Dynamic analysis and prediction of rear slope affected area of the Jianshanying landslide in Shuicheng County, Guizhou Province
-
摘要: 2020年9月16日,受地下采动和降雨影响,贵州水城县发耳镇尖山营不稳定斜坡发生山体滑坡,约80×104 m3的岩土体倾泻而下,在运动过程中破碎解体形成碎屑流。滑坡最大运动距离达到1 km,最大高差约300 m。文章基于高精度无人机航测影像建立滑坡区三维数值模型,利用DAN3D动力分析软件对尖山营滑坡-碎屑流运动全过程开展数值模拟,分析了滑体动力学特征和堆积分布。在此基础上,利用反演确定的数值流变模型和参数,对尖山营不稳定斜坡潜在滑坡区开展致灾范围预测。研究成果为高位远程滑坡致灾范围预测和尖山营地区危险性评估提供了依据。Abstract: On September 16, 2020, the combination of mining activities and constant rainfall triggered a long runout landslide in Jianshanying area, Guizhou Province, China, causing a landslide of approximately 80×104 m3 of rock and soil to slide down and form a debris flow. The maximum movement distance of the landslide reached 1 km, with a maximum height difference of about 300 m. Many houses and two roads were destroyed, fortunately without causing casualties. In this study, detailed field investigation combined with the UAV aerial photography were conducted to obtain the geological setting and the digital elevation model of the landslide region. Subsequently, the dynamic model DAN3D was utilized to study the dynamic characteristics and deposit distribution of the Jianshanying landslide. Simulated results were found to match the actual situation well, and the Frictional-Voellmy rheology was identified as an accurate tool for simulating the long runout landslide. Based on the numerical parameters determined from the inversion work, the sliding process and possible travel distance of the potential landslide were simulated. The findings from this study will be helpful aid in predicting landslide runout in high-altitude regions, particularly for the residents in the potential danger zone of the Jianshanying landslide.
-
0. 引言
贵州岩溶山区地质环境复杂、人类活动强烈,是我国特大崩滑灾害高发区[1-3]。特别是近年来,随着采矿活动强度增大,矿山崩滑灾害频发。据贵州省地质环境监测院资料统计,截至2019年,由采矿诱发的地质灾害总数达到996处。矿山崩滑灾害不仅监测预警难度大、体量大,而且致灾动力过程复杂,导致空间预测难度大,群死群伤性崩滑灾害不断发生。例如:2004年12月3日,受地下采动诱发,贵州省纳雍县鬃岭镇突发崩塌灾害,约1×104 m3的崩塌体倾泻而下。崩塌体受微地貌影响,于海拔1913 m处产生分流,西支碎屑流摧毁了12栋房屋,共造成39人死亡和5人失联[4];2017年8月28日纳雍县张家湾镇发生高位崩塌,约50×104 m3的崩塌体自源区高位启动,沿途铲刮运动800 m,最终形成体积约80万方的堆积体。碎屑流在运动过程中受一20 m高的小山包阻挡产生分流,摧毁了下游大树脚组和桥边组的23栋房屋,造成26人遇难,9人失踪[5]。因此,如何对贵州省矿山崩滑灾害潜在隐患点开展致灾范围预测,防范特大崩滑灾害造成的群死群伤事故,成为当前亟须解决的重要科学难题。
尖山营不稳定斜坡是贵州省典型的矿山崩滑灾害潜在隐患点,自2005年开始进行大规模采煤,截至2019年,开采煤层多达8层,坡体已发生显著变形,并于2020年9月16日受地下采动和降雨影响触发滑坡灾害,严重威胁到当地279户1062名居民的生命财产安全。刘兵 [6] 综合了现场调查、遥感影像分析和地表GPS实时监测技术,对尖山营不稳定斜坡位移和变形破坏特征进行了分析;CHEN等[7] 通过光学遥感解译分析,探究了尖山营不稳定斜坡变形演化规律,并提出了变形失稳模式。ZHAO等 [8] 和DONG等[9] 通过数值仿真,分析了地下采动影响下尖山营不稳定斜坡裂隙发展和变形演化规律,探究了坡体结构对边坡稳定性的影响。可见,当前对尖山营不稳定斜坡的研究主要集中于边坡失稳机理和变形监测,针对尖山营滑坡运动过程动力学特性和潜在滑坡区致灾范围预测的研究还十分欠缺。因此,本文在现场调查的基础上,通过动力分析软件DAN3D反演再现了尖山营滑坡动力致灾全过程,并利用确定的流变模型和参数,对潜在滑坡区开展了致灾范围预测,为尖山营地区地质灾害危险性评价提供了依据。
1. 尖山营滑坡基本概况
1.1 地质环境条件
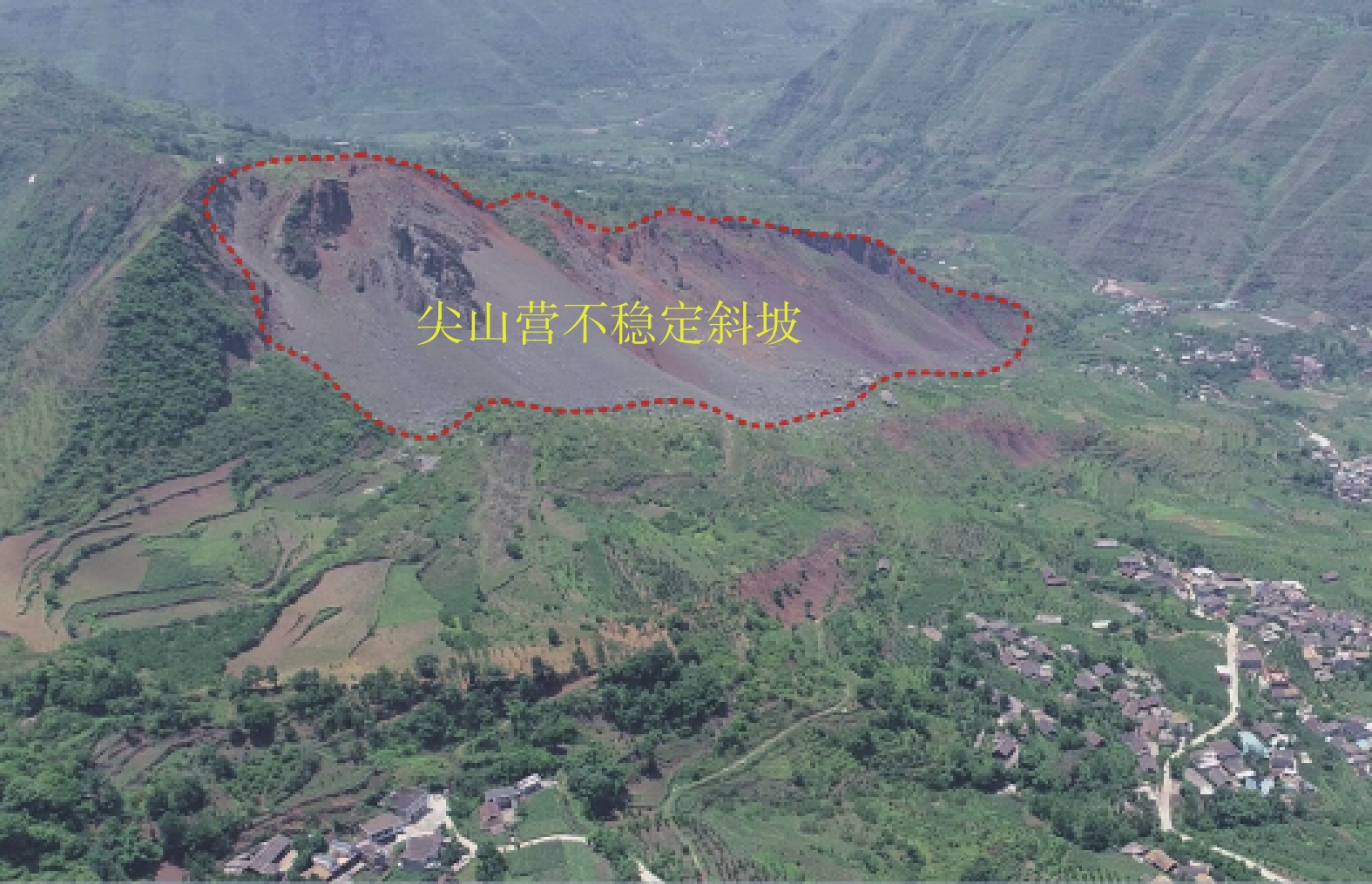
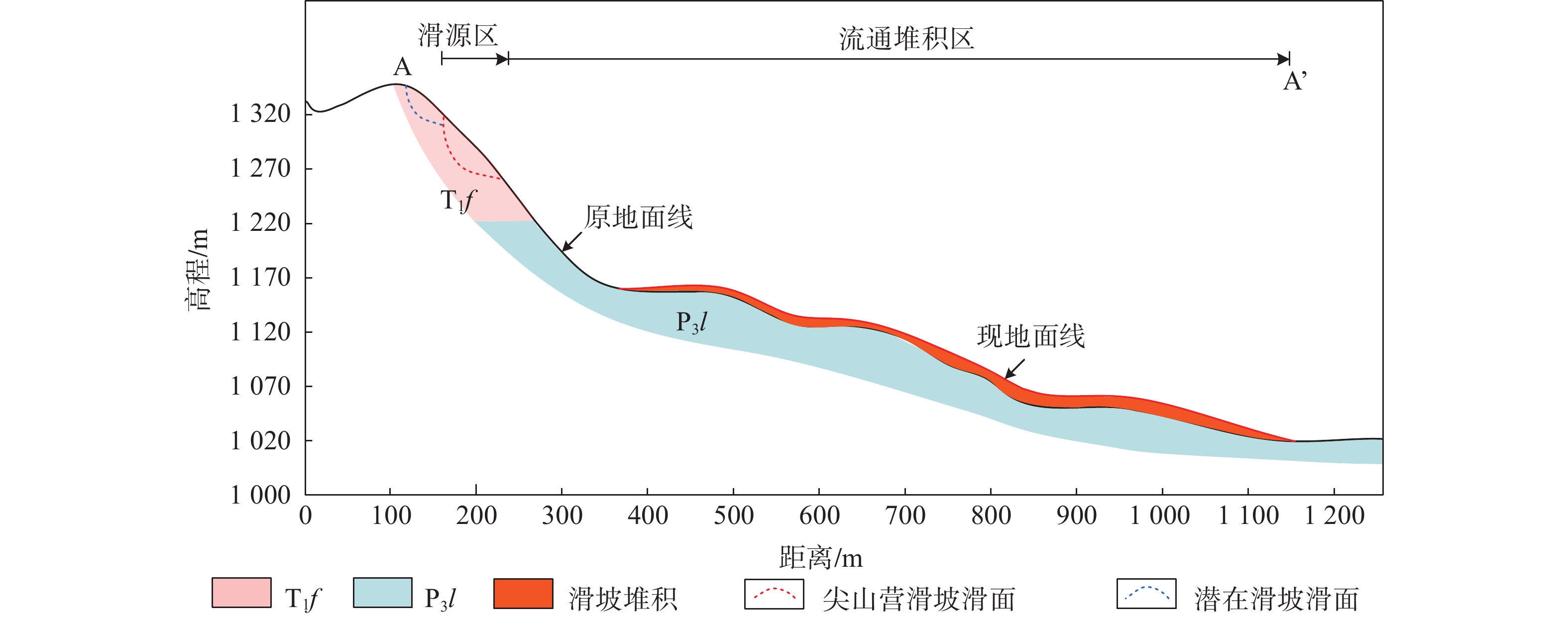
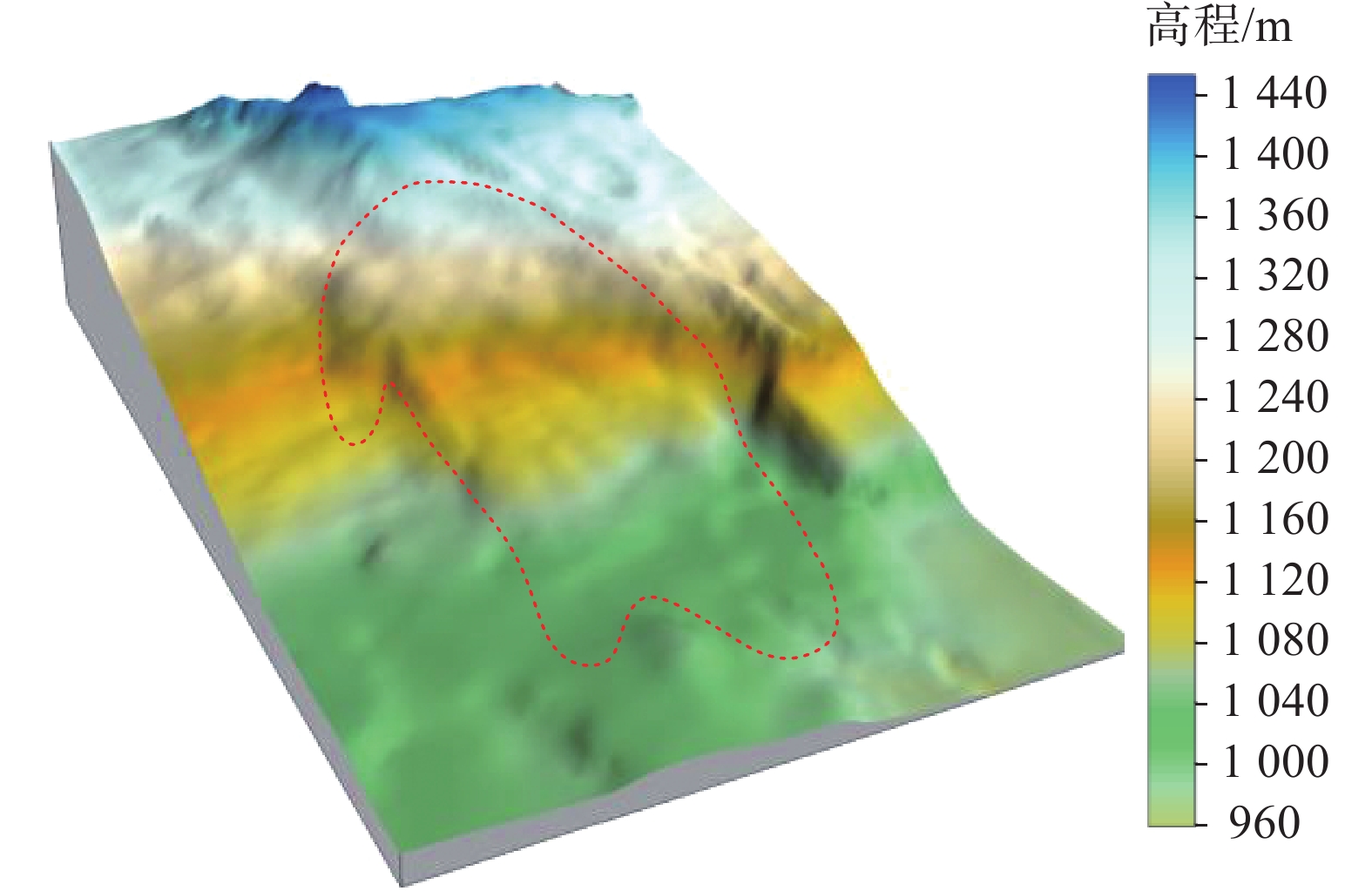
尖山营不稳定斜坡位于水城县发耳镇西侧,地形跌宕起伏,属于构造侵蚀而成的低中山至中低山地貌。最高处位于斜坡山顶,海拔1526 m,最低处位于发耳河西出口河床,海拔949 m,最大高差达577 m。斜坡所在区域位于水城县发耳煤矿三采区范围内,是典型的地下采动控制型崩滑灾害潜在隐患点,严重威胁到当地279户1062名居民的生命财产安全 (图1)。
研究区出露地层由老至新分别为:二叠系上统龙潭组(P3l)、三叠系下统飞仙关组(T1f)和第四系松散堆积物(Qh)[10]。
二叠系上统龙潭组(P3l)由粉砂岩、细砂岩、泥岩和煤组成。底部2~3 m为铝质岩层,含大量菱铁矿结核、黄铁矿结核。厚度分布410~430 m,主要位于研究区东部。
三叠系下统飞仙关组(T1f)主要分布于研究区西侧,不稳定斜坡主要出露于该层。岩性上部为紫色、灰绿色相间钙质泥岩与细砂岩互层,夹薄至厚层状细砂岩;中部为泥质粉砂岩及粉砂质泥岩或细砂岩;底部见黑色斑粒,碳化植物化石。
第四系松散堆积物以残、坡积物和崩积物为主,厚度为0~80 m,残、坡积物主要分布在同向坡及单斜谷中,崩积物分布于陡崖脚下。
1.2 滑坡体特征
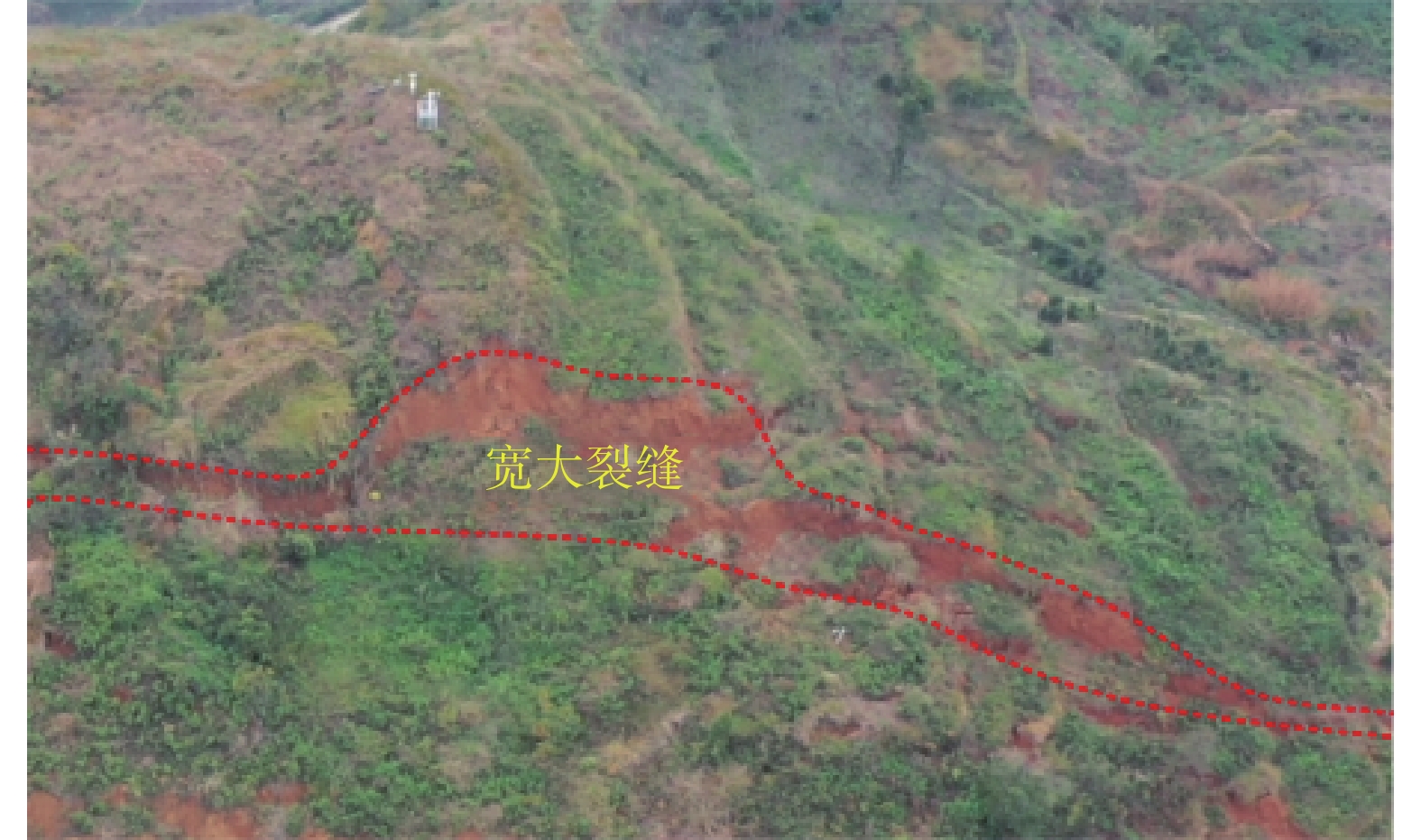
2020年9月16日,受地下采动和降雨等因素影响,尖山营不稳定斜坡触发大规模滑坡灾害,滑坡体积约80万方,摧毁了两条公路,所幸未造成人员伤亡。滑体后缘海拔1320 m,前缘高程1020 m,相对高差300 m。滑体自源区高位启动后,沿正北向以碎屑流的形式高速向前运动,最终滑体前缘停止于范家沙坝和酒店子组,运动距离达1 km,后缘岩土体受其牵引作用影响,已出现明显下错,形成潜在滑体(图2、图3),并发育有宽大裂隙(图4)。根据尖山营滑坡-碎屑流运动特征,可将其分为滑源区和流通堆积区(图2、图3)。
(1) 滑源区:位于尖山营不稳定斜坡西南侧,滑源区后缘高程为1320 m,前缘高程约1260 m,主要由第四系松散堆积和飞仙关组泥岩、砂岩组成。因长期地下采空失去有效支撑,在重力作用下产生变形,坡体裂隙发育,为雨水快速入渗提供通道,最终在长期地下采矿和降雨综合作用下发生失稳。
(2) 流通堆积区:位于海拔1020~1260 m处。滑体失稳后,沿前缘临空方向向下运动,于海拔1160 m处受地形阻碍,发生碰撞分流。滑坡主体在运动过程中不断破碎解体形成碎屑流,最终运动了约1 km,摧毁了范家沙坝和酒店子组、小寨组部分房屋,并掩埋了两条公路,未造成人员伤亡。
2. 滑坡-碎屑流动力学特性分析
2.1 数值方法及计算参数
DAN3D(Dynamic Analysis)是加拿大学者HUNGR[11]和其团队成员基于等效流体理论开发的动力分析软件,已在全球范围内高位远程滑坡动力学分析中得到了广泛应用。软件基本原理是将滑体等效为连续介质流体,通过设定不同流变关系,模拟滑坡运动速度、时间、路径及堆积等特征。目前,大量学者已采用DAN3D对我国西南山区高位远程滑坡动力致灾过程进行了深入分析,研究结果表明:Frictional-Voellmy组合模型能较好地模拟滑坡-碎屑流动力学特征[12-16]。因此,本文在滑源区选用Frictional模型,流通堆积区采用考虑流体湍流项的Voellmy流变模型,对尖山营滑坡-碎屑流进行数值仿真,并基于反分析法系统地调整数值流变参数,直至模拟结果与实际情况基本一致。
Frictional模型假设滑体所受剪切阻力(
(1) 式中:
Voellmy模型将滑体所受剪切阻力视为摩擦力和湍流流动产生的阻力之和,表达式为:
(2) 式中:
基于高精度无人机航测影像,采用PIX4D及Surfer软件分析处理无人机航测数据,建立滑坡区数字高程模型(图5),尖山营滑坡模型精度为2.5 cm。在此基础上,结合现场精细调查,明确了滑坡分区和致灾范围(图2)。以滑坡运动路径及致灾范围为参考,通过反分析法调整数值流变参数,直至数值模拟得到的滑坡运动路径和致灾范围与实际情况基本一致。本文选用的流变模型及参数如表1所示。
表 1 尖山营滑坡流变模型和参数取值Table 1. Selected rheological models and parameter values of the Jianshanying landslide流变模型 摩擦角 孔压
系数摩擦
系数湍流
系数滑源区 Frictional 27 0.5 − − 流通
堆积区Voellmy − − 0.18 600 2.2 尖山营滑坡运动过程模拟结果
尖山营滑坡-碎屑流运动全过程的DAN3D模拟结果如图6所示。滑坡-碎屑流最大运动距离约1 km,运动时间持续约50 s,随后只有少量的内部蠕变和侧向变形,滑坡已基本停止运动。碎屑流最终堆积厚度为0~15 m,几乎覆盖整个堆积区,最大堆积厚度位于滑体左侧前缘,滑坡运动距离和堆积形态与实际情况较为吻合。
滑坡启动后,受地形影响沿正北方向运动并不断加速,20 s时滑体已全部离开源区。受海拔1160 m处山脊影响,少量滑体分流,滑坡主体仍沿主滑方向向前运动。40 s时,滑体前缘抵达范家沙坝和酒店子组公路,阻断公路正常运行。最终至50 s时,滑体前缘抵达小寨组并基本停止运动,堆积形态不再发生改变。
尖山营滑坡-碎屑流速度分布如图7所示。研究区地形地貌呈现典型的“上陡下缓”特征,滑源区海拔较高,坡度较陡,滑坡启动后,巨大的势能转化为动能,在10 s时,前缘速度达到峰值,约36 m/s,随后,滑体仍保持25 m/s的高速向前运动。20 s后,滑体前缘运动至海拔1100 m处,受地形变缓影响开始减速,直至运动停止。
3. 潜在隐患点致灾范围预测
尖山营滑坡发生后,后缘岩土体受其牵引作用影响,已出现明显下错,形成潜在滑体。如图2所示,潜在滑坡区面积约2.6×104 m2,呈三角形分布,结合三维数字高程模型分析和现场精细调查,预估体积约40×104 m3。潜在滑坡区后缘已明显下错形成宽大裂隙,前缘为凌空面,在后续降雨和自身重力作用下极易失稳,形成高位远程滑坡灾害。因此,亟须对其开展致灾范围预测,预测其可能的影响范围,为尖山营地区人居安全和居民搬迁提供依据。
由于潜在滑坡与2020年已发生滑坡具有相似的工程地质条件,因此本文利用尖山营滑坡数值反演结果已确定的流变模型及参数,对潜在滑坡区致灾范围进行预测,尖山营不稳定斜坡潜在滑体动力致灾全过程的数值模拟结果如图8所示。潜在滑体的运动时间为60 s,滑体运动距离同样达到了约1 km。滑体高位启动后,沿15°方向高速运动并随后逐渐转为正北向运动。与2020年9月16日发生的高位滑坡运动过程相似,潜在滑体在运动中于海拔1160 m处受山脊阻碍产生分流,滑坡主体仍沿正北向运动,最终覆盖于已发生滑坡堆积体上。潜在滑坡堆积厚度为0~11 m,滑体将再次淹没新修公路,并摧毁酒店子组部分房屋,造成可能的人员伤亡和财产损失。因此,亟须对当地居民进行适当搬迁,并进行地质灾害安全教育,防范群死群伤性滑坡灾害的发生。
4. 结论
针对2020年9月16日贵州尖山营不稳定斜坡发生的高位远程滑坡灾害,本文基于现场精细调查和高精度无人机航测影像建立了滑坡区三维数字高程模型,利用动力分析软件DAN3D分析了其致灾过程和动力学特性,并在此基础上对潜在滑坡区进行了致灾范围预测,得到如下结论:
(1) 基于动力分析软件DAN3D,采用Frictional-Voellmy组合模型模拟了尖山营滑坡动力致灾全过程。结果表明:尖山营滑坡-碎屑流运动时长约50 s,最终堆积厚度为0~15 m,滑坡最大速度达到36 m/s,模拟的滑坡运动距离、堆积范围和方量与实际情况较为吻合。
(2) 基于数值反演确定的流变模型和参数对潜在滑坡开展致灾范围预测,潜在滑坡区预估体积约40×104 m3,模拟结果表明:潜在滑体运动距离可达1 km,将再次淹没新修公路,并摧毁酒店子组部分房屋。因此需对当地居民进行搬迁,避免人员伤亡和不必要的财产损失。
-
表 1 尖山营滑坡流变模型和参数取值
Table 1 Selected rheological models and parameter values of the Jianshanying landslide
流变模型 摩擦角 孔压
系数摩擦
系数湍流
系数滑源区 Frictional 27 0.5 − − 流通
堆积区Voellmy − − 0.18 600 -
[1] 李滨,殷跃平,高杨,等. 西南岩溶山区大型崩滑灾害研究的关键问题[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):5 − 13. [LI Bin,YIN Yueping,GAO Yang,et al. Critical issues in rock avalanches in the karst mountain areas of southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):5 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Bin, YIN Yueping, GAO Yang, et al. Critical issues in rock avalanches in the Karst Mountain areas of southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(4)5-13(in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 贺凯,李滨,赵超英,等. 基于易滑地质结构与多源数据差异的岩溶山区大型崩滑灾害识别研究[J]. 中国岩溶,2020,39(4):467 − 477. [HE Kai,LI Bin,ZHAO Chaoying,et al. Identification of large-scale landslide hazards based on differences of geological structure prone to sliding and multiple-source data in karst mountainous areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2020,39(4):467 − 477. (in Chinese with English abstract) He Kai, Li Bin, Zhao Chaoying, et al. Identification of large-scale landslide hazards based on differences of geological structure prone to sliding and multiple-source data in Karst mountainous areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(4): 467-477. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 王琦,胡亚净,宋伟利,等. 岩溶山区危岩稳定性分析及危害性预测—以贵州松桃县长冲危岩体为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(1):75 − 84. [WANG Qi, HU Yajing, SONG Weili, et al. Stability analysis and hazard prediction of dangerous rock masses in karst mountainous area:A case study of Changchong dangerous rock mass in Songtao County, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(1):75 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) [WANG Qi, HU Yajing, SONG Weili, et al. Stability analysis and hazard prediction of dangerous rock masses in Karst mountainous area: a case study of Changchong dangerous rock mass in Songtao County, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(1)75-84(in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 吴彩燕,乔建平,王成华,等. 贵州省纳雍县鬃岭镇 “12·3” 大型崩塌灾害分析[J]. 水土保持研究,2006,13(6):100 − 102. [WU Caiyan,QIAO Jianping,WANG Chenghua,et al. Analysis on “12·3” super large-scaled landslide in zongling,Nayong,Guizhou[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2006,13(6):100 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2006.06.031 WU Caiyan, QIAO Jianping, WANG Chenghua, et al. Analysis on “12·3” super large-scaled landslide in zongling, Nayong, Guizhou[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 13(6)100-102(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2006.06.031
[5] ZHU Yaoqiang,XU Shimin,ZHUANG Yu,et al. Analysis of characteristics and runout behaviour of the disastrous 28 August 2017 rock avalanche in Nayong,Guizhou,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,259(3):105154.
[6] 刘兵. 贵州尖山营滑坡变形监测分析与滑动机理研究[J]. 中国水运,2021,21(4):109 − 110. [LIU Bing. Deformation monitoring analysis and sliding mechanism research of Jianshanying landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. China Water Transport,2021,21(4):109 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract) Liu Bing. Deformation monitoring analysis and sliding mechanism research of Jianshanying landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. China Water Transport, 2021, 21(4): 109-110. . (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] CHEN Liquan,ZHAO Chaoying,LI Bin,et al. Deformation monitoring and failure mode research of mining-induced Jianshanying landslide in karst mountain area,China with ALOS/PALSAR-2 images[J]. Landslides,2021,18(8):2739 − 2750. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-021-01678-6
[8] ZHAO Jianjun,XUN Wan,SHI Yanbing,et al. Deformation behavior of mining beneath flat and sloping terrains in mountainous areas[J]. Geofluids,2021,2021(8):1 − 16.
[9] DONG Jianhui,LI Haijun,WANG Yangshuang,et al. Characteristics and monitoring-based analysis on deformation mechanism of Jianshanying landslide,Guizhou Province,southwestern China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2021,14(3):184. DOI: 10.1007/s12517-021-06473-0
[10] 朱要强. 贵州岩溶山区特大崩(滑)-碎屑流致灾机理研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学 ZHU Yaoqiang. Study on the mechanism of catastrophic collapse (slip)-debris flow in Guizhou karst mountain area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] HUNGR O. A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slides,debris flows,and avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1995,32(4):610 − 623. DOI: 10.1139/t95-063
[12] 康孟羽,朱月琴,陈晨,等. 基于多元非线性回归和BP神经网络的滑坡滑动距离预测模型研究[J]. 地质通报,2022,41(12):2281 − 2289. [KANG Mengyu,ZHU Yueqin,CHEN Chen,et al. Study on landslide sliding distance prediction model based on multivariate nonlinear regression and BP neural network[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2022,41(12):2281 − 2289. (in Chinese with English abstract) Kang Mengyu, Zhu Yueqin, Chen Chen, et al. Study on landslide sliding distance prediction model based on multivariate nonlinear regression and BP neural network[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(12)2281-2289(in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] XING Aiguo. Dynamic analysis and field investigation of a fluidized landslide in Guanling,Guizhou,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,181:1 − 14. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.022
[14] XING Aiguo,YUAN Xiaoyi,XU Qiang,et al. Characteristics and numerical runout modelling of a catastrophic rock avalanche triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake in the Wenjia valley,Mianzhu,Sichuan,China[J]. Landslides,2017,14(1):83 − 98. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-016-0707-5
[15] ZHUANG Yu,YIN Yueping,XING Aiguo,et al. Combined numerical investigation of the Yigong rock slide-debris avalanche and subsequent dam-break flood propagation in Tibet,China[J]. Landslides,2020,17(9):2217 − 2229. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-020-01449-9
[16] ZHUANG Yu,XING Aiguo,CHENG Qiangong,et al. Characteristics and numerical modeling of a catastrophic loess flow slide triggered by the 2013 Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake in Yongguang Village,Minxian,Gansu,China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2020,79(1):439 − 449. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-019-01542-x
-
期刊类型引用(28)
1. 李超然,袁广祥. 甘肃省宕昌县地质灾害易发性评价. 地质灾害与环境保护. 2025(01): 21-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈余生,肖拥军,丁海洋,李鑫. 典型乡镇人居斜坡地质灾害风险评价研究. 西部探矿工程. 2025(05): 16-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 兰盈盈,郭昶成,朱云福. 地质灾害易发性评价方法综述. 地质与资源. 2024(01): 65-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨晶晶,肖玉,安泉,刘浩,公斌. 黔东北地区地质灾害时空分布规律及孕灾地质环境研究. 中国煤炭地质. 2024(02): 64-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李晓玮,刘翠娜. 基于AHP法山区公路边坡稳定性评价及危害性分析. 河北地质大学学报. 2024(02): 61-65+134 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 南赟,翟淑花,李岩,曹颖,罗守敬,王云涛,郭学飞. 北京地区“23·7”特大暴雨型地质灾害特征及预警成效分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(02): 66-73 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 曾欣,黄梦妮,胡毓灵,邓新林,谢倩雯. 株洲市地质灾害特征与降雨量的关系. 气象研究与应用. 2024(01): 83-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 唐朝. 基于ArcGIS的当涂县地质灾害风险调查与评价. 现代矿业. 2024(04): 187-190+196 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 蔡佳明. 北京东部山区地质灾害危险性评价. 地质灾害与环境保护. 2024(02): 49-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 李晓玮. 北京北宫镇大灰厂路牵引式岩质滑坡勘查及防治对策. 城市地质. 2024(02): 139-148 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 赵丹凝,焦润成,杨春. “23·7”强降雨对北京西山曹家坊泥石流隐患易发性影响. 城市地质. 2024(03): 353-364 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 尹展,郝玉军,卜鹏,杨艳绪. 湘南中低山区滑坡孕灾因子分析及易发性评价——以江华县为例. 矿产勘查. 2024(10): 1878-1884 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 李晓玮,郑晓钰,史昕宇. 北京西部采空区初勘及场地适宜性评价. 防灾减灾学报. 2024(04): 7-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 曹颖,李岩,翟淑花,于家烁,刘宗明. 北京潮白河流域突发地质灾害风险情景模拟研究与应用. 城市学报. 2024(06): 98-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 支泽民,刘峰贵,周强,夏兴生,陈琼. 基于流域单元的地质灾害易发性评价——以西藏昌都市为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(01): 139-150 .  本站查看
本站查看
16. 王涛,李鹏洋,逯兴娅,苏生瑞,董永超. 陕西省韩城市地质灾害易发性评价. 甘肃科学学报. 2023(02): 55-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 张群,冯辉,贾三满,张沁瑞,贾磊. 基于CF与Logistic回归模型耦合的地质灾害易发性评价——以北京市大清河流域生态涵养区为例. 城市地质. 2023(01): 17-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 罗琳,刘雄,翁建,王锦阳,楼雄标. 某乡镇地质灾害风险评价. 科技通报. 2023(04): 93-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 孙佩,杨良哲,康全国,张驰,尹伟,周凌云,易洁伟,王雯雯. 一般调查区地质灾害易发性评价——以咸丰县为例. 资源信息与工程. 2023(04): 95-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 叶泽宇,徐尚智,刘欢欢,于家烁,翟淑花,冒建. 基于信息量与逻辑回归耦合模型的北京西山崩塌易发性评价. 城市地质. 2023(03): 9-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 阳清青,余秋兵,张廷斌,易桂花,张恺. 基于GDIV模型的大渡河中游地区滑坡危险性评价与区划. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(05): 130-140 .  本站查看
本站查看
22. 王海芝,曾庆利,许冰,胡福根,于淼. 北京“7·21”特大暴雨诱发的地质灾害类型及其特征分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(02): 125-132 .  本站查看
本站查看
23. 焦伟之,张明,谢鑫鹏,李成文,刘涛,庞海松. 基于GIS与加权信息量模型的城镇地质灾害易发性评价——以大新镇为例. 安全与环境工程. 2022(04): 119-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 简鹏,李文彦,张治家,时伟,党发宁,郭红东,李松. 基于多因素加权指数和法的区域地质灾害易发性评价研究——以麦积区为例. 甘肃地质. 2022(03): 63-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 白光顺,杨雪梅,朱杰勇,张世涛,祝传兵,康晓波,孙滨,周琰嵩. 基于证据权法的昆明五华区地质灾害易发性评价. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(05): 128-138 .  本站查看
本站查看
26. 庄卓涵. 广州北部山区斜坡类地质灾害致灾机理及易发性分析——以广州从化良口—吕田一带为例. 地下水. 2022(06): 158-161 .  百度学术
百度学术
27. 王小东,罗园,付景保. 基于GIS的白龙江引水工程水源区地质灾害易发性评价. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文). 2022(06): 1231-1239 .  百度学术
百度学术
28. 郭富赟,宋晓玲,刘明霞. 黄河流域甘肃段地质灾害发育特征. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2021(05): 130-136 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(7)





 下载:
下载:


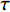

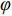
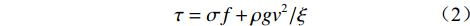
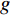
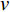
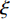



 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS