Susceptibility analysis on influencing factors of rockfalls and landslides in Tibet
-
摘要: 西藏地区地形地貌复杂,构造活动强烈,气候条件多样,地质灾害频发,对全区经济建设和社会发展的影响日趋显著。其中,崩塌、滑坡是西藏地区常见的地质灾害,为了定量分析研究区内崩塌、滑坡影响因子的敏感性,文中基于GIS与确定性系数分析方法,选取了坡度、坡向、地形起伏度、坡形、高程、距地质构造距离、河网密度、工程地质岩组等8个因子开展了崩塌、滑坡影响因子敏感性分析。分析结果表明:(1)西藏地区崩塌、滑坡影响因子高敏感性区间为:斜坡坡度大于30°,坡向为南东向、南向、南西向,地形起伏度在200~800 m/km2,坡形为凹形坡,高程在1 500~4 500 m,距地质构造距离0~3 km,河网密度>0.5 km/km2,代号为YJ2、TS1、TS2、BZ1的岩组,灾害与影响因子之间表现出较好的相关性。(2)影响因子间的敏感性大小:坡度>工程地质岩组>高程>坡形>河网密度>地形起伏度>坡向>距地质构造距离。研究结果对西藏地区崩塌、滑坡易发性评价工作提供了参考。Abstract: Geological disasters such as rockfalls and landslides are common in the Tibet region due to its complex topography, strong tectonic movements, and diverse climate conditions. These disasters have an increasingly significant impact on the region's economic construction and social development. In order to assess the susceptibility of rockfalls and landslides in a quantitative manner, this study selected eight factors, including slope, aspect, topographic relief, slope shape, elevation, distance to fault, river density, and engineering geological group, to conduct the sensitivity analysis of the influencing factors by applying GIS and certainty factor analysis methods. The research shows that there is a direct correlation between rockfall, landslide and influencing factors, and the susceptibility of these hazards is high in the areas with: (1) a slope greater than 30°, (2) aspect facing southeast, south, or southwest direction, (3) topographic relief of 200~800 m/km2, (4) concave slope, (5) elevation between 1500 and 4500 m, (6) distance between 0 and 3 km to fault, (7) river density greater than 0.5 km/km2, (8) lithologies identified by the codes of YJ2, TS1, TS2, and BZ1. The susceptibility of the factors is ranked in descending order as slope > engineering geological group > elevation > slope shape > river density > topographic relief > aspect > distance to fault. These results can be used as a reference for assessing the susceptibility of rockfalls and landslides in Tibet.
-
Keywords:
- Tibet region /
- rockfall /
- landslide /
- influencing factor /
- susceptibility analysis /
- certainty factor
-
0. 引言
地质灾害敏感性评价是地质灾害风险评价工作的基础,它是以地质环境背景条件为基础,参考区内不同影响因子与已有地质灾害发育及分布关系,分析相关因子的敏感性大小[1]。早期的地质灾害敏感性评价研究多以定性评价为主,如李渝生[2]在雅砻江中上游雅江至打罗段480 km长岸坡岩体变形破坏的系统调研基础之上,分析了主要典型崩塌滑坡灾害的成因机制及其影响因素的敏感性。惠振德等[3]在历史文献、遥感信息和实地考察资料分析研究的基础之上,对陕南山区滑坡发育特征进行了归纳,分析了岩性与构造、地貌条件、植被因子、气候因素及人类活动对滑坡发育敏感性的影响。随着3S技术的快速发展,空间数据获取及分析能力得到极大提升,目前地质灾害敏感性评价研究多以定量分析为主,尤其是基于GIS的逻辑回归法、信息量法以及确定性系数法等定量评价方法的组合使用在地质灾害敏感性评价中得到了广泛的应用并取得良好效果。如张辉等[4]基于GIS空间分析和确定性系数分析方法对滇东北滑坡孕灾环境因子敏感性分析;覃乙根等[5]采用确定性系数模型(CF)对开阳县斜坡地质灾害孕灾因子敏感性分析;吴森等[6]基于贡献率权重法对平昌县滑坡影响因子敏感性进行了分析;杨先全等[7]采用层次分析法对肯尼亚滑坡敏感性进行了分析评价;杨光等[8]采用确定性系数+层次分析法(CF-AHP)、确定性系数+逻辑回归方法(CF-LR) 和确定性系数+神经网络的多层感知器方法(CF-MLP) 3种方法对研究区滑坡敏感性进行了评价;张晓东等[9]分别采用信息量模型+逻辑回归模型(I+LR)和确定性系数模型+逻辑回归模型(CF+LR) 2种组合模型对盐池县地质灾害敏感性进行评价。
西藏地区是中国地质灾害最严重的省(区)之一,地质灾害对全区经济建设和社会发展的影响日趋显著。部分学者已在该区域开展了相关的地质灾害敏感性的相关研究工作,熊德清等[10]以西藏日喀则地区为例,对喜马拉雅山脉地震带主要地质灾害与地形地貌因子关系开展了分析与评价;孙妍等[11]基于RS与GIS综合分析了G318拉萨—日喀则段内地质灾害与地形地貌、岩性构造、水文气象的关系;杜国梁等[12]基于逻辑回归-信息量模型,选取岩性、坡度、坡向、坡形、地形起伏度、地形粗糙度、断裂密度和河流距离8个因子作为评价因子,分析了各因子的敏感性,最终对川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性进行了分析与评价。虽然前人已经在西藏地区开展了相关的地质灾害敏感性研究工作,但多为某一区域或结合某一线状工程,鲜有针对全区地灾敏感性分析研究。本文以西藏为研究区,以区内现有的崩塌与滑坡灾害为样本,基于确定性系数模型,选取相关因子,对西藏地区崩塌、滑坡影响因子敏感性进行了分析与评价。研究结果可以对西藏地区崩塌、滑坡易发性评价工作提供参考与借鉴。
1. 研究区概况
西藏位于我国西南边陲,平均海拔4000 m,素有“世界屋脊”之称,面积122.84×104 km2,约占中国总面积的1/8[13]。区内地质构造复杂,地震多发频发,地形切割强烈,水网发育密集,地形高差悬殊,地层岩性多样,气候复杂多变,降水时空分布不均。区内地质灾害具有“点多面广、险情重、危害大、成灾快”特点[14]。
根据西藏地质灾害详细调查数据库,截至2020年底,全区共发育崩塌、滑坡地质灾害点共计4 717处(图1)。其中滑坡2 388处(含不稳定斜坡1 003处),崩塌2 329处,多分布于藏南、藏东地区。
2. 影响因子敏感性分析方法
确定性系数方法是一种概率函数统计方法,它可以通过已发生灾害建立与影响因子之间的关系,通过确定性系数来表征影响因子对灾害贡献的敏感程度[4-5,8,15],其计算公式如下:
$$ {CF}_{ij}=\left\{\begin{aligned}&\frac{{P}_{i}{P}_{j}-{PP}_{{\rm{S}}}}{{P}_{i}{P}_{j}\left(1-{PP}_{{\rm{S}}}\right)},&{P}_{i}{P}_{j}\geqslant {PP}_{{\rm{S}}}\\ &\frac{{P}_{i}{P}_{j}-{PP}_{{\rm{S}}}}{{PP}_{S}\left(1-{P}_{i}{P}_{j}\right)},&{P}_{i}{P}_{j} < {PP}_{{\rm{S}}}\end{aligned}\right. $$ (1) 式中:CFij ——第i个影响因子下第j个分级的确定性系 数值,用以表征其对灾害的敏感性,其值 域为[−1,1],正值代表灾害发生的确定性 高,表明该评价单元为灾害易发单元,负 值代表确定性低,表示评价单元不易发 生灾害,当CF值接近于0时,表示条件 概率与先验概率很接近,无法确定评价 单元是否为灾害易发区[14];
PiPj—第i个影响因子下第j个分级内灾害发生 的概率,用其分级区间内灾害发育密度 表示/(处·km−2);
PPS —灾害事件在整个研究区中发生的先验概 率,用研究区内灾害发育平均密度表示/ (处·km −2)。
通过求取灾害影响因子下各分级的确定性系数值的标准差,用以表征灾害影响因子间的敏感性大小,其计算公式如下:
$$ {CF}_{i}=\sqrt{\frac{1}{n} \sum _{j=1}^{n}{\left({CF}_{ij}-\overline{{CF}_{i}}\right)}^{2}} $$ (2) 式中:CFi—第i个影响因子的确定性系数值,用以表征该影响因子对灾害的敏感性,以CFij的标准差表示,该值可以衡量因子内部确定性系数值的波动大小,其值域为[0,1],值越大表明该因子敏感性越高;
n——第i个影响因子分级数量;
$ \overline{{CF}_{i}} $ —第i个影响因子下所有分级确定性系数的平均值;CFij ——同式(1)。
3. 崩塌、滑坡影响因子敏感性分析
结合西藏地区地质灾害详细调查、典型灾害点勘查资料研究分析,以30 m精度的数字高程模型(DEM)、西藏自治区1∶100万地质图等数据作为基础数据图层,选取坡度、坡向、地形起伏度、坡形、高程、距地质构造距离、河网密度、工程地质岩组等8个因子作为西藏地区崩塌、滑坡敏感性影响因子,基于GIS与确定性系数分析方法分别对各影响因子敏感性进行分析。
(1)坡度
地形坡度是崩塌、滑坡发生的重要条件,地形坡度大小对斜坡表面径流量、斜坡表体岩土体剩余下滑力等都影响巨大,可以在一定程度上影响着崩塌、滑坡发育的强度和规模。以5°为间隔将研究区坡度划分为12级(表1),见图2(a),坡度分类敏感性分布图,见图3(a)表明:研究区内不同坡度与崩塌、滑坡的发育有密切的关联,呈现较好的正相关性,即随着坡度增加,CFij呈现逐步递增趋势,区内崩塌、滑坡主要分布在大于30°斜坡范围,且坡度越大,敏感性越高。
表 1 影响因子分级标准及确定性系数值Table 1. Classification standard for influencing factors and value of certainty factors影响因子 因子分级 灾害点/处 PiPj/(处·km−2) CFij CFi 坡度/ (°) [0,5] 0 0.000 00 −1.000 0.79 (5,10] 7 0.000 04 −0.990 (10,15] 55 0.000 41 −0.894 (15,20] 115 0.001 00 −0.741 (20,25] 233 0.002 21 −0.425 (25,30] 374 0.003 90 0.015 (30,35] 565 0.007 03 0.456 (35,40] 724 0.012 71 0.701 (40,45] 855 0.026 24 0.857 (45,50 779 0.048 39 0.924 (50,55] 576 0.074 80 0.952 >55 434 0.070 67 0.949 坡向 平地 0 0.000 00 −1.000 0.36 北向 473 0.003 01 −0.217 北东 434 0.002 88 −0.250 东向 564 0.003 75 −0.022 南东 676 0.004 68 0.180 南向 795 0.005 08 0.245 南西 778 0.005 15 0.255 西向 550 0.003 73 −0.030 北西 447 0.003 15 −0.181 地形起伏度/( m·km−2) [0,100] 65 0.000 18 −0.952 0.49 (100,200] 378 0.001 71 −0.557 (200,300] 871 0.005 04 0.239 (300,400] 1 242 0.007 57 0.495 (400,500] 1 110 0.008 71 0.561 (500,600] 594 0.007 16 0.466 (600,700] 263 0.005 24 0.268 (700,800] 129 0.004 52 0.151 (800,900] 42 0.002 81 −0.270 >900 23 0.001 99 −0.483 坡形
(负值为凹形坡,
0为直线形坡,
正值为凸形坡,
负值越大坡形越凹,
正值越大坡形越凸)−4 41 0.048 35 0.924 0.59 −3 231 0.034 19 0.891 −2 918 0.016 77 0.774 −1 1 147 0.007 03 0.455 0 1 288 0.002 02 −0.475 1 741 0.002 89 −0.248 2 261 0.003 62 −0.058 3 84 0.002 71 −0.295 4 6 0.001 05 −0.728 高程/ m [0,1 000] 31 0.002 28 −0.407 0.68 (1 000,1 500] 34 0.003 30 −0.141 (1 500,2 000 113 0.010 31 0.630 (2 000,2 500] 121 0.011 36 0.664 (2 500,3 000] 297 0.023 65 0.841 (3 000,3 500] 796 0.042 13 0.912 (3 500,4 000] 1 348 0.030 21 0.876 (4 000,4 500] 1 335 0.010 64 0.642 (4 500,5 000] 590 0.001 19 −0.691 >5 000 52 0.000 11 −0.972 距地质构造
距离/ km[0,1] 855 0.006 32 0.394 0.33 (1,2] 748 0.005 97 0.358 (2,3] 583 0.005 24 0.268 (3,4] 417 0.004 26 0.098 (4,5] 351 0.004 04 0.049 (5,6] 314 0.004 06 0.055 (6,7] 217 0.003 16 −0.177 (7,8] 128 0.002 11 −0.451 (8,9] 98 0.001 85 −0.520 (9,10] 95 0.002 04 −0.468 >10 911 0.002 49 −0.352 河网密度/( km·km−2) [0,0.25] 339 0.000 64 −0.834 0.56 (0.25,0.50] 645 0.002 38 −0.380 (0.50,0.75] 1 574 0.006 97 0.451 (0.75,1.00] 1 381 0.010 35 0.631 (1.00,1.25] 591 0.011 53 0.670 (1.25,1.50] 168 0.012 77 0.702 >1.50 19 0.007 37 0.481 工程地质岩组 坚硬块状中酸性岩岩组(YJ1) 16 0.000 08 −0.979 0.73 坚硬—较坚硬块状基性超基性岩岩组(YJ2) 904 0.057 63 0.937 坚硬—较坚硬层状块状火山岩组(YJ3) 120 0.002 64 −0.314 坚硬层状砂岩岩组(SX1) 51 0.000 31 −0.920 较坚硬—软弱层状砾岩、粉砂岩、泥岩岩组(SX2) 984 0.003 90 0.015 坚硬层状—块状弱岩溶化灰岩岩组(TS1) 1 047 0.016 22 0.766 坚硬—较坚硬层状弱岩溶化灰岩夹碎屑岩岩组(TS2) 898 0.006 85 0.441 坚硬—较坚硬块状混合岩岩组(BZ1) 556 0.012 67 0.700 较坚硬—较软弱层块状片岩、片麻岩岩组(BZ2) 29 0.000 15 −0.960 第四系松散岩组(Q) 112 0.001 09 −0.717 (2)坡向
坡向即坡面的朝向,因为不同坡向的斜坡接受太阳的辐射强度不同,直接影响着坡面植被覆盖及岩体的风化程度,最终影响着崩塌、滑坡发生的可能。将研究区坡向划分为9级(表1),见图2(b),坡向分类敏感性分布图,见图3(b)表明:研究区内不同坡向分区与崩塌、滑坡的发育有一定的关联,CFij在南东向、南向、南西向坡为正值,这3个坡向为主要的向阳坡,该3个坡向区间受温差、蒸发影响,植被发育较少,岩体物理风化严重,这些地方是崩塌、滑坡的高易发区。
(3)地形起伏度
地形起伏度表示区域的相对高差,代表地形起伏状况与地表支离破碎程度。以100 m/km2为间隔将研究区地形起伏度划分为10级(表1),见图2(c),地形起伏度分类敏感性分布图,见图3(c)表明:地形起伏度与崩塌、滑坡存在“单峰”正态分布特征,在200~800 m/km2具有较高的敏感性。
(4)坡形
坡形是指斜坡地表坡面的弯曲形态,一般可以分为凹形坡、直线形坡、凸形坡。坡形能够通过影响岩土体应力状态和地下水分布,进而影响斜坡稳定性[15]。按照坡形从凹形→直线形→凸形划分为9个等级,其中负值为凹形坡,0为直线形坡,正值为凸形坡,负值越大坡形越凹,正值越大坡形越凸[16](表1),见图2(d)。坡形分类敏感性分布图,见图3(d)表明:研究区内不同坡形分区与崩塌、滑坡的发育存在负相关关系,随着坡形从凹形→直线形→凸形,CFij呈现逐步递减趋势,说明区内崩塌、滑坡主要分布在凹型坡,且凹形坡越凹,灾害越易发,敏感性越高,这主要是由于区内凹形负地形坡易形成汇水,汇水沿斜坡入渗,降低岩土体抗剪强度,从而影响崩塌、滑坡的发生。
(5)高程
研究区内高程24~8 848 m分布不等,不同高程范围内气候、人类工程活动强度不同,影响着崩塌、滑坡的发生。以500 m为间隔将研究区高程划分为10级(表1),见图2(e),高程分类敏感性分布图,见图3(e)表明:高程与崩塌、滑坡存在“单峰”正态分布关系,高程在1500~4500 m,CFij为正值,表明该高程范围内具有较高的灾害敏感性。该区间为人类主要工程活动聚集区,人类通过不同的活动改变着周边的地质环境,且该区间范围内年平均降雨较大,从而影响着崩塌、滑坡的发生[17]。
(6)距地质构造距离
区内地质构造复杂,强烈的构造作用使得区内地层十分破碎,为崩塌、滑坡的发育提供了有利的条件。以1 km为缓冲步长,按照距离断裂距离不同,由远及近划分为11级(表1),见图2(f)。距地质构造距离分类敏感性分布图,见图3(f)表明:地质构造与崩塌、滑坡具有显著正相关性,随着距离增加,崩塌、滑坡发育呈现明显递减趋势,在0~3 km范围内,地质构造对崩塌、滑坡敏感性较高。
(7)河网密度
受构造运动影响,研究区内河网密布,以0.25 km/km2为间隔将研究区河网密度划分为7级(表1),见图2(g)。河网密度分类敏感性分布图,见图3(g)表明:研究区内不同河网密度分区与灾害的发育有显著的关联,崩塌、滑坡在河网密度>0.5 km/km2具有较高的敏感性;随着河网密度增加,CFij呈现逐步递增趋势;当大于1.50 km/km2时,CFij曲线出现下降拐点,这主要是由于斜坡在受到河流侵蚀、侧蚀作用导致坡脚掏蚀,沟谷地应力分布状态发生变化,引起斜坡卸荷拉裂,加之河流水位升降等均易增加斜坡不稳定性[16],当河网密度大于一定程度时,地形起伏较小,崩塌、滑坡发育密度受其影响有所降低。
(8)工程地质岩组
地层是崩塌、滑坡发生的物质基础,综合考虑地层岩性、岩体结构及力学强度等因素,将区内工程地质岩组划分为10种类型[18-19](表1),见图2(h)。工程地质岩组分类敏感性分布图,见图3(h)表明:研究区内不同工程地质岩组与崩塌、滑坡的发育有一定的关联,崩塌、滑坡在坚硬—较坚硬块状基性超基性岩岩组(YJ2)、坚硬层状—块状弱岩溶化灰岩岩组(TS1)、坚硬—较坚硬层状弱岩溶化灰岩夹碎屑岩岩组(TS2)、坚硬—较坚硬块状混合岩岩组(BZ1)具有较强的敏感性。
4. 结论
结合西藏地区地质环境背景,基于GIS与确定性系数分析方法,对8个崩塌、滑坡影响因子开展了敏感性分析,研究结果形成以下认识:
(1)从地形地貌条件上来看,研究区内崩塌、滑坡在坡度大于30°斜坡范围内,坡向为南东向、南向、南西向,地形起伏度在200~800 m/km2,高程在1500~4500 m范围内,崩塌、滑坡敏感性较高。与其它地区不同,区内崩塌、滑坡在凹形坡表现出的敏感性最高,直线形坡次之,凸形坡敏感性最差,这主要是由于区内斜坡土体以粗颗粒碎块石土为主,凹形负地形坡易形成地表水积蓄,汇水沿斜坡入渗,降低岩土体抗剪强度,从而影响崩塌、滑坡的发生。
(2)区内崩塌、滑坡受地质构造控制显著,灾害沿断裂呈现明显的“带状”分布特征,地质构造与崩塌、滑坡具有显著正相关性,随着距离增加,崩塌、滑坡发育呈现明显递减趋势,在0~3 km范围内,地质构造对崩塌、滑坡敏感性较高。
(3)区内崩塌、滑坡呈现沿河网展布的特征,崩塌、滑坡在河网密度>0.5 km/km2具有较高的敏感性;随着河网密度增加,敏感性呈现逐步递增趋势,当大于1.50 km/km2时,敏感性有所降低。
(4)坚硬-较坚硬块状基性超基性岩岩组(YJ2)、坚硬层状-块状弱岩溶化灰岩岩组(TS1)、坚硬—较坚硬层状弱岩溶化灰岩夹碎屑岩岩组(TS2)、坚硬—较坚硬块状混合岩岩组(BZ1)为区内崩塌、滑坡的高敏感性岩组。
(5)选取的8个影响因子敏感性大小依次为:坡度>工程地质岩组>高程>坡形>河网密度>地形起伏度>坡向>距地质构造距离。
-
表 1 影响因子分级标准及确定性系数值
Table 1 Classification standard for influencing factors and value of certainty factors
影响因子 因子分级 灾害点/处 PiPj/(处·km−2) CFij CFi 坡度/ (°) [0,5] 0 0.000 00 −1.000 0.79 (5,10] 7 0.000 04 −0.990 (10,15] 55 0.000 41 −0.894 (15,20] 115 0.001 00 −0.741 (20,25] 233 0.002 21 −0.425 (25,30] 374 0.003 90 0.015 (30,35] 565 0.007 03 0.456 (35,40] 724 0.012 71 0.701 (40,45] 855 0.026 24 0.857 (45,50 779 0.048 39 0.924 (50,55] 576 0.074 80 0.952 >55 434 0.070 67 0.949 坡向 平地 0 0.000 00 −1.000 0.36 北向 473 0.003 01 −0.217 北东 434 0.002 88 −0.250 东向 564 0.003 75 −0.022 南东 676 0.004 68 0.180 南向 795 0.005 08 0.245 南西 778 0.005 15 0.255 西向 550 0.003 73 −0.030 北西 447 0.003 15 −0.181 地形起伏度/( m·km−2) [0,100] 65 0.000 18 −0.952 0.49 (100,200] 378 0.001 71 −0.557 (200,300] 871 0.005 04 0.239 (300,400] 1 242 0.007 57 0.495 (400,500] 1 110 0.008 71 0.561 (500,600] 594 0.007 16 0.466 (600,700] 263 0.005 24 0.268 (700,800] 129 0.004 52 0.151 (800,900] 42 0.002 81 −0.270 >900 23 0.001 99 −0.483 坡形
(负值为凹形坡,
0为直线形坡,
正值为凸形坡,
负值越大坡形越凹,
正值越大坡形越凸)−4 41 0.048 35 0.924 0.59 −3 231 0.034 19 0.891 −2 918 0.016 77 0.774 −1 1 147 0.007 03 0.455 0 1 288 0.002 02 −0.475 1 741 0.002 89 −0.248 2 261 0.003 62 −0.058 3 84 0.002 71 −0.295 4 6 0.001 05 −0.728 高程/ m [0,1 000] 31 0.002 28 −0.407 0.68 (1 000,1 500] 34 0.003 30 −0.141 (1 500,2 000 113 0.010 31 0.630 (2 000,2 500] 121 0.011 36 0.664 (2 500,3 000] 297 0.023 65 0.841 (3 000,3 500] 796 0.042 13 0.912 (3 500,4 000] 1 348 0.030 21 0.876 (4 000,4 500] 1 335 0.010 64 0.642 (4 500,5 000] 590 0.001 19 −0.691 >5 000 52 0.000 11 −0.972 距地质构造
距离/ km[0,1] 855 0.006 32 0.394 0.33 (1,2] 748 0.005 97 0.358 (2,3] 583 0.005 24 0.268 (3,4] 417 0.004 26 0.098 (4,5] 351 0.004 04 0.049 (5,6] 314 0.004 06 0.055 (6,7] 217 0.003 16 −0.177 (7,8] 128 0.002 11 −0.451 (8,9] 98 0.001 85 −0.520 (9,10] 95 0.002 04 −0.468 >10 911 0.002 49 −0.352 河网密度/( km·km−2) [0,0.25] 339 0.000 64 −0.834 0.56 (0.25,0.50] 645 0.002 38 −0.380 (0.50,0.75] 1 574 0.006 97 0.451 (0.75,1.00] 1 381 0.010 35 0.631 (1.00,1.25] 591 0.011 53 0.670 (1.25,1.50] 168 0.012 77 0.702 >1.50 19 0.007 37 0.481 工程地质岩组 坚硬块状中酸性岩岩组(YJ1) 16 0.000 08 −0.979 0.73 坚硬—较坚硬块状基性超基性岩岩组(YJ2) 904 0.057 63 0.937 坚硬—较坚硬层状块状火山岩组(YJ3) 120 0.002 64 −0.314 坚硬层状砂岩岩组(SX1) 51 0.000 31 −0.920 较坚硬—软弱层状砾岩、粉砂岩、泥岩岩组(SX2) 984 0.003 90 0.015 坚硬层状—块状弱岩溶化灰岩岩组(TS1) 1 047 0.016 22 0.766 坚硬—较坚硬层状弱岩溶化灰岩夹碎屑岩岩组(TS2) 898 0.006 85 0.441 坚硬—较坚硬块状混合岩岩组(BZ1) 556 0.012 67 0.700 较坚硬—较软弱层块状片岩、片麻岩岩组(BZ2) 29 0.000 15 −0.960 第四系松散岩组(Q) 112 0.001 09 −0.717 -
[1] 韩培锋,王镁河,姜兆华,等. 西藏吉隆县地质灾害及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(2):111 − 118. [HAN Peifeng,WANG Meihe,JIANG Zhaohua,et al. Geological disasters and their influencing factors in Jilong County,Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(2):111 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN Peifeng, WANG Meihe, JIANG Zhaohua, et al. Geological disasters and their influencing factors in Jilong County, Tibet [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(2): 111-118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 李渝生. 雅砻江(雅江—打罗段)岸坡崩塌、滑坡地质灾害形成条件及典型实例分析[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,1992,3(2):30 − 39. [LI Yusheng. Formation conditions and typical examples of collapse and landslide along Yalong River (Yajiang and Daluo section)[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservtion,1992,3(2):30 − 39. (in Chinese) LI Yusheng. Formation conditions and typical examples of collapse and landslide along Yalong River (Yajiang and Daluo section)[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservtion, 1992(02): 30-39+46. (in Chinese)
[3] 惠振德,李晓玲,孙虎. 陕南山区滑坡发育特征与敏感性分析[J]. 陕西师大学报(自然科学版),1996,24(1):96 − 101. [HUI Zhende,LI Xiaoling,SUN Hu. Characteristics and sensitivity of landslide in mountainous areas of southern Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition),1996,24(1):96 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUI Zhende, LI Xiaoling, SUN Hu. Characteristics and sensitivity of landslide in mountainous areas of Southern Shaanxi province [J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 1996, 24(1): 96-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张辉,谈树成,汪栟旭. 滇东北滑坡孕灾环境因子敏感性分析[J]. 人民长江,2020,51(11):134 − 139. [ZHANG Hui,TAN Shucheng,WANG Bingxu. Sensitivity analysis on environmental factors for landslides in northeastern Yunnan[J]. Yangtze River,2020,51(11):134 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2020.11.023 ZHANG Hui, TAN Shucheng, WANG Benxu. Sensitivity analysis on environmental factors for landslides in Northeastern Yunnan [J]. Yangtze River, 2020, 51(11): 134-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2020.11.023
[5] 覃乙根,杨根兰,谢金,等. 贵州省开阳县斜坡地质灾害孕灾因子敏感性分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(4):190 − 198. [QIN Yigen,YANG Genlan,XIE Jin,et al. Sensitivity analysis of disaster-pregnant environmental factors for slope geological hazards in Kaiyang County,Guizhou Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2020,48(4):190 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.026 QIN Yigen, YANG Genlan, XIE Jin, et al. Sensitivity analysis of disaster-pregnant environmental factors for slope geological hazards in Kaiyang County, Guizhou Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(04): 190-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.04.026
[6] 吴森,李虎杰,陈国辉,等. 基于贡献率权重法的区域滑坡影响因子敏感性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2016,27(1):26 − 31. [WU Sen,LI Hujie,CHEN Guohui,et al. Regional landslides influence factors sensitivity analysis based on contributing weight method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2016,27(1):26 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Sen, LI Hujie, CHEN Guohui, et al. Regional landslides influence factors sensitivity analysis based on contributing weight method [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2016, 27(01): 26-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 杨先全,周苏华,邢静康,等. 肯尼亚滑坡灾害分布特征及敏感性区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):65 − 74. [YANG Xianquan,ZHOU Suhua,XING Jingkang,et al. Distribution patterns and susceptibility mapping of landslides in Kenya[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):65 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.05.09 YANG Xianquan, ZHOU Suhua, XING Jingkang, et al. Distribution patterns and susceptibility mapping of landslides in Kenya [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(05): 65-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.05.09
[8] 杨光,徐佩华,曹琛,等. 基于确定性系数组合模型的区域滑坡敏感性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(5):1153 − 1163. [YANG Guang,XU Peihua,CAO Chen,et al. Assessment of regional landslide susceptibility based on combined model of certainty factor method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(5):1153 − 1163. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Guang, XU Peihua, CAO Shen, et al. Assessment of regional landslide susceptibility based on combined model of certainty factor method [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(05): 1153-1163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 张晓东,刘湘南,赵志鹏,等. 信息量模型、确定性系数模型与逻辑回归模型组合评价地质灾害敏感性的对比研究[J]. 现代地质,2018,32(3):602 − 610. [ZHANG Xiaodong,LIU Xiangnan,ZHAO Zhipeng,et al. Comparative study of geological hazards susceptibility assessment:Constraints from the information value + logistic regression model and the CF + logistic regression model[J]. Geoscience,2018,32(3):602 − 610. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Xiaodong, LIU Xiangnan, ZHAO Zhipeng, et al. Comparative study of geological hazards susceptibility assessment: constraints from the information value + logistic regression model and the CF + logistic regression model [J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(03): 602-610. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 熊德清, 崔笑烽. 喜马拉雅山脉地震带主要地质灾害与地形地貌关系—以西藏日喀则地区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(11): 1967 − 1980 XIONG Deqing, CUI Xiaofeng. The relationship between main geological hazard and topography in the Himalayan seismic belt: A case study in the Xigaze area, Tibet [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(11): 1967 − 1980. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 孙妍,陈海云,张志,等. G318拉萨-日喀则沿线地质灾害分布规律及其影响因素[J]. 自然灾害学报,2014,23(4):111 − 119. [SUN Yan,CHEN Haiyun,ZHANG Zhi,et al. Distribution regularities of geological hazards along the G318 Lhasa-Shigatse section and their influence factors[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2014,23(4):111 − 119. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13577/j.jnd.2014.0415 SUN Yan, CHEN Haiyun, ZHANG Zhi, et al. Distribution regularities of geological hazards along the G318 Lhasa-Shigatse section and their influence factors[J]. , 2014, 23(04): 111-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13577/j.jnd.2014.0415
[12] 杜国梁,杨志华,袁颖,等. 基于逻辑回归–信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang,YANG Zhihua,YUAN Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression- information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, REN Sanshao, REN Tao. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression- information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 102-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 姚杰. 西藏地区国道318线泥石流灾害分析与防治措施[D].重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2012 YAO Jie. Debris flow disaster analysis and prevention and control measures of national highway No. 318 in Tibet[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 罗开洋, 苏鹏程, 李胜伟, 等. 西藏自治区地质灾害调查评价工作方案[R]. 拉萨: 西藏自治区国土资源厅, 2018 LUO Kaiyang, SU Pengcheng, LI Shengwei, et al. Work plan report of geological hazard investigation and assessment in Tibet Region[R]. Lhasa: Department of Land and Resources of Tibet Autonomous Region, 2018. (in Chinese)
[15] 冯杭建,周爱国,唐小明,等. 基于确定性系数的降雨型滑坡影响因子敏感性分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(2):436 − 446. [FENG Hangjian,ZHOU Aiguo,TANG Xiaoming,et al. Susceptibility analysis of factors controlling rainfalltriggered landslides using certainty factor method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(2):436 − 446. (in Chinese with English abstract) FENG Hangjian, ZHOU Aiguo, TANG Xiaoming, et al. Susceptibility analysis of factors controlling rainfall-triggered landslides using certainty factor method [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(02): 436-446. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 杨志华,张永双,郭长宝,等. 青藏高原东缘地质灾害影响因子敏感性分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(3):673 − 683. [YANG Zhihua,ZHANG Yongshuang,GUO Changbao,et al. Sensitivity analysis on causative factors of geohazards in eastern margin of Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(3):673 − 683. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Zhihua, ZHANG Yongshuang, GUO Changbao, et al. Sensitivity analysis on causative factors of geohazards in eastern margin of Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(03): 673-683. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 吴森,李虎杰,张魁,等. 高程因素对平昌县滑坡灾害发育的敏感性分析[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版),2015,37(4):62 − 66. [WU Sen,LI Hujie,ZHANG Kui,et al. Sensitivity analysis of elevation to landslide growth in Pingchang County[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University(Natural Sciences),2015,37(4):62 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Sen, LI Hujie, ZHANG Kui, et al. Sensitivity analysis of elevation to landslide growth in Pingchang County [J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University(Natural Sciences), 2015, 37(04): 62-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 周成灿, 吕文明, 赵炜, 等. 西藏自治区县(市)地质灾害调查与区划综合研究报告[R]. 拉萨: 西藏自治区地质环境监测总站, 2010 ZHOU Chengcan, LYU Wenming, ZHAO Wei, et al. Comprehensive research report on geological disaster investigation and zoning in Tibet Autonomous Region with the scale of county [R]. Lhasa: Geological Environmental Monitoring Station of Tibet Autonomous Region, 2010. (in Chinese)
[19] 彭勃,赵拓飞,李宝龙,等. 西藏拉萨地块阿翁错北二长花岗岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学及Hf同位素制约[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(5):1594 − 1609. [PENG Bo, ZHAO Tuofei, LI Baolong, et al. Petrogenesis of the monzonitic granite from the north Awengcuo of Lhasa Terrane, Tibet: Constraints from zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and Hf isotopic composition[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(5):1594 − 1609. (in Chinese with English abstract) PENG Bo, ZHAO Tuofei, LI Baolong, et al. Petrogenesis of the monzonitic granite from the north Awengcuo of Lhasa Terrane, Tibet: Constraints from zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and Hf isotopic composition[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2022, 52 (5):1594-1609.(in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 陈玉波,徐世光,陈梦瑞. 以确定性系数法为基础的不同滑坡易发性评价模型对比分析——以云南保山盆地为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2025(01): 119-130 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 郭英,申健,刘晓晓,周亮,石向菲,王聪毅. 北京门头沟区“23·7”特大暴雨诱发地质灾害特征及分布规律研究. 中国防汛抗旱. 2025(03): 39-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘磊磊,肖浩,王璨,姚腾飞. 湖南红层地区滑坡地质灾害致灾因子敏感性分析. 矿冶工程. 2024(04): 169-174 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 卫璐宁,郭永刚. 西藏崩滑流地质灾害孕灾环境分区及形成机制. 西藏科技. 2024(09): 25-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 周鹏,万忠焱,李强,元旦措姆,西若平措,索朗拥措,巴桑吉巴. 拉萨市堆龙德庆区滑坡灾害时空分布规律和孕灾背景分析. 西藏科技. 2024(11): 37-42+75 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 余明威,郭永刚,苏立彬. 西藏林芝地区崩滑流灾害影响因子定量评价. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(06): 33-43 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 欧家婷,陶治强,刘宇宁,刘文荐,朱亦舒. 山南地区某滑坡稳定性分析. 农业灾害研究. 2024(11): 65-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
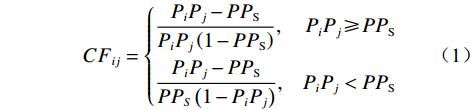
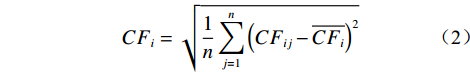


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS