Research on risk early warning for rainfall-induced shallow landslides in Guangdong Province based on a dynamic slope instability model
-
摘要:
针对县级地质灾害气象风险预警面临的精度及模型建设问题,根据广东省地质灾害主要发生在坡面残坡积浅表层的突出特点,通过对典型地质灾害进行物理模拟试验和数值模拟,研究广东省浅表层斜坡失稳发生机理。研究表明:边坡在暴雨条件下,斜坡岩土体容易在浅表层首先造成失稳,影响因素主要有降雨量、降雨历时、土体类别和坡体结构等因素。由此,对研究区划分斜坡单元,按各斜坡单元的坡长、坡度、岩土类型、分层及其关键物理力学参数开展斜坡单元概化分类,并将Green-Ampt降雨入渗模型和无限边坡稳定性评价方法相结合,优化构建了动力学斜坡稳定性评价模型。结合龙川县贝岭镇流域应用实例,初步探索了坡面单元尺度下地质灾害气象风险预警斜坡失稳动力学预警技术,可为广东省开展以斜坡单元预警为主要方式的县级地质灾害气象风险预警提供支撑。
Abstract:In light of the accuracy and model construction challenges in county-level meteorological risk early warning for geo-hazards, and considering the prominent characteristics that these geo-hazards mainly occur on the shallow surface of residual slopes, the mechanism of shallow surface slope instability in Guangdong Province was studied through physical simulation experiments and numerical simulations of typical geo-hazards. The results show that the slope is easy to lose stability in the shallow surface layer under the condition of rainstorm, and the main factors are rainfall, rainfall duration, soil type and slope structure. Subsequently, by dividing the study area into slope units, we developed a generalized classification and numerical modeling of these units based on parameters such as slope length, slope gradient, rock and soil type, stratification, and key physical and mechanical parameters of each slope unit, and by combining the Green-Ampt rainfall infiltration model with the infinite slope stability evaluation method, the slope instability dynamics warning model was then constructed. Through the application in the basin of Beiling Town in Longchuan County, and the application of dynamic early-warning technology for slope instability in meteorological risk early warning for geological hazards was preliminarily explored at the scale of slope units, which can provide support for county-level geo-hazards meteorological risk early-warning based on slope unit early-warning in Guangdong Province.
-
0. 引 言
广东省是我国地质灾害多发省份之一,地质灾害类型以滑坡、崩塌和泥石流为主,具有点多、分布广、规模较小、危害性大等特点。降雨是诱发广东省地质灾害的主要因素。 2004年起,广东省就开展了汛期地质灾害气象风险预警工作,并取得了较好的防灾减灾效果。受地质灾害基础调查精度和气象数据共享程度等多因素影响,目前广东省地质灾害气象风险预警工作只开展到地市级,预警精度为乡镇。随着广东乡镇(街道)1∶1万地质灾害调查工作的实施,开展了以斜坡为单元的地质灾害风险调查评价,并控制性地布设测绘、钻探和岩土样测试等勘查测绘工作,划定风险区,构建了行政村风险管控网格。大量翔实的调查、勘查测绘数据进一步揭示斜坡类地质灾害的成灾机理,证实了广东省暴雨型滑坡主要发生在斜坡的浅表层这一显著特点,为以斜坡为单元构建预警模型开展地质灾害气象风险预警奠定了基础,同时精准的预警又是实施以风险斜坡为单元的行政村级风险管控的前提条件。因此,聚焦斜坡浅表层开展强降雨作用下坡面尺度的斜坡失稳动力预警模型研究,具有重要的理论和实践意义。
按照基于降雨因素的地质灾害区域预警理论,可将区域地质灾害气象风险预警为隐式统计预警、显式统计预警和动力预警三种类型[1 − 3]。隐式统计预警是把除降雨以外的其他地质环境因素的作用隐含在降雨中, 重点利用降雨参数建立模型的预警方法。显式统计预警是通过把地质环境因素变化与激发因素相迭,建立相互耦合判据模型的预警方法。隐式统计预警和隐式统计预警主要是运用数理统计分析的方法建模。动力预警是一种针对地质体因降雨影响自身发生动力变化过程构建数学物理判据方程的预警方法, 本质上是一种解析预警方法。三种预警模型与工作区地质灾害基础调查评价工作精度、灾害机理研究程度密切相关,是针对不同程度地质灾害调查研究成果转化应用发展的体现。目前在区域地质灾害气象风险预警中使用比较广泛的预警方法主要以显式统计预警为主,而动力学预警由于斜坡失稳条件、降雨对滑坡作用机理的复杂性,以及模型参数的不确定性,仍处于研究阶段[4]。本研究在广东省1∶5万地质灾害风险调查、乡镇(街道)1∶1万地质灾害风险调查评价、前期地质灾害气象风险预警等一系列工作成果的基础上,以风险管控斜坡为单元进行概化分类及几何模型建立,进一步构建降雨量为因、斜坡稳定性为果的动力预警模型,分析不同降雨变量条件下斜坡的稳定系数,实现坡面尺度级斜坡失稳风险预警,探索适应以斜坡单元预警为主要方式的县级地质灾害气象风险预警技术。
1. 广东省地质灾害特点
据统计,2003—2022年20年间广东省共发生各类突发性斜坡类地质灾害5597起,死亡 759 人(含失踪),受伤200 人,直接经济损失约30.4亿元。灾害类型主要以崩塌、滑坡、泥石流为主,具有点多面广、危害严重、灾害规模以中小型为主、群发性强等特点[5]。灾害主要集中分布在粤东、粤西和粤北等广大中低山区、丘陵区以及人类工程活动强烈的珠三角局部地区[3],地质灾害空间分布上有明显的地域性;与不同地区地层岩性、地质构造、地形地貌、残坡积层岩土体类型以及人类工程活动等因素关系密切;同时地质灾害的发生时间具有明显的季节性,据有明确发生时间的4773处地质灾害统计,其中有4456处发生在4—9月的汛期雨季,占93%,特别是5月、6月“龙舟水”和8月台风强降雨期间,10月至次年3月发生地质灾害的频率较小。强降雨引发的地质灾害与月均降雨量呈明显正相关关系,当月均降雨量大于100 mm时,地质灾害发生数量呈明显增多[6](图1);地质灾害相对强降雨滞后时间短或与强降雨同步发生,具有群发性;群发性地质灾害主要以发育于第四系全新统残坡积层的浅层小型破坏为主,发育厚度范围为1~3 m,一般情况下崩滑体厚度均小于5 m,主要发生于坡度为35°~45°,坡高为30~60 m的凸形自然边坡。
2. 坡面尺度下区域动力学预警技术研究
2.1 斜坡类地质灾害成灾机理研究
广东省群发性地质灾害主要发生在岩土体的浅表层,在残坡积层形成易破坏层。不同母岩风化后形成的岩土体的矿物成分、结构构造、物理力学性质和工程性质差异性很大。为进一步探究广东省地质灾害成灾机理,为坡面尺度下区域动力学预警技术应用提供理论和数据支撑,本研究通过典型地质灾害物理模拟试验和地质灾害数值模拟构建了不同类型坡面单元的斜坡稳定评价物理模型、数值分析模型以及连续介质动力模型,揭示了强降雨过程斜坡体水力特征、破坏模式和变形特征。
2.1.1 典型地质灾害物理模拟试验
(1)模型试验总体思路
基于典型滑坡灾害调查勘查成果资料,采用物理模拟试验研究边坡在强降雨条件下的失稳模式和变形破坏特征,分析边坡失稳机理。模型试验以实际边坡原型为研究对象,采用1∶50比例,在坡内埋置监测传感器,通过自然工况下的模拟人工强降雨试验,探究强降雨条件下广东省典型滑坡失稳破坏机理。
(2)模型试验系统组成
试验系统与设备主要由模型箱、降雨模拟系统、数据监测系统和高清摄像机四个部分组成(图2)。通过试验模型箱、模拟降雨系统的组合,并配合土压力计等传感器的数据采集系统与数字影像实时监测系统形成一套降雨诱发型滑坡模拟的试验设备;试验的传感器有土压力传感器、水分仪和孔隙水压力传感器。传感器的布置,需要保证传感器不破坏边坡模型的整体完整;在降雨试验对模型边界的处理中,模型边坡除了具有应力边界外,还具有水力边界,即将边坡的上表面视为降雨入渗边界,边坡前缘作为自由边界,边坡底部及背部可近似地看作隔水边界。
(3)模型试验及结果
试验模拟50 mm/h降雨,持续160 min后边坡完全破坏。通过进行强降雨条件下物理模型试验,获得了滑坡模型各观测点的土壤含水率、孔隙水压力、土压力的变化过程曲线,并记录了不同时间模型变形及破坏的信息(图3)。
通过滑坡模型试验水力特征变化曲线(图4)可以看到:土壤体积含水率随时间变化曲线规律为快速上升-缓慢上升-快速上升-平稳趋于饱和,从坡脚到坡顶依次达到平稳饱和;孔隙水压随时间变化规律为孔隙水压力先逐渐增加,当测点处发生失稳破坏时孔隙水压消散,产生突降;土压力随时间变化规律为前期上升或下降,在测点处破坏时,土压力值突降。
通过物理模型试验,揭示边坡在强降雨条件下坡面土体在一定深度范围内由坡脚至坡顶逐步产生主动土压破坏,塑性区向上游扩展,影响因素主要有降雨量、降雨历时、土体类别和坡体结构等因素。
2.1.2 典型地质灾害数值模拟及结果
基于以上地质灾害物理模拟研究结果,选择18处典型灾害点,结合地质灾害现场调查、工程地质测绘、勘察及土工试验成果,提取各灾害点原始坡体的坡长、坡度、岩土分层几何参数,选取相关物理力学参数,如:容重、弹性模量、泊松比、黏聚力和内摩擦角等(表1),利用Midas GTS /NX 软件分别构建二维、三维数值模型,分析降雨前后边坡体稳定系数变化情况斜坡应力云图、应变增量场变化情况(表2),对地质灾害及灾害链在暴雨下的动态演化机制进行研究,对其成灾机理进行解析,为降雨入渗的斜坡稳定性评价模型优化提供依据。研究发现,降雨前各斜坡稳定系数绝大多数在1.2以上,相对比较稳定,降雨后,各斜坡稳定系数均发生大幅下降,多数在1.0以下,处于失稳状态;暴雨条件下受降雨入渗影响,斜坡应力集中带向前扩展比较明显,应变场增量沿坡体上部增量明显,说明斜坡岩土体容易在浅表层首先造成失稳,与灾害事实相符。
表 1 天然及暴雨状态下斜坡岩土体计算参数Table 1. Calculation parameters of rock and soil mass of the slope under natural and rainstorm conditions名称 弹性模量
/MPa孔隙比 天然状态 饱水状态 γ/(kN·m−3) c/kPa ϕ/(°) γsat/(kN·m−3) c/kPa ϕ/(°) 砂质黏性土①-1 8.0 0.99 18.0 19.1 18.0 18.5 18.1 17.0 砂质黏性土①-2 8.5 0.88 18.1 20.2 19.2 18.7 19.3 18.3 砂质黏性土①-3 9.2 0.83 19.1 28.3 22.5 19.6 26.2 21.1 全风化花岗岩 50.0 0.71 21.0 38.0 35.0 21.5 − − 中风化花岗岩 100.0 0.65 22.0 50.0 45.0 22.5 − − 表 2 河源市龙川县地质灾害数值模拟(部分示例)Table 2. Numerical simulation of geo-hazards in Longchuan County, Heyuan City (some examples)灾害体特征 二/三维数值模拟 稳定系数 

1.25
(自然状态)1.01
(饱和状态)

1.22
(自然状态)0.80
(饱和状态)2.2 基于降雨入渗的斜坡稳定性评价模型优化
以上基于降雨入渗导致斜坡体失稳发生机理建立的物理模型试验和数值模型模拟结果证明以往研究认为的降雨引起的斜坡失稳大部分发生在极限入渗深度范围的浅层土质中[7 − 9]结论相吻合。因此,基于降雨入渗对斜坡单元构建以降雨为因、稳定性为果的预测评价具有可行性。本文聚焦斜坡残坡积层,以斜坡为单元,将Green-Ampt降雨入渗模型和无限边坡稳定性评价方法相结合,进行优化构建了相应的斜坡稳定性评价模型[10 − 11]。
袁畅等[12]结合广东的特点进一步分析总结认为:斜坡残坡积层在不同的降雨强度、降雨历时条件下,具有不同的湿润深度Zw,降雨入渗过程存在入渗极限深度Zw,深度与相对雨强和降雨历时具有较好的函数关系。
湿润深度:
$$ {Z}_{{\mathrm{w}}}=(0.13\eta +0.03){t}^{-0.03\eta +0.78} $$ (1) 式中:Zw——湿润锋深度/cm;
$ t $ ——降雨历时/min;$ \eta $ ——相对雨强。本文选取粤东地区花岗岩残积土边坡数值模型进行不同降雨强度条件下湿润峰入渗深度随时间的变化关系。
当
$ \eta < 10 $ 时,湿润锋深度与相对雨强以及降雨强度存在较好的函数关系。相对雨强:
$$ \eta =q/{k}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $$ (2) 式中:
$ q $ ——雨量强度/(cm·min−1);$ {k}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $ ——饱和渗透系数/(cm·min−1)。基于湿润锋最大深度与降雨历时以及相对雨强的关系,建立基于降雨入渗斜坡稳定性系数与降雨关键参数的数学模型。公式如下:
$$ F_{\mathrm{s}}=\frac{c'+(\gamma_{\mathrm{sat}}-\gamma_{\mathrm{w}})Z_{\mathrm{w}}\cos^2\alpha\tan\varphi'}{\gamma_{\mathrm{sat}}Z_{\mathrm{w}}\sin\alpha\cos\alpha} $$ (3) 式中:
$ {c}' $ ——有效黏聚力/kPa;$ {\varphi }' $ ——有效内摩擦角/(°);$ {\gamma }_{\text{sat}} $ ——土的饱和重度/(kN·m−3);$ {\gamma }_{{\mathrm{w}}} $ ——水的重度/(kN·m−3);$ \alpha $ ——边坡坡角/(°);Zw——湿润锋深度/cm。
由以上公式可以看出斜坡稳定性系数Fs与Zw存在负相关的关系。
3. 坡面尺度下区域动力学预警技术应用初探
3.1 应用技术流程
以斜坡为单元的区域地质灾害气象风险预警的基础是对设定区域进行预警区划,按斜坡单元划分预警分析单元[6],构建预警分析模型,同步获取降雨监测、预报数据,计算对应时空雨量下各斜坡单元的稳定性,根据稳定性动态分析结果发布预警[13 − 16]。具体方法如下:
(1)划分预警分析单元(斜坡单元)
斜坡单元是斜坡类地质灾害孕育、发生的最基本单元[17 − 18]。广东省1∶10000乡镇(街道)地质灾害风险调查评价基于斜坡单元开展,主要以承灾体作为斜坡单元划分的控制性因素,综合考岩土体特征、致灾因素、地层岩性、已发地质灾害隐患、变形特征等因素合理圈定,上限划到分水岭,下限将可能的承灾体圈划进去,单个斜坡单元面积控制在0.1~0.3 km2。主要通过DEM提取地表形态信息,借助GIS软件通过正向DEM提取出分水线,反向DEM提取出汇水线,将分水线和汇水线融合成一个闭合区域,期间要经过填洼、水流方向提取等众多步骤,再通过人机交互完善斜坡单元(图5)。
(2)预警分析单元参数赋值
斜坡单元岩土特性与水文地质特征基本一致,以坡面为单位基于地面调查多渠道提取各斜坡的相关地质环境调查信息或采用GIS技术叠加专题图层挖掘相关地质环境因子,对每个斜坡单元进行地质环境因子赋值(图6)。
(3)斜坡数值建模与预警分析
构建降雨量-斜坡稳定系数动力预警模型,基于调查、勘察及土工试验数据等,对研究区的各斜坡单元完成参数设置(图7),同步接入研究区降雨实测、预报数据,以不同的降雨性质如降雨强度、降雨持续时间、前期降雨等数据为变量计算出每个斜坡单元的稳定系数。
稳定系数分析结果按(0,1.05)、[1.05,1.1)、[1.1,1.2)、[1.2,1.4)区间分段划分为红、橙、黄、蓝4个等级,通过对研究区每个坡面单元的稳定系数的集合和前期易损性评价结果,从而实现对某一降雨过程诱发群发性地质灾害的时空分布及风险等级进行预报预警(图8)。
3.2 应用实例及效果——以龙川县贝岭镇流域为例
本次研究选取近年群发性地质灾害比较突出的广东河源龙川县贝岭镇流域,开展以斜坡为单元的地质灾害动力预警。河源市龙川县贝岭小流域面积为15.29 km2,属中低山地地形,地势北高南低,沟谷两侧山势陡峭、尖峰状、花岗岩呈平缓山顶,“V”型谷居多,地形切割强烈,相对高差500~700 m,地形坡度40°~45°基岩风化强烈,残积层厚10~25 m。2019年6月10日夜间至13日,受“龙舟水”影响,贝岭镇普降暴雨,导致山洪暴发、地质灾害群发,发生72起地质灾害,造成数人死亡以及重大经济损失。
导入龙川贝岭镇小流域的DEM等数据,系统将15.29 km2划分为259个坡面分析单元,并自动批量量测出各坡面单元坡度(α)、坡高(H)、体积(V)等几何物理参数(图9)。
基于小流域浅表层岩土体力学参数(表1),以2019年6月10日夜间至13日期间持续降雨过程期间的实测、预报降雨以及持续降雨时间为变量(持续降雨时长75 h,最大小时雨量48.4 mm,单日最大雨量153.5 mm,累计雨量达到了275.2 mm),计算湿润锋深度Zw,通过基于降雨入渗的斜坡稳定性评价模型批量自动计算各斜坡单元的稳定系数,按红、橙、黄、蓝4个等级显示。分析结果显示,此轮降雨共有22个斜坡单元达到红色预警,10个斜坡单元为橙色预警,38个斜坡单元为黄色预警(图10),黄色及以上斜坡单元与群发性地质灾害实际发生位置比较吻合。
4. 结 论
(1)本文选择典型历史地质灾害,通过物理模型试验,揭示了边坡在暴雨条件下坡面土体在一定深度范围内的含水率、应力及破坏特征,影响因素主要有降雨量、降雨历时、土体类别和坡体结构等因素。
(2)本文通过典型地质灾害数值模拟,揭示了强降雨过程斜坡体应力云图、应变增量场、斜坡稳定系数等变化情况,结果表明受降雨入渗影响,斜坡应力集中带向前扩展比较明显,应变场增量沿坡体上部增量明显,斜坡岩土体容易在浅表层首先造成失稳。
(3)基于降雨入渗导致斜坡体失稳发生机理建立的物理模型试验和数值模型模拟结果,聚焦斜坡残坡积层,将Green-Ampt降雨入渗模型和无限边坡稳定性评价方法相结合,进行优化构建了动力学斜坡稳定性评价模型。
(4)探索了斜坡失稳动力预警模型对广东省暴雨型浅层滑坡灾害气象风险预警的可行性,包括按斜坡单元划分预警分析单元,构建降雨量-斜坡稳定系数动力预警模型,以不同时空雨量为变量动态计算对应时空各斜坡单元的稳定系数,基于稳定性的动态变化实时发布预警等应用流程,并结合龙川县贝岭镇流域应用实例验证了其可行性,可为广东省开展以斜坡单元预警为主要方式的县级地质灾害气象风险预警提供支撑。
-
表 1 天然及暴雨状态下斜坡岩土体计算参数
Table 1 Calculation parameters of rock and soil mass of the slope under natural and rainstorm conditions
名称 弹性模量
/MPa孔隙比 天然状态 饱水状态 γ/(kN·m−3) c/kPa ϕ/(°) γsat/(kN·m−3) c/kPa ϕ/(°) 砂质黏性土①-1 8.0 0.99 18.0 19.1 18.0 18.5 18.1 17.0 砂质黏性土①-2 8.5 0.88 18.1 20.2 19.2 18.7 19.3 18.3 砂质黏性土①-3 9.2 0.83 19.1 28.3 22.5 19.6 26.2 21.1 全风化花岗岩 50.0 0.71 21.0 38.0 35.0 21.5 − − 中风化花岗岩 100.0 0.65 22.0 50.0 45.0 22.5 − − 表 2 河源市龙川县地质灾害数值模拟(部分示例)
Table 2 Numerical simulation of geo-hazards in Longchuan County, Heyuan City (some examples)
灾害体特征 二/三维数值模拟 稳定系数 

1.25
(自然状态)1.01
(饱和状态)

1.22
(自然状态)0.80
(饱和状态) -
[1] 张君霞,黄武斌,李安泰,等. 甘肃省主要地质灾害精细化气象风险预警预报[J]. 干旱区地理,2023,46(9):1443 − 1452. [ZHANG Junxia,HUANG Wubin,LI Antai,et al. Fine meteorological risk early warning forecast of main geological disasters in Gansu Province[J]. Arid Land Geography,2023,46(9):1443 − 1452. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Junxia, HUANG Wubin, LI Antai, et al. Fine meteorological risk early warning forecast of main geological disasters in Gansu Province[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(9): 1443 − 1452. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 刘艳辉,刘传正,连建发,等. 基于显式统计原理的地质灾害区域预警方法初步研究[J]. 中国地质,2008,35(2):344 − 350. [LIU Yanhui,LIU Chuanzheng,LIAN Jianfa,et al. Method of regional early warning of geohazards based on the explicit statistical theory[J]. Geology in China,2008,35(2):344 − 350. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Yanhui, LIU Chuanzheng, LIAN Jianfa, et al. Method of regional early warning of geohazards based on the explicit statistical theory[J]. Geology in China, 2008, 35(2): 344 − 350. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 魏平新,李秀娟. 广东省突发性地质灾害气象预警实践[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(1):138 − 144. [WEI Pingxin,LI Xiujuan. The meteorologic early warning research of sudden geo-hazard in Guangdong Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(1):138 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WEI Pingxin, LI Xiujuan. The meteorologic early warning research of sudden geo-hazard in Guangdong Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2015, 26(1): 138 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 李朝奎,陈建辉,魏振伟,等. 显式统计预警模型下地质灾害预警方法及应用[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):1020 − 1026. [LI Chaokui,CHEN Jianhui,WEI Zhenwei,et al. Method and application of geological hazard early warning based on explicit statistical principle[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):1020 − 1026. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Chaokui, CHEN Jianhui, WEI Zhenwei, et al. Method and application of geological hazard early warning based on explicit statistical principle[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 1020 − 1026. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 李秀娟,魏平新. 广东省典型降雨型滑坡自动监测点变形分析[J]. 西部探矿工程,2019,31(2):5 − 10. [LI Xiujuan,WEI Pingxin. Deformation analysis of automatic monitoring points of typical rainfall landslides in Guangdong Province[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering,2019,31(2):5 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Xiujuan, WEI Pingxin. Deformation analysis of automatic monitoring points of typical rainfall landslides in Guangdong Province[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2019, 31(2): 5 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 童纪伟. 广东省“十三·五” 期间地质灾害发育特征及影响因素分析[J]. 现代矿业,2021,37(10):219 − 221. [TONG Jiwei. Analysis of development characteristics and influencing factors of geological hazards during the “thirteenth five-year plan” period in Guangdong Province[J]. Modern Mining,2021,37(10):219 − 221. (in Chinese with English abstract)] TONG Jiwei. Analysis of development characteristics and influencing factors of geological hazards during the “thirteenth five-year plan” period in Guangdong Province[J]. Modern Mining, 2021, 37(10): 219 − 221. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 陈伟,莫海鸿,陈乐求. 非饱和土边坡降雨入渗过程及最大入渗深度研究[J]. 矿冶工程,2009,29(6):13 − 16. [CHEN Wei,MO Haihong,CHEN Leqiu. Study on rainfall infiltration process and the biggest infiltration depth for unsaturated soil slope[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering,2009,29(6):13 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHEN Wei, MO Haihong, CHEN Leqiu. Study on rainfall infiltration process and the biggest infiltration depth for unsaturated soil slope[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2009, 29(6): 13 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘贤, 揭鸿鹄, 蒋水华, 等. 融合历史降雨下斜坡稳定性观测信息的可靠度分析[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(5):1865 − 1874. [LIU Xian, JIE Honghu, JIANG Shuihua, et al. Slope reliability analysis incorporating observation of stability performance under A past rainfall event[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(5):1865 − 1874. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Xian, JIE Honghu, JIANG Shuihua, et al. Slope reliability analysis incorporating observation of stability performance under A past rainfall event[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(5): 1865 − 1874. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 许旭堂, 鲜振兴, 杨枫, 等. 水-力耦合及干湿循环效应对浅层残积土斜坡稳定性的影响[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):28 − 36. [XU Xutang, XIAN Zhenxing, YANG Feng, et al. Influence of hydraulic-mechanical coupling and dry-wet cycle effect on surficial layer stability of residual soil slopes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):28 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XU Xutang, XIAN Zhenxing, YANG Feng, et al. Influence of hydraulic-mechanical coupling and dry-wet cycle effect on surficial layer stability of residual soil slopes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 28 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李诚诚. 强降雨作用下基于Green-Ampt入渗模型的边坡稳定性分析[D]. 长沙:湖南大学,2019. [LI Chengcheng. Stability analysis of slope based on green-ampt infiltration model under heavy rainfall[D]. Changsha:Hunan University,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Chengcheng. Stability analysis of slope based on green-ampt infiltration model under heavy rainfall[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 马世国. 强降雨条件下基于Green-Ampt入渗模型的无限边坡稳定性研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2014. [MA Shiguo. Study on the stability of infinite slope based on green-ampt infiltration model under intense rainfall[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)] MA Shiguo. Study on the stability of infinite slope based on green-ampt infiltration model under intense rainfall[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 袁畅,宋雁,李慧生,等. 基于降雨监测的群发性滑坡灾害预警技术研究[J]. 广州建筑,2022,50(4):29 − 32. [YUAN Chang,SONG Yan,LI Huisheng,et al. Research on early warning technology of regional mass shallow landslide based on rainfall monitoring[J]. Guangzhou Architecture,2022,50(4):29 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YUAN Chang, SONG Yan, LI Huisheng, et al. Research on early warning technology of regional mass shallow landslide based on rainfall monitoring[J]. Guangzhou Architecture, 2022, 50(4): 29 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 荣广智,张继权,李天涛,等. 极端降水诱发地质灾害链风险评估研究——以贵州省水城县为例[J]. 灾害学,2022,37(4):201 − 210. [RONG Guangzhi,ZHANG Jiquan,LI Tiantao,et al. Risk assessment of extreme precipitation-induced geological disaster chain:A case study of Shuicheng County,Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2022,37(4):201 − 210. (in Chinese with English abstract)] RONG Guangzhi, ZHANG Jiquan, LI Tiantao, et al. Risk assessment of extreme precipitation-induced geological disaster chain: A case study of Shuicheng County, Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2022, 37(4): 201 − 210. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 刘正华,余丰华,夏跃珍,等,基于斜坡单元的地质灾害气象预警系统建设初探[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(6):131-136. [LIU Zhenghua,YU Fenghua,XIA Yuezhen,et al. Primary exploration of the geological hazard meteorological warning system based on slope unit[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(6):131-136. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Zhenghua, YU Fenghua, XIA Yuezhen, et al. Primary exploration of the geological hazard meteorological warning system based on slope unit[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(6): 131-136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 刘艳辉,苏永超. 四川青川县区域地质灾害气象风险预警模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(1):134 − 143. [LIU Yanhui,SU Yongchao. Early-warning model of regional geological disasters based on meteorological factor in Qingchuan County,Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(1):134 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Yanhui, SU Yongchao. Early-warning model of regional geological disasters based on meteorological factor in Qingchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(1): 134 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 罗鸿东,李瑞冬,张勃,等. 基于信息量法的地质灾害气象风险预警模型:以甘肃省陇南地区为例[J]. 地学前缘,2019,26(6):289 − 297. [LUO Hongdong,LI Ruidong,ZHANG Bo,et al. An early warning model system for predicting meteorological risk associated with geological disasters in the Longnan area,Gansu Province based on the information value method[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2019,26(6):289 − 297. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LUO Hongdong, LI Ruidong, ZHANG Bo, et al. An early warning model system for predicting meteorological risk associated with geological disasters in the Longnan area, Gansu Province based on the information value method[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(6): 289 − 297. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 阳帅, 谭泽颖, 陈宏信, 等. 基于修正Green-Ampt模型的降雨诱发区域浅层斜坡失稳灾害分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):219 − 227. [YANG Shuai, TAN Zeying, CHEN Hongxin, et al. Analysis of instability disaster of rainfall induced shallow landslides at the regional scale based on the modified Green Ampt model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):219 − 227. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Shuai, TAN Zeying, CHEN Hongxin, et al. Analysis of instability disaster of rainfall induced shallow landslides at the regional scale based on the modified Green Ampt model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 219 − 227. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 缪海波, 王功辉. 风振影响下乔木坡地暴雨型浅层滑坡演化机制[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):60 − 70. [MIAO Haibo, WANG Gonghui. Evolution mechanism of rainstorm-induced shallow landslides on slopes covered by arbors considering the influence of wind-induced vibration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):60 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)] MIAO Haibo, WANG Gonghui. Evolution mechanism of rainstorm-induced shallow landslides on slopes covered by arbors considering the influence of wind-induced vibration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 60 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 曾新雄,刘佳,赖波,赵风顺,江山. 广东珠海市降雨型崩塌滑坡预警阈值研究. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 141-150 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 李建颖,蔡文权,张国沅,纪振付,张明亮. 不同降雨工况下地质灾害综合评价——以汕头市潮阳区金灶镇重点调查区为例. 中国资源综合利用. 2024(10): 81-87+92 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 韦勇. 广东省韶关市2009-2023年地下水变化特征研究. 云南地质. 2024(04): 577-581 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:



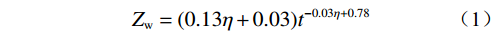
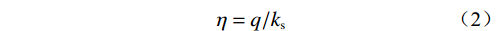
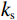
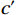
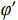
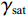
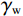






 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS