Mechanism of the “7•15” debris flow in Baiguoshu gully, Tianquan County, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
相较于宽缓沟道型泥石流,小流域窄陡沟道型泥石流具有更高的隐蔽性和突发性,揭示此类灾害成灾机理无疑对工程治理及灾害预防具有重要意义。文章以2021年发生的四川省天全县白果树沟“7•15”突发性泥石流为例,借助野外调查、无人机航测与RAMMS流体动力学模拟,揭示了此次泥石流的成灾过程。结果表明:白果树沟泥石流是累计前期降雨和短时强降雨共同作用的结果,其起动源于上游饱水物源被山洪揭底,而沿途侧蚀冲刷沟岸形成的滑坡为泥石流提供了物源补给,沟内局部堵溃后又进一步放大流量、导致沟口成灾,淤埋雅康高速公路路面。从发展趋势看,白果树沟现阶段物源丰富,水动力条件良好,仍存在暴发泥石流的可能性。
Abstract:Compared to wide-gentle debris flows, narrow-steep gully debris flow in small watersheds are characterized by their invisible and sudden nature. Therefore, understanding the mechanism behind such disasters are crucial for engineering management and disaster prevention. This paper presents a case study of the “7•15” debris flow that occurred in Baiguoshu gully, Tianquan County, Sichuan Province in 2021. The process of this debris flow was thoroughly investigated through field surveys, aerial photography, and hydrodynamic simulations using RAMMS. The findings revealed that Baiguoshu gully debris flow was triggered by the cumulative antecedent rainfall and short-term heavy rainfall. The mobilized materials during the “7•15” debris flow consisted of saturated materials upstream that were eroded by floods, as well as landslides triggered by bank erosion along the gully. Subsequently, the amplification of flow discharge caused by blockages and bursting in the main channel resulted in a disaster at the gully outlet and the buried of the Yakang Expressway. The Baiguoshu gully is prone to debris flow occurrences due to the abundance of source materials and favorable hydrodynamic conditions.
-
Keywords:
- narrow-steep gully /
- debris flow /
- small watershed area /
- disaster mechanism /
- RAMMS
-
0. 引言
泥石流是介于滑坡和高含沙水流之间的特殊洪流,是具有突发性及强大破坏力的地质灾害之一。近年统计资料表明,我国泥石流活动区域面积高达4.3×105 km2,泥石流已经成为中国山区可持续发展中不容忽视的严重地质灾害[1-2]。频繁的泥石流灾害不仅破坏基础生活设施、生态环境、阻碍经济发展,甚至会造成惨重人员伤亡[3]。因此,系统研究泥石流成灾机理对于防灾减灾具有重要意义。
国内外学者对不同类型泥石流成灾机理进行了大量的探索和研究。胡卸文等[4]将汶川震区桃关沟泥石流成灾机理归纳为崩滑物源、坡面物源和沟道物源三者的起动及相互叠加;黄健等[5]根据不同林火烈度下,渗透特征、坡面侵蚀和沟道侵蚀的差异,分析了响水沟火后泥石流的成灾机理;倪化勇等[6]将石棉县沟床侵蚀主导型泥石流形成机理归纳为强降雨的诱发和沟床质侵蚀与起动;吴凯等[7]阐明了隆德县坡面泥石流形成机理与降雨、斜坡地层岩性的关系;杜野等[8]将烧房沟弃渣型泥石流成灾机理归纳为弃渣的不合理堆放与强降雨的耦合作用;黄洪等[9]阐明了前期降雨和崩滑类物源对大流域泥石流成灾机理的影响。但目前对具有高隐蔽性、突然性、强破坏性等特点的小流域窄陡沟道型泥石流成灾机理研究还较少。随着计算机技术的发展,数值模拟成为泥石流灾害研究的重要方法,例如Ouyang等[10]采用Massflow模拟了意大利阿尔卑斯山Nora泥石流的演化过程;胡明鉴等[11]利用PFC2D研究了降雨作用下松散碎屑物质起动形成泥石流的过程;罗超鹏等[12]基于FLOW3D研究了理县二经里沟泥石流运动特征;Liu等[13]利用RAMMS反演了汶川锄头沟泥石流的运动过程,并分析了其形成机制和发展过程。以上数值模拟软件均能较好再现泥石流运动过程,但RAMMS相较于其他软件,其释放方式多样且可设置物源延迟释放时间的功能使得模拟结果与泥石流实际暴发运动过程更为吻合。
2021年7月15日,四川省天全县白果树沟受暴雨袭击暴发一次中等规模泥石流灾害,共冲出固体物质约2.2×104 m3,淤埋雅康高速公路近100 m,造成雅安—康定高速公路交通中断18 h。本文基于野外调查、无人机航测与RAMMS流体动力学模拟,再现了白果树沟“7•15”泥石流运动过程,揭示了此次泥石流成灾机理。成果可为类似区域地质环境条件下探究小流域窄陡沟道型泥石流成灾机理及工程减灾提供参考。
1. 研究区概况
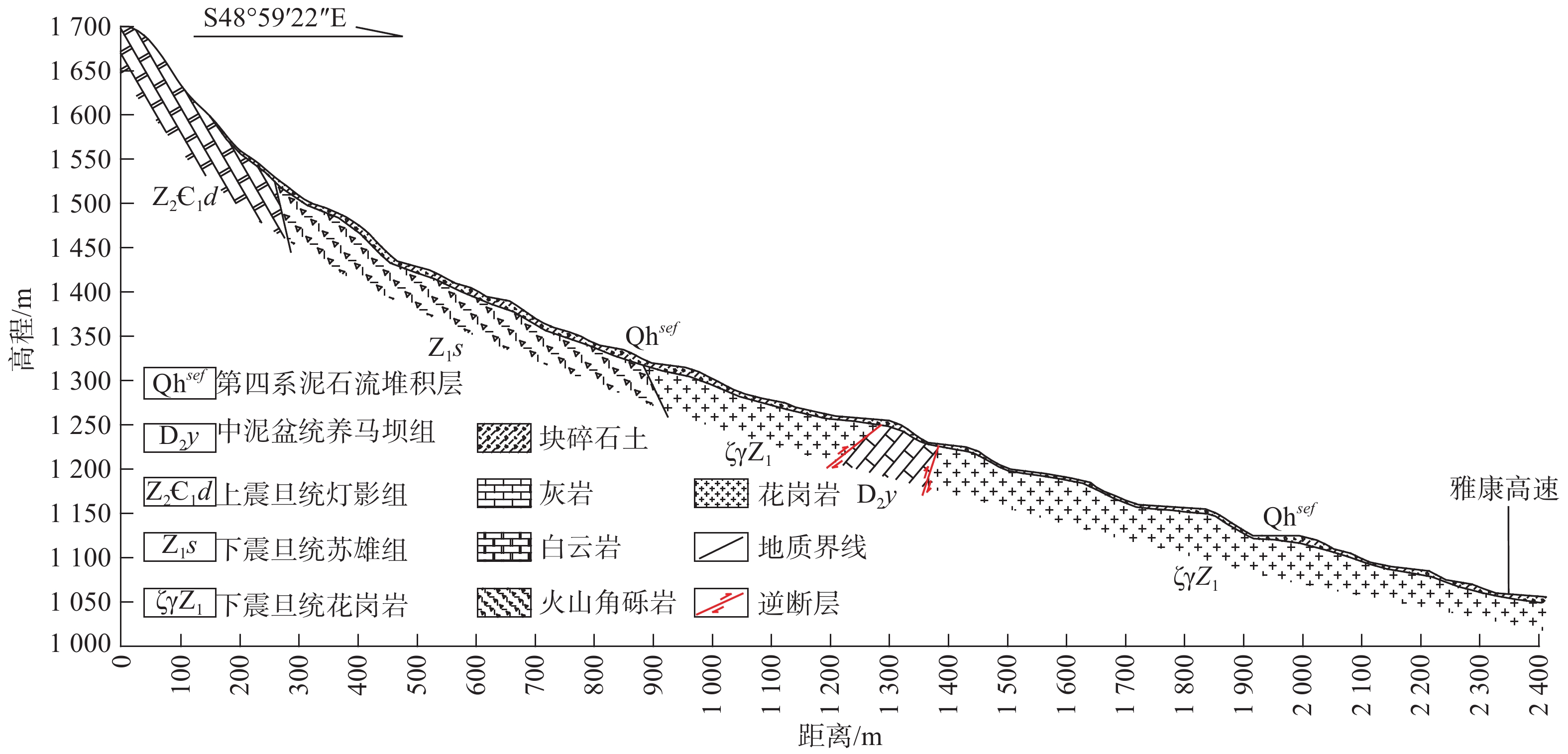
白果树沟泥石流位于四川省天全县思经镇小沟村、雅康高速(K51+400)紫石隧道附近(图1)。研究区地形陡峻,支沟纵横,相对高差达762 m,属冰川、水流、日照温差等强劲外力破坏、搬运下形成的切割中山地貌。
研究区处于北东向龙门山断裂带和北西向鲜水河及南东向安宁河断裂带构成的“Y”字形构造交汇部位东侧,地质构造复杂。区内地层主要为震旦系(Z)白云岩、花岗岩,奥陶系(O)页岩,志留系(S)灰岩,泥盆系(D)灰岩、石英砂岩以及第四系松散堆积层(Qh)。
受以亚热带季风气候为基带的山地气候影响,区内降水充沛,多年平均降雨量为1 660 mm,雨季集中在5—9月,占比达73%。
2. “7•15”泥石流形成条件
2.1 地形条件
白果树沟流域形态近似芭蕉叶型,流域面积2.06 km2,主沟长度2.21 km,区内最高点高程
1870 m,沟口高程1108 m,相对高差762 m,主沟平均纵坡降363‰(图2)。白果树沟沟道深切,横断面多呈“V”型,岸坡普遍陡峻,坡度一般在35°以上,有利于水源和物源的汇合。流域内共发育有5条支沟,呈树枝状分布在白果树沟上游,各支沟具有沟道狭窄、岸坡陡峻、水动力条件良好的特点,各支沟平均纵坡降从264‰到542‰不等。白果树沟流域内陡峻的“漏斗状”地形,便于地表径流快速汇集,为“7•15”泥石流发生提供了充分地形条件。2.2 降雨条件
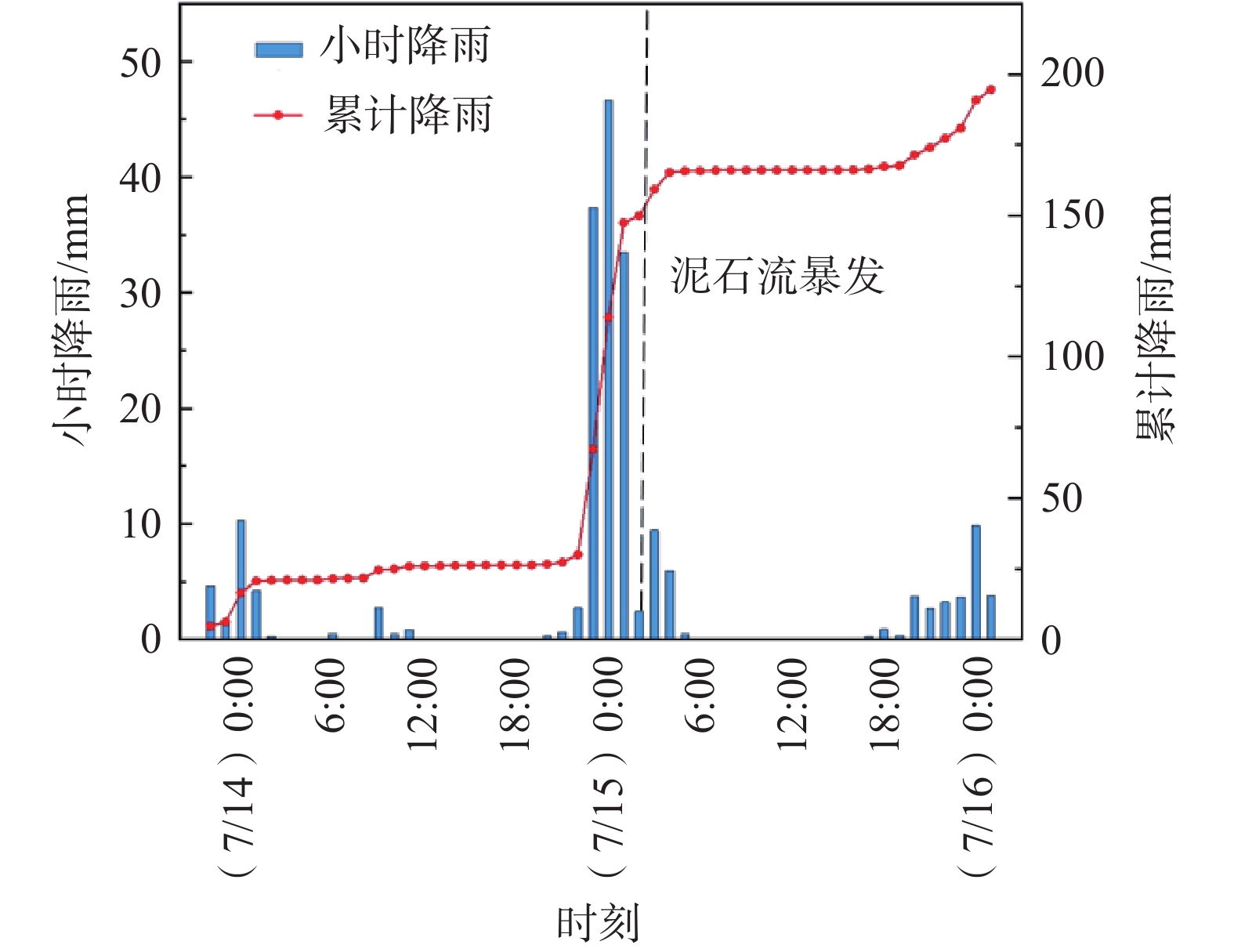
泥石流的发生通常是充足累积降雨和短时强降雨的结果[14]。根据天全国家气象观测站收集的白果树沟“7•15”泥石流暴发前后降雨数据(图3)可以看出,白果树沟流域此轮降雨始于2021年7月13日,主要集中于7月14日夜间,泥石流发生于7月15日凌晨1时55分,持续降雨时间为泥石流暴发前29 h,累计降雨量达149.5 mm,最大小时雨强为46.9 mm。长时间的降雨使流域内松散物源含水量饱和,稳定性显著降低,同时也使流域内地表包气带饱和,导致激发泥石流所需雨强显著降低[15]。
综上分析,引发“7•15”泥石流的降雨条件具有雨量大,降雨历时长、雨强较大的特点,是此次泥石流暴发的直接诱因。
2.3 物源条件
研究区地质构造复杂,崩塌、滑坡等地质灾害频发,加上人类活动对流域内植被的破坏及人工切坡后未采取相应支护措施,导致流域内新增了大量松散物源。根据野外调查,流域内松散物源类型主要为崩滑物源、沟道物源、坡面物源,各类物源共44处,总静储量约123.2×104 m3,总动储量约9.2×104 m3,详见表1及图4。
表 1 白果树沟松散物源统计表Table 1. Statistical table of loose sediment sources in Baiguoshu gully物源名称 静储量
/(104 m3)动储量
/(104 m3)基本特点 崩滑物源 64.9 6.6 各种规模数量达29处,主要
分布于主、支沟沟岸边坡沟道物源 7.8 0.6 沿沟道分布的早期或
新近泥石流堆积体坡面物源 50.5 2.0 因植被砍伐裸露的松散堆积体 总计 123.2 9.2 从物源分布位置来看,流域内各类物源无明显聚集性,主要沿沟道分布于各支沟及主沟两侧岸坡。总体来说,物源条件在此次“7•15”泥石流孕灾中的作用主要体现在:早期各类松散物源堆积提供丰富的可起动物源、降雨后沟道侧蚀及崩滑物源激增形成沿途物源补给、物源堵塞沟道产生泥石流堵溃放大效应。
3. “7•15”泥石流成灾机理
3.1 暴发及运动特征
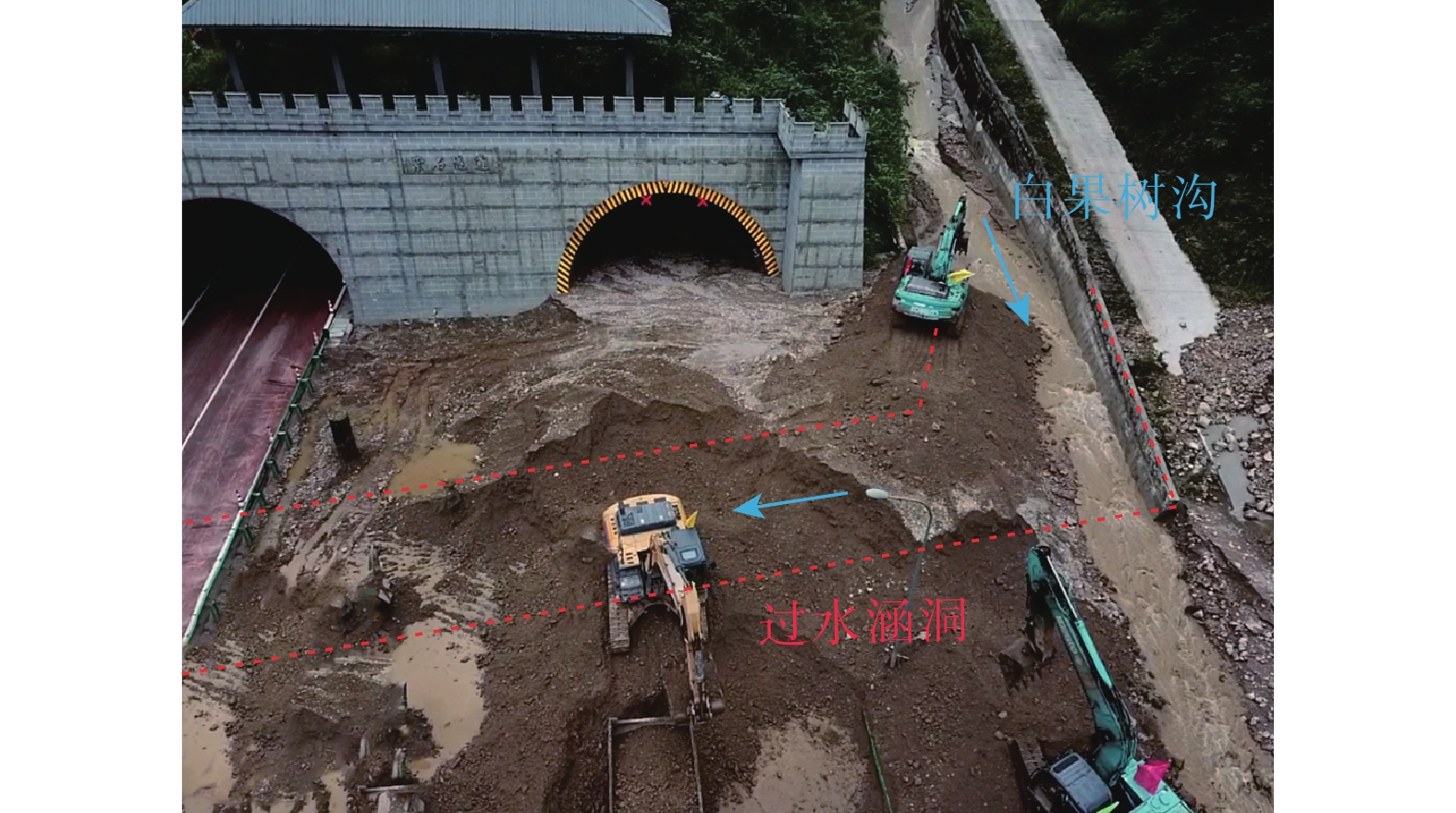
根据现场调查与访问,2021年7月15日凌晨1时55分左右,白果树沟上游沟道率先暴发泥石流,且随着降雨持续增强,泥石流携带大量松散堆积物源沿途不断冲刷侵蚀沟床,造成多处岸坡失稳,泥石流规模进一步扩大,至凌晨2点30分左右,由于雅康高速公路下涵洞过流断面有限,致使泥石流冲出沟道,淤埋高速公路近100 m,造成雅安至康定高速公路交通中断18 h(图5)。此次泥石流造成沟岸边坡多处发生崩塌、滑坡,至今仍有部分堆积物堆积于沟道内,堆积平均厚度约为1.0 m。泥石流最大流量过程约为0.5 h,并在随后持续性降雨作用下,以高含沙洪水形式流动数小时。
综合上述分析,“7•15”泥石流具有暴发隐蔽、持续时间短,泥石流暴发后仍以高含沙洪水流动数小时的特点。
3.2 成灾机理分析
结合野外调查总结出2021年“7•15”泥石流成灾机理如下:
(1)短时强降雨汇水形成山洪揭底导致饱水物源起动。长历时前期降雨促使流域内松散沟道堆积物源饱水,而短历时强降雨导致坡面迅速形成地表径流,汇集于主沟道后形成山洪,山洪揭底冲刷上游饱水沟道物源初步形成小规模泥石流,见图6(a)(b)。
(2)泥石流沿途侧蚀岸坡形成物源补给。上游形成的小规模泥石流在势动能转化过程中不断冲刷侵蚀下游沟床和岸坡坡脚,使坡脚出现临空面,导致原本已被降雨浸润的坡体失稳下滑,为泥石流提供物源补给,泥石流规模进一步扩大,见图6(d)(e)。
(3)沟内局部堵溃导致流量放大。流域中游因植被砍伐残留的大量的枯枝树干随地表径流向下加入泥石流活动,并在沟内狭窄且树木丛生地段形成堵塞体,堵塞体汇集大量流体后,在短时间内发生溃决,显著增大了泥石流瞬时洪峰流量。由于沟口涵洞过流能力不足,致使大量泥石流固体物质冲出沟道、掩埋高速公路。
因此,强降雨是“7•15”泥石流暴发的直接诱因,沿途侧蚀滑坡是泥石流重要的物源补给,而沟内局部堵溃放大流量以及沟口涵洞过流能力不足则是泥石流致灾的重要原因。
4. 泥石流动力学模拟分析
4.1 原理
本文采用RAMMS:DEBRIS FLOW软件对白果树沟进行动力学模拟分析。Hungr等[16]认为利用连续介质法模拟分析时,最困难的问题是选取合适的流变模型,这是由于泥石流在运动全过程中,会因受不确定因素的干扰而发生特征改变。而RAMMS采用基于Voellmy-Salm模型的Voellmy-Fluid摩擦模型,该模型将泥石流流体视为非稳定及非均质的,利用物质能量与运动转化法则来处理泥石流运动过程,并运用RKE(random kinetic energy)模型进行补充调整。经实际运用验证,RAMMS应用两个模型能较好模拟泥石流运动过程,得到泥石流运动特征参数[17-18]。
4.2 动力学模拟
第一步地形数据处理,提取研究区等高线,并使用ArcGIS将等高线转化成TIN不规则三角形网格,再将其栅格化转为DEM,最后转化为ASCLL文件并导入RAMMS,并采用物源释放的方式启动泥石流。
第二步物源释放处理,根据野外调查、无人机航测及卫星图影像解译等手段,确定了白果树沟流域内共44个可启动物源,其中“7•15”泥石流主要物源体积由现场确定,其余物源厚度及体积参考Tang等[19]方法估计。此外结合现场调查和多次模拟校核,为各物源设置对应延迟释放时间,并在主沟中下游设置了一个侵蚀区域,最大可侵蚀厚度为0.8 m。
第三步设置模拟参数,泥石流密度(ρ)取三次现场重度试验的平均值,为1.785 g/cm3,重力加速度(g)为9.8 m/s2,土压力系数和Lambda和零深度截止值均取默认值。根据RAMMS软件操作手册结合多次模拟校核,摩擦系数(μ)取0.200,湍流系数(ξ)取220 m/s2。
根据上述参数,利用RAMMS对白果树沟进行动力学模拟,经多次测试,模拟时长最终设置为1 800 s,得到模拟结果如图7、图8所示。
由图7可以看出,随着降雨持续增强,主沟及各支沟上游物源开始起动,最大泥深为3.52 m(图7a);约500 s时,流域内大部分固体物质已经聚集到主沟,此时中游主、支沟交汇处泥石流泥深最大,为2.49 m(图7b);约
1000 s时,固体物质全部汇入主沟道后,泥石流流体运动主要集中于中下游区域,此时泥石流规模随着沿途沟岸侧蚀崩滑物源补给进一步增大,同时由于沟道局部堵溃,泥石流流体具有明显的阵流性质,最大泥深约3.26 m(图7c);1800 s时泥石流运动结束,沟道内形成新的残余堆积体,沟口形成堆积扇,堆积扇厚度为0~2.78 m(图7d)。由图8可以看出,由于沟道上游地形坡度较大,泥石流最大速度可达5.98 m/s(图8a);约500 s时,由于地形逐渐平缓且受到沟道物质摩擦力作用,泥石流流速迅速减小至3.78 m/s(图8b);约
1000 s时,泥石流向下游运动,由于局部堵溃,最大速度可达4.31 m/s(图8c);1800 s时,泥石流流速逐渐下降,沟口区域流速下降至0~1.61 m/s,表明泥石流此时处于减速沉积阶段(图8d)。4.3 堆积范围
泥石流沟口堆积范围在一定程度上受沟口地形条件和防治措施影响[12]。图9显示了白果树沟“7•15”泥石流沟口区域模拟及实际堆积范围对比。受沟口高速公路路堤及排导槽影响,实际堆积范围略小于模拟堆积范围,原因在于实际堆积过程中沟口排导槽有效降低了泥石流出沟速度,而高速公路路堤则起到了阻挡泥石流的作用,二者限制了泥石流在沟口扩散,但造成局部区域泥石流堆积厚度较大。
另外,采用RAMMS的沉积分析功能对此次泥石流冲出体积进行计算,结果显示此次泥石流冲出体积约2.68×104 m3,与现场调查结果2.20×104 m3基本一致。
综上分析,“7•15”泥石流动力学模拟结果显示此次泥石流的起动、物源补给过程及沟口堆积情况与实际情况较为吻合,进一步论证了“7•15”泥石流成灾机理的合理性。
4.4 泥石流发展趋势分析
研究区属亚热带季风气候区,年降水量较大且降雨多集中于夏季,加之白果树沟流域面积较小和地形陡峻的特点十分有利于雨水快速汇聚,因此,在极端天气下,白果树沟会在短时间内形成山洪,届时会为泥石流形成提供充分的水源水动力条件。自2021年“7•15”泥石流暴发后,区内崩塌、滑坡等地质灾害数量激增,流域内现存物源总量达123.22×104 m3,而一旦各松散堆积物源在强降雨作用下失稳,则会为泥石流的暴发提供充足物源补给,加之现有防治措施治理效果十分有限,泥石流极易堵塞沟口过水涵洞,造成泥石流冲出沟道,从而威胁高速公路安全。因此白果树沟泥石流在自身地质环境、降雨等诱发因素的共同影响下,未来仍有较大可能暴发泥石流,并对雅康高速公路持续构成威胁。
5. 结论
(1)白果树沟流域面积为2.06 km2,主沟长度为2.21 km,主沟平均纵坡降为363‰,区内有利于雨水汇集的地形、充足的降雨及丰富的物源储备孕育了“7•15”泥石流成灾条件。
(2)白果树沟“7•15”泥石流是累计前期降雨和短时强降雨共同作用的结果,其起动源于上游饱水物源被山洪揭底,而沿途不断侧蚀冲刷形成的多处滑坡为泥石流提供了物源补给,沟内局部堵溃后流量放大则导致沟口成灾。
(3)动力学模拟体现了泥石流运动过程,结果显示此次泥石流的起动、物源补给过程及沟口堆积情况与实际情况较为吻合,进一步论证了“7•15”泥石流成灾机理,可信度较高。
(4)白果树沟流域内水源水动力条件良好,现存松散固体物源丰富且稳定性显著性降低,极端天气下仍有较大可能暴发泥石流。
-
表 1 白果树沟松散物源统计表
Table 1 Statistical table of loose sediment sources in Baiguoshu gully
物源名称 静储量
/(104 m3)动储量
/(104 m3)基本特点 崩滑物源 64.9 6.6 各种规模数量达29处,主要
分布于主、支沟沟岸边坡沟道物源 7.8 0.6 沿沟道分布的早期或
新近泥石流堆积体坡面物源 50.5 2.0 因植被砍伐裸露的松散堆积体 总计 123.2 9.2 -
[1] 康志成, 李焯芬, 马蔼乃, 等. 中国泥石流研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004 KANG Zhicheng, LI Zhuofen, MA Ainai, etal. Study on debris flow in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
[2] 王伟奇. 中国泥石流现状及浅析[J]. 科技信息, 2009(29): 597 WANG Weiqi. Present situation and analysis of debris flow in China[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2009(29): 597. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 刘佳, 赵海军, 马凤山, 等. 我国高寒山区泥石流研究现状[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(增刊1): 77-85 LIU Jia, ZHAO Haijun, MA Fengshan, et al. Research status of debris flow in alpine mountainous areas of China [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28 (Sup1): 77-85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 胡卸文,韩玫,梁敬轩,等. 汶川震区桃关沟2013-07-10泥石流成灾机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(2):286 − 293. [HU Xiewen,HAN Mei,LIANG Jingxuan,et al. Hazard mechanism analysis of Taoguan giant debris flow in Wenchuan earthquake area on July 10th,2013[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2015,50(2):286 − 293. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU Xiewen, HAN Mei, LIANG Jingxuan, et al. Hazard mechanism analysis of Taoguan giant debris flow in Wenchuan earthquake area on July 10th, 2013[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(2): 286-293. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 黄健,胡卸文,金涛,等. 四川西昌“3•30”火烧区响水沟火后泥石流成灾机理[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):15 − 22. [HUANG Jian,HU Xiewen,JIN Tao,et al. Mechanism of the post-fire debris flow of the Xiangshui gully in “3•30” fire area of Xichang,Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):15 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG Jian, HU Xiewen, JIN Tao, et al. Mechanism of the post-fire debris flow of the Xiangshui gully in “3·30” fire area of Xichang, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3): 15-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 倪化勇,宋志,徐伟. 沟床侵蚀主导型泥石流形成机理与成灾特征—以石棉县2013-07-04群发泥石流为例[J]. 自然灾害学报,2015,24(2):97 − 106. [NI Huayong,SONG Zhi,XU Wei. Formation mechanism and disaster characteristics of debris flows originated predominately from gully erosion:Taking the 2013-07-04 clusted debris flows in Shimian County as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2015,24(2):97 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract) NI Huayong, SONG Zhi, XU Wei. Formation mechanism and disaster characteristics of debris flows originated predominately from gully erosion: taking the 2013-07-04 clusted debris flows in Shimian County as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2015, 24(2): 97-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 刘鑫, 张文, 李根, 等. 高位远程崩滑碎屑流-泥石流灾害链的演变过程与影响范围预测—以“4•5” 四川洪雅县铁匠湾地质灾害链为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2023,53(6):1799 − 1811. [LIU Xin, ZHANG Wen, LI Gen, et al. Research on evolution process and impact range prediction of high level remote collapse and landslide-debris flow disaster chain:Taking the “4•5” tiejiangwan geological disaster chain in Hongya County, Sichuan Province as an example[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2023,53(6):1799 − 1811. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Xin, ZHANG Wen, LI Gen, et al. Research on evolution process and impact range prediction of high level remote collapse and landslide-debris flow disaster chain—Taking the “4·5” tiejiangwan geological disaster chain in Hongya County, Sichuan Province as an example[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1799-1811. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 杜野,裴向军,张御阳,等. 云南东川区烧房沟“7·31”弃渣型泥石流成灾机理[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2016,14(6):171 − 175. [DU Ye,PEI Xiangjun,ZHANG Yuyang,et al. Hazard mechanism analysis of Shaofang ditch waste slag debris flow in Yunnan Dongchuan District on July 31th[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2016,14(6):171 − 175. (in Chinese with English abstract) DU Ye, PEI Xiangjun, ZHANG Yuyang, et al. Hazard mechanism analysis of Shaofang ditch waste slag debris flow in Yunnan Dongchuan district on July 31th[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2016, 14(6): 171-175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 黄洪,陈宁生,胡桂胜,等. 大流域泥石流成灾特征与形成机制—以金川县曾达沟“6•27”特大型泥石流为例[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(5):207 − 216. [HUANG Hong,CHEN Ningsheng,HU Guisheng,et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of debris flow in large watershed:take the “6•27” super large debris flow in Zengda gully,Jinchuan County as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(5):207 − 216. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG Hong, CHEN Ningsheng, HU Guisheng, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of debris flow in large watershed: take the “6.27” super large debris flow in Zengda gully, Jinchuan County as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(5): 207-216. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] OUYANG Chaojun,HE Siming,XU Qiang,et al. A MacCormack-TVD finite difference method to simulate the mass flow in mountainous terrain with variable computational domain[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2013,52:1 − 10.
[11] 胡明鉴, 汪稔, 陈中学, 等. 泥石流启动过程PFC数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(增刊1): 394 − 397 HU Mingjian, WANG Ren, CHEN Zhongxue, et al. Initiation process simulation of debris deposit based on particle flow code[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(Sup 1): 394 − 397. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 罗超鹏,常鸣,武彬彬,等. 基于FLOW-3D的泥石流龙头运动过程模拟研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):53 − 62. [LUO Chaopeng,CHANG Ming,WU Binbin,et al. Simulation of debris flow head movement process in mountainous area based on FLOW-3D[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):53 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) LUO Chaopeng, CHANG Ming, WU Binbin, et al. Simulation of debris flow head movement process in mountainous area based on FLOW-3D[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(6): 53-62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] LIU Bo,HU Xiewen,MA Guotao,et al. Back calculation and hazard prediction of a debris flow in Wenchuan meizoseismal area,China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2021,80(4):3457 − 3474. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-021-02127-3
[14] COSTA J E. Physical geomorphology of debris flows[M]//Developments and Applications of Geomorphology. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1984: 268 − 317.
[15] 赵宾杰,余斌,常鸣,等. 窄陡型泥石流沟特征研究[J]. 泥沙研究,2021,46(5):61 − 67. [ZHAO Binjie,YU Bin,CHANG Ming,et al. Characteristics of debris flow in narrow-steep channel[J]. Journal of Sediment Research,2021,46(5):61 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO Binjie, YU Bin, CHANG Ming, et al. Characteristics of debris flow in narrow-steep channel[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2021, 46(5): 61-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] HUNGR O, COROMINAS J, EBERHARDT E. Estimating landslide motion mechanism, travel distance and velocity[J]//HUNGR O, FELL R, COUTURE R, et al. , Eds. Estimating landslide motion mechanism, travel distance and velocity [J]. Landslide Risk Management, 2005: 109-138.
[17] 安雪莲, 密长林, 孙德亮, 等. 基于不同评价单元的三峡库区滑坡易发性对比—以重庆市云阳县为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2024,54(5):1629 − 1644. [AN Xuelian, MI Changlin, SUN Deliang, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility in Three Gorges Reservoir area based on different evaluation units:Take Yunyang County in Chongqing as an example[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2024,54(5):1629 − 1644. (in Chinese with English abstract) AN Xuelian, MI Changlin, SUN Deliang, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility in Three Gorges Reservoir area based on different evaluation units—Take Yunyang County in Chongqing as an example[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1629-1644. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 甘建军,罗昌泰. 中低山冲沟型泥石流运动参数及过程模拟[J]. 自然灾害学报,2020,29(2):97 − 110. [GAN Jianjun,LUO Changtai. Runout and process simulation of gully debris flow in middle and low mountains[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2020,29(2):97 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13577/j.jnd.2020.0210 GAN Jianjun, LUO Changtai. Runout and process simulation of gully debris flow in middle and low mountains[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2020, 29(2): 97-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13577/j.jnd.2020.0210
[19] TANG Chuan,ZHU Jing,DING Jun,et al. Catastrophic debris flows triggered by a 14 August 2010 rainfall at the epicenter of the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Landslides,2011,8(4):485 − 497. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-011-0269-5





 下载:
下载:






 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS