Landslide early warning based on improved tangential angle and displacement rate: A case study of the Leijiashan landslide in Shimen County, Hunan Province
-
摘要:
为了研究湖南省滑坡监测预警方法,提高预警成功率,以石门县雷家山滑坡为例展开研究。通过对灾害现场进行详细地质调查,对滑坡特征进行了描述,初步阐述了滑坡发生的成因机理。研究结果表明,独特的地形地貌、结构松散的土体是滑坡形成的内在因素,强降雨和工程切坡活动是导致滑坡的外因。基于GNSS系统获取滑坡的全过程变形-时间曲线,并对变形曲线特征进行分析,发现该滑坡具有明显的初始变形、等速变形、加速变形三阶段演化特征,属于渐变型滑坡。将切线角和变形速率阈值作为滑坡预警的重要指标,建立了预警判据,并对接群防群测信息平台,可以为相关部门展开防灾减灾工作和应急响应提供直接依据。雷家山滑坡实现成功避险,验证了该监测预警方法的实用价值。
Abstract:To study landslide monitoring and early warning methods in Hunan Province, and to improve the success rate of early warning, the Leijiashan landslide in Shimen County is used as a representative case. Through a detailed site investigation, this paper describes the characteristics of the landslide and provides a comprehensive analysis of its failure mechanism. The results reveal that the unique landscape and loose soil structure are internal factors contributing to the occurrence of the landslide, while heavy rainfall and the engineering excavation are external factors. By utilizing the GNSS system, complete displacement-time curves are obtained, and the types and features of these curves are analyzed to identify the evolutionary characteristics of the landslide, which include three stages: initial deformation, constant deformation, and accelerated deformation. Therefore, the landslide is classified as a gradual change type. By using the tangent angle and deformation rate thresholds as important indicators for landslide early warning, an early warning criterion is established. It is integrated with the community-based disaster prevention and early warning information platform, providing direct evidence for relevant departments to carry out disaster prevention, reduction, and emergency response. Successful mitigation of the Leijiashan landslide validates the practicality of this monitoring and early warning method.
-
0. 引言
“地质灾害何时发生”一直是困扰世界的难题,不少学者致力于地质灾害预警预报研究,并取得了新的进展[1 − 4]。许强等[5 − 6]自主研发一套自适应智能变频监测设备,建立多级预警模型,实现突发型黄土滑坡预警。周琪等[7]利用数值模拟对突发型滑坡危险范围进行了预测,准确度可达60%以上。程素珍等[8]系统研究了近 15 年来北京市突发地质灾害时空分布规律和监测预警状况。张凯翔[9]认为基于过程仿真模拟,可以提高地质灾害预报的时间、地点、发生强度的准确性。2020年,为实现“专群结合”的监测预警工作目标,自然资源部部署普适型地质灾害监测预警设备的研发和现场试验工作[10]。随着普适性地质灾害监测预警技术的推广,提升了市县级监测预警能力[11]。侯圣山等[12]在甘肃省岷县建立专群结合地质灾害监测预警系统,能够捕捉毫米级变形。马娟等[13]选用普适型多参数集成监测设备,对三峡库区滑坡开展监测,通过判据模型自动触发预警。何满潮等[14]提出基于“滑坡发生的充分必要条件是牛顿力变化”的监测预警新方法,解决滑坡短临预报科学难题。青海省已构建监测预警信息化平台可自动分析实时采集地质灾害监测数据[15]。
目前湖南省已部署近
3000 处地质灾害专业监测点,以普适型设备为主,构建了“人防+技防”监测预警体系。2020年以来,全省已出现了近40起成功预警和有效预警的案例,为转移避险提供了科学依据并赢得了宝贵时间。雷家山滑坡就是其中的典范案例。但湖南省地质灾害监测预警理论方法研究相对滞后,跟不上实际专业监测点建设速度,因此急需加强相关研究力度,形成符合我省的可以复制的监测预警方法,促进湖南省地质灾害监测预警工作更上新的台阶。以雷家山滑坡为例,本文在收集资料和野外调查的基础上,梳理防灾应对全链条,分析滑坡失稳前监测数据,建立预警判据,总结监测预警方法,期望为预警发布和相关部门预警响应提供技术支撑。1. 滑坡概况
1.1 滑坡基本特征
雷家山滑坡位于湖南省西北部的常德市石门县南北镇潘坪村雷家山附近(图1),为在册隐患点。2020年7月6日16时52分,该滑坡隐患点发生大规模滑动。经实地调查结合无人机低空摄影等技术手段,滑坡主滑方向150°,滑体长500 m,宽300 m,平均厚度20 m,滑坡体积约300×104 m3(图2)。滑体主要由含砾粉质黏土组成,滑动面整体呈圆弧状(图3),下伏基岩为震旦系陡山沱组泥灰岩及炭质页岩组成,属大型中层土质滑坡。滑坡毁坏5栋民房、1座小型水电站、300 m省道、35 kV高压电线路及通讯设施设备、村组道路、桥梁、水利设施及机械设备,造成直接经济损失共约
2000 万元,灾情等级为特大型。因调查巡查到位、人防和技防监测预警到位、当地政府与相关部门防灾措施到位,提前组织受威胁的居民以及工厂的员工共计33人撤离,交通部门提前封闭道路,电力部门提前切断附近高压供电,虽然雷家山隐患点发生了大规模滑坡,却没有出现人员伤亡。雷家山滑坡是近年湖南乃至全国规模最大一起地质灾害成功预警事件,是湖南省地灾综防体系建设以来地质灾害主动防范全链条最完整的成功避险案例。
1.2 滑坡成因分析
滑坡区属剥蚀中山地貌,最高海拔约
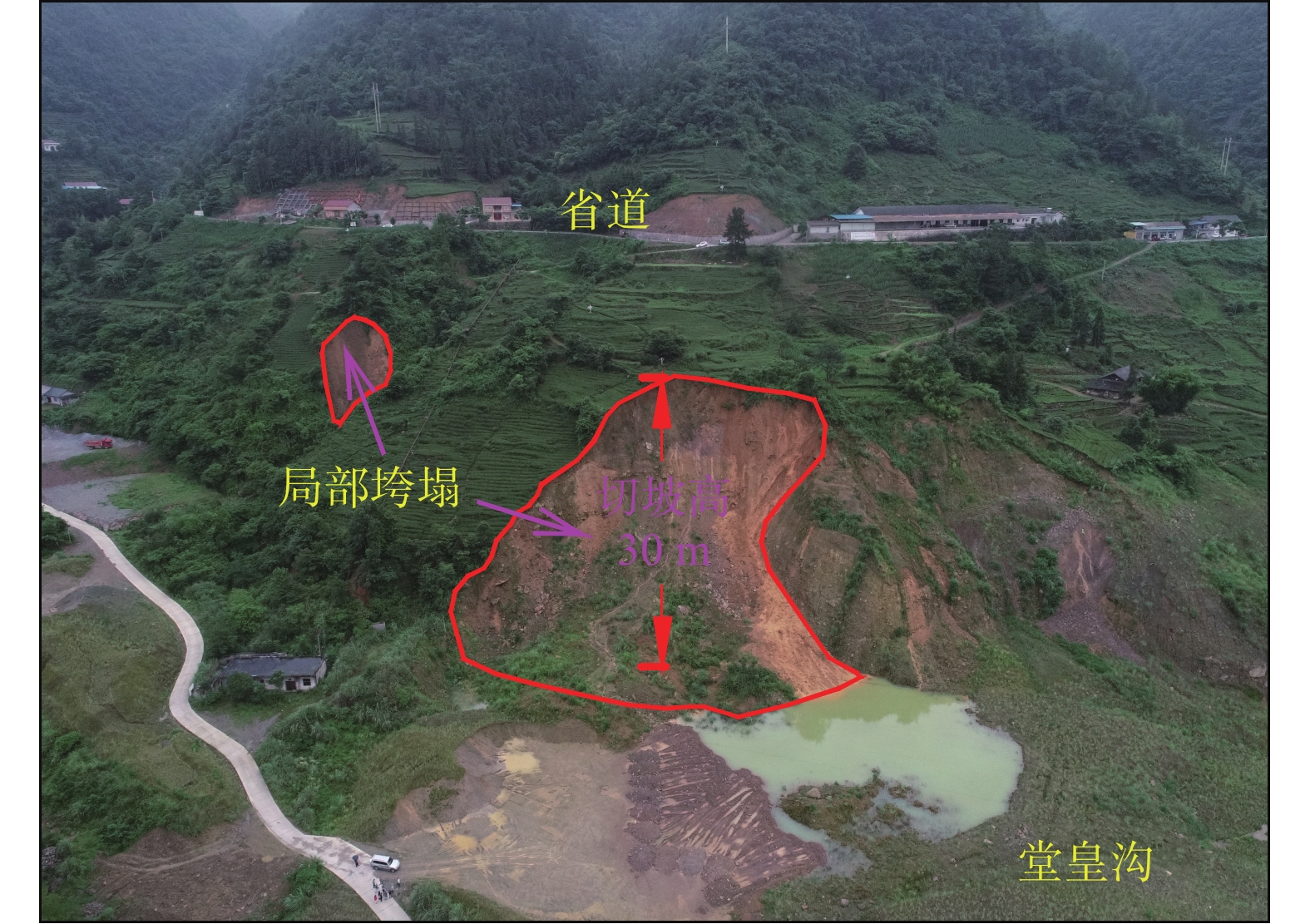
1000 m,最低海拔为南部堂皇沟570 m,最大高差近430 m。区内地形切割较强烈,沟谷发育,总体地势北高南低,山体坡度20°~40°,局部大于50°。山坡中上部植被发育,多为乔木,未见基岩出露;山坡中下部主要为茶园、油菜地,呈梯田式,民居分布于公路两侧。根据现场调查与访问,该隐患点为老滑坡复活,老滑坡成灾于1935年,之后滑体逐渐稳定,植被茂盛。随着近年当地经济快速发展,老滑坡区人类工程活动变得日益强烈,主要有修建省道村道、切坡建房及农业种植活动等。农业活动主要是茶叶、油菜等经济作物种植,长年耕作,疏松局部表土,雨水等浸润软化岩土体,并下渗补给地下水,不利于斜坡的稳定。修路、建房切坡高度最大可达30 m,坡度一般70°~75°,破坏了老滑坡原始应力平衡状态,为老滑坡复活创造了临空条件。雷家山滑坡属于老滑坡前缘部分滑体。2018年12月,滑坡前缘曾出现多处浅层垮塌(图4)。
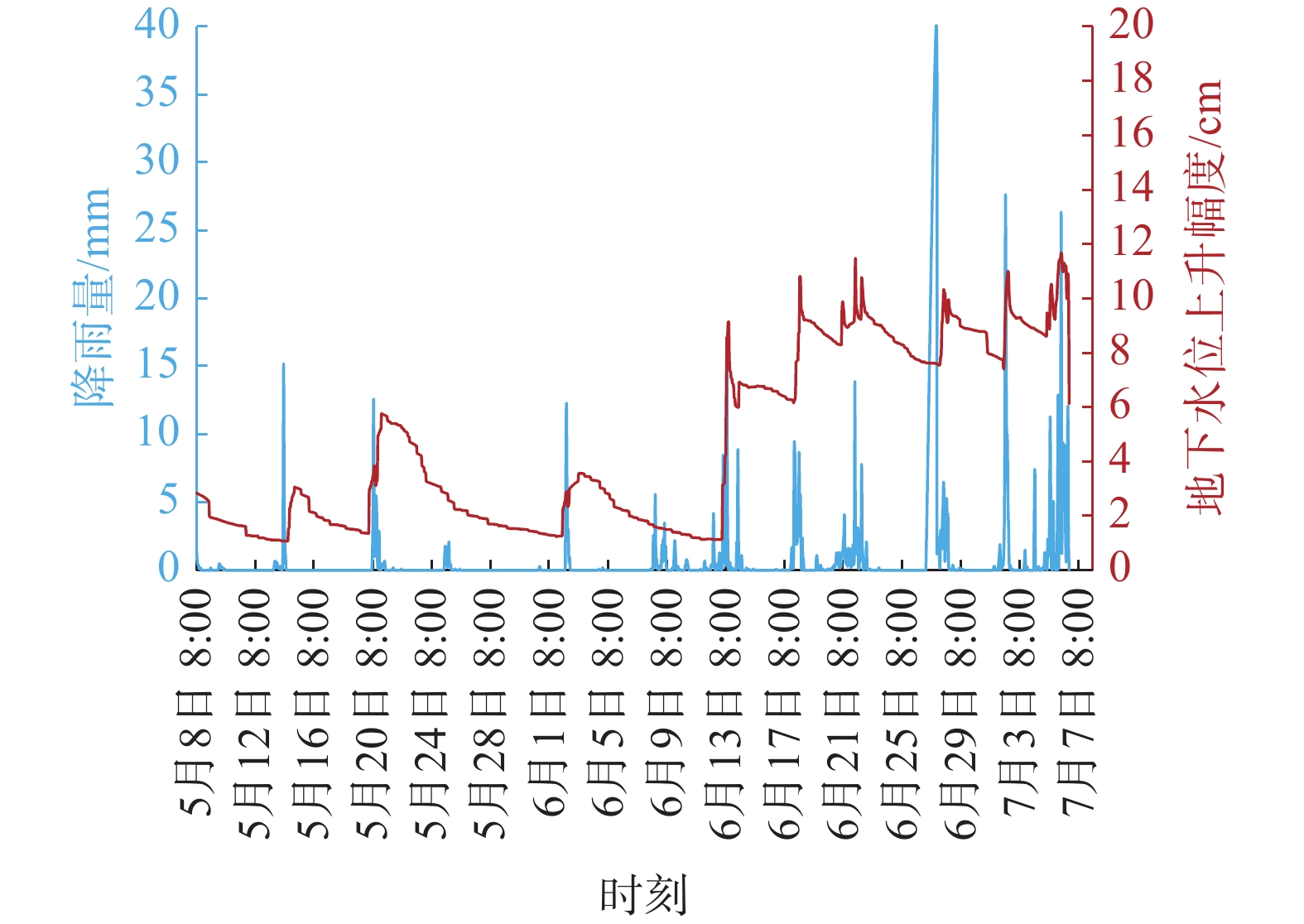
滑体物质为老滑坡堆积体的含砾粉质黏土组成,其特征是结构松散、颗粒物质大小混杂,凝聚力小。滑坡区微地貌呈下陡、中缓、上陡特点,地表水易于汇集下渗,整个坡体土体长期处于浸水-干燥-浸水-干燥的干湿交替环境中,加之不同深度堆积层岩相多变,其渗水性也存在差异,造成了相对隔水层,这种分界面逐渐演变成利于斜坡变形的滑面。失稳前区内连续遭受几轮强降雨,其中滑前24 h累计降雨量达146.4 mm,前2 天雨量180.9 mm,近7 天雨量291.8 mm;大量雨水下渗,地下水水位上升,滑前一直处于高位,最大涨幅11.68 cm,地下水涨幅与降雨量吻合度较高(图5)。坡体含水量增加,一方面增加了滑体自重,增大了下滑力;另一方面软化滑动面,降低抗剪强度,最终导致坡体变形失稳滑移。
综上所述,地形地貌、岩性条件是形成该滑坡内在因素,而主要外界影响因素是大气降水和人类工程活动。该滑坡是在内因与外因耦合作用下产生的。
2. 监测过程和预警响应
雷家山滑坡从调查发现到失稳破坏,历时1年半,采取了全链条的主动防御措施,最终实现无人员伤亡的结果。主要预警实施流程如下:
(1)调查入库。该滑坡为老滑坡,大约于2018年12月复活,发生明显变形,滑坡后缘及中部出现大量拉张裂缝。经技术人员现场调查,登记为滑坡隐患点,纳入全省地质灾害隐患数据库。当地主管部门安排专人担任监测员,负责滑坡日常监测工作。
(2)巡查。2019年1月开始,对该滑坡定期开展巡查。2019年6月,巡查人员发现滑坡变形加剧,主要变形迹象为前缘垮塌、坡脚渗水、房屋及公路开裂等。
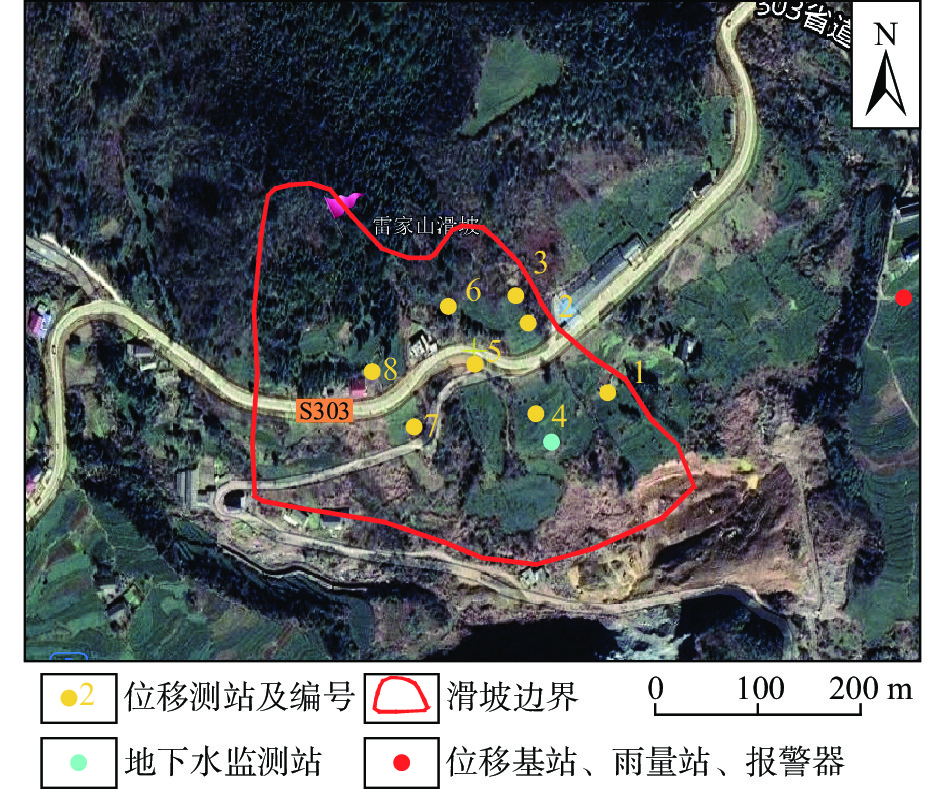
(3)专业监测网络建设。为掌握滑坡变形趋势,保障人民生命财产安全,尽可能减少灾害损失,对该滑坡实施了专业化自动监测,采用北斗微芯技术。共布设8台GNSS地表位移监测站,1台地下水位监测站,1台自动化雨量计、1台广播报警器与监测基准站安装在同一部位(图6)。2019年11月,雷家山滑坡监测预警系统投入使用。
(4)初始变形阶段。2019年12月—2020年5月中旬,所有位移监测站均有不同程度的位移变化,位移速率总体平缓,位移总量很小。
(5)等速变形阶段。2020年5月下旬—2020年6月13日,从监测曲线看呈现出位移持续增大的趋势,但位移速率变化不明显。
(6)初加速变形阶段。6月14日—6月25日,该监测点受2020年6月连续高强度降雨影响,部分位移监测站出现加速变形特征。省自然资源厅21—23日连续向石门县发布橙色或黄色地质灾害气象风险预警,该滑坡处于预警区。鉴于上述情况,2020年6月24日向主管部门发布黄色预警信息及险情分析报告,建议加强巡查。
(7)中加速变形阶段。6月26日—7月1日,滑坡已出现明显的加速形变的特征, 6月30日17:29发布橙色预警,建议撤离人员。接报后,市、县自然资源部门迅速组织监测员和专业技术人员实地核查,发现滑坡部分已经下滑,此时滑坡稳定性状态极差,存在整体下滑的可能性。当地政府召开专家组现场会商会后,决定立即启动防灾预案,组织隐患区域群众33人全部撤离,并将所有房屋贴上封条,禁止人员再次入内。
(8)临滑直至成灾阶段。7月2日—7月6日。7月2日开始持续降雨,变形进一步加剧。经过专家分析研判,于7月6日14:00紧急发布红色预警。7月6日省自然资源厅向石门等地再次发出橙色气象风险预警。收到预警后,自然资源部门组织技术人员加密巡查,并于7月6日15时,会同交通部门果断将省道隐患点周边区域路段全面戒严封路,通知电力部门切断高压供电。当天16时52分,滑坡失稳发生大规模滑动,瞬间摧毁5栋民房、1座水电站、一段省道。通过人防和技防,33人提前撤离,实现“零伤亡”奇迹。
3. 预警方法研究
3.1 监测数据分析
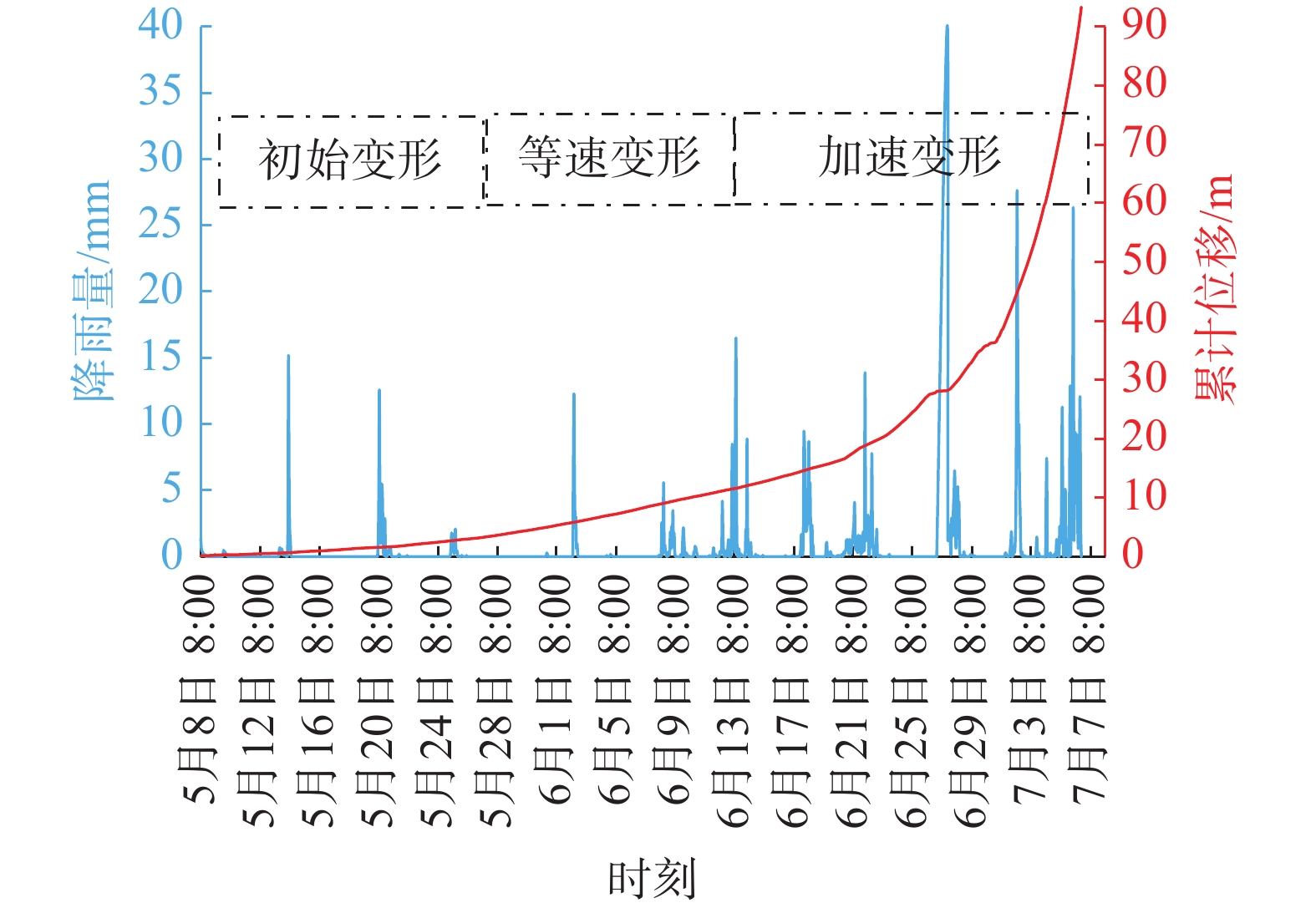
从省监测预警平台上线以来,雷家山滑坡监测系统运行良好,设备在线率一直是90%以上。进入到2020年5月,监测数据开始出现比较明显和持续的变形,直至7月6日失稳滑动,监测到滑坡整个变形破坏过程。运用最小二乘法对原始监测数据进行滤波处理,得到比较平滑的时间-位移曲线图(图7)。从图7可以看出,5月初至5月下旬,位移总量微弱,曲线几乎呈水平状,滑坡处于初始变形阶段;5月下旬—6月13日,曲线呈向上的直线状,加速度等于0,说明处于匀速运动状态,此时滑坡为等速变形阶段;6月14日—7月6日,曲线明显上凹,加速度大于0,这是典型的加速运动状态,此时为加速变形阶段。由于雷家山滑坡具有明显的初始变形、等速变形、加速变形3个变形演化阶段,且每个阶段历时近20 天或以上,滑坡成灾之前变形明显,共历时1年半,明显不属于突发型滑坡,因此属于渐变型滑坡。
结合图7分析滑坡位移变形与降雨量的相互关系。整个5月份累计降雨91.4 mm,滑坡累计位移5 m;进入6月后降雨强度和日数明显提升,6月累计降雨369.8 mm,滑坡累计位移31 m。这说明累计降雨量越大,滑坡累计位移变形也越大,两者的相关性较为明显。
3.2 预警判据
由于单一的速率阈值难以准确识别滑坡变形阶段,加之不同坐标尺度绘制的时间-位移曲线存在切线角不确定性的问题,这也是预警经常出现空报、误报的主要原因。基于滑坡演化全过程,许强等[16]总结出改进切线角模型,很好的解决了这个难题。
为了真实反映切线角变化情况,首先需要对变形位移进行统一的量纲变换:
$$ {T}_{i}=\frac{{S}_{i}}{v} $$ (1) 式中:Ti——量纲变换后的位移变化量;
Si——位移变化量;
v——等速阶段的变形速率。
最终得到改进切线角的计算公式:
$$ {\alpha }_{i}=\frac{180}{\text{π}}{\rm{acrctan}}\frac{{T}_{i}-{T}_{i-1}}{{t}_{i}-{t}_{i-1}} $$ (2) 式中:αi——改进切线角/(°);
ti——某一监测时刻。
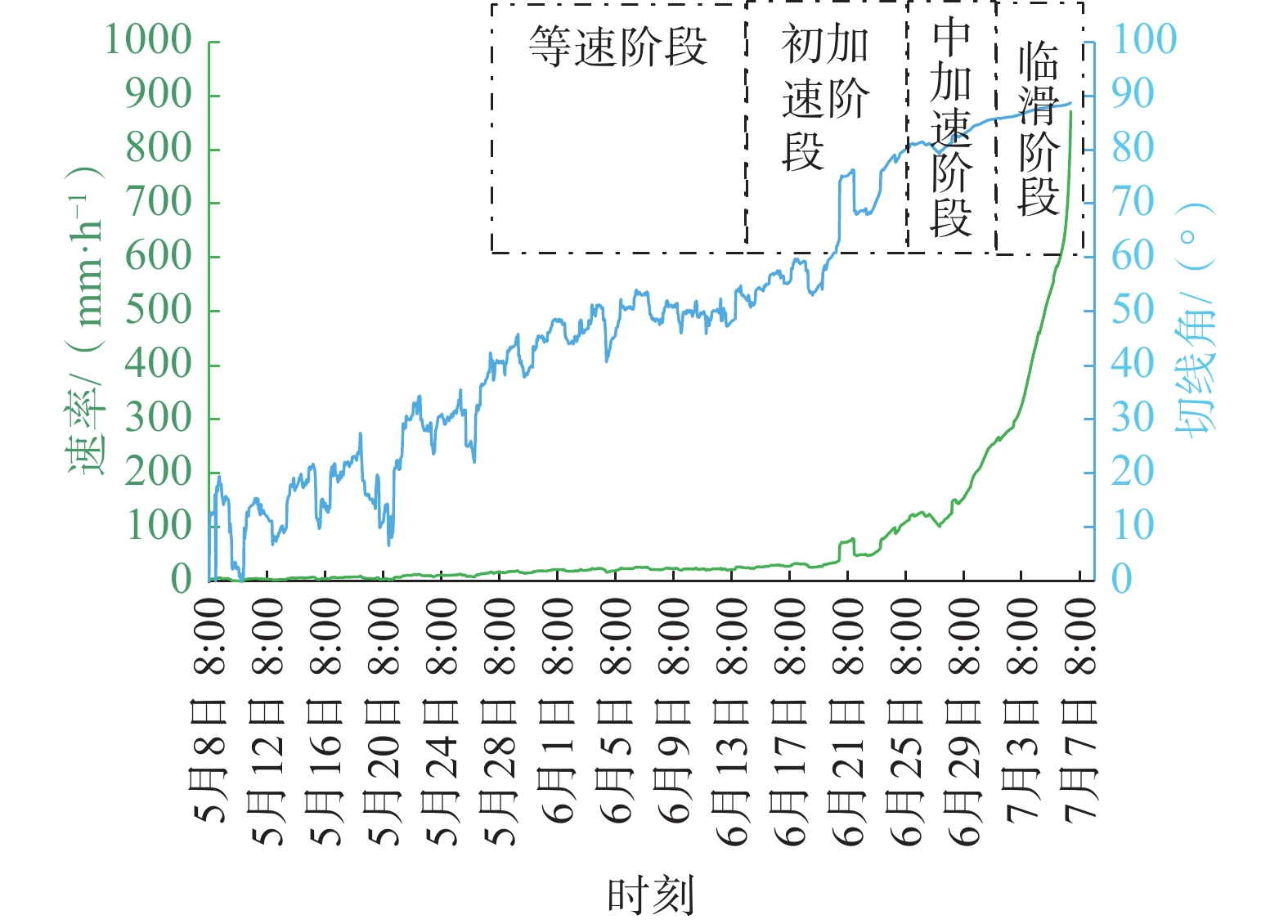
依据上述原理,绘制出切线角与变形速率相互关系曲线图(图8)。
分析图8的切线角和变形速率变化规律,构建了滑坡的综合预警判据(表1)。通过变形全过程分析,以切线角和变形速率为主要判据,结合专家判断,综合判定滑坡处于何种阶段,再确定发布预警信息,降低虚警率,可以有效提高预警的准确率。
表 1 基于切线角阈值和变形速率综合预警判据Table 1. Comprehensive early warning criteria based on tangential angle threshold and deformation rate预警级别 注意级 警示级 警戒级 警报级 预报形式 蓝色 黄色 橙色 红色 变形阶段 等速变形阶段 初加速变形阶段 中加速变形阶段 临滑阶段 切线角/(°) α≈45 45<α<80 80≤α<85 α≥85 速率/(mm·h-1) 17~20 20~112 112~262 >262 滑坡变形时间 5月27日—6月13日 6月14日—6月25日 6月26日—7月1日 7月2日—7月6日 3.3 预警发布
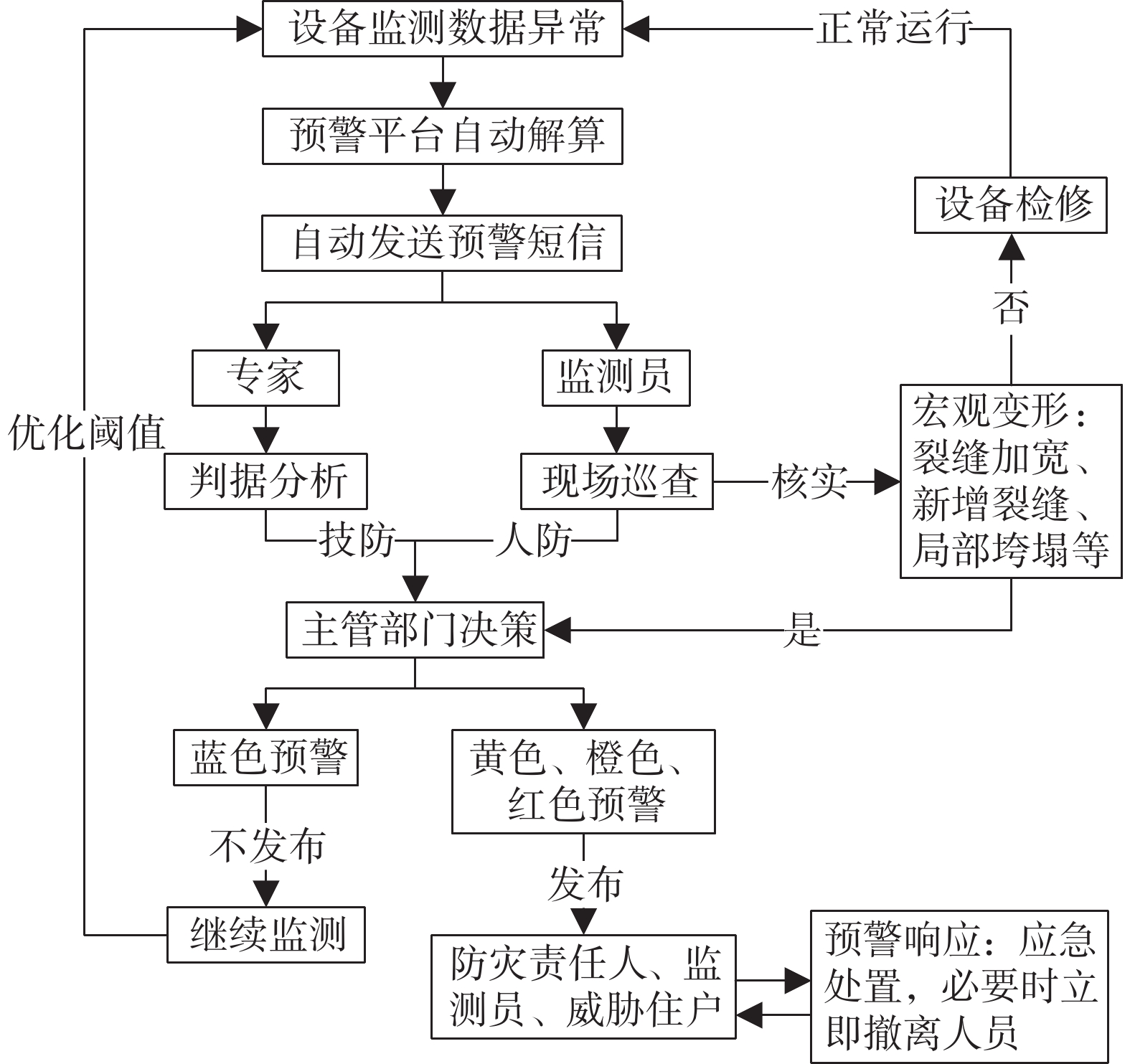
预警信号实现及时准确地发布,对撤离受灾害威胁的群众、避免人员伤亡来讲至关重要。结合湖南多年预警工作经验,设计出一套人技融合预警发布流程(图9)。该预警发布机制,同时结合了变形趋势线法和宏观变形法,专家负责分析灾害变形处于哪种阶段,当地的监测员通过现场巡查,核实预警信息,掌握实际变形程度和部位,地质灾害主管部门将二者综合考虑,最终确定是否发布预警,避免了误报和漏报。该预警流程做到了有预警就有响应,很好地形成预警闭环。
4. 结论
雷家山滑坡是中国地质灾害防治工作中“人防+技防”成功避险的典范案例,本文从发育特征、成因机理、预警过程、预警方法等方面,对该滑坡监测预警到成功避险全过程进行了综述研究,主要获得如下结论:
(1)雷家山滑坡属于大型土质中层滑坡,险情级别为特大型。经成因分析,发现地形地貌、岩性条件是形成该滑坡的内在因素,而强降雨和人类工程活动等外部作用力共同影响下加速了滑坡的演化进程,并最终导致了滑坡失稳。
(2)该滑坡从发现开始,经过调查、建网(群防网、专业网)、监测、巡查、区域气象风险预警、监测数据异动、预警发布、启动预案、发出警报、省市县乡村组+部门联动、警戒管制撤离等一系列周密的主动防范工作程序,最终实现成功避灾、零伤亡。
(3)运用最小二乘法对该滑坡原始监测数据进行滤波处理,得到时间-位移曲线图,经过系统分析,发现该滑坡具有明显的初始变形、等速变形、加速变形3个变形演化阶段,属于渐变型滑坡。
(4)基于切线角和变形速率构建预警判据,结合变形全过程分析和专家判断,确定发布预警信息,提高了预警准确率。该滑坡的成功预警,验证了该判据的可靠性。
(5)本文提出人技融合预警发布流程,有助于高效地开展预警工作,可为群众紧急避险争取黄金时间。
-
表 1 基于切线角阈值和变形速率综合预警判据
Table 1 Comprehensive early warning criteria based on tangential angle threshold and deformation rate
预警级别 注意级 警示级 警戒级 警报级 预报形式 蓝色 黄色 橙色 红色 变形阶段 等速变形阶段 初加速变形阶段 中加速变形阶段 临滑阶段 切线角/(°) α≈45 45<α<80 80≤α<85 α≥85 速率/(mm·h-1) 17~20 20~112 112~262 >262 滑坡变形时间 5月27日—6月13日 6月14日—6月25日 6月26日—7月1日 7月2日—7月6日 -
[1] 许强,董秀军,李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957 − 966. [XU Qiang,DONG Xiujun,LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection,monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 957-966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 伍法权,沙鹏. 中国工程地质学科成就与新时期任务—2018年全国工程地质年会学术总结[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(1):184 − 194. [WU Faquan,SHA Peng. Achievements of engineering geology in China and the mission in the new era:A review on 2018 annual symposium of engineering geology of China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(1):184 − 194. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Faquan, SHA Peng. Achievements of engineering geology in China and the mission in the new era—a review on 2018 annual symposium of engineering geology of China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(1): 184-194. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 刘传正. 崩塌滑坡灾害风险识别方法初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(1):88 − 97. [LIU Chuanzheng. Analysis methods on the risk identification of landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(1):88 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Chuanzheng. Analysis methods on the risk identification of landslide disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(1): 88-97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 许强. 滑坡的变形破坏行为与内在机理[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(2):145 − 151. [XU Qiang. Theoretical studies on prediction of landslides using slope deformation process data[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(2):145 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.02.001 XU Qiang. Theoretical studies on prediction of landslides using slope deformation process data[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(2): 145-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.02.001
[5] 许强,彭大雷,何朝阳,等. 突发型黄土滑坡监测预警理论方法研究—以甘肃黑方台为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(1):111 − 121. [XU Qiang,PENG Dalei,HE Chaoyang,et al. Theory and method of monitoring and early warning for sudden loess landslide:A case study at Heifangtai Terrace[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(1):111 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Qiang, PENG Dalei, HE Chaoyang, et al. Theory and method of monitoring and early warning for sudden loess landslide—a case study at Heifangtai Terrace[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(1): 111-121. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 许强. 对滑坡监测预警相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):360 − 374. [XU Qiang. Understanding the landslide monitoring and early warning:Consideration to practical issues[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):360 − 374. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Qiang. Understanding the landslide monitoring and early warning: consideration to practical issues[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(2): 360-374. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 周琪,许强,周小棚,等. 突发型滑坡危险范围预测方法研究—以黑方台焦家6#滑坡为例[J]. 灾害学,2020,35(1):216 − 221. [ZHOU Qi,XU Qiang,ZHOU Xiaopeng,et al. Research on the predicting hazard range of abrupt loess landslide:A case study of 6# landslide in Heifangtai tableland[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2020,35(1):216 − 221. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU Qi, XU Qiang, ZHOU Xiaopeng, et al. Research on the predicting hazard range of abrupt loess landslide—a case study of jj6# landslide in Heifangtai tableland[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2020, 35(1): 216-221. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 程素珍,路璐,翟淑花,等. 2004—2018年北京市突发地质灾害时空分布特点和监测预警状况[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):38 − 46. [CHENG Suzhen,LU Lu,ZHAI Shuhua,et al. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and monitoring and early warning status of sudden geological disasters in Beijing from 2004 to 2018[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):38 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHENG Suzhen, LU Lu, ZHAI Shuhua, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and monitoring and early warning status of sudden geological disasters in Beijing from 2004 to 2018[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 38-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 张凯翔. 基于“3S”技术的地质灾害监测预警系统在我国应用现状[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):1 − 11. [ZHANG Kaixiang. Application status of geological disaster monitoring and early warning system based on “3S” technology in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Kaixiang. Application status of geological disaster monitoring and early warning system based on “3S” technology in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李慧,王欣泉,宗爽. 现阶段我国地质灾害防治工作新思路—中国地质灾害防治工程行业协会“5·12全国防灾减灾日”云服务活动综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):5 − 8. [LI Hui,WANG Xinquan,ZONG Shuang. New ideas of geological disaster prevention and control in China at the present stage:A summary of cloud service activities of “may 12th national disaster prevention and mitigation day” of China geological disaster prevention and control engineering industry association[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):5 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Hui, WANG Xinquan, ZONG Shuang. New ideas of geological disaster prevention and control in China at the present stage—a summary of cloud service activities of “may 12th national disaster prevention and mitigation day” of China geological disaster prevention and control engineering industry association[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(3): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 杨江涛,李波,李伯宣,等. 自贡市地质灾害专群结合监测预警模式升级与实践[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):130 − 134. [YANG Jiangtao,LI Bo,LI Boxuan,et al. Upgrading and practice of monitoring and early warning mode combining geological disasters with special groups in Zigong City[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):130 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Jiangtao, LI Bo, LI B X, et al. Upgrading and practice of monitoring and early warning mode combining geological disasters with special groups in Zigong city[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 130-134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 侯圣山,李昂,陈亮,等. 基于普适型仪器的滑坡监测预警初探—以甘肃兰州岷县三处滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):47 − 53. [HOU Shengshan,LI Ang,CHEN Liang,et al. Application of universal geo-hazard monitoring instruments in landslides and early warning of three landslides in Gansu Province:A case study in Minxian County and Lanzhou City of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):47 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.06.06 HOU Shengshan, LIANG, CHEN Liang, et al. Application of universal geo-hazard monitoring instruments in landslides and early warning of three landslides in Gansu Province: a case study in Minxian County and Lanzhou City of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 47-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.06.06
[13] 马娟,赵文祎,齐干,等. 基于普适型监测的多参数预警研究—以三峡库区卡门子湾滑坡为例[J]. 西北地质,2021,54(3):259 − 269. [MA Juan,ZHAO Wenyi,QI Gan,et al. Study on the multi-parameter early warning based on universal equipment:A case of Kamenziwan landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Northwestern Geology,2021,54(3):259 − 269. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA Juan, ZHAO Wenyi, QI Gan, et al. Study on the multi-parameter early warning based on universal equipment: a case of kamenziwan landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(3): 259-269. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 何满潮,任树林,陶志刚. 滑坡地质灾害牛顿力远程监测预警系统及工程应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(11):2161 − 2172. [HE Manchao,REN Shulin,TAO Zhigang. Remote monitoring and forecasting system of Newton force for landslide geological hazards and its engineering application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(11):2161 − 2172. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE Manchao, REN Shulin, TAO Zhigang. Remote monitoring and forecasting system of Newton force for landslide geological hazards and its engineering application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(11): 2161-2172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 隋嘉,孙皓,张丽华,等. 青海省地质灾害监测预警信息化平台建设与实现[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(2):92 − 101. [SUI Jia,SUN Hao,ZHANG Lihua,et al. Construction and realization of information platform for geological disaster monitoring and early warning in Qinghai Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(2):92 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract) SUI Jia, SUN Hao, ZHANG Lihua, et al. Construction and realization of information platform for geological disaster monitoring and early warning in Qinghai Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(2): 92-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 许强,曾裕平,钱江澎,等. 一种改进的切线角及对应的滑坡预警判据[J]. 地质通报,2009,28(4):501 − 505. [XU Qiang,ZENG Yuping,QIAN Jiangpeng,et al. Study on a improved tangential angle and the corresponding landslide pre-warning criteria[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2009,28(4):501 − 505. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Qiang, ZENG Yuping, QIAN Jiangpeng, et al. Study on a improved tangential angle and the corresponding landslide pre-warning criteria[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(4): 501-505. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 肖自为,马源,李金林,龚弦,邓修林,程曦. 基于过程预警模型的矿山边坡监测系统研究与应用. 地质灾害与环境保护. 2024(04): 91-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS