Analysis on deformation mechanism of the Lingwan Village landslide in Shaanxi Province section of the West-East Gas Pipeline Project
-
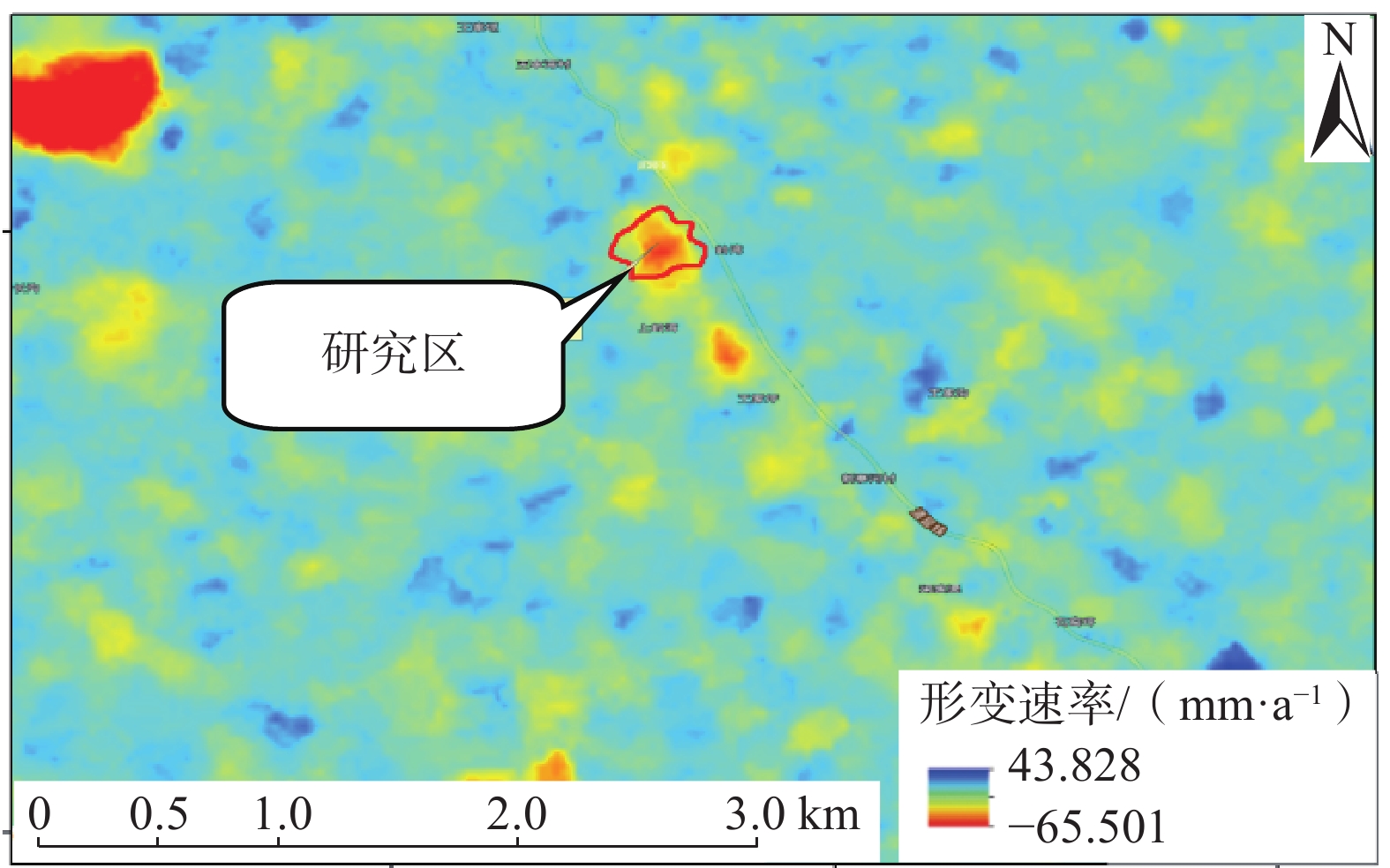
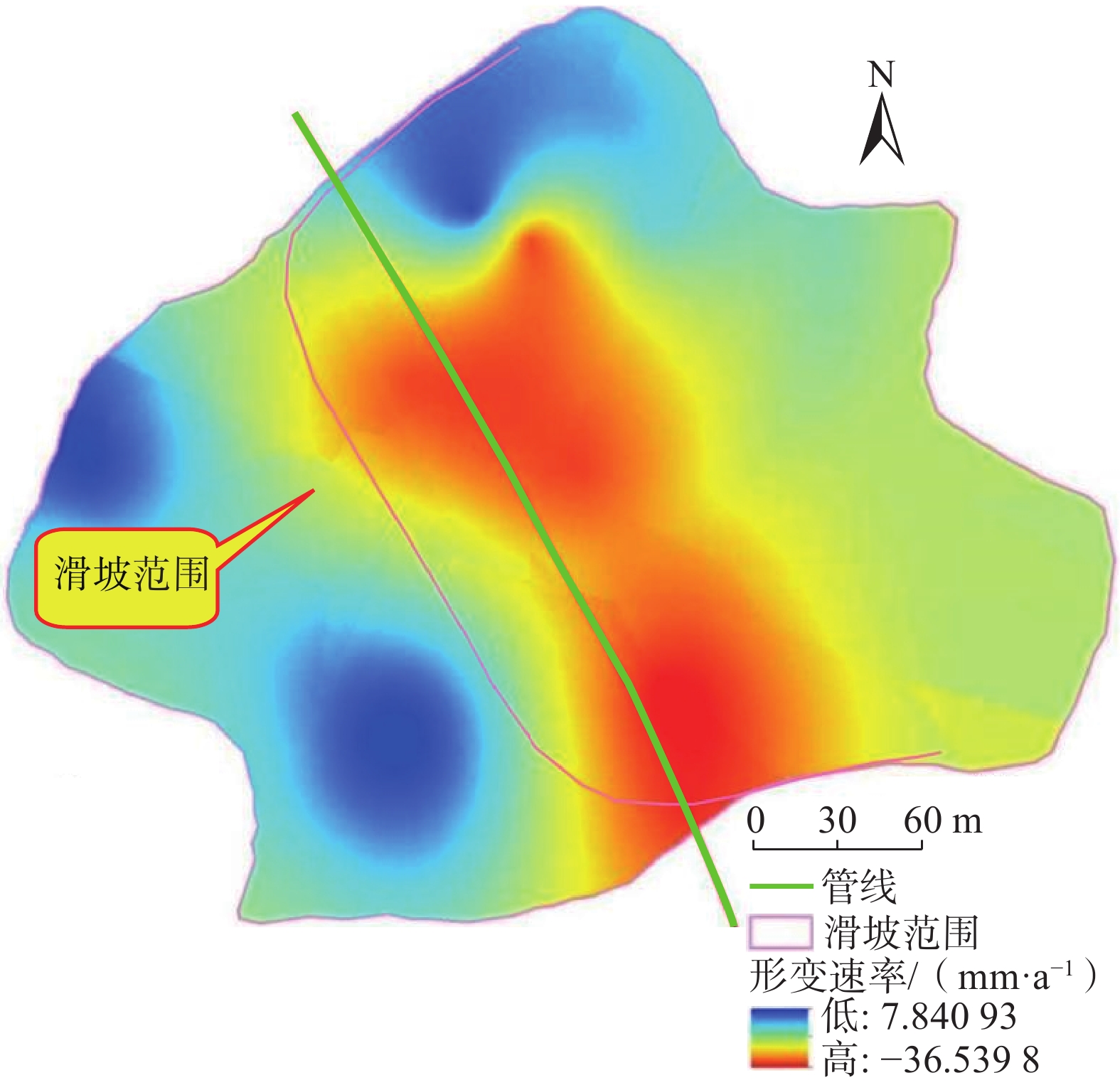
摘要: 以西气东输管道余家坪镇岭湾村一处正在变形的黄土滑坡为研究对象,基于现场勘察、InSAR、GNSS监测和深部位移监测等,分析滑坡2017—2022年的变形特征及滑坡成因机制。研究表明:滑坡地下水位已达坡脚,滑坡前缘形成多处“土溜”,滑坡地表垂直潜蚀裂缝发育,后缘可见贯通的裂缝,滑坡内管道周边裂缝发育;InSAR数据显示滑坡一直缓慢变形,年变形量2.0~4.0 cm; GNSS变形及裂缝变形显示,2020年8月至今地表变形速率增大,变形明显,变形量在4~10 cm;深部变形监测数据变化量在0.05~1.36 mm,变化很小;降雨及土体含水率数据分析表明滑坡在暴雨后发生位移变形。综合分析监测数据表明,岭湾村滑坡属于降雨诱发的浅层滑坡;区域内的自然强降雨、人类工程经济活动作为滑坡的诱发因素,对滑坡的发生及发展作用明显。结合管道应变监测数据,目前西气东输管道遭受滑坡灾害的风险可控。Abstract: Based on field investigation, InSAR, GNSS monitoring, and deep displacement monitoring, a deformed loess landslide in Lingwan Village, Yujiaping Town, West-East Gas Pipeline Project was analyzed to understand its deformation characteristics and landslide formation mechanism from 2017 to 2022. The analysis shows that the groundwater level of the landslide has reached the toe of the slope, and numerous soil slips have been formed at the front edge of the landslide. The surface of the landslide exhibits vertical subsurface erosion cracks, while the penetrating cracks can be seen at the trailing edge. InSAR data shows that the landslide has been slowly deformed, with an annual deformation rate between 2.0 - 4.0 cm. GNSS deformation and crack deformation show that since August 2020, the surface deformation rate has increased significantly, with a deformation rate between 4.0 - 10.0 cm. The variation of deep deformation monitoring data is minimal, between 0.05 to 1.36 mm. Analysis of rainfall and soil moisture data shows that the landslide has displacement deformation after rainstorm. The comprehensive analysis of monitoring data reveals that the landslide in Lingwan Village is a shallow landslide induced by rainfall. Natural heavy rainfall and human engineering economic activities in the region are the primary inducing factors for the occurrence and development of landslide. Combined with pipeline strain monitoring data, the risk of landslide disasters in Shaanxi Province section of West-East Gas Pipeline Project is controllable.
-
0. 引言
滑坡是我国发育最广泛的地质灾害之一,尤其是21世纪以来,随着人类工程活动的开展,滑坡发生频率上升,造成了巨大的人员伤亡和经济损失。对滑坡的风险评估和预测是目前防灾减灾的重要途径之一。随着计算机技术的发展,目前对滑坡风险评估逐渐由定性向定量转变,在定量评价中,堆积层厚度对滑坡识别具有重要意义,并且是一个重要的控制因素,能否对其进行准确预测是定量评价的关键。
目前,国内外对于土壤厚度的预测研究较为成熟,主要有基于物理机制、基于点采样插值、基于遥感的方法和基于环境相关推理的方法[1]。李岩等[2]采用多种插值方法对草原栗钙土层厚度空间分布进行预测,并选出适合研究区的最优插值方法。王桂林等[3]基于粒子群优化对协同克里金法进行了优化,结果表明该法对提高土层厚度的预测精度有较大作用。Scarphone等[4]采用广义线性模型(GLM)、随机森林(RF)、GLM残差克里格法和RF残差克里格法预测土壤厚度,结果表明GLM残差克里格法是预测浅层土壤厚度的最佳方法。Pradhan等[5]基于相对起伏度开发了一种空间土壤厚度模型,结果表明该模型的预测能力要优于多元线性回归模型和S模型。Li等[6]采用多元线性回归(MLR)、支持向量回归(SVR)、随机森林(RF)和极端梯度推进(XGBoost)4种常用机器学习方法分别对河南省土壤厚度进行预测。
堆积层厚度预测与土壤厚度预测有相似之处,区别在于堆积层厚度预测需要更多地考虑地质成因,国内对堆积层厚度的研究较少,多以空间插值为主,但对外界因素考虑不足,难以满足精度要求。刘磊等[7]根据已知区域堆积层厚度与其标志因子之间的关系,建立了基于随机森林算法的堆积层厚度模型,估算了整个万州主城区的堆积层厚度的空间分布。段贵娟等[8]以水平相关距离为基础数据,采用普通克里金法对南海区域的厚度分布进行了空间预测,预测效果良好。邵晨灿等[9]通过分析各成因类型土层厚度的影响因素,采用决策树模型建立影响因素与土层厚度之间的关系,推测了贵州省瓮安县的土层厚度分布。虽然目前国内外对于堆积层厚度的研究较少,但是对于土壤厚度的预测研究较为成熟,对堆积层厚度的研究可以借鉴土壤学中基于环境相关推理的方法,该方法假设相同的土壤景观单元发育相同的土壤类型,如Wang等[10]通过采用模糊C-均值法和模糊隶属函数构建土壤景观模型,从而预测中国三峡秭归地区土壤深度的空间变化。Akumu等[11]开发了一种基于GIS模糊逻辑建模方法的土壤深度建模和制图技术,制图精度达到94%,优于随机森林模型。Cheng等[12]提出了一种从单个土壤多边形中挖掘土壤-环境关系的方法,对传统土壤图进行了更新。基于环境相关推理法应用到堆积层厚度中为:相同地质环境下的堆积层厚度相似,可通过已知点的堆积层厚度与影响因子之间的关系预测整个区域的堆积层厚度。
三峡库区万州区铁峰乡地质灾害以滑坡为主,探索区内堆积层厚度对于滑坡稳定性评价显得尤为重要。鉴于此,本文以铁峰乡为研究对象,在实地调查的基础上,首先总结了区域堆积层的成因模式,并据此添加区域堆积层厚度控制点;其次定量分析了堆积层厚度与影响因子之间的相关性,并基于Apriori算法挖掘并分析影响因子与堆积层厚度的关联准则;最后,选用三种机器学习模型对研究区堆积层厚度进行空间预测,并对预测结果进行对比分析。研究结果揭示了区域第四系堆积层的成因机制,为机器学习在堆积层厚度预测领域奠定了基础。
1. 数据挖掘与预测模型
1.1 数据挖掘
数据挖掘流程主要由数据采集,数据预处理,数据离散化和关联准则挖掘四步组成。本文采用两步聚类算法及Apriori算法,通过数据挖掘流程处理堆积层厚度数据,得到堆积层厚度与影响因子间的关联准则。
(1)数据采集:将堆积层厚度进行收集归纳,获得基础数据。
(2)数据预处理:对已有数据进行审核、筛选、排序等处理措施。
(3)数据离散化:由于Apriori算法只能处理离散型变量,故采用两步聚类法将堆积层厚度离散化。
(4)关联准则挖掘:应用Apriori算法对离散后的变量进行关联规则集合选择,生成有效的关联规则。
通过两步聚类算法对堆积层厚度类型进行转化,将分类所得的变量采用Apriori算法计算,挖掘堆积层厚度的关联准则。
Apriori算法由Agrawal和Srikant提出[13],该算法首先生成高于最小支持度的频繁项目集,在第一步产生的频繁项目集中生成高于最小可信度的关联准则。
频繁项目集是指对包含项目a的项集T,其支持度大于或等于用户指定的支持度阈值,即:
(1) 包含k个项目的频繁项目集称为频繁k项集,记为
Apriori算法实现过程详见图1。首先,搜索出产生长度为1的频繁项集
从频繁项目集中产生简单的关联准则,按置信度大于置信度阈值的条件,选择出有效规则集合。对每个频繁项目集L,计算L所有非空子集
(2) 则生成关联准则
1.2 GWO-SVM
支持向量回归机模型(Support vector regression,SVR)由美国学者Vapnik[14]提出,主要用于解决非线性问题的回归,其基本思想是:将样本数据分为两部分,分别为训练样本和测试样本,通过事先选择的非线性映射将输入向量(训练样本)映射到高维度特征空间,利用其有限的样本数据进行训练计算,求得达到最佳拟合效果时在这个空间中构造出的最优决策函数模型,对比测试项以分析模型的测试效果。该模型以统计训练理论为基础,实现小样本条件下的统计规律和学习,特点为结构简单,且性能比传统的BP神经网络有明显的优势。因此,本模型在堆积层厚度预测方面具有一定的优越性。
在SVM模型的参数优化方法中,灰狼算法(Grey wolf optimization,GWO)较粒子群算法(Particles swarm optimization,PSO)、遗传算法(Genetic algorithm,GA)等传统启发式算法而言,在研究组合式优化问题上已被证明具有显著优势,能够有效地解决多种参数的联合寻优问题。此外,GWO-SVM模型更适合小样本数据,且具有更好的学习效果。
GWO优化SVM的基本思想是将SVM的惩罚因子
采用GWO-SVM耦合模型,对堆积层厚度进行预测,具体预测流程如下:
(1)输入训练集和测试集。
(2)初始化狼群数量、迭代次数,设置惩罚因子
(3)GWO以
(4)利用寻优得到的参数构建预测模型,利用该模型进行堆积层厚度预测。
2. 区域地质背景
2.1 研究区概况
铁峰乡位于重庆市万州区北部山区(图2),长江上游,东邻九池乡,南靠石龙乡、石和乡,西连两汇乡,北接开州区,总面积为51.46 km2。属亚热带季风气候,四季分明,雨量充沛。地势总体上南北两侧高,中间海拔低,以构造侵蚀中低山-河谷地貌为主。区内出露地层有侏罗系中统沙溪庙组和新沟组、侏罗系下统自流井组和珍珠冲组、三叠系须家河组和巴东组。第四系覆盖物广,主要为残坡积物、崩滑堆积物和河流冲洪积物。研究区位于铁峰山背斜北西翼核部,背斜全长约114 km,走向50°~70°,轴线呈凸向NNW的弧形,轴部地层为三叠系巴东组,两翼为侏罗系中、下统。
2.2 研究区地质灾害
铁峰乡发育的地质灾害类型包括堆积层滑坡、顺层岩质滑坡和岩质崩塌。根据地质灾害调查资料,研究区共发育历史滑坡灾害14处(堆积层滑坡12处,岩质滑坡2处),新生滑坡灾害12处(堆积层滑坡9处,岩质滑坡3处),堆积层滑坡主要分布于研究区南侧的顺向坡区段,目前多处于蠕滑变形状态;顺层岩质滑坡主要发育于自流井组和珍珠冲组地层内,以软弱夹层为主要的控滑结构,其稳定状态受公路开挖的影响极大。研究区崩塌灾害点主要分布于研究区斜交坡、北侧逆向坡结构的自然高陡边坡,以及公路开挖形成的高切坡之上,总计87处,以楔形体滑移式崩塌为主,占崩塌灾害点总量的56.3%,其次为坠落式崩塌,占比32.2%。
2.3 研究区堆积物成因模式
本次野外调查共确定了192个堆积层厚度数据控制点。对于全区而言,这些控制点不足以完成铁峰乡的堆积层厚度预测。因此,需在野外调查的基础上分析堆积层的成因模式,并据此添加一定量的堆积层控制点。根据铁峰乡坡体结构和岩层组合关系,对堆积层的成因进行分析总结,将研究区第四系堆积层分为残坡积和崩滑堆积两大类,崩滑堆积又可分为顺向坡远程滑动堆积、顺向坡近距离滑动堆积、顺向坡侧向崩塌堆积和软硬相间岩层崩滑堆积四种成因模式。
2.3.1 残坡积
指地表岩石风化后残留在原地的堆积物(图3),可区分为机械风化作用和化学风化作用。
(1)坡顶及原地残积物
由于重力和流水的搬运,宏观上沟谷及山麓地区多为冲、洪积物分布。残积物范围较为局限,山顶及未受扰动的风化原地堆积较为明显。常见的差异为较软的岩性风化堆积厚度较大,较硬的岩性厚度较薄。
(2)斜坡上部残积物
主要为风化堆积的残积物,未受重力作用及流水侵蚀而发生崩滑运动。该处第四系堆积形态与原岩较为相似,层状结构与地层一致。多位于发生过崩滑区域的上部,且相对于中下部厚度较薄。
(3)软硬相间岩性残积物
由于岩性差异形成的风化差异,不同的岩性处风化厚度不同,堆积形态也有所差异。整体上表现为原生堆积物在软岩处风化强烈,地形较缓且堆积较厚;在硬质岩处风化较弱,地形较陡而堆积较薄。
2.3.2 崩滑堆积
指因崩塌滑坡运动造成的堆积物,原始堆积物形态发生改变。可分为顺向坡远程滑动堆积、顺向坡近距离滑动堆积、顺向坡侧向崩塌堆积和软硬相间岩层崩滑堆积四种成因模式。
(1)顺向坡远程滑动堆积
原岩风化形成的堆积物发生远程滑动从而改变坡面原始形态。从纵剖面上来看,斜坡后部地形较缓,且堆积体较薄,主要为残留的滑坡堆积物和较薄的残坡积物;中前部由于滑坡下滑堆积,厚度较大,且易形成局部平台,主要物质为滑坡堆积物。若滑坡运动距离较大,滑坡堆积物可能覆盖坡底冲沟内的冲洪积物,甚至冲入河道,改变河道形态(图4)。
(2)顺向坡近距离滑动堆积
原岩风化形成的堆积物在内外地质作用的影响下沿软弱层面发生失稳破坏,改变原始地貌形态。原始地貌平面上为正常侵蚀堆积的山坡,沟谷之间过渡平衡,而发生滑动后横剖面中部可见明显的非正常侵蚀,堆积物下移而导致中间地形下错明显,平面上可见明显的洼地。剖面上原地形为自然过渡的缓坡,滑动部分导致前缘鼓胀、堆积较厚;后缘发生滑动出现地形下陷。坡顶为基岩,上部为风化后未完全滑动的残积物,中下部为风化后滑动堆积的滑坡堆积物,厚度较大,前部可能存在被滑坡堆积所部分覆盖的冲洪积物(图5)。
(3)顺向坡侧向崩塌堆积
顺向坡两侧冲沟陡崖在侧向侵蚀的作用下发生崩塌,崩积物堆积于陡崖下部,从而改变原始地貌。近崖处地形较陡,堆积层厚度较薄;随陡崖向外地形逐渐变缓,堆积厚度增厚;由于崩积物运动能量有限,远处堆积厚度逐渐变薄直到停止运动。由于崩坡积物粒径差异大,其形成的堆积结构特点明显,粒径较大的崩积物运动距离较大,多堆积于中前部,形成整体上前粗后细的堆积特点(图6)。
(4)软硬相间岩层崩滑堆积
软硬相间地层且临空条件较好,存在明显的差异风化特征,导致地形上出现了多级陡缓相间的差异变化,且不同位置堆积厚度及范围不同。平台堆积物厚度与陡崖的剖面形态相关,可分为三种类型:①坡下坡上陡崖高度一致,侧向的侵蚀范围相当,堆积厚度一定,以崩积物为主;②坡下陡崖高于坡下时,坡下堆积范围较坡上大,且厚度较大,以崩积物为主;③当侧向侵蚀同时存在滑坡时,坡上以崩积物为主,坡下滑动区则下伏滑坡堆积物,上覆新生崩积物(图7)。
3. 堆积物关联准则挖掘与预测
3.1 堆积层厚度影响因子
在研究区野外调查获得的192个堆积层厚度数据点的基础上,结合上述堆积层成因模式,添加包含0点和非0点在内的堆积层厚度控制点,累计共得到1211个数据样本点。根据堆积层成因模式和堆积特点,本文考虑了坡度、坡向、流向、地形起伏、剖面曲率、斜坡结构等13个影响因子。采用ArcGIS软件对研究区的1∶10000地形图进行栅格划分,并对上述13个因子进行提取并分级,统计各调查点的堆积层厚度,分析堆积层厚度的分布规律。本文选取坡度、坡向、流向、高程、地形起伏、剖面曲率、斜坡结构六个因子进行分析(图8)。
(1)坡度
从坡度因子图可以看出,研究区坡度主要集中在10°~40°范围内,该坡度范围内堆积层平均厚度为2.5~3.0 m。从堆积层平均厚度可以看出,堆积层厚度与坡度成反比,在坡度大于50°时,堆积层厚度接近0,而在0~40°范围内,堆积层厚度大于1.0 m,这表明在坡度低的地方,土层更容易堆积保留,从而形成一定的堆积层厚度,见图8(a)。
(2)坡向
从坡向因子图中可以看出,研究区内整体呈现出越接近于南北向的地方土层厚度越大的规律,在坡向近东西的区域内,堆积层的厚度普遍较小,通常小于0.5 m,在坡向为南北向的区域内堆积层的平均厚度达到最大值,通常在1.5~2 m。此规律与研究区内的地形地貌相吻合,研究区内坡向基本都是沿南北向分布,土体的崩滑运动主要也是沿这个方向发展,从而使土体在此方向上的堆积厚度大于其他方向,见图8(b)。
(3)流向
从流向因子图可以看出,堆积层平均厚度在大体上呈现出越容易向北汇水的区域堆积层厚度越厚,这与坡向因子相似,当堆积层点向北汇水时,该点更可能位于顺向坡内,而顺向坡更易发生崩滑运动,从而造成向北汇水点的堆积层厚度更厚,见图8(c)。
(4)地形起伏
从地形起伏因子可以看出,堆积层厚度分布规律与坡度因子完全一致,与地形起伏程度呈反比,地形起伏越小的区域内,土体越容易堆积,堆积层平均厚度在2.5~3 m之内,而当地形起伏达到4 m时,堆积层平均厚度仅为0.5 m,地形起伏超过5 m时,堆积层难以形成,平均厚度接近0。该规律与研究区地形相符合,由于研究区位于山区,地形起伏较大的区域往往也是坡度较大的区域,受地形限制,土体难以堆积,见图8(d)。
(5)剖面曲率
从剖面曲率因子可以看出,堆积层调查点主要集中在0~10、60~70、>70三个分级内。堆积层厚度分布呈现出与剖面曲率呈反比的规律,当剖面曲率位于0~10之内时,堆积层平均厚度达2.5~3 m,而当剖面曲率达到70时,厚度仅有0.5 m。剖面曲率大代表地表高程变化率大,即地势急剧变化,因此土层难以堆积保留,见图8(e)。
(6)斜坡结构
从斜坡结构因子可以看出,研究区主要为斜交坡和顺向坡。从堆积层厚度上看,土体在顺向坡中更容易堆积,从而形成一定的堆积层,顺向坡中的堆积层厚度在2.5~3 m之间,而斜交坡中堆积层厚度仅为1 m左右。这与地形作用息息相关,在顺向坡中,山体上部的土体由于崩滑等一系列作用从而向下移动,在顺向坡中往下堆积,从而在下部容易形成一定厚度的堆积层,见图8(f)。
3.2 关联准则挖掘
采用GRA(Grey relation analysis)和MIC(Maximal information coefficient)两种算法来分析上述13个影响因子与堆积层厚度的相关性,计算结果如表1所示。根据计算结果,各因子与堆积层厚度的GRA值差异不大,但是对于MIC算法,因子1、2、3、6、10、12与堆积层厚度的MIC值均大于0.2,表示具有较强的相关性。因此,本文选取以上6个因子(坡度、坡向、流向、地形起伏、剖面曲率、斜坡结构)作为关联前项,堆积层厚度作为关联后项,根据已知样本点数据挖掘两者的关联准则。
表 1 各因子与堆积层厚度相关性指标Table 1. Correlation index between each factor and accumulation layer thickness因子 GRA MIC 因子1 坡度 0.6923 0.6977 因子2 坡向 0.6878 0.5285 因子3 流向 0.8673 0.4696 因子4 高程 0.7050 0.0752 因子5 汇水条件 0.6349 0.0417 因子6 地形起伏 0.6856 0.6933 因子7 地层 0.7546 0.0486 因子8 距水系距离 0.6366 0.0525 因子9 距陡崖距离 0.6063 0.0637 因子10 剖面曲率 0.6953 0.2141 因子11 平面曲率 0.6783 0.0784 因子12 斜坡结构 0.6364 0.3271 因子13 植被覆盖 0.6440 0.0943 由于数据挖掘中Apriori算法仅能处理离散型变量,因此,需要对影响因子进行聚类。采用两步聚类算法对坡度、坡向、流向、地形起伏、剖面曲率、斜坡结构6个因子进行聚类,如表2所示。堆积层厚度按照(0~2 m)、(2~4 m)、(4~6 m)、(6~8 m)、(>8 m)划分为HD1、HD2、HD3、HD4、HD5五类。
表 2 各因子属性指标Table 2. Attribute indicators of each factor因子 属性 类别 因子1 坡度 0~20° F11 20°~40° F12 >40° F13 因子2 坡向 337.5°~67.5° F21 67.5°~157.5° F22 157.5°~247.5° F23 247.5°~337.5° F24 因子3 流向 1&2 F31 4&8 F32 16&32 F33 64&128 F34 因子6 地形起伏 0~2 F61 2~4 F62 >4 F63 因子10 剖面曲率 0~20 F101 20~40 F102 40~60 F103 >60 F104 因子12 斜坡结构 顺向坡 F121 逆向坡 F122 斜交坡 F123 根据已知样本点数据,以上述六个影响因子作为关联前项,堆积层厚度作为关联后项,设定支持度阈值为0,置信度阈值为100%,以前项最大为3生成堆积层厚度与影响因子的关联准则。共生成关联准则193条(部分准则如表3所示)。从关联准则可以看出,当堆积层厚度大于2 m时,坡度小于40°、地形起伏小于4 m,而当堆积层厚度小于2 m时,坡度大于40°、地形起伏大于4 m,说明坡度和地形起伏是造成堆积层厚度空间分布差异的主要因素。
表 3 堆积层厚度关联准则Table 3. Association criterion of accumulation layer thickness规则 ID 规则 支持度/% 置信度/% 1 YZ3=F31 & YZ6=F62 & YZ2=F21 0.08 100.00 2 YZ3=F31 & YZ2=F21 & YZ1=F12 0.08 100.00 3 YZ2=F22 & YZ3=F34 & YZ1=F11 0.08 100.00 4 YZ2=F22 & YZ3=F34 & YZ6=F61 0.08 100.00 5 YZ3=F34 & YZ1=F12 & YZ2=F24 0.17 100.00 6 YZ2=F23 & YZ10=F102 & YZ1=F11 0.08 100.00 7 YZ10=F102 & YZ2=F22 & YZ1=F11 0.08 100.00 8 YZ3=F31 & YZ6=F63 18.58 100.00 9 YZ3=F31 & YZ1=F13 & YZ6=F63 17.18 100.00 10 YZ2=F22 & YZ1=F13 & YZ6=F63 17.01 100.00 3.3 堆积物厚度预测
研究区共划分了486097个栅格点,其中1211个堆积层调查点,484886个预测栅格点。从1211个调查点中,随机选取1011个点作为训练样本,剩余200个作为测试样本,484886个未知堆积层厚度的栅格点作为预测样本,分别采用PSO-SVM、GA-SVM、GWO-SVM 3种机器学习模型对研究区堆积层厚度分布开展训练及预测。采用PSO、GA、GWO三种算法对SVM模型进行三参数寻优,各种优化方法的搜索区间如下:惩罚因子
预测模型 MSE RMSE Q C 平均厚度/m PSO-SVM 401.22 1.42 0.47 0.79 1.49 GA-SVM 198.57 1.00 0.23 0.76 1.76 GWO-SVM 152.24 0.87 0.19 0.83 1.83 采用上述3种模型对区域堆积层厚度进行预测,预测结果如图10所示。根据图9和表4可知,GWO-SVM模型的测试结果与实际最为吻合,预测结果MSE为152.24,RMSE为0.87,精度最佳。另外,采用GWO-SVM的全区堆积层厚度预测结果平均值为1.83 m,与现场实际调查的结果较为相符(根据调查点数据,堆积层平均厚度为1.43 m)。因此,选取GWO-SVM模型得到的区域堆积层厚度分布图为最终结果,如图10(c)所示。
由图10(c)可知,颜色较深区域为堆积层厚度较薄地区,对应于研究区坡度较陡以及陡崖带附近,与上述坡度越大堆积层厚度越小的规律相符;从近陡崖处到远离陡崖的位置,堆积层厚度呈现出薄-厚-薄的规律;总体沿南北方向呈条带状分布,与研究区地形地貌相契合,在坡脚处堆积较厚。
4. 结论
(1)万州区铁峰乡第四系堆积层可分为残坡积和崩滑堆积两类,崩滑堆积有四种成因模式,分别为:顺向坡远程滑动堆积、顺向坡近距离滑动堆积、顺向坡侧向崩塌堆积和软硬相间岩层崩滑堆积。
(2)堆积层厚度与六种因子表现出较强的相关性:坡向、坡度、流向、地形起伏、剖面曲率和斜坡结构。其中坡度和地形起伏是造成堆积层厚度空间分布差异的主要因素。
(3)采用三种机器学习模型对铁峰乡堆积层厚度进行预测,结果显示GWO-SVM模型的预测结果与实际最为吻合,表明该方法可较好地应用于区域第四系堆积层厚度预测,为滑坡灾害识别提供更为可靠的依据。
-
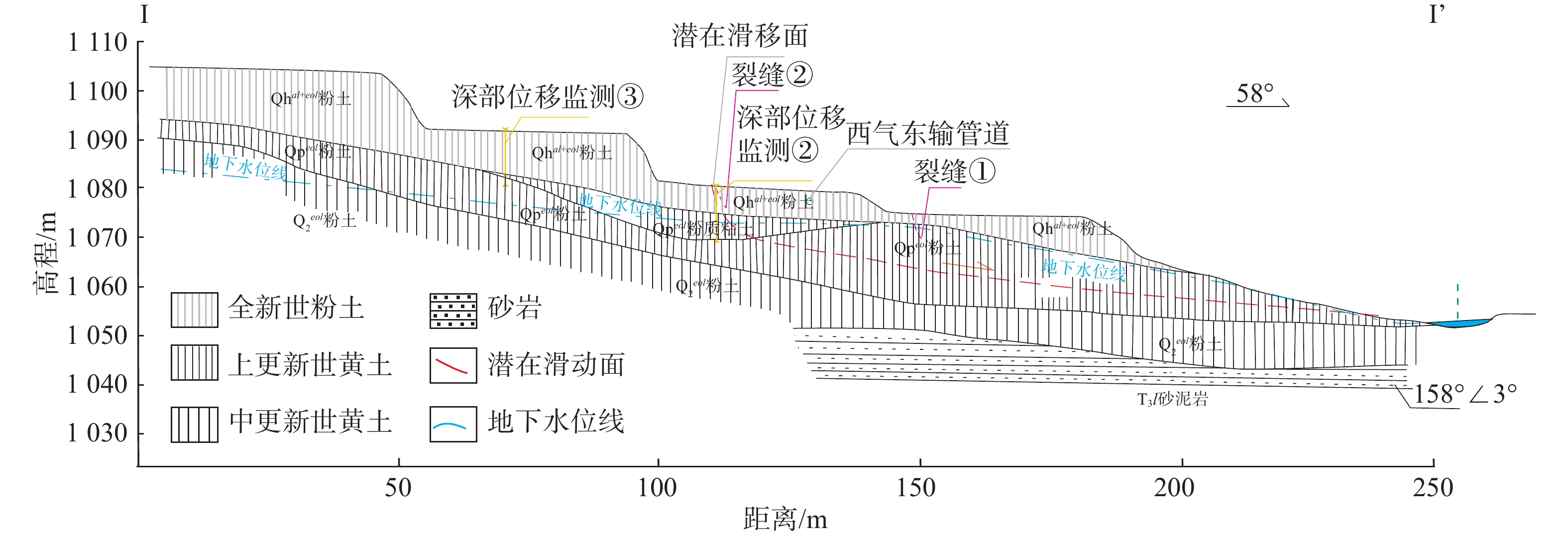
表 1 子长市岭湾村滑坡监测点布置情况
Table 1 Summary of landslide monitoring points in Lingwan Village, Zichang City
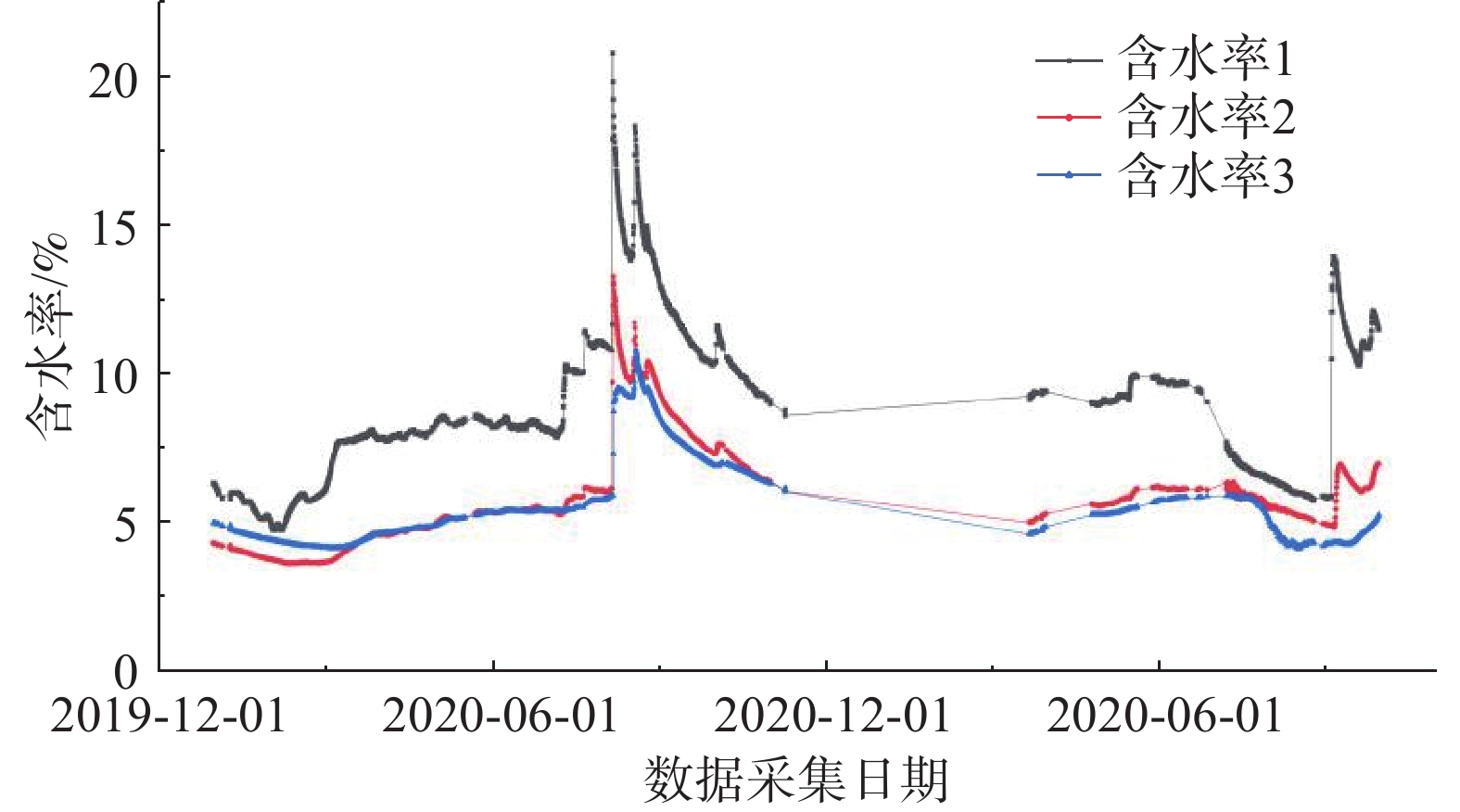
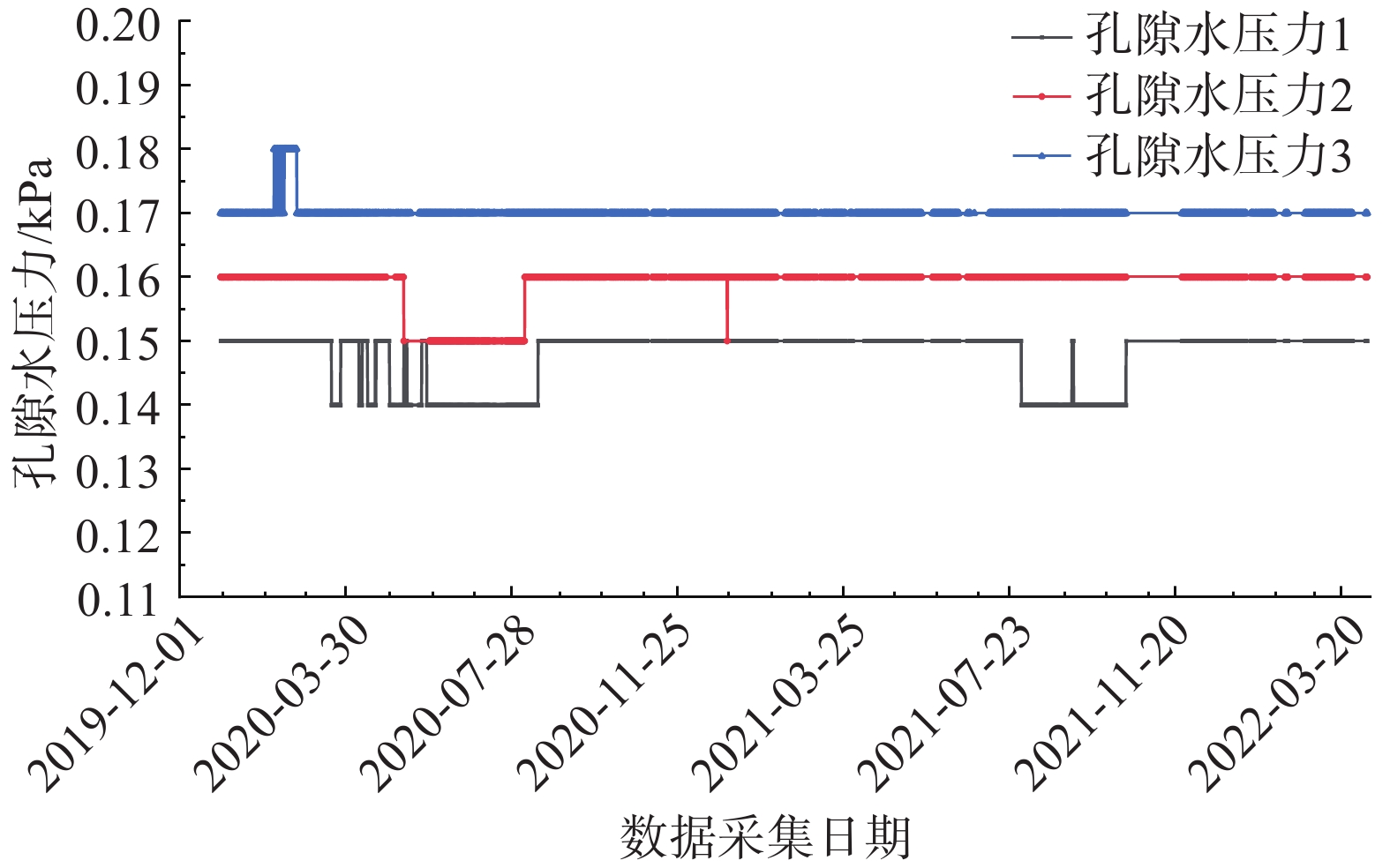
输气管道 监测点位置 监测要素 安装月份 西气东输管道 子长市余家坪镇岭湾村 雨量(1个)、裂缝(2个)、孔隙水压力(3个)、位移(3个)、
深部位移(3个)、含水率(3个)、应变计(3个截面)2019年12月 表 2 主要监测设备参数
Table 2 Main monitoring equipment parameters
序号 监测要素 监测设备 参数指标 1 地表位移监测 一体化GNSS形变自动监测站 一体化GNSS形变自动监测站全星座支持;精度平面:±(2.5 mm+0.5*10-6D),高程:±(5 mm+0.5*10-6D) 2 深部位移监测 一体化深部测斜监测站 量程:±10 °C;测量精度:±0.1%FS;长期稳定性:±0.25%FS/年;分辨率:±10弧秒(±0.05 mm/m) 3 地表裂缝监测 一体化表面裂缝自动监测站 测量范围:0~5000 mm;测量方向:双向;测量精度:±0.1%mmFS;拉线材质:铟钢丝 4 地下水位监测 测压管及透气型渗压计 量程:35 m;精度等级:±0.05~±0.2%FS;非线性度:±0.1~±0.2%FS 表 3 岭湾村滑坡区域时序地表形变量分析(2017年3月—2020年4月)
Table 3 Time-series surface deformation analysis of Lingwan Village landslide (March, 2017—April, 2020)
日期 2017年 2018年 2019年 2020年 3—6月 7—12月 1—6月 7—12月 1—6月 7—12月 1—4月 累计形变量/mm −6.81 −4.31 −6.64 −8.57 −4.87 −4.41 −0.29 表 4 地表位移监测数据分析表
Table 4 Summary table of surface displacement monitoring data
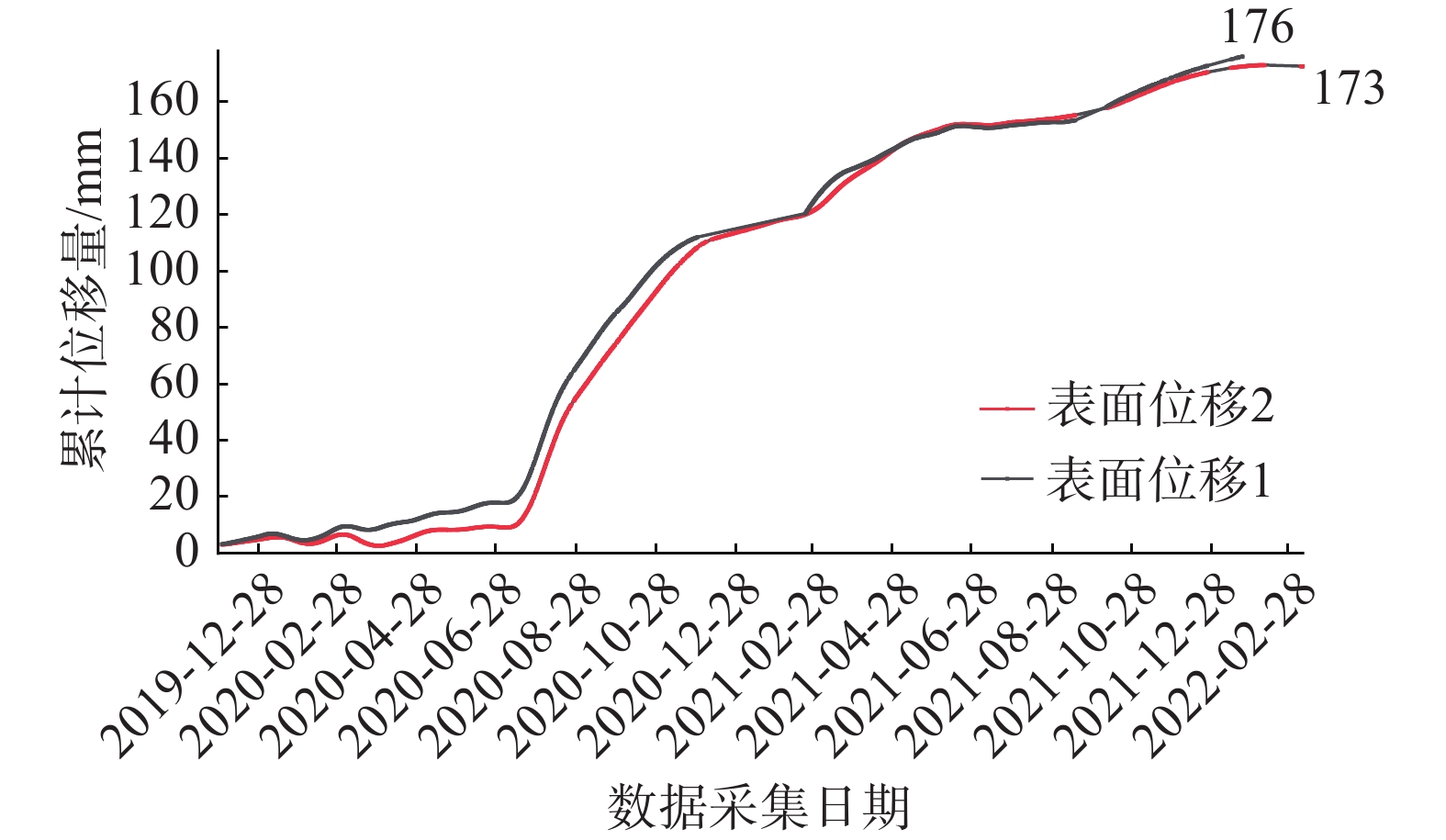
监测单元 监测要素 数据范围/mm 变化量/mm 变化方向 监测周期/d 变化趋势 GNSS地表位移监测1 地表位移1_综合 3.6~176 172.4 向东北移动(88°) 829 低速变形 地表位移1东西向 −2.8~83.2 86.0 向东移动 地表位移1南北向 1.7~−1.6 3.3 向南移动 地表位移1垂直方向 −1.4~−154.6 149.9 向下移动 GNSS地表位移监测2 地表位移2_综合 4.2~173 168.8 向东北移动(67°) 829 低速变形 地表位移2东西向 −1.8~91.5 93.3 向东移动 地表位移2南北向 1.1~36.8 35.7 向北移动 地表位移2垂直方向 3.8~−141.3 145.1 向下移动 表 5 地表裂缝监测数据分析表
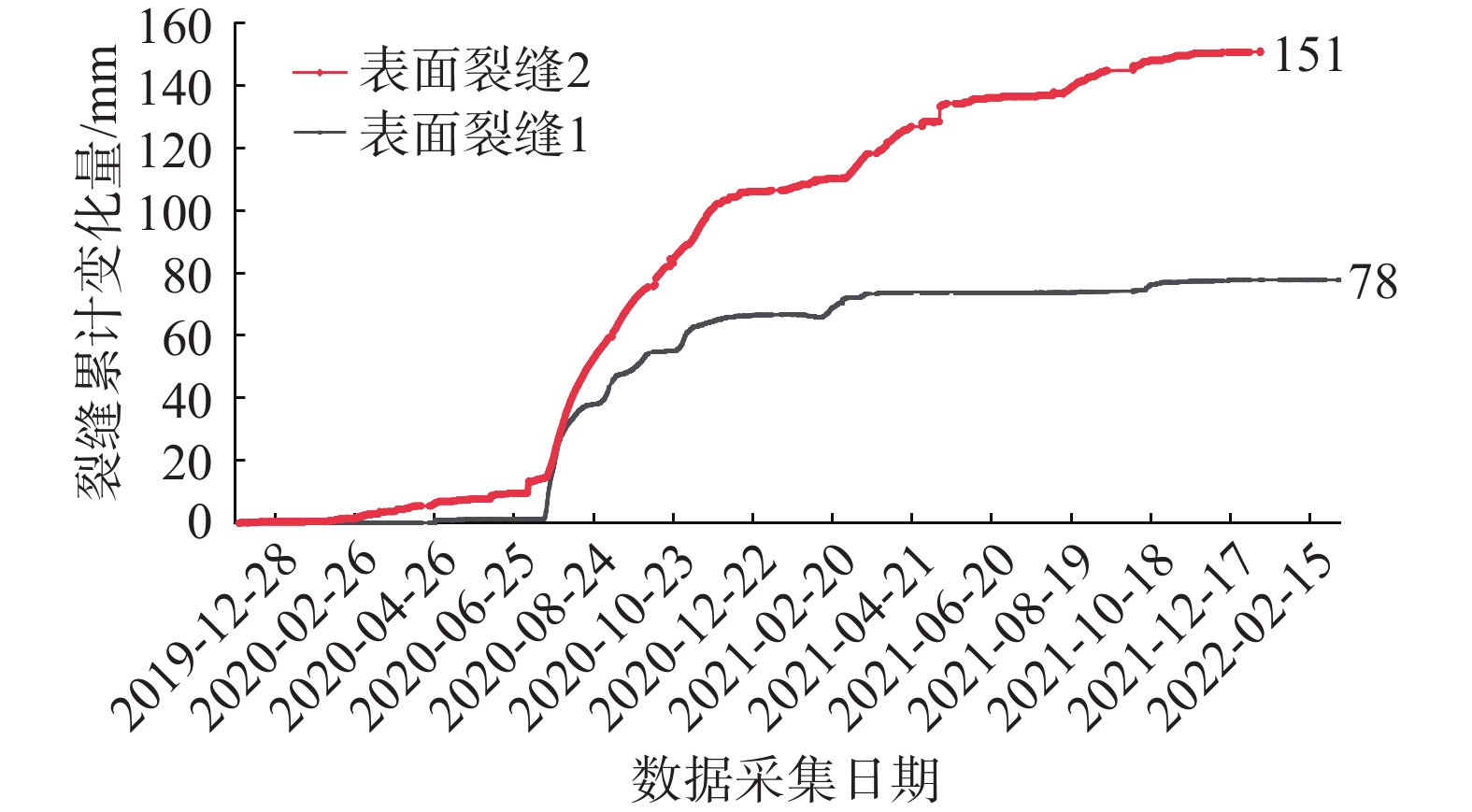
Table 5 Summary table of surface crack monitoring data
管道
桩号监测要素 数据范围/mm 变化量/mm 监测周期/d 当前变化
趋势DD282 地表裂缝1 0~78 78 829 低速变形 地表裂缝2 0~151 151 829 低速变形 表 6 深部位移监测数据分析表
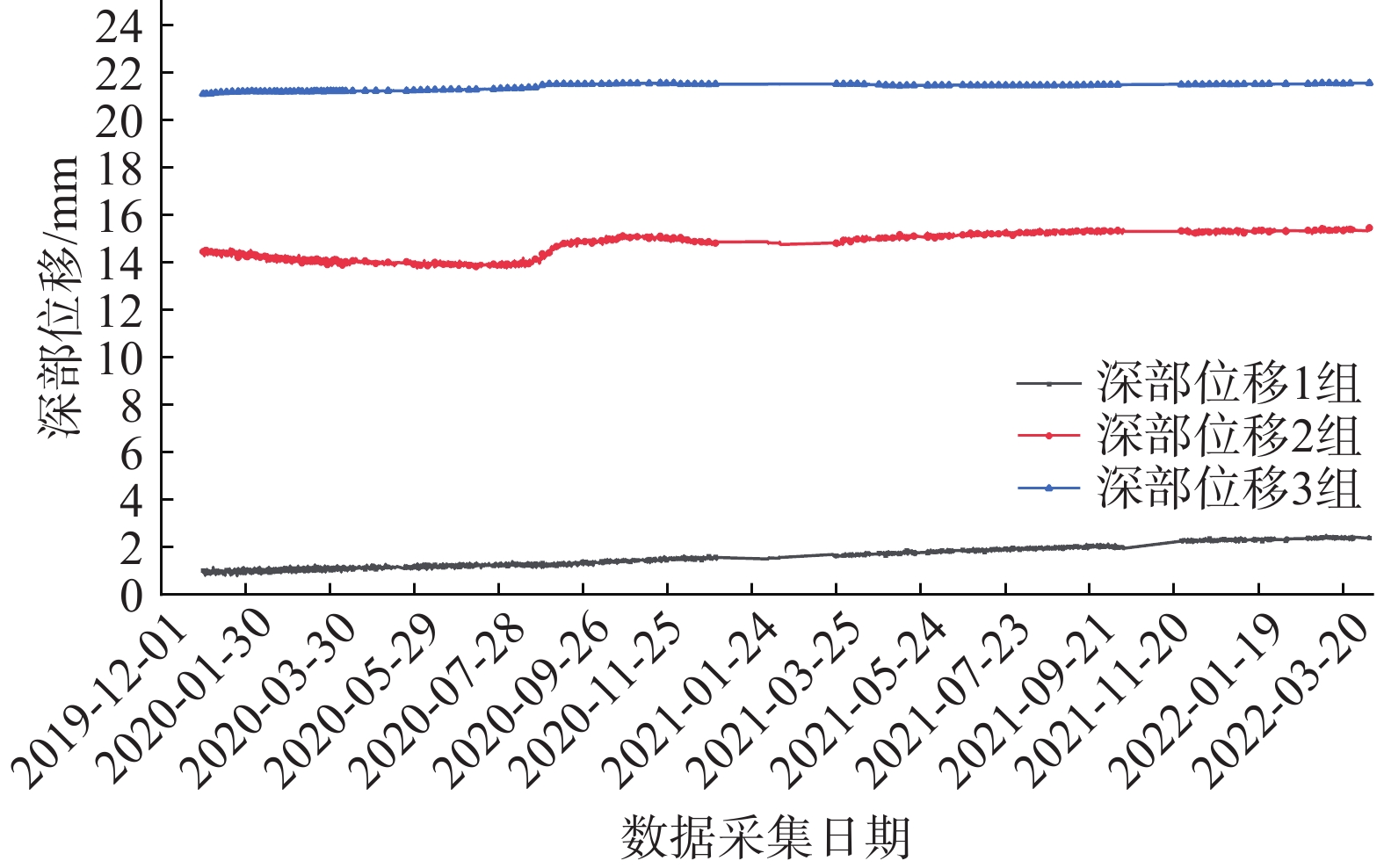
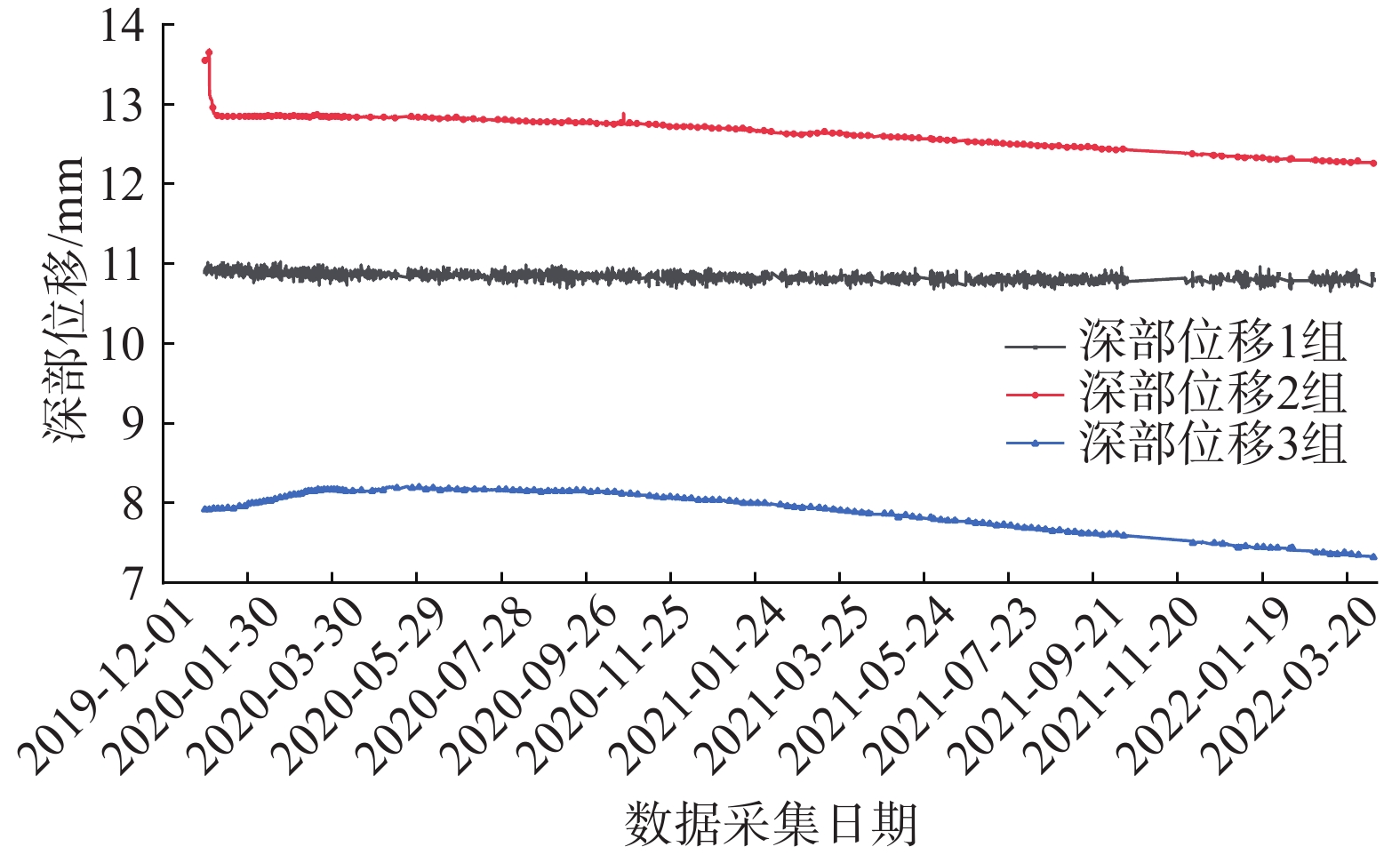
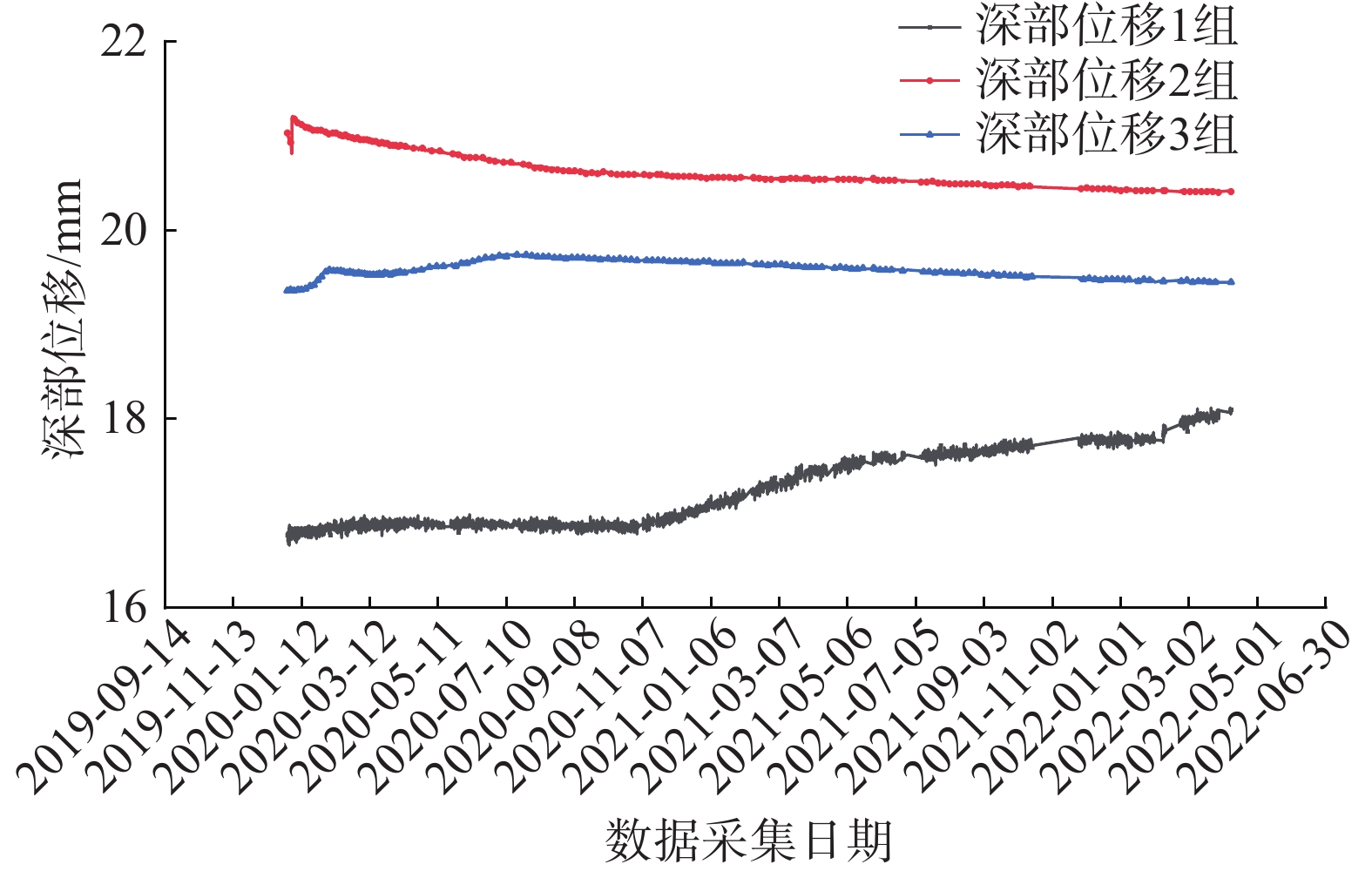
Table 6 Summary table of deep displacement monitoring data
序号 管道桩号 监测点位及传感器埋深/m 数据范围/mm 变化量/mm 变化方向/(°) 当前变化趋势 1 DD282 深部位移1_13 1.02~2.38 1.36 58 基本稳定 深部位移1_24 14.45~15.47 1.02 58 基本稳定 深部位移1_31 21.10~21.56 0.46 58 基本稳定 2 深部位移2_13 10.90~10.83 0.05 58 基本稳定 深部位移2_24 13.55~12.26 0.07 58 基本稳定 深部位移2_31 7.92~7.32 0.60 58 基本稳定 3 深部位移3_13 16.77~18.10 1.33 58 基本稳定 深部位移3_25 21.03~20.41 0.62 58 基本稳定 深部位移3_32 19.36~19.45 0.09 58 基本稳定 表 7 雨量监测数据分析表
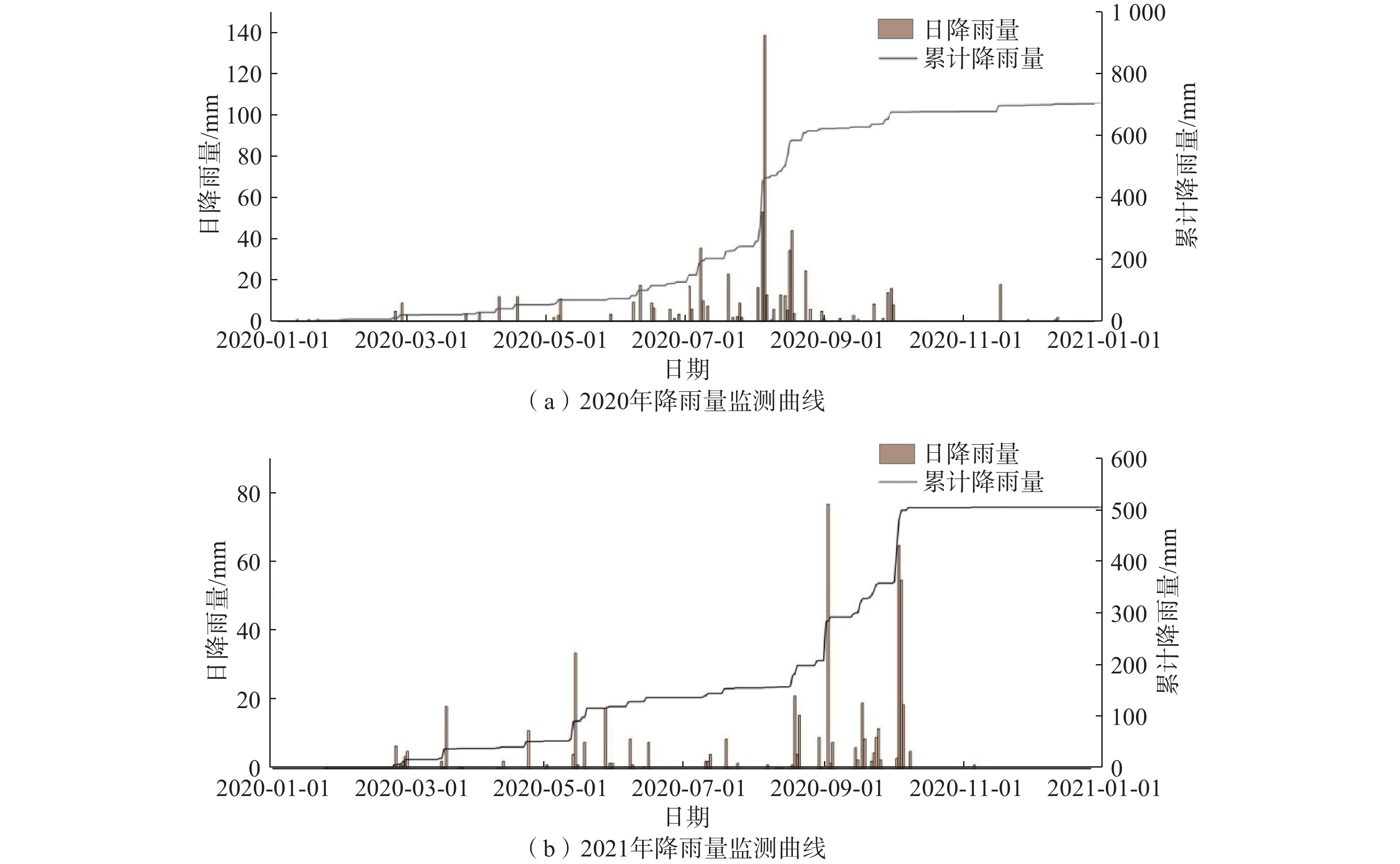
Table 7 Summary of rainfall monitoring data
管道桩号 监测要素 数据范围/mm 单日最大降雨量/mm 周期累计降雨量/mm 累计降雨量发生周期 DD282 雨量 0~138.5 138.5 221.5 2020年8月2—6日 -
[1] 李智毅,颜宇森,雷海英. 西气东输工程建设用地区的地质灾害[J]. 地质力学学报,2004,10(3):253 − 259. [LI Zhiyi,YAN Yusen,LEI Haiying. Geological hazards in the area for the construction of pipelines in the project of diversion of natural gas from the western to the eastern region[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2004,10(3):253 − 259. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Zhiyi, YAN Yusen, LEI Haiying. Geological hazards in the area for the construction of pipelines in the project of diversion of natural gas from the western to the eastern region[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2004, 10(3): 253-259. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 鲜福,关惠平,姚安林,等. 西气东输管道地质灾害辨识[J]. 油气田地面工程,2010,29(3):80 − 82. [XIAN Fu,GUAN Huiping,YAO Anlin,et al. Geological disaster identification of west - east gas peline[J]. Oil-Gas Field Surface Engineering,2010,29(3):80 − 82. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6896.2010.03.048 XIAN Fu, GUAN Huiping, YAO Anlin, et al. Geological Disaster Identification of West - East Gas Pipeline [J]. Oil-Gas Field Surface Engineering, 2010, 29(3): 80-82. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6896.2010.03.048
[3] 席莎,文宝萍. 西气东输甘-陕-晋段滑坡对管道的破坏特点[J]. 人民长江,2018,49(2):62 − 68. [XI Sha,WEN Baoping. Deformation characteristics of west-to-east gas pipelines in Gansu-Shaanxi-Shanxi caused by landslides[J]. Yangtze River,2018,49(2):62 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2018.02.013 XI Sha, WEN Baoping. Deformation characteristics of West-to-East Gas Pipelines in Gansu-Shaanxi-Shanxi caused by landslides[J]. Yangtze River, 2018, 49(2): 62-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2018.02.013
[4] 张茂省,李同录. 黄土滑坡诱发因素及其形成机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(4):530 − 540. [ZHANG Maosheng,LI Tonglu. Triggering factors and forming mechanism of loess landslides[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(4):530 − 540. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Maosheng, LI Tonglu. Triggering factors and forming mechanism of loess landslides[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(4): 530-540. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 李艳杰,唐亚明,邓亚虹,等. 降雨型浅层黄土滑坡危险性评价与区划—以山西柳林县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):105 − 114. [LI Yanjie,TANG Yaming,DENG Yahong,et al. Hazard assessment of shallow loess landslides induced by rainfall:A case study of Liulin County of Shanxi Province full text replacement[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):105 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.02-13 LI Yanjie, TANG Yaming, DENG Yahong, et al. Hazard assessment of shallow loess landslides induced by rainfall: a case study of Liulin County of Shanxi ProvinceFull text replacement[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 105-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.02-13
[6] 刘朋飞,李滨,陈志新. 陕西延安地区黄土滑坡特征及其活跃性分期[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2012,23(4):16 − 19. [LIU Pengfei,LI Bin,CHEN Zhixin. Characteristics and staging of the loess landslide in the Yan’an area,Shaanxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2012,23(4):16 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2012.04.016 LIU Pengfei, LI Bin, CHEN Zhixin. Characteristics and staging of the loess landslide in the Yan’an area, Shaanxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2012, 23(4): 16-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2012.04.016
[7] 王新刚,刘凯,王友林,等. 典型黄土滑坡滑带土不同含水率下蠕变特性试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(5):137 − 143. [WANG Xingang,LIU Kai,WANG Youlin,et al. An experimental study of the creep characteristics of loess landslide sliding zone soil with different water content[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(5):137 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Xingang, LIU Kai, WANG Youlin, et al. An experimental study of the creep characteristics of loess landslide sliding zone soil with different water content[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(5): 137-143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 李锴,李江,顾清林,等. 西气东输智慧管网建设实践[J]. 油气储运,2021,40(3):241 − 248. [LI Kai,LI Jiang,GU Qinglin,et al. Practice of intelligent pipeline network development in West-East Gas Pipeline[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation,2021,40(3):241 − 248. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Kai, LI Jiang, GU Qinglin, et al. Practice of intelligent pipeline network development in West-East Gas Pipeline[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2021, 40(3): 241-248. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 董绍华,张轶男,左丽丽. 中外智慧管网最新发展、存在问题及解决方案[J]. 油气储运,2021,40(1):1 − 8. [DONG Shaohua,ZHANG Yinan,ZUO Lili. Intelligent pipeline network at home and abroad:Recent development,existing problems and solutions[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation,2021,40(1):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) Dong Shaohua, ZHANG Yinan, ZUO Lili. Intelligent pipeline network at home and abroad: recent development, existing problems and solutions [J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2021, 40(01): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 顾清林, 毛健, 王子. 西气东输地质灾害防治实践与展望[C]//中国灾害防御协会油气储运自然灾害防治专业委员会第一届年会, 2019 GU Qinglin, MAO Jian, WANG Zi. Practice and prospect of geological disaster prevention in West - East Gas Pipeline[C]// First Annual Meeting of China Disaster Prevention Association Oil and Gas Storage and Transportation Natural Disaster Prevention Committee, 2019. (in Chinese)
[11] 邹永胜,李双琴,高建章,等. 天地联合的区域山地管道地质灾害监测预警体系研究[J]. 中国管理信息化,2020,23(15):192 − 196. [ZOU Yongsheng,LI Shuangqin,GAO Jianzhang,et al. Study on monitoring and early warning system of regional mountain pipeline geological disasters combined with heaven and earth[J]. China Management Informationization,2020,23(15):192 − 196. (in Chinese) ZOU Yongsheng, LI Shuangqin, GAO Jianzhang, et al. Study on monitoring and early warning system of regional mountain pipeline geological disasters combined with heaven and earth[J]. China Management Informationization, 2020, 23(15): 192-196. (in Chinese)
[12] 李星宇. 滑坡变形高精度智能化监测预警技术研究与实践[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):21 − 29. [LI Xingyu. Research and practice of high-precision intelligent monitoring and early warning technology for landslide deformation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):21 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.06.03 LI Xingyu. Research and practice of high-precision intelligent monitoring and early warning technology for landslide deformation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(6): 21-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.06.03
[13] 杨成业,张涛,高贵,等. SBAS-InSAR技术在西藏江达县金沙江流域典型巨型滑坡变形监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):94 − 105. [YANG Chengye,ZHANG Tao,GAO Gui,et al. Application of SBAS-InSAR technology in monitoring of ground deformation of representative giant landslides in Jinsha River Basin,Jiangda County,Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):94 − 105. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.03-11 YANG Chengye, ZHANG Tao, GAO Gui, et al. Application of SBAS-InSAR technology in monitoring of ground deformation of representative giant landslides in Jinsha River Basin, Jiangda County, Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3): 94-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.03-11
[14] ROGERS A E,INGALLS R P. Venus:Mapping the surface reflectivity by radar interferometry[J]. Science,1969,165(3895):797 − 799. DOI: 10.1126/science.165.3895.797
[15] MASSONNET D,ROSSI M,CARMONA C,et al. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry[J]. Nature,1993,364(6433):138 − 142. DOI: 10.1038/364138a0
[16] 西气东输一线DD282滑坡治理项目岩土工程勘察报告[R]. 南京: 江苏省地质工程有限公司, 2015 Geotechnical investigation report of DD282 landslide treatment project in West-East Gas Pipeline[R]. Nanjing: Jiangsu Geological Engineering Co. Ltd. , 2015. (in Chinese)
[17] 西气东输一线管道工程DD282滑坡补充勘查项目岩土工程勘查报告[R]. 北京: 中国石油天然气管道工程有限公司, 2021. Geotechnical investigation report of DD282 landslide supplementary exploration project of West-East Gas Pipeline Project[R]. Beijing: China National Petroleum Pipeline Engineering Co. Ltd. , 2021. (in Chinese)
[18] 国家管网公司西气东输分公司输气管道地质灾害监测报告[R]. 北京: 北京中地华安科技股份有限公司, 2022 Geological disaster monitoring report of gas transmission pipeline of national pipe network company West - East Gas transmission branch[R]. Beijing: Beijing Zhongdi Huaan Technology Co. Ltd. , 2022. (in Chinese)
[19] 刘银鹏,李同录,胡向阳,等. 陇东陕甘边界降雨水毁灾情调查与启示[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):77 − 83. [LIU Yinpeng,LI Tonglu,HU Xiangyang,et al. Investigation of water induced damages triggered by rainfall in east Gansu and the implications[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):77 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.03-09 LIU Yinpeng, LI Tonglu, HU Xiangyang, et al. Investigation of water induced damages triggered by rainfall in East Gansu and the implications[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3): 77-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.03-09
[20] LI Ping,LI Tonglu,VANAPALLI S K. Influence of environmental factors on the wetting front depth:a case study in the Loess Plateau[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,214:1 − 10. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.09.008
[21] 黄玉华,武文英,冯卫,等. 陕北延安“7·3暴雨”诱发地质灾害主要类型与特征[J]. 西北地质,2014,47(3):140 − 146. [HUANG Yuhua,WU Wenying,FENG Wei,et al. Main types and characteristics of the geo-hazards triggered by heavy rain on July 3 in Yan’an,Shaanxi[J]. Northwestern Geology,2014,47(3):140 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG Yuhua, WU Wenying, FENG Wei, et al. Main types and characteristics of the geo-hazards triggered by heavy rain on July 3 in Yan’an, Shaanxi[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2014, 47(3): 140-146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 张茂省,韩乾隆,黄玉华,等. 黄土高原沟谷型滑坡整治研究—以延安市子长县阎家沟滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2011,38(2):135 − 138. [ZHANG Maosheng,HAN Qianlong,HUANG Yuhua,et al. A study of remediation of valley-type landslides in the Loess Plateau:Exemplified by the Yanjiagou landslide in Zichang County of Yan’an[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2011,38(2):135 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.024 ZHANG Maosheng, HAN Qianlong, HUANG Yuhua, et al. A study of remediation of valley-type landslides in the Loess Plateau: exemplified by the Yanjiagou landslide in Zichang County of Yan’an[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2011, 38(2): 135-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.024
[23] 范立民,李勇,宁奎斌,等. 黄土沟壑区小型滑坡致大灾及其机理[J]. 灾害学,2015,30(3):67 − 70. [FAN Limin,LI Yong,NING Kuibin,et al. Small landslide and disaster-causing mechanism in gully loess area[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2015,30(3):67 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract) FAN Limin, LI Yong, NING Kuibin, et al. Small landslide and disaster-causing mechanism in gully loess area[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2015, 30(3): 67-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 王滔,赵学理,齐普荣. 持续强降雨对黄土地区滑坡地质灾害的影响—以延安地区为例[J]. 地质调查与研究,2014,37(3):224 − 229. [WANG Tao,ZHAO Xueli,QI Purong. Impact of continued heavy rainfall on loess land slide hazard areas:A case study on Yan’an[J]. Geological Survey and Research,2014,37(3):224 − 229. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2014.03.011 WANG Tao, ZHAO Xueli, QI Purong. Impact of continued heavy rainfall on loess land slide hazard areas: a case study on Yan’an[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2014, 37(3): 224-229. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2014.03.011
[25] 张珊珊. 黄土斜坡优势通道及优势入渗规律[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018 ZHANG Shanshan. The preferential passage and the law of preferential infiltration of loess slope[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018(in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 刘章振,阿发友,张晶,杨大慎,刘小波. 云南某高填方边坡对油气管道的致灾风险及CFG加固效果分析对油气管道的影响. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(04): 115-125 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 刘传正. 论线状工程地质灾害预防应对问题. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 1-4 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 吴森,齐得旭,李虎,兰宇,李江,孙明智. 基于灾害动态演化过程的管道滑坡灾害多因素耦合预警模型. 水文地质工程地质. 2024(06): 182-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)







 下载:
下载:



































 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS