Stability assessment of the road cut slopes in the Xigeda mudstone considering long-term creep deterioration and suggestion for countermeasures: A case study of cut slopes along the Xichang–Panzhihua Expressway
-
摘要:
昔格达黏土岩存在长期蠕变劣化强度折减及饱水软化等不利工程特性,为典型易滑地层。此地层路堑边坡在运营期会持续劣化、稳定性降低,极易产生滑坡,对公路运营安全产生重大威胁。通过对西攀高速公路K2378+900右侧滑坡进行地质分析、数值模拟计算及相互验证,得到边坡在开挖建成及临滑两阶段的抗剪强度参数值,并据此计算出昔格达黏土岩长期蠕变劣化黏聚力(c)及内摩擦角(φ)值的折减系数分别为0.87,0.84。对5类、17种昔格达黏土岩边坡进行最危险滑裂面搜索及稳定性的计算分析得出:在抗剪参数按0.84~0.87长期蠕变劣化折减时,边坡的稳定系数平均降低0.184。基于此,对边坡稳定系数取值、坡比、支挡加固方式等昔格达黏土岩公路边坡长期稳定的关键因素提出了针对性管控建议,指出采用“缓放坡+宽平台+弱加固”的建设及处治思路更有利于昔格达黏土岩边坡长期稳定。研究结果为昔格达岩层区公路建设及边坡防护处治提供了重要指导和借鉴意义。
Abstract:The Xigeda clay-rock strata exhibit typical characteristics of long-term creep deterioration and saturation softening, which is typical slide-prone stratum. Landslides are easily formed in Xigeda strata cut slope due to the continuous deterioration and stability reduction during the operation period, which poses great threats to operational safety. The reduction coefficients for the c and φ values due to long-term creep deterioration of Xigeda clay-rock are determined as 0.87 and 0.84 respectively. These values are derived from shear strength parameters of slope excavation and sliding obtained through geological analysis, discrete element numerical simulation, and mutual verification involving the K2378 + 900 right-side landslide on the Xichang-Panzhihua Expressway. By conducting critical slip surface searches and stability calculations for 17 distinct Xigeda clay-rock slopes representing 5 different types, the average decrease of stability coefficient is found to be 0.184 when shear parameters are reduced in accordance with creep deterioration within the range of 0.87~0.84. Consequently, targeted recommendations are proposed for key factors influencing the long-term stability of Xigeda clay-rock slopes, encomPassing safety coefficients, slope ratios, and reinforcement measures. It is demonstrated that employing a construction approach characterized by a gentler slope, wider platforms, and less intensive reinforcement is proved to be more conducive to the slope long-term stability. The research results provide important guidance and reference for highway construction and slope protection treatment within the Xigeda stratum area.
-
0. 引言
昔格达地层是形成于新近纪上新世(N2)—第四纪更新世(Qp)的河湖相沉积物,其作为广泛分布在四川西南攀枝花、西昌的区域性半成岩“易滑”地层[1],具成岩新、胶结差、结构松、吸水软化、易脱水崩解等特点,工程性质较差[2]。该地层赋存环境效应和时间效应强烈,岩体水敏性高,环境条件变化下其力学性能将大幅降低,即存在时间效应上的蠕变特性[3],对公路边坡开挖及公路运营的稳定造成不利影响。蠕变是滑坡演变的早期形态[4],大量研究人员[5 − 9]对滑坡滑带、软弱层剪切蠕变特性做了分析总结及模型建立研究。
针对昔格达地层的研究主要从2000年以后攀西地区西攀、攀田、丽攀等高速修建开始[10];依托新九路对昔格达地层的工程物理、水理及力学性质进行试验研究[11 − 13]。一方面,通过昔格达层黏土岩进行室内及现场剪切试验,分析昔格达滑坡及边坡的稳定性[13 − 15]。另一方面,通过模型试验、室内蠕变试验、数值模拟等方法对昔格达层黏土岩的长期蠕变特这一动力特征开展研究,吴焕恒[3]通过蠕变试验分析研究了攀西地区昔格达地层长期强度参数及强度随时间的折减情况,并结合有限元模拟分析昔格达地层边坡的蠕变过程。张家明等[16]通过大量动三轴试验建立了昔格达黏土岩的动应力-应变关系曲线。
总体上,对昔格达黏土岩长期蠕变研究主要集中在宏观的蠕变试验上,依据大量蠕变试验数据建立本构模型及应力-应变关系曲线,这也是广泛运用于在岩土体蠕变特性研究的方法[4 − 5, 17 − 19]。但由于昔格达黏土层抗剪参数受矿物成分、粒度分布、含水量等多重因素影响,实际工程中试验剪切强度值与实际值存在较大差异且变化范围极大,而获取准确的长期蠕变参数需要在较长时间维度下进行[18],因此,昔格达黏土岩边坡防护设计基本均未考虑其长期蠕变劣化特性,仅按一般边坡防护考虑,导致边坡在运营阶段出现滑移变形失稳。加之已有研究案例多针对公路建设阶段或国土部门滑坡,对长期运营中的昔格达黏土岩公路边坡长期蠕变后强度降低及稳定性劣化后产生的滑坡研究极少。
本文依托西攀高速公路K2378+900右侧路堑滑坡典型实例,在对滑坡进行详细调查的基础上,研究了昔格达黏土岩边坡长期蠕变劣化对坡体稳定性的影响,采用数值模拟及理论计算对比分析得出昔格达边坡长期蠕变劣化后强度折减系数,在考虑蠕变折减的基础上进行昔格达黏土岩边坡分类计算,并提出了针对昔格达黏土岩路堑边坡防护处治对策建议。
1. 工程概况
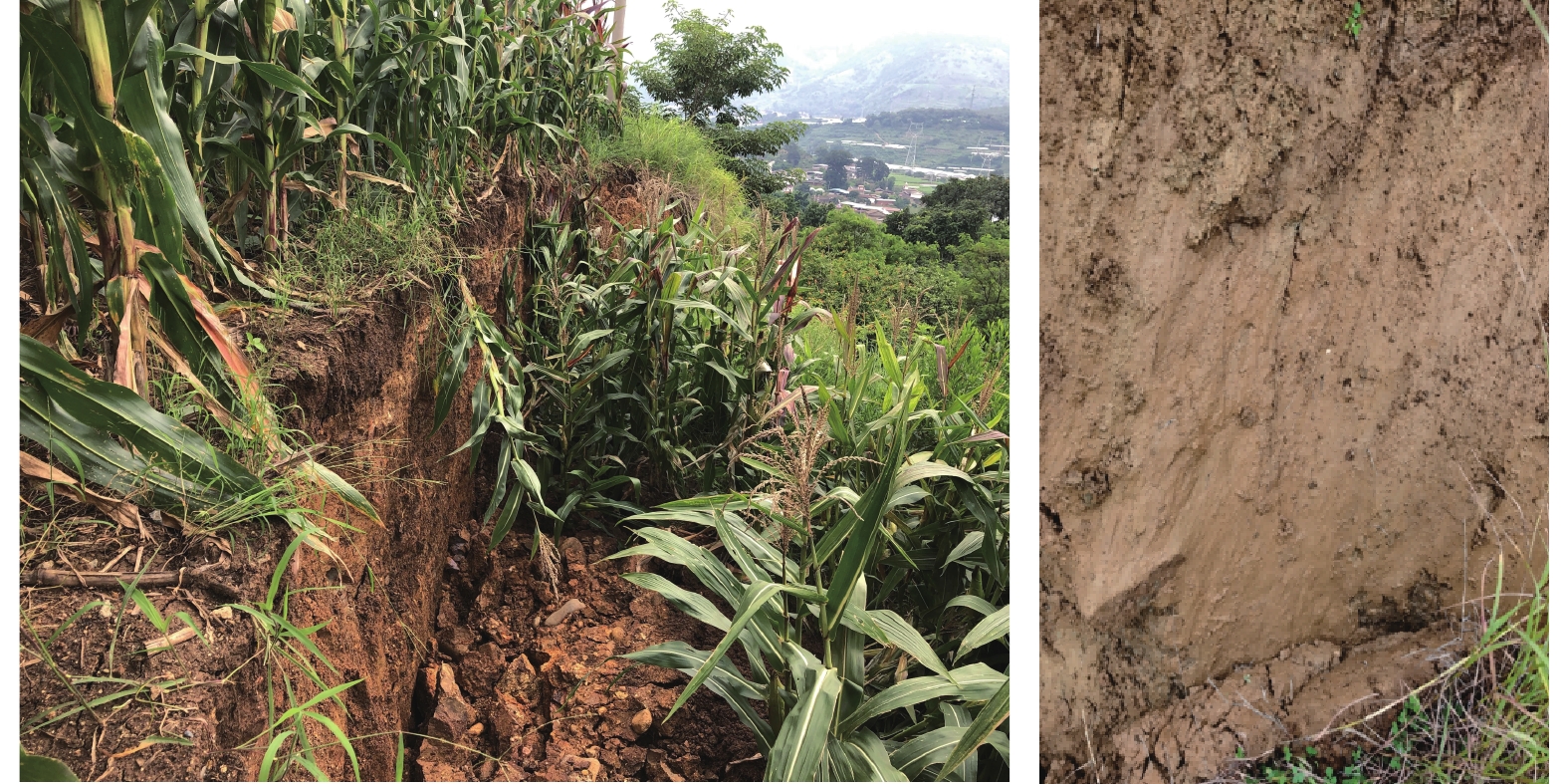
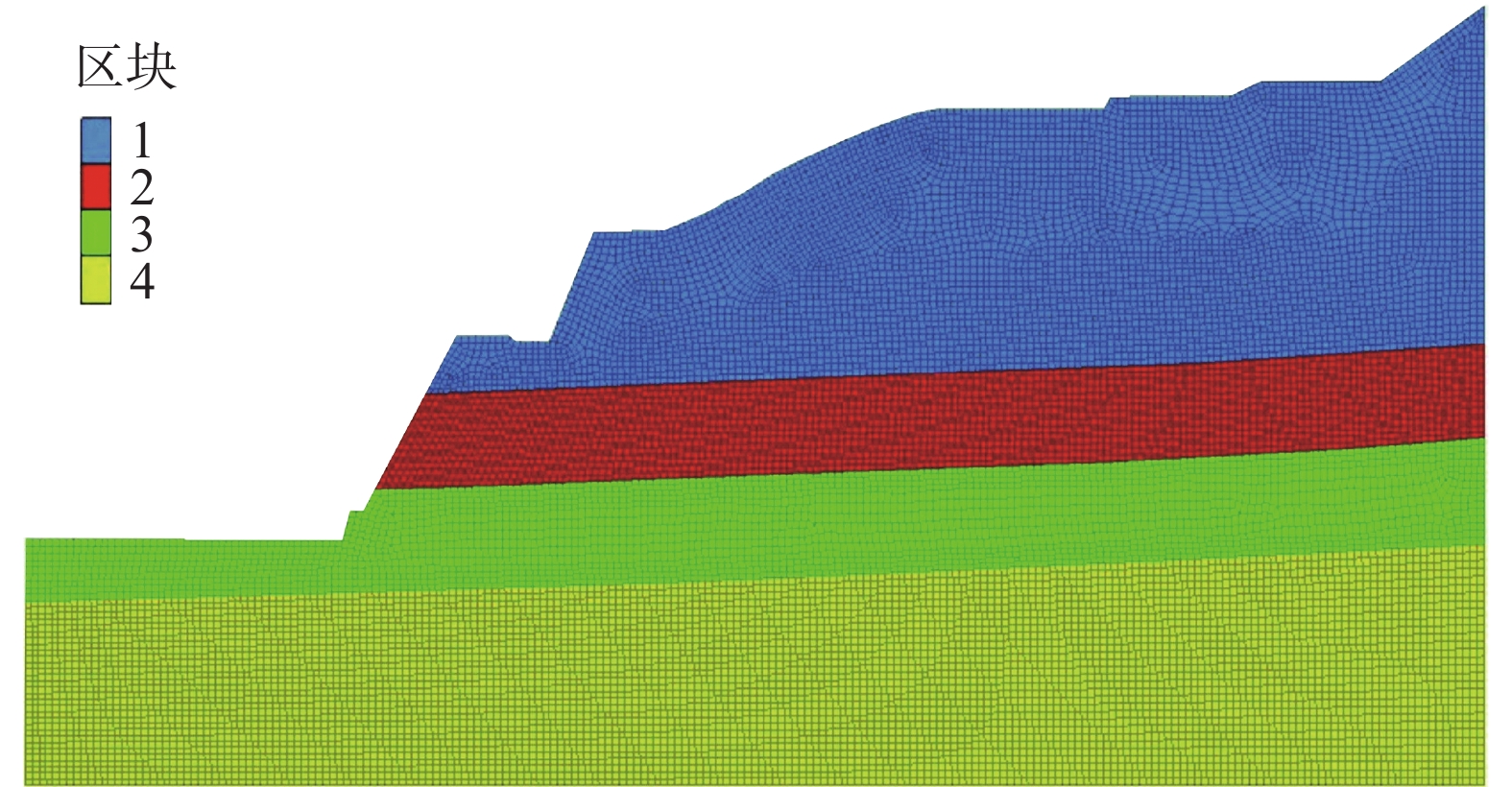
西攀高速公路K2378+900右侧滑坡位于四川米易县安宁河西侧约400 m处山前河谷冲蚀堆积区,为高17.6~19.2 m的两级路堑边坡,坡体中间设有5~6 m高重力式片石砼挡墙。2020年9月2日发生整体滑坡,导致西攀高速公路半幅中断。该滑坡平面呈圈椅状,平均厚度约10.5 m,总体积约2.3×104 m3,属小型中层滑坡(图1)。
滑坡上覆第四系晚更新统冲洪积层黄褐色含卵石黏土、黏土(Qpal+pl),下伏基岩为新近系上新统昔格达组泥岩(N2x)。滑体物质为黏土及强风化昔格达泥岩,滑面从坡体后缘穿过黏土、强风化泥岩后从坡脚剪出(图2—3)。滑动后形成2~2.5 m高的滑坡后壁,坡体中部挡墙、边沟以及砼平台大面积拱裂、反翘、挤爆,挡墙向高速公路方向整体推移超过2 m,护脚墙全部倾倒(图4—5)。
2. 昔格达黏土岩蠕变特征研究
蠕变是滑坡滑带土具有的典型特征,为诱发滑坡发生的重要因素[17, 20]。已有学者主要通过室内剪切蠕变试验,研究滑坡滑带土长期强度、蠕变曲线特征[21 − 23]。结果明确了滑带应力-应变特征的时效性及其对边坡长期稳定性的重要性[24 − 25]。而实际工程中很难取到典型的滑带样,因此很难通过取样进行室内剪切试验获取蠕变后的长期强度。本文对西攀高速K2378+900右侧滑坡昔格达黏土岩蠕变折减研究主要通过数值模拟和反演分析与现场实际变形情况进行对比验证确定。
2.1 滑带长期蠕变劣化强度折减系数
2.1.1 滑带长期强度参数
长期强度是土体经历长期荷载作用后的最小强度值,其与时间密切相关,为滑坡长期稳定性计算的重要参数[26]。西攀高速公路K2378+900右侧昔格达黏土岩边坡由于岩体的长期蠕变劣化而产生了整体滑坡,采用滑坡极限平衡计算分析及离散元数值计算相互校核验证以确定滑坡临滑状态滑带的强度参数,得到的强度参数即为昔格达黏土岩边坡历时13a蠕变折减后的长期强度参数。
根据滑坡变形特征、范围等推测确定了滑面位置(图6),恢复滑动前地面线按暴雨工况下0.98稳定系数进行临滑状态抗剪参数反算,反算取值及结果见表1,另外,西攀地区昔格达地层参数在原建设时期有大量实验数据在反算取值过程中可供参考[11, 15, 27]。
表 1 滑带参数反算结果表Table 1. Inversion calculation results of slope zone parameters地层 岩性 抗剪参数 备注 主滑段 抗滑段 牵引段 Qpal+pl 黏土 c=12 kPa、φ=10º — c=0 kPa
φ=40º按《公路滑坡防治设计规范》
稳定性计算采用“三段式”含卵石黏土 c=10 kPa、φ=13º — N2x 泥岩(强风化) c=18.4 kPa、φ=15.1º c=0 kPa、φ=25º 2.1.2 数值模拟分析
为研究该滑坡变形发展过程,验证根据变形特征推测滑移面深度、形态及反算得到的滑面长期抗剪强度参数的准确性,采用离散元数值模拟计算分析在临滑状态下滑坡的稳定状态(图7),该方法广泛用于滑坡实际工程案例分析[28],模拟在滑动前坡体变形失稳发展及应变等特征,数值模拟参数采用表1中的反算值(表2)。
表 2 数值模拟参数取值Table 2. Parameter value of numerical simulation参数 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 饱和 数值模拟采用层序号 重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) Qpal+pl黏 土 150 0.30 20.2 12.0 10.0 1 Qpal+pl含卵石黏土 220 0.29 20.7 10.0 13.0 2 N2x泥岩(强风化) 460 0.27 22.5 15.3 12.6 3 N2x泥岩(中风化) 510 0.26 17.4 14.3 4 图8(a)(b)为暴雨和地震工况边坡无支护条件下的剪应变增量图,表明了坡体内的强烈变形区潜在最危险滑面呈半径约25.6 m的圆弧形,最大变形深度为11.1~12.5 m,最大剪切变形位置距前缘坡脚平距约27 m。数值模拟结果显示其在无支护条件下边坡很容易变形发展为一边界清晰、滑面贯通的滑坡体,前缘坡脚为滑面剪出口,若产生滑动后缘可能整体下错产生较大位移。
图8(c)(d)为暴雨和地震工况路边坡无支护条件下的位移增量图,结果显示无支护条件的弹性自然状态下模拟计算结果不收敛,即如无外部约束,在暴雨和地震作用下的边坡变形将会无限制地逐渐增加,直至最终发生滑移破坏而失稳。若在弹性自然状态下计算6万步,得到的最大位移量出现在位移图红色区域内,说明该区域为最易产生滑移变形区域,暴雨及地震工况下最大位移分别为0.51,0.15 m,位移方向为向路面的临空面方向。
图8(e)(f)显示了暴雨和地震工况边坡的塑性变形区分布情况,剪切和张拉塑性变形区主要集中分布在滑坡坡口至前缘坡脚贯通的潜在滑面附近及二级边坡坡脚,最大深度约10 m。
综上:从数值模拟得到的应变增量、位移及塑形区分布结果来看,潜在滑面塑性区分布与其最大剪应变增量云图结果基本吻合,在暴雨和地震工况下边坡均处于欠稳定或不稳定状态,暴雨工况变形更为严重,边坡坡脚为塑性集中变形区,与本次滑坡体中部次级滑移面位置完全一致;坡体后缘与前缘坡脚形成一条弧形塑性变形带,该塑形变形带在坡体内的深度、位置与稳定性计算推测的滑移面也完全一致,表明滑坡就是沿该塑形变形带发展形成的贯通剪切滑移面产生。因此,地质分析及数值模拟两者的相互验证结果可基本确定昔格达泥岩历经13 a蠕变劣化后的长期强度为:c=15.3 kPa,φ=12.6°。
2.2 滑带初始峰值强度确定
在一定正压力条件下岩土体的剪切破坏前的临界抗剪强度值为峰值强度,严格意义上室内试验得到的抗剪参数均小于真实的峰值强度,昔格达黏土岩由于具吸水软化、弱膨胀等特殊性,很难获取抗剪峰值。吴焕恒[3]进行的18组昔格达黏土岩室内剪切试验及6组长期(90~120 d)蠕变剪切试验得到的西昌地区昔格达泥岩峰值强度和长期强度的关系为:φ∞=0.81φ峰,并建议采用0.78的折减系数,但由于试验数量偏少,本文不能直接使用。周罕等[29]对西昌某钢铁厂房基地的昔格达黏土岩进行了多组现场直剪试验,发现在饱和状态下抗剪强度黏聚力(c)及内摩擦角(φ)较天然状态分别降低29.7%、20.2%,同时统计得出了中风化黏土岩平均饱和内摩擦角为18.2°~22.8°。另外,根据西攀高速原建设阶段C7合同段K95—K99多处深挖路堑边坡的中风化昔格达泥岩试验值,推荐其抗剪强度指标为:30 kPa,25°。
由于该滑坡为岩土二元结构,黏土滑带土也存在蠕变,而黏性滑带土的蠕变试验已有大量研究成果[21, 25],黏性土c、φ值长期劣化折减系数为0.81~0.76,且随所含砂、砾等粗粒物质含量增高劣化幅度减小,本次黏土、含卵石黏土折减系数分别取0.80、0.78。
选取K2378+900边坡刚开挖完成时的土体强度作为初始峰值强度,上文模拟及计算得到的临滑状态参数为蠕变劣化后长期强度,即可得到昔格达黏土岩的长期蠕变劣化幅度。根据查阅原边坡设计及施工变更等相关资料,2008年该边坡前缘施工开挖完成后二级边坡靠红线附近产生浅表的滑动,一级边坡拱形骨架也有轻微拱起变形迹象,因此增加了挡墙对边坡进行支挡。
边坡开挖完成时稳定及应变情况数值模拟参数模拟取值详见表3。
表 3 边坡开挖完成时数值模拟参数取值Table 3. Parameter value of numerical simulation after slope excavation参 数 弹性模量
/MPa泊松比 饱和 重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/ kPa 内摩擦角/(°) Qpal+pl黏土 160 0.3 20.2 15.38 12.82 Qpal+pl含卵石黏土 230 0.28 20.7 12.50 16.25 N2x泥岩(强风化) 480 0.26 22.5 17.60 15.00 N2x泥岩(中风化) 520 0.25 27.70 18.20 数值模拟结果(图9)表明在边坡初始开挖完成后位移及剪切应变均出现在坡表附近,但位移量极小,累计位移不足3 cm,出现的位置及变形大小和原建设施工阶段产生的变形基本吻合,造成拱形骨架小范围变形及二级边坡的浅表溜滑,表明数值模拟计算采用的边坡建成初始强度参数合理基本合理,视其为初始峰值强度,即c=17.6 kPa、φ=15.0°。
综合上文来看,昔格达组黏土岩经历13 a蠕变劣化后c、φ值分别折减约0.87,0.84,这与上文吴焕恒[3]蠕变试验得到的0.81折减系数基本一致因为其历时大于20 a,因此折减系数更低。采用昔格达黏土岩初始强度参数对西攀K2378+900右侧边坡进行稳定性计算,得到开挖建成时暴雨工况下F=1.161,因此该边坡在经历13 a坡体的长期蠕变劣化后稳定性系数降低约0.181。
3. 长期稳定性防护对策建议
3.1 长期蠕变劣化稳定性分析
昔格达地层在攀西地区安宁河谷基座阶地及新九一带大面积分布,公路路堑边坡主要分为山前堆积斜坡区的岩土二元边坡及剥蚀强烈的陡坡段岩质边坡。为研究昔格达黏土岩在长期(t≥13 a)蠕变劣化后对开挖边坡的稳定性影响,根据上文对西攀高速K2 378+900右侧边坡滑坡的数值模拟结果及相关研究成果,取昔格达黏土岩长期蠕变劣化c、φ值强度折减系数分别为0.87、0.84,上覆第四系更新统(含砾、卵石)黏土综合折减系数取0.8。
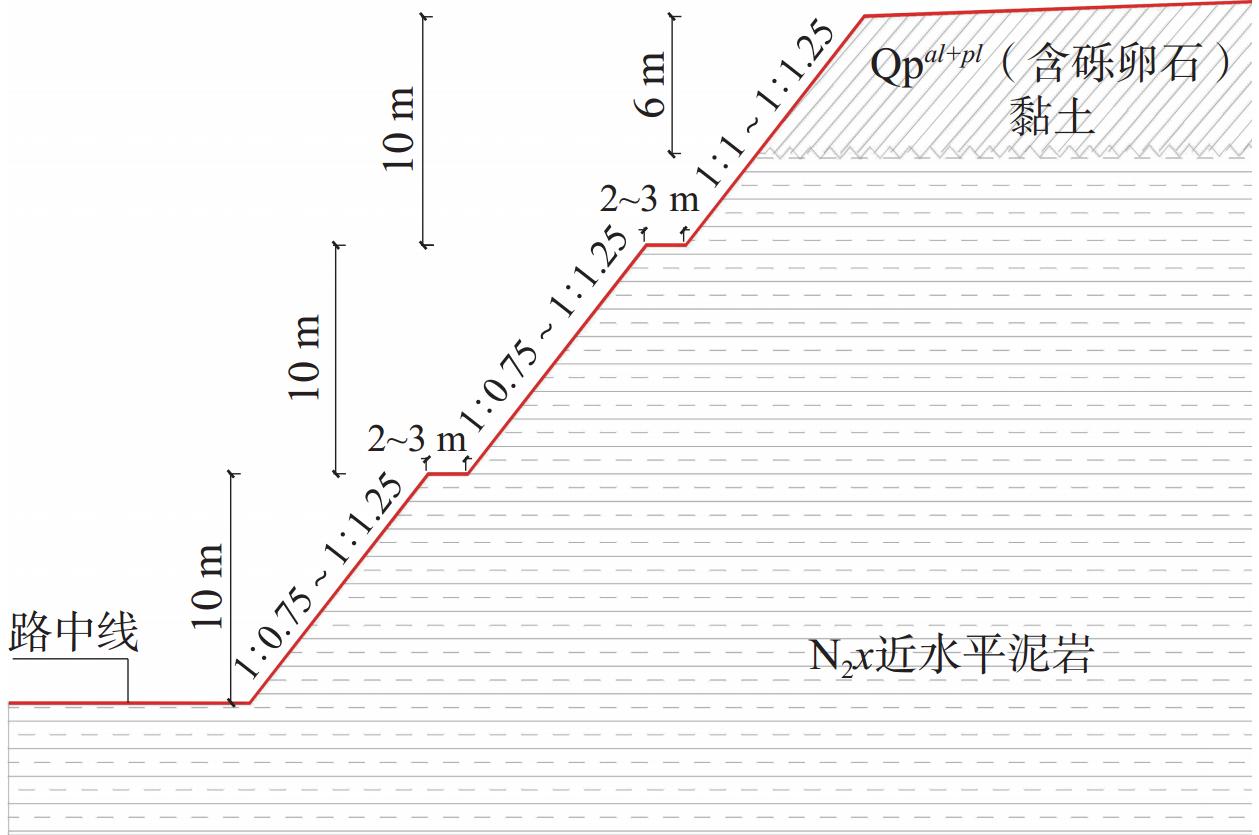
按坡高、坡比及结构性质分5个大类、17种昔格达黏土岩边坡,并分别进行计算分析。为简化模型,对岩土二元边坡按基覆界面近水平、厚度按5~8 m、平均约6 m考虑(表4、图10)。由于昔格达黏土岩边坡滑动面基本为圆弧形,采用理正中简化Bishop法自动搜索和计算最危险滑面位置、稳定系数,覆盖层饱和重度取20.2 kN/m3,昔格达黏土岩饱和重度取值22.5 kN/m3,根据周罕等[29]、邓夷明等[15]、杨碧等[30]的大量室内、现场剪切试验及文丽娜等[10 − 11]在原西攀高速新九段建设时昔格达层岩土参数的试验统计成果,取边坡开挖后初始状态的力学参数c=30 kPa、φ=25 kPa,对表4中17种昔格达黏土岩边坡进行蠕变劣化强度折减前后的两阶段计算(表5)。
表 4 路堑边坡分类表Table 4. Classification table for cut slopes坡型 坡高/m 坡比 坡体结构 Ⅰ型 10 岩质 1∶0.5 10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡 Ⅱ-1型 20 岩质 1∶0.5 两级10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡+2 m宽平台 Ⅱ-2型 20 岩质:1∶0.75 Ⅱ-3型 20 岩质 1∶0.75 两级10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡+3 m宽平台 Ⅱ-4型 20 岩质 1∶1 两级10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡+2 m宽平台 Ⅲ-1型 30 岩质 1∶0.75 三级10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡+2 m宽平台 Ⅲ-2型 30 岩质 1∶1 Ⅲ-3型 30 岩质 1∶1 三级10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡+3 m宽平台 Ⅳ-1型 20 岩质 1∶0.75
土质 1∶1两级10 m高边坡+2 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 Ⅳ-2型 20 岩质 1∶0.75
土质 1∶1两级10 m高边坡+3 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 Ⅳ-3型 20 岩、土质 1∶1 两级10 m高边坡,+2 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 Ⅳ-4型 20 岩质 1∶1
土质 1∶1.25Ⅴ-1型 30 岩质 1∶0.75
土质 1∶1三级10 m高边坡+2 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 Ⅴ-2型 30 岩、土质 1∶1 Ⅴ-3型 30 岩质 1∶1
土质 1∶1.25Ⅴ-4型 30 岩质 1∶1
土质 1∶1.25三级10 m高边坡+3 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 Ⅴ-5型 30 岩、土质 1∶1.25 三级10 m高边坡+2 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 表 5 边坡蠕变劣化稳定性变化结果Table 5. Result of slope stability variation considering creep degradation边坡
类型开挖完成后
(未蠕变劣化)参数蠕变前
稳定系数长期蠕变劣化强度
折减后参数蠕变劣化折减后
稳定系数稳定系数
减小值滑裂面
最大厚度/mⅠ型 c=30 kPa,
φ=25°1.272 c=26.1 kPa,φ=21.0°
(黏土岩)1.083 0.189 3~4 Ⅱ-1型 c=30 kPa,
φ=25°0.967 — — — 5~6 Ⅱ-2型 1.111 c=26.1 kPa,φ=21.0°
(黏土岩)0.936 0.175 6~7 Ⅱ-3型 1.151 0.970 0.181 6~7 Ⅱ-4型 1.265 1.066 0.199 5~6 Ⅲ-1型 c=30 kPa,
φ=25°0.969 — — — 9~10 Ⅲ-2型 1.101 c=26.1 kPa,φ=21.0°
(黏土岩)0.924 0.177 10.5 Ⅲ-3型 1.148 0.963 0.185 9~10 Ⅳ-1型 c=30 kPa,φ=25°
(黏土岩)
c=15 kPa,φ=16°
(黏土)1.147 c=26.1 kPa,φ=21.0°
(黏土岩)
c=12 kPa,φ=12.8°
(黏土)0.962 0.185 6~7 Ⅳ-2型 1.186 0.995 0.191 6 Ⅳ-3型 1.235 1.054 0.181 6 Ⅳ-4型 1.295 1.086 0.209 5~6 Ⅴ-1型 c=30 kPa,φ=25°
(黏土岩)
c=15 kPa,φ=16°
(黏土)0.990 — — — 9~10 Ⅴ-2型 1.093 c=26.1 kPa,φ=21.0°(黏土岩)
c=12 kPa,φ=12.8°
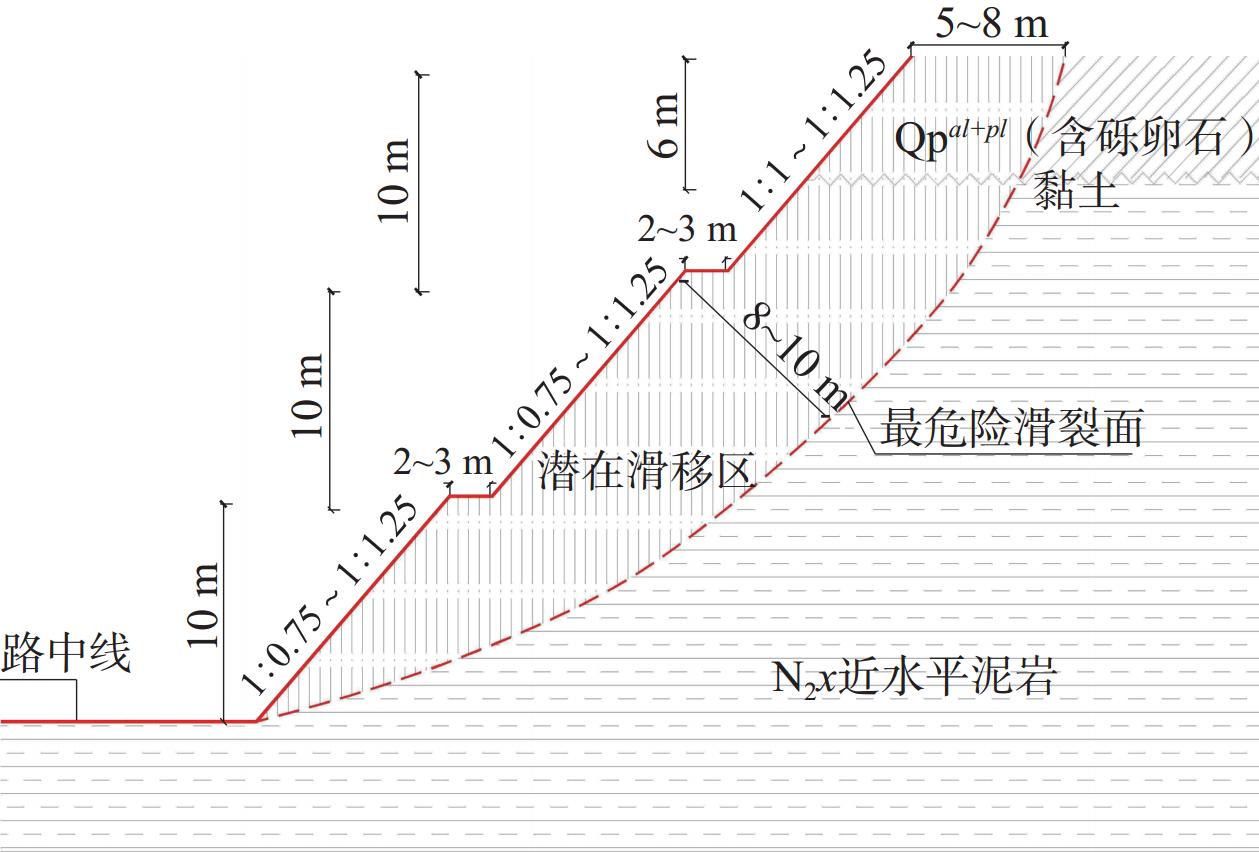
(黏土)0.915 0.178 8~9 Ⅴ-3型 1.121 0.938 0.183 10 Ⅴ-4型 1.167 0.976 0.191 9~10 Ⅴ-5型 1.229 1.028 0.201 9~10 注:表中加粗数字均为稳定系数小于1.0。 计算结果表明,在无限制的条件下按圆弧滑动法自动搜索30 m内昔格达黏土岩边坡最危险滑裂面是以坡口后缘5~8 m范围为剪切入口,前缘坡脚0~1 m高范围为剪切出口的弧面,高度20 m及30 m的昔格达黏土岩边坡最危险滑面最大平均厚分别5~6 m、8~10 m(图11)。
昔格达黏土岩岩质边坡在长期蠕变劣化强度折减后稳定系数平均降低0.181,岩土二元边坡在覆盖(含砾、卵石)黏土厚度为6 m的情况下稳定系数平均降低0.187,综合来看,平均降低0.184。20~30 m高昔格达黏土岩质边坡、20 m及30 m高岩土二元边坡开挖时全坡坡比每放缓0.25,边坡稳定系数分别提高约0.14,0.07,0.12,平均提高0.11。此外,边坡平台宽度从2 m增到3 m时稳定系数平均提高0.043。
3.2 防护对策建议
昔格达黏土岩存在长期蠕变劣化特性,该类特殊性质半成岩地层工程地质性质与一般基岩差异较大,对该类边坡的工程防护应重点考虑其长期蠕变劣化及强度折减导致的稳定性降低及防护工程结构物失效等方面问题,根据前文计算分析,对昔格达黏土岩边坡的加固及防护建议如下:
(1)进行昔格达黏土岩边坡稳定性及滑坡推力计算时应考虑强度折减,建议 c、φ值按0.84~0.87进行折减。计算时不利工况下稳定系数应取《公路路基设计规范》(JTG D30—2015)《公路滑坡防治设计规范》(JTG/T 3334—2018)中规定的大值。
(2)无防护的昔格达黏土岩边坡除坡高小于10 m岩质边坡外,两级开挖边坡坡比不宜陡于1∶0.75,三级边坡坡比不宜陡于1∶1,建议边坡平台设置宽度不小于3 m,对无支挡加固防护的边坡开挖坡比在规范规定的坡比基础上放缓不小于1∶0.25。
(3)边坡坡脚位置为最不利滑面剪出口,也是边坡应力的集中部位,建议采用小型护脚或者挡墙防护,避免坡脚黏土岩长期暴露风化或者饱水软化后加剧坡体滑移变形。
(4)对昔格达边坡进行如抗滑桩等支挡加固时建议使用蠕变劣化后的参数,没有试验资料的情况下可按0.8~0.85进行折减,且应适当增加桩体嵌固长度[27]。
(5)昔格达黏土岩中含有的膨胀性、易溶性有机矿物,随着岩体劣化坡面锚固工程加固效果变差,锚固体计算时需对岩土体参数进行折减。此外,根据王伟[31]对昔格达边坡锚固机理的研究成果及上文最危险滑裂面的计算分析,对高度大于20 m昔格达黏土岩边坡的锚固措施不宜一味加大锚固体长度,不建议采用“陡放坡+全锚固”措施进行防护,采用“缓坡比+宽平台+弱加固”的思路对坡体长期稳定性及加固结构物耐久性更为有利。
(6)设计及施工时应尽量避免在半坡设置大尺寸挡墙支挡,挡墙基础位于黏土岩内,其承载力在长期降雨及蠕变影响下会持续降低,挡墙无法对后部土体起到有效支挡,长期稳定性降低后易产生整体“坐船”式滑坡失稳。
(7)水是导致昔格达岩土二元边坡长期蠕变劣化失稳的主要自然因素,基覆界面是岩土二元边坡内水的主要汇集面,防护时建议加强对岩土界面地下水排泄。
4. 结论
(1)西攀高速公路K2378+900右侧滑坡昔格达黏土岩长期蠕变劣化后c、φ值强度折减系数分别约0.87,0.84,蠕变后边坡整体稳定系数降低约0.181。
(2)按模拟计算得到的强度折减系数分别对5类、17种昔格达黏土岩边坡进行计算。蠕变劣化后高30 m内的昔格达黏土岩边坡潜在最危险失稳滑裂面是以坡口后缘5~8 m为剪切入口、坡脚为剪出口的圆弧面,两级20 m及三级30 m高度的边坡滑裂面厚度分别5~6 m、8~10 m。
(3)为确保长期蠕变劣化后边坡的稳定,昔格达黏土岩边坡防护处治时稳定系数需取规范对应上限值。建议无支挡加固防护措施的边坡开挖坡比在规范规定的坡比上放缓不小于1∶0.25。此外,对昔格达黏土岩边坡进行支挡及锚固防护时也需对参数进行相应折减,没有试验资料的情况下可按0.8~0.85折减,以提高支挡及锚固结构物耐久性及处治效果。
(4)建议对昔格达黏土岩边坡采用“缓坡比+宽平台+弱加固”的防护处治思路,尤其是放缓坡比对昔格达边坡整体稳定性提高较为明显,2~3级边坡全坡坡比每放缓1∶0.25,边坡整体稳定系数平均提高约0.11,边坡平台由2 m加宽至3 m边坡稳定系数提高约0.043。同时,加强对岩土二元边坡基覆界面位置的地下水排泄也十分重要。
-
表 1 滑带参数反算结果表
Table 1 Inversion calculation results of slope zone parameters
地层 岩性 抗剪参数 备注 主滑段 抗滑段 牵引段 Qpal+pl 黏土 c=12 kPa、φ=10º — c=0 kPa
φ=40º按《公路滑坡防治设计规范》
稳定性计算采用“三段式”含卵石黏土 c=10 kPa、φ=13º — N2x 泥岩(强风化) c=18.4 kPa、φ=15.1º c=0 kPa、φ=25º 表 2 数值模拟参数取值
Table 2 Parameter value of numerical simulation
参数 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 饱和 数值模拟采用层序号 重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) Qpal+pl黏 土 150 0.30 20.2 12.0 10.0 1 Qpal+pl含卵石黏土 220 0.29 20.7 10.0 13.0 2 N2x泥岩(强风化) 460 0.27 22.5 15.3 12.6 3 N2x泥岩(中风化) 510 0.26 17.4 14.3 4 表 3 边坡开挖完成时数值模拟参数取值
Table 3 Parameter value of numerical simulation after slope excavation
参 数 弹性模量
/MPa泊松比 饱和 重度/(kN·m−3) 黏聚力/ kPa 内摩擦角/(°) Qpal+pl黏土 160 0.3 20.2 15.38 12.82 Qpal+pl含卵石黏土 230 0.28 20.7 12.50 16.25 N2x泥岩(强风化) 480 0.26 22.5 17.60 15.00 N2x泥岩(中风化) 520 0.25 27.70 18.20 表 4 路堑边坡分类表
Table 4 Classification table for cut slopes
坡型 坡高/m 坡比 坡体结构 Ⅰ型 10 岩质 1∶0.5 10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡 Ⅱ-1型 20 岩质 1∶0.5 两级10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡+2 m宽平台 Ⅱ-2型 20 岩质:1∶0.75 Ⅱ-3型 20 岩质 1∶0.75 两级10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡+3 m宽平台 Ⅱ-4型 20 岩质 1∶1 两级10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡+2 m宽平台 Ⅲ-1型 30 岩质 1∶0.75 三级10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡+2 m宽平台 Ⅲ-2型 30 岩质 1∶1 Ⅲ-3型 30 岩质 1∶1 三级10 m高昔格达泥岩黏土岩边坡+3 m宽平台 Ⅳ-1型 20 岩质 1∶0.75
土质 1∶1两级10 m高边坡+2 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 Ⅳ-2型 20 岩质 1∶0.75
土质 1∶1两级10 m高边坡+3 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 Ⅳ-3型 20 岩、土质 1∶1 两级10 m高边坡,+2 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 Ⅳ-4型 20 岩质 1∶1
土质 1∶1.25Ⅴ-1型 30 岩质 1∶0.75
土质 1∶1三级10 m高边坡+2 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 Ⅴ-2型 30 岩、土质 1∶1 Ⅴ-3型 30 岩质 1∶1
土质 1∶1.25Ⅴ-4型 30 岩质 1∶1
土质 1∶1.25三级10 m高边坡+3 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 Ⅴ-5型 30 岩、土质 1∶1.25 三级10 m高边坡+2 m宽平台,顶部6 m厚(含砾、卵石)黏土 表 5 边坡蠕变劣化稳定性变化结果
Table 5 Result of slope stability variation considering creep degradation
边坡
类型开挖完成后
(未蠕变劣化)参数蠕变前
稳定系数长期蠕变劣化强度
折减后参数蠕变劣化折减后
稳定系数稳定系数
减小值滑裂面
最大厚度/mⅠ型 c=30 kPa,
φ=25°1.272 c=26.1 kPa,φ=21.0°
(黏土岩)1.083 0.189 3~4 Ⅱ-1型 c=30 kPa,
φ=25°0.967 — — — 5~6 Ⅱ-2型 1.111 c=26.1 kPa,φ=21.0°
(黏土岩)0.936 0.175 6~7 Ⅱ-3型 1.151 0.970 0.181 6~7 Ⅱ-4型 1.265 1.066 0.199 5~6 Ⅲ-1型 c=30 kPa,
φ=25°0.969 — — — 9~10 Ⅲ-2型 1.101 c=26.1 kPa,φ=21.0°
(黏土岩)0.924 0.177 10.5 Ⅲ-3型 1.148 0.963 0.185 9~10 Ⅳ-1型 c=30 kPa,φ=25°
(黏土岩)
c=15 kPa,φ=16°
(黏土)1.147 c=26.1 kPa,φ=21.0°
(黏土岩)
c=12 kPa,φ=12.8°
(黏土)0.962 0.185 6~7 Ⅳ-2型 1.186 0.995 0.191 6 Ⅳ-3型 1.235 1.054 0.181 6 Ⅳ-4型 1.295 1.086 0.209 5~6 Ⅴ-1型 c=30 kPa,φ=25°
(黏土岩)
c=15 kPa,φ=16°
(黏土)0.990 — — — 9~10 Ⅴ-2型 1.093 c=26.1 kPa,φ=21.0°(黏土岩)
c=12 kPa,φ=12.8°
(黏土)0.915 0.178 8~9 Ⅴ-3型 1.121 0.938 0.183 10 Ⅴ-4型 1.167 0.976 0.191 9~10 Ⅴ-5型 1.229 1.028 0.201 9~10 注:表中加粗数字均为稳定系数小于1.0。 -
[1] 杨世豪. 基于物元理论的昔格达地层边坡稳定性评价模型研究[D]. 成都:中国科学院大学(中国科学院水利部成都山地灾害与环境研究所),2020. [YANG Shihao. Study on evaluation model of Xigeda stratum slope stability based on matter-element theory[D]. Chengdu:Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment,Chinese Academy of Sciences,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Shihao. Study on evaluation model of Xigeda stratum slope stability based on matter-element theory[D]. Chengdu: Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 黄绍槟,吉随旺,朱学雷,等. 西攀路昔格达地层滑坡分析[J]. 公路交通科技,2005,22(增刊1):41 − 44. [HUANG Shaobin,JI Suiwang,ZHU Xuelei,et al. Analysis on xigeda landslide in Xipan expressway[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2005,22(Sup 1):41 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HUANG Shaobin, JI Suiwang, ZHU Xuelei, et al. Analysis on xigeda landslide in Xipan expressway[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2005, 22(Sup 1): 41 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 吴焕恒. 西昌某边坡昔格达组地层蠕变试验及其边坡蠕变变形分析[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2010. [WU Huanheng. Creep test of Xigeda formation on a slope in Xichang and its slope creep deformation analysis[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University,2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WU Huanheng. Creep test of Xigeda formation on a slope in Xichang and its slope creep deformation analysis[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 陈茂,张家明,龙郧铠. 黏性土剪切蠕变特性研究进展[J]. 工业安全与环保,2021,47(7):15 − 21. [CHEN Mao,ZHANG Jiaming,LONG Yunkai. Research progress on shear creep characteristics of cohesive soil[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection,2021,47(7):15 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2021.07.004 CHEN Mao, ZHANG Jiaming, LONG Yunkai. Research progress on shear creep characteristics of cohesive soil[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 47(7): 15 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2021.07.004
[5] 孙淼军,唐辉明,王潇弘,等. 蠕动型滑坡滑带土蠕变特性研究[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(2):385 − 391. [SUN Miaojun,TANG Huiming,WANG Xiaohong,et al. Creep properties of sliding-zone soil from a creeping landslide[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(2):385 − 391. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.02.011 SUN Miaojun, TANG Huiming, WANG Xiaohong, et al. Creep properties of sliding-zone soil from a creeping landslide[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(2): 385 − 391. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.02.011
[6] 周静静,赵法锁,祝艳波,等. 低速缓动滑坡滑带土剪切蠕变特性[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(1):107 − 112. [ZHOU Jingjing,ZHAO Fasuo,ZHU Yanbo,et al. Shear creep characteristics of soil in sliding zone of low-speed slow-moving landslide[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(1):107 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.01.17 ZHOU Jingjing, ZHAO Fasuo, ZHU Yanbo, et al. Shear creep characteristics of soil in sliding zone of low-speed slow-moving landslide[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(1): 107 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.01.17
[7] BHAT D R,BHANDARY N P,YATABE R. Residual-state creep behavior of typical clayey soils[J]. Natural Hazards,2013,69(3):2161 − 2178. DOI: 10.1007/s11069-013-0799-3
[8] XIE Xing,QI Shengwen,ZHAO Fasuo,et al. Creep behavior and the microstructural evolution of loess-like soil from Xi’an area,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,236:43 − 59. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.11.003
[9] DI MAIO C,SCARINGI G,VASSALLO R. Residual strength and creep behaviour on the slip surface of specimens of a landslide in marine origin clay shales:Influence of pore fluid composition[J]. Landslides,2015,12(4):657 − 667. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-014-0511-z
[10] 文丽娜,朱学雷,白志勇,等. 西攀高速公路新九地区昔格达地层岩土特性[J]. 公路,2005,50(7):145 − 148. [WEN Lina,ZHU Xuelei,BAI Zhiyong,et al. Characteristics of rock and soil of Xigeda strata in Xinjiu District of Xipan expressway[J]. Highway,2005,50(7):145 − 148. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2005.07.031 WEN Lina, ZHU Xuelei, BAI Zhiyong, et al. Characteristics of rock and soil of Xigeda strata in Xinjiu District of Xipan expressway[J]. Highway, 2005, 50(7): 145 − 148. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2005.07.031
[11] 文丽娜,冯义从,邬玉娟. 攀西地区昔格达地层边坡稳定性评价[J]. 四川建筑,2004,24(3):45 − 46. [WEN Lina,FENG Yicong,WU Yujuan. Stability evaluation of Xigeda stratum slope in Panxi area[J]. Sichuan Architecture,2004,24(3):45 − 46. (in Chinese)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8983.2004.03.019 WEN Lina, FENG Yicong, WU Yujuan. Stability evaluation of Xigeda stratum slope in Panxi area[J]. Sichuan Architecture, 2004, 24(3): 45 − 46. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8983.2004.03.019
[12] 杨世豪,苏立君,张崇磊,等. 强降雨作用下昔格达边坡渗流特性及稳定性分析[J]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2020,42(4):19 − 27. [YANG Shihao,SU Lijun,ZHANG Chonglei,et al. Analysis of seepage characteristics and stability of Xigeda formation slope under heavy rainfall[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering,2020,42(4):19 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.2096-6717.2020.024 YANG Shihao, SU Lijun, ZHANG Chonglei, et al. Analysis of seepage characteristics and stability of Xigeda formation slope under heavy rainfall[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2020, 42(4): 19 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.2096-6717.2020.024
[13] 丁文富,张广泽,宋章. 成昆铁路昔格达地层工程地质特性及对策研究[J]. 铁道工程学报,2017,34(4):1 − 5. [DING Wenfu,ZHANG Guangze,SONG Zhang. Research on the engineering geological characteristics and engineering countermeasures of Xigeda strata of Chengdu-Kunming railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2017,34(4):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2017.04.001 DING Wenfu, ZHANG Guangze, SONG Zhang. Research on the engineering geological characteristics and engineering countermeasures of Xigeda strata of Chengdu-Kunming railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2017, 34(4): 1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2017.04.001
[14] 尹紫红,周志林,梁明学. 昔格达组地层研究现状与牛坪子滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 路基工程,2005(2):12 − 15. [YIN Zihong,ZHOU Zhilin,LIANG Mingxue. Research status of Xigeda formation strata and stability analysis of Niupingzi Landslide[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2005(2):12 − 15. (in Chinese)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2005.02.004 YIN Zihong, ZHOU Zhilin, LIANG Mingxue. Research status of Xigeda formation strata and stability analysis of Niupingzi Landslide[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2005(2): 12 − 15. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2005.02.004
[15] 崔雪婷,邓夷明,冯世清,等. 昔格达地层力学参数取值研究[C]//中国地质学会.第十一届全国工程地质大会论文集. 中国建筑西南勘察设计研究院有限公司,2020:6. [CUI Xueting,DENG Yiming,FENG Shiqing,etal. Study on the values of geotechnical mechanical parameters of Xigeda stratum[C]//Geological society of China. Proceedings of the 11th National Engineering Geology Congress. China Southwest Geotechnical Investigation & Pesign Institute Co. Ltd., 2020:6. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CUI Xueting, DENG Yiming, FENG Shiqing, etal. Study on the values of geotechnical mechanical parameters of Xigeda stratum[C]//Geological society of China. Proceedings of the 11th National Engineering Geology Congress. China Southwest Geotechnical Investigation & Pesign Institute Co. Ltd., 2020: 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 张家明,刘文连,徐则民,等. 西昌昔格达组黏土岩动力特性试验研究[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2012,32(1):154 − 160. [ZHANG Jiaming,LIU Wenlian,XU Zemin,et al. Experimental research on dynamic characteristics of Xigeda formation claystone in Xichang[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration,2012,32(1):154 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.13197/j.eeev.2012.01.005 ZHANG Jiaming, LIU Wenlian, XU Zemin, et al. Experimental research on dynamic characteristics of Xigeda formation claystone in Xichang[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2012, 32(1): 154 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13197/j.eeev.2012.01.005
[17] 古鹏翔,骆俊晖,刘先林,等. 考虑滑带土蠕变特性的边坡长期稳定性分析[J]. 安全与环境工程,2020,27(4):94 − 101. [GU Pengxiang,LUO Junhui,LIU Xianlin,et al. Long-term stability analysis of slope considering creep behaviors of sliding zone soils[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2020,27(4):94 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.2020.04.013 GU Pengxiang, LUO Junhui, LIU Xianlin, et al. Long-term stability analysis of slope considering creep behaviors of sliding zone soils[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2020, 27(4): 94 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.2020.04.013
[18] 贾逸,魏良帅,黄海峰. 红层滑坡滑带土蠕变力学特性及经验模型研究[J]. 水力发电,2021,47(3):25 − 30. [JIA Yi,WEI Liangshuai,HUANG Haifeng. Study on creep mechanics characteristics and empirical model of soil in the slip zone of red layer landslide[J]. Water Power,2021,47(3):25 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2021.03.006 JIA Yi, WEI Liangshuai, HUANG Haifeng. Study on creep mechanics characteristics and empirical model of soil in the slip zone of red layer landslide[J]. Water Power, 2021, 47(3): 25 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2021.03.006
[19] 赵建磊,王涛,梁昌玉,等. 基于风化红层泥岩蠕变特性的滑坡时效变形分析——以天水雒堡村滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(1):30 − 39. [ZHAO Jianlei,WANG Tao,LIANG Changyu,et al. Time-dependent deformation analysis of landslide based on creep characteristics of weathered red mudstone:Taking Luobaocun landslide in Tianshui as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(1):30 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202112027 ZHAO Jianlei, WANG Tao, LIANG Changyu, et al. Time-dependent deformation analysis of landslide based on creep characteristics of weathered red mudstone: Taking Luobaocun landslide in Tianshui as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(1): 30 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202112027
[20] 张笛,滕伟福,安琪. 黄土坡临江1号滑坡体滑带土残余强度试验研究[J]. 安全与环境工程,2017,24(2):39 − 45. [ZHANG Di,TENG Weifu,AN Qi. Residual strength test of the soil in landslide zone of Huangtupo riverside landslide mass No. 1[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2017,24(2):39 − 45. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.2017.02.007 ZHANG Di, TENG Weifu, AN Qi. Residual strength test of the soil in landslide zone of Huangtupo riverside landslide mass No. 1[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2017, 24(2): 39 − 45. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.2017.02.007
[21] 王体俊,王大群. 某滑坡滑体土蠕变特性及长期强度研究[J]. 路基工程,2021(5):70 − 74. [WANG Tijun,WANG Daqun. Study on creep characteristics and long-term strength of sliding-body soil of a landslide[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2021(5):70 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.13379/j.issn.1003-8825.202102006 WANG Tijun, WANG Daqun. Study on creep characteristics and long-term strength of sliding-body soil of a landslide[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2021(5): 70 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13379/j.issn.1003-8825.202102006
[22] 于洪丹,陈卫忠,卢琛,等. 黏土岩时效变形特性试验与理论研究[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(2):317 − 326. [YU Hongdan,CHEN Weizhong,LU Chen,et al. Experimental and theoretical study of the time-dependent deformation characteristics of clayey rock[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(2):317 − 326. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YU Hongdan, CHEN Weizhong, LU Chen, et al. Experimental and theoretical study of the time-dependent deformation characteristics of clayey rock[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(2): 317 − 326. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 陈爱云,龚标,杨宇轩,等. 云南宣威群地层路堑边坡滑带土蠕变特性研究[J]. 安全与环境工程,2022,29(1):111 − 118. [CHEN Aiyun,GONG Biao,YANG Yuxuan,et al. Creep properties of sliding zone soil in roadcut slope of Xuanwei formation strata in Yunnan Province[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2022,29(1):111 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHEN Aiyun, GONG Biao, YANG Yuxuan, et al. Creep properties of sliding zone soil in roadcut slope of Xuanwei formation strata in Yunnan Province[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(1): 111 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 关顺,王来贵,孙闯. 滑带土分数阶损伤蠕变本构模型研究[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2019,38(1):52 − 57. [GUAN Shun,WANG Laigui,SUN Chuang. Study on fractional damage creep constitutive model of slip zone soil[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science),2019,38(1):52 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)] GUAN Shun, WANG Laigui, SUN Chuang. Study on fractional damage creep constitutive model of slip zone soil[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science), 2019, 38(1): 52 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 周静静,赵法锁,袁湘秦,等. 滑带土蠕变过程及微观结构演化分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):115 − 121. [ZHOU Jingjing,ZHAO Fasuo,YUAN Xiangqin,et al. Creep process and the microstructural evolution of sliding-zone soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):115 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019010011 ZHOU Jingjing, ZHAO Fasuo, YUAN Xiangqin, et al. Creep process and the microstructural evolution of sliding-zone soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(3): 115 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019010011
[26] 孙淼军. 库水作用下滑坡—抗滑桩体系变形时效规律与长期稳定性研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学,2015. [SUN Miaojun. Study on deformation aging law and long-term stability of landslide-anti-slide pile system under the action of reservoir water[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences,2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)] SUN Miaojun. Study on deformation aging law and long-term stability of landslide-anti-slide pile system under the action of reservoir water[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 杨旭. 昔格达组地层中抗滑桩的嵌固深度研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2008. [YANG Xu. Study on embedding depth of anti-slide piles in Xigeda formation[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University,2008. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Xu. Study on embedding depth of anti-slide piles in Xigeda formation[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 夏敏,任光明,郭亚莎,等. 地震诱发滑坡复活机制的FLAC3D数值模拟分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(3):305 − 311. [XIA Min,REN Guangming,GUO Yasha,et al. FLAC3D numerical simulation of recurrence mechanism of landslide under earthquake loading[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(3):305 − 311. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XIA Min, REN Guangming, GUO Yasha, et al. FLAC3D numerical simulation of recurrence mechanism of landslide under earthquake loading[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(3): 305 − 311. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 周罕,曹平,张科. 昔格达组黏土岩和粉砂岩现场直剪试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2014,45(10):3544 − 3550. [ZHOU Han,CAO Ping,ZHANG Ke. In-situ direct shear test on Xigeda formation clay stone and siltstone[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2014,45(10):3544 − 3550. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHOU Han, CAO Ping, ZHANG Ke. In-situ direct shear test on Xigeda formation clay stone and siltstone[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(10): 3544 − 3550. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 杨碧,范柱国,刘文连,等. 攀钢钒钛钢铁新基地昔格达地层岩土工程特性研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2010,10(4):973 − 976. [YANG Bi,FAN Zhuguo,LIU Wenlian,et al. Engineering property of Xigeda strata of Panzhihua new steel V-Ti base[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2010,10(4):973 − 976. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2010.04.027 YANG Bi, FAN Zhuguo, LIU Wenlian, et al. Engineering property of Xigeda strata of Panzhihua new steel V-Ti base[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2010, 10(4): 973 − 976. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2010.04.027
[31] 王伟. 昔格达土质边坡锚杆锚固机理研究与应用[D]. 成都:西华大学,2015. [WANG Wei. Research and application of anchor rod anchoring mechanism in Xigeda soil slope[D]. Chengdu:Xihua University,2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Wei. Research and application of anchor rod anchoring mechanism in Xigeda soil slope[D]. Chengdu: Xihua University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 李彦娥,赵振明,冯卫,马红娜,王化齐. 沿黄公路边坡地质灾害破坏模式及风险管控:以陕西绥德–清涧段为例. 西北地质. 2025(02): 186-196 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙磊,王钰轲. 交通荷载下饱和软黏土的不排水变形特性. 水文地质工程地质. 2024(06): 126-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:







 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS