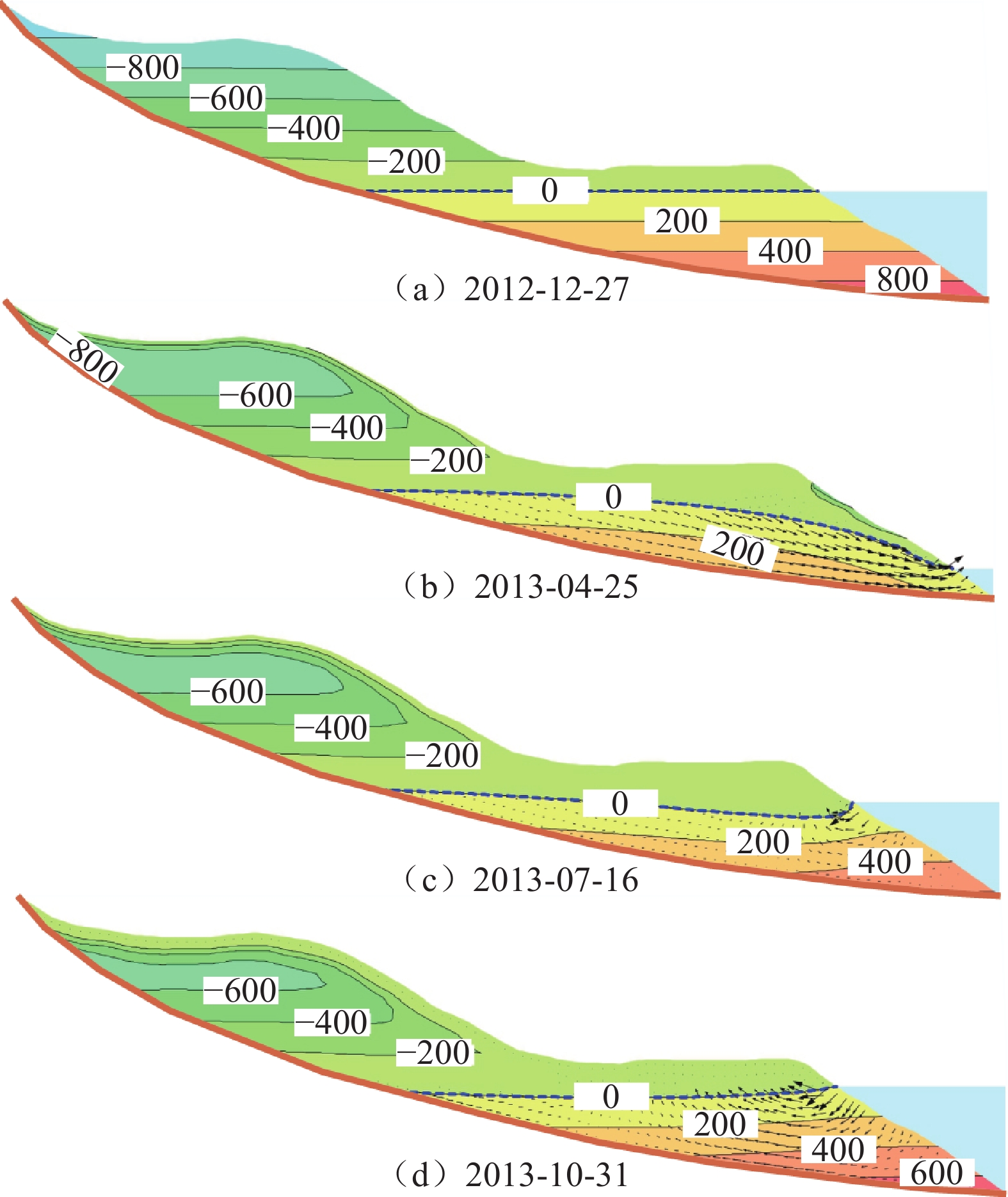
库水和降雨共同作用下滑坡的渗流场如图11所示,初始时刻,滑坡体内水位线平缓,与库水位基本持平,见图11(a);库水位下降期,滑坡前部地下水位显著降低,后部则变化较慢,这导致滑体前后、坡体内外产生水位差,产生向外的渗流,且随着库水位下降幅度与速率的增大,渗流明显增强,见图11(b);库水位上升期,坡体内外产生水位差减小,当库水位上升速度较大时,库水回灌坡体,产生指向坡内的渗流,见图11(c);当库水位恢复至高水位时,坡体内水位又渐渐与库水位持平,见图11(d)。在以上各个时段内,降雨对滑坡内部渗流均无影响,仅在高库水位时期对滑坡中后部表层孔隙水压有所影响。
图12为库水+降雨条件下滑体J01、J02、J03三点孔隙水压变化曲线,滑坡前部J01孔隙水压受库水位影响大,且对库水位响应迅速;中部监测点J02孔隙水压受库水位影响相对较小;后部监测点J03曲线平缓,受库水位影响很小。
3.4 稳定性演化分析
(1)降雨条件下稳定性分析
将SEEP/W中降雨条件下滑坡渗流场计算结果导入SLOPE/W,采用M—P法,计算结果表明,降雨对滑坡整体稳定性基本无影响,滑坡稳定系数稳定在1.147左右。分析认为,降雨仅影响滑坡表层孔隙水压,难以入渗滑坡滑带部位,对坡体自重的增加很有限,也无法影响滑坡体内部渗流,故难以对滑坡整体稳定性造成影响。
(2)降雨+库水条件下稳定性分析
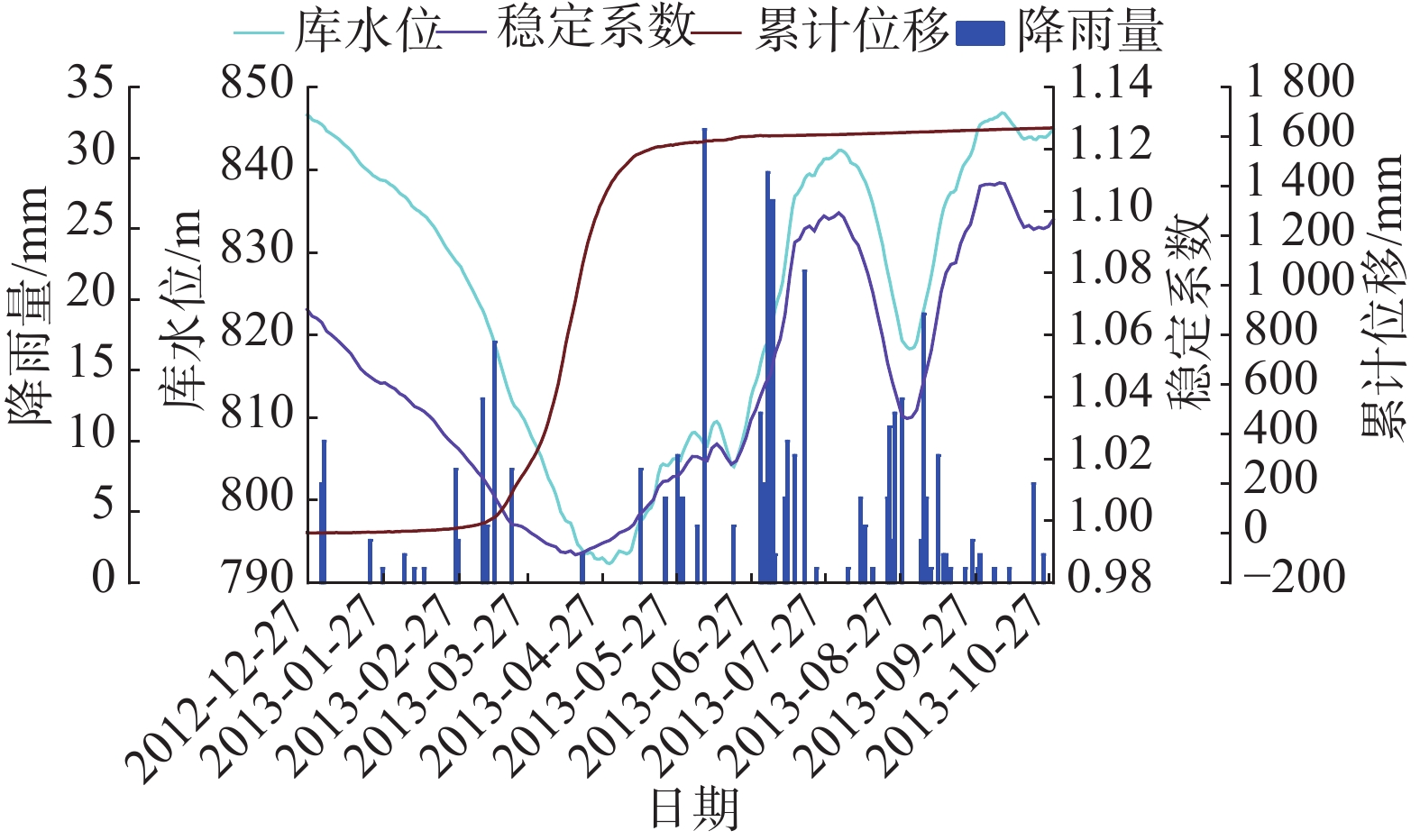
由图13可知,在库水位+降雨条件下,滑坡稳定系数基本只随库水升降变化,与降雨关联性极小。2013年1月1日—4月16日,库水位下降,由于滑坡渗透系数较小,导致坡体中的地下水难以排出,坡体内外水头差增大,产生向外的渗透力,滑坡稳定系数由1.068降至0.989,库水下降速率越大,渗透力越大,滑坡稳定系数下降越快;4月16日—4月25日,滑坡处于排水状态,坡体内地下水位不断降低,渗透力减小,滑坡稳定系数有所回升;4月26日—8月3日,库水位上升,库水逐渐回灌坡体形成指向坡内的渗透力,反推坡体,故滑坡稳定系数由0.989上升至1.109;8月4日—9月23日,库水位出现大幅波动,滑坡稳定系数也随之出现波动;9月23日之后,库水位稳定在840~845 m,滑坡稳定系数也趋于稳定。整个过程中滑坡稳定系数变化规律与库水位基本保持一致,可见库水波动是影响滑坡稳定性的主要因素。对比G2累计位移曲线,位移快速增长期正好对应最低稳定系数,说明模拟的合理性。
值得注意的是,随着库水位的变化,滑坡的稳定系数能立即得到响应,基本无滞后性,分析认为,由于滑坡渗透系数较小,坡体内部地下水位响应很慢,水库水位直接决定了坡体内外的水位差,从而决定了渗透力的大小,决定了滑坡的稳定性,故稳定系数响应迅速。对比仅降雨条件下滑坡的稳定性,库水作用下滑坡最高稳定系数为1.109,小于仅降雨条件下的1.147,说明高库水位时的浮托力对滑坡的稳定性仍有影响。
4. 滑坡变形机理
(1)地质条件对滑坡变形起控制作用
红岩子滑坡位于大渡河右岸,地形上陡缓相间,平均坡度25°,据统计,滑坡发生概率最大的地形坡度在 10°~45°。滑坡前缘为高70 m,坡度30°~40°的陡坎,滑坡前部两侧发育冲沟,使滑坡具备良好的临空条件。红岩子滑坡历史上曾发生过滑动,滑体结构强度相对较低,渗透系数为0.45 m/d,易受降雨或库水影响而发生变形破坏。滑床为侏罗系中统地层,由红色泥质粉砂岩组成,岩体软弱,遇水易软化,是典型的易滑地层,滑坡易沿堆积体与基岩的基覆接触带发生滑动。综合以上分析,地形和地质条件控制着滑坡的形成和发展。
(2)库水位下降是滑坡变形主要诱发因素
红岩子滑坡前部790~850 m高程位于库水消落带上,瀑布沟水库每年库水变幅达60 m,库水的涨落将对滑坡的变形与稳定性产生直接影响。库水涨落对红岩子滑坡的主要作用包括:对滑体和滑床的浸泡、冲刷和软化作用,这是导致滑坡前缘塌岸的主要因素之一;对滑体的浮托力作用,尤其是高库水位时;库水位下降时坡体内的渗透力作用,这是红岩子滑坡蠕变的主要诱发因素。
红岩子滑坡变形模式为蠕滑-拉裂,库水诱发滑坡发生“阶跃”变形的作用机制为库水升降引发滑体内部渗透力的变化,具体可分为3个阶段。①渗透力积聚-阶跃准备阶段:在库水位从850 m下降至830 m过程中,随着库水位的下降,坡体内外水位正落差加大,库水位以上滑体饱水部分不断增加,滑坡稳定系数不断降低,此时库水位下降越快,渗透力越大,能越早使滑坡稳定性到达临界值;②渗透力溢出-变形加速阶段:库水位下降至830 m以下,滑坡稳定性达到临界值后,滑坡步入“阶跃”变形阶段,此时当库水下降速率大于0.5 m/d时,将使渗透力溢出而使滑坡变形加速,当库水下降速率小于0.5 m/d时,此时的渗透力无法维持滑坡高速运动,滑坡将因此减速;③渗透力减小-滑坡趋稳阶段:在库水位下降后期及库水上升期间,坡体内外正落差减小,渗透力逐渐减小至指向坡内,反推坡体,滑坡稳定性回升,变形速率减小,滑坡逐渐趋于稳定。
5. 结论
(1)红岩子滑坡地表宏观变形显著,主要包括中部及后部裂缝、前缘塌岸和后缘滑塌。
(2)滑坡累计位移曲线呈“阶跃”特征, “阶跃”主要集中在每年3—5月份,触发于每年库水位由850 m高水位集中下降至830 m以下之后, 库水位下降速率0.5 m/d是决定滑坡加速变形的阈值,持续的0.5 m/d的库水位下降速率是诱发滑坡发生“阶跃”的驱动因素,“阶跃”段的累计变形量占全年总变形量的90%以上。
(3)库水升降对红岩子滑坡内部渗流场影响很大,是影响滑坡稳定性的主要因素,库水上升时滑坡稳定系数升高,库水下降时滑坡稳定系数降低。
(4)红岩子滑坡的变形模式为蠕滑-拉裂,库水升降导致滑体内部渗透力的变化,从而引发滑坡“阶跃”变形,可分为3个变形阶段。随着库水位的下降,库水累计降幅增加,库水下降速率突破0.5 m/d,在滑体内渗透力的作用下,滑坡开始发生显著变形,滑坡失去渗透力的作用后,滑坡变形逐渐减小直至停止。
-
表 1 滑坡变形加速阶段库水下降速率均值
Table 1 Summary table of mean decline rate of reservoir water during landslide deformation acceleration phase
年份 日期 库水下降速率/(m·d−1) 2013 3月1日—3月22日 0.76 3月27日—4月12日 0.72 4月15日—4月17日 0.87 2014 3月2日—3月9日 0.59 4月4日—4月10日 0.67 4月15日—4月25日 0.91 2018 1月23日—2月10日 0.85 3月27日—3月31日 0.56 2019 2月22日—3月2日 0.72 3月22日—4月2日 0.89 4月26日—4月29日 0.70 表 2 滑坡物理力学参数
Table 2 Physical and mechanical parameters of the landslide
岩性 重度
/(kN·m−3)黏聚力
/kPa内摩擦角
/(°)渗透系数
/(m·d−1)堆积层 20 20 15 0.450 基岩 26 3200 44 0.001 表 3 滑坡计算参数
Table 3 Landslide calculation parameters
编号 模拟工况 荷载组合 I 降雨 自重+2013年真实降雨 II 降雨+库水 自重+2013年真实降雨+2013年库水位 -
[1] 朱宇航,黄海峰,殷坤龙,等. 基于滑坡破坏模式分析的易发性评价—以三峡库区首段泄滩河左岸为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(2):156 − 166. [ZHU Yuhang,HUANG Haifeng,YIN Kunlong,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide failure mode analysis: A case study of the left bank of Xietan River in the first section of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(2):156 − 166. (in Chinese with English abstract) [ZHU Yuhang, HUANG Haifeng, YIN Kunlong, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide failure mode analysis: a case study of the left bank of Xietan River in the first section of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(2): 156-166.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 殷跃平. 三峡库区地下水渗透压力对滑坡稳定性影响研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2003,14(3):1 − 8. [YIN Yueping. Seepage pressure effect on landslide stability at the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2003,14(3):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2003.03.001 YIN Yueping. Seepage pressure effect on landslide stability at the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2003, 14(3): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2003.03.001
[3] 杨金,简文星,杨虎锋,等. 三峡库区黄土坡滑坡浸润线动态变化规律研究[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(3):853 − 858. [YANG Jin,JIAN Wenxing,YANG Hufeng,et al. Dynamic variation rule of phreatic line in Huangtupo landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(3):853 − 858. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.03.032 YANG Jin, JIAN Wenxing, YANG Hufeng, et al. Dynamic variation rule of phreatic line in Huangtupo landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(3): 853-858. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.03.032
[4] MÜLLER LEOPOLD. The rock slide in the Vajont Valley[J]. Rock Mechanics and Engineering Geology, 2(3): 148 − 212.
[5] 王兰生. 意大利瓦依昂水库滑坡考察[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2007,18(3):145 − 148. [WANG Lansheng. Investigation on landslide of Vaion Reservoir in Italy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2007,18(3):145 − 148. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2007.03.033 WANG Lansheng. Investigation on landslide of Vaion Reservoir in Italy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2007, 18(3): 145-148. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2007.03.033
[6] 冯文凯,顿佳伟,张国强,等. 库水作用下青杠坪滑坡堆积体变形演化趋势[J]. 科学技术与工程,2020,20(27):11003 − 11011. [FENG Wenkai,DUN Jiawei,ZHANG Guoqiang,et al. Deformation evolution trend of Qinggangping landslide accumulation under the action of reservoir water[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2020,20(27):11003 − 11011. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.27.004 FENG Wenkai, DUN Jiawei, ZHANG Guoqiang, et al. Deformation evolution trend of qinggangping landslide accumulation under the action of reservoir water[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(27): 11003-11011. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.27.004
[7] 郑颖人,时卫民,孔位学. 库水位下降时渗透力及地下水浸润线的计算[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(18):3203 − 3210. [ZHENG Yingren,SHI Weimin,KONG Weixue. Calculation of seepage forces and phreatic surface under drawdown conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004,23(18):3203 − 3210. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.18.031 ZHENG Yingren, SHI Weimin, KONG Weixue. Calculation of seepage forces and phreatic surface under drawdown conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(18): 3203-3210. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.18.031
[8] 时卫民,郑颖人. 库水位下降情况下滑坡的稳定性分析[J]. 水利学报,2004,35(3):76 − 80. [SHI Weimin,ZHENG Yingren. Analysis on stability of landslide during reservoir drawdown[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2004,35(3):76 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2004.03.013 SHI Weimin, ZHENG Yingren. Analysis on stability of landslide during reservoir drawdown[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2004, 35(3): 76-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2004.03.013
[9] ZANGERL C,EBERHARDT E,PERZLMAIER S. Kinematic behaviour and velocity characteristics of a complex deep-seated crystalline rockslide system in relation to its interaction with a dam reservoir[J]. Engineering Geology,2010,112(1/2/3/4):53 − 67.
[10] PARONUZZI P,RIGO E,BOLLA A. Influence of filling-drawdown cycles of the Vajont Reservoir on Mt. Toc slope stability[J]. Geomorphology,2013,191:75 − 93. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.03.004
[11] 李松林,许强,汤明高,等. 库水位升降作用下不同滑面形态老滑坡响应规律[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(3):841 − 852. [LI Songlin,XU Qiang,TANG Minggao,et al. Response patterns of old landslides with different slipsurface shapes triggered by fluctuation of reservoir water level[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(3):841 − 852. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.03.032 LI Songlin, XU Qiang, TANG Minggao, et al. Response patterns of old landslides with different slipsurface shapes triggered by fluctuation of reservoir water level[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(3): 841-852. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.03.032
[12] 朱赛楠,殷跃平,黄波林,等. 三峡库区大型单斜顺层新生滑坡变形特征与失稳机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(3):657 − 667. [ZHU Sainan,YIN Yueping,HUANG Bolin,et al. Deformation characteristics and instability mechanism of large monoclinal layered neogenic bedrock landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(3):657 − 667. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0178 ZHU Sainan, YIN Yueping, HUANG Bolin, et al. Deformation characteristics and instability mechanism of large monoclinal layered neogenic bedrock landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(3): 657-667. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0178
[13] 黄达,匡希彬,罗世林. 三峡库区藕塘滑坡变形特点及复活机制研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(5):127 − 135. [HUANG Da,KUANG Xibin,LUO Shilin. A study of the deformation characteristics and reactivation mechanism of the Outang landslide near the Three Gorges Reservoir of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(5):127 − 135. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG Da, KUANG Xibin, LUO Shilin. A study of the deformation characteristics and reactivation mechanism of the Outang landslide near the Three Gorges Reservoir of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(5): 127-135. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 代贞伟,殷跃平,魏云杰,等. 三峡库区藕塘滑坡特征、成因及形成机制研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(6):145 − 153. [DAI Zhenwei,YIN Yueping,WEI Yunjie,et al. Characteristics,origin and formation mechanism of the Outang landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(6):145 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract) DAI Zhenwei, YIN Yueping, WEI Yunjie, et al. Characteristics, origin and formation mechanism of the Outang landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(6): 145-153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 尚敏,廖芬,马锐,等. 白家包滑坡变形与库水位、降雨相关性定量化分析研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(3):742 − 750. [SHANG Min,LIAO Fen,MA Rui,et al. Quantitative correlation analysis on deformation of baijiabao landslide between rainfall and reservoir water level[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(3):742 − 750. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-045 SHANG Min, LIAO Fen, MA Rui, et al. Quantitative correlation analysis on deformation of baijiabao landslide between rainfall and reservoir water level[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(3): 742-750. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-045
[16] 邓茂林,周剑,易庆林,等. 三峡库区靠椅状土质滑坡变形特征及机制分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2020,42(7):1296 − 1303. [DENG Maolin,ZHOU Jian,YI Qinglin,et al. Characteristics and mechanism of deformation of chair-shaped soil landslides in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2020,42(7):1296 − 1303. (in Chinese with English abstract) DENG Maolin, ZHOU Jian, YI Qinglin, et al. Characteristics and mechanism of deformation of chair-shaped soil landslides in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(7): 1296-1303. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 邓茂林,易庆林,韩蓓,等. 长江三峡库区木鱼包滑坡地表变形规律分析[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(8):3145 − 3152. [DENG Maolin,YI Qinglin,HAN Bei,et al. Analysis of surface deformation law of Muyubao landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area of the Yangtze River[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(8):3145 − 3152. (in Chinese) DENG Maolin, YI Qinglin, HAN Bei, et al. Analysis of surface deformation law of Muyubao landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area of the Yangtze River[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(8): 3145-3152. (in Chinese)
[18] 汤明高,吴川,吴辉隆,等. 水库滑坡地下水动态响应规律及浸润线计算模型—以石榴树包滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(2):115 − 125. [TANG Minggao,WU Chuan,WU Huilong,et al. Dynamic response and phreatic line calculation model of groundwater in a reservoir landslide:Exemplified by the Shiliushubao landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(2):115 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202105041 TANG Minggao, WU Chuan, WU Huilong, et al. Dynamic response and phreatic line calculation model of groundwater in a reservoir landslide: exemplified by the Shiliushubao landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 115-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202105041
[19] 裴小龙,杨瀚文,宋东阳,等. 雅砻江中游楞古水电站夏日滑坡发育特征及稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):75 − 82. [PEI Xiaolong,YANG Hanwen,SONG Dongyang,et al. Characteristics and stability analysis of Xiari landslide at Lenggu hydropower station in the middle reach of the Yalong River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):75 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.01-09 PEI Xiaolong, YANG Hanwen, SONG Dongyang, et al. Characteristics and stability analysis of Xiari landslide at Lenggu hydropower station in the middle reach of the Yalong River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(1): 75-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.01-09
[20] 卢书强,易庆林,易武,等. 三峡库区树坪滑坡变形失稳机制分析[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(4):1123 − 1130. [LU Shuqiang,YI Qinglin,YI Wu,et al. Analysis of deformation and failure mechanism of Shuping landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(4):1123 − 1130. (in Chinese with English abstract) LU Shuqiang, YI Qinglin, YI Wu, et al. Analysis of deformation and failure mechanism of Shuping landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(4): 1123-1130. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 韩冰. 雅安地区滑坡灾害监测预警研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016. HAN Bing. Study on monitoring and early warning of landslide disaster in Ya’an area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 祝斌. 四川汉源红岩子库岸边坡稳定性研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. ZHU Bin. Study on stability of bank slope of hongyan sub-reservoir in Hanyuan, Sichuan Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 张岩岩,文海家,麻超超,等. 基于多源数据的蔡家坝特大型滑坡成因机制研究及稳定性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(9):2048 − 2063. [ZHANG Yanyan,WEN Haijia,MA Chaochao,et al. Failure mechanism and stability analysis of huge landslide of Caijiaba based on multi-source data[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(9):2048 − 2063. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0448 ZHANG Yanyan, WEN Haijia, MA Chaochao, et al. Failure mechanism and stability analysis of huge landslide of Caijiaba based on multi-source data[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(9): 2048-2063. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0448
[24] 朱彦鹏,杜一博,杨校辉,等. 甘肃舟曲河那滑坡变形特征及孕灾机理[J]. 科学技术与工程,2022,22(25):10884 − 10895. [ZHU Yanpeng,DU Yibo,YANG Xiaohui,et al. Disaster mechanism and stability evaluation of hena landslide in Zhouqu,Gansu Province[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2022,22(25):10884 − 10895. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.25.007 ZHU Yanpeng, DU Yibo, YANG Xiaohui, et al. Disaster mechanism and stability evaluation of hena landslide in Zhouqu, Gansu Province[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(25): 10884-10895. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.25.007
[25] 汤明高,吴川,吴辉隆,等. 水库滑坡地下水动态响应规律及浸润线计算模型—以石榴树包滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(2):115 − 125. [TANG Minggao, WU Chuan, WU Huilong, et al. Dynamic response and phreatic line calculation model of groundwater in a reservoir landslide: Exemplified by the Shiliushubao landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(2):115 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract) TANG Minggao, WU Chuan, WU Huilong, et al. Dynamic response and phreatic line calculation model of groundwater in a reservoir landslide: exemplified by the Shiliushubao landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 115-125.(in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 郑伟,李俊宏. 白鹤滩库区水位变动条件下某滑坡成因分析及稳定性评价. 甘肃科技. 2025(02): 45-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 叶永,毛旭巍,谢旋. 三峡库区卧沙溪滑坡变形机理及稳定性的研究. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(05): 25-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张亮华,田秋丰,阮迪,熊华盛,宋琨. 库水位条件影响下的大地坪滑坡稳定性分析及运动预测研究. 资源环境与工程. 2023(06): 766-775 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:



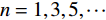
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS