Kinematics and mechanism analysis of Tangjiawan landslide on the Xinshi—Jinyang Highway in Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
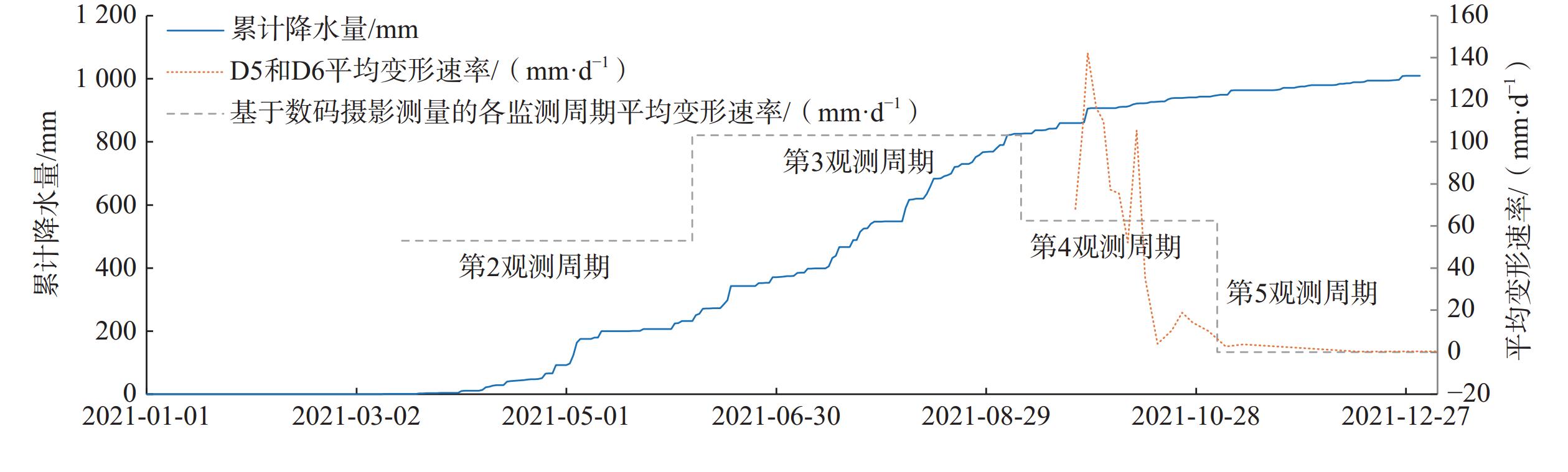
研究滑坡变形特征对于分析滑坡形成机理和制定防治措施至关重要。文章以工程诱发的唐家湾滑坡为研究对象,通过工程施工前后的6期无人机影像得到高分辨率DOM,基于相邻两期DOM中识别的特征点作为监测点,根据其位置的变化得出地表位移矢量数据,进而结合地质勘探和深部位移监测分析滑坡变形特征和形成机理。研究表明:工程建设前滑坡区无明显变形(第1个观测周期),工程施工后的第2观测周期(2021-03-15—2021-06-06)、第3 观测周期(2021-06-06—2021-09-08)和第4观测周期(2021-09-08—2021-11-03)滑坡主滑区平均变形速率分别为53.0,103.2和62.5 mm/d,至第5观测周期(2021-11-03—2022-01-03)变形速率趋于0;第2观测周期滑坡后缘的弃渣堆载是滑坡的直接触发因素,降雨促进了滑坡变形的发展,而随着雨季的结束和前缘的堆载反压滑坡变形速率逐渐降低;利用多期无人机高清影像可获取大范围、长时序地表变形信息,可作为一种有效的滑坡变形监测手段。
Abstract:Studying the kinematics of landslides is crucial for analyzing failure mechanism and designing remedial measures. This paper focuses on the Tandjiawan landslide that occurred during a highway construction. Five periods of high-resolution digital orthophoto maps (DOM) were generated using unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)- based photogrammetry, spanning both pre- and post- landslide conditions. Two successive UAV orthophotos were treated as observation periods, and corresponding features were identified in both images to establish monitoring points. Furthermore, two-dimensional displacement vectors were then computed by comparing orthographic images from each observation period based on these corresponding features. The analysis of kinematics and failure mechanism were conducted in conjunction with geological surveys and inclinometer measurements. The findings reveal that there was no significant deformation in the landslide area before the engineering construction of the highway (1st observation period). After construction, during the second observation period (March 15, 2021, to June 6, 2021), the third observation period (June 6, 2021, to September 8, 2021), and the fourth observation period (September 8, 2021, to November 3, 2021), the average deformation rates of the main sliding area of the landslide were 53.0 mm/day, 103.2 mm/day and 62.5 mm/day, respectively. By the fifth observation period (November 3, 2021, to January 3, 2022), the deformation rates had trended towards zero. The deposition of spoil at the rear of the landslide during the second observation period was the direct triggering factor, and rainfall facilitated the development of landslide deformation. As the rainy season ended and the front-end loading increased, the landslide deformation rate gradually decreased. This paper demonstrates that multi-period UAV photogrammetry can provide spatiotemporal surface deformation information for landslide areas, serving as an effective tools for landslide deformation monitoring.
-
Keywords:
- UAV images /
- photogrammetry /
- landslide /
- kinematics
-
0. 引言
据统计,季节性寒区面积在我国国土面积中占比为75%,而在自然界中具有层状构造的岩石约占陆地面积的三分之二,在中国更是占到77%以上[1],说明在寒区工程中面临更多的层状岩石冻融破坏问题,在冻融环境下,温度下降使岩石内部孔隙水冻结,体积膨胀,而固体介质遇冷收缩,致使冻胀力的产生,导致岩石内部原生孔隙和裂隙发展,同时产生新的孔隙,并破坏岩石内的胶结物;温度上升使岩石内部冰融化成水,并在岩石内部渗流迁移,形成裂隙通道并带走破坏后的胶结物质与颗粒,使岩石孔隙率进一步增大,进而导致岩石的损伤[2]。而对于层状岩石的层理面更易于发生冻融损伤,这对寒区工程稳定性存在一定的威胁,容易发生工程事故[3]。所以研究层状岩石受冻融作用后的力学特征,对寒区工程具有一定的指导意义。
层状岩石是指具有一组占绝对优势的结构面(层理面或者片理面)的岩体,与普通岩石相比具有一些特殊的特征。一些沉积岩(如砂岩、石灰石和页岩)和变质岩(如花岗岩、玄武岩和麻粒岩)具有明显的层理结构,声发射(acoustic emission,AE)技术可以有效、连续地实时监测脆性材料中细裂纹的产生和扩展,并实现裂纹的定位,已成为岩石变形和破坏的重要监测方法。Jia等[4]在不同次数的冻融循环后,测试了不同层理砂岩的P波速度、单轴抗压强度、拉伸强度和剪切强度。通过上述参数定义了几个各向异性指数,并分析了它们随冻融循环的变化;常森等[5]研究了冲击作用下冻融循环层理砂岩的强度、变形性质,针对性地对岩石的层理动荷载关系进行了力学响应的试验研究;张东明等[6]、Wang等[7]研究了含层理岩石在单轴压缩下损伤破坏声发射参数及能量耗散规律;姜德义等[8]、刘慧等[9]、宋彦琦等[10]、杨更社等[11]开展了不同冻融循环次数岩石单轴声发射试验,获得相应的物理力学参数,并分析声发射信号与冻融灰岩内部微裂纹活动的相关性; Qiao等[12]研究了冻融压缩荷载作用下非永久性节理岩石的断裂和声发射特征,结果表明,随着冻融循环次数的增加,材料的物理力学参数有不同程度的劣化;郑坤等[13 − 14]、付斌等[15]、王桂林等[16]、张艳博等[17]、蒋利松等[18]开展了岩石的声发射监测试验,获取了岩石的声发射累计振铃计数、累计能量计数等参数演化特征;赵娜等[19]、陈东升等[20]、何建华等[21]分析了岩石变形破坏过程中岩石损伤与声发射特征参数的变化情况。
综上,虽然学者对层状岩石的研究较多,但是对在冻融循环下层状岩石声发射特征研究还是相对较少。本文对层理砂岩进行了单轴压缩和声发射试验,研究了声发射振铃计数、振铃累计数、RA-AF值以及b值的演化特征。
1. 试样准备与试验方法
1.1 试样准备
砂岩试样取自四川省某露天矿区,该地气候寒冷,冬季寒冷漫长,昼夜温差大。试样表面呈黄色,层理发育明显。取样后经过切割、打磨等加工工序,根据ISRM标准,将试件制成50×100 mm、表面平行度小于0.02的标准圆柱体试件。由于层状岩石的力学特性在同一层面内大致相同,但在平行和垂直方向上差异较大。因此,仅选用平行和垂直于层理面的两种试样,平行层理试样和垂直层理试样分别简称为P试样和V试样,两种试样用声波测速仪筛选出波速相近,剔除波速离散度较高的试件,减小试验的离散程度。选出层理均匀、结构完整的试样后,将其分为8组试样,每组平行、垂直层理试样各一个,如图1所示。
1.2 试验方案和试验设备
将试样在模拟环境试验机内进行冻融循环,在试验机里−20 °C冻结6 h,然后在20 °C下融化6 h,如图2所示,循环次数分别为0,20,40,60次,每个循环次数设置两个平行组。先将所有试样在105 °C烘箱中干燥24 h后,留下两组(0次冻融循环)试样,直接进行单轴声发射试验,然后将剩下的试样真空饱水24 h后,放入环境模拟试验机分别进行冻融循环20,40,60次,其中将需要进行60次冻融循环的两组试样每隔20次冻融循环取出并烘干,同时对试样的波速、质量进行统计,最后进行单轴声发射试验。
加载系统采用DSZ-1000型应力应变三轴剪切渗透试验仪。加载试验设备由加载系统、声发射系统和观测系统组成。该设备由伺服液压动力系统、伺服介质控制系统和数据采集及控制系统组成,针对岩石和混凝土材料,该设备可以进行单轴、三轴应力应变试验,剪切试验,岩石力学流变试验,岩石力学渗透试验,温度条件下的岩石力学试验等。试验设备最大轴向力1000 kN,最大切向力300 kN,试验力测量精度小于±0.5%;声发射系统采用PIC-Express型声发射监测系统。该系统由1台计算机、1个软件、8个波形通道、8个放大器和探头组成;该系统支持多通道声发射信号检测,稳定性好,灵敏度高,传输高速。单轴轴向压缩试验加载采用位移控制方式,加载速率为0.05 mm/min,试样失去承载能力时停止加载。AE监测系统的主放大器设置为40 dB,阈值为40 dB。试验设备见图3。
2. 力学特性
2.1 冻融循环后试样孔隙发育
岩石在经过冻融循环后,岩石内部孔隙得到较好的发育,孔隙率和波速都能定量地反映出岩石内部孔隙的发育情况以及岩石质量的优劣程度[22]。在本次试验中将试样分别在0,20,40,60次冻融循环后取出烘干后测波速和称重,测完后将试样进行饱水24 h称重继续进行冻融循环直到60次,采用称重法计算试样的孔隙率[23],如式(1):
(1) 式中:n——岩石孔隙率/%;
V——岩样块体体积/cm3。
根据60次冻融循环过程中所测得孔隙率和波速,对结果取平均值得到图4。如图所示平行、垂直层理岩石的孔隙率都随着冻融循环次数的增加而增大,平行层理试样从14.99%增大到15.47%,垂直层理试样从14.34%增大到15.07%;而纵波波速随着冻融循环次数增加而变小,平行层理试样从2.785 km/h下降到2.555 km/h,垂直层理试样3.125 km/h下降到2.850 km/h。平行、垂直层理试样纵波波速岩石孔隙度增加、纵波波速降低可集中反应结构体密度的降低,进一步表明随着冻融循环次数的增加,岩石内部孔隙等微观缺陷数量也在增加,岩石本身存在孔隙,在冻融循环过程中,孔隙中的水冻结成冰,产生冻胀力,扩大了孔隙体积;在融化过程中,孔隙里面的冰消融,液态水在新增微孔隙的虹吸作用下不断补充进来,在这样的冻融循环过程中,试样的孔隙率逐渐变大,纵波波速逐渐变小。由于层理角度的不同,相同条件下,在图中可以看出,垂直组试样的纵波波速比水平组试样的纵波波速大,这是由于层理弱面角度不同而导致的,垂直组试样具有的层理弱面更利于纵波传播,这说明不同层理角度的试样具有各向异性。
2.2 力学性质及参数变化
图5为不同冻融循环次数下两组层理砂岩的单轴压缩应力-应变曲线,在图中可以看出两组试样的应力-应变曲线,整体变化趋势相近,可分为OA孔隙压密阶段,AB线弹性阶段,BC非稳定破裂发展阶段,CD峰后失稳破坏阶段,随着冻融循环次数的增加,可以看出两组试样的应力峰值降低,曲线都有向下压缩,向右拉伸的趋势。
图6为不同冻融循环次数试样应力峰值及最大轴向应变的变化趋势,在对比0到60次冻融循环后,平行组试样的抗压强度下降比例和应变增大比例都大于垂直组试样,说明平行组试样的劣化程度高于垂直组试样。
岩石在低温冻结下,水凝结成冰,体积会膨胀9%,这时会产生冻胀力,使试样内部孔隙发育,微裂纹开始产生;当温度升高时,冰融化,水在孔隙之间连通,形成水流通道,充满微裂纹空间。随着冻融循环作用的增强,试样内部微裂纹发育逐渐增强,直至微裂纹互相连接贯通。试样内部由于冻融损伤的累积,微观孔隙缺陷数量增多并造成了压密阶段增大,导致应力峰值降低,应变增加。所以两组试样的OA段孔隙压密阶段和CD段峰后破坏阶段明显变长,岩石从脆性破坏变为延性破坏的特征显著。但对比两组试样,平行组试样的峰后破坏阶段更加平缓,时间更长,这是由于层理方向不同。对于平行组试样,当轴向压力与层理面垂直时,在应力达到峰值时,平行层理弱面相对于垂直层理弱面能更充分发挥抵抗轴向压力的作用(表1)。
表 1 试样冻融前后应力、应变峰值变化情况Table 1. Peak stress and strain changes of samples before and after freeze-thaw冻融循环
次数应力峰值下降比例/% 应变峰值增加比例/% 平行层理试样 垂直层理试样 平行层理试样 垂直层理试样 20 37.9 13.4 13.4 16.5 40 41.3 29.1 33.7 30.4 60 57.5 52.8 40.7 35.7 3. 声发射特征参数研究
3.1 声发射振铃计数特征
声发射信号如果越过门槛值,就被定义为一次撞击,一个或若干个撞击构成一个AE事件,其主要作用是反映AE源(材料内部缺陷)的活跃度。事件率是单位时间内AE事件发生的次数,累计事件数则是单位时间内AE事件的累计叠加。因岩石在损伤破裂过程中1 s内对应若干个AE事件,故以1 s时间为单位,统计砂岩在单轴压缩试验全过程中AE事件率及其累计事件数,对比分析其演化特征[24 − 25]。
如图7、图8所示,两组不同层理砂岩在不同冻融循环作用下的声发射振铃计数演化曲线趋势变化一致,所以可整体分析将其分为三个阶段,平静阶段、阶梯式增长阶段、骤增阶段。
(1) 平静阶段振铃计数和振铃累计数增长缓慢,声发射事件较少,原生缺陷渐进压密使得岩样内部整体趋于完整,不具备发生明显声发射活动条件。
(2) 阶梯式增长阶段处在砂岩的弹性阶段及非稳定破裂发展阶段振铃计数及振铃累计数显著增长,其中振铃累计数多呈阶段式增长。这是随着应力的增加,岩石内部开始产生微裂纹,更利于声发射事件的发生。
(3) 骤增阶段声发射信号显著增强。此时应力达到峰值,试样内部微裂纹连接贯通,同时试样外部出现宏观裂纹,试样破坏前声发射的信号多且间隔时间短,声发射接收信号灯此时长亮,是试样破坏的前兆特征。
岩石的劣化程度与AE事件数有明显的变化关系,随着冻融循环次数的增加,可以看到两组试样的平静阶段相对一个完整试验过程逐渐变短,阶梯增长阶段逐渐变长,试样在冻融循环作用下,内部孔隙之间发生联通,向外扩张,使岩石的抗压强度下降,在轴向应力增大时,AE事件也更容易发生;每个试样的对应的骤增阶段都很明显,说明试样在破坏时AE事件大量发生,声发射信号显著增强,是一个明显的破坏前兆特征。
3.2 声发射b值演化特征
AE监测中使用较多的是借鉴于地震学中的破裂源参数统计指标,主要有b值以及对该统计指标的进一步统计分析。b值(b-value)起源于地震学中的 Gutenberg Richter(G-R)关系,即区域地震中大于M级的累计次数N的对数,与M级呈线性关系,如式(2)所示。
(2) 式中,a和b是常数。在分析AE参数时,通常可以用振幅(A)除以20来表示声发射震级M,即 M=A/20。在计算b值时,A的单位是dB[26]。
在监测压缩岩石过程发生的小破裂事件和大断裂事件的相对数量可以用b值表示,并且可以代表 AE事件的规模分布,因此,在分析和预测岩石破裂的前兆中被广泛利用[27]。声发射b值与岩石内部裂纹萌生扩展过程密切相关,b值较大时对应大量弱声发射事件产生,说明小破裂占据主导,而当b值迅速降低时,则说明岩石内部大破裂开始增加或裂纹扩展的速度突增。
在图9中可以得知两组不同层理砂岩的声发射b值变化有很大的区别,说明不同层理方向的砂岩单轴破坏模式不同。平行组试样声发射b值变化呈倒“V”型,随着冻融循环次数的增加,b值变化明显,在经过20,40次冻融循环后,b值都随着冻融循环次数的增加而变大,说明这些阶段以微破裂或者小破裂为主导,而在60次冻融循环后b值又变小,说明此时由微破裂转为大破裂。垂直组试样声发射b值变化与平行组试样相反呈正“V”型,在经过20,40次冻融循环后,b值都随着冻融循环次数的增加而变小,说明在这些阶段垂直层理砂岩以大破裂为主,在60次冻融循环后,b值开始变大,这时岩石在冻融循环作用下,内部微破裂增多,产生的微裂纹相互连接贯通,岩石整体劣化程度高,以微破裂为主导。
对于平行层理岩石,层理弱面与外界环境的接触程度更高,试件侧面平行层理弱面分布更广,更利于冻融损伤的累积。因此,随着冻融循环作用的加强,平行层理弱面劣化程度要高于垂直层理试样,这与前面两组试样的单轴抗压强度的变化结果一致。故在0~40次冻融循环作用下,由于平行层理试样的劣化程度高于垂直层理试样,故更可能发生大破裂,则b值变小。而在60次冻融循环后,试样内部得到充分劣化,又因为层理方向与轴向应力方向垂直,平行层理弱面相对于垂直层理弱面更能起到抵抗外力的作用,岩石内部以微破裂为主,则b值变大。
3.3 声发射RA-AF值演化特征
基于声发射参数特征判别法是使用上升时间与最大振幅的比值(risetime/amplitude,RA)与平均频率(average frequency,AF)来进行破裂类型的判断。一般而言,拉伸破坏对应的声发射事件具有较小的 RA值和较大的 AF值;与剪切破坏对应的声发射事件具有较大的RA值和较小的AF值。
图10显示了使用RA和AF的声发射参数方法对拉伸和剪切裂纹进行分类的方法[28]。对角线可以用来作为拉伸裂纹和剪切裂纹的分界直线,直线上侧的裂纹即为拉伸裂纹,直线下侧的裂纹则为剪切裂纹,而直线的斜率AF/RA称之为拉剪裂纹判断的阈值。
由图11、图12可知,我们可以看到对于不同冻融循环次数的平行层理砂岩的破坏模式主要以拉伸裂纹为主,带有少量的剪切裂纹或者复合裂纹,在经过20,40,60次冻融循环的试样同样是以拉伸裂纹为主,剪切裂纹或者复合裂纹的变化比较小,但是没有经过冻融循环处理的试样对照经过冻融循环作用的试样组,它的剪切裂纹或者复合裂纹较多,与图13试样的宏观破裂特征与其对应一致。对于垂直层理砂岩的破坏模式与平行层理砂岩有所区别,在未经过冻融处理的试样主要以拉伸裂纹和剪切裂纹为主,但随着冻融作用的加强,试样的拉伸裂纹逐渐增多,剪切裂纹逐渐减少,在经过60次冻融循环处理后,试样破坏基本以拉伸裂纹为主,这与图13试样在宏观上的拉伸破裂特征一致。
4. 结论
(1) 平行、垂直层理岩石的孔隙率都随着冻融循环次数的增加而增大,平行层理试样从14.99%增大到15.47%,垂直层理试样从14.34%增大到15.07%;而纵波波速随着冻融循环次数增加而变小,平行层理试样从2.785 km/h下降到2.555 km/h,垂直层理试样3.125 km/h下降到2.850 km/h。
(2) 在对比0到60次冻融循环后,水平层理试样的应力峰值下降了57.5%、应变增大40.7%,而垂直层理砂岩应力峰值下降52.8%、应变增大35.4%,平行组试样的抗压强度下降比例和应变增大比例都大于垂直组试样,说明平行组试样的劣化程度高于垂直组试样,
(3) 两组不同层理砂岩在冻融循环作用下的声发射振铃计数演化曲线趋势变化一致,可分为三个阶段:平静阶段、阶梯式增长阶段、骤增阶段。
(4) 不同层理方向的砂岩单轴破坏模式不同。平行组试样声发射b值变化呈倒“V”型,而垂直组试样声发射b值变化呈正“V”型,基于RA-AF值变化特征表明平行层理黄砂岩基本以拉伸破坏为主,而垂直层理砂岩在未处理时以拉伸破坏和剪切破坏为主,在60次冻融循环处理后,以拉伸破坏为主。
-
表 1 数据汇总
Table 1 Summary of the data
阶段 使用设备 像控设置 影像分辨率
/cm获取日期 滑前 直升机搭载飞思相机(1亿像素)
和Optech eclipse 激光雷达沿线测绘
地面控制点<10 2018-05-15 DJI Mavic2 勘察期间
测绘控制点<3 2019-03-26 滑后 DJI Mavic2 滑坡周边4个
地面控制点<3 2021-06-06 DJI Mavic2 <3 2021-09-08 DJI Mavic2 <3 2021-11-03 DJI Mavic2 <3 2022-01-03 表 2 各观测周期的观测时长和监测点数量
Table 2 Observation period duration and number of monitoring points for each observation period
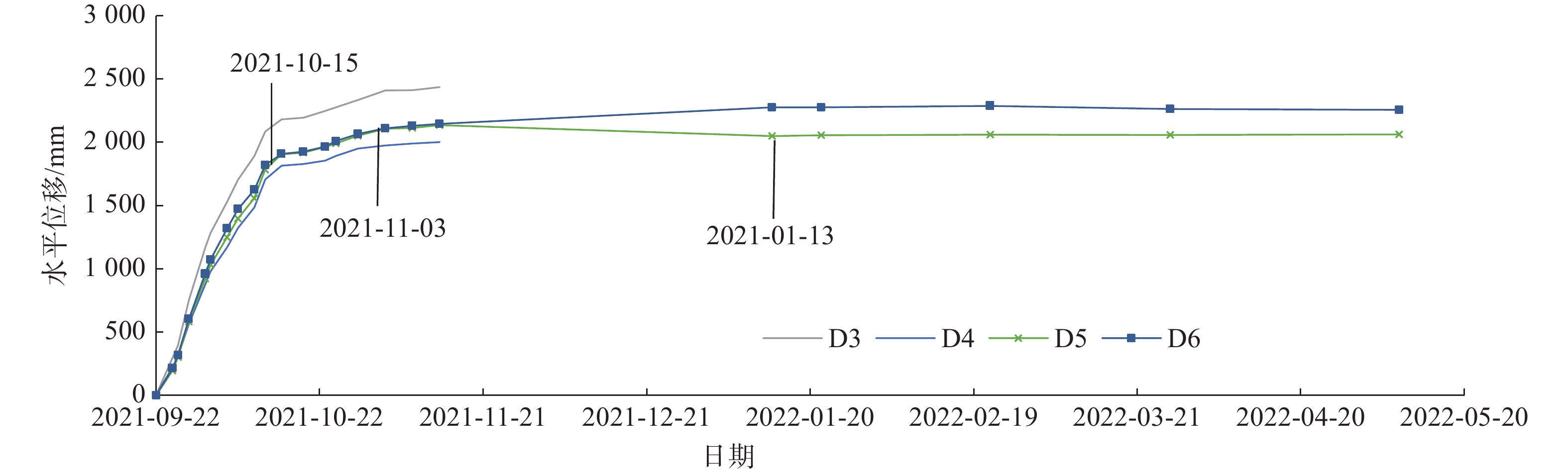
观测期 起止日期 时间间隔/d 监测点数量/个 1 2018-05-15—2019-03-26 325 17 2 2019-03-26—2021-06-06 803 7 3 2021-06-06—2021-09-08 94 25 4 2021-09-08—2021-11-03 56 68 5 2021-11-03—2022-01-03 61 49 表 3 各监测周期监测点平均变形量及变形速率
Table 3 Average displacement vectors and average deformation rates of monitoring points for each monitoring period
分区 数据类型 第1观测期
(2018-05-15—
2019-03-26)第2观测期
(2019-03-26—
2021-06-06)第3观测期
(2021-06-06—
2021-09-08)第4观测期
(2021-09-08—
2021-11-03)第5观测期
(2021-11-03—
2022-01-03)I区 平均变形量/m <0.1 — 3.8 0.7 — 平均变形速率/(mm·d−1) 0 — 40.4 12.5 — II-1区 变形量平均值/m <0.1 — — 3.2 0.140 平均变形速率/(mm·d−1) 0 — — 57.1 0.002 II-2区 变形量平均值/m <0.1 4.4 9.7 3.5 0.090 平均变形速率/(mm·d−1) 0 53.0 103.2 62.5 0 注:—标示该区内施工导致地形变化,无法取得匹配监测点;第2观测周期变形速率计算起始时间为工程开始施工的2021年3月15日。 -
[1] 贾会会,薛建志,郭利召,等. “空天地”一体化技术在采空区形变监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(3):69 − 82. [JIA Huihui,XUE Jianzhi,GUO Lizhao,et al. Application of combined space,arial and ground based multiple technologies in deformation monitoring of mining areas[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(3):69 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202202015 JIA Huihui, XUE Jianzhi, GUO Lizhao, et al. Application of combined space, arial and ground based multiple technologies in deformation monitoring of mining areas[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(3): 69 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202202015
[2] 许强. 对滑坡监测预警相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):360 − 374. [XU Qiang. Understanding the landslide monitoring and early warning:Consideration to practical issues[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):360 − 374. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-025 XU Qiang. Understanding the landslide monitoring and early warning: Consideration to practical issues[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(2): 360 − 374. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-025
[3] 刘春,万红,李巍岳,等. 基于无人机影像的大型滑坡区域精细地形构建研究[J]. 井冈山大学学报(自然科学版),2015,36(1):1 − 7. [LIU Chun,WAN Hong,LI Weiyue,et al. The research on construction of large-scale landslide precise terrain based on uav images[J]. Journal of Jinggangshan University (Natural Science),2015,36(1):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8085.2015.01.001 LIU Chun, WAN Hong, LI Weiyue, et al. The research on construction of large-scale landslide precise terrain based on uav images[J]. Journal of Jinggangshan University (Natural Science), 2015, 36(1): 1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8085.2015.01.001
[4] 王俊豪,魏云杰,梅傲霜,等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影的黄土滑坡信息多维提取与应用分析[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(2):388 − 401. [WANG Junhao,WEI Yunjie,MEI Aoshuang,et al. Multidimensional extraction of UAV tilt photography-based information of loess landslide and its application[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(2):388 − 401. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.12029/gc20210204 WANG Junhao, WEI Yunjie, MEI Aoshuang, et al. Multidimensional extraction of UAV tilt photography-based information of loess landslide and its application[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(2): 388 − 401. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12029/gc20210204
[5] 孔嘉旭,谷天峰,孙萍萍,等. 基于多期无人机影像的黑方台硅化厂滑坡形态变形演化研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2021,35(1):100 − 107. [KONG Jiaxu,GU Tianfeng,SUN Pingping,et al. Research on deformation evolution of landslides in Heifangtai silicified plant based on multi-stage UAV images[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2021,35(1):100 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2021.015 KONG Jiaxu, GU Tianfeng, SUN Pingping, et al. Research on deformation evolution of landslides in Heifangtai silicified plant based on multi-stage UAV images[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(1): 100 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2021.015
[6] 彭大雷,许强,董秀军,等. 无人机低空摄影测量在黄土滑坡调查评估中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展,2017,32(3):319 − 330. [PENG Dalei,XU Qiang,DONG Xiujun,et al. Application of unmanned aerial vehicles low-altitude photogrammetry in investigation and evaluation of loess landslide[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2017,32(3):319 − 330. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.03.0319 PENG Dalei, XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, et al. Application of unmanned aerial vehicles low-altitude photogrammetry in investigation and evaluation of loess landslide[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(3): 319 − 330. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.03.0319
[7] 张欢,巨能攀,陆渊,等. 基于无人机的滑坡地形快速重建与稳定性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):171 − 179. [ZHANG Huan,JU Nengpan,LU Yuan,et al. Rapid remodeling of three-dimensional terrain and stability analyses of landslide based on UAV[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):171 − 179. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202008010 ZHANG Huan, JU Nengpan, LU Yuan, et al. Rapid remodeling of three-dimensional terrain and stability analyses of landslide based on UAV[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(6): 171 − 179. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202008010
[8] 陈巧,袁飞云,付霞,等. 无人机摄影测量技术在阿娘寨滑坡应急调查中的应用[J]. 测绘通报,2023(1):77 − 83. [CHEN Qiao,YUAN Feiyun,FU Xia,et al. Application of unmanned aerial vehicle photogrammetry technology in emergency investigation of Aniangzhai landslide[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2023(1):77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHEN Qiao, YUAN Feiyun, FU Xia, et al. Application of unmanned aerial vehicle photogrammetry technology in emergency investigation of Aniangzhai landslide[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2023(1): 77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 赵婷婷,高文娟,李志林,等. 实景三维技术在“8•8”九寨沟地震地质灾害快速调查中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(3):93 − 99. [ZHAO Tingting,GAO Wenjuan,LI Zhilin,et al. Application of real-scene 3D technology in the rapid survey of geological disasters after the “8•8” Jiuzhaigou earthquake[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(3):93 − 99. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202209016 ZHAO Tingting, GAO Wenjuan, LI Zhilin, et al. Application of real-scene 3D technology in the rapid survey of geological disasters after the “8•8” Jiuzhaigou earthquake[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(3): 93 − 99. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.202209016
[10] PETERNEL T,KUMELJ Š,OŠTIR K,et al. Monitoring the Potoška planina landslide (NW Slovenia) using UAV photogrammetry and tachymetric measurements[J]. Landslides,2017,14(1):395 − 406. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-016-0759-6
[11] LARIBI A,WALSTRA J,OUGRINE M,et al. Use of digital photogrammetry for the study of unstable slopes in urban areas:Case study of the El Biar landslide,Algiers[J]. Engineering Geology,2015,187:73 − 83. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.12.018
[12] CHENG Qiang,YANG Yinghui,DU Yi. Failure mechanism and kinematics of the Tonghua landslide based on multidisciplinary pre- and post-failure data[J]. Landslides,2021,18(12):3857 − 3874. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-021-01770-x
[13] SASAKI Y,FUJII A,ASAI K. Soil creep process and its role in debris slide generation:Field measurements on the north side of Tsukuba Mountain in Japan[J]. Developments in Geotechnical Engineering,2000,84:199 − 219.
[14] REGMI N R,WALTER J I. Detailed mapping of shallow landslides in eastern Oklahoma and western Arkansas and potential triggering by Oklahoma earthquakes[J]. Geomorphology,2020,366:106806. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.05.026
[15] 张克利,姚爱敏,张建全,等. GB-InSAR滑坡应急监测的快速建模与三维匹配试验及应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(6):190 − 197. [ZHANG Keli,YAO Aimin,ZHANG Jianquan,et al. Rapid modeling and 3D matching of GB InSAR landslide emergency monitoring: Method and application[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(6):190 − 197. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Keli, YAO Aimin, ZHANG Jianquan, et al. Rapid modeling and 3D matching of GB InSAR landslide emergency monitoring: Method and application[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(6): 190 − 197. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 黄永芳,郭永刚,黄艳婷. 基于加权信息量和加权确定性系数的藏东南滑坡易发性评价[J]. 中国地质调查,2024,11(3):108 − 116. [HUANG Yongfang,GUO Yonggang,HUANG Yanting. Landslide susceptibility assessment in the southeastern Tibet based on weighted informativeness and weighted certainty factor[J]. Geological Survey of China,2024,11(3):108 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HUANG Yongfang, GUO Yonggang, HUANG Yanting. Landslide susceptibility assessment in the southeastern Tibet based on weighted informativeness and weighted certainty factor[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2024, 11(3): 108 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 岳磊,刘昌义,丛晓明,等. 基于InSAR技术的夏藏滩滑坡区地表变形监测与分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(3):158 − 170. [YUE Lei,LIU Changyi,CONG Xiaoming,et al. Surficial deformation monitoring and analyzing to the Xiazangtan landslides based on InSAR method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(3):158 − 170. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YUE Lei, LIU Changyi, CONG Xiaoming, et al. Surficial deformation monitoring and analyzing to the Xiazangtan landslides based on InSAR method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(3): 158 − 170. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 安雪莲,密长林,孙德亮,等. 基于不同评价单元的三峡库区滑坡易发性对比——以重庆市云阳县为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2024,54(5):1629 − 1644. [AN Xuelian,MI Changlin,SUN Deliang,et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility in Three Gorges Reservoir area based on different evaluation units:Take Yunyang County in Chongqing as an example[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2024,54(5):1629 − 1644. (in Chinese with English abstract)] AN Xuelian, MI Changlin, SUN Deliang, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility in Three Gorges Reservoir area based on different evaluation units: Take Yunyang County in Chongqing as an example[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1629 − 1644. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 薛强,张茂省,董英,等. 基于DEM和遥感的黄土地质灾害精细化风险识别——以陕北黄土高原区米脂县为例[J]. 中国地质,2023,50(3):926 − 942. [XUE Qiang,ZHANG Maosheng,DONG Ying,et al. Refinement risk identification of loess geo-hazards based on DEM and remote sensing:Taking Mizhi County in the Loess Plateau of northern Shaanxi as an example[J]. Geology in China,2023,50(3):926 − 942. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XUE Qiang, ZHANG Maosheng, DONG Ying, et al. Refinement risk identification of loess geo-hazards based on DEM and remote sensing: Taking Mizhi County in the Loess Plateau of northern Shaanxi as an example[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(3): 926 − 942. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 王雪冬,张超彪,王翠,等. 基于Logistic回归与随机森林的和龙市地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(6):1957 − 1970. [WANG Xuedong,ZHANG Chaobiao,WANG Cui,et al. Geological disaster susceptibility in Helong City based on logistic regression and random forest[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(6):1957 − 1970. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Xuedong, ZHANG Chaobiao, WANG Cui, et al. Geological disaster susceptibility in Helong City based on logistic regression and random forest[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1957 − 1970. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 孙小勇,魏龙,唐华,等. 基于GIS的崩滑地质灾害孕灾地质条件分析——以西藏嘉黎县为例[J]. 中国地质调查,2024,11(4):92 − 100. [SUN Xiaoyong,WEI Long,TANG Hua,et al. Analysis of the disaster-pregnancy geological conditions of collapse and landslide based on GIS:A case study of Jiali County in Tibet[J]. Geological Survey of China,2024,11(4):92 − 100. (in Chinese with English abstract)] SUN Xiaoyong, WEI Long, TANG Hua, et al. Analysis of the disaster-pregnancy geological conditions of collapse and landslide based on GIS: A case study of Jiali County in Tibet[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2024, 11(4): 92 − 100. (in Chinese with English abstract)





 下载:
下载:























 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS