Analysis on the characteristics of geological disasters and effectiveness of early warning duiring heavy rainfall on “23•7” in Beijing
-
摘要:
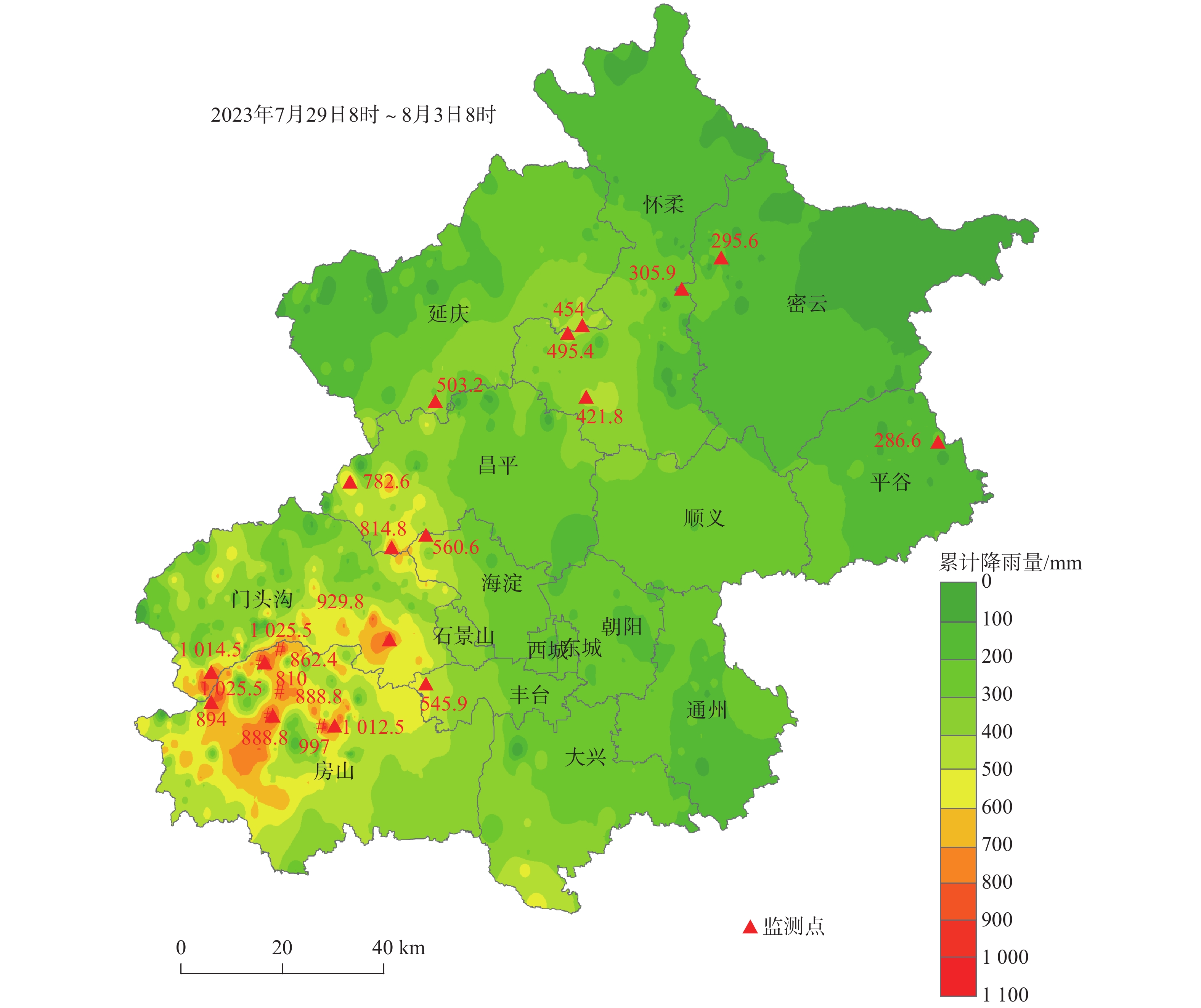
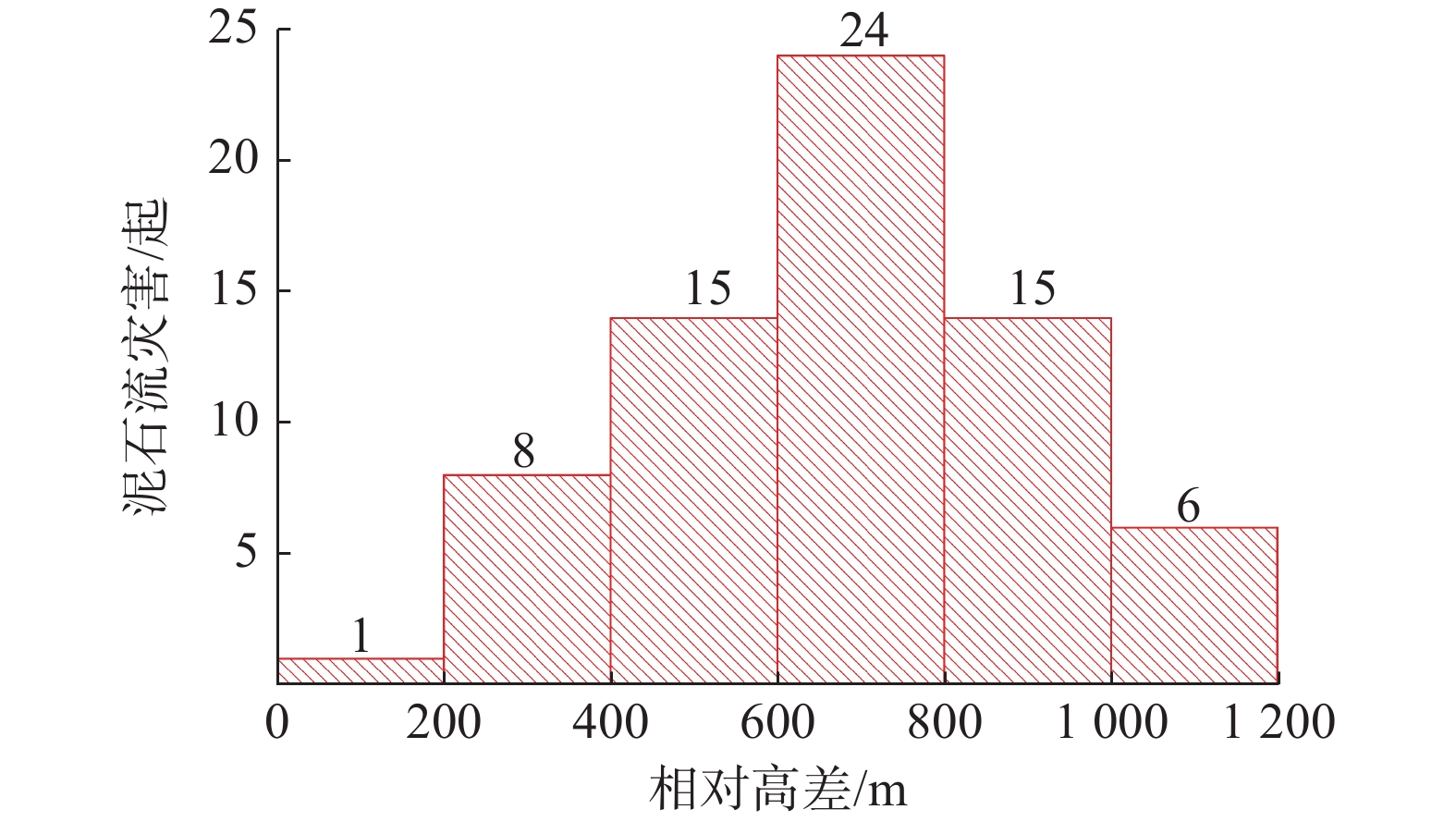
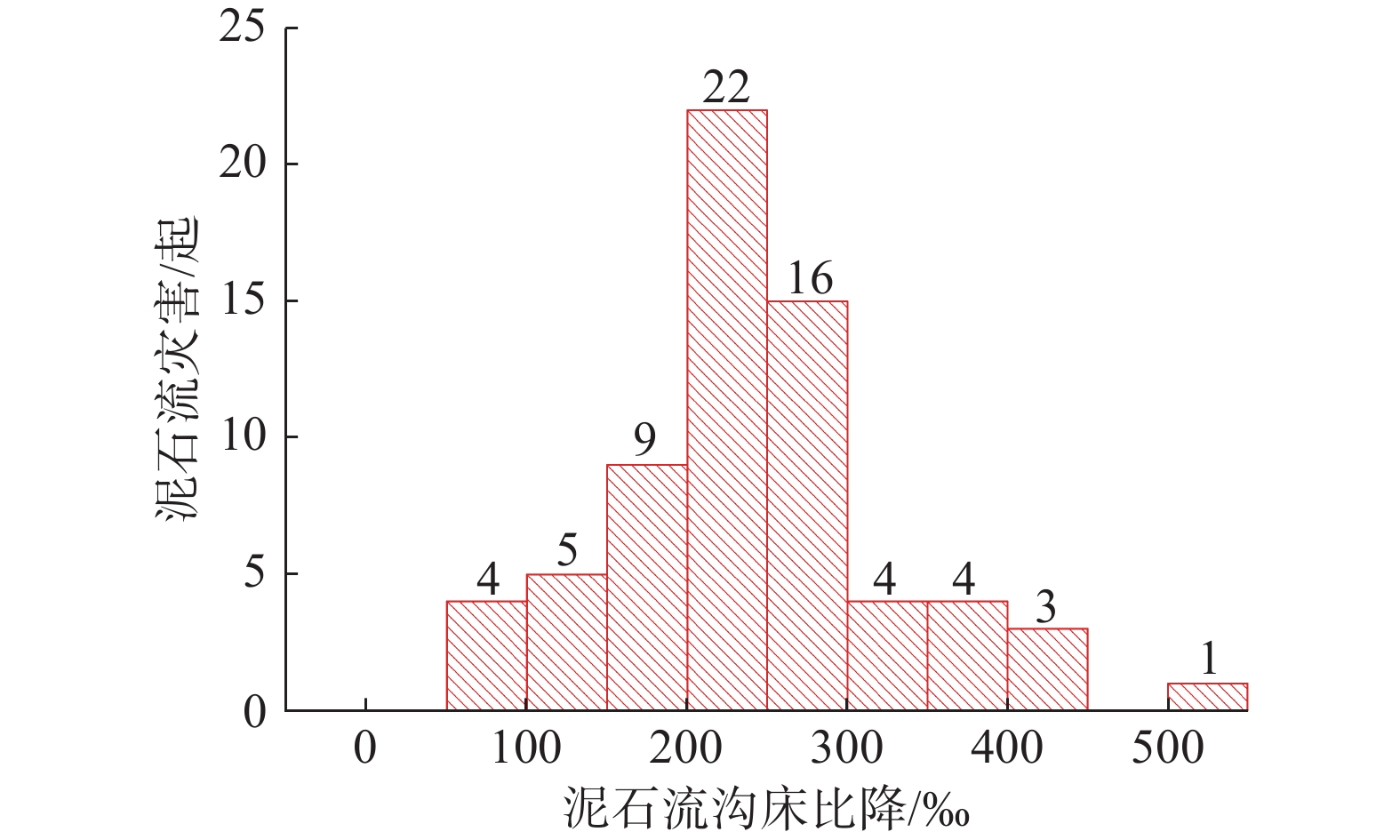
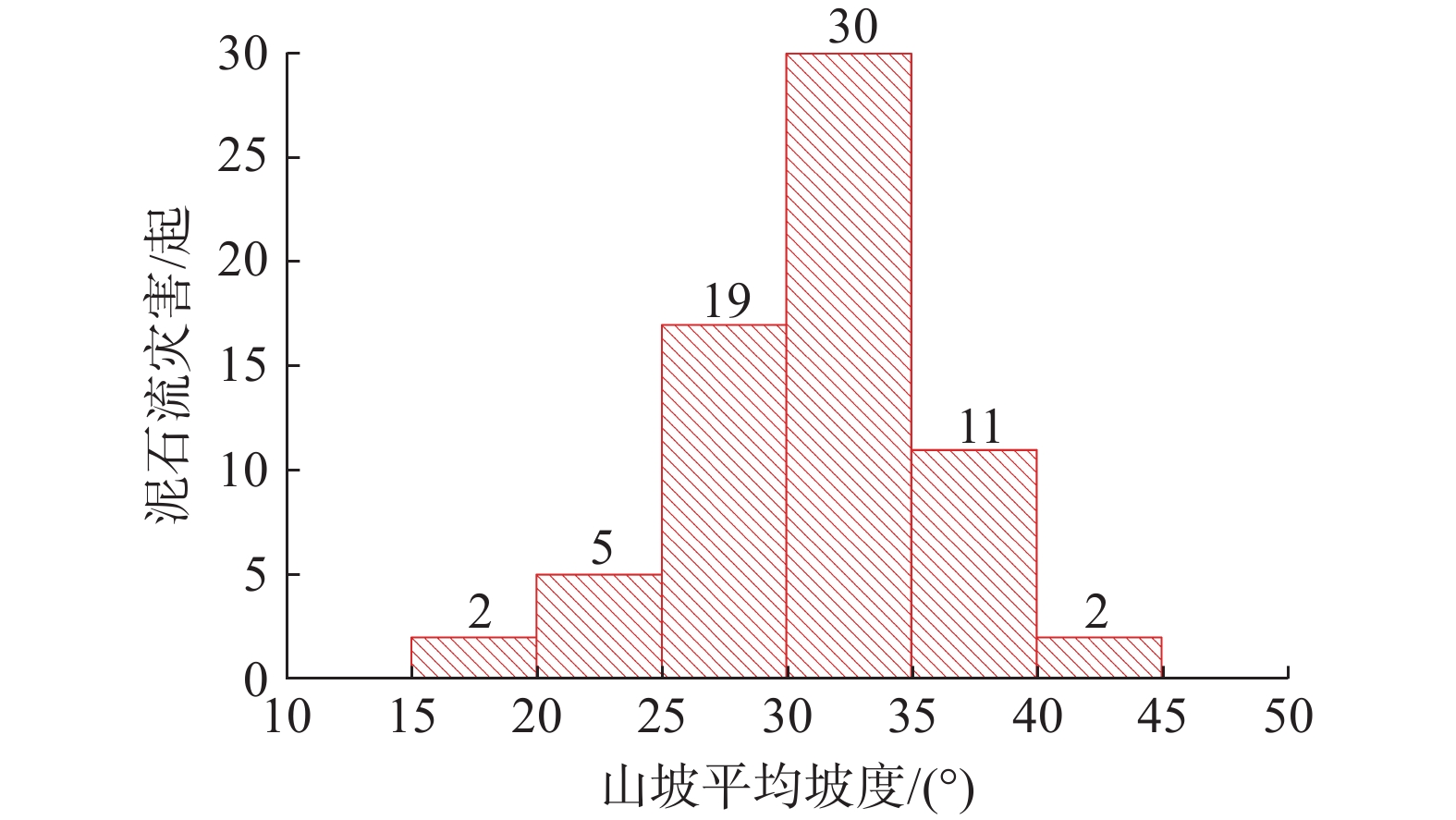
极端降雨常伴随群发性地质灾害发生,严重危害易发区人民群众生命财产安全,影响经济社会健康发展。总结分析极端降水灾害时空分布特点及预警成效,对于提高地质灾害综合防御能力具有重要意义。以2023年“23•7”强降水引发的突发地质灾害为研究对象,以“北京市突发地质灾害监测预警系统”精细化降水数据为基础,分析了“23•7”强降水时空分布特性和地质灾害发育分布特征,剖析了地质灾害预警成效,结果表明:“23•7”强降水具有总量大、雨强大、历时长、范围广等特点,极端降水灾害具有群发性,地质灾害分级分类多维度预警成效显著,实现了极端天气条件下因地质灾害零伤亡的目标。研究成果可为积极防范和科学应对极端降水地质灾害提供参考。
Abstract:Extreme rainfall is often accompanied by mass geological disasters, which seriously endangers the safety of people 's lives and property in prone areas and affects the healthy development of the economy and society. Summarizing and analyzing the time-space distribution characteristics of geological disasters due to extreme rainfall and the effectiveness of early warning is of great significance for improving the comprehensive defense ability against geological disasters. Taking the sudden geological disasters caused by “23•7” heavy rainfall in 2023 as the research object, based on the refined precipitation data from the Beijing sudden geological disaster monitoring and early warning system, the time-space distribution characteristics of “23•7” heavy rainfall and the development and distribution characteristics of geological disasters were analyzed, and the early warning effect of geological disasters was discussed. The results show that the“23•7”heavy rainfall has the characteristics such as a large total amount, strong rainfall, long duration and wide range, and the disasters due to extreme rainfall have the characteristics of group occurrence. The multi-dimensional early warning of geological disaster classification has achieved remarkable results and has achieved the goal of zero casualties due to geological disasters under extreme weather conditions. The research results can provide a reference for actively preventing and scientifically responding to extreme rainfall geological disasters.
-
0. 引言
滑坡的突发性强,危害性大[1],是一种在陆地环境中普遍存在的地质灾害,对人类社会具有较大影响和威胁[2]。滑坡预警的研究一直以来都备受国内外学者的关注[3 − 4],很多国家在滑坡灾害的应对中,都选择布设了早期监测预警系统[5]。通过预警系统得到的相关位移数据,可直观地体现滑坡的变形演化。由此可见,监测预警数据在滑坡的预警预报中起到了至关重要的作用。
在这个信息技术快速发展的时代,人工智能被广泛应用,而机器学习是其中的一个重要分支。从20世纪80年代以来,机器学习已在算法、理论和应用等方面获得了巨大的成功[6]。近年来,机器学习也在预测领域中得到了广泛的运用,常见的几种算法如随机森林[7]、支持向量机[8]、人工神经网络[9]和循环神经网络[10]等在环境、金融、电力和交通等方面都有相关的应用。长短期记忆网络(long short term memory network,LSTM)是一种时间循环神经网络,是循环神经网络(recurrent neural network,RNN)中的一个变体,但与传统RNN不同,LSTM的记忆单元更复杂,对于时间跨度较大的时间序列有良好的记忆[11],同时也解决了神经网络的易陷入局部最小值、梯度消失和梯度爆炸等问题[12]。LSTM在语音识别[13]、图像处理[14]以及最常见的股票预测[15 − 16]中运用广泛,但目前在滑坡的位移时序预测中较少。
本文将LSTM应用到立节北山滑坡的变形预测中,预测监测点位移数据,并将预测数据与实际数据进行对比分析,为立节北山滑坡提供新的预测参考。
1. 研究区概况
立节北山滑坡灾害位于舟曲县西部的白龙江上游左岸立节镇的北侧山体,由多个滑坡共同构成,滑坡区涵盖已经发生过变形滑动的古滑坡体、老滑坡体、正在发生变形的新滑坡体以及已有明显变形迹象的但未发生位移的潜在滑坡体的区域,共有古、老、新滑坡10处,整体范围南北长1388 m,东西宽610 m,总面积约0.85 km2。
根据立节北山的滑坡性质、地形条件、地层分布和滑动条件等特征将滑坡分为7个块体(图1),以滑坡中部的地形转折处为界,分为上下两级。上级滑坡主要是老滑坡,其覆盖区域为H1,以及已有明显变形迹象但未发生滑动的潜在滑坡H1-1和H1-2;下级滑坡主要为变形滑动明显,并且变形面积较大的H2—H7滑坡。统计数据显示,滑坡区内堆积体总体积为3.270 54×106 m3,滑坡变形量从大到小排序为:H4>H5>H3>H2>H7>H6>H1。
2. 预测方法及数据源
2.1 LSTM模型
LSTM早在1997年就被提出,它的出现解决了隐变量一直存在的长期信息贮存和短期输入缺失的问题。和传统神经网络相比,LSTM引入了记忆元和三种门结构(图2),其中记忆元(C)用于记录附加的信息,而门结构用于控制记忆元,分别为遗忘门(f)、输入门(i)和输出门(o)。
首先在遗忘门中决定记忆或忽略隐状态的输入信息,此处的sigmoid激活函数(σ)将判断当前输入是否遗忘;其次输入门用于决定在记忆元中读取哪些信息,此处有两个分支构成,一个是记忆门决定要读入的值,另一个是tanh激活函数得到新的候选记忆元
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) 其中,Wxf、Wxi、Wxo、Wxc和Whf、Whi、Who、Whc分别是遗忘门、输入门、输出门和候选记忆元的权值向量,bf、bi、bo、bc分别是遗忘门、输入门、输出门和候选记忆元的偏置向量,Xt是t时刻的输入值。
2.2 评价指标
为了衡量预测结果的精度,本文采用均方根误差(RMSE)、平均绝对误差(MAE)、决定系数(R2)以及可解释方差(Evar)作为评价指标,具体表达式如下:
(7) (8) (9) (10) (11) 式中:
m——数据个数;
Var——方差。
2.3 数据源
立节北山滑坡监测点分布如图1所示,共布设11个GNSS监测点。本文的数据来源于监测点实时监测的位移数据,数据范围为2021年3—12月的每日位移数据,其中有少量缺失数据,对其进行了采取邻日数据的中间值的填充预处理。
3. 结果与分析
3.1 影响因素
立节北山滑坡稳定性除了受滑坡本身内在结构影响,也受外在因素影响。除累计位移外,图3为GNSS1监测站垂直和水平位移和雨量的相关曲线,由图可知,位移量与雨量间具有明显相关性。雨水下渗需要一定的时间,将导致滑坡体的下滑力增大,因此影响滑坡的稳定性。
Pearson相关系数是用来表示两个变量之间线性相关程度的大小与方向的指标,数值范围为−1≤r≤1,小于0为负相关,大于0为正相关,等于0则不存在相关性,绝对值越大,则表示两变量间的相关程度越强烈。通过GNSS1位移量与雨量的Pearson相关性分析,得到相关系数值为0.993,接近于1,说明之间有显著的正相关关系,雨量对滑坡的应力状态影响明显,特征评价因子选取适宜。
将影响因素累计位移、雨量作为模型的输入变量,因数据的类型、量纲以及取值范围不同,需先对数据进行归一化处理,进而输出模型预测值。
3.2 确定隐藏层神经元数
本文基于LSTM模型建立了立节北山滑坡的变形预测模型,首先以GNSS1监测站为例,GNSS1监测站发出红色预警,形变量显著,通过2021年4月9日至12月2日的数据进行预测,其中GNSS1因该处形变量过大,于12月3日掉落数据中断,所以采取前八月的数据进行相应的预测试验。运用Python 3.7语言和PyTorch 1.12机器学习框架进行构建LSTM模型,在试验中,首先需要对参数进行初始化,发现采用不同的隐藏层神经元数预测结果的精度会有所不同。如图4所示,选取8、16以及几个32的倍数为不同隐藏神经元数量进行精度对比:以64为转折点,神经元数量在8~64时,RMSE呈下降趋势;神经元数量在64~128时,RMSE呈上升趋势,所以选取隐藏层神经元数为64,此时RMSE最低,精度最高。
3.3 预测结果
通过参数初始化调整,设置LSTM模型循环层数为2,隐藏层神经元数为64,序列长度为30,将数据集以6∶4的比例,划分为训练集和测试集。首先对GNSS1的垂直位移进行预测,在LSTM预测模型训练中,损失函数(Loss)变化正常,随训练次数的增加,损失函数值越接近于0(图5)。
测试集预测精度结果见表1,均方根误差为12.88 mm,平均绝对误差为6.56 mm,决定系数及可解释方差均达到0.99,精度评价良好,本文的LSTM模型试验性能有效。
表 1 GNSS1垂直位移精度评价指标Table 1. Evaluation metrics for vertical displacement precision of GNSS1评价指标 RMSE/mm MAE/mm R2 Evar 数值 12.88 6.56 0.99 0.99 监测站GNSS1最终预测结果见图6,分别为垂直及水平位移的预测,测试数据与预测数据的比例为5∶1。
为进一步验证本文LSTM模型在滑坡位移中预测的广泛性,又选取了蓝色预警区域GNSS8监测站数据,进行预测对比,评价指标见表2、3,决定系数及可解释方差均达到0.99,预测结果如图7。
表 2 GNSS8垂直位移精度评价指标Table 2. Evaluation metrics for vertical displacement precision of GNSS8评价指标 RMSE/mm MAE/mm R2 Evar 数值 6.63 5.66 0.99 0.99 以GNSS1水平位移为例,见图8所示,对2021年12月2日后48 d(测试数据与预测数据的比例为2∶1)的数据进行预测,位移值超过20000 mm后,预测值增长趋势明显增加,故选取测试数据与预测数据的比例为5∶1。说明LSTM模型具有短期预测的能力,但不适用于长期预测,长期预测呈现的效果不佳,可能导致模型失去预测效能。
表 3 GNSS8水平位移精度评价指标Table 3. Evaluation metrics for horizontal displacement precision of GNSS8评价指标 RMSE/mm MAE/mm R2 Evar 数值 4.00 3.79 0.99 0.99 本文以GNSS1和GNSS8两个发出预警的典型监测站为例进行预测试验,其中GNSS1位于块体H4,其为立节北山滑坡变形量最大的块体,故以GNSS1监测站为首要监测对象进行预测试验,GNSS8监测站为辅,进行进一步验证。立节北山滑坡后续进行施工防治措施,如图9治理工程三维地表分布图所示,上部进行了格构护坡和抗滑桩等的施工措施见图9(b),下部GNSS1处进行了削坡措施,见图9(c)。施工成效显著,目前处于稳定状态,本文仅以研究新方法与应用为目的进行相关预测。
4. 结论
本文运用LSTM神经网络预测模型对立节北山滑坡的变形进行预测,并说明北山滑坡主要的影响因素,以选取恰当的特征因子,是将人工智能机器学习应用于北山滑坡变形预测的有效实验,实现了北山滑坡的定量位移预测。
GNSS1在损坏掉落前,水平及垂直位移分别已达15 000 mm和12 000 mm,通过本次LSTM模型预测,可良好的预测出位移数值,对于测点仪器及财产安全也将起到良好的预警作用。
预测结果性能显示良好,精度评价较高,虽然LSTM模型在长期预测中表现不突出,但短期预测的能力显著,不仅为立节北山滑坡变形预测提供了辅助参考,也为滑坡预警预测打开了新的思路,对早期预警预报和地质灾害防治具有重要的意义。LSTM模型更是在GNSS8监测站的水平位移预测值中的评价指标较为良好,均方根误差为4.00 mm,平均绝对误差为3.79 mm,体现出了在滑坡变形预测中很好的适用性,进一步说明在滑坡变形预测中引入人工智能,是一个可实行的策略方法。
-
表 1 地质灾害预警风险等级划分依据
Table 1 Classification criteria for geological hazard warning risk levels
预警等级 预警指数 无预警 Tl <0.55 蓝色预警(有一定风险) 0.55≤Tl <0.68 黄色预警(风险较高) 0.68≤Tl <0.74 橙色预警(风险高) 0.74≤Tl <0.98 红色预警(风险极高) Tl≥0.98 -
[1] 罗守敬,王珊珊,付德荃. 北京山区突发性地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):126 − 133. [LUO Shoujing,WANG Shanshan,FU Dequan. Assessment on the susceptibility of sudden geological hazards in mountainous areas of Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):126 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LUO Shoujing, WANG Shanshan, FU Dequan. Assessment on the susceptibility of sudden geological hazards in mountainous areas of Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(4): 126 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 王海芝,曾庆利,许冰,等. 北京“7•21” 特大暴雨诱发的地质灾害类型及其特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):125 − 132. [WANG Haizhi,ZENG Qingli,XU Bing,et al. Types and characteristics of geological disasters induced by the “7•21” rainstorm in Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):125 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Haizhi, ZENG Qingli, XU Bing, et al. Types and characteristics of geological disasters induced by the “7•21” rainstorm in Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 125 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 李岩,南赟,曹颖. 北京山区道路沿线崩塌灾害特征分析与防治思路探讨[J]. 城市地质,2022,17(3):291 − 298. [LI Yan,NAN Yun,CAO Ying. Characteristics analysis and prevention discussion of collapse disasters along roads in mountainous areas of Beijing[J]. Urban Geology,2022,17(3):291 − 298. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Yan, NAN Yun, CAO Ying. Characteristics analysis and prevention discussion of collapse disasters along roads in mountainous areas of Beijing[J]. Urban Geology, 2022, 17(3): 291 − 298. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 韩建超. 北京地区崩塌监测预警初探——以琉辛路监测路段为例[J]. 城市地质,2020,15(2):148 − 153. [HAN Jianchao. Preliminary study on collapse monitoring and early warning in Beijing area:Taking the monitoring section of Liuxin Road as an example[J]. Urban Geology,2020,15(2):148 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HAN Jianchao. Preliminary study on collapse monitoring and early warning in Beijing area: Taking the monitoring section of Liuxin Road as an example[J]. Urban Geology, 2020, 15(2): 148 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 程素珍,路璐,翟淑花,等. 2004—2018年北京市突发地质灾害时空分布特点和监测预警状况[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):38 − 46. [CHENG Suzhen,LU Lu,ZHAI Shuhua,et al. Temporal-spatial distribution and monitoring and early warning of sudden geological disasters in Beijing during the period of 2004 to 2018[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):38 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHENG Suzhen, LU Lu, ZHAI Shuhua, et al. Temporal-spatial distribution and monitoring and early warning of sudden geological disasters in Beijing during the period of 2004 to 2018[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 38 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 赵忠海,李敏. 北京山区公路边坡地质灾害隐患监测预警技术研究[J]. 城市地质,2018,13(3):72 − 83. [ZHAO Zhonghai,LI Min. Study on monitoring and early warning technology of the potential slope geological disaster along the mountainous roads in Beijing[J]. Urban Geology,2018,13(3):72 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHAO Zhonghai, LI Min. Study on monitoring and early warning technology of the potential slope geological disaster along the mountainous roads in Beijing[J]. Urban Geology, 2018, 13(3): 72 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李晓玮. G109国道门头沟段边坡稳定性及崩滑灾害危险性评估[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2012. [LI Xiaowei. The slope stability and slump hazard assessment along the G109 National highway in Mentougou[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Xiaowei. The slope stability and slump hazard assessment along the G109 National highway in Mentougou[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 曹亚男. 房山山区公路地质灾害的预防与应急管理研究[D]. 北京:北京建筑大学,2019. [CAO Yanan. Study on prevention and emergency management of highway geological hazardsin Fangshan district mountain area[D]. Beijing:Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CAO Yanan. Study on prevention and emergency management of highway geological hazardsin Fangshan district mountain area[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 南赟,曹颖,李岩. 新形势下北京市突发地质灾害防治工作思路探析[J]. 城市地质,2020,15(3):233 − 238. [NAN Yun,CAO Ying,LI Yan. An analysis on prevention and control of abrupt geo-hazards in Beijing under the new situation[J]. Urban Geology,2020,15(3):233 − 238. (in Chinese with English abstract)] NAN Yun, CAO Ying, LI Yan. An analysis on prevention and control of abrupt geo-hazards in Beijing under the new situation[J]. Urban Geology, 2020, 15(3): 233 − 238. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 贾三满,翟淑花,姜媛. 北京突发地质灾害防控对策[J]. 城市地质,2017,12(4):16 − 23. [JIA Sanman,ZHAI Shuhua,JIANG Yuan. Prevention and controlling idea on emergent geological disasters of Beijing[J]. Urban Geology,2017,12(4):16 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)] JIA Sanman, ZHAI Shuhua, JIANG Yuan. Prevention and controlling idea on emergent geological disasters of Beijing[J]. Urban Geology, 2017, 12(4): 16 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 刘艳辉,唐灿,吴剑波,等. 地质灾害与不同尺度降雨时空分布关系[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2011,22(3):74 − 83. [LIU Yanhui,TANG Can,WU Jianbo,et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of geo-hazards and rainfall in different scales[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2011,22(3):74 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Yanhui, TANG Can, WU Jianbo, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of geo-hazards and rainfall in different scales[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2011, 22(3): 74 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 张鸣之,杨飞,马娟,等. 区块链技术在全国地质灾害风险预警系统建设中的应用探索[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(6):168 − 174. [ZHANG Mingzhi,YANG Fei,MA Juan,et al. Exploration of blockchain technology application in the construction of national risk warning system on landslides[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(6):168 − 174. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Mingzhi, YANG Fei, MA Juan, et al. Exploration of blockchain technology application in the construction of national risk warning system on landslides[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(6): 168 − 174. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 伊明. 软弱围岩条件下高速公路隧道施工围岩滑坡变形检测. 科技创新与生产力. 2025(04): 144-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 姜鑫,张卫雄,杨校辉,陈昆全,丁保艳. 甘肃舟曲县江顶崖滑坡抗滑桩变形监测与治理效果分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 174-182 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:


























 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS