Comparative analyses of susceptibility assessment for landslide disasters based on information value, weighted information value and logistic regression coupled model in Luoping County, Yunnan Province
-
摘要: 以罗平县崩滑地质灾害为研究对象,选取工程岩组、坡度、坡向、高程、起伏度、曲率、地貌类型、距河流距离、距断裂距离9个评价因子,基于共线性诊断和相关性分析对其进行独立性检验。然后采用信息量法计算各评价因子分类分级的信息量值,采用层次分析法和逻辑回归法对各评价因子进行权重的定量计算,从而构建信息量、加权信息量和信息量-逻辑回归耦合易发性评价模型并进行对比分析。基于GIS的自然断点法将评价结果划分为非、低、中和高4个等级,并采用ROC曲线对其精度进行检验。结果表明:3种评价模型的AUC值分别为0.757、0.723和0.852,信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型的精度最高,模型结果分区与崩滑地质灾害点的分布较吻合,其非、低、中和高的面积(分级比)分别为771.1 km2(25.55%)、836.6 km2(27.73%)、864.36 km2(28.64%)和545.94 km2(18.08%)。Abstract: This study focuses on landslide susceptibility assessments in Luoping County, where 9 evaluation factors, including engineering rock group, slope, slope aspect, elevation, undulation, curvature, landform type, distance from rivers, and distance from fault, were selected as the research variables. After conducting collinearity diagnosis and correlation analysis, the information value method was applied to calculate the information value for each classification level of the evaluation factors. Quantitative weights for each evaluation factor were determined using the AHP and logistic regression methods, leading to the construction and comparison of three susceptibility evaluation models: information value, and weighted information value, and information-logistic regression coupled model. The results were categorized into four grades -- none, low, medium, and high – using the GIS-based natural breakpoint method, and their accuracy was validated using ROC curves. The results show that the AUC values of the three evaluation models were 0.757, 0.723 and 0.852 respectively, with the information-logistic regression coupled model demonstrating the highest accuracy. Moreover, the model results were in good agreement with the distribution of landslide geological disaster points. The respective areas (classification ratios) for the none, low, medium, and high categories were 771.1 km2 (25.55%), 836.6 km2 (27.73%), 864.36 km2 (28.64%), and 545.94 km2 (18.08%).
-
0. 引言
云南以红河深大断裂为界,滇西为高山纵谷区,滇东为喀斯特高原[1],滇东北为地质灾害高易发区,滇西地质灾害易发性南相对较弱[2]。罗平县地处云南滇东喀斯特高原地区,是典型的岩溶山区。目前,崩滑易发性制图主要分为定性、定量和机器学习3种方法[3 − 4]。定性分析是通过对成因机制的全面认识,基于专家经验和知识确定评价因子权重,定量分析方法通过数学或数值算法估计滑坡易发性[5]。定性分析方法主要有层次分析法[6 − 8],定量分析方法主要有频率比法[9 − 10]、信息量法[11 − 12],机器学习方法有逻辑回归法、随机森林法、K近邻、支持向量机和神经网络等[13 − 15]。国内外学者进行研究分析,并采用多种研究方法进行对比,吉日伍呷等[15]通过逻辑回归、K近邻、朴素贝叶斯和随机森林算法对鲁甸进行地震滑坡易发性评价,并得出统计建模地更多的是寻找变量之间的可解释关系;樊芷吟等[16]通过信息量法+Logistic回归模型对汶川县进行易发性评价;张晓东[17]通过定量信息量法和确定性系数法分别与Logistic回归耦合对宁夏盐池县进行易发性评价,得出耦合模型结果均优于单一模型评价结果。根据以上研究,易发性评价模型首先选取崩滑评价影响因子,再通过分类分级进行计算,根据不同方法得出的结果基于ArcGIS进行等级划分。信息量法只考虑了评价因子分类分级状态下的权重,其优点在于原理简单,易于实现;缺点在于无法体现所选取的评价因子的权重。因此选取层次分析法和逻辑回归法分别赋予评价因子的权重,其中层次分析法依据崩滑灾害成因分析,通过专家法构建矩阵计算得出评价因子的权重,逻辑回归法是依据样本数据和连接方法,通过两种方法得出评价因子的权重分别与信息量法进行耦合,其耦合模型将评价因子的权重和分类分级的权重叠加得到综合权重,降低了单一评价模型人为主观性因素的影响,论证不同方法评价结果的准确性。
本文以罗平县作为研究区域,基于野外详实的地质灾害调查成果,综合分析孕灾地质条件和崩滑点分布规律,选取岩土体(工程岩组)、地形地貌(坡度、坡向、高程、起伏度、曲率、地貌类型)、地质构造(距断裂距离)、气象水文(距河流距离)等评价因子。采用信息量法、加权信息量法、信息量-逻辑回归耦合法构建易发性评价模型进行对比分析,并对评价结果进行精度检验分析,选取精度最高模型易发性分布图,可为罗平县今后地质灾害治理提供参考依据,对今后城市的发展和防灾减灾有重要意义,也可为岩溶地区地质灾害易发性评价提供参考。
1. 研究区概况及数据来源
1.1 研究区概况
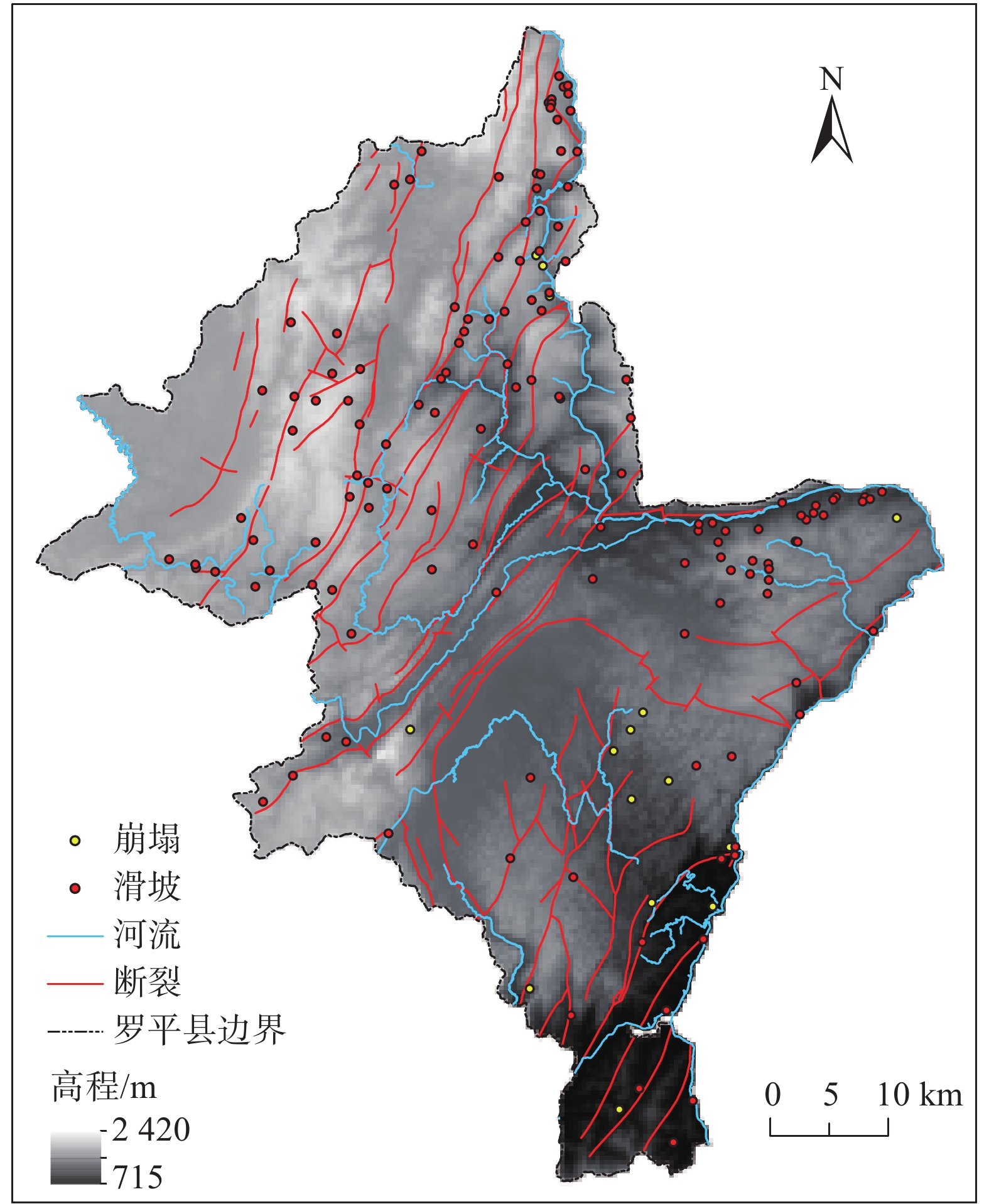
研究区(罗平县)位于云南省曲靖市东部。东西最大横距75 km,南北最大纵距99 km。相对高差为1705 m,全县面积3018 km2,山区面积占78%,坝区面积占22%(图1)。研究区西部和北部属于岩溶盆地地貌和岩溶低中山地貌,中部属岩溶断陷湖形盆地,东部和南部受九龙河和南盘江流域侵蚀切割,形成峰林洼地和岩溶中山地貌。区内地层出露主要有古生界泥盆系(D)浅灰、深灰色中厚层状灰岩、泥灰岩、泥质白云岩;石炭系(C)深灰、灰黑色块状灰岩、白云质灰岩、泥质灰岩;古生界二叠系(P)灰、深灰色厚层块状、生物碎屑灰岩,结晶灰岩夹虎斑状灰岩及白云岩;中生界三叠系(T)上统为黄褐色粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩及细砂岩、中统为深灰色灰岩夹泥质灰岩、中上部为黄色白云岩、下统为紫红色含长石粉细砂夹泥灰岩页岩及含铜页岩;新生界古近系(E)+新近系(N)褐黄紫红色砾岩、细砂岩及粉砂质泥岩、底部砾岩;新生界第四系(Q)细砂、砂砾石及砂质黏土。主要构造体系和构造型式有北东向构造、新华夏系构造、网状构造等。北东向构造为区内主导构造,是研究区内最重要的构造成分之一,主要断裂有:金鸡山断裂、长家湾断裂和腊庄断裂等。其次为新华夏系构造,多发育在褶皱边缘、密集成束、规模大、延伸远、呈舒缓波状,主要分布在西部及南盘江两岸。主要断裂有:洒土革断裂、大水塘断裂、罗格断裂等。
1.2 数据来源
本研究数据主要包括:(1)12.5 m分辨率数字高程模型(DEM)收集自ASF,用于提取坡度、坡向、起伏度、曲率等评价因子;(2)1∶20万地质图收集自全国地质资料馆,用于提取岩性、断裂等因子;(3)1∶5万地理数据库提取水系;(4)历史崩滑数据:主要来自地矿眉山工程勘察院1∶5万全区调查结果,共154个崩滑灾害点的数据。
2. 研究方法
2.1 信息量模型
信息量模型是对崩滑历史数据进行统计分析,将影响崩滑的各因子的实测值转化为信息量值,来衡量崩滑的易发性[18]。首先计算各评价因子的信息量值,再对各因子信息量值进行总和,作为崩滑易发性的综合指标[19]。单因子信息量计算公式为:
(1) 式中:I——评价因子j下的信息量;
Nj——评价因子j内发生的崩滑数;
N——研究区崩滑总数;
Sj——评价因子j下所占栅格数;
S——研究区总栅格数。
将每个评价单元各分类分级进行叠加计算,其地质灾害发生的总信息量计算公式为:
(2) 式中:Ij——总信息量,为地质灾害易发性指数;Ij值 越大且为正值则表示该单元内有利于崩滑 发生。
2.2 层次分析模型
层次分析模型是一种将决策者定性判断和定量计算有效结合起来的分析方法。通过比较相邻影响因子的重要性[19],根据专家法构建判断矩阵[20]:
(3) 式中:A——要素判断矩阵;
aij——因子i和因子j重要性比较的结果,有以下性质:
(4) 为保证求得的权重的正确性及合理性,还需要进行一致性检验。
(5) (6) 式中:CI——一致性指标;
n——判断矩阵的阶数;
λmax——判断矩阵的最大特征值;
CR——随机一致性比;当其<0.1时一致性检验通过;
RI——随机一致性指标。
2.3 逻辑回归模型
逻辑回归模型是一种研究二分类因变量常用的统计方法[16,21]。通过研究崩滑易发性与评价因子之间的关系,预测崩滑发生的概率。其中自变量为评价因子指标值(x1, x2, ···, xn),是否发生地质灾害作为因变量(分别用1和0代表崩滑点和非崩滑点)。逻辑回归函数如下:
(7) (8) 式中:α——常数项;
x1, x2, ···, xn——自变量;
β1, β2, ···, βn——回归系数;
Z——崩滑发生的可能性与各评价因子之间的关系;
P——崩滑灾害发生的概率,范围0~1。
2.4 加权信息量模型
根据层次分析法得出各评价因子的权重值,结合信息量法各评价因子分类分级的信息量值,两者相乘得出加权信息量值,其计算公式可表示为:
(9) 式中:Ij——加权信息量;
ωi——每个评价因子的权重;
Ii——评价因子i的信息量值。
2.5 信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型
将信息量模型与逻辑回归模型进行耦合,通过逻辑回归确定评价因子的权重,可降低信息量模型评价因子分级的主观性影响。其原理将信息量模型中评价因子分类分级的信息量值作为逻辑回归模型中的自变量,建立回归方程进行逻辑回归运算,得出各评价因子的回归系数,以此为依据建立信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型。
3. 评价因子选取分级
3.1 评价因子选取分级
本文在罗平县资料收集和野外地质调查的基础上,选取岩土体(工程岩组)、地形地貌(坡度、坡向、高程、起伏度、曲率、地貌类型)、地质构造(距断裂距离)、气象水文(距河流距离)等评价因子进行分析。根据12.5 m×12.5 m栅格单元作为易发性评价的制图单元,通过对研究区评价因子与崩滑点数据进行归纳分析,得出各评价因子的分类分级处理(图2)。
3.2 评价因子共线性诊断
进行逻辑回归时,需确保所选评价因子之间的相互独立,相关性高会出现多重共线性[22 − 23]。采用容忍度(tolerance,TOL)和方差膨胀因子(variance inflation factor,VIF)对自变量进行多重共线性诊断:
(10) 式中:R2——以xi为因变量时对其他自变量回归的复测 定系数;
TOL是VIF的倒数,当TOL大于0.1且VIF小于10时,则不存在多重共线性。
根据308个独立属性样本,提取每个样本的各类级信息量值,在SPSS软件中进行多重共线性诊断。结果显示对所选9个评价因子其VIF值在1~1.5(表1)。其VIF<5,表明各因子之间相互独立,不存在共线性。
表 1 评价因子VIF计算结果表Table 1. Calculation results of VIF for evaluation factors评价因子 TOL VIF 工程岩组 0.818 1.222 坡度 0.656 1.524 坡向 0.954 1.048 高程 0.904 1.107 地貌类型 0.713 1.402 起伏度 0.669 1.495 曲率 0.970 1.031 距断裂距离 0.945 1.058 距河流距离 0.717 1.396 3.3 评价因子相关性分析
崩滑的易发性与评价因子之间存在一定的相关性。为了保证各评价因子间的相互独立性和结果的可靠性,进行因子相关性检验[24]。结果显示各评价因子之间的相关系数均<0.3(表2),评价因子之间的相关性较小,所以9个评价因子均可以进入模型。
表 2 评价因子之间的相关系数矩阵Table 2. Correlation coefficient matrix of evaluation factors评价因子 工程岩组 坡度 坡向 高程 地貌类型 起伏度 曲率 距断裂距离 距河流距离 工程岩组 1 坡度 0.07 1 坡向 −0.09 0.07 1 高程 0.03 −0.08 0.08 1 地貌类型 0.02 0.11 0.03 0.01 1 起伏度 0.11 0.03 0.04 0.00 0.01 1 曲率 0.07 −0.07 0.08 0.03 0.06 0.04 1 距断裂距离 0.09 −0.03 −0.04 0.06 0.09 −0.05 0.08 1 距河流距离 0.01 0.04 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.06 0.06 0.07 1 4. 易发性评价结果
4.1 信息量模型评价结果
信息量模型中,崩滑的易发性与因子信息量值有关,信息量值越大且为正值则表示单元内崩滑越容易发生[25 − 28]。根据已有154个地质灾害进行重分类统计,根据公式(1)计算各评价因子分类分级的信息量值(表3)。
表 3 评价因子分类分级信息量值Table 3. Information value of classification levels for evaluation factors评价因子 因子分级 崩滑数量 栅格数量 信息量值 加权信息量值 工程岩组 软硬相间碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩岩组 2 205041 0.1347 0.0396 块状结构坚硬玄武岩岩组 50 1817099 1.1717 0.3433 坚硬层状碳酸盐岩岩组 97 15380267 −0.3014 −0.0883 第四系冲洪积松散岩组 5 661729 −0.1206 −0.0353 坡度
/(°)0~6 7 3162705 −1.3501 −0.2012 6~12 33 3790902 0.0193 0.0029 12~18 50 3707425 0.4571 0.0681 18~24 31 3008341 0.1880 0.0280 24~30 17 2054943 −0.0316 −0.0047 30~36 5 1186737 −0.7064 −0.1053 36~60 11 1091533 0.1657 0.0247 60~90 0 33429 0 0 坡向 北 16 2219489 −0.1692 −0.0129 东北 15 1920437 −0.0891 −0.0068 东 22 2493207 0.0329 0.0025 东南 31 2704414 0.2946 0.0224 南 20 2304895 0.0161 0.0012 西南 13 1974899 −0.2601 −0.0198 西 17 2138397 −0.0714 −0.0054 西北 20 2280277 0.0269 0.0020 高程/m 715~860 8 350496 0.9848 0.1468 860~1200 8 1149066 −0.2025 −0.0233 1200~1350 14 1312775 0.2239 0.4811 1350~1500 26 3226787 −0.0097 −0.1776 1500~1650 26 3079467 0.3627 −0.0402 1650~1800 29 2366839 −0.1401 1.8675 1800~1950 30 4047954 −0.5067 −0.8614 1950~2420 13 2530843 −0.5067 −3.6224 地貌类型 岩溶低中山地貌 22 2824754 −0.0904 −0.0037 构造侵蚀剥蚀地貌 18 1200919 0.5643 0.0231 岩溶中山地貌 40 3833292 0.2021 0.0083 岩溶盆地地貌 0 1948623 0 0 峰林谷地地貌 0 91609 0 0 峰丛洼地地貌 16 3752094 −0.6927 −0.0284 断块上升岩溶地貌 1 177099 −0.4119 −0.0169 断坳盆地 1 116724 0.0049 0.0002 石丘(垅岗) 2 390319 −0.5091 −0.0209 侵蚀谷地地貌 52 2561268 0.8677 0.0356 构造侵蚀岩溶地貌 2 1167462 −1.6047 −0.0658 起伏度/m 0~4 13 4183395 −1.0071 −0.0594 4~8 40 4306129 0.0879 0.0052 8~15 74 5697380 0.4232 0.0249 15~23 17 2685735 −0.2956 −0.0174 23~30 2 750479 −1.1607 −0.0684 30~38 7 294073 1.0289 0.0607 38~50 0 128414 0 0 50~220 1 57698 0.7117 0.0419 曲率 <0 70 7431512 0.0997 0.0041 0 20 3330755 −0.3505 −0.0144 >0 64 7301960 0.0277 0.0011 距断裂距离/m 0~600 70 6123046 0.2934 0.0194 600~1200 26 4659019 −0.4237 −0.0279 1200~1800 20 2742459 −0.1561 −0.0103 1800~2400 8 1599989 −0.5336 −0.0352 2400~3000 5 1028561 −0.5617 −0.0371 >3000 25 1911080 0.4281 0.0282 距河流距离/m 0~600 57 3404716 0.6748 0.0445 600~1200 32 2816455 0.2872 0.0189 1200~1800 21 2280631 0.0771 0.0051 1800~2400 14 1898512 −0.1451 −0.0096 2400~3000 6 1564553 −0.7989 −0.0528 >3000 24 6099326 −0.7731 −0.0511 4.2 加权信息量模型评价结果
根据加权信息量法构建模型,对研究区地质灾害及其背景因素和影响因素的相对重要性进行分析,依据所选取的评价因子,按照专家法对选取的评价因子根据式(3)构建判断矩阵计算出各评价因子的权重值,根据式(5)求出每个判断矩阵的一致性指标CI,并通过式(6)进行一致性检验(表4),各评价因子的权重值与各评价因子分类分级的信息量值根据式(9)得出加权信息量值(表3)。
表 4 评价因子分类分级判断矩阵及其权重Table 4. Judgment matrix and weight of classification levels for evaluation factors评价因子 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 权重 CI/CR 工程岩组 1 2 4 2 6 8 4 4 6 0.31 0.003
0.002坡度 1/2 1 2 1 3 4 2 2 3 0.155 坡向 1/4 1/2 1 1/2 2 2 1 1 2 0.083 高程 1/2 1 2 1 3 4 2 2 3 0.155 起伏度 1/6 1/3 1/2 1/3 1 1 1/2 1/2 1 0.046 曲率 1/8 1/4 1/2 1/4 1 1 1/2 1/2 1 0.041 距断裂距离 1/4 1/2 1 1/2 2 2 1 1 2 0.082 距河流距离 1/4 1/2 1 1/2 2 2 1 1 2 0.082 地貌类型 1/6 1/3 1/2 1/3 1 1 1/2 1/2 1 0.046 4.3 信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型评价结果
根据研究区已有的154个崩滑点,并随机选取等量的非崩滑点,共计有308个独立属性样本。将全部样本点依次赋予相应评价因子的信息量值,导入SPSS 25软件进行二项逻辑回归分析(表5),各评价因子的信息量值作为自变量,是否发生地质灾害作为因变量(1和0代表崩滑点和非崩滑点)。
表 5 逻辑回归分析结果Table 5. Results of logistic regression analysis评价因子 B S.E Wals df sig 工程岩组 0.698 0.261 7.142 1 0.002 坡度 1.331 0.513 6.721 1 0.000 坡向 0.761 0.862 0.780 1 0.007 高程 0.309 0.246 1.570 1 0.002 地貌类型 0.171 0.421 0.165 1 0.006 起伏度 0.641 0.304 4.455 1 0.005 曲率 1.523 0.907 2.820 1 0.003 距断裂距离 0.528 0.365 2.090 1 0.004 距河流距离 0.458 0.264 3.001 1 0.000 常量 −0.165 0.142 1.336 1 0.005 注:B为回归系数,S.E为标准误,wals为卡方值,df为自由度,sig为显著性。 在逻辑回归分析结果中,sig值越小,代表评价因子的显著性越高,表(3)中sig小于0.05,说明9个因子均有统计意义。基于模型分析结果中的各因子系数值根据公式(7)得逻辑回归公式如下:
(11) 式中:x1~x9分别为地层岩组、坡度、坡向、高程、地貌类型、起伏度、曲率、距断裂距离、距河流距离的信息量值;运用ArcGIS的栅格计算器功能将z值代入式(8)得到崩滑灾害发生的概率p。
信息量模型根据信息量法求出各评价因子分类分级的信息量,然后进行叠加分析,加权信息量模型根据表(4)得出的各评价因子的权重值,结合公式(9)求出各分类分级的加权信息量值(表3)。信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型根据公式(11)所求出的概率值构建模型,将结果进行重分类处理,并利用自然断点法将3种评价模型结果划分为非、低、中和高4个等级(图3)。
4.4 易发性评价结果精度检验
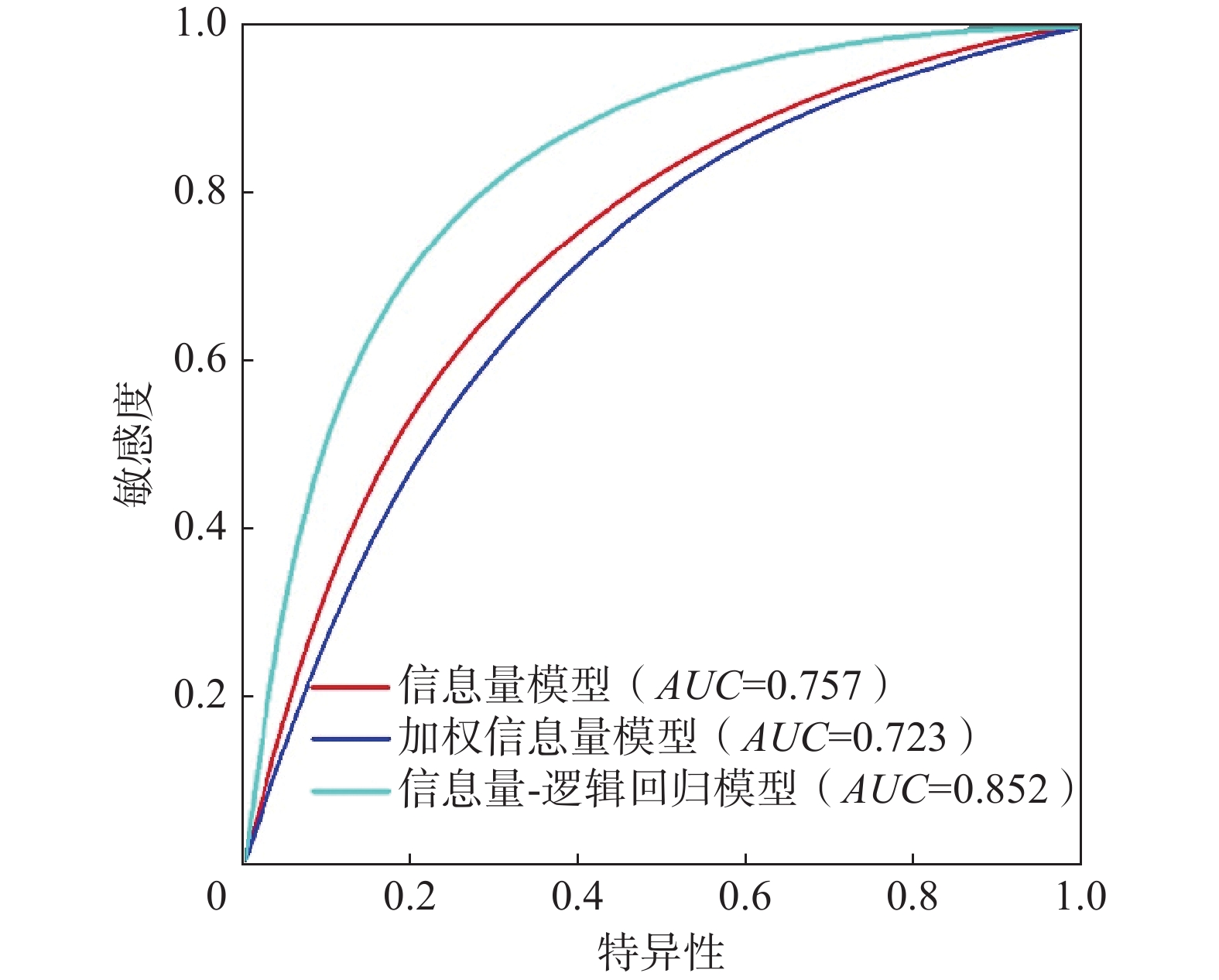
为进一步验证3种评价模型分区结果的精度,本文采用ROC(receiver operating characteristic)曲线进行精度检验。ROC曲线又称接收者工作特征曲线,其横轴特异性代表易发性面积百分比累积量,纵轴敏感度代表崩滑地质灾害点数百分比累积量。ROC曲线与坐标轴围成的面积用AUC值来表示,其线下的面积大小表示预测成功率,值越大准确率越高,模型的预测效果越好[28]。3种评价模型ROC曲线中AUC值分别为0.757,0.723,0.852(图4),加权信息量模型的精度最低,其原因是在采用层次分析法得出评价因子权重时,依据专家打分法构建判断矩阵时主观性因素较大,导致权重综合时降低了准确性,信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型的精度最高,其模型构建主要依据样本点与信息量法中分类分级信息量值进行连接,其精度与所构建的样本点存在紧密的联系,样本点统计规律越明显预测效果越好。
4.5 评价结果分析
根据所得出的评价结果,利用ArcGIS自然断点法将其划分为非、低、中和高4个等级,并将各易发性等级之间的面积(分级比)进行统计(表6),根据3种模型精度评价结果,信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型精度最高,其非-高易发区崩滑面积(分级比)分别为771.1 km2(25.55%)、836.6 km2(27.73%)、864.36 km2(28.64%)和545.94 km2(18.08%)。
表 6 崩滑易发性等级分布预测结果Table 6. Prediction results of landslide susceptibility grade distribution易发性等级 信息量模型 加权信息量模型 信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型 分级比/% 崩滑比/% 分级面积/km2 分级比/% 崩滑比/% 分级面积/km2 分级比/% 崩滑比/% 分级面积/km2 非易发区 17.56 5.84 529.96 16.17 7.14 489.03 25.55 6.49 771.1 低易发区 28.27 14.29 853.18 31.80 15.58 959.02 27.73 20.13 836.6 中易发区 32.46 31.17 979.64 33.82 35.06 1020.68 28.64 25.32 864.36 高易发区 21.71 48.70 655.22 18.20 42.21 549.27 18.08 48.05 545.94 5. 结论
(1)以罗平县为研究对象,选取工程岩组、坡度、坡向、高程、地貌类型、起伏度、曲率、距断裂距离、距河流距离等9个评价因子,进行独立性检验,选取3种评价方法构建易发性评价模型进行对比分析。
(2)通过对评价因子的分类分级处理,计算信息量值和权重值,值较大的因子类分别是:工程岩组中的层状结构坚硬长石石英砂岩岩组、地貌类型中的岩溶中山地貌和侵蚀谷地地貌、坡度主要分布在6°~30°度之间、高程集中在1350~1950 m、起伏度在23 m以下、距断裂距离和距河流距离1800 m之内,信息量值总体为正,对崩滑发育具有促进作用。
(3)根据构建的信息量模型、加权信息量模型和信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型进行对比,通过ROC曲线对3种模型的精度检验,其AUC值分别为0.757,0.723,0.852,模型的精度均大于0.7。结合崩滑点分布图,信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型评价与灾点分布情况相符合,可为快速建立评价指标体系和区域崩滑易发性提供参考依据。
-
表 1 评价因子VIF计算结果表
Table 1 Calculation results of VIF for evaluation factors
评价因子 TOL VIF 工程岩组 0.818 1.222 坡度 0.656 1.524 坡向 0.954 1.048 高程 0.904 1.107 地貌类型 0.713 1.402 起伏度 0.669 1.495 曲率 0.970 1.031 距断裂距离 0.945 1.058 距河流距离 0.717 1.396 表 2 评价因子之间的相关系数矩阵
Table 2 Correlation coefficient matrix of evaluation factors
评价因子 工程岩组 坡度 坡向 高程 地貌类型 起伏度 曲率 距断裂距离 距河流距离 工程岩组 1 坡度 0.07 1 坡向 −0.09 0.07 1 高程 0.03 −0.08 0.08 1 地貌类型 0.02 0.11 0.03 0.01 1 起伏度 0.11 0.03 0.04 0.00 0.01 1 曲率 0.07 −0.07 0.08 0.03 0.06 0.04 1 距断裂距离 0.09 −0.03 −0.04 0.06 0.09 −0.05 0.08 1 距河流距离 0.01 0.04 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.06 0.06 0.07 1 表 3 评价因子分类分级信息量值
Table 3 Information value of classification levels for evaluation factors
评价因子 因子分级 崩滑数量 栅格数量 信息量值 加权信息量值 工程岩组 软硬相间碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩岩组 2 205041 0.1347 0.0396 块状结构坚硬玄武岩岩组 50 1817099 1.1717 0.3433 坚硬层状碳酸盐岩岩组 97 15380267 −0.3014 −0.0883 第四系冲洪积松散岩组 5 661729 −0.1206 −0.0353 坡度
/(°)0~6 7 3162705 −1.3501 −0.2012 6~12 33 3790902 0.0193 0.0029 12~18 50 3707425 0.4571 0.0681 18~24 31 3008341 0.1880 0.0280 24~30 17 2054943 −0.0316 −0.0047 30~36 5 1186737 −0.7064 −0.1053 36~60 11 1091533 0.1657 0.0247 60~90 0 33429 0 0 坡向 北 16 2219489 −0.1692 −0.0129 东北 15 1920437 −0.0891 −0.0068 东 22 2493207 0.0329 0.0025 东南 31 2704414 0.2946 0.0224 南 20 2304895 0.0161 0.0012 西南 13 1974899 −0.2601 −0.0198 西 17 2138397 −0.0714 −0.0054 西北 20 2280277 0.0269 0.0020 高程/m 715~860 8 350496 0.9848 0.1468 860~1200 8 1149066 −0.2025 −0.0233 1200~1350 14 1312775 0.2239 0.4811 1350~1500 26 3226787 −0.0097 −0.1776 1500~1650 26 3079467 0.3627 −0.0402 1650~1800 29 2366839 −0.1401 1.8675 1800~1950 30 4047954 −0.5067 −0.8614 1950~2420 13 2530843 −0.5067 −3.6224 地貌类型 岩溶低中山地貌 22 2824754 −0.0904 −0.0037 构造侵蚀剥蚀地貌 18 1200919 0.5643 0.0231 岩溶中山地貌 40 3833292 0.2021 0.0083 岩溶盆地地貌 0 1948623 0 0 峰林谷地地貌 0 91609 0 0 峰丛洼地地貌 16 3752094 −0.6927 −0.0284 断块上升岩溶地貌 1 177099 −0.4119 −0.0169 断坳盆地 1 116724 0.0049 0.0002 石丘(垅岗) 2 390319 −0.5091 −0.0209 侵蚀谷地地貌 52 2561268 0.8677 0.0356 构造侵蚀岩溶地貌 2 1167462 −1.6047 −0.0658 起伏度/m 0~4 13 4183395 −1.0071 −0.0594 4~8 40 4306129 0.0879 0.0052 8~15 74 5697380 0.4232 0.0249 15~23 17 2685735 −0.2956 −0.0174 23~30 2 750479 −1.1607 −0.0684 30~38 7 294073 1.0289 0.0607 38~50 0 128414 0 0 50~220 1 57698 0.7117 0.0419 曲率 <0 70 7431512 0.0997 0.0041 0 20 3330755 −0.3505 −0.0144 >0 64 7301960 0.0277 0.0011 距断裂距离/m 0~600 70 6123046 0.2934 0.0194 600~1200 26 4659019 −0.4237 −0.0279 1200~1800 20 2742459 −0.1561 −0.0103 1800~2400 8 1599989 −0.5336 −0.0352 2400~3000 5 1028561 −0.5617 −0.0371 >3000 25 1911080 0.4281 0.0282 距河流距离/m 0~600 57 3404716 0.6748 0.0445 600~1200 32 2816455 0.2872 0.0189 1200~1800 21 2280631 0.0771 0.0051 1800~2400 14 1898512 −0.1451 −0.0096 2400~3000 6 1564553 −0.7989 −0.0528 >3000 24 6099326 −0.7731 −0.0511 表 4 评价因子分类分级判断矩阵及其权重
Table 4 Judgment matrix and weight of classification levels for evaluation factors
评价因子 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 权重 CI/CR 工程岩组 1 2 4 2 6 8 4 4 6 0.31 0.003
0.002坡度 1/2 1 2 1 3 4 2 2 3 0.155 坡向 1/4 1/2 1 1/2 2 2 1 1 2 0.083 高程 1/2 1 2 1 3 4 2 2 3 0.155 起伏度 1/6 1/3 1/2 1/3 1 1 1/2 1/2 1 0.046 曲率 1/8 1/4 1/2 1/4 1 1 1/2 1/2 1 0.041 距断裂距离 1/4 1/2 1 1/2 2 2 1 1 2 0.082 距河流距离 1/4 1/2 1 1/2 2 2 1 1 2 0.082 地貌类型 1/6 1/3 1/2 1/3 1 1 1/2 1/2 1 0.046 表 5 逻辑回归分析结果
Table 5 Results of logistic regression analysis
评价因子 B S.E Wals df sig 工程岩组 0.698 0.261 7.142 1 0.002 坡度 1.331 0.513 6.721 1 0.000 坡向 0.761 0.862 0.780 1 0.007 高程 0.309 0.246 1.570 1 0.002 地貌类型 0.171 0.421 0.165 1 0.006 起伏度 0.641 0.304 4.455 1 0.005 曲率 1.523 0.907 2.820 1 0.003 距断裂距离 0.528 0.365 2.090 1 0.004 距河流距离 0.458 0.264 3.001 1 0.000 常量 −0.165 0.142 1.336 1 0.005 注:B为回归系数,S.E为标准误,wals为卡方值,df为自由度,sig为显著性。 表 6 崩滑易发性等级分布预测结果
Table 6 Prediction results of landslide susceptibility grade distribution
易发性等级 信息量模型 加权信息量模型 信息量-逻辑回归耦合模型 分级比/% 崩滑比/% 分级面积/km2 分级比/% 崩滑比/% 分级面积/km2 分级比/% 崩滑比/% 分级面积/km2 非易发区 17.56 5.84 529.96 16.17 7.14 489.03 25.55 6.49 771.1 低易发区 28.27 14.29 853.18 31.80 15.58 959.02 27.73 20.13 836.6 中易发区 32.46 31.17 979.64 33.82 35.06 1020.68 28.64 25.32 864.36 高易发区 21.71 48.70 655.22 18.20 42.21 549.27 18.08 48.05 545.94 -
[1] 赵维城. 论云南地貌体系[J]. 云南地理环境研究,1998,10(增刊1):47 − 55. [ZHAO Weicheng. On Yunnan geomorphological system[J]. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research,1998,10(Sup 1):47 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO Weicheng. On Yunnan geomorphological system[J]. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 1998, 10(Sup 1): 47 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 陶云,唐川,段旭. 云南滑坡泥石流灾害及其与降水特征的关系[J]. 自然灾害学报,2009,18(1):180 − 186. [TAO Yun,TANG Chuan,DUAN Xu. Landslide and debris flow hazards in Yunnan and their relationship with precipitation characteristics[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2009,18(1):180 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract) TAO Yun, TANG Chuan, DUAN Xu. Landslide and debris flow hazards in Yunnan and their relationship with precipitation characteristics[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2009, 18(1): 180 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 汪民. 关于地质灾害防治需要关注的几个问题[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):1 − 5. [WANG Min. Several problems needing attention in the prevention and control of geological disasters[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Min. Several problems needing attention in the prevention and control of geological disasters[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(1): 1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 梁丽萍,刘延国,唐自豪,等. 基于加权信息量的地质灾害易发性评价——以四川省泸定县为例[J]. 水土保持通报,2019,39(6):176 − 182. [LIANG Liping,LIU Yanguo,TANG Zihao,et al. Geologic hazards susceptibility assessment based on weighted information value:A case study in Luding County,Sichuan Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,39(6):176 − 182. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIANG Liping, LIU Yanguo, TANG Zihao, et al. Geologic hazards susceptibility assessment based on weighted information value: A case study in Luding County, Sichuan Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(6): 176 − 182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] YU Chenglong,CHEN Jianping. Application of a GIS-based slope unit method for landslide susceptibility mapping in Helong city:Comparative assessment of ICM,AHP,and RF model[J]. Symmetry,2020,12(11):1848.
[6] 杨峰,薛桂澄,柳长柱,等. 基于层次分析法的地质灾害危险性评估——以文昌木兰湾新区建设项目为例[J]. 资源环境与工程,2021,35(1):72 − 75. [YANG Feng,XUE Guicheng,LIU Changzhu,et al. Geological disaster risk assessment based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2021,35(1):72 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Feng, XUE Guicheng, LIU Changzhu, et al. Geological disaster risk assessment based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2021, 35(1): 72 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 辛存林,施紫越,任文秀,等. 甘肃天水市北山地质灾害危险度区划[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2020,56(1):16 − 24. [XIN Cunlin,SHI Ziyue,REN Wenxiu,et al. Geological hazard zoning in Beishan Mountain of Tianshui District[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2020,56(1):16 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIN Cunlin, SHI Ziyue, REN Wenxiu, et al. Geological hazard zoning in Beishan Mountain of Tianshui District[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2020, 56(1): 16 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 段顺荣,李延福,李春阳. 基于GIS和层次分析法的青海甘德县地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 矿产勘查,2021,12(2):453 − 460. [DUAN Shunrong,LI Yanfu,LI Chunyang. Geological hazard risk assessment based on GIS and analytical hierarchy process in Gande County,Qinghai Province[J]. Mineral Exploration,2021,12(2):453 − 460. (in Chinese with English abstract) DUAN Shunrong, LI Yanfu, LI Chunyang. Geological hazard risk assessment based on GIS and analytical hierarchy process in Gande County, Qinghai Province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2021, 12(2): 453 − 460. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 张钟远,邓明国,徐世光,等. 镇康县滑坡易发性评价模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(1):157 − 171. [ZHANG Zhongyuan,DENG Mingguo,XU Shiguang,et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment models in Zhenkang County,Yunnan Province,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2022,41(1):157 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Zhongyuan, DENG Mingguo, XU Shiguang, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility assessment models in Zhenkang County, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(1): 157 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 邓念东,崔阳阳,郭有金. 基于频率比-随机森林模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 科学技术与工程,2020,20(34):13990 − 13996. [DENG Niandong,CUI Yangyang,GUO Youjin. Frequency ratio-random forest-model-based landslide susceptibility assessment[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2020,20(34):13990 − 13996. (in Chinese with English abstract) DENG Niandong, CUI Yangyang, GUO Youjin. Frequency ratio-random forest-model-based landslide susceptibility assessment[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(34): 13990 − 13996. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 周天伦,曾超,范晨,等. 基于快速聚类-信息量模型的汶川及周边两县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):137 − 150. [ZHOU Tianlun,ZENG Chao,FAN Chen,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on K-means cluster information model in Wenchuan and two neighboring counties,China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):137 − 150. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU Tianlun, ZENG Chao, FAN Chen, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on K-means cluster information model in Wenchuan and two neighboring counties, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(5): 137 − 150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 蒋万钰,陈冠,孟兴民,等. 基于卷积神经网络模型的区域滑坡敏感性评价——以川藏铁路沿线为例[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2022,58(2):203 − 211. [JIANG Wanyu,CHEN Guan,MENG Xingmin,et al. Evaluation of regional landslide susceptibility based on the convolution neural network model:A case study along the Sichuan Tibet Railway[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2022,58(2):203 − 211. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIANG Wanyu, CHEN Guan, MENG Xingmin, et al. Evaluation of regional landslide susceptibility based on the convolution neural network model: A case study along the Sichuan Tibet Railway[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2022, 58(2): 203 − 211. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘璐瑶,高惠瑛,李照. 基于CF与Logistic回归模型耦合的永嘉县滑坡易发性评价[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2021,51(10):121 − 129. [LIU Luyao,GAO Huiying,LI Zhao. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on coupling of CF model and logistic regression model in Yongjia County[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China,2021,51(10):121 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Luyao, GAO Huiying, LI Zhao. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on coupling of CF model and logistic regression model in Yongjia County[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(10): 121 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 金朝,费雯丽,丁卫,等. 基于信息量模型和Logistic回归模型的地质灾害易发性评价——以十堰市郧阳区为例[J]. 资源环境与工程,2021,35(6):845 − 850. [JIN Zhao,FEI Wenli,DING Wei,et al. Evaluation of geological disaster susceptibility based on information model and logistic regression model[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering,2021,35(6):845 − 850. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIN Zhao, FEI Wenli, DING Wei, et al. Evaluation of geological disaster susceptibility based on information model and logistic regression model[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2021, 35(6): 845 − 850. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 吉日伍呷,田宏岭,韩继冲. 基于不同机器学习算法的地震滑坡易发性评价——以鲁甸地震为例[J]. 昆明理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,47(2):47 − 56. [JI R,TIAN Hongling,HAN Jichong. Evaluation of the susceptibility of earthquake landslides based on different machine learning algorithms:Taking Ludian earthquake as an example[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Natural Science),2022,47(2):47 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) JI R, TIAN Hongling, HAN Jichong. Evaluation of the susceptibility of earthquake landslides based on different machine learning algorithms: Taking Ludian earthquake as an example[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2022, 47(2): 47 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 樊芷吟,苟晓峰,秦明月,等. 基于信息量模型与Logistic回归模型耦合的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(2):340 − 347. [FAN Zhiyin,GOU Xiaofeng,QIN Mingyue,et al. Information and logistic regression models based coupling analysis for susceptibility of geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(2):340 − 347. (in Chinese with English abstract) FAN Zhiyin, GOU Xiaofeng, QIN Mingyue, et al. Information and logistic regression models based coupling analysis for susceptibility of geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(2): 340 − 347. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张晓东. 基于遥感和GIS的宁夏盐池县地质灾害风险评价研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2018. [ZHANG Xiaodong. Study on geological disaster risk assessment based on RS and GIS in Yanchi County,Ningxia[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Xiaodong. Study on geological disaster risk assessment based on RS and GIS in Yanchi County, Ningxia[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 陈立华,李立丰,吴福,等. 基于GIS与信息量法的北流市地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 地球与环境,2020,48(4):471 − 479. [CHEN Lihua,LI Lifeng,WU Fu,et al. Evaluation of the geological hazard vulnerability in the Beiliu City based on GIS and information value model[J]. Earth and Environment,2020,48(4):471 − 479. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Lihua, LI Lifeng, WU Fu, et al. Evaluation of the geological hazard vulnerability in the Beiliu City based on GIS and information value model[J]. Earth and Environment, 2020, 48(4): 471 − 479. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 杨盼盼,王念秦,郭有金,等. 基于加权信息量模型的临潼区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 长江科学院院报,2020,37(9):50 − 56. [YANG Panpan,WANG Nianqin,GUO Youjin,et al. Assessment of landslide susceptibility in Lintong district using weighted information value model[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2020,37(9):50 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Panpan, WANG Nianqin, GUO Youjin, et al. Assessment of landslide susceptibility in Lintong district using weighted information value model[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2020, 37(9): 50 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 庞栋栋,刘刚,何敬,等. 基于层次分析法的甘肃省地质灾害风险评估分析[J]. 国土资源信息化,2021(6):41 − 47. [PANG Dongdong,LIU Gang,HE Jing,et al. Analysis of geological hazard risk assessment in Gansu Province based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Land and Resources Informatization,2021(6):41 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract) PANG Dongdong, LIU Gang, HE Jing, et al. Analysis of geological hazard risk assessment in Gansu Province based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Land and Resources Informatization, 2021(6): 41 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 郭谦. 层次分析法在生态环境综合评价应用中的优化[J]. 国土资源遥感,2008,20(3):104 − 107. [GUO Qian. The optimization of AHP in its application to the comprehensive evaluation of ecological environment[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources,2008,20(3):104 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO Qian. The optimization of AHP in its application to the comprehensive evaluation of ecological environment[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2008, 20(3): 104 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 张玘恺,凌斯祥,李晓宁,等. 九寨沟县滑坡灾害易发性快速评估模型对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(8):1595 − 1610. [ZHANG Qikai,LING Sixiang,LI Xiaoning,et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping rapid assessment models in Jiuzhaigou County,Sichuan Province,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(8):1595 − 1610. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Qikai, LING Sixiang, LI Xiaoning, et al. Comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping rapid assessment models in Jiuzhaigou County, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(8): 1595 − 1610. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 杜国梁,杨志华,袁颖,等. 基于逻辑回归-信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 杜国梁,杨志华,袁颖,等. 基于逻辑回归-信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang,YANG Zhihua,YUAN Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 王涛,刘甲美,栗泽桐,等. 中国地震滑坡危险性评估及其对国土空间规划的影响研究[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(1):21 − 39. [WANG Tao, LIU Jiamei, LI Zetong, et al. Seismic landslide hazard assessment of China and its impact on national territory spatial planning[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(1):21 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Tao, LIU Jiamei, LI Zetong, et al. Seismic landslide hazard assessment of China and its impact on national territory spatial planning[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(1): 21 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 周苏华,付宇航,邢静康,等. 基于不同统计模型的肯尼亚滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(4): 114 − 124. [ZHOU Suhua, FU Yuhang, XING Jingkang, et al. Assessment of landslide hazard risk in Kenya based on different statistical models[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(4):114 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU Suhua, FU Yuhang, XING Jingkang, et al. Assessment of landslide hazard risk in Kenya based on different statistical models[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(4): 114 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 孙滨,祝传兵,康晓波,等. 基于信息量模型的云南东川泥石流易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(5):119 − 127. [SUN Bin, ZHU Chuanbing, KANG Xiaobo, et al. Susceptibility assessment of debris flows based on information model in Dongchuan, Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(5):119 − 127.(in Chinese with English abstract) SUN Bin, ZHU Chuanbing, KANG Xiaobo, et al. Susceptibility assessment of debris flows based on information model in Dongchuan, Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(5): 119 − 127.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 刘璐瑶,高惠瑛. 基于证据权与Logistic回归模型耦合的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(1):165 − 175. [LIU Luyao,GAO Huiying. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on coupling of woe model and logistic regression model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023,31(1):165 − 175. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Luyao, GAO Huiying. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on coupling of woe model and logistic regression model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2023, 31(1): 165 − 175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(15)
1. 王秀琴,牛全福,王浩,程西安,李克恭,牛虎林. 甘肃积石山M_s6.2级地震区滑坡危险性评价与区划. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2025(01): 169-181 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 苏志萍,杨成生,王子倩. 结合负样本优化与机器学习模型的怒江洲峡谷段滑坡易发性评价. 地球信息科学学报. 2025(04): 979-993 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈宾,李颖懿,张联志,屈添强,魏娜,刘宁,黄春林. 地质灾害易发性评价因子分级的AIFFC算法优化. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(01): 72-81 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 赵佳忆,田述军,李凯,侯鹏鹂. 岷江上游汶川地震前后泥石流易发性评价. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(01): 51-59 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 曾韬睿,王林峰,张俞,程平,吴帆. 基于CatBoost-SHAP模型的滑坡易发性建模及可解释性. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(01): 37-50 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 于宪煜,汤礼. 基于SMOTE-Tomek和CNN耦合的滑坡易发性评价模型及其应用——以三峡库区秭归—巴东段为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(03): 141-151 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 李德. 怀宁县地质灾害风险调查评价. 地下水. 2024(04): 164-167 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 朱浩,李书,史超,丁凡桠. 基于INF-Logistic回归耦合模型的云阳县迁建区滑坡易发性评价. 中国水运(下半月). 2024(10): 36-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 吴问楚,王朝,管后春,黄蒙,乔雯. 基于GIS与加权信息量模型的汤口断裂南段地区地质灾害易发性评价. 科学技术与工程. 2024(26): 11121-11130 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 朱浩,李书,史超,丁凡桠. 基于INF-Logistic回归耦合模型的云阳县迁建区滑坡易发性评价. 中国水运. 2024(20): 36-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 刘家恺,朱杰勇,喻聪骏,王灿星,祝传兵,代旭升. 基于多源遥感的高山峡谷区崩滑识别及易发性评价. 化工矿物与加工. 2024(12): 62-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 吴雅睿,娄春辉,侯龙君,刘峰. 基于信息量与机器学习耦合模型的滑坡易发性评价对比分析. 西安科技大学学报. 2024(06): 1140-1153 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 郁是瞻. 基于MapGIS的信息量法在输电线路工程中的应用. 四川地质学报. 2024(04): 750-755 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 张平平,李滨,高浩源,万佳威. 西藏林芝多雄河流域高位雪崩易发性评价. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(06): 44-57 .  本站查看
本站查看
15. 康晓波,杨迎冬,王宇,祝传兵,黄成,张杰,周翠琼,柴金龙,张文鋆. 云南省地质灾害综合防治体系建设系列专项研究进展. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(06): 146-157 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载:
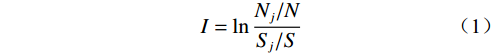
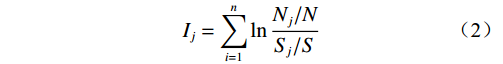
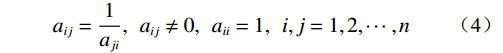
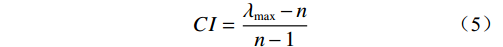
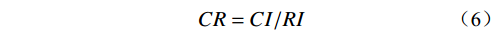
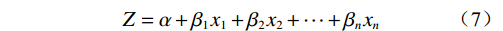
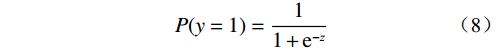
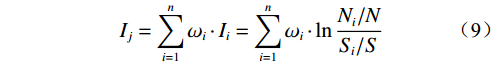

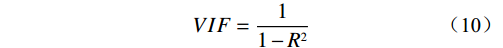
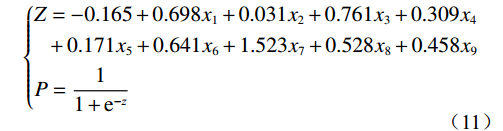

 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS