Research on high-altitude and long-runout rockslides: Review and prospects
-
摘要:
在全球范围内,高位远程地质灾害造成了多起群死群伤事件和特大经济损失,是特大型地质灾害防灾减灾科技攻关的难点。文章系统回顾了高位远程地质灾害的研究历程,认为常规的“高速远程滑坡”研究难以适应高山、极高山区复合型地质灾害防灾减灾的要求,提出了从高位失稳、远程成灾和风险防控全链条的高位远程地质灾害研究思路,探讨了高位崩滑启动源区的易灾地质结构特征和早期识别技术、高速碎屑流远程链动机理和边界层效应以及风险评估和防灾减灾问题。通过对青藏高原高山、极高山区的高位远程地质灾害研究,揭示了高位滑坡碎屑流势流体链动传递机理,以及紊流体和犁切体的边界层效应,提出可以通过改造高势能碎屑流体的边界层底坡、增大湍流边界层内湍动能的生成与组合障桩前死区范围的消能降险方法。最后,针对铁路、公路、水电工程、边疆城镇和国防建设的发展,讨论了复合型高位远程滑坡灾害的防灾减灾将面临的新挑战,提出了易灾地质结构孕灾机理、高位远程链灾动力过程和风险防控理论与技术等3方面亟待加强的研究方向。
Abstract:Long-runout rockslides at high altitude have caused lots of severe casualties and huge economic losses in the world, becoming a focus issue in researches on mitigation for large-scale geological disasters. This paper systematically reviews the research process of high-altitude and long-runout rockslides and believes that conventional research on “high velocity and long runout” is difficult to adapt to the requirements of complex geohazards prevention and mitigation in high and extra-high mountains. The methodology on high-altitude and long-runout rockslides has been proposed that includes in the initiation at the high-position, the dynamics of chain-style disasters with a long-runout traveling and the risk assessment and mitigation. Then, the disaster-prone geostructure characteristics and early identification techniques of the high-altitude initiation zone, the long-runout transferring mechanism and boundary layer effect of high-velocity debris avalanche, and risk assessment and mitigation issues have been explored. Through the study in the high mountain and extra-high mountains of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau indicates that the potential flow transferring mechanism of debris avalanche in high-altitude rockslides, the boundary layer effect of turbulent fluid and the plowing bodies. It is proposed that energy dissipation and risk mitigation methods can be used by modifying the boundary layer bottom slope of high potential debris avalanche, to increase the generation of turbulent kinetic energy in the boundary layer, and the dead zone range in front of barrier piles. Three research directions have been discussed, including the initiating mechanism of disaster-prone geostructure, the dynamic process of high-altitude and long-runout disaster chains, and the theory and technology of risk prevention and mitigation.
-
0. 引言
近年来,受全球变化影响[1],青海省地质灾害发生的频率明显上升[2],地质灾害进入相对活跃期,地质灾害呈现出频发、群发的态势[3-4],而地质灾害具有隐蔽性、突发性和周期性的特征,防灾形势十分严峻[5]。现阶段青海省地质灾害治理率低,许多地质灾害威胁城镇、学校等人员集中区[6]的重大地质灾害隐患点,工程治理或避险搬迁难度大、资金困难,基层预防和自我救助能力弱,地质灾害防治任重道远。
2004年三峡库区着手建立了地质灾害监测预警信息管理系统[7],随后北京、江苏、贵州等省市也都分别针对本省的地质环境条件特点建立了基于WebGIS、CORS、物联网等的地质灾害监测预警系统[8-10],接着在甘肃兰州建立了基于普适性监测设备的黄土滑坡监测预警系统[11],同时“空天地一体化”地质灾害监测预警系统也有了理论基础[12],地质灾害监测预警平台蓬勃发展。
因此,加强普适型地质灾害监测预警工作,加速地质灾害综合防治体系建设已迫在眉睫。“十三五”以来,青海省建立了已知地质灾害隐患点全覆盖的群测群防体系,防灾减灾成效显著,但仍存在群测群防员更换频繁、兼职、专业技术掌握不足、信息传递速度慢等问题。自动化专业监测仅处于初步阶段,尚未推广。省内地质灾害自动化监测应用极为缺乏,原有的地质灾害排查工作效率低、基层班组巡查工作量大、人工监测区域受限且频次低、应急抢险时效性差,与新形势下地质灾害防治工作的需求还相差甚远[13-14]。
为积极贯彻落实自然资源部关于推进地质灾害监测预警设备试点工作的相关精神,根据《中国地质调查局地质灾害监测预警普适型仪器设备示范试用工作方案》的总体要求。青海省在地质灾害防治信息化建设现有的基础上,结合地质灾害防治新理论、新方法,根据其行政管理各项需求,达到地质灾害不同来源,不同批次的灾害点信息统一管理,动态更新。
1. 工作区及监测点布设
1.1 工作区概况
青海省地处青藏高原东北部,地质条件复杂,生态环境脆弱。全省地形地貌以山地、丘陵为主,占全省总面积的72%,地质灾害极高易发区仅存在极少部分,占青海省全省面积的1.66%;高易发区占9.56%,中易发区占26.50%。地质灾害呈现范围广、数量多、群发突发、灾情严重、治理难等特点。
全省各类地质灾害隐患点共有4279处,其中崩塌455处、滑坡1034处、泥石流1183处、不稳定斜坡1595处、地面塌陷9处、地裂缝1处、地面沉降2处。地质灾害隐患对20.36万人口和76.38亿元财产构成威胁。地质灾害隐患点主要分布在青海省东部地区西宁市、海东市和黄南藏族自治州,占全省地质灾害隐患点总数的54.6%,南部地区其次,数量占全省总数的27.7%(图1)。
1.2 监测预警选点原则与布置情况
第一,以尚未规划或尚未实施搬迁、治理、威胁人数较多的监测等级达到二、三级的滑坡、崩塌、泥石流等地质灾害隐患点为主要监测对象。按照“统筹安排、重点突出、统一接口、融合共享、边建边用、以用促建”的原则,部署工作任务。
第二,对于不同的地质灾害隐患类型,需有针对性地选取符合隐患特点的普适型监测设备,设备要求功能简单、精度得当、运行牢靠、成本适当、推广适用性强的特点。
第三,根据以往建设经验,自动化监测效果的保障关键在于地质灾害隐患点可监测性的综合分析和科学研究,选取合理的隐患监测点位,制定监测方案,明确设备选型和布局,达到有效监测和预警预报的目的。同时系统应统一数据接口,不同厂商不同设备数据要通过统一数据结构标准进入系统进行处理。
经过前期资料研究,现场实地踏勘、航测、复核、专家组综合分析论证的基础上进行甄选,选点合理。对威胁全省人数大于30人以上的422处高风险隐患点选取安装普适型自动化监测设备及自动报警设备,增加地质灾害隐患自动化监测覆盖面,监测点部署情况见表1。
表 1 青海省地质灾害监测预警总体部署表Table 1. Qinghai Province geological disaster monitoring and early warning general deployment table市州 监测预警点 分布特征 西宁市 145 共威胁人员8221人。其中西宁市区5处,湟中区85处,
湟源县8处,大通县47处。海东市 202 共威胁人员24594人。其中乐都区64处,平安区4处,
民和县42处,互助县44处,化隆县32处,循化县16处。黄南州 19 共威胁人员1902人。其中同仁市15处,尖扎县4处。 海南州 17 共威胁人员2432人,其中共和县1处,同德县3处,
贵南县2处,贵德县9处,兴海县2处。海北州 3 共威胁人员188人,门源县3处。 果洛州 10 共威胁人员834人。其中玛沁县7处,
班玛县2处、达日县1处。玉树州 26 共威胁人员2770人。其中囊谦县20处,
玉树市5处,称多县1处。合计 422 其中滑坡247处,不稳定斜坡131处,
崩塌4处,泥石流47处1.3 监测工程布设方式
监测工程应尽量沿灾害体变形主体方向布设监测剖面,用来监测灾害体的总体变形,并检验仪器的适用性。剖面布设宜优先考虑“十”字型,即一条纵剖面和一条横剖面。在此基础上,可根据监测需求扩展为“卄”字型、“卅”字型、“#”字型或“丰”字型等。在有地形限制的情况下,可采用放射型。
监测点应布设在地表变形显著部位;监测仪器设施的安装需严格执行有关技术要求说明;监测点布设应考虑其运行条件及解决方案;监测点布设在实现本项目目标的前提下应尽可能减少建设成本;为相互印证对比,同时从安全角度出发,监测点成组分布组成现场站。
滑坡主要监测降雨、地表位移、土壤含水率等,对重要隐患点安装视频系统加强监测;崩塌主要监测降雨量、倾角、加速度等;不稳定斜坡按照发展趋势按潜崩或潜滑进行监测设备布设;泥石流主要监测降雨量、泥位等,同时安装视频监测系统进行监测预警。
对布设普适性监测仪器的灾害点进行不间断监测,监测周期要求经地质人员综合分析确定地质灾害体变形阶段,以具体确定监测周期,在外界扰动较大时,如暴雨期间或汛期,应加密观测次数。
在仪器的选择中,应选取普适型设备及组合针对性的开展专群结合监测预警(表2),对地质灾害体出现、发生过程及降雨等关键性指标和指示性信息开展实时监测[15]。
表 2 灾害类型与测项选择Table 2. Types of hazards and selection of measurement items灾害类型 监测设备 声光报警 备注 测项 GNSS 裂缝 倾角 加速度 含水率 雨量 泥位 滑坡(潜滑) 岩质 ● ● ⊙ ⊙ ● 按需布置 具体安装位置及数量,根据灾害体规模及特征综合确定 土质 ● ● ⊙ ⊙ ⊙ ● 崩塌(潜崩) 岩质 ⊙ ● ● ● ● 土质 ⊙ ● ⊙ ⊙ ● 泥石流 沟谷型 ⊙ ● ● 坡面型 ⊙ ⊙ ⊙ ● ⊙ 注:●为宜测项,⊙为选测项。来自《地质灾害专群结合监测预警技术指南(试行)》 2. 系统建设
地质灾害监测预警系统一方面要实现地质灾害隐患多手段、多维度、多通道的监测数据融合,提高地质灾害隐患监测效果;达到常态巡查、专业排查、群测群防、自动化监测以及InSAR/LiDAR监测[16]等各类地质灾害监测数据的汇聚并与历史数据进行对比。另一方面要达到地质灾害隐患预警预报的自动化、智能化的目标。融合气象风险、群测群防、自动化监测实现针对气象局提供的多类型雨量数据、气象数据的查询、浏览、可视化,在此基础上综合气象风险预警预报分析的其他参数模型,进行地质灾害气象风险预警预报分析,并生成预警预报成果。能够签批管理预警预报产品成果,对政府工作人员决策支持起到一定辅助作用。对各类地质灾害风险进行预判,并在第一时间发布预警信息,实现地质灾害隐患监测预警自动化、智能化。
2.1 平台设计
地质灾害监测预警信息化平台在已有地质灾害信息化建设成果基础上,基于B/S架构,面向服务架构(SOA),采用WebGIS技术、物联网技术等关键技术,按照“一个中心、两个平台、多个应用”的总体架构建设,实现业务系统的统一用户身份认证、统一GIS服务、统一数据支撑、统一工作流引擎(图2)[17]。
基础支撑层:即支撑地质灾害监测预警信息化平台数据及软件系统的硬件设备与网络环境。
数据中心与数据交换共享平台:数据中心包括基础地理数据库、业务数据库、智能数据仓库与相应的数据管理、分析、监控工具。数据交换共享平台主要与省级应急管理平台、气象数据、国家地质灾害平台对接。
支撑平台:用于支撑整个地质灾害信息化应用系统建设,提供一套统一的技术支撑组件,包括业务需要使用的关系数据库、工作流、消息队列、消息通知、任务调度、报表服务等。另外为了让系统统一集成,支撑平台层提供快速开发框架以及单点登录系统用于统一构建业务系统,保证业务系统风格统一,集成方便。建设物联网云平台、Web三维地理信息平台、无人机调查公有云平台,支撑地质灾害监测应用。最后是开发大数据和机器学习组件,包含实时数据传输、NoSQL计算引擎、全文检索、机器学习算法库、深度学习算法库等。这样可以保证数据从数据仓库中获取之后,可以通过业务选择算法进行模型训练。
应用平台系统:基于数据中心提供的数据,支撑平台提供相应的支持,展开各类业务应用平台建设,主要包括地质灾害调查评价系统、地质灾害监测预警系统、指挥调度决策支持管理系统、项目管理系统、信息管理发布系统等,包含地质灾害调查、监测预警、统计分析、综合防治、应急支撑、地质遗迹保护等地质灾害业务。
整个系统平台以信息化推动地质灾害防治工作的系统化、科学化、规范化,支持地质灾害防灾、减灾,保障人民的生命财产安全,为青海省各级主管部门的地质灾害战略规划与工作部署提供技术支撑和决策支持服务。
2.2 数据中心建设
通过建立地质环境标准体系,需统一规范的地质环境业务工作流程、数据结构、数据处理标准以及系统界面、编码等。标准体系主要由基础设施标准、数据资源标准、应用开发标准、信息安全标准、业务系统建设管理标准等组成。确保地质环境数据从生产、汇交、整合、管理、更新、共享到应用整个过程的标准化、规范化。实现青海省地质环境数据的管理一体化(图3)。
依据地质灾害大数据的创建要求,实现数据的一体化存储、管理和服务,为青海省地质灾害监测预警信息化平台建设提供数据支撑;为业务信息系统、专业软件及工具、应用系统提供统一的数据服务。最终形成地质灾害数据的一体化服务体系。
2.3 支撑平台建设
平台采用Web三维地理信息平台,用于支持各类业务数据、空间数据、无人机三维模型等数据的三维叠加查看,同时可以提供三维量测、空间分析等基础工具。支持矢量点线面、icon、标注、DOM、DEM、模型、点云、场景、等高线、等值线、等值面、热点图、动态线、视频、全景图等几十种数据类型,支持谷歌地图、天地图、本地数据等不同种数据源。
无人机监测主要包括重点项目、重点区域定期的无人机数据采集与调查。基于云计算技术,建立无人机数据处理云平台,实现无人机数据的半自动化到自动化采集、无人值守数据处理和数据分析、解译、应用。无人机云平台主要由3个部分组成,其中包括无人机数据采集平台、无人机数据云平台以及无人机数据发布平台等模块组成。
物联网监测云平台提供地质灾害感知设备的接入,实现监测数据采集、数据传输、数据管理(包括数据接入、数据存储、数据处理、数据挖掘、数据转发)和数据应用。物联网监测系统包括前端传感器、物联网数据智能采集终端、物联网传输链路、物联网平台。基于物联网平台提供的接口,业务应用可以基于物联网监测数据,进行进一步的业务数据分析。
2.4 地质灾害监测预警信息平台组成
围绕地质灾害监测预警服务应用,在总体技术架构基础上,对现有业务系统进行整合完善,建立集管理、查询、统计分析、报表生成等功能于一体的地质灾害监测预警信息平台,达到对地质灾害防治的全流程管控与决策支撑。
青海省地质灾害监测预警信息化平台包括地质灾害调查评价系统、地质灾害监测预警系统、地质灾害气象预警系统、信息管理发布系统、指挥调度决策支持管理系统、项目管理系统、无人机调查云平台、移动端、监测预警系统(切线角方法)、气象风险预报系统,共10个部分(图4)。
3. 平台系统功能模块
3.1 常用系统功能模块
地质灾害调查评价系统针对实际工作中的地质灾害调查评价业务,包括以项目形式的调查评价以及日常巡查、排查工作。紧扣实际业务,整合完善现有的系统,建立集管理、审核、查询、统计分析、报表生成等功能于一体,主要有地质灾害调查评价、地质灾害巡、排查监管数据的管理维护、审核、查询、统计等。
地质灾害监测预警系统满足对监测对象的自动、连续、实时的监测,并具备将不同厂商设备的实时监测数据根据统一数据格式进行实时接收和存储的功能;系统进行前端业务数据管理和监测数据分析展示界面以及相应数据服务和应用服务;同时系统能以信息采集和预报分析决策为基础,依据预警信息的预警等级和地质灾害波及范围,借助传真、短信、无线广播等预警方式及相对应的预警流程,快速精准的将预警信息传达到地质灾害可能危及的地区,使收到预警信息地区的人员依据实时掌握的地质灾害整体的安全状态,及时采取相应防范措施,最大程度的降低人员伤亡及财产损失(图5)。
地质灾害气象预警系统包括气象信息查询分析、预警模型管理、气象预警签批发布等模块。气象信息查询包括雨量站、历史雨量、预报雨量的查询浏览和实时雨量监测功能。预警模型管理包括预警参数设置与预警分析计算两部分内容。预警计算过程在界面上展示,用户可以实时看到预警计算的进度情况。预警计算完成后可发布预警信息。
3.2 辅助系统功能模块
信息管理发布系统包括信息发布、文章发布、链接发布、通讯录管理和门户网站等模块。
指挥调度决策支持管理系统主要建设灾险情、汛期值班、应急调查、应急资源管理、决策支持功能模块,完全满足对指挥调度决策支持管理体系的总体要求。
项目管理系统包括项目管理、资料查阅、项目审批、专家库管理等模块。
无人机云平台主要是处理空间数据,实现数据从采集到处理、再到服务发布的全流程管理。使用无人机APP,可以控制飞行路线、范围,实现无人机数据的采集与传输,数据传输至云端后,讲对数据进行处理。对于拍摄回来的数据,可以利用裂缝识别模型,对图片进行分析,查看哪些地方有裂缝。处理后的数据可以通过发布后,即可在一张图中进行浏览。
地质灾害监测预警移动端主要建设灾险情速报、任务管理、巡查管理、项目过程管控、监测预警、调查处置、应急调查、信息发布、信息公开、微信公众号功能模块,完全满足对移动端的总体要求。
3.3 特色系统功能模块
围绕青海省在地质灾害防治方面面临的系列问题,借鉴国内外先进经验,在充分利用、整合已有地质灾害建设成果基础上,主要基于改进的切线角方法研发了独具青海特色的青海省滑坡地质灾害实时监测预警系统。主要的改进体现在两点,首先改进切线角α作为预警判据,同时考虑初始变形阶段、等速变形阶段和加速变形阶段的变形速率临界值V[18]。其次地灾预警是一个复杂的多方面的问题所以引入了神经网络模型收集监测数据不断优化预警阈值提高预警准确率(图6)。
并且系统平台能够实现快速融合InSAR/LiDAR数据、无人机正射影像、三维倾斜模型、现场调查等地质灾害应急数据;通过ETL工具,提取气象、交通、受灾对象、应急物资等数据至系统智能数据仓库,构建青海省地质灾害综合信息模型,实现从数据汇聚、数据管理、动态监测、预警预报、指挥调度、综合防治等全过程信息化、智能化和标准化管理。
同时基于青海省的地区分异也设计了独具青海特色的青海省地质灾害气象风险预警系统(图7)。气象风险预警分析主要包括不同自然区划的参数设置、预警计算等功能[19-23]。
4. 监测预警运行
4.1 预警运行情况与响应机制
根据监测预警机制,省级单位负责地质灾害专群结合监测预警工作的组织、协调、监督和管理。承担单位与设备供应商共同负责站点建设、运行维护工作。州、县级单位负责站点建设期间的协调工作。
为加强和提升地质灾害监测预警管理能力,夯实监测预警的各项基础工作,打造“自下而上、分级管理、责任监督”的省、市、县、乡、村“五级管理”系统,提高地质灾害监测预警的日常监督和监管,适应新形势下的地质灾害监测预警大数据的采集、传输、存储、共享、分析和预警,从各方面提高基层地质灾害综合防治能力。
根据地质灾害监测预警预报的等级分四级响应,分别为乡、县、市、省四级,分工有序、共同协作。乡级政府及时组织撤离、监测;县级政府组织技术单位调查、风险评估、制定处置措施;市级政府督导,技术支撑;省级监管,技术指导。预警信息遵守“政府主导,统一发布;属地管理,分级负责;纵向到底,全部覆盖。”的发布原则,由县级自然资源部门发布,第一时间将相应等级的预警信息告知有关防灾负责人、监测负责人、群测群防员、并根据有关规定决定是否向全社会发布。
报警方式及响应结合专业监测的成果及灾害宏观地质现象专业监测人员评价灾害的稳定性,一旦达到预警级别需按照不同的等级进行处置。对应于四个预警等级,红色警报级、橙色警戒级、黄色警示级、蓝色注意级。报警方式及响应的内容也不同,按照各个等级给不同的对象发送预警信息。
蓝色预警发出后,群测群防员应去现场对宏观迹象进行巡查,并将有关情况进行反馈至乡(镇、街道办事处)自然资源主管部门。
黄色预警发出后,地质灾害隐患点监测责任人、群测群防员应去现场对宏观迹象进行巡查;技术支撑单位加强监测数据分析,开展中期预警,预测发展趋势,并到现场进一步核查,并将有关情况反馈至乡(镇、街道办事处)自然资源主管部门。
橙色预警发出后,地质灾害隐患点监测责任人、群测群防员应去现场对宏观迹象进行巡查,加强对宏观变形迹象的监测;技术支撑单位加强监测数据分析,开展短期预警,预测发展趋势;乡(镇、街道办事处)防灾责任人会同技术支撑单位前往现场进一步核查,并将有关情况反馈至县(区)级自然资源主管部门。
红色预警发出后,地质灾害隐患点监测责任人、群测群防员应去现场对宏观迹象进行巡排查,加强宏观变形监测及短临前兆监测,开展短临预警,由其根据现场宏观变形等实际情况判定是否提前组织地质灾害危险区群众进行转移。县级自然资源主管部门会同乡(镇、街道办事处)和技术支撑单位前往现场进一步调查处置,若确属灾险情,则立即按照应急预案和灾险情速报机制采取相应行动。地质灾害应急响应人员主要由各灾害点所在的村、乡(镇)相关负责人负责。
4.2 预警系统日常管理
监测预警日常管理以地质灾害点、地质灾害监测人员、自动化监测设备以及应急救援物资等为基础对象,坚持分层分级管理的原则,实现对群测群防日常地质灾害点的监测、巡检、综合管理等工作落实情况的监管,为上级地质灾害监管单位提供险情判断的有效依据。
对于目前没有地质灾害隐患点的行政村,建立群众和地质灾害信息员(由村支部书记或村委会主任担任)上报机制,并通过监测预警管理平台实现地质灾害群测群防体系的落地。通过自动化监测设备的监测数据挖掘、分析和处理,综合历史数据和实时采集的降水量、形变等数据,利用平台设定的自动预警、报警功能和监测预警警戒值,实现自动化监测设备的自动化报警,为有关部门提供及时可靠的依据,从而有效预防事故。
为保证自动化监测设备能持久可靠运行,一定要对监测设备、通信链路等进行实时检查校验,建立运行电子档案,及时处置任何可能影响系统运行的问题。在信息分发与反馈方面,实现向上下级或平级部门及时分发监测预警预报信息,及时反馈上下级单位部门或平级部门分发的信息。在层级管理方面,县、市、省三级分层管理,通过平台分别实现对所辖区域下级单位工作落实情况的量化监督管理和考核。在权责管理方面,地质灾害监测预警预报系统自动匹配对应管理权限的责任部门,建立台账确保所有通过平台的工作来往都有据可查,保障监测预警预报数据合理、有效和可靠。
4.3 典型预警成果
2021年8月20日青海省玉树藏族自治州囊谦县吉曲乡白玛俄林寺普适性监测预警设备成功预警,白玛俄林寺滑坡共布设有4台GNSS,2台裂缝计,1台GNSS基准站和1台雨量计(图8)。
根据实时监测曲线(图9)和宏观变形趋势综合研判,监测预警设备首先发布了黄色预警信息通知群测群防员。随着滑坡不断发展,于当日04:09在白玛俄林寺的02GP01(地表位移GNSS)触发单参数预警,预警等级升级为橙色。设备及时记录预警信息通知市级主管人员加强值守指导和现场管控,做好紧急转移准备。
5. 结论与展望
(1) 青海省地质灾害监测预警信息化平台在设备布设、系统结构、功能搭建、数据中心、预警模型、数据库建设等方面形成了较为完整的体系,包涵了地质灾害监测、预警、应急、治理,核销的全生命周期信息的管理;
(2) 信息化平台通过数据集成化、成果可视化、信息综合化、系统一体化等技术手段,实现了青海省地质灾害不同来源,不同批次灾害点信息的统一管理和动态更新,极大提高了青海省地质灾害隐患监测的预警效果;
(3) 通过系统试运行,平台数据可靠,能够满足监测预警的需求。
通过信息化平台的试运行已经获得了很多的预警信息,数据积累初见成效为以后的工作打下基础。信息化平台仍存在数据集成度较低、缺乏数据共享及服务和综合分析能力不足的缺陷。在未来的工作中将会主要着重于以下几个方面首先基于区块链技术保证可信数据平台;其次构建云网融合高性能的智能预警分析计算框架,大数据环境下地质灾害监测预警样本库;接着建立基于数据驱动的预警模型,实现动态阈值设定;最后实现基于人工智能的重大事件速报。充分满足各类用户需求,保障人民生命财产安全。
-
表 1 不同海拔山区高位远程地质灾害识别InSAR集成方法
Table 1 Integrated method of InSAR for identification of high-altitude and long-runout rockslides in mountain areas with different altitudes
海拔 典型灾害 技术方法 主要技术 低山(500~ 1000 m) 滑坡、崩塌、塌陷 ① SBAS-InSAR技术(一般情况推荐);
② PS-InSAR技术(相干性较好时推荐)①基于数值气象模型的大气延迟改正;
②解缠误差探测及改正技术;
③坡向形变投影技术中山(1000~ 3500 m) 大型滑坡、崩塌等 ① SBAS-InSAR技术(一般情况推荐);
② PS-InSAR技术(相干性较好时推荐);
③ POT时序技术(大量级形变监测推荐)①基于数值气象模型的大气延迟改正;
②解缠误差探测及改正技术;
③坡向形变投影技术;
④升降轨数据联合监测;
⑤叠掩、阴影掩膜技术高山(3500~ 5000 m) 高位滑坡、崩塌、冰川 ① SBAS-InSAR技术(时间序列形变监测推荐);
② Stacking-InSAR技术(大范围调查推荐);
③ POT时序技术(大量级形变监测推荐)①基于数值气象模型的大气延迟改正;
②解缠误差探测及改正技术;
③坡向形变投影技术;
④升降轨数据联合监测;
⑤叠掩、阴影掩膜技术;
⑥顾及DEM的配准技术极高山(>5000 m) 超高位滑坡、崩塌、冰川 ① SBAS-InSAR技术(时间序列形变监测推荐);
② Stacking-InSAR技术(大范围调查推荐);
③ POT时序技术(大量级形变监测推荐)①基于数值气象模型的大气延迟改正;
②解缠误差探测及改正技术;
③坡向形变投影技术;
④升降轨数据联合监测;
⑤叠掩、阴影掩膜技术;
⑥顾及DEM的配准技术;
⑦可变窗口偏移量跟踪技术;
⑧跨平台偏移量跟踪技术表 2 高位远程地质灾害链动机理与成灾模式简表
Table 2 Summary of chain mechanism and disaster mode of high-altitude and long-runout rockslides
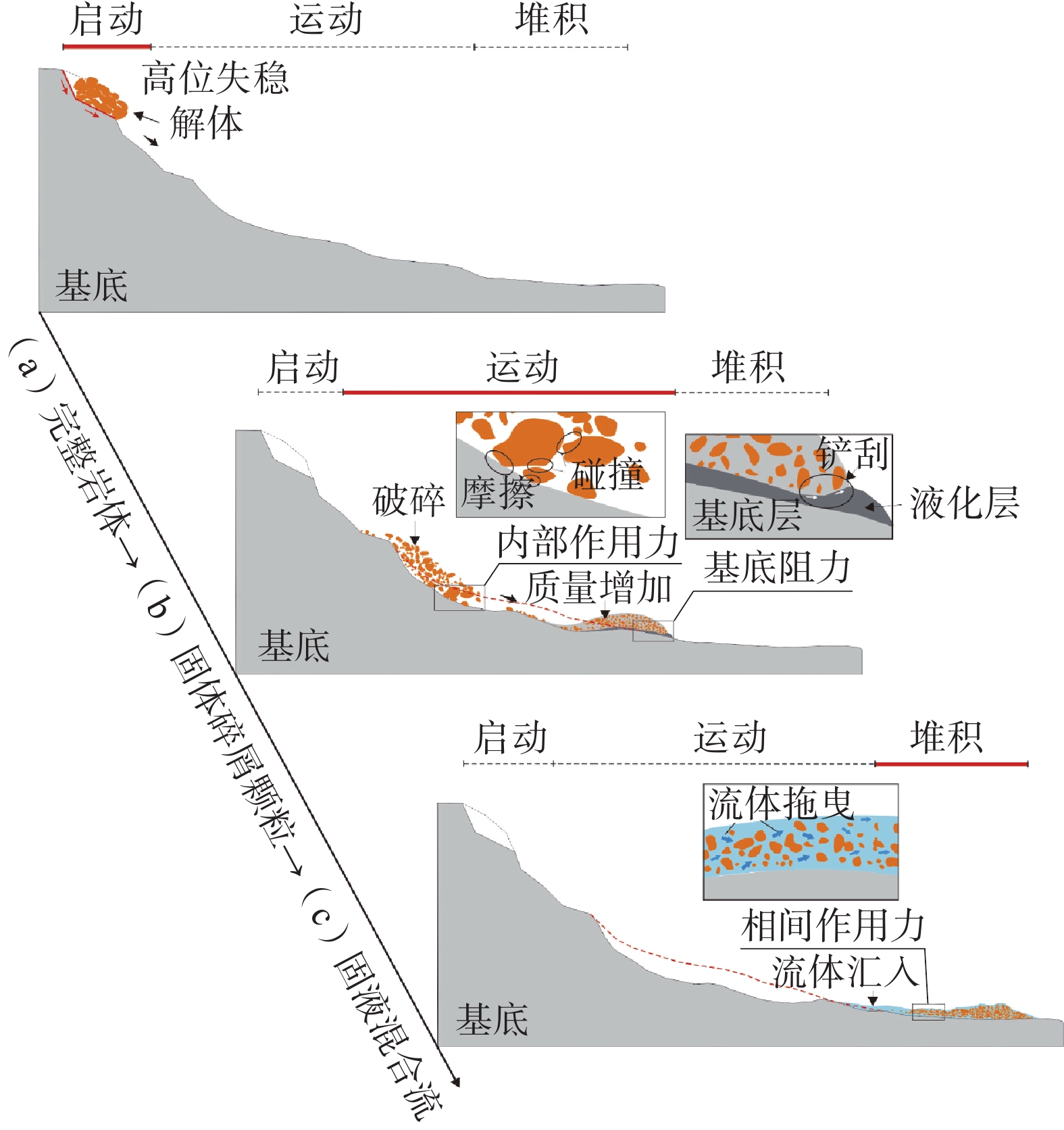
分区 地质特征 动力特征 基本方程 高位
启动在重力长期蠕变下的不稳定山体、冰雪和冰湖等危险体形成高位滑坡或崩塌,特别是暴雨、地震和融雪等特殊工况会加剧高位成灾体的启动 物源初始启动具有较高的重力势能;在锁固效应和特殊工况作用下,具初始动能 极限平衡 势动
转化高位剪出后,在陡坡地段具有加速特征;大型崩滑体在气垫圈闭效应作用下,运动距离会增加;逐渐解体成为链状散体结构 重力势能逐渐转化为动能,流滑加速效应明显,形成链条冲击加载;转化过程中可产生空气层压缩效应 能量守恒、
动量守恒、
撞击理论等动力
剪切崩滑块体通过高势能转化为高速流滑体,撞击、剪切、铲刮沟道斜坡,形成底蚀铲刮体积增大效应;侧向冲刷岸坡坡脚,牵引触发滑坡,形成流体堵溃放大效应 因铲刮冲蚀效应流滑体运动速度降低;受堵溃效应影响流速和流量会出现明显的放大特征;由摩擦块体向流动散体转化 摩擦模型、
犁切模型等液滑/
流滑沟道含水量增加,形成剪切液化效应;流滑体碰撞粉碎化,形成碎屑流体;沟道宽缓,纵坡降较低,形成掩埋堆积成灾区 流滑体滑带形成剪切液化层,剪切阻力减小,导致运动距离增加;或干碎屑流体在剩余驱动力作用下保持远程运动 滑带液化效应、
颗粒流模型、
Voellmy模型等 -
[1] YIN Yueping,LI Bin,GAO Yang,et al. Geostructures,dynamics and risk mitigation of high-altitude and long-runout rockslides[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2023,15(1):66 − 101. DOI: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.11.001
[2] 殷跃平. 西藏波密易贡高速巨型滑坡特征及减灾研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2000,27(4):8 − 11. [YIN Yueping. Study on characteristics and disaster reduction of high-speed giant landslide in Bhumi Yigong,Xizang Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology2000,27(4):8 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YIN Yueping. Study on characteristics and disaster reduction of high-speed giant landslide in Bhumi Yigong, Xizang Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology2000, 27(4): 8 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 殷跃平,朱赛楠,李滨,等. 青藏高原高位远程地质灾害[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2021. [YIN Yueping,ZHU Sainan,LI Bin,et al. High-level remote geological disasters in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2021. (in Chinese)] YIN Yueping, ZHU Sainan, LI Bin, et al. High-level remote geological disasters in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021. (in Chinese)
[4] 崔鹏,贾洋,苏凤环,等. 青藏高原自然灾害发育现状与未来关注的科学问题[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2017,32(9):985 − 992. [CUI Peng,JIA Yang,SU Fenghuan,et al. Natural hazards in Tibetan Plateau and key issue for feature research[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2017,32(9):985 − 992. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CUI Peng, JIA Yang, SU Fenghuan, et al . Natural hazards in Tibetan Plateau and key issue for feature research[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2017 ,32 (9 ):985 −992 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 彭建兵,崔鹏,庄建琦. 川藏铁路对工程地质提出的挑战[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(12):2377 − 2389. [PENG Jianbing,CUI Peng,ZHUANG Jianqi. Challenges to engineering geology of Sichuan—Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(12):2377 − 2389. (in Chinese with English abstract)] PENG Jianbing, CUI Peng, ZHUANG Jianqi . Challenges to engineering geology of Sichuan—Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020 ,39 (12 ):2377 −2389 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] ORENSE R,SAPUAY S. Preliminary report on the 17 February 2006 Leyte,Philippines landslide[J]. Soils and Foundations,2006,46(5):685 − 693. DOI: 10.3208/sandf.46.685
[7] 许强,郑光,李为乐,等. 2018年10月和11月金沙江白格两次滑坡-堰塞堵江事件分析研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(6):1534 − 1551. [XU Qiang,ZHENG Guang,LI Weile,et al. Study on successive landslide damming events of Jinsha River in Baige village on October 11 and November 3,2018[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(6):1534 − 1551. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, LI Weile, et al . Study on successive landslide damming events of Jinsha River in Baige village on October 11 and November 3, 2018[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018 ,26 (6 ):1534 −1551 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 邓建辉,高云建,余志球,等. 堰塞金沙江上游的白格滑坡形成机制与过程分析[J]. 工程科学与技术,2019,51(1):9 − 16. [DENG Jianhui,GAO Yunjian,YU Zhiqiu,et al. Analysis on the formation mechanism and process of Baige landslides damming the upper reach of Jinsha River,China[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2019,51(1):9 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DENG Jianhui, GAO Yunjian, YU Zhiqiu, et al . Analysis on the formation mechanism and process of Baige landslides damming the upper reach of Jinsha River, China[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2019 ,51 (1 ):9 −16 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] WANG Wenpei,YIN Yueping,ZHU Sainan,et al. Investigation and numerical modeling of the overloading-induced catastrophic rockslide avalanche in Baige,Tibet,China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2020,79(4):1765 − 1779. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-019-01664-2
[10] ZHANG Shilin,YIN Yueping,HU Xiewen,et al. Dynamics and emplacement mechanisms of the successive Baige landslides on the Upper Reaches of the Jinsha River,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,278:105819. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105819
[11] ZHANG Shilin,YIN Yueping,HU Xiewen,et al. Initiation mechanism of the Baige landslide on the upper reaches of the Jinsha River,China[J]. Landslides,2020,17(12):2865 − 2877. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-020-01495-3
[12] SHUGAR D H,JACQUEMART M,SHEAN D,et al. A massive rock and ice avalanche caused the 2021 disaster at Chamoli,Indian Himalaya[J]. Science,2021,373(6552):300 − 306. DOI: 10.1126/science.abh4455
[13] 殷跃平,李滨,张田田,等. 印度查莫利“2•7”冰岩山崩堵江溃决洪水灾害链研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):1 − 8. [YIN Yueping,LI Bin,ZHANG Tiantian,et al. The February 7 of 2021 glacier-rock avalanche and the outburst flooding disaster chain in Chamoli,India[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YIN Yueping, LI Bin, ZHANG Tiantian, et al . The February 7 of 2021 glacier-rock avalanche and the outburst flooding disaster chain in Chamoli, India[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (3 ):1 −8 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] ZHANG Tiantian,YIN Yueping,LI Bin,et al. Characteristics and dynamic analysis of the February 2021 long-runout disaster chain triggered by massive rock and ice avalanche at Chamoli,Indian Himalaya[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2023,15(2):296 − 308. DOI: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.04.003
[15] FAN Xuanmei,YUNUS A P,YANG Yinghui,et al. Imminent threat of rock-ice avalanches in High Mountain Asia[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,836:155380. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155380
[16] PINYOL N,ALONSO E. Criteria for rapid sliding II:Thermo-hydro-mechanical and scale effects in Vaiont case[J]. Engineering Geology,2010,114:211 − 227. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.04.017
[17] SASSA K,NAGAI O,SOLIDUM R,et al. An integrated model simulating the initiation and motion of earthquake and rain induced rapid landslides and its application to the 2006 Leyte landslide[J]. Landslides,2010,7(3):219 − 236. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-010-0230-z
[18] HUNGR O,LEROUEIL S,PICARELLI L. The Varnes classification of landslide types,an update[J]. Landslides,2014,11(2):167 − 194. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-013-0436-y
[19] CROSTA G B,AGLIARDI F,RIVOLTA C,et al. Long-term evolution and early warning strategies for complex rockslides by real-time monitoring[J]. Landslides,2017,14(5):1615 − 1632. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-017-0817-8
[20] 殷跃平,王文沛,张楠,等. 强震区高位滑坡远程灾害特征研究——以四川茂县新磨滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(5):827 − 841. [YIN Yueping,WANG Wenpei,ZHANG Nan,et al. Long runout geological disaster initiated by the ridge-top rockslide in a strong earthquake area:A case study of the Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County,Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China,2017,44(5):827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YIN Yueping, WANG Wenpei, ZHANG Nan, et al . Long runout geological disaster initiated by the ridge-top rockslide in a strong earthquake area: A case study of the Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China,2017 ,44 (5 ):827 −841 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[21] XU Wenjie,ZHOU Qian,DONG Xueyang. SPH-DEM coupling method based on GPU and its application to the landslide tsunami. Part II:Reproduction of the Vajont landslide tsunami[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2022,17(6):2121 − 2137. DOI: 10.1007/s11440-021-01387-3
[22] GAO Yang,YIN Yueping,LI Bin,et al. The role of fluid drag force in the dynamic process of two-phase flow-like landslides[J]. Landslides,2022,19(7):1791 − 1805. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-022-01858-y
[23] BUSS E,HEIM Α. Der bergsturz von elm [J]. Zurich,Wurster & Cie,1881:163.
[24] HEIM A. Bergsturz und Menschenleben (Landslides and human lives)[J]. Fretz und Wasmuth,Zurich,1932:218.
[25] MCCONNELL R G,BROCK R W. Report on the great landslide at Frank,Alberta[R]. Ottawa:Department of the Interior,Government of Canada,1904.
[26] CRUDEN D. Major rock slides in the Canadian Rockies[C]//Proceedings of the 27th Canadian Geotechnical Conference. Edmonton,Alta:[s.n.],1974:59 − 66.
[27] CRUDEN D M,VARNES D J. Landslide types and processes[M]//Turner A K,Schuster R L. Landslides. Washington D C:National Academy Press,1996:36 − 75.
[28] CHARRIÈRE M,HUMAIR F,FROESE C,et al. From the source area to the deposit:collapse,fragmentation,and propagation of the Frank Slide[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,2015:B31243.1.
[29] CRUDEN D M,HUNGR O. The debris of the Frank Slide and theories of rockslide–avalanche mobility[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences,1986,23(3):425 − 432. DOI: 10.1139/e86-044
[30] MELOSH H J. The mechanics of large rock avalanches[C]//Debris Flows/Avalanches:Process,Recognition,and Mitigation. Boulder:Geological Society of America,1987:41 − 50.
[31] BENKO B,STEAD D. The Frank slide:a reexamination of the failure mechanism[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1998,35(2):299 − 311. DOI: 10.1139/t98-005
[32] LOCAT P,COUTURE R,LEROUEIL S,et al. Fragmentation energy in rock avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2006,43(8):830 − 851. DOI: 10.1139/t06-045
[33] MÜLLER L. The rock slide in the Vajont Valley[J]. Rock Mechanics & Engineering Geology,1964,2:148 − 212.
[34] MÜLLER-SALZBURG L. The Vajont catastrophe:A personal review[J]. Engineering Geology,1987,24(1/2/3/4):423 − 444.
[35] MÜLLER L. The Vajont slide[J]. Engineering Geology,1987,24(1/2/3/4):527 − 532.
[36] BROILI L. New knowledge on the geomorphology of the Vaiont slide slip surface[J]. Rock Mechanics & Rock Engineering,1967,5:38 − 88.
[37] KILBURN C R J,PETLEY D N. Forecasting giant,catastrophic slope collapse:Lessons from Vajont,Northern Italy[J]. Geomorphology,2003,54(1/2):21 − 32.
[38] BISTACCHI A,MASSIRONI M,SUPERCHI L,et al. A 3D geological model of the 1963 Vajont landslide[J]. Italian Journal of Engineering Geology & Environment,2013(TOPIC 6):531-539.
[39] BOON C W,HOULSBY G T,UTILI S. New insights into the 1963 Vajont slide using 2D and 3D distinct-element method analyses[J]. Géotechnique,2014,64(10):800 − 816.
[40] HUTCHINSON J N,KOJEAN E. On the rock slide-debris flow of 25 April 1974 in the Quebrada Ccochacay on the Rio Mantaro[R]. UNESCO Mission to the Mantaro Valley,Peru,1975:49.
[41] KOJAN E,HUTCHINSON J N. Mayunmarca rockslide and debris flow,Peru[M]//Developments in Geotechnical Engineering. Amsterdam:Elsevier,1978:315-353.
[42] EVANS S G,GUTHRIE R H,ROBERTS N J,et al. The disastrous 17 February 2006 rockslide-debris avalanche on Leyte Island,Philippines:a catastrophic landslide in tropical mountain terrain[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2007,7(1):89 − 101. DOI: 10.5194/nhess-7-89-2007
[43] GUTHRIE R H,EVANS S G,CATANE S G,et al. The 17 February 2006 rock slide-debris avalanche at Guinsaugon Philippines:a synthesis[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2009,68(2):201 − 213. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-009-0205-2
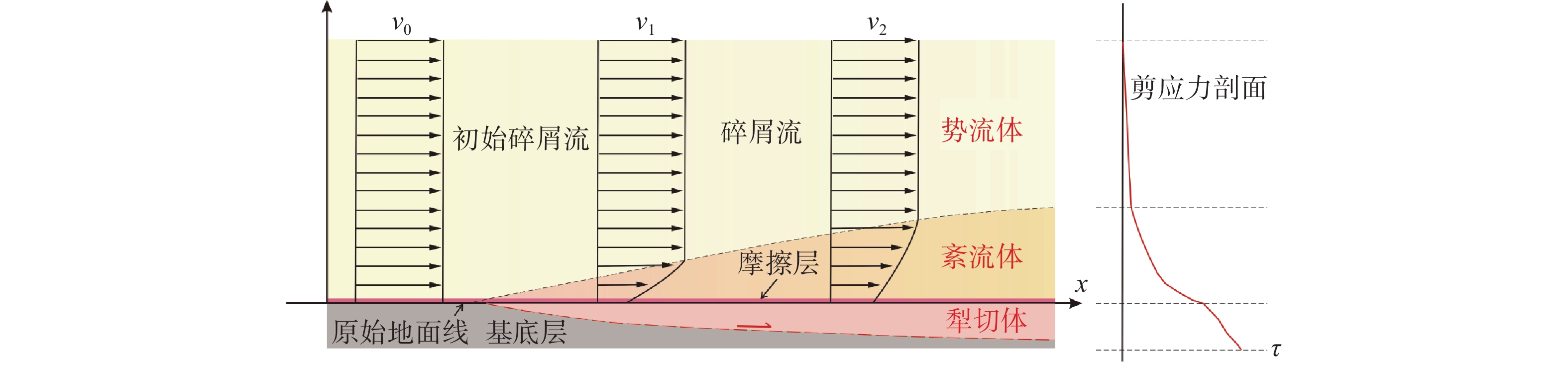
[44] LUZON P K,MONTALBO K,GALANG J,et al. Hazard mapping related to structurally controlled landslides in Southern Leyte,Philippines[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2016,16(3):875 − 883. DOI: 10.5194/nhess-16-875-2016
[45] 孙玉科,姚宝魁. 盐池河磷矿山体崩坍破坏机制的研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1983,10(1):1 − 7. [SUN Yuke,YAO Baokui. Study on the mechanism of mountain collapse in Yanchihe phosphate mine[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1983,10(1):1 − 7. (in Chinese)] SUN Yuke, YAO Baokui . Study on the mechanism of mountain collapse in Yanchihe phosphate mine[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1983 ,10 (1 ):1 −7 . (in Chinese)[46] 孙玉科. 宜昌盐池河磷矿山崩及其崩坍破坏机制[C]//中国典型滑坡. 宜昌,1986:99-108. [SUN Yuke. Collapse and failure mechanism of Yanchihe phosphate mine,Yichang,China[C]//Typical landslides in China. Yichang,1986:99-108. (in Chinese)] SUN Yuke. Collapse and failure mechanism of Yanchihe phosphate mine, Yichang, China[C]//Typical landslides in China. Yichang, 1986: 99-108. (in Chinese)
[47] 艾南山,王民新. 洒勒山滑坡速度的估算[J]. 水土保持通报,1983,3(3):72 − 74. [AI Nanshan,WANG Minxin. An estimate of velocity of the landslide at sale mountain[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,1983,3(3):72 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)] AI Nanshan, WANG Minxin . An estimate of velocity of the landslide at sale mountain[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,1983 ,3 (3 ):72 −74 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[48] 冯学才,田植甲. 洒勒山滑坡的特征及其预报[J]. 水土保持通报,1983,3(3):75 − 81. [FENG Xuecai,TIAN Zhijia. Characteristics and prediction of Saleshan landslide[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,1983,3(3):75 − 81. (in Chinese)] FENG Xuecai, TIAN Zhijia . Characteristics and prediction of Saleshan landslide[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,1983 ,3 (3 ):75 −81 . (in Chinese)[49] 苏伯苓. 高速超大型洒勒山滑坡及其研究[C]//中国典型滑坡. 宜昌,1986:43 − 48. [SUBoling. Study on high speed super-large scale Saleshan landslide[C]//Typical landslides in China. Yichang,1986:43 − 48. (in Chinese)] SUBoling. Study on high speed super-large scale Saleshan landslide[C]//Typical landslides in China. Yichang, 1986: 43 − 48. (in Chinese)
[50] 王士天,詹铮,刘汉超. 洒勒山高速滑坡的基本特征及动力学机制[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,1990,1(2):66 − 74. [WANG Shitian,ZHAN Zheng,LIU Hanchao. Basic characteristics and dynamic mechanism of Saleshan high-speed landslide[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,1990,1(2):66 − 74. (in Chinese)] WANG Shitian, ZHAN Zheng, LIU Hanchao . Basic characteristics and dynamic mechanism of Saleshan high-speed landslide[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,1990 ,1 (2 ):66 −74 . (in Chinese)[51] 杨志双,洪勇. 中国洒勒山大型滑坡高速运动成因机制和灾害预测[C]//第五届全国工程地质大会文集. 辉县,1996:126 − 131. [YANG Zhishuang,HONG Yong. Genetic mechanism and disaster prediction of high speed large-scale landslide in Salleshan Mountain,China[C]//Proceedings of the 5th National Engineering Geology Congress. Hui County,1996:126 − 131. (in Chinese)] YANG Zhishuang, HONG Yong. Genetic mechanism and disaster prediction of high speed large-scale landslide in Salleshan Mountain, China[C]//Proceedings of the 5th National Engineering Geology Congress. Hui County, 1996: 126 − 131. (in Chinese)
[52] 李绍武. 新滩滑坡滑动机制的探讨[J]. 水土保持通报,1985,5(5):15 − 19. [LI Shaowu. Discussion on sliding mechanism of Xintan landslide[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,1985,5(5):15 − 19. (in Chinese)] LI Shaowu . Discussion on sliding mechanism of Xintan landslide[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,1985 ,5 (5 ):15 −19 . (in Chinese)[53] 陆业海. 新滩滑坡征兆及其成功的监测预报[J]. 水土保持通报,1985,5(5):1 − 9. [LU Yehai. Symptoms of Xintan landslide and its successful monitoring and prediction[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,1985,5(5):1 − 9. (in Chinese)] LU Yehai . Symptoms of Xintan landslide and its successful monitoring and prediction[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,1985 ,5 (5 ):1 −9 . (in Chinese)[54] 刘雄. 新滩大滑坡机制探讨[J]. 岩土力学,1986,7(2):53 − 60. [LIU Xiong. Discussion of the mechanism for Xintan beach landslide[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,1986,7(2):53 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Xiong . Discussion of the mechanism for Xintan beach landslide[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,1986 ,7 (2 ):53 −60 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[55] 吕贵芳,任江. 新滩滑坡研究[C]//中国典型滑坡. 宜昌,1986:210 − 220. [LYUGuifang,REN Jiang. Research on Xintan landslide[C]//Typical landslideS in China. Yichang,1986:210 − 220. (in Chinese)] LYUGuifang, REN Jiang. Research on Xintan landslide[C]//Typical landslideS in China. Yichang, 1986: 210 − 220. (in Chinese)
[56] 黄润秋. 灾害性崩滑地质过程的全过程模拟[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,1994,5(增刊1):11 − 17. [HUANG Runqiu. Full-course simulation of hazardous rockfalls and avalanches[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,1994,5(Sup 1):11 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HUANG Runqiu. Full-course simulation of hazardous rockfalls and avalanches[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1994, 5(Sup 1): 11 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[57] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(3):433 − 454. [HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(3):433 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HUANG Runqiu . Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007 ,26 (3 ):433 −454 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[58] 胡广韬. 论斜坡环境中滑坡之剧动与高速的机理[J]. 陕西水力发电,1986,2(3):7 − 18. [HU Guangtao. On the mechanism of landslide violent movement and high speed in slope environment[J]. Power System and Clean Energy,1986,2(3):7 − 18. (in Chinese)] HU Guangtao . On the mechanism of landslide violent movement and high speed in slope environment[J]. Power System and Clean Energy,1986 ,2 (3 ):7 −18 . (in Chinese)[59] 胡广韬. 灾害性滑坡启程剧动与行程高速的机理[J]. 灾害学,1987,2(1):17 − 28. [HU Guangtao. On the mechanisms of initial intense moving and high speed travelling of disastrous landslides[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,1987,2(1):17 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HU Guangtao . On the mechanisms of initial intense moving and high speed travelling of disastrous landslides[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,1987 ,2 (1 ):17 −28 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[60] 胡广韬,毛延龙,赵法锁. 论基岩高速滑坡的弹冲动力学机理[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,1992,3(4):21 − 33. [HU Guangtao,MAO Yanlong,ZHAO Fasuo. The elastic impulsive motion dynamics mechanisim of high-speed landslide on bed rock[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,1992,3(4):21 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HU Guangtao, MAO Yanlong, ZHAO Fasuo . The elastic impulsive motion dynamics mechanisim of high-speed landslide on bed rock[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,1992 ,3 (4 ):21 −33 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[61] 王士天,张倬元,詹铮,等. 龙羊峡水电站:重大工程地质问题研究[M]. 成都:成都科技大学出版社,1989. [WANG Shitian,ZHANG Zhuoyuan,ZHAN Zheng,et al. Longyangxia Hydropower Station:Research on major engineering geological problems[M]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press,1989. (in Chinese)] WANG Shitian, ZHANG Zhuoyuan, ZHAN Zheng, et al. Longyangxia Hydropower Station: Research on major engineering geological problems[M]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press, 1989. (in Chinese)
[62] 胡广韬. 滑坡动力学[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1995. [HU Guangtao. Landslide dynamics[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1995. (in Chinese)] HU Guangtao. Landslide dynamics[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1995. (in Chinese)
[63] 程谦恭,彭建兵,胡广韬. 高速岩质滑坡动力学[M]. 成都:西南交通大学出版社,1999. [CHENG Qiangong,PENG Jianbing,HU Guangtao. Dynamics of high-speed rock landslide[M]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University Press,1999. (in Chinese)] CHENG Qiangong, PENG Jianbing, HU Guangtao. Dynamics of high-speed rock landslide[M]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
[64] 王家鼎,张倬元. 典型高速黄土滑坡群的系统工程地质研究[M]. 成都:四川科学技术出版社,1999. [WANG Jiading,ZHANG Zhuoyuan. Systematic engineering geological study on typical high-speed loess landslide group[M]. Chengdu:Sichuan Scientific & Technical Publishers,1999. (in Chinese)] WANG Jiading, ZHANG Zhuoyuan. Systematic engineering geological study on typical high-speed loess landslide group[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Scientific & Technical Publishers, 1999. (in Chinese)
[65] 晏同珍,杨顺安,方云. 滑坡学[M]. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社,2000. [YAN Tongzhen,YANG Shun’an,FANG Yun. Landslidologies[M]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press,2000. (in Chinese)] YAN Tongzhen, YANG Shun’an, FANG Yun. Landslidologies[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
[66] 王恭先,徐峻龄,刘光代,等. 滑坡学与滑坡防治技术[M]. 北京:中国铁道出版社,2004. [WANG Gongxian,XU Junling,LIU Guangdai,et al. Landslide science and landslide prevention technology[M]. Beijing:China Railway Publishing House,2004. (in Chinese)] WANG Gongxian, XU Junling, LIU Guangdai, et al. Landslide science and landslide prevention technology[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 2004. (in Chinese)
[67] 黄润秋,许强. 中国典型灾难性滑坡[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2008. [HUANG Runqiu,XU Qiang. Catastrophic landslides in China[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2008. (in Chinese)] HUANG Runqiu, XU Qiang. Catastrophic landslides in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008. (in Chinese)
[68] 许强,裴向军,黄润秋,等. 汶川地震大型滑坡研究[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2009. [XU Qiang,PEI Xiangjun,HUANG Runqiu,et al. Large-scale landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2009. (in Chinese)] XU Qiang, PEI Xiangjun, HUANG Runqiu, et al. Large-scale landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[69] 崔鹏,何思明,姚令侃. 汶川地震山地灾害形成机理与风险控制[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2011. [CUI Peng,HE Siming,YAO Lingkan. Formation mechanism and risk control of mountain disasters in Wenchuan earthquake[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2011. (in Chinese)] CUI Peng, HE Siming, YAO Lingkan. Formation mechanism and risk control of mountain disasters in Wenchuan earthquake[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011. (in Chinese)
[70] 殷跃平,张永双. 汶川地震工程地质与地质灾害[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2013. [YIN Yueping,ZHANG Yongshuang. Engineering geology and geological disasters of Wenchuan earthquake[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2013. (in Chinese)] YIN Yueping, ZHANG Yongshuang. Engineering geology and geological disasters of Wenchuan earthquake[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013. (in Chinese)
[71] 崔鹏,邹强. 川藏交通廊道山地灾害演化规律与工程风险[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2021. [CUI Peng,ZOU Qiang. Evolution law and engineering risk of mountain disasters in Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2021. (in Chinese)] CUI Peng, ZOU Qiang. Evolution law and engineering risk of mountain disasters in Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021. (in Chinese)
[72] 邓建辉,陈菲,赵思远. 白格滑坡致灾调查[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2021. [DENG Jianhui,CHEN Fei,ZHAO Siyuan. Investigation on the disaster caused by Baige landslide[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2021. (in Chinese)] DENG Jianhui, CHEN Fei, ZHAO Siyuan. Investigation on the disaster caused by Baige landslide[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021. (in Chinese)
[73] VARNES D J. Slope movement types and processes[C]//Schuster R L,Krizek R J. Landslides,analysis and control,special report 176:Transportation research board. Washington,D C:National Academy of Sciences,1978:11 − 33.
[74] YIN Yueping,WANG Fawu,SUN Ping. Landslide hazards triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake,Sichuan,China[J]. Landslides,2009,6(2):139 − 152. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-009-0148-5
[75] YIN Yueping,XING Aiguo. Aerodynamic modeling of the Yigong gigantic rock slide-debris avalanche,Tibet,China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2012,71(1):149 − 160. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-011-0348-9
[76] WANG Fawu,SUN Ping,HIGHLAND L,et al. Key factors influencing the mechanism of rapid and long runout landslides triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake,China[J]. Geoenvironmental Disasters,2014,1(1):1 − 16. DOI: 10.1186/s40677-014-0001-6
[77] INTRIERI E,RASPINI F,FUMAGALLI A,et al. The Maoxian landslide as seen from space:Detecting precursors of failure with Sentinel-1 data[J]. Landslides,2018,15(1):123 − 133. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-017-0915-7
[78] 葛大庆,戴可人,郭兆成,等. 重大地质灾害隐患早期识别中综合遥感应用的思考与建议[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):949 − 956. [GE Daqing,DAI Keren,GUO Zhaocheng,et al. Early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies:Thoughts and recommendations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):949 − 956. (in Chinese with English abstract)] GE Daqing, DAI Keren, GUO Zhaocheng, et al . Early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies: Thoughts and recommendations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019 ,44 (7 ):949 −956 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[79] GAO Yang,LI Bin,GAO Haoyuan,et al. Dynamic characteristics of high-elevation and long-runout landslides in the Emeishan basalt area:A case study of the Shuicheng “7•23”landslide in Guizhou,China[J]. Landslides,2020,17(7):1663 − 1677. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-020-01377-8
[80] 李振洪,宋闯,余琛,等. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用:挑战与对策[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):967 − 979. [LI Zhenhong,SONG Chuang,YU Chen,et al. Application of satellite radar remote sensing to landslide detection and monitoring:Challenges and solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):967 − 979. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Zhenhong, SONG Chuang, YU Chen, et al . Application of satellite radar remote sensing to landslide detection and monitoring: Challenges and solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019 ,44 (7 ):967 −979 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[81] YIN Yueping,LIU Xiaojie,ZHAO Chaoying,et al. Multi-dimensional and long-term time series monitoring and early warning of landslide hazard with improved cross-platform SAR offset tracking method[J]. Science China Technological Sciences,2022,65(8):1891 − 1912. DOI: 10.1007/s11431-021-2008-6
[82] MASSIRONI M,ZAMPIERI D,SUPERCHI L,et al. Geological structures of the Vajont landslide[J]. Italian Journal of Engineering Geology & Environment,2013(TOPIC 6):573 − 582.
[83] GLASTONBURY J,FELL R. Report on the analysis of “rapid” natural rock slope failures[R]. Sydney:University of New South Wales,2000.
[84] BADGER T C. Fracturing within anticlines and its kinematic control on slope stability[J]. Environmental and Engineering Geoscience,2002,8(1):19 − 33. DOI: 10.2113/gseegeosci.8.1.19
[85] BRIDEAU M A,YAN Ming,STEAD D. The role of tectonic damage and brittle rock fracture in the development of large rock slope failures[J]. Geomorphology,2009,103(1):30 − 49. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.04.010
[86] AMBROSI C,CROSTA G B. Valley shape influence on deformation mechanisms of rock slopes[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications,2011,351(1):215 − 233. DOI: 10.1144/SP351.12
[87] HUMAIR F,PEDRAZZINI A,EPARD J L,et al. Structural characterization of Turtle Mountain anticline (Alberta,Canada) and impact on rock slope failure[J]. Tectonophysics,2013,605:133 − 148. DOI: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.04.029
[88] STEAD D,WOLTER A. A critical review of rock slope failure mechanisms:The importance of structural geology[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2015,74:1 − 23. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsg.2015.02.002
[89] 彭建兵,马润勇,卢全中,等. 青藏高原隆升的地质灾害效应[J]. 地球科学进展,2004,19(3):457 − 466. [PENG Jianbing,MA Runyong,LU Quanzhong,et al. Geological hazards effects of uplift of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences,2004,19(3):457 − 466. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.03.018 PENG Jianbing, MA Runyong, LU Quanzhong, et al . Geological hazards effects of uplift of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences,2004 ,19 (3 ):457 −466 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.03.018[90] 许强,李为乐. 汶川地震诱发大型滑坡分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(6):818 − 826. [XU Qiang,LI Weile. Distribution of large-scale landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(6):818 − 826. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.06.002 XU Qiang, LI Weile . Distribution of large-scale landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010 ,18 (6 ):818 −826 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.06.002[91] 胡新丽,唐辉明,朱丽霞. 汶川震中岩浆岩高边坡破坏模式与崩塌机理[J]. 地球科学,2011,36(6):1149 − 1154. [HU Xinli,TANG Huiming,ZHU Lixia. Collapse mode and mechanism of high magmatite rock slope in Wenchuan epicentral area[J]. Earth Science,2011,36(6):1149 − 1154. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HU Xinli, TANG Huiming, ZHU Lixia . Collapse mode and mechanism of high magmatite rock slope in Wenchuan epicentral area[J]. Earth Science,2011 ,36 (6 ):1149 −1154 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[92] 李滨,王国章,冯振,等. 地下采空诱发陡倾层状岩质斜坡失稳机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(6):1148 − 1161. [LI Bin,WANG Guozhang,FENG Zhen,et al. Failure mechanism of steeply inclined rock slopes induced by underground mining[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015,34(6):1148 − 1161. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Bin, WANG Guozhang, FENG Zhen, et al . Failure mechanism of steeply inclined rock slopes induced by underground mining[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015 ,34 (6 ):1148 −1161 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[93] 唐辉明,鲁莎. 三峡库区黄土坡滑坡滑带空间分布特征研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(1):129 − 136. [TANG Huiming,LU Sha. Research on the spatial distribution of slip zone of Huangtupo landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(1):129 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract)] TANG Huiming, LU Sha . Research on the spatial distribution of slip zone of Huangtupo landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018 ,26 (1 ):129 −136 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[94] 兰恒星,仉义星,伍宇明. 岩体结构效应与长远程滑坡动力学[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(1):108 − 122. [LAN Hengxing,ZHANG Yixing,WU Yuming. Effect of rock mass structure on the dynamics of longrunout landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(1):108 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LAN Hengxing, ZHANG Yixing, WU Yuming . Effect of rock mass structure on the dynamics of longrunout landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019 ,27 (1 ):108 −122 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[95] XUE Lei,QIN Siqing,PAN Xiaohua,et al. A possible explanation of the stair-step brittle deformation evolutionary pattern of a rockslide[J]. Geomatics,Natural Hazards and Risk,2017,8(2):1456 − 1476. DOI: 10.1080/19475705.2017.1345793
[96] CHEN Hongran,QIN Siqing,XUE Lei,et al. A physical model predicting instability of rock slopes with locked segments along a potential slip surface[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,242:34 − 43. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.05.012
[97] 杨百存,秦四清,薛雷,等. 锁固段损伤过程中的能量转化与分配原理[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2020,41(7):975 − 981. [YANG Baicun,QIN Siqing,XUE Lei,et al. Energy conversion and allocation principle during the damage process of locked segment[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2020,41(7):975 − 981. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Baicun, QIN Siqing, XUE Lei, et al . Energy conversion and allocation principle during the damage process of locked segment[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2020 ,41 (7 ):975 −981 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[98] 殷跃平,朱继良,杨胜元. 贵州关岭大寨高速远程滑坡-碎屑流研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(4):445 − 454. [YIN Yueping,ZHU Jiliang,YANG Shengyuan. Investigation of a high speed and long Run-out rockslide-debris flow at Dazhai in Guanling of Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(4):445 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YIN Yueping, ZHU Jiliang, YANG Shengyuan . Investigation of a high speed and long Run-out rockslide-debris flow at Dazhai in Guanling of Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010 ,18 (4 ):445 −454 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[99] 殷跃平. 斜倾厚层山体滑坡视向滑动机制研究——以重庆武隆鸡尾山滑坡为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2010,29(2):217 − 226. [YIN Yueping. Mechanism of apparent dip slide of inclined bedding rockslide:A case study of Jiweishan rockslide in Wulong,Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2010,29(2):217 − 226. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YIN Yueping . Mechanism of apparent dip slide of inclined bedding rockslide: A case study of Jiweishan rockslide in Wulong, Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2010 ,29 (2 ):217 −226 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[100] 殷跃平,王猛,李滨,等. 汶川地震大光包滑坡动力响应特征研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(10):1969 − 1982. [YIN Yueping,WANG Meng,LI Bin,et al. Dynamic response characteristics of Daguangbao landslide triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(10):1969 − 1982. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.10.003 YIN Yueping, WANG Meng, LI Bin, et al . Dynamic response characteristics of Daguangbao landslide triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012 ,31 (10 ):1969 −1982 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.10.003[101] 黄波林,殷跃平,李滨,等. 库区城镇滑坡涌浪风险评价与减灾研究[J]. 地质学报,2021,95(6):1949 − 1961. [HUANG Bolin,YIN Yueping,LI Bin,et al. Study of risk assessment and mitigation for landslide-induced impulse wave near towns in reservoir areas[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2021,95(6):1949 − 1961. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HUANG Bolin, YIN Yueping, LI Bin, et al . Study of risk assessment and mitigation for landslide-induced impulse wave near towns in reservoir areas[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2021 ,95 (6 ):1949 −1961 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[102] 黄波林,殷跃平. 水库区滑坡涌浪风险评估技术研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(3):621 − 629. [HUANG Bolin,YIN Yueping. Risk assessment research on impulse wave generated by landslide in reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(3):621 − 629. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HUANG Bolin, YIN Yueping . Risk assessment research on impulse wave generated by landslide in reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018 ,37 (3 ):621 −629 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[103] 李滨,殷跃平,高杨,等. 西南岩溶山区大型崩滑灾害研究的关键问题[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):5 − 13. [LI Bin,YIN Yueping,GAO Yang,et al. Critical issues in rock avalanches in the karst mountain areas of southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):5 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Bin, YIN Yueping, GAO Yang, et al . Critical issues in rock avalanches in the karst mountain areas of southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020 ,47 (4 ):5 −13 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[104] 朱赛楠,殷跃平,王猛,等. 金沙江结合带高位远程滑坡失稳机理及减灾对策研究——以金沙江色拉滑坡为例[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(4):688 − 697. [ZHU Sainan,YIN Yueping,WANG Meng,et al. Instability mechanism and disaster mitigation measures of long-distance landslide at high location in Jinsha River junction zone:Case study of Sela landslide in Jinsha River,Tibet[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(4):688 − 697. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHU Sainan, YIN Yueping, WANG Meng, et al . Instability mechanism and disaster mitigation measures of long-distance landslide at high location in Jinsha River junction zone: Case study of Sela landslide in Jinsha River, Tibet[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021 ,43 (4 ):688 −697 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[105] HSÜ K J. Albert heim:Observations on landslides and relevance to modern interpretations[M]//Developments in Geotechnical Engineering. Amsterdam:Elsevier,1978:71 − 93.
[106] DAVIES T R,MCSAVENEY M J,HODGSON K A. A fragmentation-spreading model for long-runout rock avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1999,36(6):1096 − 1110. DOI: 10.1139/t99-067
[107] RUBEY W W,KING HUBBERT M. Role of fluid pressure in mechanics of overthrust faulting[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,1959,70(2):167. DOI: 10.1130/0016-7606(1959)70[167:ROFPIM]2.0.CO;2
[108] KENT P E. The transport mechanism in catastrophic rock falls[J]. The Journal of Geology,1966,74(1):79 − 83. DOI: 10.1086/627142
[109] SHREVE R L. The blackhawk landslide[M]//Geological Society of America Special Papers. Boulder:Geological Society of America,1968:1 − 48.
[110] SCHEIDEGGER A E. On the prediction of the reach and velocity of catastrophic landslides[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts,1974,11(3):65.
[111] HSÜ K J. Catastrophic debris streams (sturzstroms) generated by rockfalls[J]. Boulder:Geological Society of America Bulletin,1975,86(1):129. DOI: 10.1130/0016-7606(1975)86<129:CDSSGB>2.0.CO;2
[112] HOWARD K A. Avalanche mode of motion:Implications from Lunar examples[J]. Science,1973,180:1052 − 1055. DOI: 10.1126/science.180.4090.1052
[113] IVERSON R M. Mechanics of debris flows and rock avalanches[M]. Boca Raton:CRC Press,2012b.
[114] HUNGR O. Dynamics of rock avalanches and other types of mass movements[D]. Edmonton:University of Alberta,1981.
[115] HUNGR O. Mobility of rock avalanches[R]. Tsukuba:National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention,1990:11-20.
[116] HUNGR O. A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slides,debris flows,and avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1995,32(4):610 − 623. DOI: 10.1139/t95-063
[117] HUNGR O,MORGENSTERN N R. Experiments in high velocity open channel flow of granular materials[J]. Geotechnique,1984,34(3):405 − 413. DOI: 10.1680/geot.1984.34.3.405
[118] HUNGR O,EVANS S G. Rock avalanche runout prediction using a dynamic model[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Landslides. Trondheim,Norway:[s.n.],1996:21.
[119] HUNGR O,EVANS S G. A dynamic model for landslides with changing mass[C]//Proceedings of IAEG on Engineering Geology and the Environment. Athens,Greece:[s.n.],1997:719,724.
[120] HUNGR O,EVANS S G,HAZZARD J. Magnitude and frequency of rock falls and rock slides along the main transportation corridors of southwestern British Columbia[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1999,36(2):224 − 238. DOI: 10.1139/t98-106
[121] HUNGR O,EVANS S G,BOVIS M J,et al. A review of the classification of landslides of the flow type[J]. Environmental and Engineering Geoscience,2001,7(3):221 − 238. DOI: 10.2113/gseegeosci.7.3.221
[122] HUNGR O. Rock avalanche occurrence,process and modelling[C]//Landslides from Massive Rock Slope Failure. Dordrecht:Springer,2006:243-266.
[123] XING Aiguo,WANG Gonghui,YIN Yueping,et al. Investigation and dynamic analysis of a catastrophic rock avalanche on September 23,1991,Zhaotong,China[J]. Landslides,2016,13(5):1035 − 1047. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-015-0617-y
[124] GAO Yang,YIN Yueping,LI Bin,et al. Characteristics and numerical runout modeling of the heavy rainfall-induced catastrophic landslide-debris flow at Sanxicun,Dujiangyan,China,following the Wenchuan Ms 8.0 earthquake[J]. Landslides,2017,14(4):1361 − 1374. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-016-0793-4
[125] YIN Yueping,XING Aiguo,WANG Gonghui,et al. Experimental and numerical investigations of a catastrophic long-runout landslide in Zhenxiong,Yunnan,southwestern China[J]. Landslides,2017,14(2):649 − 659. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-016-0729-z
[126] IVERSON R M. Elementary theory of bed-sediment entrainment by debris flows and avalanches[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2012,117(F3):F03006.
[127] IVERSON R M. The physics of debris flows[J]. Reviews of Geophysics,1997,35(3):245 − 296. DOI: 10.1029/97RG00426
[128] IVERSON R M,OUYANG Chaojun. Entrainment of bed material by earth-surface mass flows:Review and reformulation of depth-integrated theory[J]. Reviews of Geophysics,2015,53(1):27 − 58. DOI: 10.1002/2013RG000447
[129] IVERSON R M,REID M E,LOGAN M,et al. Positive feedback and momentum growth during debris-flow entrainment of wet bed sediment[J]. Nature Geoscience,2011,4(2):116 − 121. DOI: 10.1038/ngeo1040
[130] IVERSON R M. Scaling and design of landslide and debris-flow experiments[J]. Geomorphology,2015,244:9 − 20. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.02.033
[131] SAVAGE S B,IVERSON R M. Surge dynamics coupled to pore-pressure evolution in debris flows[C]//RICKENMANN D,CHEN C. International conference on debris-flow hazards mitigation:Mechanics,prediction,and assessment,proceedings. Rotterdam:Millpress,2003:503-514.
[132] PITMAN E B,LE Long. A two-fluid model for avalanche and debris flows[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A:Mathematical,Physical and Engineering Sciences,2005,363(1832):1573-1601.
[133] TAKAHASHI T. Debris flow:mechanics,prediction and countermeasures[M]. London:Taylor & Francis,2007.
[134] 唐春安,赵文. 岩石破裂全过程分析软件系统RFPA2D[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,1997,16(5):507 − 508. [TANG Chun’an,ZHAO Wen. Software system RFPA2D for analyzing the whole process of rock fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,1997,16(5):507 − 508. (in Chinese)] DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.1997.05.018 TANG Chun’an, ZHAO Wen . Software system RFPA2D for analyzing the whole process of rock fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,1997 ,16 (5 ):507 −508 . (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.1997.05.018[135] 李世海,高波,燕琳. 三峡永久船闸高边坡开挖三维离散元数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学,2002,23(3):272 − 277. [LI Shihai,GAO Bo,YAN Lin. 3-D simulation of the excavation of high steep slope of Three-Gorges permanent lock by distinct element method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2002,23(3):272 − 277. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Shihai, GAO Bo, YAN Lin . 3-D simulation of the excavation of high steep slope of Three-Gorges permanent lock by distinct element method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2002 ,23 (3 ):272 −277 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[136] 刘春,张晓宇,许强,等. 三维离散元模型的滑坡能量守恒模拟研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2017,13(增刊2):698 − 704. [LIU Chun,ZHANG Xiaoyu,XU Qiang,et al. Research on energy conservation simulation of three dimensional discrete element model[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2017,13(Sup 2):698 − 704. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Chun, ZHANG Xiaoyu, XU Qiang, et al. Research on energy conservation simulation of three dimensional discrete element model[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2017, 13(Sup 2): 698 − 704. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[137] 徐文杰,王忠静. 一个共享的软件服务系统——水利云计算平台[J]. 长江科学院院报,2021,38(9):141 − 148. [XU Wenjie,WANG Zhongjing. A shared software service system:Hydraulic cloud computing platform[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2021,38(9):141 − 148. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200674 XU Wenjie, WANG Zhongjing . A shared software service system: Hydraulic cloud computing platform[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2021 ,38 (9 ):141 −148 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200674[138] SHREVE R L. Sherman landslide,Alaska[J]. Science,1966,154(3757):1639 − 1643. DOI: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1639
[139] 邢爱国,殷跃平,齐超,等. 高速远程滑坡气垫效应的风洞模拟试验研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报,2012,46(10):1642 − 1646. [XING Aiguo,YIN Yueping,QI Chao,et al. Study on the wind tunnel testing of air cushion effect of high-speed and long-runout landslide[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University,2012,46(10):1642 − 1646. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XING Aiguo, YIN Yueping, QI Chao, et al . Study on the wind tunnel testing of air cushion effect of high-speed and long-runout landslide[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University,2012 ,46 (10 ):1642 −1646 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[140] GOGUEL J. Scale-dependent rockslide mechanisms,with emphasis on the role of pore fluid vaporization[M]//Developments in Geotechnical Engineering. Amsterdam:Elsevier,1978:693-705.
[141] ERISMANN T H. Mechanisms of large landslides[J]. Rock Mechanics,1979,12(1):15 − 46. DOI: 10.1007/BF01241087
[142] HABIB P. Production of gaseous pore pressure during rock slides[J]. Rock Mechanics,1975,7(4):193 − 197. DOI: 10.1007/BF01246865
[143] GOGUEL J, PACHOUD A. Geology and dynamics of the rockfall of the granier range which occurred in November 1248. Bulletin, Bureau de Récherches Geologiques et Miniéres, Hydrogeologie, Lyon, 1972(1):29 − 38.
[144] PINYOL N M, ALVARADO M, ALONSO E E, et al. Thermal effects in landslide mobility[J]. Géotechnique,2018,68(6):528 − 545.
[145] ALONSO E E. Triggering and motion of landslides[J]. Géotechnique,2021,71(1):3 − 59.
[146] TAMBURI A J. Creep of single rocks on bedrock[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,1974,85(3):351. DOI: 10.1130/0016-7606(1974)85<351:COSROB>2.0.CO;2
[147] WANG Yufeng,DONG Jiajuan,CHENG Qianggong. Velocity-dependent frictional weakening of large rock avalanche basal facies:implications for rock avalanche hypermobility?[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2017,122(3):1648 − 1676. DOI: 10.1002/2016JB013624
[148] HU Wei,HUANG Runqiu,MCSAVENEY M,et al. Mineral changes quantify frictional heating during a large low-friction landslide[J]. Geology,2018,46(3):223 − 226. DOI: 10.1130/G39662.1
[149] HU Wei,HUANG Runqiu,MCSAVENEY M,et al. Superheated steam,hot CO2 and dynamic recrystallization from frictional heat jointly lubricated a giant landslide:field and experimental evidence[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2019,510:85 − 93. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2019.01.005
[150] HE Siming,LIU Wei,WANG Juan. Dynamic simulation of landslide based on thermo-poro-elastic approach[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2015,75:24 − 32.
[151] HUTCHINSON J N,BHANDARI R K. Untrained loading,a fundamental-mechanism of mud slide and other mass movements[J]. Geotechnique,1971,21(4):353 − 358. DOI: 10.1680/geot.1971.21.4.353
[152] SEED H B. The fourth Terzaghi lecture:landslides during earthquakes due to liquefaction[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division,1968,94(5):1053 − 1122. DOI: 10.1061/JSFEAQ.0001182
[153] SASSA K,FUKUOKA H,WANG Gonghui,et al. Undrained dynamic-loading ring-shear apparatus and its application to landslide dynamics[J]. Landslides,2004,1(1):7 − 19. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-003-0004-y
[154] SASSA K. Development of a new cyclic loading ring-shear apparatus to study earthquake-induced landslides[R]. Tokyo:Ministry of Education,Science and Culture,Japan,1994:106.
[155] SASSA K. Special lecture:Geotechnical model for the motion of landslides:Proc 5th International Symposium on Landslides,Lausanne,10–15 July 1988V1,P37–55. Publ Rotterdam:a Balkema,1988[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences \& Geomechanics Abstracts,1989,26:88.
[156] SASSA K. The mechanism starting liquefied landslides and debris flows[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Landslides. Toronto:[s.n.],1984:349-354.
[157] WANG Fawu,WAFID A N M,ZHANG Fanyu,et al. Tandikek and Malalak rapid and long runout landslides triggered by West Sumatra earthquake 2009 ( M7.6) in Indonesia[J]. Journal of the Japan Landslide Society,2011,48(4):215 − 220. DOI: 10.3313/jls.48.215
[158] WANG Gonghui,JIANG Yao,CHANG Chengrui,et al. Volcaniclastic debris avalanche on Motomachi area of Izu-Oshima,Japan,triggered by severe storm:Phenomenon and mechanisms[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,251:24 − 36. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.02.003
[159] XING Aiguo,WANG Gonghui,LI Bin,et al. Long-runout mechanism and landsliding behaviour of large catastrophic landslide triggered by heavy rainfall in Guanling,Guizhou,China[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2015,52(7):971 − 981. DOI: 10.1139/cgj-2014-0122
[160] YIN Yueping,LI Bin,WANG Wenpei,et al. Mechanism of the December 2015 catastrophic landslide at the Shenzhen landfill and controlling geotechnical risks of urbanization[J]. Engineering,2016,2(2):230 − 249. DOI: 10.1016/J.ENG.2016.02.005
[161] TAKAHASHI T. Mechanical characteristics of debris flow[J]. Journal of the Hydraulics Division,1978,104(8):1153 − 1169. DOI: 10.1061/JYCEAJ.0005046
[162] EGASHIRA S,HONDA N,ITOH T. Experimental study on the entrainment of bed material into debris flow[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,Part C:Solar,Terrestrial & Planetary Science,2001,26(9):645-650.
[163] BOUCHUT F,FERNÁNDEZ-NIETO E D,MANGENEY A,et al. On new erosion models of Savage-Hutter type for avalanches[J]. Acta Mechanica,2008,199(1):181 − 208.
[164] MANGENEY A. Landslide boost from entrainment[J]. Nature Geoscience,2011,4(2):77 − 78. DOI: 10.1038/ngeo1077
[165] 殷跃平,王文沛. 高位远程滑坡动力侵蚀犁切计算模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(8):1513 − 1521. [YIN Yueping,WANG Wenpei. A dynamic erosion plowing model of long Run-out landslides initialized at high locations[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(8):1513 − 1521. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YIN Yueping, WANG Wenpei . A dynamic erosion plowing model of long Run-out landslides initialized at high locations[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020 ,39 (8 ):1513 −1521 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[166] 高杨,高浩源,李滨,等. 滑坡冲击铲刮变量的计算方法研究[J]. 计算力学学报,2022,39(1):105 − 112. [GAO Yang,GAO Haoyuan,LI Bin,et al. Study on calculation method of landslide impact and scraping variable[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics,2022,39(1):105 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.7511/jslx20201022001 GAO Yang, GAO Haoyuan, LI Bin, et al . Study on calculation method of landslide impact and scraping variable[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics,2022 ,39 (1 ):105 −112 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.7511/jslx20201022001[167] 高杨,李滨,高浩源,等. 高位远程滑坡冲击铲刮效应研究进展及问题[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(4):510 − 519. [GAO Yang,LI Bin,GAO Haoyuan,et al. Progress and issues in the research of impact and scraping effect of high-elevation and long-runout landslide[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(4):510 − 519. (in Chinese with English abstract)] GAO Yang, LI Bin, GAO Haoyuan, et al . Progress and issues in the research of impact and scraping effect of high-elevation and long-runout landslide[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020 ,26 (4 ):510 −519 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[168] WANG Wenpei,YIN Yueping,ZHU Sainan,et al. Dynamic analysis of a long-runout,flow-like landslide at Areletuobie,Yili River valley,northwestern China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2019,78(5):3143 − 3157. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-018-1322-6
[169] 陆鹏源,侯天兴,杨兴国,等. 滑坡冲击铲刮效应物理模型试验及机制探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(6):1225 − 1232. [LU Pengyuan,HOU Tianxing,YANG Xingguo,et al. Physical modeling test for entrainment effect of landslides and the related mechanism discussion[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(6):1225 − 1232. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LU Pengyuan, HOU Tianxing, YANG Xingguo, et al . Physical modeling test for entrainment effect of landslides and the related mechanism discussion[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016 ,35 (6 ):1225 −1232 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[170] VOELLMY A. Uber die Zerstorungskraft von Lawinen (On the destructive power of avalanche)[J]. Schweizerische Bauzeitung,1955,73:212 − 285.
[171] MAHBOOB M A, IQBAL J, ATIF I. Modeling and simulation of glacier avalanche:A case study of gayari sector glaciers hazards assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2015,53(11):5824 − 5834.
[172] HUNGR O,MORGENSTERN N R. Discussion:Experiments on the flow behavior of granular materials at high velocity in an open channel[J]. Géotechnique,1985,35(3):383 − 385.
[173] DAVIES T R,MCSAVENEY M J. Runout of dry granular avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1999,36(2):313 − 320. DOI: 10.1139/t98-108
[174] 崔鹏,邹强. 山洪泥石流风险评估与风险管理理论与方法[J]. 地理科学进展,2016,35(2):137 − 147. [CUI Peng,ZOU Qiang. Theory and method of risk assessment and risk management of debris flows and flash floods[J]. Progress in Geography,2016,35(2):137 − 147. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.02.001 CUI Peng, ZOU Qiang . Theory and method of risk assessment and risk management of debris flows and flash floods[J]. Progress in Geography,2016 ,35 (2 ):137 −147 . (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.02.001[175] FAN Xuanmei,DUFRESNE A,SIVA SUBRAMANIAN S,et al. The formation and impact of landslide dams:State of the art[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2020,203:103116. DOI: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103116
[176] 孙萍,汪发武,殷跃平,等. 汶川地震高速远程滑坡机制实验研究[J]. 地震地质,2010,32(1):98 − 106. [SUN Ping,WANG Fawu,YIN Yueping,et al. An experimental study on the mechanism of rapid and long Run-out landslide triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology,2010,32(1):98 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)] SUN Ping, WANG Fawu, YIN Yueping, et al . An experimental study on the mechanism of rapid and long Run-out landslide triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology,2010 ,32 (1 ):98 −106 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[177] DAI Fuchu,TU Xinbin,XU Chong,et al. Rock avalanches triggered by oblique-thrusting during the 12 May 2008 Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake,China[J]. Geomorphology,2011,132(3/4):300 − 318.
[178] 王玉峰,程谦恭,朱圻. 汶川地震触发高速远程滑坡-碎屑流堆积反粒序特征及机制分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(6):1089 − 1106. [WANG Yufeng,CHENG Qiangong,ZHU Qi. Inverse grading analysis of deposit from rock avalanches triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(6):1089 − 1106. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Yufeng, CHENG Qiangong, ZHU Qi . Inverse grading analysis of deposit from rock avalanches triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012 ,31 (6 ):1089 −1106 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[179] 胡卸文,顾成壮,牛彦博,等. 芦山地震触发大岩崩滑坡-碎屑流特征与运动过程[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2013,48(4):590 − 598. [HU Xiewen,GU Chengzhuang,NIU Yanbo,et al. Debris flow characteristics and movement process of dayanbeng landslide in Tianquan County triggered by “4•20” Lushan earthquake[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2013,48(4):590 − 598. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HU Xiewen, GU Chengzhuang, NIU Yanbo, et al . Debris flow characteristics and movement process of dayanbeng landslide in Tianquan County triggered by “4•20” Lushan earthquake[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2013 ,48 (4 ):590 −598 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[180] 孟兴民,陈冠,郭鹏,等. 白龙江流域滑坡泥石流灾害研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2013,33(4):1 − 15. [MENG Xingmin,CHEN Guan,GUO Peng,et al. Research of landslides and debris flows in Bailong river basin:Progress and prospect[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2013,33(4):1 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)] MENG Xingmin, CHEN Guan, GUO Peng, et al . Research of landslides and debris flows in Bailong river basin: Progress and prospect[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2013 ,33 (4 ):1 −15 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[181] 刘传正. 论崩塌滑坡-碎屑流高速远程问题[J]. 地质论评,2017,63(6):1563 − 1575. [LIU Chuanzheng. Research on high speed and long-distance of the avalanches or landslide-debris streams[J]. Geological Review,2017,63(6):1563 − 1575. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Chuanzheng . Research on high speed and long-distance of the avalanches or landslide-debris streams[J]. Geological Review,2017 ,63 (6 ):1563 −1575 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[182] XING Aiguo,YUAN Xiaoyi,XU Qiang,et al. Characteristics and numerical runout modelling of a catastrophic rock avalanche triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake in the Wenjia valley,Mianzhu,Sichuan,China[J]. Landslides,2017,14(1):83 − 98. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-016-0707-5
[183] ZHANG Ming,MCSAVENEY M J. Rock avalanche deposits store quantitative evidence on internal shear during runout[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2017,44(17):8814 − 8821. DOI: 10.1002/2017GL073774
[184] CHEN Xiaoqing,HU Kai,CHEN Jiangang,et al. Laboratory investigation of the effect of initial dry density and grain size distribution on soil-water characteristic curves of wide-grading gravelly soil[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering,2018,36(2):885 − 896.
[185] 裴向军,崔圣华,黄润秋. 大光包滑坡启动机制:强震过程滑带动力扩容与水击效应[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(2):430 − 448. [PEI Xiangjun,CUI Shenghua,HUANG Runqiu. A model of initiation of Daguangbao landslide:Dynamic dilation and water hammer in sliding zone during strong seismic shaking[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(2):430 − 448. (in Chinese with English abstract)] PEI Xiangjun, CUI Shenghua, HUANG Runqiu . A model of initiation of Daguangbao landslide: Dynamic dilation and water hammer in sliding zone during strong seismic shaking[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018 ,37 (2 ):430 −448 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[186] 许冲,徐锡伟,周本刚,等. 同震滑坡发生概率研究——新一代地震滑坡危险性模型[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(5):1122 − 1130. [XU Chong,XU Xiwei,ZHOU Bengang,et al. Probability of coseismic landslides:A new generation of earthquake-triggered landslide hazard model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(5):1122 − 1130. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XU Chong, XU Xiwei, ZHOU Bengang, et al . Probability of coseismic landslides: A new generation of earthquake-triggered landslide hazard model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019 ,27 (5 ):1122 −1130 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[187] GUO Changbao,MONTGOMERY D R,ZHANG Yongshuang,et al. Evidence for repeated failure of the giant Yigong landslide on the edge of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Scientific Reports,2020,10:14371. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-71335-w
[188] 文宝萍,曾启强,闫天玺,等. 青藏高原东南部大型岩质高速远程崩滑启动地质力学模式初探[J]. 工程科学与技术,2020,52(5):38 − 49. [WEN Baoping,ZENG Qiqiang,YAN Tianxi,et al. Preliminary study on geomechanical model of large-scale rock mass in southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau starting from high-speed long-distance collapse and slip[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2020,52(5):38 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WEN Baoping, ZENG Qiqiang, YAN Tianxi, et al . Preliminary study on geomechanical model of large-scale rock mass in southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau starting from high-speed long-distance collapse and slip[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2020 ,52 (5 ):38 −49 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[189] 罗刚,程谦恭,沈位刚,等. 高位高能岩崩研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(3):913 − 934. [LUO Gang,CHENG Qiangong,SHEN Weigang,et al. Research status and development trend of the high-altitude extremely-energetic rockfalls[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(3):913 − 934. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LUO Gang, CHENG Qiangong, SHEN Weigang, et al . Research status and development trend of the high-altitude extremely-energetic rockfalls[J]. Earth Science,2022 ,47 (3 ):913 −934 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 周诗凯,刘正华,余丰华,朱浩濛,黄丽,佘恬钰. 浙江省地质灾害气象风险预警一体化建设的探索与实践. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(02): 21-29 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 黄炜敏,陈全明,陈吉祥. 湖南省“631”地质灾害预警模式及避险案例研究. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(02): 74-80 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 张志希,陈克勋,侯均洪,李迎. 危岩变形自动化监测预警技术与应用——以重庆市江北区唐郭路为例. 自然资源信息化. 2024(01): 35-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 洛松群培,单增卓玛,单增顿珠,达娃,格桑扎西,吴传建. 普适型地质灾害监测预警系统应用及存在问题——以西藏拉萨、林芝为例. 西藏科技. 2024(05): 55-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 施唯,王东明. 全国房屋设施抗震设防信息化管理平台设计与实现. 震灾防御技术. 2024(02): 229-240 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 温兰冲,赵健赟,高崇越,王志超,陈风,杨成龙. 基于Cesium的湟水流域地质灾害三维可视化与信息系统设计. 科学技术与工程. 2024(21): 8843-8852 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 李学良,李宏艳,白国良,李大猛,余洋. 深部条带老采空区覆岩破坏多参量监测研究. 矿业安全与环保. 2024(04): 156-161+167 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈全明,黄炜敏,李姣. 基于改进切线角和变形速率的滑坡预警——以湖南省石门县雷家山滑坡为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 133-140 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 王雅洁,张成梅,杨鑫,秦梅元. 基于K-means-LSTM组合算法的地质灾害监测设备故障排查模型设计. 现代信息科技. 2024(20): 61-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 罗昌华. 基于实景三维的地质灾害监测预警平台建设. 测绘标准化. 2024(04): 86-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 委民正. 福建地质灾害监测预警专项平台设计与实现. 福建地质. 2023(03): 211-216 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:









 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS