Analysis of the dynamic fragmentation process of debris flow in the Madaling landslide in Duyun, Guizhou
-
摘要:
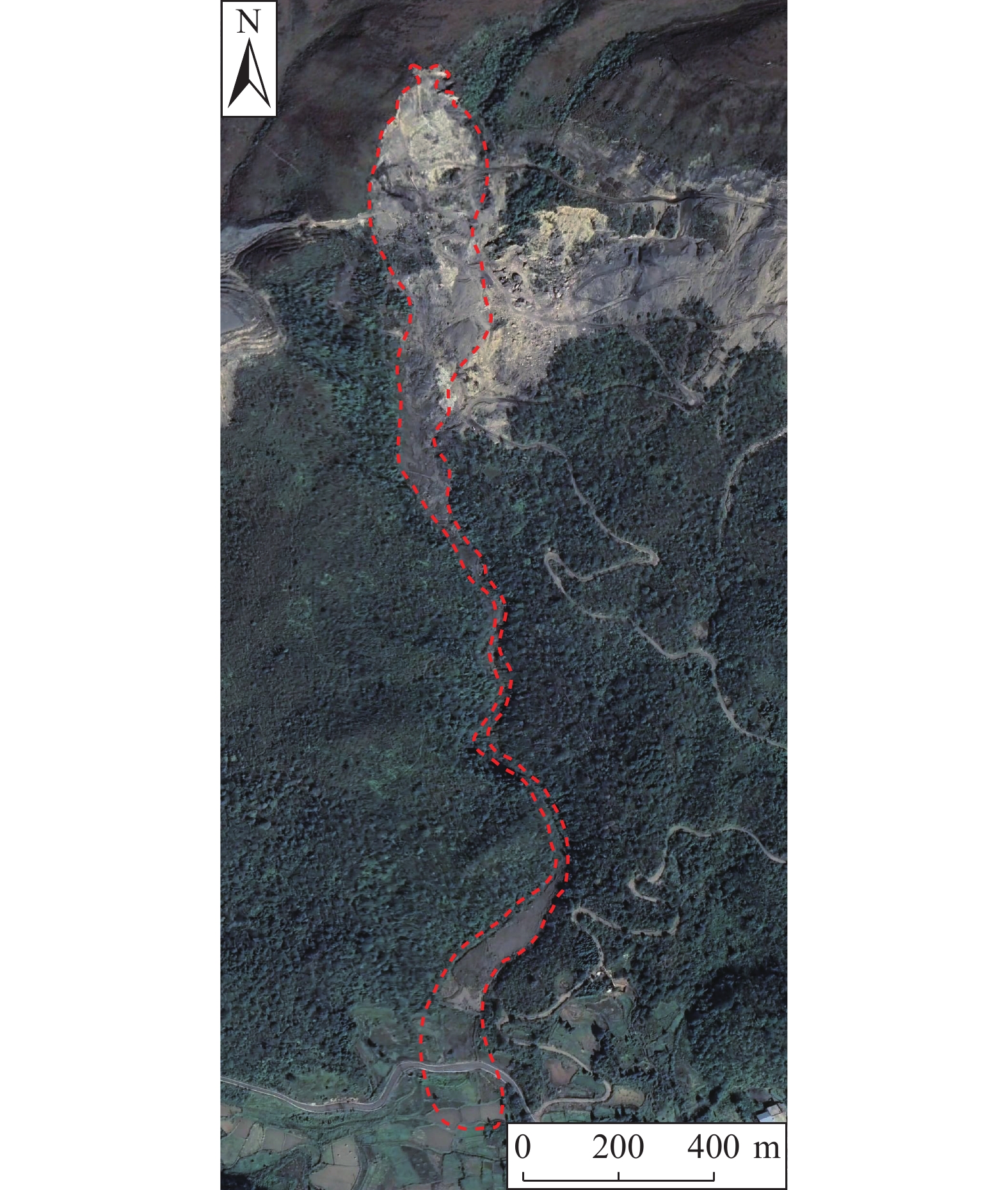
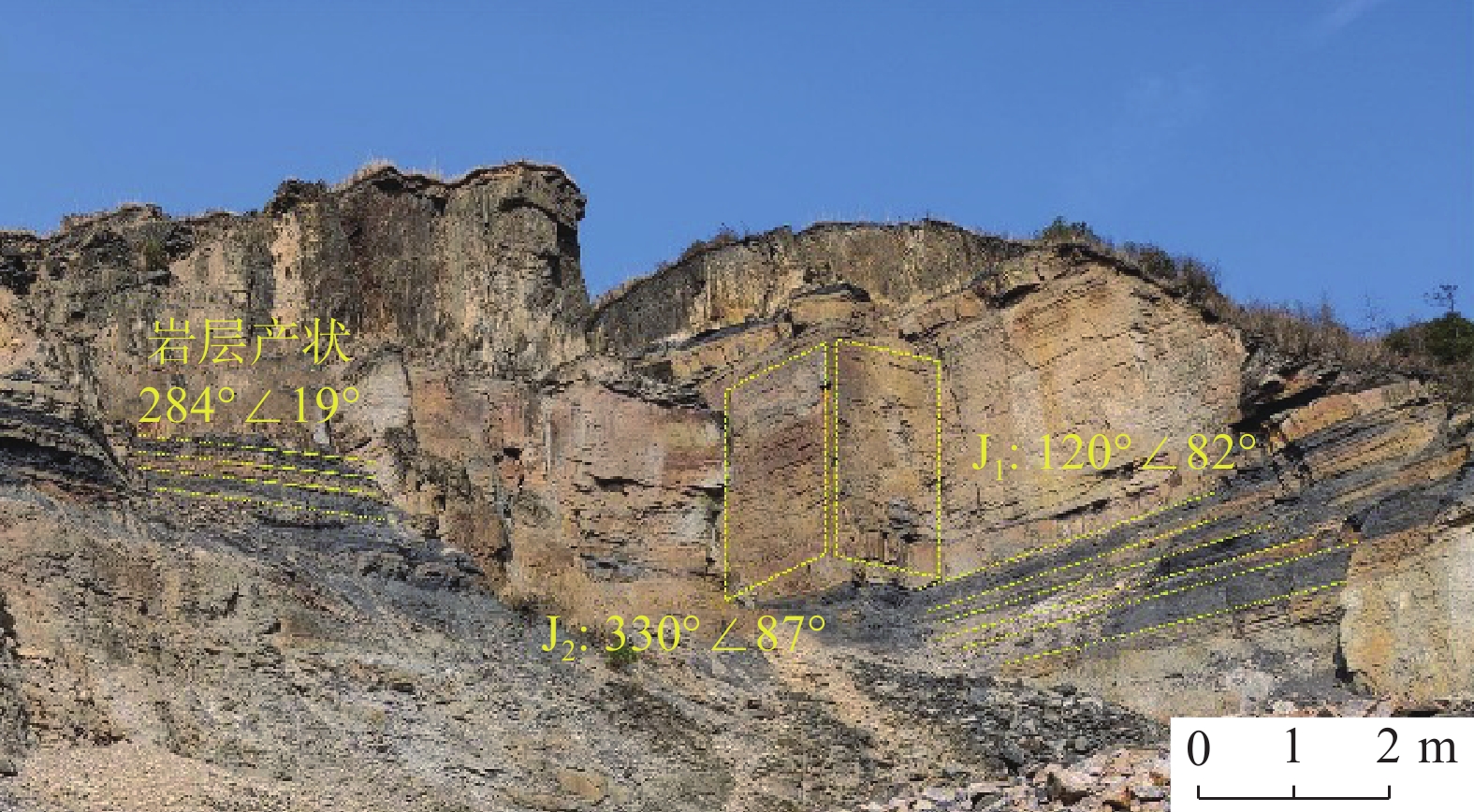
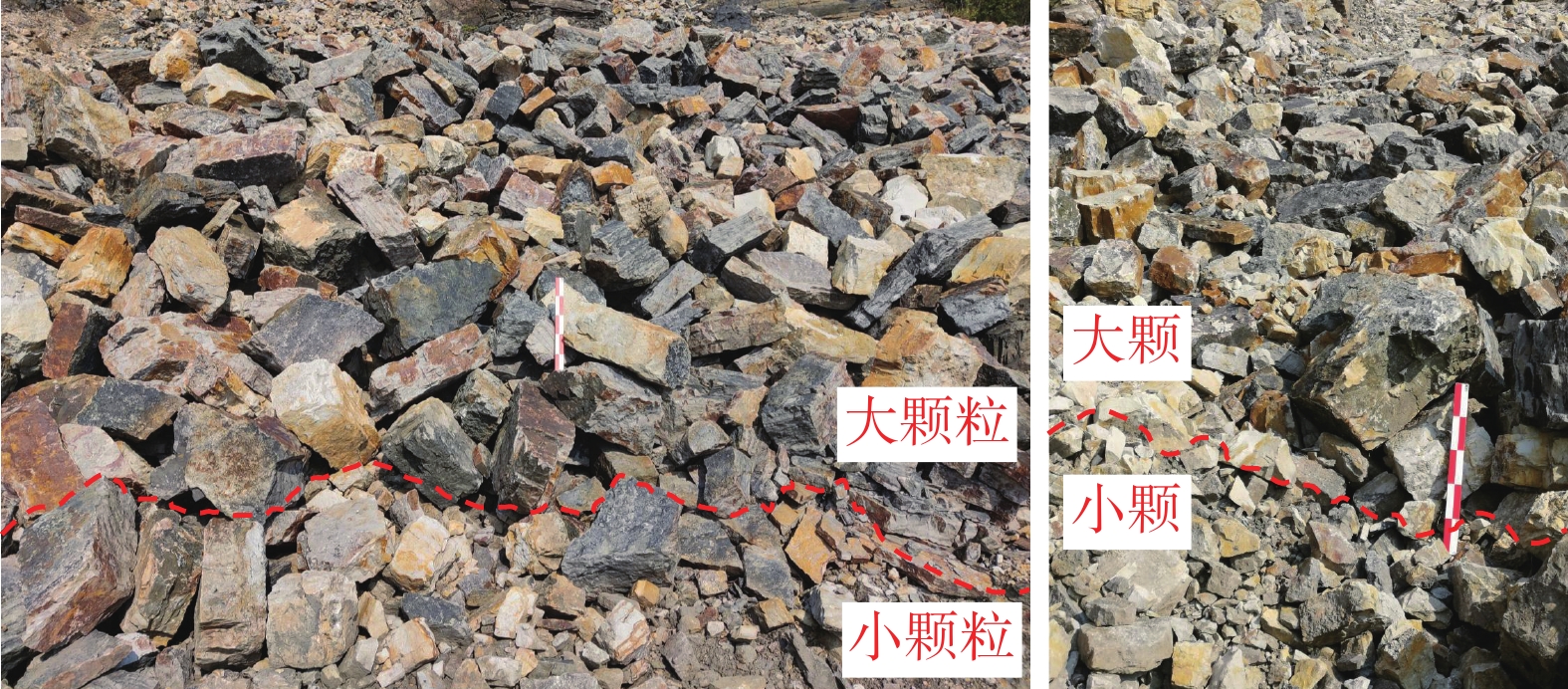
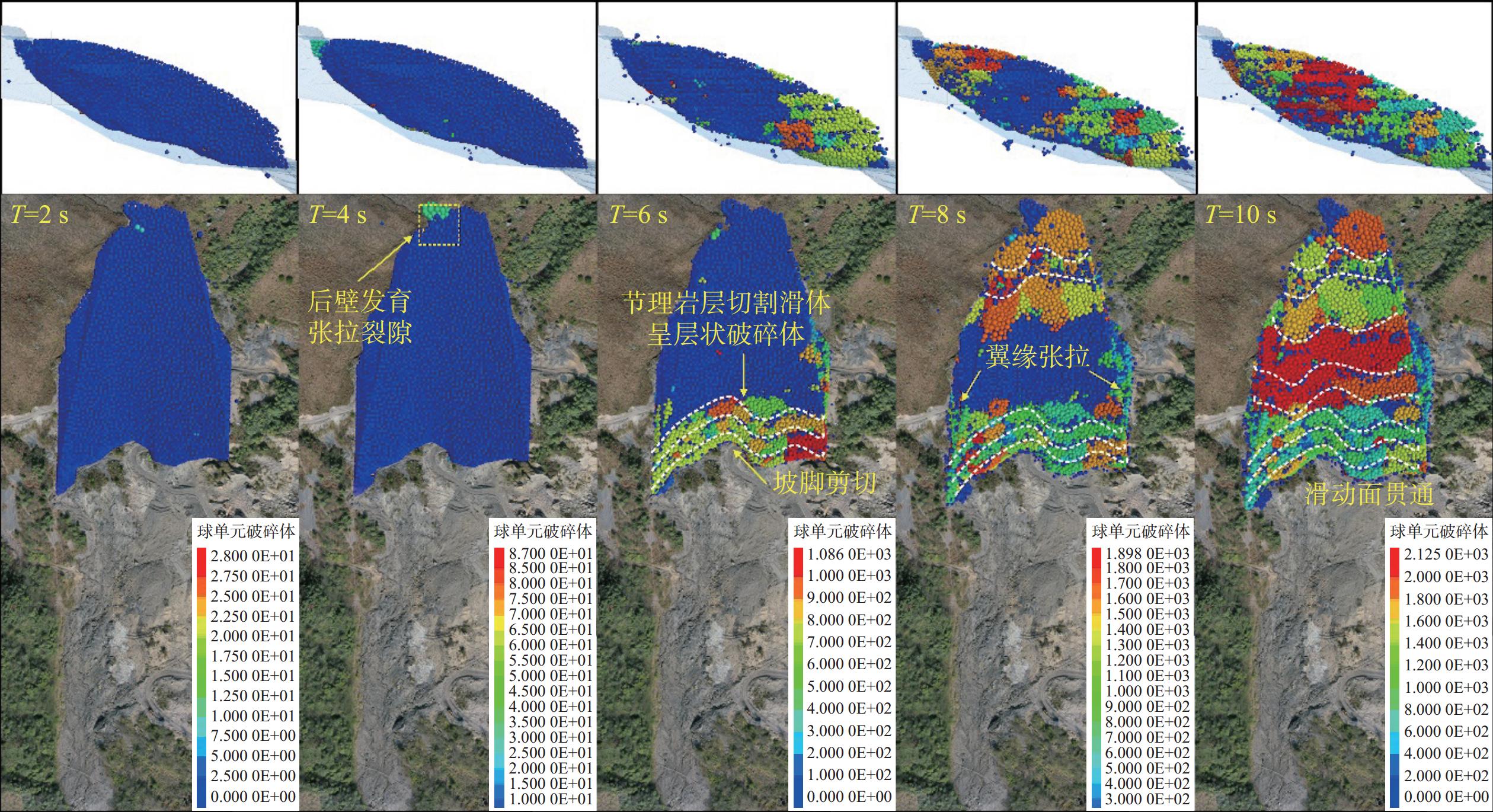
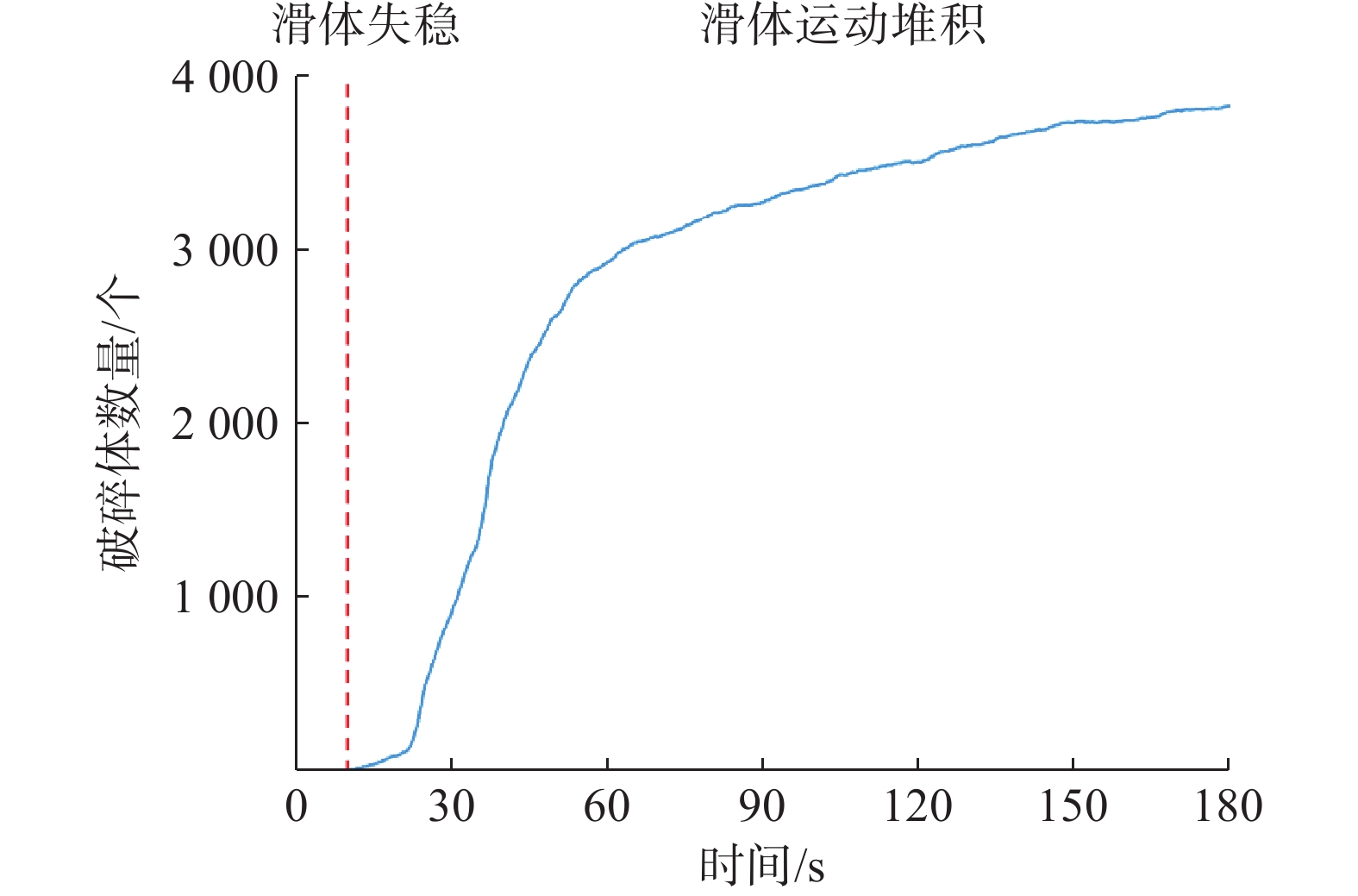
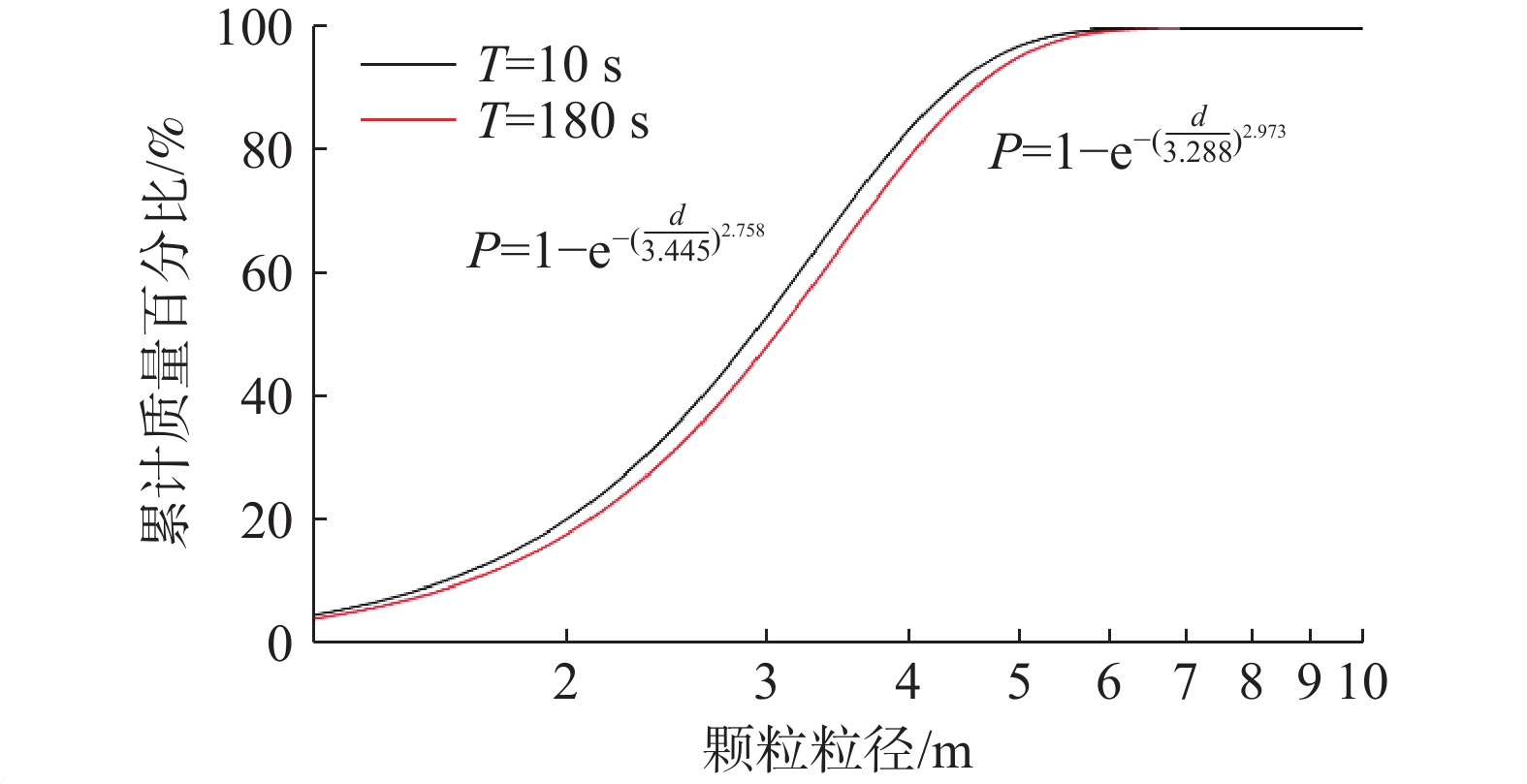
下伏采空层及节理发育对滑坡崩塌致灾过程具有重要影响。为进一步探究节理对岩体的切割破碎作用与特征,基于无人机航摄及对马达岭滑坡碎屑流的野外调查,采用颗粒离散元方法模拟了下伏采空区含节理的滑坡碎屑流动力破碎过程,对产生破碎体的数量变化和粒径分布进行了分析。结果表明:(1)马达岭滑坡碎屑流发育过程可归纳为后缘拉裂-阶梯状蠕滑拉裂-剪切变形-滑面贯通-滑体整体破坏,节理与下伏采空区的冒落作用促进了滑体破坏破碎过程;(2)破碎在滑体破坏和运动堆积过程中均有发生,且运动堆积中的破碎占主导地位;(3)采用Weibull双参数模型拟合的结果表明,滑体内的细粒径破碎体持续增加,最终堆积体以中小粒径破碎体为主,论证了滑体运动堆积过程中的破碎解体现象。研究为此类下伏采空区含节理的滑坡碎屑流的破碎机理分析提供了新的思路,证明了下伏采空区冒落作用及节理切割作用对岩体破碎的影响,对类似地质条件区域的滑坡碎屑流灾害防治具有一定指导意义。
Abstract:The presence of underlying mined-out layer and developed joints have an important impact on the fragmentation process of landslide collapse. In order to further explore the cutting and fragmentation effects and characteristics of joints on rock masses, based on UAV aerial photography and field investigations of debris flows in the Madaling landslide, the particle discrete element method was used to simulate the flow force crushing process of landslide debris with joints in the underlying layer. Changes in the quantity and particle size distribution of fragmented bodies were analyzed. The conclusions are as follows: 1. The development process of debris flow in the Madaling landslide can be summarized as the following: trailing edge tension fracture, stepped creeping tension fracture, shear deformation, slip surface connection, and overall failure of the sliding mass. The collapse of joints and underlying layer promotes the failure and fragmentation process of the sliding mass; 2. Fragmentation occurs during both the failure and movement deposition processes of the sliding mass, with fragmentation dominating during movement deposition; 3. Results fitted with the Weibull dual-parameter model show continuous increase in fine particle fragmentation within the sliding body, ultimately resulting in predominantly medium to small particle size fragmentation in the deposited mass, demonstrating the phenomenon of fragmentation and disintegration during the movement and deposition of the sliding body. This study provides new insights for the analysis of the fracture mechanism of the landslide debris flow with joints in such underlying layer, and proves that the effect of the caving and joint cutting of the underlying layer on the rock mass fracture has a certain guiding significance for the prevention and control of landslide debris flow disasters in areas with similar geological conditions.
-
-
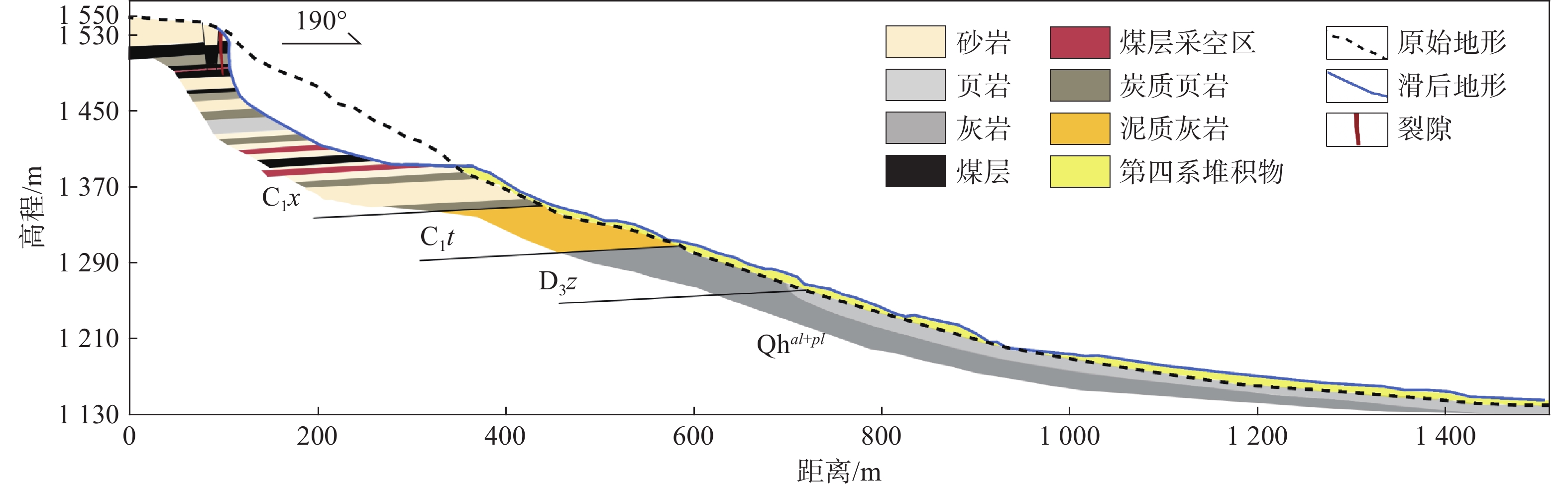
表 1 马达岭砂岩物理力学性质室内试验结果
Table 1 Laboratory experiment results of mechanical properties of sandstone at Madaling
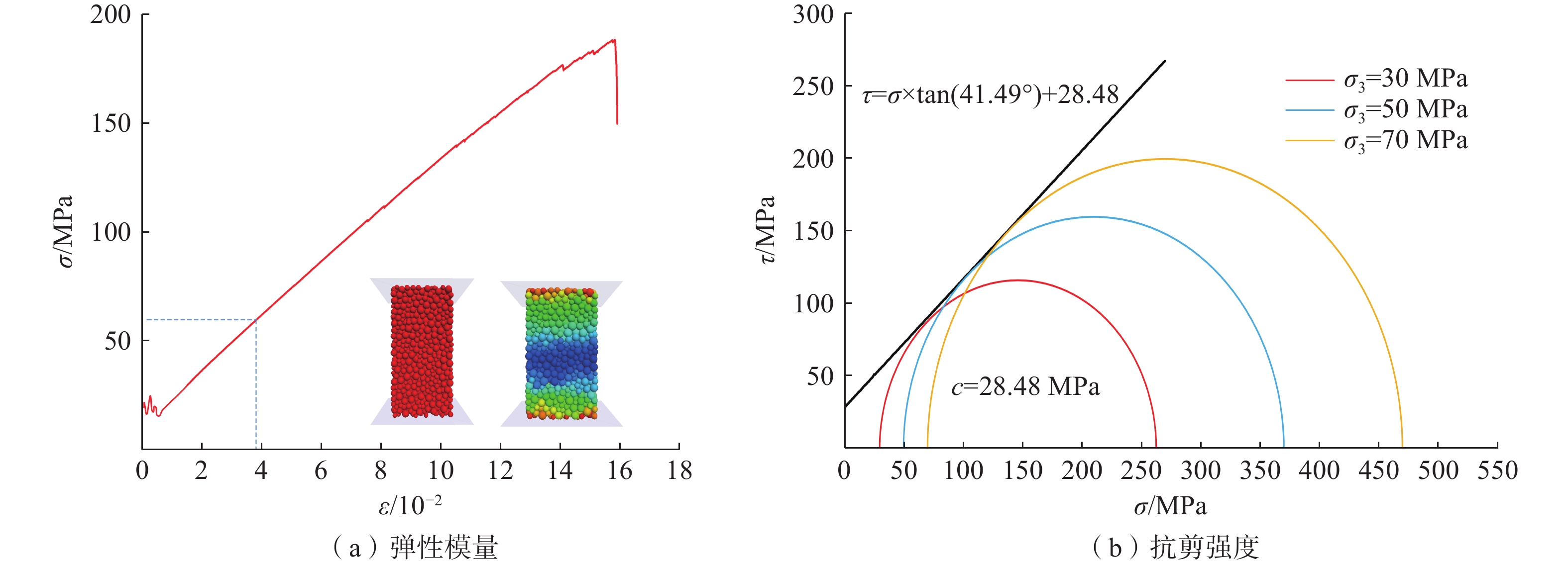
指标 σt/MPa σc/MPa E/GPa μ c/MPa φ/(°) ρ/(g·cm−3) 数值 0.91 80 15.59 0.19 28.02 42.08 2.63 表 2 PFC标定数值模拟微观参数
Table 2 Micromechanical parameters for numerical simulation calibrated from PFC
材料参数 取值 材料参数 取值 颗粒密度(ρ)/(kg·m−3) 2630 胶结法向切向刚度比( 1.0 颗粒有效模量(E*)/(N·m−2) 1.7e10 胶结抗拉强度(pb_ten)/(N·m−2) 7.2e8 法向切向刚度比(κ*) 1.0 胶结黏聚力(pb_coh )/(N·m−2) 3.5e8 胶结有效模量( 3.9e7 胶结内摩擦角(pb_fa)/(°) 40 -
[1] 李腾飞,陈洪涛,王瑞青. 湖北宜昌盐池河滑坡成因机理分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(4):578 − 583. [LI Tengfei,CHEN Hongtao,WANG Ruiqing. Formation mechanism of Yanchihe landslide in Yichang City,Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(4):578 − 583. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Tengfei, CHEN Hongtao, WANG Ruiqing. Formation mechanism of Yanchihe landslide in Yichang City, Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(4): 578 − 583. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 金德山. 云南元阳老金山滑坡[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,1998,9(4):98 − 101. [JIN Deshan. Laojinshan landslide in Yuanyang,Yunnan[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,1998,9(4):98 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract)] JIN Deshan. Laojinshan landslide in Yuanyang, Yunnan[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1998, 9(4): 98 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 刘传正. 重庆武隆鸡尾山危岩体形成与崩塌成因分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(3):297 − 304. [LIU Chuanzheng. Mechanism analysis on the Jiweishan rockfall disaster happened in Wulong,Chongqing,June 5,2009[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(3):297 − 304. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.03.002 LIU Chuanzheng. Mechanism analysis on the Jiweishan rockfall disaster happened in Wulong, Chongqing, June 5, 2009[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(3): 297 − 304. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.03.002
[4] 张磊,周银朋,庄宇,等. 贵州水城尖山营滑坡动力学特性分析与隐患点致灾范围预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(3):1 − 7. [ZHANG Lei,ZHOU Yinpeng,ZHUANG Yu,et al. Dynamic analysis and prediction of rear slope affected area of the Jianshanying landslide in Shuicheng County,Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(3):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Lei, ZHOU Yinpeng, ZHUANG Yu, et al. Dynamic analysis and prediction of rear slope affected area of the Jianshanying landslide in Shuicheng County, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(3): 1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 陶泽,孙闯,金淳哲,等. 抚顺西露天矿弱层强度衰减特性及边坡滑移大变形规律[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(3):31 − 39. [TAO Ze,SUN Chuang,JIN Chunzhe,et al. Characteristics of strength reduction in the weak layer and large-slip displacement of the cut slope on the Fushun west open-pit mining area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(3):31 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)] TAO Ze, SUN Chuang, JIN Chunzhe, et al. Characteristics of strength reduction in the weak layer and large-slip displacement of the cut slope on the Fushun west open-pit mining area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(3): 31 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 马杰,何开明,常文斌,等. 基于离散元的采空诱发山体滑塌失稳模式研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(3):171 − 179. [MA Jie, HE Kaiming, CHANG Wenbin, et al. Study on the failure pattern of mining-induced landslides based on discrete elements[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(3):171 − 179. (in Chinese with English abstract)] MA Jie, HE Kaiming, CHANG Wenbin, et al. Study on the failure pattern of mining-induced landslides based on discrete elements[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(3): 171 − 179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王玉川,巨能攀,赵建军,等. 缓倾煤层采空区上覆山体滑坡形成机制分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2013,21(1):61 − 68. [WANG Yuchuan,JU Nengpan,ZHAO Jianjun,et al. Formation mechanism of landslide above the mined out area in gently inclined coal beds[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2013,21(1):61 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.01.007 WANG Yuchuan, JU Nengpan, ZHAO Jianjun, et al. Formation mechanism of landslide above the mined out area in gently inclined coal beds[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(1): 61 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.01.007
[8] 赵建军,蔺冰,马运韬,等. 缓倾煤层采空区上覆岩体变形特征物理模拟研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(6):1369 − 1374. [ZHAO Jianjun,LIN Bing,MA Yuntao,et al. Physical modeling on deformation characteristics of overlying rock mass above mined-out area in gently inclined coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2016,41(6):1369 − 1374. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHAO Jianjun, LIN Bing, MA Yuntao, et al. Physical modeling on deformation characteristics of overlying rock mass above mined-out area in gently inclined coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(6): 1369 − 1374. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 赵建军,肖建国,向喜琼,等. 缓倾煤层采空区滑坡形成机制数值模拟研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(3):424 − 429. [ZHAO Jianjun,XIAO Jianguo,XIANG Xiqiong,et al. Failure mechanism numerical simulation of mining landslide with gentle bedding coal strata[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2014,39(3):424 − 429. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHAO Jianjun, XIAO Jianguo, XIANG Xiqiong, et al. Failure mechanism numerical simulation of mining landslide with gentle bedding coal strata[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(3): 424 − 429. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] ZHAO Tao,CROSTA G B. On the dynamic fragmentation and lubrication of coseismic landslides[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2018,123(11):9914 − 9932. DOI: 10.1029/2018JB016378
[11] RUIZ-CARULLA R,COROMINAS J,MAVROULI O. A fractal fragmentation model for rockfalls[J]. Landslides,2017,14(3):875 − 889. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-016-0773-8
[12] 陶伟,胡晓波,姜元俊,等. 颗粒粒径对滑坡碎屑流动力特征及能量转化的影响——以四川省三溪村滑坡为例[J]. 地质通报,2023,42(9):1610 − 1619. [TAO Wei, HU Xiaobo, JIANG Yuanjun, et al. Influence of particle size on dynamic characteristics and energy conversion of debris flow in landslide:A case study of Sanxicun landslide in Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2023,42(9):1610 − 1619. (in Chinese with English abstract)] TAO Wei, HU Xiaobo, JIANG Yuanjun, et al. Influence of particle size on dynamic characteristics and energy conversion of debris flow in landslide: A case study of Sanxicun landslide in Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(9): 1610 − 1619. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王玉川,巨能攀,赵建军. 马达岭滑坡室内岩石力学试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(3):52 − 57. [WANG Yuchuan,JU Nengpan,ZHAO Jianjun. Testing studies of rock mechanics in lab for the Madaling landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(3):52 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Yuchuan, JU Nengpan, ZHAO Jianjun. Testing studies of rock mechanics in lab for the Madaling landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2013, 40(3): 52 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] GAO Ge,MEGUID M A,CHOUINARD L E,et al. Insights into the transport and fragmentation characteristics of earthquake-induced rock avalanche:Numerical study[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics,2020,20(9):04020157. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001800
[15] ZHAO Tao,CROSTA G B,UTILI S,et al. Investigation of rock fragmentation during rockfalls and rock avalanches via 3-D discrete element analyses[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2017,122(3):678 − 695. DOI: 10.1002/2016JF004060
[16] CAMPBELL C S. Self-lubrication for long runout landslides[J]. The Journal of Geology,1989,97(6):653 − 665. DOI: 10.1086/629350
[17] CLEARY P W,CAMPBELL C S. Self-lubrication for Long Runout Landslides:examination by computer simulation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,1993,98(B12):21911 − 21924. DOI: 10.1029/93JB02380
[18] WEIBULL W. A statistical distribution function of wide applicability[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,1951,18:293 − 297. DOI: 10.1115/1.4010337





 下载:
下载:




 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS