Dynamic analysis and prediction of rear slope affected area of the Jianshanying landslide in Shuicheng County, Guizhou Province
-
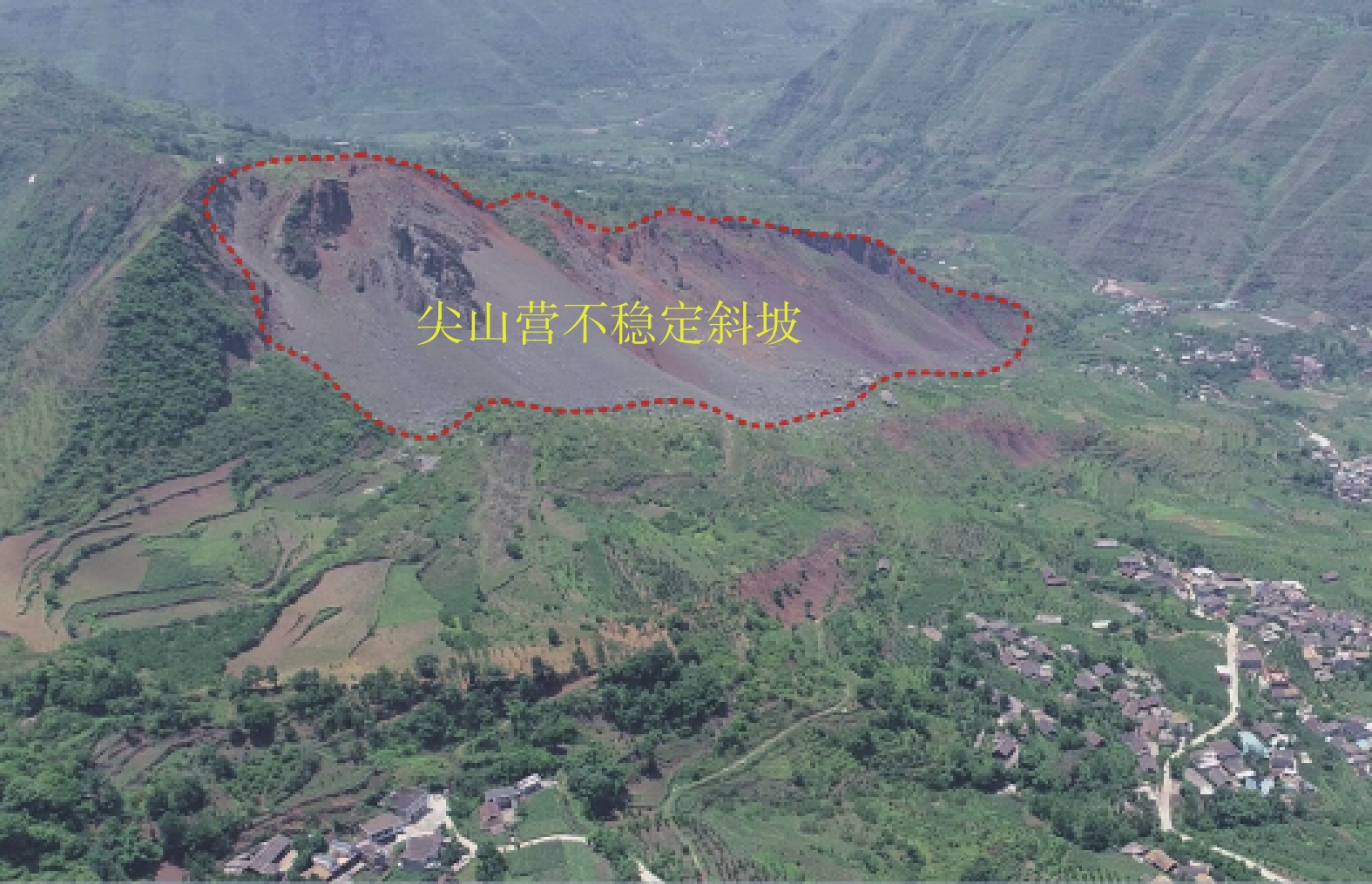
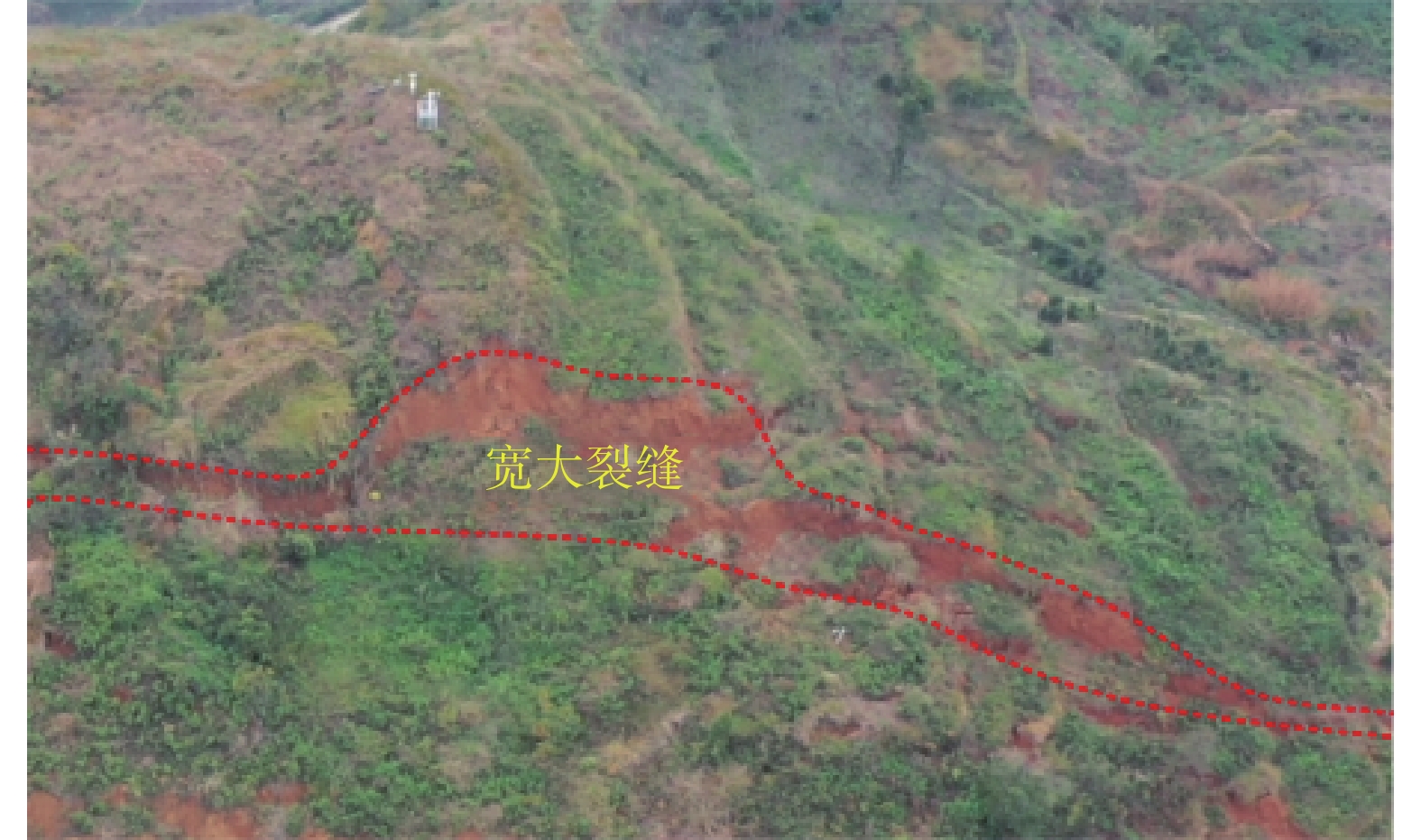
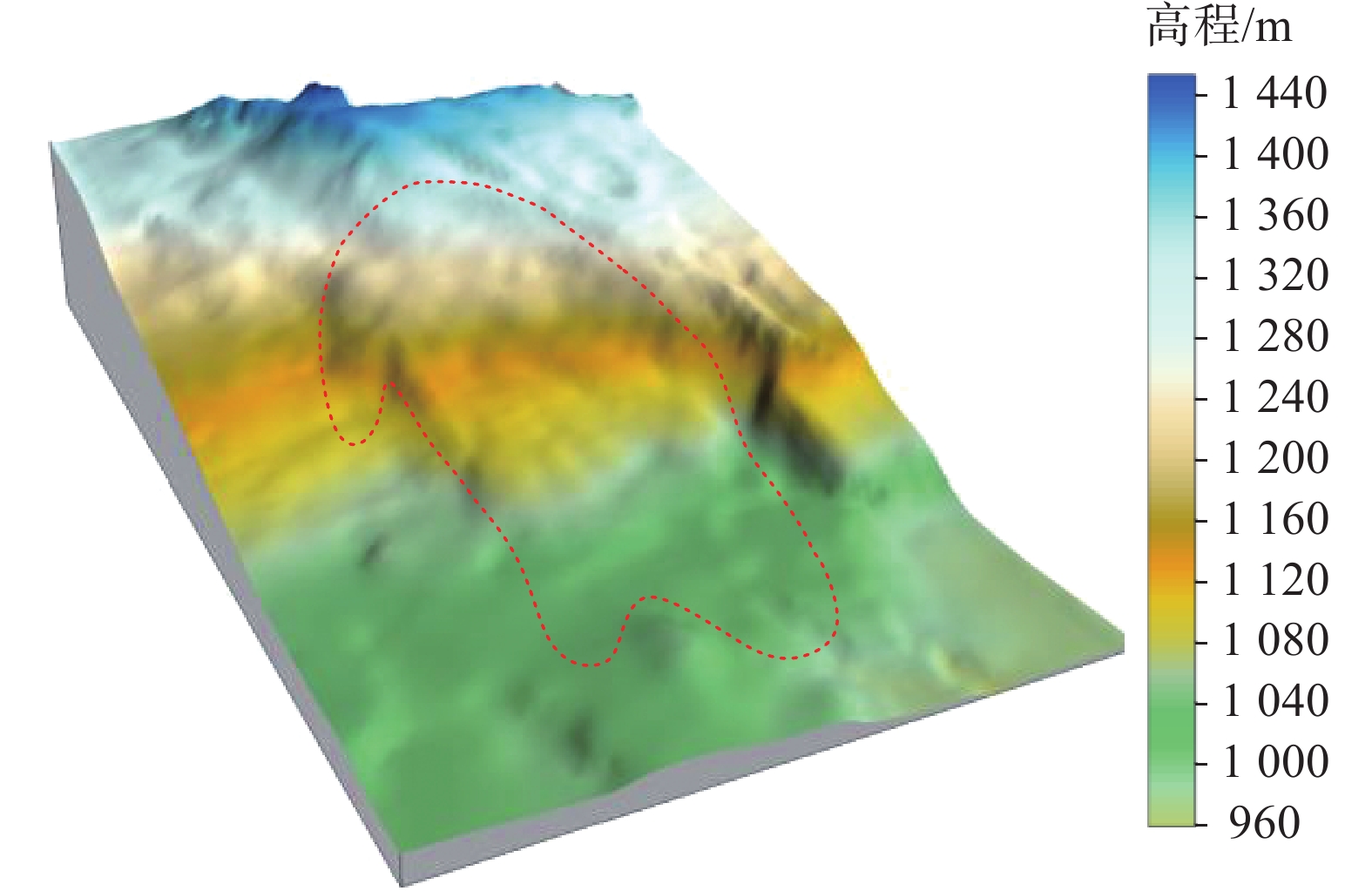
摘要: 2020年9月16日,受地下采动和降雨影响,贵州水城县发耳镇尖山营不稳定斜坡发生山体滑坡,约80×104 m3的岩土体倾泻而下,在运动过程中破碎解体形成碎屑流。滑坡最大运动距离达到1 km,最大高差约300 m。文章基于高精度无人机航测影像建立滑坡区三维数值模型,利用DAN3D动力分析软件对尖山营滑坡-碎屑流运动全过程开展数值模拟,分析了滑体动力学特征和堆积分布。在此基础上,利用反演确定的数值流变模型和参数,对尖山营不稳定斜坡潜在滑坡区开展致灾范围预测。研究成果为高位远程滑坡致灾范围预测和尖山营地区危险性评估提供了依据。Abstract: On September 16, 2020, the combination of mining activities and constant rainfall triggered a long runout landslide in Jianshanying area, Guizhou Province, China, causing a landslide of approximately 80×104 m3 of rock and soil to slide down and form a debris flow. The maximum movement distance of the landslide reached 1 km, with a maximum height difference of about 300 m. Many houses and two roads were destroyed, fortunately without causing casualties. In this study, detailed field investigation combined with the UAV aerial photography were conducted to obtain the geological setting and the digital elevation model of the landslide region. Subsequently, the dynamic model DAN3D was utilized to study the dynamic characteristics and deposit distribution of the Jianshanying landslide. Simulated results were found to match the actual situation well, and the Frictional-Voellmy rheology was identified as an accurate tool for simulating the long runout landslide. Based on the numerical parameters determined from the inversion work, the sliding process and possible travel distance of the potential landslide were simulated. The findings from this study will be helpful aid in predicting landslide runout in high-altitude regions, particularly for the residents in the potential danger zone of the Jianshanying landslide.
-
-
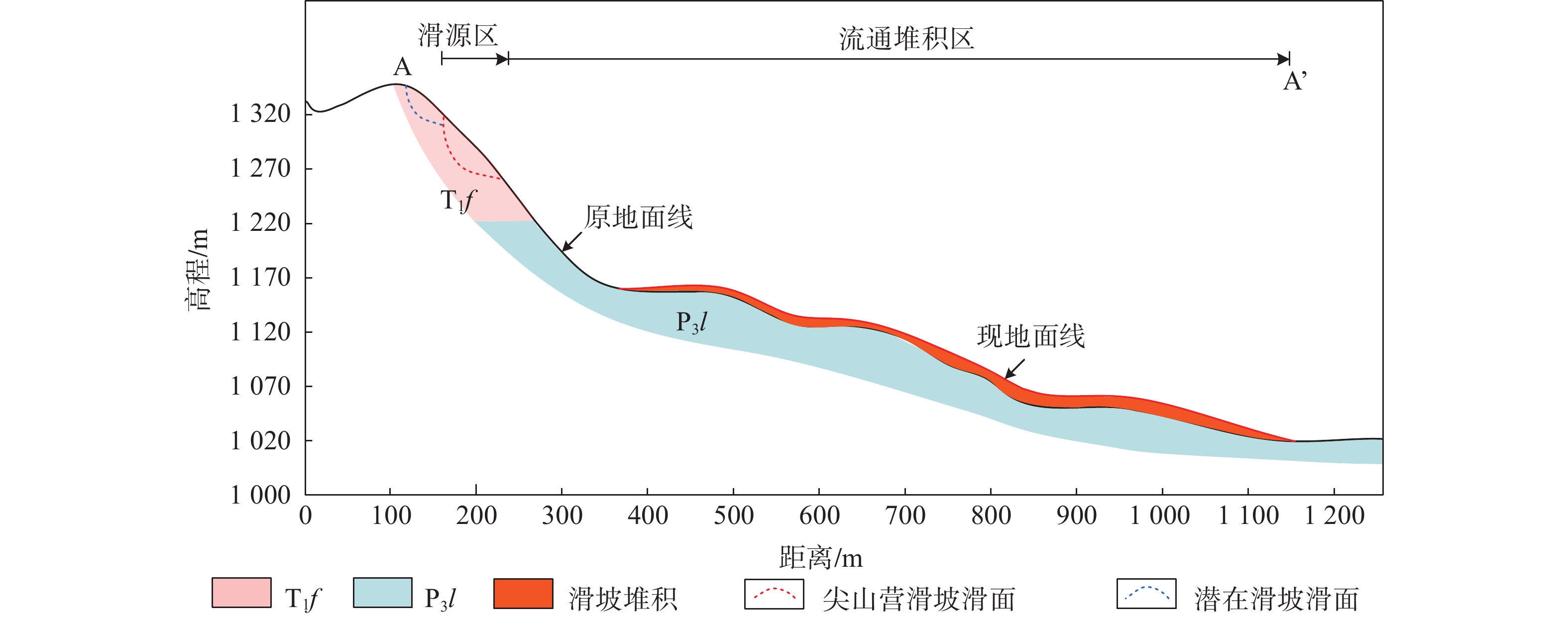
表 1 尖山营滑坡流变模型和参数取值
Table 1 Selected rheological models and parameter values of the Jianshanying landslide
流变模型 摩擦角 孔压
系数摩擦
系数湍流
系数滑源区 Frictional 27 0.5 − − 流通
堆积区Voellmy − − 0.18 600 -
[1] 李滨,殷跃平,高杨,等. 西南岩溶山区大型崩滑灾害研究的关键问题[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):5 − 13. [LI Bin,YIN Yueping,GAO Yang,et al. Critical issues in rock avalanches in the karst mountain areas of southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):5 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Bin, YIN Yueping, GAO Yang, et al. Critical issues in rock avalanches in the Karst Mountain areas of southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(4)5-13(in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 贺凯,李滨,赵超英,等. 基于易滑地质结构与多源数据差异的岩溶山区大型崩滑灾害识别研究[J]. 中国岩溶,2020,39(4):467 − 477. [HE Kai,LI Bin,ZHAO Chaoying,et al. Identification of large-scale landslide hazards based on differences of geological structure prone to sliding and multiple-source data in karst mountainous areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2020,39(4):467 − 477. (in Chinese with English abstract) He Kai, Li Bin, Zhao Chaoying, et al. Identification of large-scale landslide hazards based on differences of geological structure prone to sliding and multiple-source data in Karst mountainous areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(4): 467-477. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 王琦,胡亚净,宋伟利,等. 岩溶山区危岩稳定性分析及危害性预测—以贵州松桃县长冲危岩体为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(1):75 − 84. [WANG Qi, HU Yajing, SONG Weili, et al. Stability analysis and hazard prediction of dangerous rock masses in karst mountainous area:A case study of Changchong dangerous rock mass in Songtao County, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(1):75 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) [WANG Qi, HU Yajing, SONG Weili, et al. Stability analysis and hazard prediction of dangerous rock masses in Karst mountainous area: a case study of Changchong dangerous rock mass in Songtao County, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(1)75-84(in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 吴彩燕,乔建平,王成华,等. 贵州省纳雍县鬃岭镇 “12·3” 大型崩塌灾害分析[J]. 水土保持研究,2006,13(6):100 − 102. [WU Caiyan,QIAO Jianping,WANG Chenghua,et al. Analysis on “12·3” super large-scaled landslide in zongling,Nayong,Guizhou[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2006,13(6):100 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2006.06.031 WU Caiyan, QIAO Jianping, WANG Chenghua, et al. Analysis on “12·3” super large-scaled landslide in zongling, Nayong, Guizhou[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 13(6)100-102(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2006.06.031
[5] ZHU Yaoqiang,XU Shimin,ZHUANG Yu,et al. Analysis of characteristics and runout behaviour of the disastrous 28 August 2017 rock avalanche in Nayong,Guizhou,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,259(3):105154.
[6] 刘兵. 贵州尖山营滑坡变形监测分析与滑动机理研究[J]. 中国水运,2021,21(4):109 − 110. [LIU Bing. Deformation monitoring analysis and sliding mechanism research of Jianshanying landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. China Water Transport,2021,21(4):109 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract) Liu Bing. Deformation monitoring analysis and sliding mechanism research of Jianshanying landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. China Water Transport, 2021, 21(4): 109-110. . (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] CHEN Liquan,ZHAO Chaoying,LI Bin,et al. Deformation monitoring and failure mode research of mining-induced Jianshanying landslide in karst mountain area,China with ALOS/PALSAR-2 images[J]. Landslides,2021,18(8):2739 − 2750. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-021-01678-6
[8] ZHAO Jianjun,XUN Wan,SHI Yanbing,et al. Deformation behavior of mining beneath flat and sloping terrains in mountainous areas[J]. Geofluids,2021,2021(8):1 − 16.
[9] DONG Jianhui,LI Haijun,WANG Yangshuang,et al. Characteristics and monitoring-based analysis on deformation mechanism of Jianshanying landslide,Guizhou Province,southwestern China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2021,14(3):184. DOI: 10.1007/s12517-021-06473-0
[10] 朱要强. 贵州岩溶山区特大崩(滑)-碎屑流致灾机理研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学 ZHU Yaoqiang. Study on the mechanism of catastrophic collapse (slip)-debris flow in Guizhou karst mountain area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] HUNGR O. A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slides,debris flows,and avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1995,32(4):610 − 623. DOI: 10.1139/t95-063
[12] 康孟羽,朱月琴,陈晨,等. 基于多元非线性回归和BP神经网络的滑坡滑动距离预测模型研究[J]. 地质通报,2022,41(12):2281 − 2289. [KANG Mengyu,ZHU Yueqin,CHEN Chen,et al. Study on landslide sliding distance prediction model based on multivariate nonlinear regression and BP neural network[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2022,41(12):2281 − 2289. (in Chinese with English abstract) Kang Mengyu, Zhu Yueqin, Chen Chen, et al. Study on landslide sliding distance prediction model based on multivariate nonlinear regression and BP neural network[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(12)2281-2289(in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] XING Aiguo. Dynamic analysis and field investigation of a fluidized landslide in Guanling,Guizhou,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,181:1 − 14. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.022
[14] XING Aiguo,YUAN Xiaoyi,XU Qiang,et al. Characteristics and numerical runout modelling of a catastrophic rock avalanche triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake in the Wenjia valley,Mianzhu,Sichuan,China[J]. Landslides,2017,14(1):83 − 98. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-016-0707-5
[15] ZHUANG Yu,YIN Yueping,XING Aiguo,et al. Combined numerical investigation of the Yigong rock slide-debris avalanche and subsequent dam-break flood propagation in Tibet,China[J]. Landslides,2020,17(9):2217 − 2229. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-020-01449-9
[16] ZHUANG Yu,XING Aiguo,CHENG Qiangong,et al. Characteristics and numerical modeling of a catastrophic loess flow slide triggered by the 2013 Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake in Yongguang Village,Minxian,Gansu,China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2020,79(1):439 − 449. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-019-01542-x
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 高冬辰,伍国军,杨典森. 滑坡区域管道不同穿越模式的力学响应与影响因素分析. 武汉大学学报(工学版). 2024(08): 1077-1087 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 裴鹏程,黄帅,袁静,张智康. 走滑断层作用下上覆土层的变形破坏机理. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(06): 115-127 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 武彬彬,罗超鹏,余波,刘沛源. 基于FLOW-3D的滑坡运动过程模拟研究. 甘肃水利水电技术. 2023(03): 17-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:





 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS