Application of effective rainfall in assessing water damage risk to highways in Liaoning Province
-
摘要:
文章利用2017—2021年辽宁省降水诱发的高速公路、干线公路损毁记录数据,分析损毁事故发生的时间、空间特征,计算事故发生前有效雨量,并建立公路水毁概率拟合模型。结果表明:降水诱发的辽宁省公路损毁事件一般出现在5—10月,其中7—8月为高发期。公路水毁的发生时间呈现出从西北向东南逐渐延后的规律,事故数量与降水量有较高相关性。辽宁东部、西部为高发区域,丹东、朝阳、葫芦岛、本溪为省内高发地区。对比多种方法,公路水毁概率的拟合效果符合高斯分布概率密度函数。辽宁东部、南部致灾临界雨量值大于中部、北部,相同有效雨量条件下,平原地区发生公路水毁的风险高于山地丘陵地区。对2022年辽宁一次洪涝过程中公路水毁情况进行检验,综合评价结果具有较强的防汛指导作用。
Abstract:This paper utilizes data on the records of damage to expressways and main roads caused by precipitation in Liaoning Province from 2017 to 2021. It analyzes the temporal and spatial characteristics of damage accidents, calculates the effective rainfall before the occurrence of accidents, and establishes a probability fitting model for road water damage. The results show that precipitation-induced road damage events in Liaoning Province generally occur from May to October, with a peak in July and August. The occurrence of road water damage follows a pattern of gradually delaying from northwest to southeast, and the number of accidents is highly correlated with precipitation. The eastern and western parts of Liaoning are high-incidence areas, with Dandong, Chaoyang, Huludao, and Benxi being the high-incidence areas within the province. Among various methods compared, the fitting effect of the road water damage probability conforms to the Gaussian distribution probability density function. The critical rainfall threshold for disaster in the eastern and southern parts of Liaoning is higher than that in the central and northern parts. Under the same effective rainfall conditions, the risk of road water damage in plain areas is higher than in mountainous and hilly areas. The road water damage situation during a flooding process in Liaoning in 2022 is used for verification, indicating a strong role in flood control guidance.
-
Keywords:
- road water damage /
- critical rainfall /
- risk assessment /
- Liaoning Province
-
0. 引言
公路水毁属地质灾害中的一种特殊类型,通常在地形地貌、地质构造、地层岩性、新构造运动等内部因素,以及气候、水文环境等外部因素耦合作用下产生[1]。
作为多要素影响下的灾害,地质、交通和气象领域专家从不同角度开展了广泛研究。地质领域专家一般从地形地貌、地层岩性出发,分析不同地质构造对公路交通可能造产生的风险。赵建军[2]分析公路边坡岩体结构面、结构体特征,建立“边坡不稳定指数”实现对降雨条件下的公路边坡不稳定性的快速评价。杨志华等[3] 研究巴塘断裂带碎裂岩体结构与典型滑坡发育特征,分析发现公路工程与河道之间存在的相互影响关系。刘艳辉等[4]将与公路距离作为人类影响因子带入分析过程,建立了基于地质、环境、雨量等多个因子的区域滑坡灾害预警模型。交通工程领域着重针对地质灾害多发路段开展影响因素分析。祝建等[5]分析川藏公路(西藏境)主要地质灾害类型,利用多因素叠加法得到重大地质灾害密集频发路段。于秀珍等[6]利用频率比模型与信息熵理论相结合,分析地质、地貌、降雨条件对公路地质灾害的影响。李守定等[7]分析中巴公路沿线冻融型与冰川型地质灾害的天气诱因,建立基于温度—降雨双参数的地质灾害预警模型。气象领域多以公路水毁发生前的降水作为研究对象,分析灾害发生前不同时段内累计雨量对水毁的影响。狄靖月等[8]统计西南地区公路损毁发生频次及降水量,建立了公路损毁风险预报模型。王志等[9]采用信息量法将多种公路环境因子及降水因子在公路损毁中的影响进行了对比。
辽宁地貌特征复杂,东部、西部多为山地丘陵,中部、北部为平原,属于中国滑坡崩塌泥石流高易发区[10],并且近年来呈多发频发态势[11]。随着极端天气事件趋多,局地暴雨多发,辽宁公路交通安全面临的山体滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害的防御压力不断增加。已有地质灾害研究多针对中国西部山区开展,缺少适用东北地区交通的地质灾害风险评估方法。目前辽宁公路水毁防御主要依据气象降水预报等级和灾害隐患点风险普查结果,亟需制定针对不同区域特点的防御标准。
本文在分析辽宁公路水毁发生时间、空间分布特征基础上,充分考虑辽宁不同区域气候特征、地理特性,利用有效雨量分区域建立公路水毁概率反演模型,划分风险等级,制定辽宁各区域致灾雨量。公路交通地质灾害风险研究成果将为辽宁汛期公路沿线地质灾害防治预警、公路交通安全保障提供科学的参考,对提高地质灾害的风险预测与综合防治水平具有理论和实际意义[12]。
1. 数据与方法
1.1 数据来源
收集整理2017—2021年辽宁国省级干线公路、高速公路水毁灾害记录,灾害种类包括路面及路基冲毁、路面下沉、桥涵破坏、防护与加固工程损坏。公路水毁吉林数据来源是辽宁省交通运输事业发展中心、辽宁省高速公路运营管理有限责任公司。气象数据采用辽宁省
1660 个自动气象观测站点的日降水量、归属地信息,数据来源是中国气象局气象大数据云平台系统。1.2 数据处理方法
1.2.1 水毁与气象数据匹配
提取公路水毁记录中发生日期、地点以及线路名称,共得到
1806 条灾害记录。首先按照公路水毁发生地所在乡镇与气象站点进行匹配,若水毁事故发生乡镇无对应气象观测站则查找所在县区内气象观测站点。利用气象大数据云平台系统,根据灾害发生时间、临近气象站点编号查询事故发生当天至前14 天的20—20时的日降水量数据。1.2.2 有效雨量计算
有效雨量概念最早由Crozier[13]提出,用于研究滑坡地质灾害发生前降水产生的作用,近年来广泛应用于诱发地质灾害的雨量研究中。本文引用有效雨量分析公路水毁与前期降水关系,参考已有气象行业标准[14]确定有效雨量计算,见式(1)。
(1) 式中:PA——有效雨量;
Pi ——第i 天降水量。
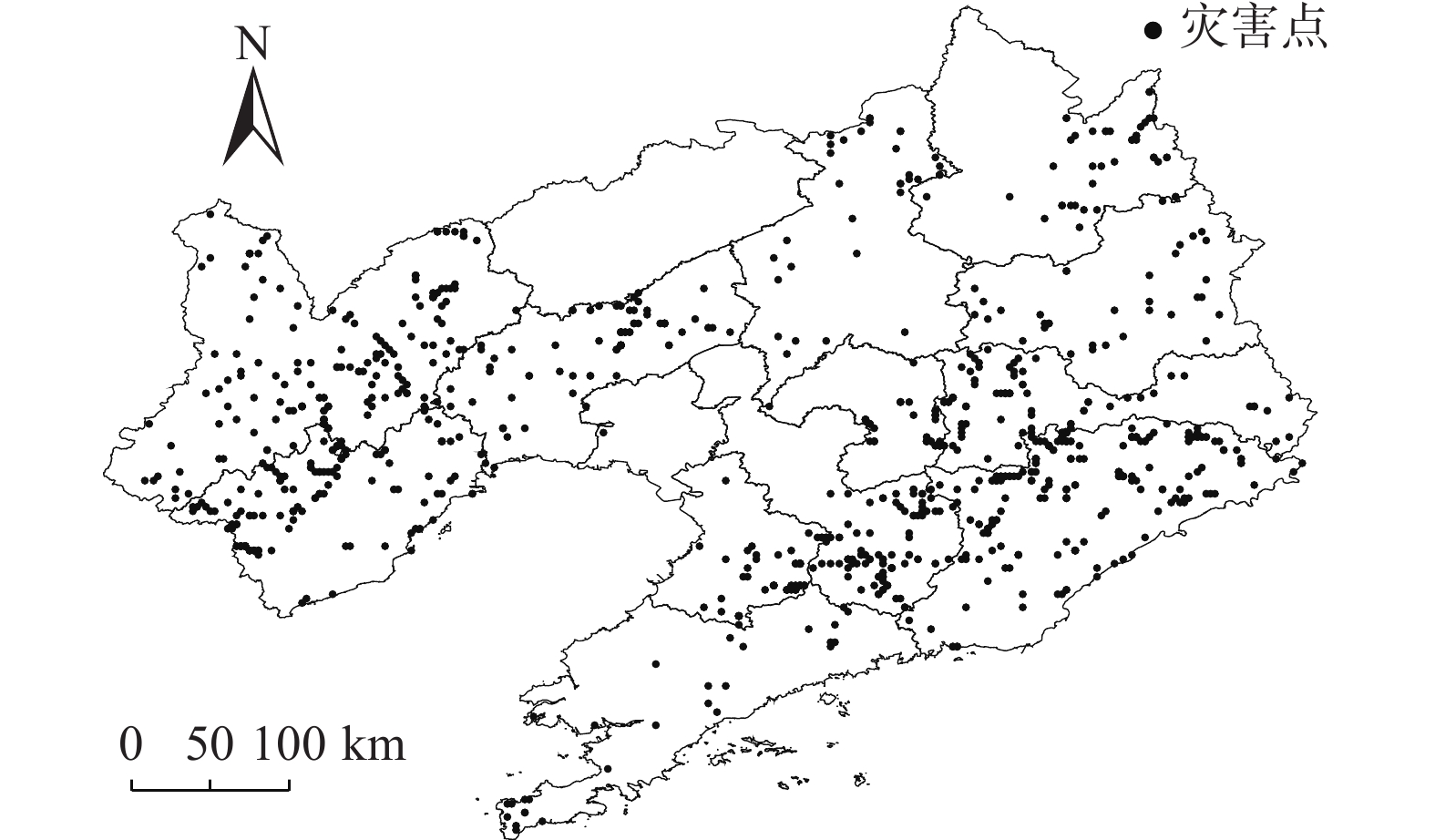
在计算有效雨量过程中,参考相关降雨型地质灾害研究[14 − 16],同时计算短期0—2 d、中期3—5 d、长期6—14 d有效雨量进行真实性核对。发现部分水毁事故发生前短期、中期雨量不足25 mm,长期雨量不足50 mm。经与公路养护人员核实,该部分公路水毁事故主要由河流上游泄洪或人为原因导致。剔除非降水原因导致的水毁记录,最终整理得到因降水诱发的公路水毁灾害数据
1383 条,具体分布见图1。1.2.3 有效雨量正态化处理
在进行建模前,为保证降水数据接近正态分布,对有效雨量数据进行预处理。常用的正态化方法包括对原始数据求平方根、对数或者倒数等。陈力强等[17]对辽宁地区降水正态化处理研究中发现,对降水量开四次方处理,可以使数据服从正态分布,还可以得到其连续变化。因此本文采用此方法进行降水量数据的正态化处理,见式(2)。
(2) 式中:
1.2.4 高斯拟合
高斯拟合方程见式(3):
(3) 式中:
1.2.5 辽宁气象地理分区
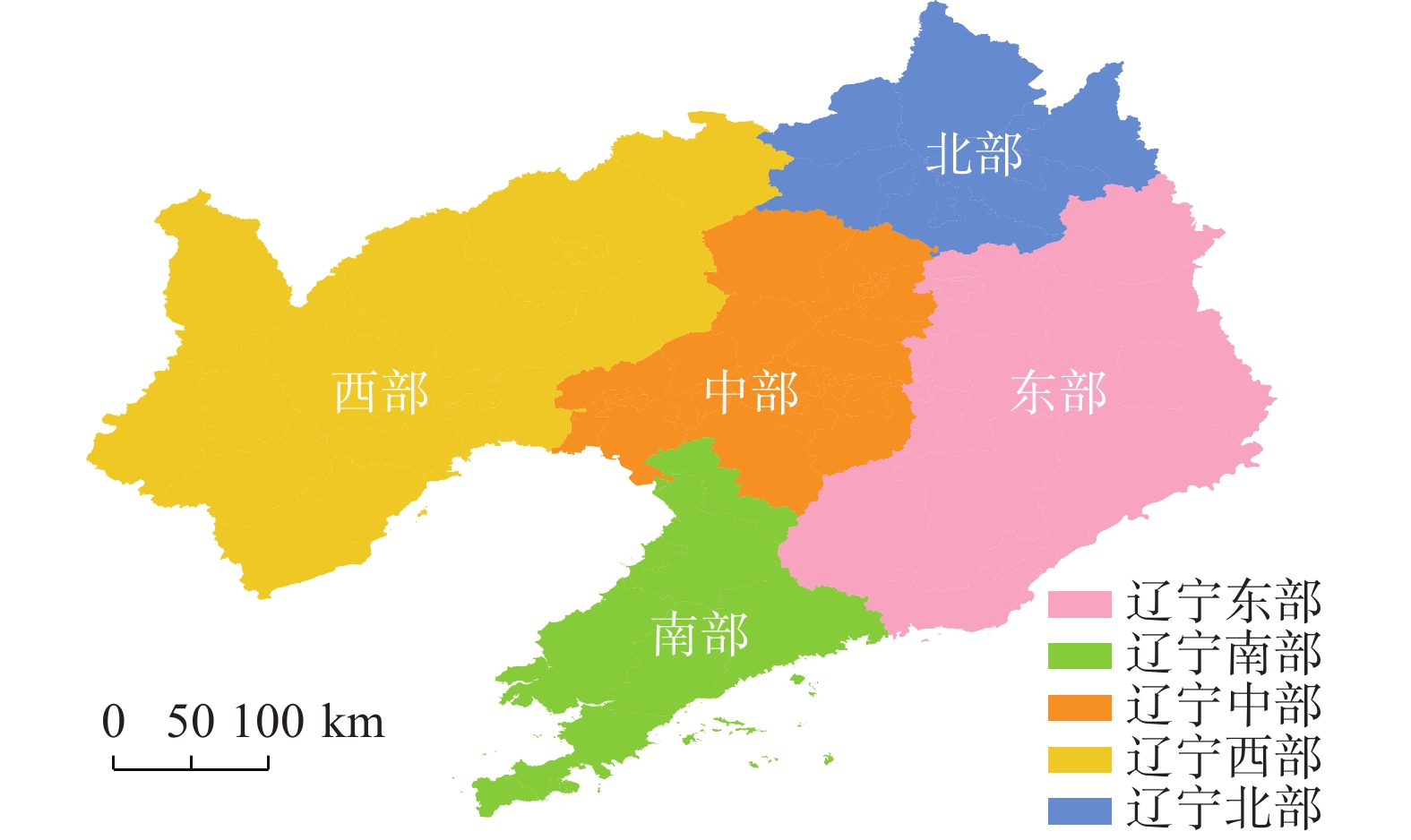
根据辽宁各地区地形、气候及常规习惯,将辽宁省分为东部、南部、中部、西部、北部共5个气象地理分区。本文按照图2对公路水毁记录进行分区处理,按分区分析诱发公路水毁的降水特征。
2. 结果分析
2.1 降水诱发的公路水毁
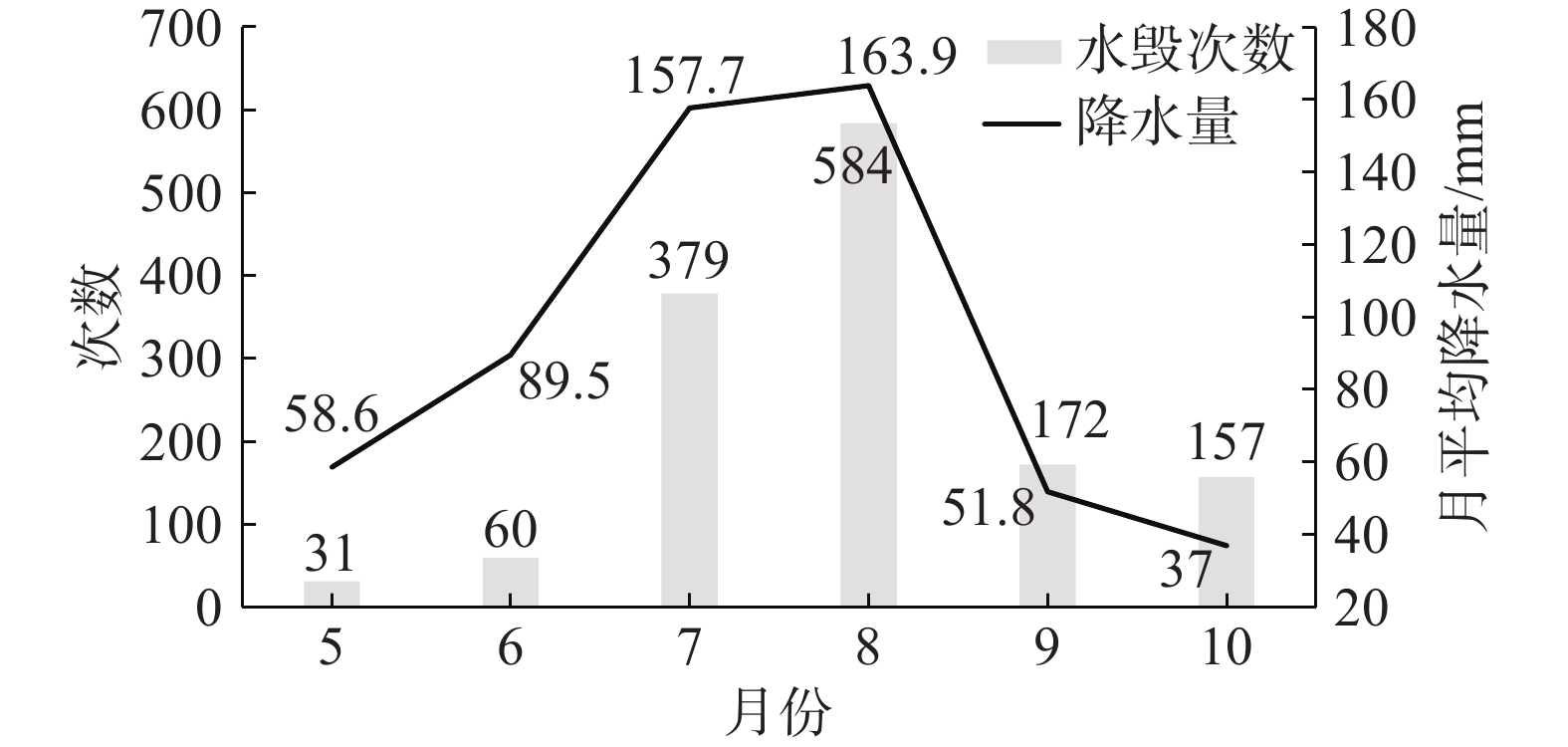
2017—2021年辽宁省公路水毁灾害发生数量及降水量见图3。辽宁公路水毁最早发生在5月,最晚发生在10月。初夏的5—6月平均降水量为58.6 mm和89.5 mm,公路水毁数量也相对较少。辽宁主汛期为每年7—8月,8月降水量为全年最多达到163.9 mm,其次为7月157.7 mm。7—8月辽宁公路水毁灾害发生量明显高于其他月份,其中8月水毁事故量为全年最多达到584起。9—10月辽宁进入秋季降水减少,虽然降水量低于5—6月,但公路水毁数量高于初夏阶段。综合分析5—10月水毁灾害数量与月份降水量数据,两者有较好的相关性,相关系数为0.83,达到0.05显著性水平。
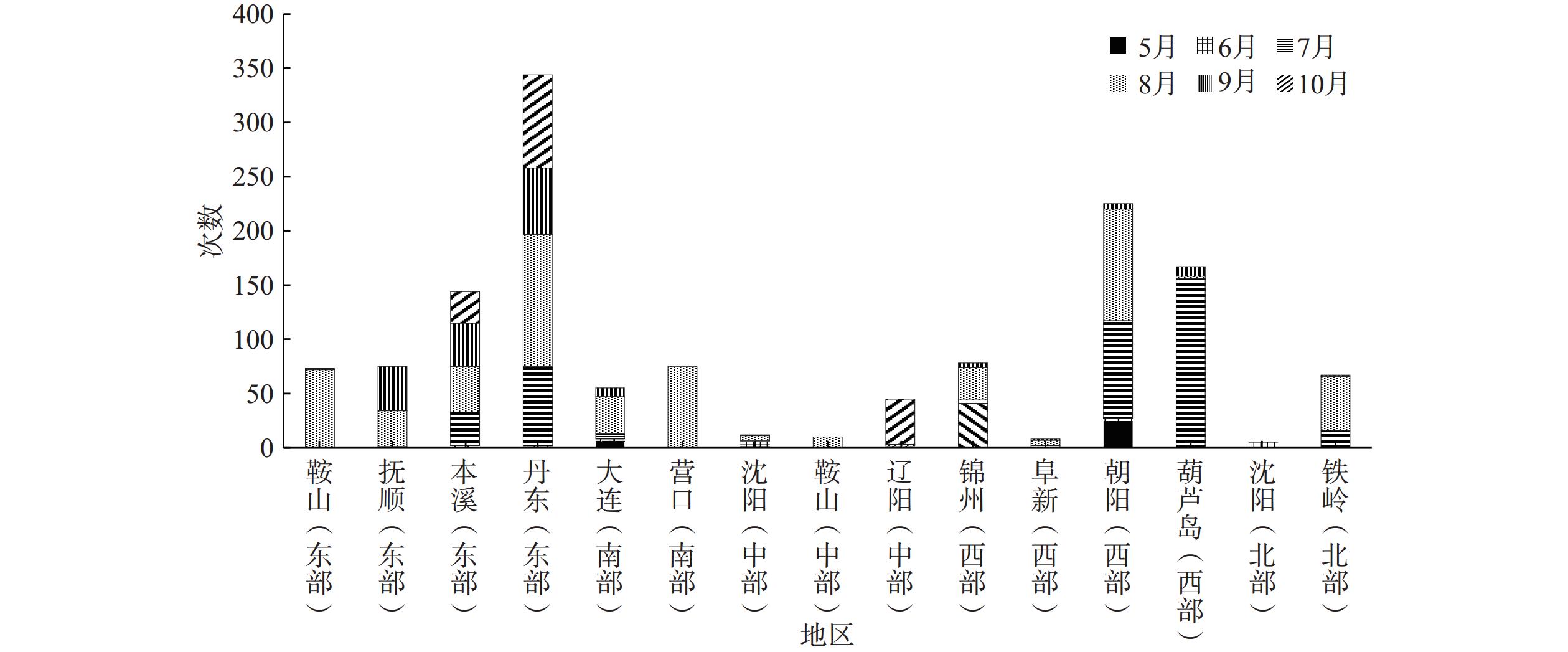
2017—2021年辽宁各地区水毁灾害统计见图4。辽宁东部发生公路水毁的数量明显高于其他地区,丹东地区共发生近350起水毁灾害,接近全省灾害总数的1/4。西部地区水毁事件发生差异性较大,朝阳、葫芦岛地区水毁数量排在全省第二和第三,而阜新为全省水毁事故发生较少地区。辽宁南部、中部、北部地区公路水毁发生相对较少。从各地区发生公路水毁的时间看,呈现出从西北向东南逐渐延后的规律。辽宁西部、东部均为公路水毁多发区域,两区域均多为山地丘陵地形,但水毁发生原因有所不同。辽东地形复杂、河流密集,山地丘陵区的棕壤土体稳定性相对较差[18]。受地形及环流影响,辽东地区为辽宁省内降雨频率最高、平均雨量最大地区[19],在气候和地质地貌条件叠加影响下东部公路水毁灾害频发。辽宁西部地区夏季平均雨量少于其他地区,辽西植被覆盖率较低砂土含量较高。近年来西部极端天气频发,在短时强降水冲击下,风化侵蚀后的土壤地区更易出现地质灾害,导致辽西公路水毁事件增多。
5月水毁主要出现在西部的朝阳地区,8月水毁主要出现在中部、南部大部,7—8月水毁多发生在西部。8—9月水毁主要出现在辽宁东部,10月公路水毁均出现在东部。9—10月辽宁进入秋季,大部地区降水明显减少,因此公路水毁数量也随之降低。9—10月东部丹东、本溪、抚顺地区月平均降雨量为137.9,111.2,104.1 mm,远高于全省其他地区月平均降水量82.3 mm,辽宁东部秋雨频繁是公路水毁的主要诱因。
2.2 基于有效雨量的公路水毁概率拟合
2.2.1 公路水毁发生概率分区拟合
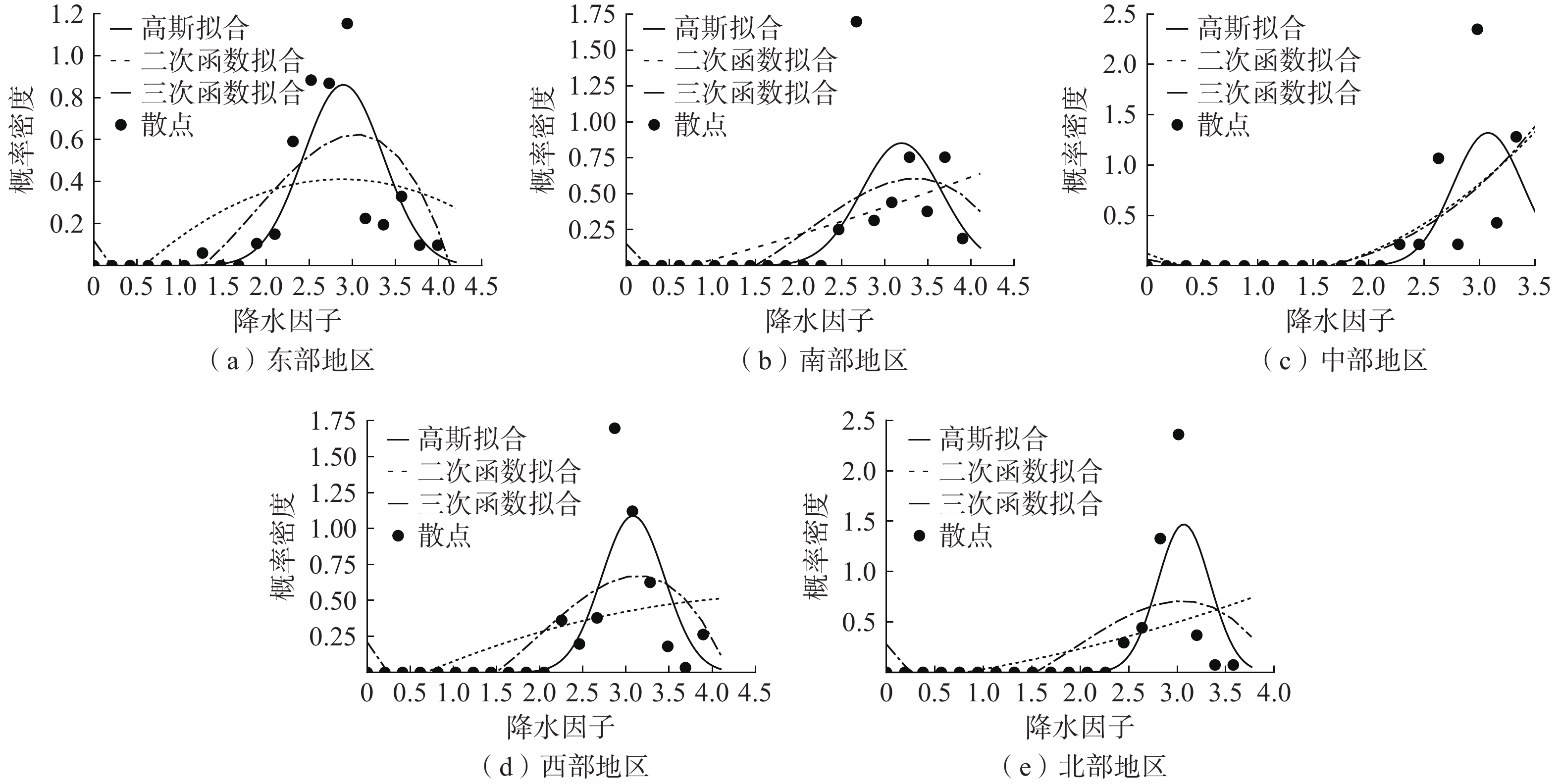
针对山洪泥石流等地质灾害的预报通常依据灾害孕灾环境和有效降雨量等雨量条件,采用统计分析方法或非线性数学模型,确定地质灾害易发性和致灾降雨阈值,建立风险概率预测预报经验公式[20]。概率密度函数对一般随机动力系统随机响应的演化分析具有普适性和高效性[21],在已有地质灾害气象风险研究中,概率密度函数和多项式方法在有效雨量拟合效果方面得到了普遍验证[22]。本文选用高斯概率密度函数建立有效雨量致灾概率拟合方程,同时利用二次、三次多项式函数拟合进行效果对比。2017—2021年辽宁各分区的致灾概率拟合结果见图5,各分区参数见表1。
表 1 高斯拟合方程参数表Table 1. Parameters of probability fitting equation for each region参数 东部 南部 中部 西部 北部 u 3.159 3.193 3.076 3.082 3.081 0.367 0.465 0.316 0.366 0.272 对比辽宁各分区的拟合效果,实际值更符合高斯拟合曲线,而三次函数拟合效果优于二次函数。尤其在公路水毁的概率密度数值较大区间,高斯拟合、三次函数均表现出对高值的拟合趋向。但高斯拟合的波峰更加接近概率密度最大值。相比高斯拟合和三次函数,二次函数由于曲线较为平直,拟合效果不佳。
2017—2021年辽宁各分区三种拟合方法的确定系数见表2。高斯拟合对于东部公路水毁概率的拟合效果最佳,确定系数达到0.970。辽宁西部、北部高斯拟合的确定系数均为0.8以上,明显优于其他两种拟合方法。而对于南部地区的拟合效果略逊于其他地区,但高斯拟合的确定系数为0.671仍高于二次函数的0.554以及三次多项式的0.643。综上所述,选择高斯拟合计算致灾雨量阈值。
表 2 三种拟合方法的确定系数Table 2. Determination coefficients of three fitting methods分区 高斯拟合 二次多项式 三次多项式 辽宁东部 0.970 0.566 0.810 辽宁南部 0.671 0.554 0.643 辽宁中部 0.769 0.733 0.735 辽宁西部 0.886 0.496 0.679 辽宁北部 0.881 0.455 0.572 2.2.2 公路水毁致灾临界雨量
根据灾害发生概率划分风险等级,通过计算灾害发生概率所对应的因子值作为灾害发生概率时的临界值。本文根据有效雨量致灾概率划分降水风险等级,有效雨量致灾概率数值<20%、20%~40%、40%~60%、60%~80%、>80%,对应降水风险等级的低风险、较低风险、中等风险、较高风险、极高风险。通过式(3)和表1对应各分区参数,分别计算不同地区致灾概率为20%、40%、60%、80%对应的有效雨量,得到的有效雨量值即为临界雨量值(表3)。
表 3 降水风险等级及致灾概率对应临界雨量Table 3. Corresponding critical rainfall for precipitation risk levels and disaster probability/mm 分区 较低风险(20%) 中等风险(40%) 较高风险(60%) 极高风险(80%) 东部 66.0 88.4 111.9 144.7 南部 61.7 89.5 120.3 165.3 中部 62.3 80.5 99.2 124.8 西部 59.2 79.8 101.6 132.1 北部 64.9 80.8 96.7 118.0 对比辽宁各分区公路水毁致灾临界雨量,当降水风险在中等以下时,各分区较为接近,同级别内最大和最小有效雨量值相差不足10 mm。当出现90 mm以内的有效雨量时,辽宁西部较其他地区相比更容易发生公路水毁。降水风险为较高和极高风险等级时,不同分区的有效雨量差距超过40 mm。辽宁南部致灾临界雨量最大,其次为东部、西部。中部、北部临界雨量接近,小于辽宁其他分区。当出现100 mm以上有效雨量的强降水时,平原地貌的中部、北部地区发生公路水毁的风险高于以山地丘陵地貌的东部、南部地区。
2.3 公路水毁风险评价结果验证
2022年7月27—30日,辽宁西部、北部出现强降水天气,多地发生洪涝灾害,29日辽河支流绕阳河发生有实测资料以来最大洪水。收集整理降水过程期间逐日降水量观测记录(20时—20时)、干线公路水毁记录,分地区计算有效雨量致灾概率及风险评价等级,通过与公路水毁发生情况比对验证风险评价效果。
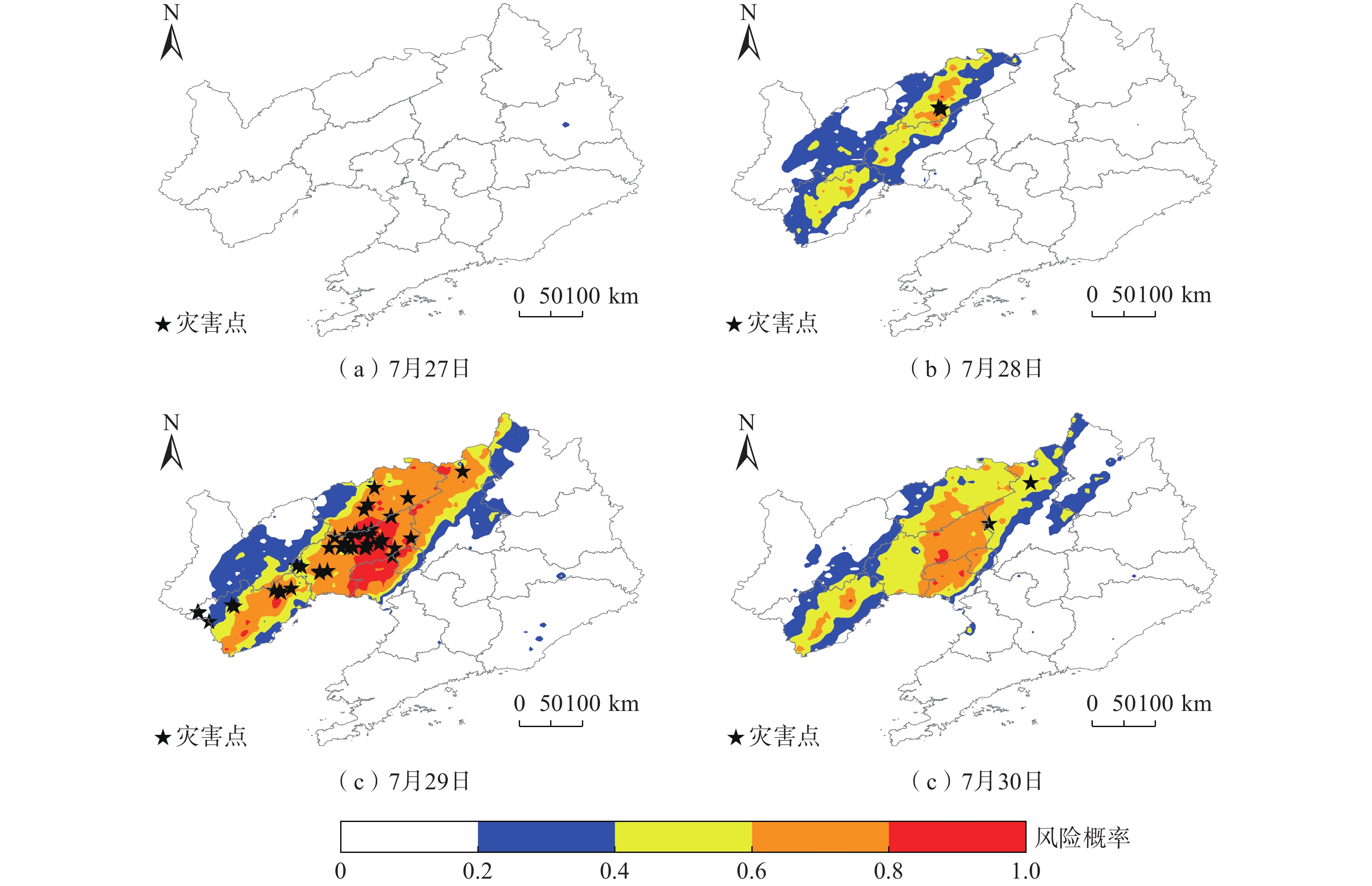
按照表3划定的降水风险等级,绘制公路水毁概率风险分布图(图6)。7月27日傍晚降水过程开始,当日全省公路水毁风险低。28日阜新、锦州、朝阳、葫芦岛多地出现100 mm以上大暴雨,锦州、阜新、葫芦岛局部地区的公路水毁风险达到极高等级,阜新、锦州大部地区公路水毁风险达到中等风险。7月29日雨带东移,沈阳、锦州、盘锦、鞍山、铁岭出现大暴雨,最大日雨量165.8 mm出现在锦州北镇市。29日公路水毁风险达极高风险范围,较28日相比向东西两侧延伸,阜新、锦州、盘锦交界地带公路水毁风险极高,辽宁西部的大部地区风险较高。30日降水减弱,铁岭、营口部分地区出现暴雨,其他大部分地区小到中雨。30日较高风险、极高风险范围明显缩小,但受前期降水影响,沈阳西部及辽西东部存在小范围极高风险区域。
2022年7月27—30日辽宁干线公路共出现89起公路沿线水毁事件,发生位置在图6中以星形标出。7月27日当天未发生公路水毁。7月28日降雨开始增强,阜新发生3起水毁事故。7月29日辽宁5个地市共发生83起公路水毁,锦州各区县累计发生51起。29日阜新降水减弱,但公路水毁数量较28日相比增多4起。葫芦岛地区出现10起,沈阳出现6起。7月30日降水减弱,公路水毁事件明显减少,沈阳新民、法库共出现3起公路水毁。从降水与水毁灾害发生时间来看,28日强降水第一天出现小范围少量水毁,29日强降雨第二天水毁数量激增且范围显著扩大,水毁类型多为河水上涨冲刷路基以及桥梁、边沟、挡墙等公路设施损毁。连续强降水作用下,河流水位超高、公路排水设施外溢对公路安全造成较大影响。
水毁风险基于致灾概率进行评价,因此利用是否发生公路水毁检验评价结果。从水毁数据中筛选出发生水毁点位数量及对应风险区(表4)。强降水期间发生的89起公路水毁分布在48处公路沿线点位,其中27处位于较高风险区内,极高风险区、中等风险区内分别出现12处、5处水毁点。本文利用召回率指标对评价结果进行衡量。计算公式见式(4):
表 4 公路水毁点位数量及所在风险区Table 4. Statistics of highway flood damage points and risk levels日期 27日 28日 29日 30日 低风险 — — 1 — 较低风险 — — 3 — 中等风险 — 1 3 1 较高风险 — 2 24 1 极高风险 — — 12 — (4) 式中:R——发生公路发生水毁的样本有多少被正确评价;
对比极高风险、较高风险、中等风险评价结果的召回率,较高风险的召回率最大为56.3%,其次为极高风险25%和中等风险10.4%。将多个公路水毁风险评价等级合并,对形成的风险综合评价结果进行验证:较高以上风险的召回率为81.3%,中等以上风险的召回率为91.7%,公路水毁综合评价能够涵盖超九成的公路水毁事件。
3. 结论
(1)2017—2021年辽宁省公路水毁一般出现在5—10月。5—6月灾害发生量较少,7—8月是水毁发生最多的2个月。辽宁公路水毁发生时间为从西北向东南逐渐延后,5月的公路水毁多出现在辽宁西北部的朝阳地区,10月出现在辽宁东部的本溪、丹东地区。公路水毁事故发生数量与月降水量有较高的相关性。辽宁东部、西部为高发区,发生数量明显高于南部、北部及中部地区。其中,丹东、朝阳、葫芦岛、本溪是辽宁公路水毁高发地区。在降水作用影响以外,还可能与辽宁东部、西部多为山地丘陵地貌有关。
(2) 高斯概率密度分布函数对公路水毁概率的拟合效果好于二次函数和三次函数,但不同分区拟合效果差别明显。高斯拟合在东部、西部的效果较好,但在中部、南部效果一般,这可能与东部、西部水毁数量较多,诱发水毁的降雨过程较为分散,因而概率分布函数更易拟合。中部、南部水毁数量较少,且水毁天气过程较为集中导致拟合效果下降。
(3)在相同降水条件下,平原地貌地区公路水毁风险高于山地丘陵地貌地区。可能与辽宁东部、南部过往强降水导致的水毁事故频发,近年来巡查及时、防范得当有关。中部、北部、西部地区由于过往水毁事故发生数量相对较少,防范准备工作没有高发地区充分。因此,公路防汛应参考致灾临界雨量及水毁风险预警,有针对性地强化汛期防灾薄弱环节。
(4)从检验结果看,超八成公路水毁发生在评价结果为较高以上风险地区,中等以上风险地区覆盖的公路水毁超九成。在公路汛期防洪工作中,应对中等以上风险公路进行巡查,重点看守较高以上风险路段。
(5)在公路防汛和交通气象服务业务中,综合利用日雨量、小时雨量和滚动降水预报形成的动态有效雨量,将有助于增强公路水毁风险评价的时效性。将公路水毁风险普查信息融入风险评价过程,能够进一步提升公路水毁隐患点风险评价的准确性。
-
表 1 高斯拟合方程参数表
Table 1 Parameters of probability fitting equation for each region
参数 东部 南部 中部 西部 北部 u 3.159 3.193 3.076 3.082 3.081 0.367 0.465 0.316 0.366 0.272 表 2 三种拟合方法的确定系数
Table 2 Determination coefficients of three fitting methods
分区 高斯拟合 二次多项式 三次多项式 辽宁东部 0.970 0.566 0.810 辽宁南部 0.671 0.554 0.643 辽宁中部 0.769 0.733 0.735 辽宁西部 0.886 0.496 0.679 辽宁北部 0.881 0.455 0.572 表 3 降水风险等级及致灾概率对应临界雨量
Table 3 Corresponding critical rainfall for precipitation risk levels and disaster probability
/mm 分区 较低风险(20%) 中等风险(40%) 较高风险(60%) 极高风险(80%) 东部 66.0 88.4 111.9 144.7 南部 61.7 89.5 120.3 165.3 中部 62.3 80.5 99.2 124.8 西部 59.2 79.8 101.6 132.1 北部 64.9 80.8 96.7 118.0 表 4 公路水毁点位数量及所在风险区
Table 4 Statistics of highway flood damage points and risk levels
日期 27日 28日 29日 30日 低风险 — — 1 — 较低风险 — — 3 — 中等风险 — 1 3 1 较高风险 — 2 24 1 极高风险 — — 12 — -
[1] 王振刚,赵甫. 公路沿线地质灾害孕灾环境与诱灾因子分析[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2020,18(5):85 − 90. [WANG Zhengang,ZHAO Fu. Geological-disaster environment and disaster-inducing factors along the highway in mountain area[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2020,18(5):85 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Zhengang, ZHAO Fu. Geological-disaster environment and disaster-inducing factors along the highway in mountain area[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2020, 18(5): 85 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 赵建军. 公路边坡稳定性快速评价方法及应用研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2007. [ZHAO Jianjun. Study and application on rapid slope stability evaluation method for highway[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHAO Jianjun. Study and application on rapid slope stability evaluation method for highway[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 杨志华,吴瑞安,郭长宝,等. 川西巴塘断裂带地质灾害效应与典型滑坡发育特征[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(2):355 − 368. [YANG Zhihua,WU Ruian,GUO Changbao,et al. Geo-hazard effects and typical landslide characteristics of the Batang fault zone in the western Sichuan[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(2):355 − 368. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Zhihua, WU Ruian, GUO Changbao, et al. Geo-hazard effects and typical landslide characteristics of the Batang fault zone in the western Sichuan[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(2): 355 − 368. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 刘艳辉,方然可,苏永超,等. 基于机器学习的区域滑坡灾害预警模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(1):116 − 124. [LIU Yanhui,FANG Ranke,SU Yongchao,et al. Machine learning based model for warning of regional landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(1):116 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Yanhui, FANG Ranke, SU Yongchao, et al. Machine learning based model for warning of regional landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(1): 116 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 祝建,朱冬春,刘卫民. 川藏公路(西藏境)地质灾害类型与分布规律研究[J]. 灾害学,2018,33(增刊1):18 − 24. [ZHU Jian,ZHU Dongchun,LIU Weimin. Types and distribution of geological hazards in Sichuan Tibet highway (Tibet Border)[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2018,33(Sup 1):18 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHU Jian, ZHU Dongchun, LIU Weimin. Types and distribution of geological hazards in Sichuan Tibet highway (Tibet Border)[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2018, 33(Sup 1): 18 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 于秀珍,牟瑞芳. 雅康高速公路沿线地质灾害分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 安全与环境学报,2022,22(2):876 − 884. [YU Xiuzhen,MOU Ruifang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of geological disasters along Yakang expressway[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2022,22(2):876 − 884. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YU Xiuzhen, MOU Ruifang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of geological disasters along Yakang expressway[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(2): 876 − 884. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李守定,乔华,马世伟,等. 基于温度-降雨双参数的新疆地质灾害预警模型[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文),2021,52(11):207 − 218. [LI Shouding,QIAO Hua,MA Shiwei,et al. Temperature-rainfall dual parameter-based early warning model for geological disasters in Xinjiang[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2021,52(11):207 − 218. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Shouding, QIAO Hua, MA Shiwei, et al. Temperature-rainfall dual parameter-based early warning model for geological disasters in Xinjiang[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2021, 52(11): 207 − 218. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 狄靖月,王志,田华,等. 降水引发的西南地区公路损毁风险预报方法[J]. 应用气象学报,2015,26(3):268 − 279. [DI Jingyue,WANG Zhi,TIAN Hua,et al. A risk forecast method for southwest road damages based on precipitation[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science,2015,26(3):268 − 279. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DI Jingyue, WANG Zhi, TIAN Hua, et al. A risk forecast method for southwest road damages based on precipitation[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2015, 26(3): 268 − 279. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王志,田华,狄靖月,等. 降水引发的中国公路损毁灾害时空变化特征[J]. 气象与环境学报,2018,34(4):98 − 104. [WANG Zhi,TIAN Hua,DI Jingyue,et al. Research on the tempo-spatial characteristics of road damage induced by precipitation in China[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment,2018,34(4):98 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Zhi, TIAN Hua, DI Jingyue, et al. Research on the tempo-spatial characteristics of road damage induced by precipitation in China[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018, 34(4): 98 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 尹春荣, 李媛, 曲雪妍, 等. 中国地质灾害数据质量评价指标体系构建[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):120 − 125. [YIN Chunrong, LI Yuan, QU Xueyan, et al. Formulation of an evaluation index system of geological hazard data quality in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):120 − 125. (in Chinese)] YIN Chunrong, LI Yuan, QU Xueyan, et al. Formulation of an evaluation index system of geological hazard data quality in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(4): 120 − 125. (in Chinese)
[11] 辽宁省国土资源厅. 辽宁省地质灾害防治规划[Z]. 2018. [Department of Land and Resources of Liaoning Province. Liaoning Province geological disaster prevention and control plan[Z].2018. (in Chinese)] Department of Land and Resources of Liaoning Province. Liaoning Province geological disaster prevention and control plan[Z].2018. (in Chinese)
[12] 殷坤龙,张桂荣. 地质灾害风险区划与综合防治对策[J]. 安全与环境工程,2003,10(1):32 − 35. [YIN Kunlong,ZHANG Guirong. Risk zonation of geo-hazards and its comprehensive control[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2003,10(1):32 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YIN Kunlong, ZHANG Guirong. Risk zonation of geo-hazards and its comprehensive control[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2003, 10(1): 32 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] CROZIER M J. Landslides:causes,consequences,and environment[M]. London:Croom Helm,1986.
[14] 中国气象局. 暴雨诱发的地质灾害气象风险预警等级:QX/T 487—2019[S]. 北京:气象出版社,2019. [China Meteorological Bureau of the People’s Republic of China. Meteorological risk early warning levels of geological disaster induced by torrential rain:QX/T 487—2019[S]. Beijing:China Meteorological Press,2019. (in Chinese)] China Meteorological Bureau of the People’s Republic of China. Meteorological risk early warning levels of geological disaster induced by torrential rain: QX/T 487—2019[S]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[15] 狄靖月,许凤雯,李宇梅,等. 东南地区引发地质灾害降水分型及阈值分析[J]. 灾害学,2019,34(1):62 − 67. [DI Jingyue,XU Fengwen,LI Yumei,et al. Precipitation type and threshold analysis of geological disasters in southeast[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2019,34(1):62 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DI Jingyue, XU Fengwen, LI Yumei, et al. Precipitation type and threshold analysis of geological disasters in southeast[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2019, 34(1): 62 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 陈静静,姚蓉,文强,等. 湖南省降雨型地质灾害致灾雨量阈值分析[J]. 灾害学,2014,29(2):42 − 47. [CHEN Jingjing,YAO Rong,WEN Qiang,et al. Hazard rainfall threshold analysis of rainfall-induced geological disasters in Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2014,29(2):42 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHEN Jingjing, YAO Rong, WEN Qiang, et al. Hazard rainfall threshold analysis of rainfall-induced geological disasters in Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2014, 29(2): 42 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 陈力强,韩秀君,张立祥. 基于MM5模式的站点降水预报释用方法研究[J]. 气象科技,2003,31(5):268 − 272. [CHEN Liqiang,HAN Xiujun,ZHANG Lixiang. Study of station precipitation forecasting method based on MM5 model output[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology,2003,31(5):268 − 272. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2003.05.003 CHEN Liqiang, HAN Xiujun, ZHANG Lixiang. Study of station precipitation forecasting method based on MM5 model output[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 2003, 31(5): 268 − 272. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2003.05.003
[18] 张若凝. 辽宁省降雨型泥石流易发区评价及预测预警[D]. 大连:辽宁师范大学,2022. [ZHANG Ruoning. Evaluation and prediction of debris flow susceptibility in Liaoning Province[D]. Dalian:Liaoning Normal University,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Ruoning. Evaluation and prediction of debris flow susceptibility in Liaoning Province[D]. Dalian: Liaoning Normal University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 公颖,周小珊,董博. 辽宁夏季降水时空分布特征及其成因分析[J]. 暴雨灾害,2018,37(4):373 − 382. [GONG Ying,ZHOU Xiaoshan,DONG Bo. The characteristic analysis and the research on the mechanism of the summer precipitation in Liaoning Province[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters,2018,37(4):373 − 382. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9045.2018.04.010 GONG Ying, ZHOU Xiaoshan, DONG Bo. The characteristic analysis and the research on the mechanism of the summer precipitation in Liaoning Province[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 2018, 37(4): 373 − 382. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9045.2018.04.010
[20] 王高峰,高幼龙,姚亚辉,等. 甘肃省白龙江流域降雨型潜在泥石流危险性预报模型[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(3):732 − 748. [WANG Gaofeng,GAO Youlong,YAO Yahui,et al. Prediction model of potential debris flow hazard of rainfall type in Bailong River Basin,Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(3):732 − 748. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Gaofeng, GAO Youlong, YAO Yahui, et al. Prediction model of potential debris flow hazard of rainfall type in Bailong River Basin, Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(3): 732 − 748. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] LI Jie,CHEN Jianbing. The principle of preservation of probability and the generalized density evolution equation[J]. Structural Safety,2008,30(1):65 − 77. DOI: 10.1016/j.strusafe.2006.08.001
[22] 李宇梅,狄靖月,许凤雯,等. 基于当日临界雨量的国家级地质灾害风险预警方法[J]. 气象科技进展,2018,8(3):77 − 83. [LI Yumei,DI Jingyue,XU Fengwen,et al. A risk warning method based on the intraday critical precipitation for national geological disaster[J]. Advances in Meteorological Science and Technology,2018,8(3):77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Yumei, DI Jingyue, XU Fengwen, et al. A risk warning method based on the intraday critical precipitation for national geological disaster[J]. Advances in Meteorological Science and Technology, 2018, 8(3): 77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)




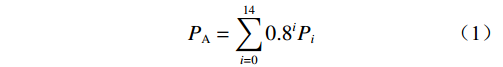
 下载:
下载:
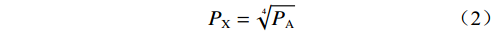
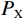
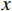
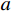
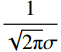
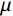
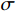
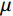
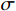
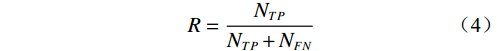
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS