Analysis of service performance characteristics of debris flow check dams: A case study in Wudu District, Longnan City, Gansu Province
-
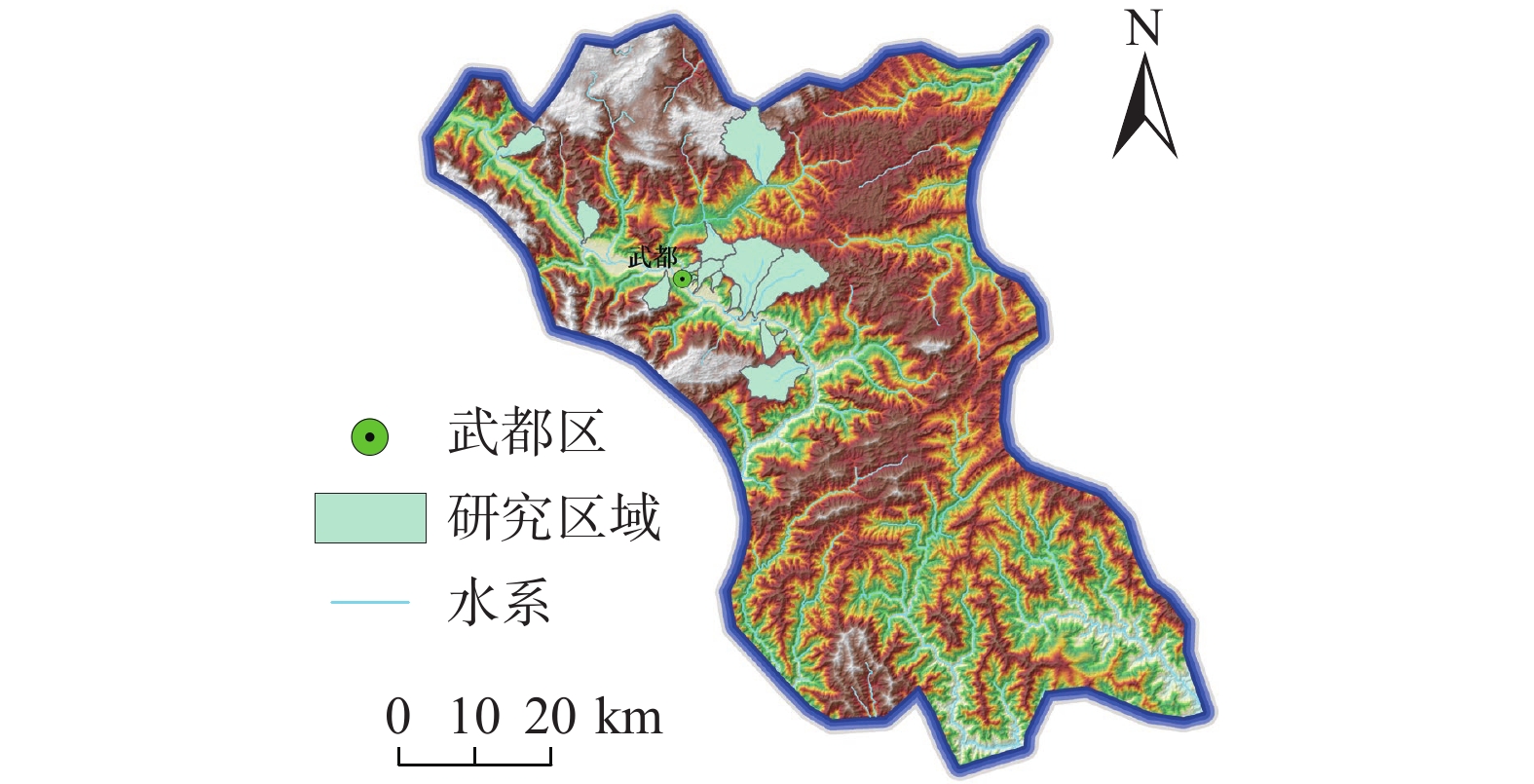
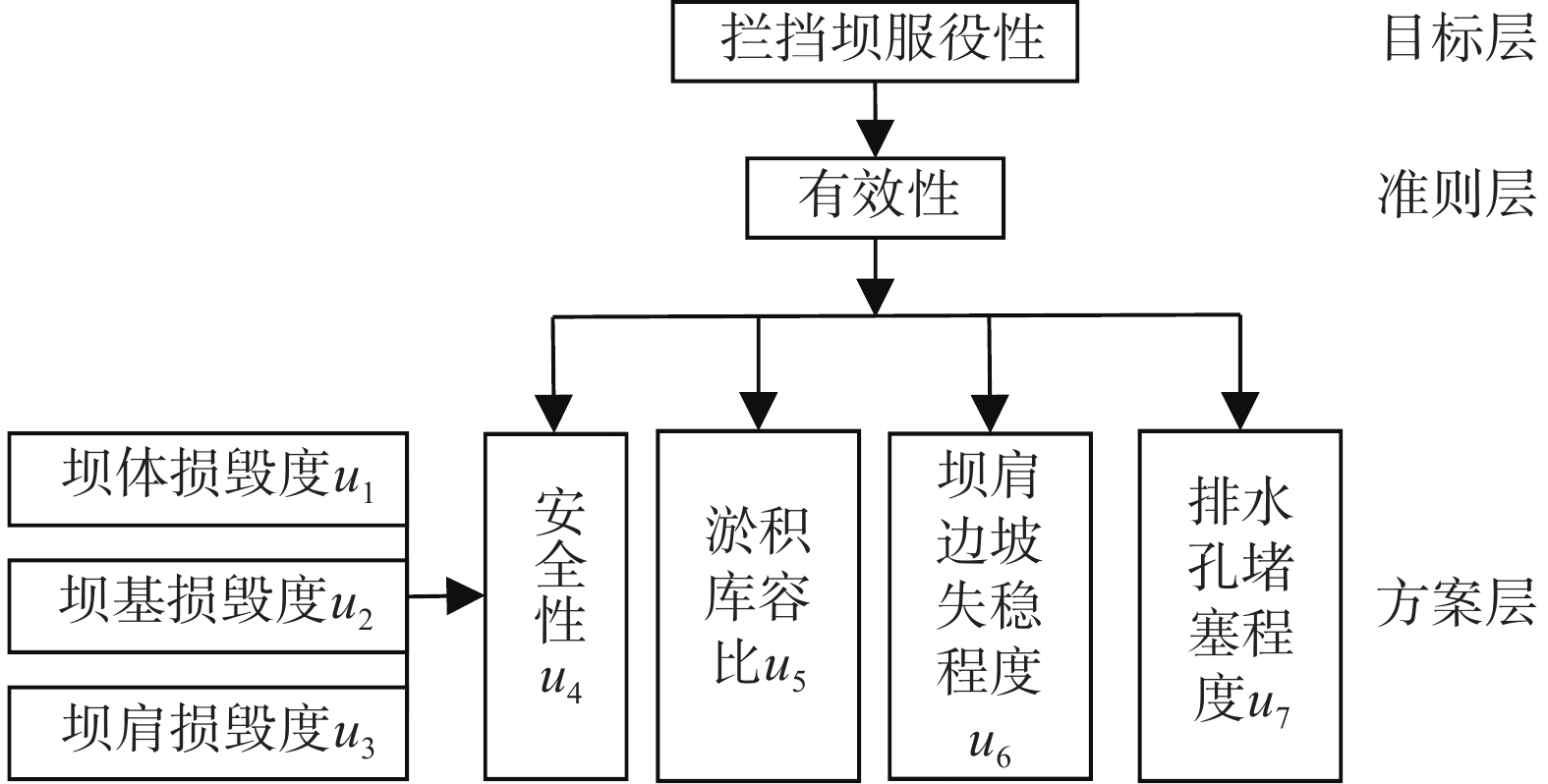
摘要: 拦挡坝是泥石流防治工程中最重要的措施之一,其防灾减灾能力在服役期间随着泥石流多次冲出逐渐降低,需开展拦挡坝服役性能特征分析。以甘肃省陇南市武都区泥石流拦挡坝为研究对象,对区内15条沟、55座拦挡坝服役性能进行了现场调查,从有效性和安全性两方面遴选了库容淤积比、坝肩边坡稳定程度、排水孔堵塞程度、坝体损毁度、坝基损毁度、坝肩损毁度、安全性等 7个评价因子,采用层次分析法和模糊综合评价法建立了拦挡坝单坝服役性和拦挡坝单沟综合服役性的评价模型,将服役性能等级划分为优、良、中等、差等4个等级。评价结果表明:拦挡坝单坝服役性等级“差”占34.5%;拦挡坝单沟综合服役性等级“差”占33.3%,评价结果与现场考察相符。研究成果为拦挡坝服役效果及服役寿命预测提供了可借鉴的依据。Abstract: Check dams play a pivotal role in debris flow prevention and control engineering. However, their disaster prevention and mitigation capacity gradually decrease over service time due to repeated debris flow impacts. The study was carried out in 15 ditches and 55 check dams within Wudu District, Longnan City, Gansu Province. Seven key evaluation factors were selected for effectiveness and safety: reservoir siltation ratio, slope stability, drainage hole blockage, dam body damage, dam foundation damage, dam shoulder damage, and safety. The evaluation model of the serviceability of the indivusual dam and the comprehensive serviceability of the single trench of the barrage was established by using hierarchical analysis and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method, and the serviceability was divided into four grades: excellent, good, medium and poor. The evaluation results show that the serviceability rating of individual dams is predominately "poor", accounting for 34.5%. Similarly, the collective serviceability rating of single trench dams for debris flow is predominately "poor", at 33.3%. The results of the evaluation are consistent with the fieldwork observations, providing a valuable reference for predicting the service performance and service life of barrage dams.
-
0. 引 言
贵州省煤炭资源丰富,素有“西南煤海”之称[1]。据贵州矿山地质灾害和地质环境调查报告调查有
6556 处矿山,矿区及其周边共分布有1165 处地质灾害,其中以煤矿开采引发的地质灾害最为严重,造成损失最大[2]。贵州煤矿主要形成于二叠纪晚期,按沉积环境分为陆相地层宣威组(P3x)、海陆交互相地层龙潭组(P3l)及海相地层吴家坪组(P3w)。其中,分布面积最广、开采价值最高的含煤地层为龙潭组(P3l),其查明资源储量占晚二叠世总资源储量的95%。龙潭组(P3l)地层煤矿开采引发的地质灾害分布面积最广、危害最大。例如,2004年纳雍县鬃岭镇孙晓煤矿佐家营崩塌冲击坡脚堆积体形成高速碎屑流,造成44人死亡[3];2017年8月28日,纳雍县张家湾镇普洒村崩塌造成26人遇难,9人失踪[4 − 7]。因此,对龙潭组(P3l)地层煤矿开采引发的地质灾害特点及成因机理进行分析,对于地质灾害防治及责任鉴定意义重大。长期以来,从事矿山地质灾害成因分析的专家学者主要从自然因素和人为因素这两方面来研究,自然因素指地形地貌、地质构造、岩溶作用、降雨、风化作用以及植物根劈等天然原因,人为因素指采矿等人为活动,但尚未论证引发地质灾害的主要原因及次要原因[7 − 19]。
本文在充分剖析贵州龙潭组地层煤矿地下开采引发地质灾害特点的基础上,从煤层开采安全深度及采空区影响范围2个维度来定量论证地质灾害发生的主要原因,将有助于完善矿山地质灾害成因分析,对于矿山地质灾害防治工作具有理论指导意义。
1. AH煤矿矿区地质环境
AH煤矿矿区地处贵州高原西部,属低中山侵蚀-溶蚀地貌,地形切割较深,总体地势南东、北西高、北东低,最高处位于矿区西部背儿坡,标高为
1436.2 m,最低点位于矿区外围东侧的凹河,河床标高为950.0 m,最大高差486.2 m,一般相对高差50~150 m。矿区中部地段多形成陡崖带,走向以近南北向为主,坡度达70°以上。总体上,矿区内地形地貌条件较为复杂(图1)。矿区及邻近出露的地层为第四系(Q)、下三叠统大冶组(T1d)、上二叠统长兴组(P3c)及龙潭组(P3l)(图2)。第四系(Q)广泛分布于矿区大部分低洼及相对平缓地段,岩性主要为残积亚黏土、砂土,厚度一般0~20 m,植被发育,耕地广泛,分布少量村落;下三叠统大冶组(T1d)出露于矿区中西部,主要为薄层状石灰岩、泥灰岩,局部夹细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩,厚度一般大于200 m;上二叠统长兴组(P3c)呈宽条带状出露于矿区中部,上部灰、深灰色薄至中厚层硅质灰岩夹泥岩及蒙脱石泥岩,下部为深灰色中厚层细晶燧石灰岩,平均厚48.86 m;上二叠统龙潭组(P3l)为矿区唯一含煤地层,属海陆交互相沉积,出露于矿区东部,深灰、灰色泥岩、细砂岩、粉砂岩、石灰岩,泥灰岩、含煤层及煤线40层,平均厚306.58 m。
矿区大地构造位于扬子准地台-黔北台隆-遵义断拱-贵阳复杂构造变形区,属凹河背斜西翼。总体为一单斜构造,地层走向北东,倾向北西,倾角10°~35°,一般为15°~20°。受西部边界断层影响,北西部见一宽缓的次级向斜构造,地层走向从东至西有一定变化。
2. 地质灾害特征
AH煤矿矿区地形切割强烈,地层岩性、地质构造中等,地质环境较为脆弱,在自然因素和人类工程活动的影响下,导致地质灾害发育强烈。调查研究发现矿区内共有地面塌陷28处(伴生地裂缝1条)、崩塌点4处(危岩体6个),各地质灾害点的基本特征如下:
2.1 地面塌陷(伴生地裂缝)
调查研究发现矿区范围内有28个地面塌陷坑(图2),根据塌陷规模类型划分标准[20],该28个地面塌陷坑均为小型采空地面塌陷。AH煤矿地面塌陷坑全部位于矿区西侧陡崖上部约0.5 km2范围内的缓坡地带。塌陷坑均发育于第四系,下伏基岩地层为大冶组及长兴组。塌陷坑口普遍呈圆形、椭圆形。圆形坑口直径为1.2~5.0 m,普遍直径约2.0 m;视深为0.4~2.3 m,普遍视深约1.5 m。椭圆形坑口长轴为2.0~10.7 m,普遍长轴约3.5 m;短轴为1.4~7.0 m,普遍短轴约2.5 m;视深为1.0 m至大于5.0 m,普遍视深约1.5 m。塌陷坑初现时间为2017年雨季,此后塌陷坑数量不断增加,普遍在汛期暴雨后出现(图3)。
矿区范围内因地面塌陷诱发1条伴生地裂缝(DLF1),位于矿区西侧陡崖上部缓坡地带(图2)。该伴生地裂缝发育于第四系,下伏基岩地层为大冶组及长兴组。走向350°~15°,长约210 m,宽度0.2~3.4 m,原深度约2.0 m。根据地裂缝规模类型划分标准[20],该条伴生地裂缝为小型地裂缝。
2.2 崩塌(危岩体)
调查发现AH煤矿矿区范围内有崩塌点4处(含危岩体6个),分布于矿区中部近南北走向的陡崖带,陡崖带全长约900 m。危岩体发育地层为上二叠统长兴组(P3c),岩性主要为深灰色中厚层细晶燧石灰岩,总体崩塌方向为95°~130°。AH煤矿陡崖带,历史上发生过大大小小十余次崩塌,单次崩塌最大体积约
6000 m3,崩落块度不均,最大崩塌块石为12 m×8 m×5 m。现存的6个危岩体总体稳定性较差,规模大小不一,其中规模最大的危岩体为WY1,体积为
14256 m3;规模最小的危岩体为WY5,体积为788 m3。按危岩体体积分类[21],WY1为中型危岩,其余均为小型危岩;按所处相对高度分类[22],均为中位危岩。参照《地质灾害防治条例》(国务院令第394号)和《地质灾害危险性评估规范》(GB/T40112—2021),AH煤矿矿区范围内4处崩塌点灾情等级均为小型,6个危岩体险情等级均为中型。6个危岩体具有凹岩腔较为发育、受陡倾裂隙控制等特点,各危岩体特征见表1。表 1 AH煤矿矿区危岩体特征表Table 1. Characteristic table of dangerous rock mass in AH coal mine area编号 宽度/m 高度/m 均厚/m 体积/m3 规模 危岩类型 坡向/(°) 坡度/(°) 主要结构面 失稳方式 威胁对象 险情等级 WY1 33 24 18 14256 中型 中位 100 80 40°∠78°、70°∠78° 倾倒 ① 中型 WY2 20 26 8 4160 小型 中位 95 80 20°∠75°、90°∠75° 倾倒 ② 中型 WY3 13 26 7 2366 小型 中位 105 80 20°∠75°、90°∠75° 倾倒 ② 中型 WY4 6 25 6 900 小型 中位 85 78 30°∠75°、115°∠75° 倾倒 ② 中型 WY5 9 35 3 788 小型 中位 135 85 40°∠80°、300°∠80° 倾倒 ② 中型 WY6 14 34 5 2380 小型 中位 150 85 45°∠80°、130°∠80° 倾倒 ② 中型 注:①为办公楼人员、危岩顶部通信塔;②为下部村民、附近人员、耕地。 2.2.1 凹岩腔较为发育
根据调查统计,AH煤矿矿区范围内现有6个危岩单体(WY1—WY6)。6个危岩体岩性均为燧石灰岩,底部粉砂质泥岩均发育有凹岩腔。凹岩腔的形状、规模尺寸各异,多呈条带状、方块状和不规则状,凹岩腔宽度为6~33 m,其中WY4宽度最小,约为6 m,WY1宽度最大,约为33 m;凹岩腔高度0.5~2.0 m,一般约为1.5 m,且凹岩腔底部一般有土层覆盖,厚度较薄,一般在1.0 m以内;凹岩腔深度一般为0.5~1.5 m。凹岩腔发育于灰岩底部与粉砂质泥岩接触带的软弱部位,受风化差异和雨水浸湿作用影响,岩土体含泥质越重,凹岩腔的规模越大,或同一地质时期内形成凹岩腔的速度越快。由于凹岩腔大多发育在危岩体的底部,随着凹岩腔的发育延伸,发生腔内垮塌、掉块等现象较多。且因危岩体重心不变,随着凹岩腔的发育延伸,转动点向内移动,抵抗力矩变小或者直接演变为荷载,将加剧倾倒式崩塌发生。
2.2.2 受陡倾裂隙控制
调查发现,AH煤矿矿区范围内危岩体除底部发育凹岩腔之外,其顶部还发育大量的外倾、陡倾裂隙,危岩体顶部陡倾裂隙为岩体内部硬性结构面,贯通性较好,裂隙走向基本与陡崖走向一致,在340°~40°范围内,倾角75°~80°不等,宽度0.1~2.5 m,大部分无充填。此类危岩体由于底部因发育凹岩腔而失去支撑,顶部发育陡倾裂隙且基本贯通至危岩体底部,其处于极限平衡状态。如:危岩体WY4,见图4(a)顶部陡倾裂隙倾向115°,倾角80°,裂隙宽度0.1~1.5 m,无充填,长度约6 m,从顶部贯穿至底部,裂缝上宽下窄,呈“V”型,且从两侧可从裂隙中看穿,使危岩体成孤石;危岩体WY5,见图4(b),顶部陡倾裂隙产状40°∠80°,宽1.2~2.5 m,长度约9 m,可视深度大于5 m,裂隙下部由碎石黏土充填。
3. 地质灾害成因分析
前述地面塌陷(伴生地裂缝)、崩塌等地质灾害的发生,既有地形地貌、地质构造、岩溶作用、降雨、风化作用甚至植物根劈等自然原因,又有煤矿地下开采等人为原因[23]。但上述地质灾害的发生均是AH煤矿开采之后产生,下面从煤层开采安全深度、采空区影响范围等2个维度来定量论证地下开采这一剧烈人类活动对矿区地质灾害的影响程度。
3.1 煤层开采安全深度
3.1.1 安全系数的确定
参照《建筑物、水体、铁路及主要井巷煤柱留设与压煤开采规程》[24],薄及中厚煤(矿)层的采深与单层采厚比大于或等于150,厚煤(矿)层及煤(矿)层群的采深与分层采厚比大于200的原则。AH煤矿含7层可采煤层,其安全系数K取值为200。
3.1.2 煤层综合作用厚度的确定
煤层群开采时需计算各层煤的综合作用厚度。根据《地方煤矿实用手册》[25],综合作用厚度的计算方法为最上面一层可采煤层分别作用于下一层可采煤层直至最后一层可采煤层的叠加计算结果,即M=M1(最下面一层可采煤层的综合作用厚度)。各层煤的综合作用厚度计算公式为:
(1) 式中:M——综合作用厚度/m,Mn=mn、Mn为最上面一 层煤的综合作用厚度;
m——煤层厚度/m;
n——煤层数;
C——两层煤之间的真厚度与下一层煤的厚度的比值的函数,可查表2。
表 2 系数C值表Table 2. Coefficient C value tableh/m① 缓倾斜煤层② 倾斜煤层③ 急倾斜煤层④ 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 10 1.00 1.00 1.00 20 0.85 0.80 0.75 30 0.70 0.60 0.50 40 0.55 0.40 0.25 50 0.45 0.20 0.00 60 0.30 0.00 0.00 70 0.15 0.00 0.00 80 0.00 0.00 0.00 注:①h/m为两层煤之间的间距与下一层煤层厚度的比值;②缓倾斜煤层指煤层倾角<15°;③倾斜煤层指煤层倾角为15°~45°;④急倾斜煤层指煤层倾角>45°。 3.1.3 安全深度的确定
安全深度为煤层综合作用厚度与安全系数的乘积,计算公式为:
(2) 式中:H——安全深度/m;
M——综合作用厚度/m;
K——安全系数。
AH煤矿含7层可采煤层,编号自上往下为14、15、16、18、21、28、32,平均厚度分别为1.38,1.66,2.96,1.86,1.13,1.63,0.94 m,按以上方法计算各煤层的安全深度见表3。
表 3 AH煤矿安全深度计算表Table 3. Calculation table safety depth in AH coal mine煤层编号 煤层厚度/m 两层煤之间的间距/m 两层煤之间的间距与
下一层煤层厚度的比值/mC 综合作用厚度/m 安全深度/m 赋存深度/m M14 1.38 1.38 276 0~185 M15 1.66 5.64 3 1.00 3.04 608 0~192 M16 2.96 26.01 9 1.00 6.00 1 200 0~220 M18 1.86 15.60 8 1.00 7.86 1 572 0~238 M21 1.13 10.90 10 1.00 8.99 1 798 0~251 M28 1.63 53.93 33 0.54 6.48 1 297 0~306 M32 0.94 30.33 32 0.56 4.57 914 0~338 从表3可以发现,AH煤矿M14号煤层赋存深度约为0~185 m,小于其安全开采深度(H14 =276 m);M15号煤层赋存深度约为0~192 m,小于其安全开采深度(H15 =608 m);M16号煤层赋存深度约为0~220 m,小于其安全开采深度(H16 =
1200 m);M18号煤层赋存深度约为0~238 m,小于其安全开采深度(H18 =1572 m);M21号煤层赋存深度约为0~251 m,小于其安全开采深度(H21 =1798 m);M28号煤层赋存深度约为0~306 m,小于其安全开采深度(H28 =1297 m);M32号煤层赋存深度约为0~338 m,小于其安全开采深度(H32=914 m)。总之,AH煤矿7层可采煤层赋存深度均小于其安全深度。因此,从竖直方向上看,AH煤矿开采后形成的采空区崩顶后,导致地表产生地裂缝、地面塌陷、崩塌等地质灾害的可能性大。3.2 采空区影响范围
3.2.1 移动角的确定
移动角采用类比法确定,类比原则是赋存地层层位相同,矿层倾角相近、矿层上覆岩层岩性和厚度相近。AH煤矿煤层出露地层时.2代为上二叠统龙潭组(P3l),覆岩类型为中硬岩石。参照《建筑物、水体、铁路及主要井巷煤柱留设与压煤开采规范》(安监总煤装[2017]66号)[24]及相关要求,本次AH煤矿各移动角取值如下:
走向移动角δ=70°;
倾向下山移动角β=70°;
倾向上山方向移动角γ=70°−0.6×矿层倾角(视倾角)。
3.2.2 采空区影响范围
AH煤矿主采煤层为M16及M18煤层,根据《AH煤矿M16煤层采掘工程平面图》及《AH煤矿M18煤层采掘工程平面图》所反映的煤矿采空区,按照前述采空区移动影响范围参数,按移动角与本次实测的地形图地面交点图解确定各采空区移动影响范围(图2、图5)。
由图2计算得出:AH煤矿现采空区影响范围约0.37 km2,矿区现状地质灾害:地面塌陷(TX1—TX28)、伴生地裂缝(DLF1)、崩塌危岩体(WY1—WY6)等均处于其采空区覆岩移动影响范围之内,AH煤矿地下采煤所形成的M16煤层采空区、M18煤层采空区崩顶是造成上述现状地质灾害产生的主要原因。矿山开采形成采空区后,随着采空区面积增大,煤层顶板岩层在失去支撑状态下弯曲、断裂、垮落,应力重新分布,达到新的平衡。顶板垮落过程中引发采空区周围岩体变形、松动乃至破坏,也使采空区上覆岩层和地表产生连续的移动、变形和非连续的破坏(开裂、冒落等),随之弯曲下沉,上覆岩层的这种破坏达到地面后形成地面塌陷(伴生地裂缝),在地表陡崖临空面处易形成危岩体并诱发崩塌地质灾害。
综上所述,AH煤矿矿区范围内地面塌陷(TX1—TX28)及伴生地裂缝(DLF1)的形成原因为地下采煤造成;崩塌危岩体(WY1—WY6)的险情形成,其原因为地下采煤为主要诱发因素、自然条件为次要因素,两者综合作用的结果。根据上述地质灾害发生的时间与地下煤矿开采时空关系,同样印证这一结论。
4. 结 论
(1)总结了贵州龙潭组地层煤矿开采引发的地质灾害特点。该地层煤矿开采主要引发地面塌陷(伴生地裂缝)、崩塌2类地质灾害,其中塌陷坑(伴生地裂缝)均发育于第四系,规模均为小型;崩塌(危岩体)发育地层岩性为上二叠统长兴组(P3c)燧石灰岩,具有凹岩腔较为发育、受陡倾裂隙控制等特点,主要为小型危岩,次为中型危岩,均为中位危岩。这些特点在该地层煤矿开采引发的地质灾害中具有普遍性和典型性。
(2)分析了贵州龙潭组地层煤矿开采引发的地质灾害成因。AH煤矿7层可采煤层的上覆岩体厚度均小于其安全深度,地质灾害均处于其采空区覆岩移动影响范围之内。因此,地面塌陷(伴生地裂缝)的形成原因为地下采煤造成;崩塌(危岩体)主要诱发因素为地下采煤、次因为自然条件,两者综合作用的结果。
(3)针对贵州龙潭组地层煤矿开采引发的地质灾害,地形地貌、地质构造、岩溶作用等是内因,而降雨、风化、采矿人类活动是外因,外因又分为自然外因、人类外因。其中采矿等人类剧烈活动属可以控制因素,建议在陡崖地带附近合理留设保护煤柱。
(4)本次研究有助于完善类似矿山地质灾害特点研究及成因分析理论,对于类似矿山地质灾害防治工作具有理论指导意义。希望在以后的研究中,能够有效监测上覆围岩在煤层开采前后的应力应变数据,以便进一步深化矿山地质灾害成因机理研究。
-
表 1 拦挡坝典型损毁特征
Table 1 Typical damage characteristics of check dams
坝体编号 拦挡坝损毁特征 燕儿沟2号 该坝位于燕儿流通区,坝体淤埋,库容已淤满,右坝肩岩土体松散,排水孔完全堵塞,右坝肩出现裂缝 马槽沟12号 该坝位于马槽沟支沟交汇处,库容已淤满,右坝肩堆积大量松散物,排水孔完全堵塞,右坝肩出现轻度裂缝,坝基裸露 马槽沟8号 该坝位于马槽沟流通区,左坝肩冲毁严重,库容未淤满,沟道切割严重,两侧岩土体松散,坝体出现明显松弛,坝基裸露 寨子沟1号 该坝位于寨子沟沟口处,毗邻建筑物,库容已淤满,右坝肩堆积物松散,排水孔完全堵塞,右坝肩冲毁严重 表 2 拦挡坝服役性能评价因子等级及赋值
Table 2 Check dam service performance evaluation factor rating and assignment
评价因子 V1 V2 V3 V4 安
全
性坝体损毁度u1 无 轻度 中度 重度 坝基损毁度u2 无 轻度 中度 重度 坝肩损毁度u3 无 轻度 中度 重度 有
效
性安全性u4 — — — — 淤积库容比u5/% <20 20~<50 50~<80 ≥80 坝肩边坡失稳程度u6 无 轻度 中度 重度 排水孔堵塞程度u7 无 轻度 中度 重度 表 3 评价值的取值依据及定量化取值
Table 3 The basis and quantitative values for evaluation values
评价值 取值依据 定量化取值 无 坝肩边坡稳定;排水孔未堵塞;坝基、坝体、坝基均未出现损、整体结构完好 0~<10 轻度 坝肩边坡出现裂痕;排水孔堵塞程度10%~20%;坝基完好,坝体表面脱落,坝肩局部产生裂缝 10~<20 中度 坝肩边坡局部岩土体松动;排水孔堵塞程度20%~40%;坝基处有积水、出现脱落,坝体张裂、掉块、局部损毁,坝肩掉块、残缺 20~<40 重度 坝肩边坡失稳、出现滑坡;排水孔堵塞;坝基出露、悬空,坝体倾倒,坝肩冲毁 ≥40 表 4 判断矩阵标度及其含义
Table 4 The scale of judgment matrix and its significance
标度 含义 1 两个因子相比较,两者具有相同的重要性 3 两个因子进行比较,前者比后者略微重要 5 两个因子进行比较,前者比后者较为重要 7 两个因子进行比较,前者比后者非常重要 9 两个因子进行比较,前者比后者极其重要 注:2,4,6,8为上述两相邻判断的中间值,aij表示因素ai与因素aj的重要性之比,aij与aji之间的关系表示为aij=1/aji。 表 5 方案层的权重
Table 5 Weights at the scheme level
评价因子 u1 u2 u3 权重 u1 1 1 4 0.444 u2 1 1 4 0.444 u3 1/4 1/4 1 0.112 表 6 准则层的权重
Table 6 Weight at the criterion level
评价因子 u4 u5 u6 u7 权重 u4 1 3 4 5 0.538 u5 1/3 1 2 3 0.230 u6 1/4 1/2 1 4 0.163 u7 1/5 1/3 1/4 1 0.069 表 7 马槽沟拦挡坝的评价因子实际取值
Table 7 Actual values of evaluation factors for check dams in Macao gully
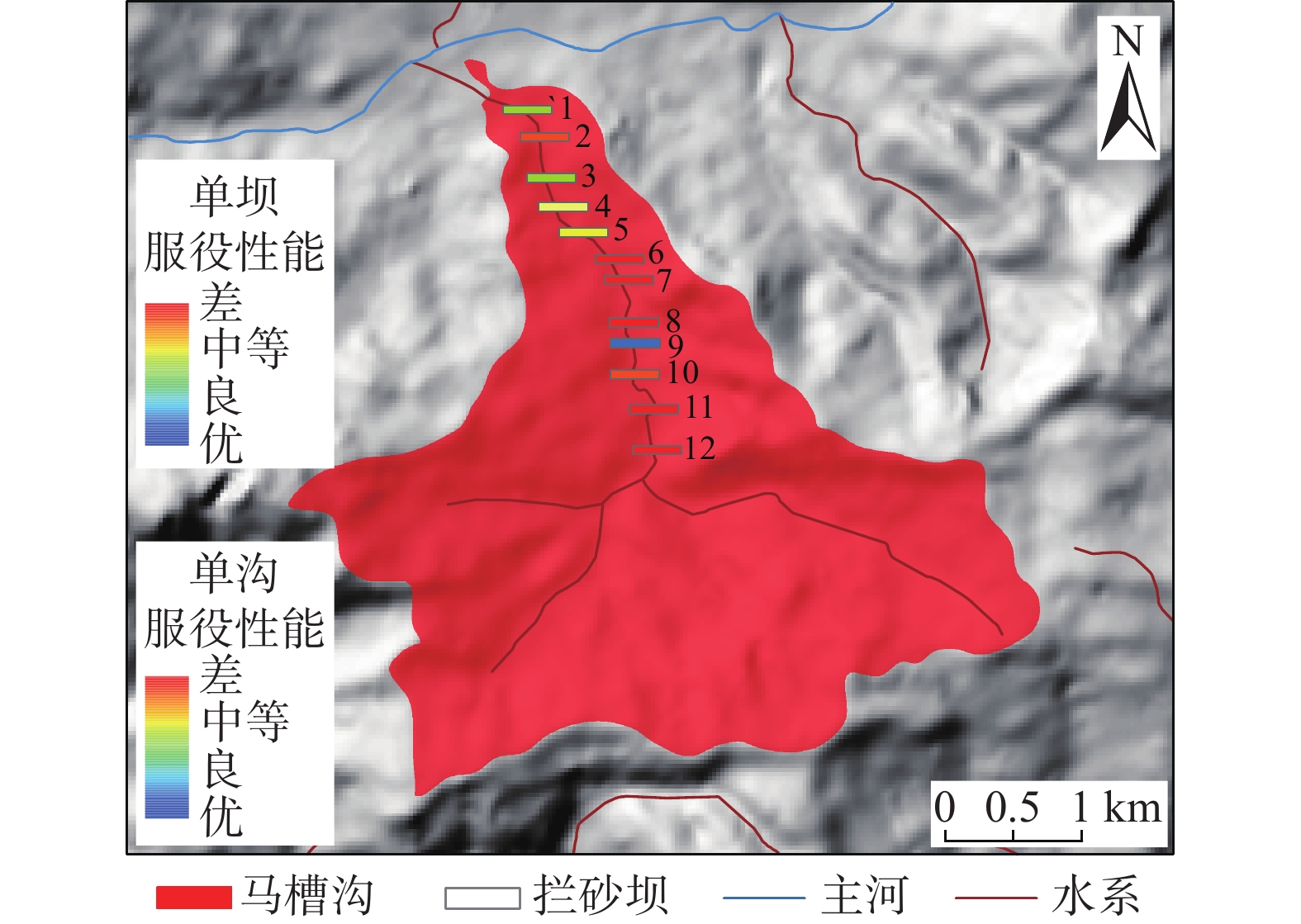
评价因子 拦挡坝编号 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 u1 25 22 24 2 85 80 80 10 15 10 85 15 u2 15 30 35 5 90 75 80 20 24 10 80 18 u3 18 35 30 0 90 40 40 10 15 5 80 10 u5 90 96 95 25 96 95 95 95 95 95 96 96 u6 30 16 15 5 18 20 22 25 25 24 18 20 u7 90 95 95 8 10 80 80 90 90 90 85 90 表 8 马槽沟拦挡坝服役性评价结果
Table 8 Results of the serviceability evaluation for check dams in Macao gully
编号 OB 结果 编号 OB 结果 编号 OB 结果 12 (0,0.167,0.426,0.440) 差 8 (0,0.102,0.130,0.768) 差 4 (0,0.150,0.463,0.388) 中等 11 (0,0.065,0.447,0.488) 差 7 (0,0,0.163,0.837) 差 3 (0.03,0.51,0.13,0.332) 良 10 (0,0.082,0.362,0.556) 差 6 (0,0,0.147,0.853) 差 2 (0,0.033,0.310,0.658) 差 9 (0.668,0.332,0,0) 优 5 (0,0.299,0.361,0.340) 中等 1 (0,0.227,0.474,0.299) 中等 表 9 重要系数取值依据及定量化取值
Table 9 Basis and quantitative values of important coefficients
重要性评价因子 取值依据 定量化取值 拦挡坝地理位置 物源区 0~<0.3 流通区 0.3~<0.7 沟口处 0.7~1 拦挡坝设计库容 坝高<5 m 0~<0.3 坝高5~15 m 0.3~<0.7 坝高>15 m 0.7~1 防治重要性 密度低 0~<0.3 密度中 0.3~<0.7 密度高 0.7~1 表 10 马槽沟重要系数取值及均值
Table 10 The value and mean of the important coefficient of Macao gully
评价因子编号 地理位置 设计库容 防治重要性 12 0.3 0.5 0.3 0.37 11 0.3 0.35 0.3 0.32 10 0.4 0.35 0.4 0.38 9 0.5 0.7 0.6 0.60 8 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.60 7 0.7 0.72 0.6 0.67 6 0.7 0.53 0.7 0.64 5 0.75 0.58 0.8 0.71 4 0.8 0.64 0.8 0.75 3 0.9 0.63 1 0.84 2 1 0.57 1 0.86 1 1 0.42 1 0.81 表 11 武都区拦挡坝单沟综合服役性评价结果
Table 11 Comprehensive service evaluation results of single gully check dam in Wudu District
沟名 D 结果 沟名 D 结果 沟名 D 结果 马槽沟 (0.426,1.340,2.083,3.079) 差 佛堂沟 (0365,0.81,0.927,2.118) 差 桔柑沟 (0.047,0.0.471,0.433,0.352) 良 马家沟 (1.313,0.686,0,0) 优 百草
坝沟(0,0.393,0.374,0.533 差 东江
水沟(1.612,0.611,0.156,0.421) 优 柏水沟 (0.544,0.708,0.386,0.212) 良 清水沟 (0,0,0.218,0.342) 差 郭家沟 (0.680,0.039,0,0) 优 大山沟 (0.985,1.188,0.421,0.672) 良 寨子沟 (0,0.023,0.357,1.191) 差 汉坪沟 (0.677,0.285,0.177,0) 优 甘家沟 (0.990,0.476,0.406,0.638) 优 燕儿沟 (0.404,0.301,0.694,0.602) 中等 小山沟 (1.092,0,0.248,0.689) 优 表 12 泥石流沟道综合服役性评价结果
Table 12 Comprehensive service evaluation results of debris flow gully
评价等级 泥石流沟道 占比/% 优 马家沟、郭家沟、汉坪沟、东江水沟、小山沟、甘家沟 40 良 柏水沟、桔柑沟、大山沟 20 中等 燕儿沟 6.7 差 马槽沟、佛堂沟、百草坝沟、清水沟、寨子沟 33.3 -
[1] 中国国家统计局. 2021中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京:中国统计出版社,2022. [National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2021 China statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing:China Statistical Publishing House,2022. (in Chinese) National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2021 China statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistical Publishing House, 2022. (in Chinese)
[2] 石振明, 张公鼎, 彭铭, 等. 考虑河床坡度和泄流槽横断面影响的堰塞坝溃决过程试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):73 − 81. [SHI Zhenming, ZHANG Gongding, PENG Ming, et al. An experimental study of the breaching process of landslide dams with different bed slopes and drainage channel cross-sections[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):73 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHI Zhenming, ZHANG Gongding, PENG Ming, et al . An experimental study of the breaching process of landslide dams with different bed slopes and drainage channel cross-sections[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022 ,49 (5 ):73 −81 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 刘兴荣, 魏新平, 陈豫津, 等. 基于增量加载法的泥石流拦挡坝抗冲击力数值模拟——以甘肃舟曲三眼峪沟泥石流拦挡坝为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):78 − 83. [LIU Xingrong, WEI Xinping, CHEN Yujin, et al. Numerical simulation of impact resistance of debris flow dam: a case study of the debris flow dam in Sanyanyu Gully, Zhouqu County, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):78 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Xingrong, WEI Xinping, CHEN Yujin, et al . Numerical simulation of impact resistance of debris flow dam: a case study of the debris flow dam in Sanyanyu Gully, Zhouqu County, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (2 ):78 −83 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[4] 张宪政, 铁永波, 宁志杰, 等. 四川汶川县板子沟“6·26”特大型泥石流成因特征与活动性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(5):134 − 145. [ZHANG Xianzheng, TIE Yongbo, NING Zhijie, et al. Characteristics and activity analysis of the catastrophic “6·26” debris flow in the Banzi Catchment, Wenchuan County of Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(5):134 − 145.(in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Xianzheng, TIE Yongbo, NING Zhijie, et al . Characteristics and activity analysis of the catastrophic “6·26” debris flow in the Banzi Catchment, Wenchuan County of Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023 ,50 (5 ):134 −145 .(in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 侯圣山, 曹鹏, 陈亮, 等. 基于数值模拟的耳阳河流域泥石流灾害危险性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):143 − 151. [HOU Shengshan, CAO Peng, CHEN Liang, et al. Debris flow hazard assessment of the Eryang River watershed based on numerical simulation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):143 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract) HOU Shengshan, CAO Peng, CHEN Liang, et al . Debris flow hazard assessment of the Eryang River watershed based on numerical simulation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (2 ):143 −151 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 王峰, 杨帆, 江忠荣, 等. 基于沟域单元的康定市泥石流易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(3):145 − 156. [WANG Feng, YANG Fan, JIANG Zhongrong, et al. Susceptibility assessment of debris flow based on watershed units in Kangding City, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(3):145 − 156.(in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Feng, YANG Fan, JIANG Zhongrong, et al . Susceptibility assessment of debris flow based on watershed units in Kangding City, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (3 ):145 −156 .(in Chinese with English abstract)[7] 严琦, 张琪. 贵州省黔东南州降雨型泥石流风险评估[J]. 气象与减灾研究,2023,46(2):141 − 148. [YAN Qi, ZHANG Qi. Risk assessment of rainfall induced debris flow in Qiandongnan prefecture of Guizhou Province[J]. Meteorology and Disaster Reduction Research,2023,46(2):141 − 148.(in Chinese with English abstract) YAN Qi, ZHANG Qi . Risk assessment of rainfall induced debris flow in Qiandongnan prefecture of Guizhou Province[J]. Meteorology and Disaster Reduction Research,2023 ,46 (2 ):141 −148 .(in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 王天健, 胡桂胜, 陈宁生, 等. 泥石流单双边防护堤防治效果对比——以曾达沟为例[J]. 防灾减灾学报,2022,38(1):1 − 8. [WANG Tianjian, HU Guisheng, CHEN Ningsheng, et al. Comparison of prevention and control effect of single and double border embankment of debris flow: a case study of zengda gully[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Reduction,2022,38(1):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Tianjian, HU Guisheng, CHEN Ningsheng, et al . Comparison of prevention and control effect of single and double border embankment of debris flow: a case study of zengda gully[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Reduction,2022 ,38 (1 ):1 −8 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 张文涛. 泥石流防治岩土-生态工程综合治理效果分析与评价[D]. 成都: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院水利部成都山地灾害与环境研究所), 2021. [ZHANG Wentao. Analysis and evaluation of comprehensive control effect of geotechnical-ecological engineering for debris flow prevention and control[D].Chengdu: Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Wentao. Analysis and evaluation of comprehensive control effect of geotechnical-ecological engineering for debris flow prevention and control[D].Chengdu: Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 齐得旭,闫俊,张云卫. 泥石流拦挡坝破坏模式调查分析[J]. 资源环境与工程,2018,32(1):89 − 91. [QI Dexu,YAN Jun,ZHANG Yunwei. Investigation and analysis on failure mode of dam[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2018,32(1):89 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract) QI Dexu, YAN Jun, ZHANG Yunwei . Investigation and analysis on failure mode of dam[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2018 ,32 (1 ):89 −91 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] TAKAYAMA S,FUJIMOTO M,SATOFUKA Y. Amplification of flood discharge caused by the cascading failure of landslide dams[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research,2021,36(3):430 − 438. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsrc.2020.10.007
[12] LYU Xiaobo,YOU Yong,WANG Zhuang,et al. Characteristics of gully bed scour and siltation between check dams[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2023,20(1):49 − 64. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-022-7474-7
[13] 陈晓清,游勇,崔鹏,等. 汶川地震区特大泥石流工程防治新技术探索[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版),2013,45(1):14 − 22. [CHEN Xiaoqing,YOU Yong,CUI Peng,et al. New control methods for large debris flows in Wenchuan earthquake area[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition),2013,45(1):14 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Xiaoqing, YOU Yong, CUI Peng, et al . New control methods for large debris flows in Wenchuan earthquake area[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition),2013 ,45 (1 ):14 −22 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] ZEMA D A,BOMBINO G,DENISI P,et al. Evaluating the effects of check dams on channel geometry,bed sediment size and riparian vegetation in Mediterranean Mountain torrents[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,642:327 − 340. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.035
[15] ZHENG Hongchao,SHI Zhenming,SHEN Danyi,et al. Recent advances in stability and failure mechanisms of landslide dams[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2021,9:659935. DOI: 10.3389/feart.2021.659935
[16] 杨春阳. 武都区典型泥石流活动机理与启动判据研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2020. [YANG Chunyang. Study on the activity mechanism and initiation criterion of typical gully debris flow in Wudu District[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Chunyang. Study on the activity mechanism and initiation criterion of typical gully debris flow in Wudu District[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 魏万鸿,刘兴荣,宿星,等. 陇南地区泥石流拦挡坝回淤比降影响因素及计算方法[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2022,58(6):744 − 748. [WEI Wanhong,LIU Xingrong,SU Xing,et al. Study on the influencing factors and calculation method of siltation behind the debris flow dam in Longnan area[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2022,58(6):744 − 748. (in Chinese with English abstract) WEI Wanhong, LIU Xingrong, SU Xing, et al . Study on the influencing factors and calculation method of siltation behind the debris flow dam in Longnan area[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2022 ,58 (6 ):744 −748 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 舒和平,齐识,宁娜,等. 甘肃省南部武都区泥石流灾害风险评价研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2016,25(6):34 − 41. [SHU Heping,QI Shi,NING Na,et al. Risk assessment of debris flow disaster:A case study of Wudu District in the south of Gansu Province,China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2016,25(6):34 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHU Heping, QI Shi, NING Na, et al . Risk assessment of debris flow disaster: A case study of Wudu District in the south of Gansu Province, China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2016 ,25 (6 ):34 −41 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] 王俊豪,金华丽,倪天翔,等. 基于层次分析法的模糊综合评判模型在康乐县泥石流沟危险性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(3):52 − 57. [WANG Junhao,JIN Huali,NI Tianxiang,et al. The application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model based on analytic hierarchy process in risk assessment of debris flow gully in Kangle County[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(3):52 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Junhao, JIN Huali, NI Tianxiang, et al . The application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model based on analytic hierarchy process in risk assessment of debris flow gully in Kangle County[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017 ,28 (3 ):52 −57 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[20] 沈简,饶军,傅旭东. 基于模糊综合评价法的泥石流风险评价[J]. 灾害学,2016,31(2):171 − 175. [SHEN Jian,RAO Jun,FU Xudong. Assessment on debris flow risk based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2016,31(2):171 − 175. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2016.02.033 SHEN Jian, RAO Jun, FU Xudong . Assessment on debris flow risk based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2016 ,31 (2 ):171 −175 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2016.02.033[21] 李晓婷,刘文龙. 模糊综合评判法在甘肃陇南武都区石门乡泥石流危险性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):71 − 76. [LI Xiaoting,LIU Wenlong. Application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method to debris flow risk evaluation in Shimen Township in Wudu District of Longnan City,Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):71 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Xiaoting, LIU Wenlong . Application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method to debris flow risk evaluation in Shimen Township in Wudu District of Longnan City, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020 ,31 (4 ):71 −76 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[22] 张文涛,柳金峰,游勇,等. 泥石流防治工程损毁度评价——以汶川地区为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):77 − 83. [ZHANG Wentao,LIU Jinfeng,YOU Yong,et al. Damage evaluation of control works against debris flow:A case study in Wenchuan area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Wentao, LIU Jinfeng, YOU Yong, et al . Damage evaluation of control works against debris flow: A case study in Wenchuan area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (4 ):77 −83 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[23] 地质灾害分类分级(试行):DZ0238—2004[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2005. [Classification and Grading of Geological Hazards (Trial):DZ0238—2004[S]. Beijing:China Standards Publishing House,2005. (in Chinese) Classification and Grading of Geological Hazards (Trial): DZ0238—2004[S]. Beijing: China Standards Publishing House, 2005. (in Chinese)
[24] LIANG B,WU LB. Application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method in tunnel construction disasters [C]. Proceedings of 2008 National Symposium on Tunnel Monitoring Measurement and Anti-Analysis,2008:14-21.
[25] YUAN Jintao. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation for risk assessment on debris flow[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2010,17(3):14 − 16.
[26] 尚慧,王明轩,罗东海,等. 基于函数赋值模型与模糊综合评判法的单沟泥石流危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):61 − 69. [SHANG Hui,WANG Mingxuan,LUO Donghai,et al. Single gully debris flow hazard assessment based on function assignment model and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):61 − 69. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.01.07 SHANG Hui, WANG Mingxuan, LUO Donghai, et al . Single gully debris flow hazard assessment based on function assignment model and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019 ,30 (1 ):61 −69 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.01.07[27] 王文沛, 殷跃平, 胡卸文, 等. 碎屑流冲击下桩梁组合结构拦挡效果及受力特征研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2022,28(6):1081 − 1089. [WANG Wenpei, YIN Yueping, HU Xiewen, et al. Study on retaining effect and mechanical characteristics of pile-beam composite structure under debris flow impact[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2022,28(6):1081 − 1089. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Wenpei, YIN Yueping, HU Xiewen, et al . Study on retaining effect and mechanical characteristics of pile-beam composite structure under debris flow impact[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2022 ,28 (6 ):1081 −1089 . (in Chinese with English abstract)





 下载:
下载:








 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS