Formation mechanism and hazard assessment of debris flow in Yizhong River, Deqin County, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
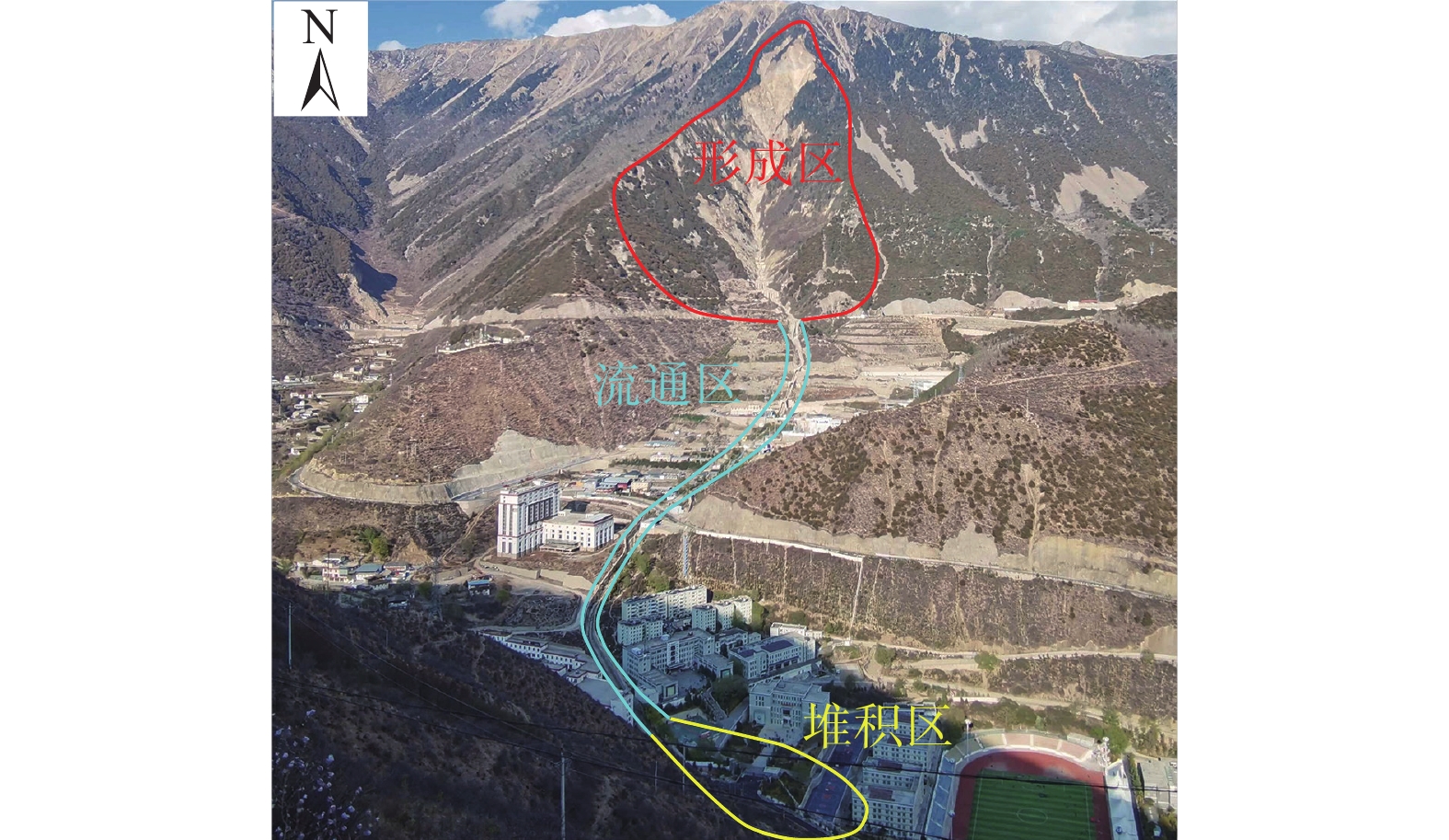
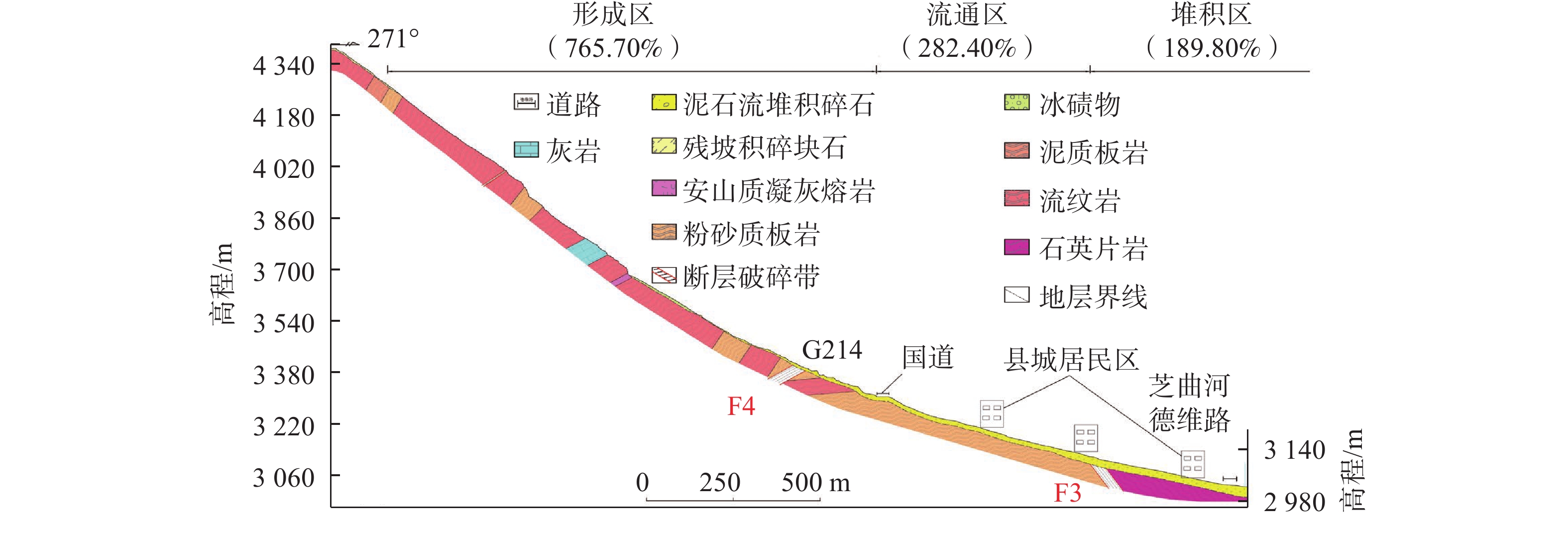
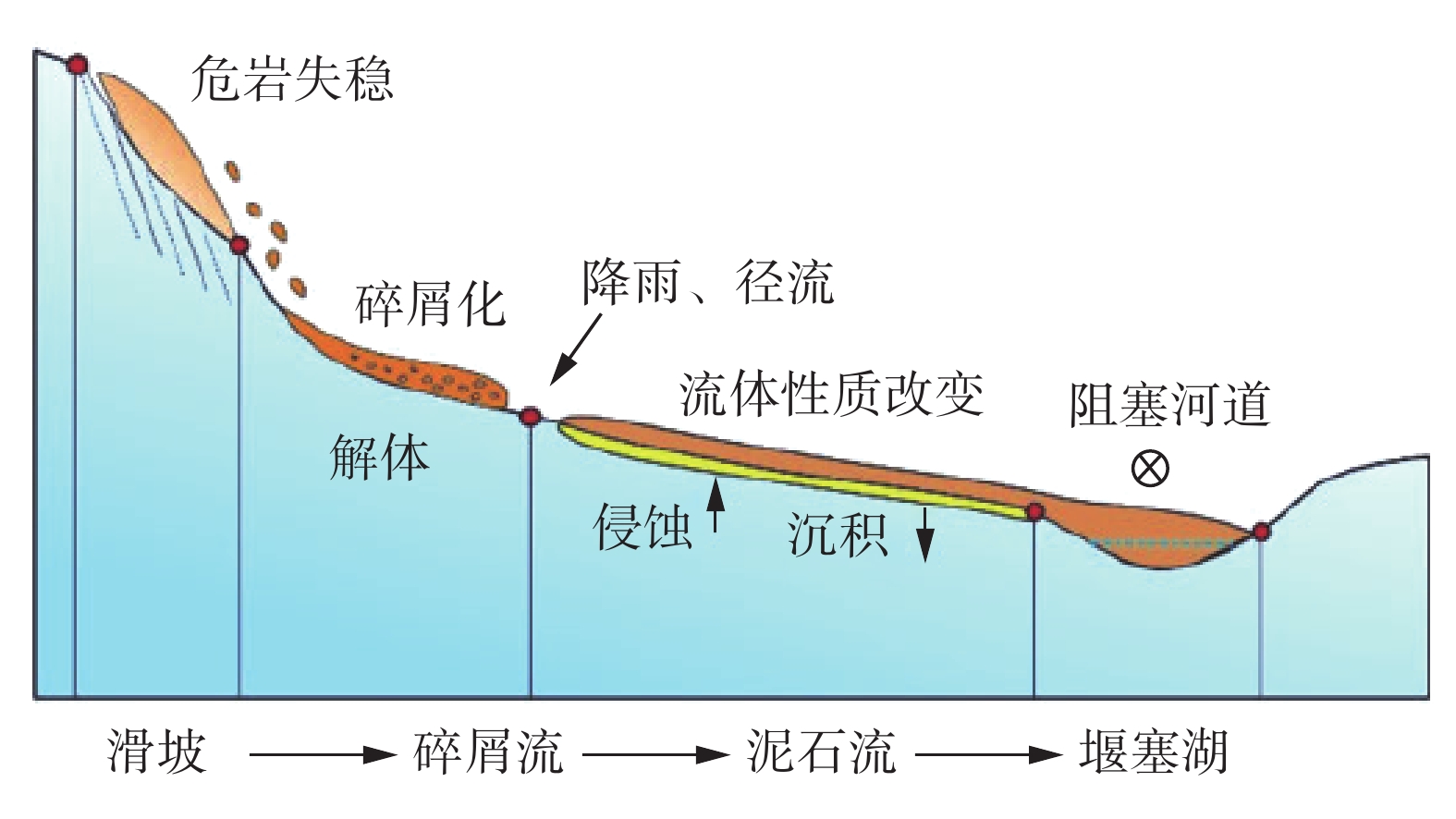
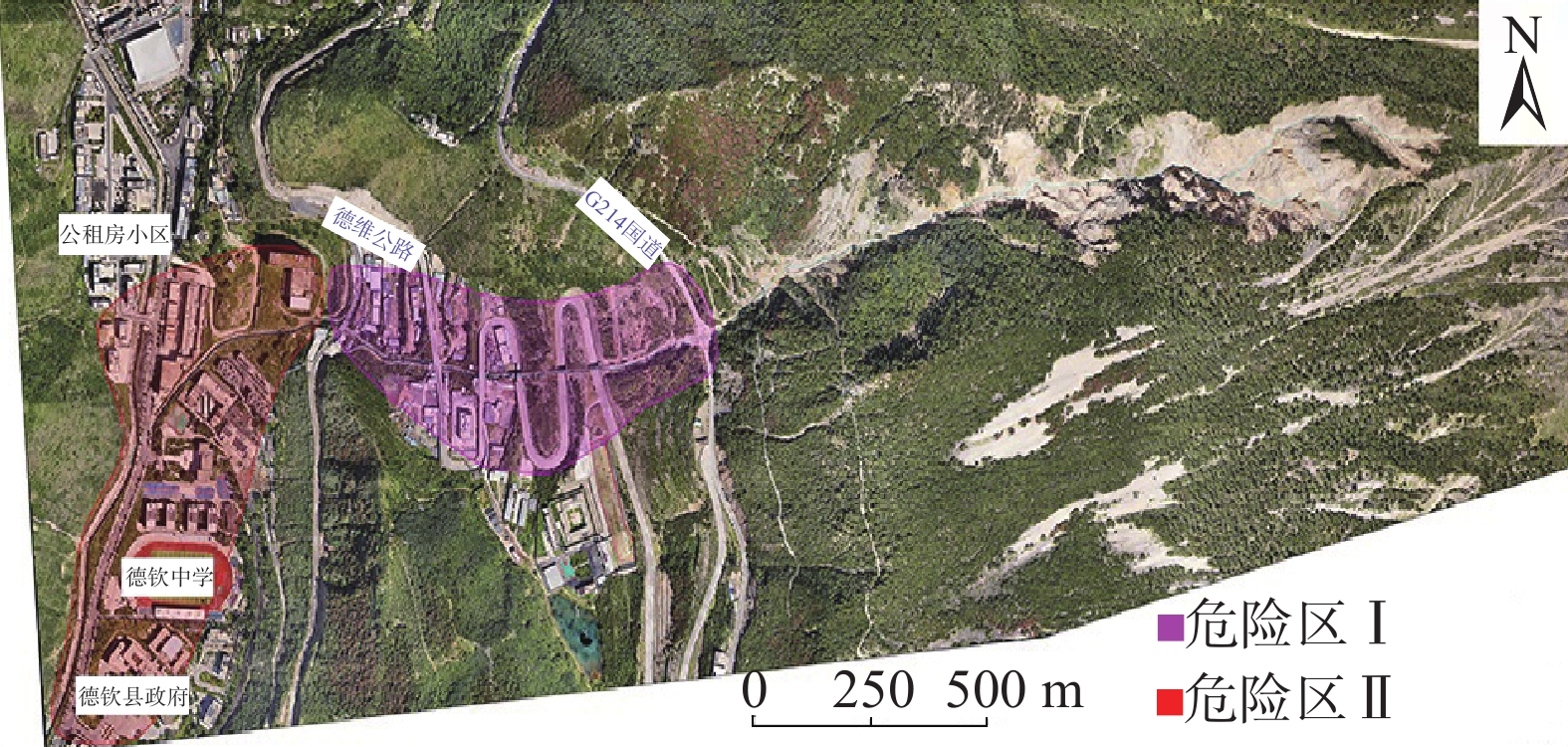
云南省德钦县是我国遭受泥石流灾害最严重的地区之一。德钦县一中河曾多次暴发大规模的泥石流灾害,对沟口处居民区及G214国道造成严重破坏和巨大经济损失。为探明一中河上游源区潜在物源在暴雨+地震工况下形成泥石流灾害的危险区范围和启动机制,在现场调查和成因分析的基础上,以无人机贴近摄影成果高精度的DEM为地形数据,运用RAMMS软件对暴雨+地震工况下体积为16.05×104 m3的泥石流进行模拟,划定了一中河流域内两处危险区,并阐述了一中河泥石流灾害成灾模式。研究结果表明:一中河泥石流属于高原山区沟谷型黏性泥石流,具有规模大、高易发、危害大的特点,其成灾机制概括为高位崩滑体-碎屑流-泥石流-堰塞湖-溃决洪水的沟谷灾害链;危险区Ⅰ位于G214国道至德维路区域,危险区Ⅱ为沟口区域,此区域易发生堆积和堵塞,危险性极高;泥石流运动过程中最大流速达23.93 m/s,最大冲击力为
1000 kPa,最大堆积深度为9.33 m,泥石流一次最大冲出体积约8×104 m3,危险区范围约0.31 km2。结果可为一中河泥石流治理工程提供科学依据,对德钦县地质灾害综合防治能力提升具有重要实际意义。Abstract:Deqin County in Yunnan Province is among the most severely affected regions in China by debris flow disasters. The Yizhong River in Deqin County has witnessed numerous large-scale debris flow disasters, causing significant damage and substantial economic losses to residential areas and the G214 national road. To elucidate the range of hazard zones and initiation mechanisms of debris flow disaster triggered by potential sources in the upstream Yizhong River under conditions of heavy rainfall and earthquakes, this study conducted field investigations and causal analyses. High-precision Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data derived from close-range UAV aerial photography were utilized as topographic data. The RAMMS software simulated a debris flow of 16.05×104 m3 under heavy rain and earthquake conditions. Two hazardous zones within the Yizhong River Basin were delineated, and the disaster initiation mode of debris flow in Yizhong River was expounded. The results show that the debris flow in Yizhong River belongs to the gully-type viscous debris flow typical of plateau mountainous regions, characterized by large scale, high frequency, and severe impact. Its disaster mechanism is summarized as a gully and valley disaster chain involving high-altitude landslide, debris flow, dammed lake, and flood breach. Risk zone I is located in the area from G214 national road to Dewei Road, while risk zone II is in the gully mouth area prone to accumulation and blockage, presenting high risk. During debris flow movement, the maximum flow velocity reached 23.93 m/s, maximum impact force was
1000 kPa, maximum accumulation depth was 9.33 m, and the maximum single outburst volume of debris flow was approximately80000 m3, with a danger area of about 0.31 km2. The research results provide a scientific basis for debris flow control projects in Yizhong River and are of practical significance for improving the comprehensive prevention and control of geological hazards in Deqin County.-
Keywords:
- Deqin County /
- debris flow /
- G214 national road /
- disaster mechanism /
- risk zone /
- numerical simulation
-
-
表 1 一中河泥石流物源统计表
Table 1 Statistical table of sources of Yizhong River debris flow
物源类型 冰碛物 滑坡 危岩崩塌 沟床堆积物 沟岸坍塌 坡面侵蚀 合计 面积/(104 m2) 4.0 4.30 10.94 1.24 0.30 31.20 51.98 体积/(104 m3) 30.0 40.12 27.25 3.70 0.80 12.25 114.12 可移储量/(104 m3) 2.75 9.52 8.98 1.95 0.80 1.23 25.23 一次最大可移储量/(104 m3) 0.14 0.55 0.90 0.39 0.24 0.12 2.34 -
[1] 刘希林,唐川. 泥石流危险性评价[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1995. [LIU Xilin,TANG Chuan. Danger assessment on debris flow[M]. Beijing:Science Press,1995. (in Chinese)] LIU Xilin, TANG Chuan. Danger assessment on debris flow[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1995. (in Chinese)
[2] 殷跃平. 链状地质灾害的特征与防范应对[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(3):3. [YIN Yueping. Characteristics of chain geological disasters and countermeasures[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(3):3. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YIN Yueping. Characteristics of chain geological disasters and countermeasures[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2017, 28(3): 3. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 于国强,张霞,顾小凡,等. 基底侵蚀作用对黄土坡面泥流动力过程影响机制研究[J/OL]. 中国地质,(2024-07-05)[2024-07-28]. [YU Guoqiang,ZHANG Xia,GU Xiaofan,et al. Influence of the basal erosion on kinetic process of loess slope debris flow[J/OL]. Geology in China,(2024-07-05)[2024-07-28]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.p.20240704.1646.002.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YU Guoqiang, ZHANG Xia, GU Xiaofan, et al. Influence of the basal erosion on kinetic process of loess slope debris flow[J/OL]. Geology in China, (2024-07-05)[2024-07-28]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.p.20240704.1646.002.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 乔成,欧国强,潘华利,等. 泥石流数值模拟方法研究进展[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2016,38(1):134 − 142. [QIAO Cheng,OU Guoqiang,PAN Huali,et al. Review on numerical modeling methods of debris flow[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2016,38(1):134 − 142. (in Chinese with English abstract)] QIAO Cheng, OU Guoqiang, PAN Huali, et al. Review on numerical modeling methods of debris flow[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2016, 38(1): 134 − 142. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 王俊豪,管建军,魏云杰,等. 德钦县城直溪河泥石流成灾模式及运动过程模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):187 − 195. [WANG Junhao,GUAN Jianjun,WEI Yunjie,et al. A study of the disaster model and movement process simulation of debris flow in the Zhixi River of Deqin County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):187 − 195. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Junhao, GUAN Jianjun, WEI Yunjie, et al. A study of the disaster model and movement process simulation of debris flow in the Zhixi River of Deqin County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(6): 187 − 195. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 宋兵,沈军辉,李金洋,等. RAMMS在泥石流运动模拟中的应用——以白沙沟泥石流为例[J]. 泥沙研究,2018,43(1):32 − 37. [SONG Bing,SHEN Junhui,LI Jinyang,et al. Application of RAMMS model on simulation of debris flow in the Baisha Gully[J]. Journal of Sediment Research,2018,43(1):32 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract)] SONG Bing, SHEN Junhui, LI Jinyang, et al. Application of RAMMS model on simulation of debris flow in the Baisha Gully[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2018, 43(1): 32 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 熊冲冲,胡卸文,刘丁毅,等. 基于RAMMS锄头沟泥石流运动过程模拟[J]. 四川地质学报,2021,41(1):107 − 111. [XIONG Chongchong,HU Xiewen,LIU Dingyi,et al. Simulation of debris flow activity in the Chutou gully based on RAMMS[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan,2021,41(1):107 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XIONG Chongchong, HU Xiewen, LIU Dingyi, et al. Simulation of debris flow activity in the Chutou gully based on RAMMS[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2021, 41(1): 107 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 段学良,马凤山,郭捷,等. 基于Massflow模型的西藏仁布杰仲沟泥石流运动特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(6):25 − 33. [DUAN Xueliang,MA Fengshan,GUO Jie,et al. Movement characteristics of Jiezhonggou debris flow of Renbu,Tibet based on massflow model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(6):25 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DUAN Xueliang, MA Fengshan, GUO Jie, et al. Movement characteristics of Jiezhonggou debris flow of Renbu, Tibet based on massflow model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(6): 25 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 刘珍. 云南德钦县城泥石流物源汇集模式探讨[J]. 云南地质,2020,39(2):284 − 287. [LIU Zhen. A probe into the convergence model of debris flow in Deqin,Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology,2020,39(2):284 − 287. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Zhen. A probe into the convergence model of debris flow in Deqin, Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 2020, 39(2): 284 − 287. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 王研. 云南省德钦县一中河泥石流形成机制和防治对策[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2016. [WANG Yan. The forming conditions and engineering revention of Yizhong River debris flow in Yunnan Province Deqin County[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Yan. The forming conditions and engineering revention of Yizhong River debris flow in Yunnan Province Deqin County[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张楠. 舟曲三眼峪沟泥石流灾害形成机理及综合防治研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学,2018. [ZHANG Nan. Study on formation mechanism and comprehensive prevention of debris flow disasters in Sanyanyu Valley,Zhouqu[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences,2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Nan. Study on formation mechanism and comprehensive prevention of debris flow disasters in Sanyanyu Valley, Zhouqu[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 杨兴国,曹志翔,邢会歌,等. 冰碛土滑坡—泥石流—堰塞湖灾害链发展过程机理与模拟技术研究构想[J]. 工程科学与技术,2022,54(3):1 − 13. [YANG Xingguo,CAO Zhixiang,XING Huige,et al. Research framework of the program:dynamic evolution mechanism and simulation of moraine landslide —debris flow —dammed lake disaster chain[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2022,54(3):1 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Xingguo, CAO Zhixiang, XING Huige, et al. Research framework of the program: dynamic evolution mechanism and simulation of moraine landslide —debris flow —dammed lake disaster chain[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2022, 54(3): 1 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王翔弘绅,胡桂胜,杨志全,等. 云南维西哈达沟中频泥石流特征及堵溃危险性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(2):42 − 52. [WANG Xianghongshen,HU Guisheng,YANG Zhiquan,et al. Characteristics of intermediate frequency debris flow and analysis of the hazard of blockage in Hada gully,Weixi County of Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(2):42 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Xianghongshen, HU Guisheng, YANG Zhiquan, et al. Characteristics of intermediate frequency debris flow and analysis of the hazard of blockage in Hada gully, Weixi County of Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(2): 42 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 赵聪,梁京涛,铁永波,等. 西藏雅鲁藏布江峡谷特大巨型泥石流活动与泥沙输移特征研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(4):45 − 55. [ZHAO Cong,LIANG Jingtao,TIE Yongbo,et al. Study on the activities of the massive debris flows and sediment transport characteristics in the Grand Bend of the Yarlung Zangbo River Gorge, Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(4):45 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHAO Cong, LIANG Jingtao, TIE Yongbo, et al. Study on the activities of the massive debris flows and sediment transport characteristics in the Grand Bend of the Yarlung Zangbo River Gorge, Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2024, 35(4): 45 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 袁东, 张广泽, 王栋, 等. 西部山区交通廊道泥石流发育特征及选线对策[J]. 地质通报,2023,42(5):743 − 752. [YUAN Dong, ZHANG Guangze, WANG Dong, et al. Analysis on development characteristics of debris flow and route selection countermeasures along the traffic lines in mountain areas of Western China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2023,42(5):743 − 752. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YUAN Dong, ZHANG Guangze, WANG Dong, et al. Analysis on development characteristics of debris flow and route selection countermeasures along the traffic lines in mountain areas of Western China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(5): 743 − 752. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 杨强,王高峰,李金柱,等. 白龙江中上游泥石流形成条件与成灾模式探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):70 − 79. [YANG Qiang,WANG Gaofeng,LI Jinzhu,et al. Formation conditions and the disaster modes of debris flows along middle and upper reaches of the Bailongjiang River Basin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):70 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Qiang, WANG Gaofeng, LI Jinzhu, et al. Formation conditions and the disaster modes of debris flows along middle and upper reaches of the Bailongjiang River Basin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(6): 70 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张宪政,铁永波,宁志杰,等. 四川汶川县板子沟“6•26” 特大型泥石流成因特征与活动性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(5):134 − 145. [ZHANG Xianzheng,TIE Yongbo,NING Zhijie,et al. Characteristics and activity analysis of the catastrophic “6•26” debris flow in the Banzi catchment, Wenchuan County of Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(5):134 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Xianzheng, TIE Yongbo, NING Zhijie, et al. Characteristics and activity analysis of the catastrophic “6•26” debris flow in the Banzi catchment, Wenchuan County of Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(5): 134 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 庞海松,谢骏锦,张小明,等. 基于RAMMS数值模拟的短时强降雨型泥石流危险性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):215 − 225. [PANG Haisong,XIE Junjin,ZHANG Xiaoming,et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow induced by short-time heavy rainfall based on RAMMS numerical simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):215 − 225. (in Chinese with English abstract)] PANG Haisong, XIE Junjin, ZHANG Xiaoming, et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow induced by short-time heavy rainfall based on RAMMS numerical simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 215 − 225. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 史继帅,姜亮,翟胜强. 四川甘洛县黑西洛沟“8•31” 泥石流动力过程[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(3):52 − 60. [SHI Jishuai,JIANG Liang,ZHAI Shengqiang. Dynamic process of the “8•31” debris flow in Luoxi gulley of Ganluo County, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(3):52 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)] SHI Jishuai, JIANG Liang, ZHAI Shengqiang. Dynamic process of the “8•31” debris flow in Luoxi gulley of Ganluo County, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2024, 35(3): 52 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 蒋涛,崔圣华,许向宁,等. 基于遥感解译的典型强震区泥石流物源发育及演化——以四川都汶高速沿线为例[J]. 地质通报,2024,43(7):1243 − 1254. [JIANG Tao, CUI Shenghua, XU Xiangning, et al. Distribution and evolution of debris flow in a typic meizoseismal area based on remote sensing: A case study of the Sichuan Duwen Expressway[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2024,43(7):1243 − 1254. (in Chinese with English abstract)] JIANG Tao, CUI Shenghua, XU Xiangning, et al. Distribution and evolution of debris flow in a typic meizoseismal area based on remote sensing: A case study of the Sichuan Duwen Expressway[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2024, 43(7): 1243 − 1254. (in Chinese with English abstract)





 下载:
下载:



 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS